Abstract
Icing in cut slopes is a serious risk to transportation safety in cold regions. Research on the occurrence process and mechanism of icing is a prerequisite for proposing effective management measures. We took the cut slopes of the K162 section of the Beihei Highway as the research object. We used a combination of field investigation, geological exploration, monitoring, and simulation to study and analyze the power source, occurrence process, and triggering mechanism of icing in cut slopes. The results show that the geologic type of this cut slope is a mudstone–sandstone interaction stratum. Abundant shallow groundwater is the source of water for icing. The excavation of cut slopes extends the effect of negative temperatures on groundwater flow during the winter period. The process of ice formation in cut slopes can be described as follows: As the environmental temperature drops, the surface soil begins to freeze, resulting in a gradual narrowing of the water channel; then, the groundwater flow is blocked, so that the internal pressure begins to rise. When the internal pressure of the pressurized groundwater exceeds the strength of the frozen soil, groundwater overflows from the sandstone layer to the surface, forming icing. The high pore water pressure inside the cut slope is the precursor for the occurrence of icing. The dynamic pressure of the pore water pressure is the main driving force for the formation of icing in cut slopes. The obstruction of the water channel due to ground freezing is the triggering condition for ice formation in cut slopes.
1. Introduction
In cold regions, especially in areas where permafrost is distributed, there exists an ice layer originating from groundwater [1] or a river [2] that overflows and freezes on top of the ground surface [3] or the surface of the frozen river [4]. This ice layer is named icing, and is widely documented in countries such as Russia [5], China [6], Canada [7], and the United States [8]. The formation of icing is related to numerous factors such as climate, geology, and artificial disturbance [9]. Icing in cut slopes seriously affects road traffic safety [10]. To effectively manage icing in cut slopes, studying its occurrence process and mechanism is necessary.
Hu [11] summarized the icing occurrence process into three stages: freezing, blockage, and overflow. As temperatures drop, soil begins to freeze from the surface downward. Ice crystals forming in the soil’s pore spaces significantly reduce its permeability, obstructing groundwater flow and causing a substantial increase in pore water pressure. When the pore water pressure rises to a high value, the pressurized groundwater will overflow at the surface weakness [12], freezing and forming icing. Groundwater plays an important role in the formation of icing. Kane [13] conducted an extensive investigation of icing in the Alaska region and found that water in the active layer plays a limited role in the formation of icing, and, correspondingly, abundant groundwater is the source of large-scale salivary icing in the region. Large-scale icing has also been recognized as a groundwater marker [6]. Combined with the results of Guo [14], Hu [11], and Xu [15], it can be concluded that the formation of pressurized groundwater is a key part of the icing occurrence process in cut slopes. The formation of pressurized groundwater is associated with a special geological structure consisting of a combination of impermeable layers and water channels. During the freezing period, the impermeable layer blocks the downward seepage of pressurized groundwater [16], which facilitates the accumulation of pressure in the groundwater. Low-permeability bedrock and permafrost [17] are common impermeable layers. Water channels store large quantities of groundwater and also serve as channels for groundwater flow. Icing is triggered when the water channel is blocked due to freezing [5,7]. The water channel consists of coarse-grained soils with high permeability [18], permeable rocks, and fissures generated by tectonic activity. No icing has been found on slopes composed of fine-grained soils [16], reflecting the importance of water channels in forming icing. The cut of the roadway slopes also contributes to the formation of pressurized groundwater. On the one hand, the cut slope can cut off the water channel, which is convenient for the soil water within the slope to seep out to the ground surface [19]. On the other hand, the cut of the slope draws the groundwater closer to the ground surface, which makes it more affected by cold temperatures [20].
There are various theories about the source of motive energy for forming pressurized groundwater during the icing occurrence process; however, these theories are not in complete agreement. Wanty [4] studied the water source of stream icing in the Arctic by analyzing the chemical composition. It was found that after the stream’s surface freezes, a steady flow of groundwater continues to collect under the ice layer along the water channel under the action of the hydraulic gradient, forming “pressurized groundwater”. In other words, dynamic pressure influenced by the hydraulic gradient during freezing is the source of the motivation for the formation of pressurized groundwater, as well as the icing, which is in agreement with Kane [3]. However, Zhou [19] presented a different opinion. In his opinion, during the freezing period, the frozen soil that lies above will keep thickening until it is interconnected with the impermeable layer below, constituting the confining space. Then, the unfrozen water inside the confining space will keep accumulating the pressure under the action of phase change until it breaks through the confining body and forms icing. In other words, it is considered that the hydrostatic pressure due to phase change in the confining space mentioned above is the source of motivation for the formation of icing. This view is also supported by Ensom [1], Zhang Hao [16], and others. Meanwhile, there are other related theories. For example, Sloan [21] proposed that after the river surface freezes, stagnant gases accumulate under the ice layer, eventually bursting the ice layer out of the channels through which the river water overflows, forming icing. The inconsistency of the above views suggests that it is necessary to conduct more research on the mechanism of the formation of icing. Recently, scholars have used techniques such as remote sensing [22,23,24], in situ surveys, and numerical simulations [12,25,26] to research the mechanism of the occurrence of icing from different perspectives. Among them, numerical simulation techniques are limited by the lack of monitoring data and have not been fully utilized.
We used numerical simulation techniques to research the occurrence process and mechanism of icing in cut slopes based on the monitoring data at the K162 section (including K161+780, K161+820, K161+860, and K161+900 sections) of the Beihei Highway from 2010 to 2015.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geographic Location and Permafrost Distribution
The Beihei Highway is located in a permafrost degradation zone in northeastern Heilongjiang Province, China (Figure 1a), spanning the northwestern foothills of the Xiaoxinganling Mountain (127°17′31″ E~127°30′24″ E, 49°20′57″ N~49°40′50″ N). The geology of the study area is influenced by the “Wuyun-Jieya new rift zone”. The study area is part of a low hilly region with gentle slopes (Figure 1c). The surface-exposed stratum contains the Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang formation (mainly shale), the Tertiary Pliocene series of Sunwu formation (sedimentary rock with basalt), and the Quaternary Holocene series of modern river alluvium layers (mainly limestone and sandstone) [27]. A part of the stratum forms an impermeable layer. The area is densely vegetated, which favors groundwater storage. The study area features a complex geologic structure and high topographic relief, and is located in a region with permafrost distribution, resulting in numerous geologic hazards [14]. A total of 318 special sections such as wetlands, soft soils, and island permafrost were identified during the construction stage of the highway [28]. After its completion, the highway experienced road hazards such as icing in cut slopes, uneven settlement, and landslides, which greatly reduced the highway’s capacity [29]. The K162 cut slope is the section where icing occurs and is the subject of this paper. Figure 1b shows the results of permafrost distribution in the study area between 2010 and 2015 obtained by combining our in situ survey data with the frozen number model [30]. This model is widely used to discriminate the distribution of permafrost [31,32]. The analysis shows that large areas of permafrost exist within Sunwu County and are also distributed along the Beihei Highway. The permafrost prevents the seepage of water above, which has a significant impact on the regional hydrologic cycle [1]. Field investigations showed that there was no permafrost below this slope, but the maximum depth of freezing could be up to 2.7 m. In Figure 1b, the area is judged to be a zone of deep-season permafrost. The deep seasonal frozen soil zone is defined as the place where the maximum freezing depth is greater than 1.8 m [33], which is consistent with the investigations mentioned above. The groundwater in this section has a short distance to the surface (less than 3.4 m), which provides an opportunity for the formation of pressurized groundwater.
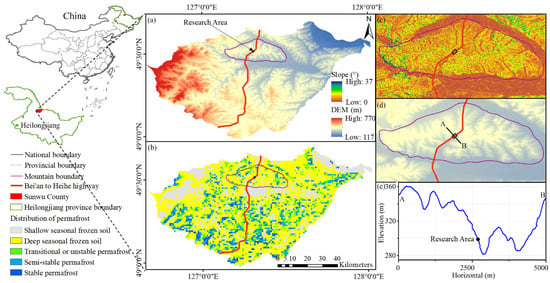
Figure 1.
Geographic location and permafrost distribution of Sunwu County. (a) DEM data; (b) distribution of permafrost [30]; (c) slope data of the low hills; (d) DEM data of the low hills; and (e) elevation of sections A–B.
Permafrost plays an important role in the formation of icing. Permafrost can work as an impermeable layer, affecting the recharge, discharge, and transport of groundwater [3] and contributing to icing. Water for large-scale icing usually comes from subpermafrost groundwater in permafrost regions [6]. Permafrost is present in the study area. However, it is generally in a degraded state [33]. The mechanisms of permafrost degradation affecting icing are complex. On the one hand, degraded permafrost releases water, making groundwater storage rise [34]. On the other hand, the degradation of permafrost also makes the impermeable layer disappear. Ensom [1] investigated the development of icing in permafrost areas in Alaskan and Russian regions. Ensom found that the trends of icing were different at different stages of permafrost degradation. In areas with continuous permafrost, the degradation of permafrost can increase the amount of exposed aquifer, leading to a reduction in the size of icing covering large areas and the formation of new icing covering small areas. In areas with discontinuous permafrost and island permafrost, the degradation of permafrost can lead to a decrease in icing. Recently, the size of icing in the K162 cut slopes has decreased significantly, which is associated with the continued degradation of permafrost.
2.1.2. Climate
The area has a continental monsoon climate, with a long, cold winter. The monthly mean temperature remains below 0 °C for five months of the year (Figure 2b). According to the monitoring data from the meteorological station in Sunwu County (Figure 2a), the average annual air temperature in the study area showed an increasing trend from 1995 to 2020, with an increasing rate of about 0.065 °C/year; the precipitation showed a slightly increasing trend. There is a wide range of air temperature variation in the study area, reaching a minimum in December to February and a maximum in June to August. In the almost 25-year period, the air temperatures in the study area reached as low as −40.4 °C (January 2010) and as high as 38.7 °C (June 2010). In May of each year, freezing depths reach a maximum of 2.2 to 2.7 m, and up to 3 m in some areas of the mountain [35]. Cold climates drive the formation of icing. Precipitation in the study area is concentrated from May to September each year and can account for 83.6% of the yearly precipitation. Abundant precipitation in summer and fall contributes to icing.
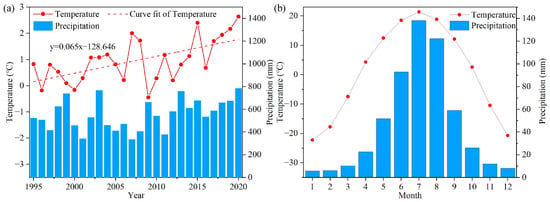
Figure 2.
Air temperature and precipitation in Sunwu County from 1995 to 2020. (a) Annual mean air temperature and precipitation; (b) monthly mean air temperature and precipitation. (The air temperature was measured at 2 m above the surface).
2.1.3. Geologic Environment
In 2009, mechanical excavation was carried out on the left slope of the K161+640~K162+200 section of the Beihei Highway (Figure 3a). Massive icing occurred on this cut slope in February 2010 (Figure 3b). In July 2010, to control icing, an infiltration trench 3.5 m deep and 0.8 m high was excavated in the second platform of the slope. Meanwhile, we embedded sensors near the seepage trench to monitor the temperature, moisture, and pore space water pressure inside the slope. The section has a gentle slope of between 3° and 15°, forming a large catchment area. The cutting of the slopes in this road section blocked the flow path of soil water and induced icing.
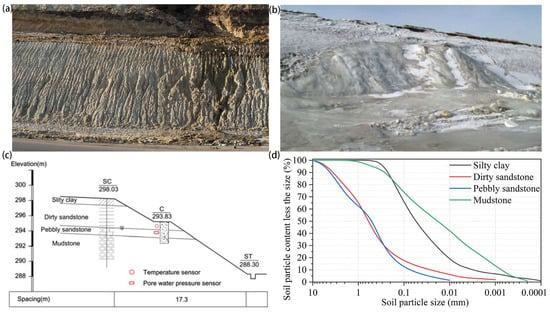
Figure 3.
The geology around the K162 section of Beihei highway. (a) Cutting slope; (b) icing in cut slopes; (c) geological profile of the left slope of the K161+860 section; (d) particle size distribution curve of rocks and soils.
In Figure 3c, the composition of the stratigraphy at section K161+860 is shown. The section can be divided into four layers from surface to depth: the silty clay layer, the dirty sandstone layer, the pebbly sandstone layer, and the mudstone layer. The particle size analysis of the soil in each layer is shown in Figure 3d. The pebbly sandstone layer, which is in the middle of the slope, has high hydraulic conductivity (2.11 × 10−5 cm/s) and is the water channel of this slope; the mudstone layer is below the pebbly sandstone layer and has low hydraulic conductivity (2.09 × 10−8 cm/s), and is an impermeable layer (Table 1).

Table 1.
Hydraulic conductivity of soil on the left side of the cut slope at section K161+860.
2.2. Analysis Methods
We used a combination of sensor monitoring with numerical simulation to investigate the icing occurrence process in cut slopes. The data collected by the sensor allow us to directly observe the changes in temperature and moisture within the slope during the icing occurrence process. Using numerical simulations, we modeled the monitoring data so as to improve the theoretical quality of our conclusions.
2.2.1. Position of Sensors
In 2010, soil moisture sensors, temperature sensors, and pore water pressure sensors were buried at the second step of the left side slope of section K162 (Figure 3c). The sensors were buried along the slope at 40 m intervals in four groups (Figure 4). The range of moisture sensors is 0~100% with an accuracy of ±3%; the range of temperature sensors is −40~60 °C with an accuracy of ±0.5 °C; the range of pore water pressure sensors is −400 KPa~400 KPa with an accuracy of ±1.5%F·S.

Figure 4.
Location of 4 groups of sensors in the K162 section of Beihei Highway.
2.2.2. Numerical Simulation
We built a water–heat coupling model of the left slope at section K161+860 using COMSOL Multiphysics 6.0 software. Meanwhile, we corrected the model with the data collected from the sensors.
2.2.3. Controlled Laboratory Experiments
This study uses a freeze–thaw experiment on a saturated sandy soil column to study the changing rule of hydrostatic pressure. A water-cooling machine (Type: TMS8037) was used as the experiment’s temperature control device. Temperature sensors, as well as pore water pressure sensors, were buried at different depths of the column.
2.2.4. Climate Data
The meteorological data involved in this study were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Center (http://data.cma.cn, accessed on 8 July 2023). We selected precipitation and air temperature data from Sunwu meteorological station from 2010 to 2015.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Monitoring Data
3.1.1. Analysis of the Monitoring Data of the K162 Section
In 2010, during the remediation of icing in cut slopes of the K162 section, we buried sensors at K161+780, K161+820, K161+860, and K161+900 on the left slope (Figure 4 and Figure 5a). With these sensors, we obtained data on the variation of ground temperature, moisture content, and pore water pressure at different depths within the slope (Figure 5b–f).
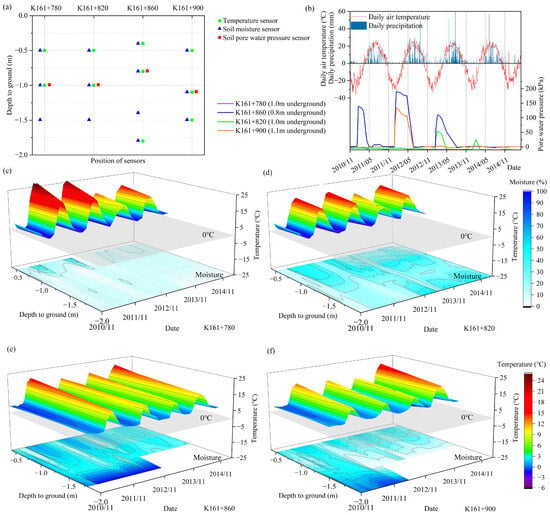
Figure 5.
Monitoring data for the K162 section of Beihei Highway from 2010 to 2015. (a) Locations of 4 groups of sensors; (b) air temperature, precipitation data, and pore water pressure data at 4 groups of sensors; (c) soil temperatures and moisture of the K161+780 section; (d) soil temperatures and moisture of the K161+820 section; (e) soil temperatures and moisture of the K161+860 section; (f) soil temperatures and moisture of the K161+900 section.
The changes in the air temperature and precipitation in Sunwu County and the corresponding pore water pressure at four points from 2010 to 2015 are shown in Figure 5b. Combined with the time of the appearance of the icing, it can be observed that the sharp increase in pore water pressure is a precursor of icing occurrence. The asynchronous change in pore water pressure at the four sections suggests that the outflow point of the icing is not fixed. There were no substantial changes in air temperature or precipitation between years in the study area. However, massive icing occurred from 2010 to 2013, while 2014 and 2015 did not experience large-scale icing. This suggests that the icing on this slope is mainly derived from groundwater rather than precipitation. The excavation of slopes can break the balance of groundwater [19], leading to massive icing. When groundwater no longer flows through that slope, the icing becomes smaller until it disappears. The pore water pressure at the monitoring point location of the K181+860 section was significantly increased in winter from 2010 to 2013, up to 187 kPa, which is the main exit point of icing in this cut slope.
We monitored the variation in the temperature and moisture at different depths on the slopes of this road graben (Figure 5c–f). In winter, the icing is accompanied by groundwater outflow. Groundwater flow is accompanied by convective heat transfer, which slows down the downward movement of the freezing front [14]. This phenomenon will disappear when icing no longer occurs. For example, in the winters of 2010, 2011, and 2012, there was icing at section K181+860, and the ground temperature at the same depth was higher than that at section K181+780, where no icing occurred; in the winters of 2013 and 2014, there was no icing at either section, and there was no significant difference in the distribution of ground temperatures.
The variation in soil moisture at different depths at the four sections of this cut slope is shown in Figure 5. The results show a direct relationship between icing and groundwater storage. There is little difference in the freezing depths at the four sections; however, the variation in pore water pressure is significantly different. In winter, the pore water pressure only rises significantly at sections with a high soil moisture content. In other words, icing in cut slopes occurs where groundwater is abundant. For example, from 2010 to 2012, the soil moisture content at section K181+860 was close to saturation (Figure 5e), and the pore space in the soil pressure increased sharply in winter. Pressurized groundwater formed under the effect of low temperature and eventually caused icing. In contrast, the soil moisture content at section K181+780 remained low during the study period (Figure 5c). In winter, there was no significant change in pore water pressure at section K181+780, and icing did not seep out of this section.
3.1.2. Analysis of Monitoring Data of the K161+860 Section
The icing occurrence process in cut slopes on the left side of the K161+860 section from July 2011 to July 2012 is shown in Figure 6, as well as the changes in ground temperature, soil moisture content, and pore water pressure during this process. This slope consists of outcropping mudstone and interbedded sandstone. Table 1 shows that the hydraulic conductivity of the upper Quaternary loose layer is high, and precipitation can seep under the influence of gravity; the hydraulic conductivity of the middle muddy sandstone layer and pebbly sandstone layer is extremely high, which can store a large amount of groundwater, and the pebbly sandstone layer is also the main water channel of the slopes (Figure 5e); and the hydraulic conductivity of the lower mudstone layer is relatively small and is considered to be an impermeable layer. The groundwater depth in this section is shallow, which is favorable for the formation of icing. The icing occurrence process in this section can be divided into five stages.
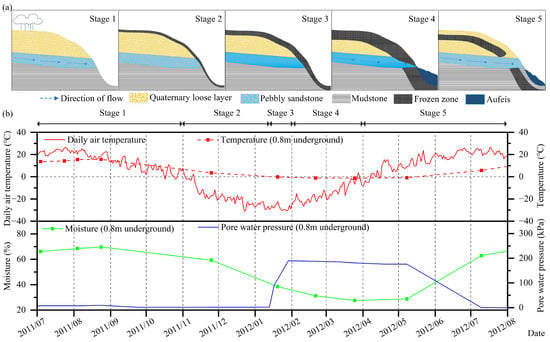
Figure 6.
Icing occurrence process in cut slopes on the left side of the K161+860 section, which is part of the K162 section. (a) The icing occurrence process of cut slopes; (b) air temperature data in Sunwu County and slope monitoring data of the K161+860 section from July 2011 to July 2012.
In stage 1, the groundwater within the slope is replenished by water sources such as precipitation. In this stage, the air temperature is positive and the whole slope is in positive temperature. There is no frozen interlayer within the slope, and precipitation infiltrates down the slope and replenishes the groundwater.
In stage 2, the slope starts to freeze. During this stage, the outside air temperature drops below 0 °C and the surface of the slope begins to freeze. Groundwater continues to flow along the temporarily unfrozen water channels within the slope.
In stage 3, as the cold continues, pressurized groundwater begins to form. During this stage, the temperature drops further and the slope freezing deepens. As ice blocks the pore space, the water channel becomes narrower, until it is completely blocked. By this time, pressurized groundwater is formed and the pore water pressure rises sharply.
In stage 4, icing begins to form. In this stage, the air temperature is below 0 °C, with freezing fronts advancing further downward. The internal pressure of the groundwater rises further, as reflected in a rise in pore water pressure to high values. Under the influence of the enormous internal pressure, the pressurized groundwater breaks through the weakness of the frozen ground surface and overflows, forming icing.
In stage 5, the icing begins to melt. During this phase, temperatures rise above 0 °C and the slope begins to thaw. The ice crystals in the soil melt, and the unfrozen water content rises so that the water channels are gradually restored. The pressure in the pressurized groundwater gradually dissipates. By now, icing enters the next cycle.
3.2. Numerical Simulation of Icing in Cut Slopes
3.2.1. Numerical Model
By analyzing the data collected by the sensors, we have a viewpoint on the process of icing occurrence. As the air temperature decreases, the freezing front within the slope gradually moves downward. Subsequently, the water channel gradually freezes and blocks, affecting the normal flow of groundwater, which triggers the formation of pressurized groundwater. The internal pressure of the groundwater rises until it expands through the soil and forms icing.
The main source of water for this icing is groundwater. The stage of the process in which icing takes part can be characterized by the variation in the pore water pressure. The rapid rise in pore water pressure to high values is considered a precursor for icing formation. Therefore, the simulation of the variation of pore water pressure inside the slope is the key to constructing the numerical model of icing in cut slopes.
In this study, a coupled hydrothermal model of icing in cut slopes was constructed based on the groundwater transport model in freeze–thaw cycles proposed by Christophe [36]. A heat transfer equation for soil was constructed based on the energy conservation theorem, as well as considering heat conduction and convective heat transfer:
where λ is the thermal conductivity of the soil; is the density of the soil; is the density of the ice; is the density of the water; T is the temperature; is time; is the volumetric heat capacity of the soil; is the volumetric weight of water; is the hydraulic conductivity of the soil; is the pore water pressure; is the volume percentage of ice in the pore space of the soil; L is the latent heat of water; and Z is a downward unit vector that represents the effect of gravity on the movement of water.
A conventional simplified model was used to calculate the thermal conductivity and the volumetric heat capacity of the soil:
where and are, respectively, the volumetric heat capacity and thermal conductivity of the soil in the frozen state. and are, respectively, the volumetric heat capacity and thermal conductivity of the soil in the melted state. is the freezing point, which is −0.5 °C in the model. is the absolute value of the difference between and the threshold value at which water and ice transform into each other’s temperature.
We assume that the slopes are at full saturation and do not consider water sources within the slopes. A seepage equation is constructed based on Darcy’s law and the conservation of matter theorem:
where is the volume percentage of ice in the pore space of the soil. is the porosity of the soil. is the gravitational acceleration. is the compression factor of the water-soil matrix.
In the model, is represented as a function related to soil quality as well as temperature:
Assume that the volume of pore space in the soil is constant. That is, the sum of the volumetric ice content and the volumetric water content in the pore space is constant at 1. The hydraulic conductivity of the soil is expressed as a function of the ice content that tends to approach zero as it rises:
where a and b are constants related to soil characteristics; is the soil permeability; is the dynamic viscosity of water; is the impedance factor; is the relative permeability; and is the initial permeability.
During the icing occurrence process, pressurized water within the slope will overflow from weak spots in the slope. The hydraulic conductivity of the soil in the above seepage equation is determined by temperature as well as soil characteristics. When the soil temperature is below 0 °C, the gradually decreases while the rises, resulting in a decrease in . To simulate the process of expansion of the soil by pressurized groundwater, it is necessary to increase the of the frozen soil at the point of icing generation when the internal pressure of the groundwater reaches a certain height. Considering this, a function is presented in this paper. Equation indirectly makes rise by increasing the of the weak parts of the slope under high pore water pressure:
where is a hypothetical function we propose in order to model the formation process of icing, which reflects the numerical relationship between pore water pressure and icing formation. is the threshold pressure when the frozen soil starts to break up due to excessive internal pressure; is the threshold pressure when the cracks in the frozen soil are fully formed and the permeability coefficient is stable and constant. The maximum value of that can be reached by is the initial value of the soil in a positive temperature. is only an exploration, and various experiments are needed to refine the form of the equation and the choice of parameters, etc.
3.2.2. Soil Parameters and Boundary Conditions
According to Figure 3c, the numerical model of the left side slope of the K161+860 section of the Beihei highway was constructed. The physical parameters such as the hydraulic conductivity, volumetric heat capacity, and thermal conductivity of various soils are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 2.
Physical parameters of the soil.
Temperature initial and boundary conditions: The initial temperature of the model is 6 °C; the left boundary of the model is the adiabatic boundary; the lower boundary is set with a heat flux of 0.05 W/m2 to simulate geothermal temperatures; and the upper and right boundaries are set according to the local temperature [37]:
where is the initial phase angle determined by the model starting time (15 October 2009), and its value is π. is time; is the climate warming rate, and the value is 0.052 °C/a; is the mean annual temperature of the slope surface, with a value of 0.44 °C; and A is the annual temperature variation amplitude, with a value of 20.63 °C.
Hydrothermal field’s initial and boundary conditions: The initial moisture content of the model is set to saturated; the upper and lower boundaries are impermeable; and a higher water head is set at the left boundary to represent the abundant water source (due to the lack of in situ water head data, the left boundary water head is a speculative result based on the process of icing formation). The right boundary is the seepage outlet. In addition, since the seepage trench was installed at the second step of the slope of this road graben in July 2010 (Figure 3c), we set the pressure head at the seepage trench to 0 kPa in the model that contains the seepage trench.
and are hypothetical values. Based on the monitoring data for the pore water pressure (Figure 6b), we set them to 200 kPa and 250 kPa, respectively.
3.2.3. Results of the Numerical Simulation
We constructed a coupled hydrothermal model of the slope without seepage trenches (Figure 7) by importing the function. When is not considered in the model, the hydraulic conductivity coefficient of the frozen slope will remain at a low level. During the freezing period, groundwater cannot flow out through the frozen slope (Figure 7d), although the internal pressure of groundwater rises sharply to a high level (Figure 7a). With taken into the model when the internal pressure of groundwater is bigger than the strength of the frozen soil, the water will overflow out of the slope (Figure 7d), forming icing. At the same time, the internal pore water pressure of the slope will decrease with the release of the water overflow (Figure 7b). In this model, the highest pressure inside the groundwater will decrease with the increase in the thickness of the seepage layer and with the decrease in the strength of the frozen slope (Figure 7b). This view is supported by Zhang [16].
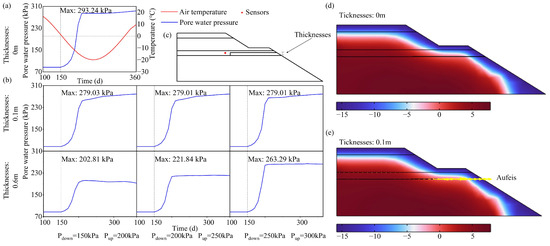
Figure 7.
Numerical model of the cut slope without seepage trenches. (a) Simulation results of pore water pressure at the monitoring point in the numerical model without ; (b) simulation results of pore water pressure at the monitoring point in the numerical model with ; (c) geometric model and monitoring points; (d) pore water pressure within the slope during freezing using the numerical model without ; (e) pore water pressure within the slope during freezing using the numerical model with . Different soil layers are separated by black lines.
By analyzing the monitoring data (Figure 5), we found that groundwater abundance influences the magnitude of icing. Since the slope is located in the bottom part of the mountain (Figure 1e), there is a fall of more than 60 m from the top of the mountain. At the same time, there is permafrost present in the upper part of the mountain, and the slope of the mountain is small (Figure 1c), which favors the pooling of water. The above analysis indicates that there is a potential for high head on the left side of this slope due to the topography as well as permafrost. Due to the phenomenon of high pore water pressure in the slope in the years of icing occurrence (2010~2012), we set the water head at the left side of the slope in these years to be 40 m (this value was obtained by combining the monitoring data with continuous adjustment). Correspondingly, in the years without icing occurrence (2013~2015), there was no significant increase in pore water pressure in the slope, and we set the head on the left side of the slope to 10 m in these years. The boundary conditions on the left side are legitimately inferred from our observations in conjunction with monitoring data and the widely used numerical modeling. The position of the sensor in the numerical model is the same as the actual position (Figure 3c). The simulation results (Figure 8b) are consistent with the monitoring data (Figure 8a). This suggests that high hydraulic gradients are the main cause of high pore water pressure in the cut slope in winter. In other words, dynamic pressure is the driving force for the occurrence of icing in cut slopes.
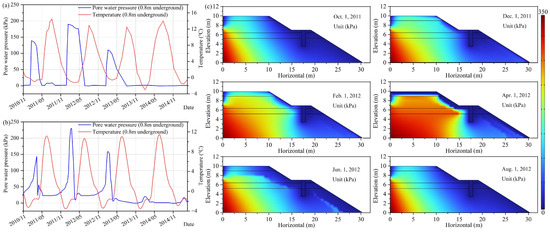
Figure 8.
Numerical model of the cut slope with seepage trenches. (a) Monitoring data for ground temperature and pore water pressure; (b) simulation results for ground temperature and pore water pressure; (c) variation in pore water pressure within the slope during the freeze–thaw cycle from 2011 to 2012. Different soil layers are separated by black lines.
Figure 8c shows the variation in the pore water pressure within the slope in winter 2011. Seepage trenches protect the slopes on the side near the highway by channeling groundwater away. Consequently, there was no significant increase in the internal pore water pressure of the slope at the right side of the seepage trench during the whole freezing process. At the left side of the seepage trench, as the seepage trench freezes and fails, pore water pressure begins to accumulate, and the pressurized underground water forms. Without adequate measures to keep seepage trenches warm, they will freeze and fail in winter. The water channel remains blocked in winter. The pressurized groundwater will not disappear, but only change its location. In July 2010, a seepage trench was constructed on the slope. However, icing still occurs in the area, which is caused by the freezing failure of the seepage trench in winter.
3.3. Unidirectional Freeze–Thaw Laboratory Experiments
In the above study, we found the importance of dynamic pressure in the process of icing generation. However, the sensor measures pore water pressure, which consists of two components: hydrostatic pressure and dynamic pressure. It is necessary to study the change in pore water pressure in saturated sandy soil (the main soil type in the strata where icing is prone to occur) during the freeze–thaw process. At the same time, this experiment can also verify the efficiency of the numerical model in reflecting the change in hydrostatic pressure.
3.3.1. The Process of Laboratory Experiments
The soil for the experiment was configured according to the soil particle size of the pebbly sandstone layer in section K162 (Figure 9a). Figure 10a shows the arrangement of this experiment. First, we saturated the soil and wrapped it in plastic wrap. Then, the soil column was placed under a constant temperature of 7 °C so that the internal temperature of the soil reached 7 °C. Next, we made a soil column 15 cm high and 10 cm in diameter by placing the saturated soil in an insulation pail. Temperature sensors and pore water pressure sensors were placed at different depths in the soil column. The sides and the bottom of the soil column were insulated from water and heat. The temperature of the upper part of the soil column was controlled using a water-cooling machine, and the freeze–thaw cycle was completed within 24 h (Figure 9b). There was no additional water supplementation in this experiment. In nature, the freeze–thaw cycle of the soil is in an open environment, so the upper part of the soil column is not insulated from the atmosphere.
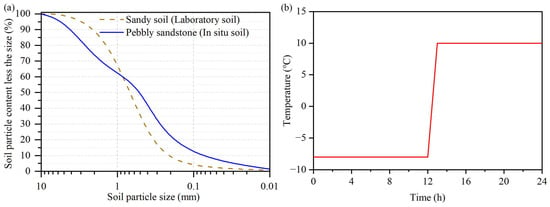
Figure 9.
Soil particle size and temperature at the top of the soil column. (a) Soil particle size; (b) Variation process of temperature at the top of the soil column.
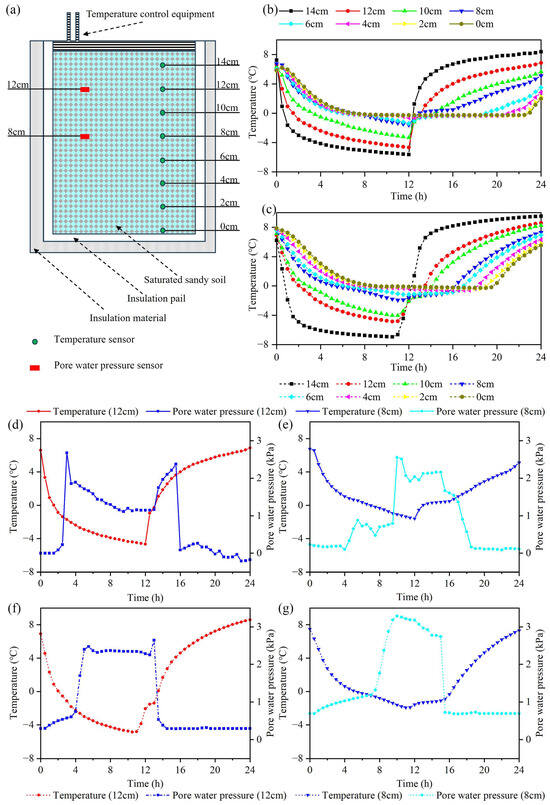
Figure 10.
Experimental results and numerical simulation results for unidirectional freeze–thaw in saturated sandy soil. (a) Experimental design diagram; (b) experimental results for temperature at different depths; (c) simulation results for temperature at different depths; (d) experimental results for pore water pressure and temperature at 12 cm; (e) experimental results for pore water pressure and temperature at 8 cm; (f) simulation results for pore water pressure and temperature at 12 cm; (g) simulation results for pore water pressure and temperature at 8 cm.
3.3.2. Results of the Experiment and Numerical Simulation
Combining the experimental results with the numerical simulation results, the pore water pressure change process and temperature in saturated sandy soil was analyzed during the freeze–thaw process. In this experiment, the role of dynamic pressure is not considered because there is no significant seepage. Therefore, the pore water pressure change process is the change process of hydrostatic pressure. In the numerical model, the physical parameters of the sandy soil were set according to the pebbly sandstone in Table 2. Temperature field: the left and right boundaries and the lower boundary are insulated boundaries; the temperature of the upper boundary is set according to soil (Figure 9b). Moisture field: the left and right boundaries and the lower boundary are impermeable boundaries; the pressure head at the upper boundary is set to 0 kPa.
Based on the experiments, there is no water supplement in the upper boundary in the model, and the upper boundary should be set as an impermeable boundary. However, when the upper boundary is set as an impermeable boundary, some problems occur. During the melting process, the ice in the upper thaw zone melts into water and the volume becomes smaller, which is reflected in the model as the pore water pressure becomes a large negative value. However, since the sandy soil used for the experiment was a coarse-grained soil, the pore water pressure would not be less than 0 in an open environment. In this way, after the upper boundary is set as an impermeable boundary, the simulation results show a huge deviation from the measured data in the melting phase. The best way to solve this problem should be to take air into account in the model. The model will be improved by the filling of the excess space by air. However, one of the main assumptions of the model is full saturation. When the effect of air is considered, the model needs to continue to be derived under the “saturated–unsaturated” assumption. This will make the model less convergent. Based on the above analysis, the air that needs to be injected into the upper thaw zone during the thawing process is replaced with water so that the model meets the full saturation assumption throughout the process. Thus, we modeled the unidirectional freeze–thaw process in saturated sandy soil (coarse-grained soil) columns with the allowance of the presence of errors.
The variation of temperature at different depths within the soil column during the freeze–thaw process is shown in Figure 10b. The soil column labeled 6 cm reached 0 °C during the freezing process. In other words, the freezing zone was conducted downward to at least 9 cm. Figure 10c shows the results of the numerical model for the temperature. We can see that this numerical model is reliable for the calculation of temperature changes in the freeze–thaw of the saturated sandy soil.
Figure 10d,e show the results of pore water pressure variation at 12 cm and 8 cm labeled on the soil column, respectively. Both of these sites are located within the freeze–thaw influence and show significant variations in pore water pressure. During the freezing process, the pore water pressure at 12 cm increases rapidly as the temperature decreased to 0 °C. Correspondingly, the pore water pressure at 8 cm starts to rise when the temperature is positive and rises more rapidly after it is lowered to 0 °C. The temperature at which the pore water pressure starts to rise is not the same at both points. This is caused by the constant downward migration of unfrozen water above in coarse-grained soils due to the combined effect of the pore water pressure gradient as well as gravity. Less moisture above the 12 cm point has less effect on the pore water pressure at this position. More moisture above the 8 cm point has a greater effect on the pore water pressure at this position, which can lead to an earlier rise in pore water pressure. Remarkably, this phenomenon is related to the characteristics of coarse-grained soils (larger pores and low matrix suction). In fine-grained soils, capillary action cannot be ignored, which will make the water in the unfrozen area migrate to the frozen area, and the change rule of pore water pressure needs further study.
The temperature and pore water pressure changes during the freeze–thaw process in saturated sandy soils are investigated using the example of the case at 12 cm (Figure 10d). The process can be divided into three stages.
In the first stage, the temperature decreases continuously from positive to 0 °C. There is no water–ice phase transition in this process, and the pore water pressure does not change significantly.
In the second stage, the temperature keeps decreasing from 0 °C. Since the volume of water expands when it turns into ice, it leads to a rapid increase in pore water pressure, which fluctuates at high values.
In the third stage, the temperature keeps rising above 0 °C, the ice melts into water, the volume shrinks, and the pore water pressure decreases rapidly and then stabilizes.
During the freezing and thawing phases, the pore water pressure shows a maximum value once in each phase. During the freezing phase, changes in pore water pressure are subject to two opposing effects. In the freezing region, the freezing of water into ice favors a rise in pore water pressure, and the migration of unfrozen water towards the unfrozen region below leads to a decrease in pore water pressure. The mutual antagonism of these two effects leads to the maximum values. During the thawing phase, the upper soil starts to thaw, and the melting water migrates downward under the influence of gravity, causing the pore water pressure at the freeze–thaw interface to rise rapidly. As the depth of thaw continues to increase, the water at the original freeze–thaw interface will continue to move downward, and the pore water pressure will decrease rapidly. The melting process also results in a single extreme value of pore water pressure.
Figure 10f,g show the results of the numerical model of the pore water pressure change process at 12 cm and 8 cm. The simulation results are in good consistency with the measured results in Figure 10d,e, which show that the model can correctly simulate the variation process of hydrostatic pressure in saturated sandy soil. The discrepancy between the simulated and experimental results may stem from three sources: the assumption of full saturation throughout; the inhomogeneity of the samples; and the lack of consideration of the displacement of the soil particles.
4. Discussion
4.1. Pressurized Groundwater and Icing
The formation of pressurized groundwater is a key stage in the icing occurrence process in cut slopes. Massive icing in cut slopes at the K162 section of the Beihei Highway originated mainly from groundwater rather than infiltrated precipitation (Figure 5b). Abundant shallow groundwater and a cold climate are prerequisites for the formation of pressurized groundwater. The narrowing of the water channel during freezing is the triggering condition for the formation of pressurized groundwater and, in turn, icing. As the temperature drops, the slope begins to freeze from the surface to the interior. The gradual decline of the freezing front results in a gradual narrowing of the groundwater channel. When groundwater flow is impeded, the internal pressure of the groundwater will accumulate, eventually leading to the formation of pressurized groundwater. When the internal pressure of the groundwater reaches a certain level, the groundwater will break through the soil and overflow, forming icing. We monitored the ground temperature, soil moisture content, and pore water pressure from November 2010 to August 2015 on the slopes where icing occurred on the left side of the K162 section of the Beihei Highway (Figure 6b). In winter, the soil moisture content gradually decreases as the ground temperatures drop. The hydraulic conductivity of the frozen soil becomes smaller, and the groundwater is gradually pressurized, which is manifested by a sharp increase in pore water pressure.
4.2. Dynamic Pressure and Icing
High dynamic pressure is the power source for the occurrence of massive icing in the cut slope. There are two different views about the main power sources contributing to the icing occurrence process: dynamic pressure [3,4] and hydrostatic pressure [1,16,19]. Dynamic pressure is related to the vertical distance between the monitoring point and the water source, etc.; hydrostatic pressure is related to the phase change in the water during the freezing process. The former emphasizes that during the freezing period, the water channel narrows and the flow of groundwater is impeded, resulting in the formation of pressurized groundwater. The latter emphasizes that in winter, frozen soil above and impermeable layers below form a confined body, where the internal water phase turns to ice and becomes larger in volume (the density of ice is less than that of water), resulting in a rise in pressure on the unfrozen water inside the confined object. Remarkably, in a closed quasi-static environment, the pore water pressure will not be sufficient to break through the soil without additional water input. In other words, the convergence of groundwater to the road rift during winter leads to a rise in dynamic pressure, which triggers icing.
4.3. Mudstone–Sandstone Combination Stratigraphy and Icing
Exposed mudstone–sandstone combination stratigraphy is conducive to icing. The sandstone layer has high hydraulic conductivity and acts as a water storage layer as well as a water channel. The mudstone layer has low hydraulic conductivity and is impervious to water. When the mudstone layer is underneath the sandstone layer, it blocks the seepage of water from the sandstone layer. In groundwater-rich environments, when this particular geologic structure is under the influence of freezing due to slope excavation, pressurized groundwater will form in winter. As Figure 7b shows, the soil strength of this mudstone–sandstone combination stratigraphy in the frozen state will determine the height of internal pore water pressure that can be accumulated when icing occurs [16]. Remarkably, this particular structure can be expanded and described as follows: the upper precipitation seepage layer, the middle water channel layer with high hydraulic conductivity, and the lower impermeable layer such as the mudstone layer or permafrost [24,25,38].
4.4. Variation of Hydrostatic Pressure in the Sandy Soil
Hydrostatic pressure in sandy soils rises in response to freezing and will dissipate with thawing. During freezing, water turns to ice and becomes larger, causing the pore water pressure to rise. During melting, the ice turns into water, which becomes smaller, and the pore water pressure drops. The pore water pressure in saturated sandy soils has “maxima” during freezing and thawing (Figure 10d). This phenomenon during freezing is related to two effects: a rise in pore water pressure due to the water–ice phase transition, and a fall in pore water pressure due to the “crowding” of unfrozen water from the frozen zone to the unfrozen zone. This phenomenon during melting is related to the convergence of melting water at the freeze–thaw interface under the influence of gravity. Comparing the simulation results with the experimental results, we verified the effectiveness of the numerical model in simulating variations in hydrostatic pressure. This also justifies, from another perspective, the setting of the left water head to a high value in the years in which icing occurs in cut slopes (Figure 8b).
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the icing occurrence process in cut slopes was monitored and modeled, which led to the following conclusions:
(1) Abundant groundwater is the main source of massive icing in cut slopes.
(2) In winter, as the temperature drops, the groundwater channel gradually freezes, triggering the icing occurrence process, which is displayed as a rapid increase in pore water pressure. In the K162 section of the Beihei Highway, we monitored pore water pressure as high as 187 kPa during the occurrence of icing.
(3) The dynamic pressure in the pore water pressure is the main driving force for groundwater to break through the frozen surface and lead to icing. In winter, groundwater converges under the influence of freezing action, which causes dynamic pressure to rise, thus triggering icing. In a quasi-static environment with hydrostatic pressure only, no icing is generated.
(4) The exposure of mudstone–sandstone combination stratigraphy by slope excavation provides the geologic conditions for icing.
Icing threatens transportation in cold regions and hinders the cross-regional transfer of people and materials. The results of this study will contribute to the management of icing in cut slopes and to the economic development of cold regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S.; data curation, P.H. and Y.G.; formal analysis, H.D.; funding acquisition, W.S.; methodology, C.Z.; project administration, P.H. and H.D.; software, P.H.; supervision, W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S., P.H., G.X. and H.D.; writing—review and editing, W.S., P.H., G.X., H.D. and Y.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41641024), the Carbon Neutrality Fund of Northeast Forestry University (CNF-NEFU), and the Science and Technology Project of Heilongjiang Communications Investment Group (Grant No. JT-100000-ZC-FW-2021-0182) for providing financial support, and the Field Scientific Observation and Research Station of the Ministry of Education—Geological Environment System of Permafrost Areas in Northeast China (MEORS-PGSNEC).
Data Availability Statement
Related data are available upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ensom, T.; Makarieva, O.; Morse, P.; Kane, D.; Alekseev, V.; Marsh, P. The Distribution and Dynamics of Aufeis in Permafrost Regions. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2020, 31, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankiewicz, A. Analysis of Winter Heat Flow in an Ice-Covered Arctic Stream (Caribou Creek, NWT). Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 11, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.L.; Yoshikawa, K.; McNamara, J.P. Regional Groundwater Flow in an Area Mapped as Continuous Permafrost, NE Alaska (USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanty, R.B.; Wang, B.; Vohden, J.; Day, W.C.; Gough, L.P. Aufeis Accumulations in Stream Bottoms in Arctic and Subarctic Environments as a Possible Indicator of Geologic Structure: Chapter F in Recent U.S. Geological Survey Studies in the Tintina Gold Province, Alaska, United States, and Yukon, Canada—Results of a 5-Year Project; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Olenchenko, V.; Zemlianskova, A.; Makarieva, O.; Potapov, V. Geocryological Structure of a Giant Spring Aufeis Glade at the Anmangynda River (Northeastern Russia). Geosciences 2023, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagarin, L.; Wu, Q.; Cao, W.; Jiang, G. Icings of the Kunlun Mountains on the Northern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China: Origins, Hydrology and Distribution. Water 2022, 14, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.D.; Wolfe, S.A. Geological and Meteorological Controls on Icing (Aufeis) Dynamics (1985 to 2014) in Subarctic Canada. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1670–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hinzman, L.D.; Kane, D.L. Spring and Aufeis (Icing) Hydrology in Brooks Range, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, G04S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T. Investigation and Analysis on the Origin of Salivating Ice Flow in Harbin Liming Road Tunnel. Ph.D. Dissertation, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Han, F.; Yi, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, D. Cut-Slope Icing Prevention: Case Study of the Seasonal Frozen Area of Western China. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2016, 30, 05016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Pollard, W.H. The Hydrologic Analysis and Modelling of River Icing Growth, North Fork Pass, Yukon Territory, Canada. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 1997, 8, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.B.; Lai, Y.M.; Bai, W.L.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhuang, D.S.; Li, Q.H.; Wang, J.W. Icing Problems on Road in Da Hinggangling Forest Region and Prevention Measures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2005, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.L. Physical Mechanics of Aufeis Growth. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1981, 8, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shan, W.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, H. Cut Slope Icing Formation Mechanism and Its Influence on Slope Stability in Periglacial Area. In Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides; Mikoš, M., Vilímek, V., Yin, Y., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Ren, H. Study on Indoor and Field Tests of Salivary Icing on Tonghuang Highway and Novel Control Measures. HIGHWAY 2017, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Study on Formation Mechanism and Control Techniques of Extruded Ice for Highway. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crites, H.; Kokelj, S.V.; Lacelle, D. Icings and Groundwater Conditions in Permafrost Catchments of Northwestern Canada. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gao, P.; An, G. Formation of icing and its management. Commun. Sci. Technol. Heilongjiang 2004, 11, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lei, J.; Zhu, S.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, H. The Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors of Highway Waterfall Ice: A Preliminary Study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qi, Y.; Shan, W. Research progress on investigation and control of highway salivary ice disease in China. J. Nat. Disasters 2022, 31, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, C.E.; Zenone, C.; Mayo, L.R. Icings along the Trans-Alaska Pipeline Route; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976. [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, O.; Nesterova, N.; Shikhov, A.; Zemlianskova, A.; Luo, D.; Ostashov, A.; Alexeev, V. Giant Aufeis—Unknown Glaciation in North-Eastern Eurasia According to Landsat Images 2013–2019. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Brombierstäudl, D.; Schmidt, S.; Nüsser, M. Giant Aufeis in the Pangong Tso Basin: Inventory of a Neglected Cryospheric Component in Eastern Ladakh and Western Tibet. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M. Study on the Formation Mechanism of Groundwater Overflow into Ice in Alpine Area. Ph.D. Dissertation, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P. Analysis of Disease Causes and Influence Main Factors for Highway Extruded Ice. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Study on the Mechanism and Prevention Measures of Extruded Ice for The Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Ph.D. Dissertation, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z. The Characteristics of Permafrost Degradation in Lesser Khingan Mountains of China and Its Effect on Road Subgrade Stability. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z. Beihei Highway—The Flying Dragon. Commun. Sci. Technol. Heilongjiang 2011, 34, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Permafrost Degradation Characteristics and Foundation Settlement Prediction along Bei-Hei Expressway. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Spatial Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Permafrost Temperature in Northeast China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C. Response of Alpine Timberline to Permafrost Degradation on Changbai Mountain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Hou, P.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C. Response of the Alpine Timberline to Residual Permafrost Degradation in Mount Wutai. Forests 2024, 15, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Spatio Temporal Evolution and Linear Engineering Response of Permafrost in Northeast China. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Striegl, R.G. Increased Groundwater to Stream Discharge from Permafrost Thawing in the Yukon River Basin: Potential Impacts on Lateral Export of Carbon and Nitrogen. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Formation Law of the Landslide and Its Effect on the Subgrade Stability in Permafrost Degradation Region. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grenier, C.; Anbergen, H.; Bense, V.; Chanzy, Q.; Coon, E.; Collier, N.; Costard, F.; Ferry, M.; Frampton, A.; Frederick, J.; et al. Groundwater Flow and Heat Transport for Systems Undergoing Freeze-Thaw: Intercomparison of Numerical Simulators for 2D Test Cases. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 114, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, M.; Shan, W.; Guo, Y. Process and Numerical Simulation of Landslide Sliding Caused by Permafrost Degradation and Seasonal Precipitation. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 5429–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. The Analysis of Numerical Simulation and Theoretical Research for Highway Saliva Ice. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).