Abstract
Floods are recognised as one of the most destructive and costliest natural disasters in the world, which impact the lives and livelihoods of millions of people. To tackle the risks associated with flood disasters, there is a need to think beyond structural interventions for flood protection and move to more non-structural ones, such as flood early warning systems (FEWSs). Firstly, this study aimed to uncover how flood forecasting models in the FEWSs have evolved over the past three decades, 1993 to 2023, and to identify challenges and unearth opportunities to assist in model selection for flood prediction. Secondly, the study aimed to assist in model selection and, in return, point to the data and other modelling components required to develop an operational flood early warning system with a focus on data-scarce regions. The scoping literature review (SLR) was carried out through a standardised procedure known as Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The SLR was conducted using the electronic databases Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) from 1993 until 2023. The results of the SLR found that between 1993 and 2010, time series models (TSMs) were the most dominant models in flood prediction and machine learning (ML) models, mostly artificial neural networks (ANNs), have been the most dominant models from 2011 to present. Additionally, the study found that coupling hydrological, hydraulic, and artificial neural networks (ANN) is the most used ensemble for flooding forecasting in FEWSs due to superior accuracy and ability to bring out uncertainties in the system. The study recognised that there is a challenge of ungauged and poorly gauged rainfall stations in developing countries. This leads to data-scarce situations where ML algorithms like ANNs are required to predict floods. On the other hand, there are opportunities to use Satellite Precipitation Products (SPP) to replace missing or poorly gauged rainfall stations. Finally, the study recommended that interdisciplinary, institutional, and multisectoral collaborations be embraced to bridge this gap so that knowledge is shared for a faster-paced advancement of flood early warning systems.
1. Introduction
Approximately 90% of all natural disasters worldwide are water-related disasters (WRD) [1]. Approximately 50% of all WRDs are caused by flooding. World disaster data from the International Disaster Database [2] from 2000 to 2023 showed that Asia was the continent most affected by flood disasters in that period, accounting for 40% of all flood catastrophe occurrences. Africa was in second place with 24%, the Americas in third place with 21%, Europe in fourth place with 12%, and, lastly, Oceania with 3% of all flood catastrophe occurrences. Multiple studies [3,4,5] have suggested the possibility of an increase in flood risk in many parts of the world due to climate change driven by fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and greenhouse gas increase in addition to poorly planned and managed infrastructure development. It is of critical importance to take into consideration that there is much regional variation when it comes to flood disasters, and determining the causes of these changes is sometimes challenging despite the existence of continental-scale assessments, which aim to record long-term patterns of floods and their underlying causes [6].
Due to the continental scale of flood patterns and other disasters, world governments have recognised the impacts of flood disasters and are on the same front to mitigate the impacts of droughts. The united effort has been evidenced by the formulation of a disaster risk reduction framework called the Sendai Framework, signed by United Nations member states in 2015 as an international plan to mitigate the impacts of natural disasters between 2015 and 2030. This mutual but voluntary agreement seeks to implement a plan that can save lives, livelihoods, and assets in case of natural disasters [7].
As indicated above, globally, all countries are struggling to adapt to natural disasters due to changing weather patterns. However, existing literature indicates that Southern Africa is at a very high risk of climate change and its effects [8,9,10]. Extreme weather events, water shortages, and economic losses caused by climate change more greatly affect South Africa’s impoverished, marginalised, and vulnerable populations [11]. A study has indicated that, between 1959 and 2019, several major floods occurred in South Africa, causing loss of life and livelihoods and extensive damage to infrastructure, among other damage [12]. After the April 2022 flooding disaster in KwaZulu-Natal, ref. [13] advocated for increased endeavours in flood disaster prevention, mitigation, and readiness to address disaster risk reduction measures effectively.
In order to address flood disaster risks, there is a need to think beyond structural interventions for flood protection and move to more non-structural ones, as advocated by various authors [14,15,16,17] for areas with high population numbers and intense economic activities. Structural flood mitigation measures include dams, levees, culverts, and individual proofing measures like solid fences and raised houses, while non-structural measures include early warning systems (EWS), catchment modelling, and land use planning controls. Therefore, while designing flood risk management systems, non-structural interventions should be considered in equal measure to structural ones. Additionally, acknowledgement of the necessity to implement flood early warning systems globally is sheer evidence of the practical constraints of structural flood defence systems.
There have been several scholarly endeavours to provide a comprehensive analysis of the flood forecasting models used in the successful implementation of flood early warning systems (FEWSs) [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Ref. [18] reviewed advances in flash flood forecasting between 2000 and 2011 and found that the Flash Flood Guidance system was the best method to determine flash flood occurrence and concluded that no existing model at that time could make reliable flash flood forecasts in urban watersheds. Ref. [19] made a brief review of different aspects of flood forecasting, including models, techniques of data collection, and display of results, while giving insight into future research, concluding that remote sensing and hydrological modelling tools are advancing rapidly, and there is a need to update FEWSs continuously. Ref. [20] reviewed the state-of-the-art machine learning (ML) models in flood prediction and gave insight into the most suitable ML models, classifying them into single and hybrid models while suggesting that ML will greatly improve both short- and long-term predictions. The future quality of flood predictions with ML was attributed to the use of novel hybridisation, data decomposition techniques, ensemble methods, and add-on optimal neural architectures. Ref. [21] made a comprehensive review of the latest modelling techniques used in flood prediction, classifying them into two main categories: hydrologic models and ML models based on AI, assessing the advantages and disadvantages of each model type. The study revealed that the selection of ML models was influenced mainly by robustness, speed, computation cost, and generalisation capability while emphasising robust data availability for higher accuracy. The study also found a growing superiority of machine learning (ML) techniques over traditional hydrologic models in flood forecasting. Ref. [22] presented a state-of-the-art review of flood prediction tools with a focus on analysing the chronological growth of flood prediction, the evolutionary trends in flood prediction, and the strengths and weaknesses of each tool. The study showed that machine learning (ML) is widely used in flood prediction, while probabilistic models like Copula and Bayesian Network (BN) hold significance in the uncertainty assessment of flood risk, hence recommending more research to be conducted in Africa, South Africa, and Australia, where less work is undertaken. Ref. [23] performed an overview of flood analysis and forecasting methods between 1979 and 2020 and highlighted various aspects, methods, and approaches of flood study methodologies, concluding that standardisation of methodologies needs to be completed at a local level and depending on the scenario. Ref. [23] also recognised that advancements in GIS, 3D hydrological models, and ML have played a significant role in revolutionising flood predictions. Ref. [24] reviewed the adoption of remote sensing methods for flood predictions between 2010 and 2023, focusing on the pre-disaster phase of the disaster management process, indicating a rapid surge of studies implementing artificial intelligence (AI) techniques coupled with remote sensing (RS) techniques for flood prediction. However, ref. [24] noted the inability of RS-based systems to measure the long-term and real-time water level at fixed points due to the orbital cyclic movement of the satellites. Ref. [25] reviewed the progress in Hydrologic Forecast Merging Techniques (HFMT) since the early 1990s, with emphasis on developments and applications in flow simulation, uncertainty analysis, monthly and seasonal streamflow predictions, ensemble forecasts, flood forecasting, and climate change analysis. The study found that the Bayesian model averaging (BMA) was the most popular due to its ability to reduce uncertainty and provide accurate and reliable forecasts in deterministic and probabilistic simulations. However, these studies failed to address flood forecasting in data-scarce regions as almost all methodologies required rich historical and current hydrometeorological data banks. Most developing nations across the globe, especially sub-Saharan Africa, lack long-term historical data banks on a local scale, which is essential for flood forecasting at both local and regional scales.
Therefore, this SLR aimed to add to the above knowledge body by studying how forecasting models in FEWSs have evolved over the past three decades (1993–2003) to aid in the selection of the best flood forecasting models in data-scarce regions for FEWSs. The following objectives were pursued in this study to assist in model selection and, in return, to point to the data and other modelling components required to develop an operational flood early warning system with a focus on data-scarce regions. The objectives of the study were:
- To examine the most advanced methods/technologies for flood forecasting in the context of FEWSs,
- To provide an overview of the chronological evolution of flood forecasting in the context of FEWSs between 1993–2023,
- To provide an overview of flood forecasting models for data-scarce regions to help in model selection for FEWSs in such areas.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2 describes the materials and methods of the study and the justification behind choosing the materials and methods. Section 3 briefly presents the statistical and bibliometric analysis results of the study. The results are discussed in Section 4 in terms of a broad view of FEWSs, flood forecasting in FEWSs, and a summary of forecasting models in FEWSs. Then, recent developments in flood forecasting in FEWSs are elaborated and a detailed discussion of flood forecasting in data-scarce regions is discussed. Section 5 provides a summary of the results, conclusions, recommendations, and administrative implications (i.e., policy implementation) of the study.
2. Materials and Methods
This scoping literature review (SLR) was carried out through a standardised procedure known as Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) [26]. There are four main stages of this methodology, which include:
- The generation of the main keywords to be used in database search,
- Choosing the relevant databases, as well as structuring the querying process,
- Screening and sorting the relevant quality documents for analysis and,
- Processing the results into understandable information for reporting.
To obtain documents (peer-reviewed journal articles, conference papers, review articles, and books) that pertain to the project’s aim and objectives, concise criteria for document selection, evaluation, and compilation were employed. Several basic statistics techniques were employed to analyse the extracted documents for reporting in a process referred to as meta-analysis. The literature search was completed using the electronic databases Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) from 1993 to 2023. Scopus and WoS were selected over the Science Citation Index (SCI) and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) since more journals are published in the first two databases than the latter; hence, more articles are visible on Scopus and WoS than SCI and SSCI.
The search string approach was used to identify the required documents from various databases relevant to this SLR. Key search words and logical Boolean operators were used to extract the relevant literature. The main logical Boolean operator used included “OR” for this SLR. Several trial database searches with various keywords relevant to the study were conducted to pick out the best search terms that return the most appropriate and highest number of publications possible. The main search phrases were queried from the document’s main titles in the databases to retrieve quality literature relevant to the SLR. The databases were selected based on their library content, quality, and trust, due to meticulous peer assessment, in addition to the amount of content available. Two reviewers conducted a thorough and unbiased search to gather papers, which was completed on 10 January 2024. The documents retrieved from Scopus and WoS databases were limited to the years from 1993 to 2023. Google Scholar was not considered for this SLR due to its inadequacies stemming from the lower number of publishers and journals compared to Scopus and WoS. However, it is recognised for its citation power, which is superior to both of the two previously mentioned databases.
Since the study documents were obtained from two separate databases, harmonising them through a process that identifies and eliminates duplicates is essential for effective and accurate analysis. After eliminating duplicates, the titles and abstracts of the remaining documents were assessed for relevance to the SLR at hand, and irrelevant documents were eliminated accordingly. With further full-text reading of the remaining publications, further documents were screened as they had no tangible contribution to this line of SLR. Each of these screening processes was conducted by two reviewers acting independently but applying the same inclusion–exclusion basis to avoid bias in the elimination process. The final criteria were to assess the remaining collection of publications to identify the main flood forecasting model methods used in FEWSs and exclude any studies that were not in line with this review scope. The remaining group of publications strictly addressed flood forecasting modelling and were exported to an Excel sheet for analysis. Publications that were not written in English were eliminated, in addition to publications that were just reviews of the subject matter.
The authors aimed to gather essential material and details to provide a comprehensive overview of the chronological evolution of flood forecasting models. This includes key motivations, problems, recommendations, and methodological features. The relevant publications were thoroughly analysed to extract all the crucial material following the purpose of this study. The summarised scoping literature review (SLR) methodology is illustrated in Figure 1.
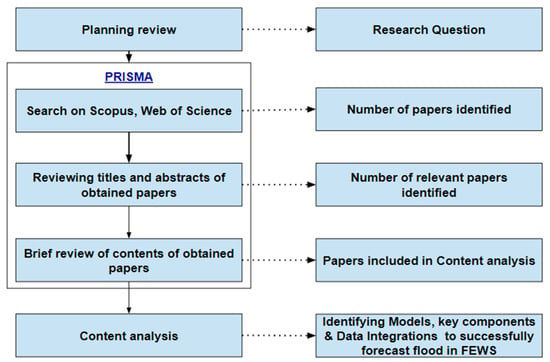
Figure 1.
The summarised SLR methodology.
3. Results
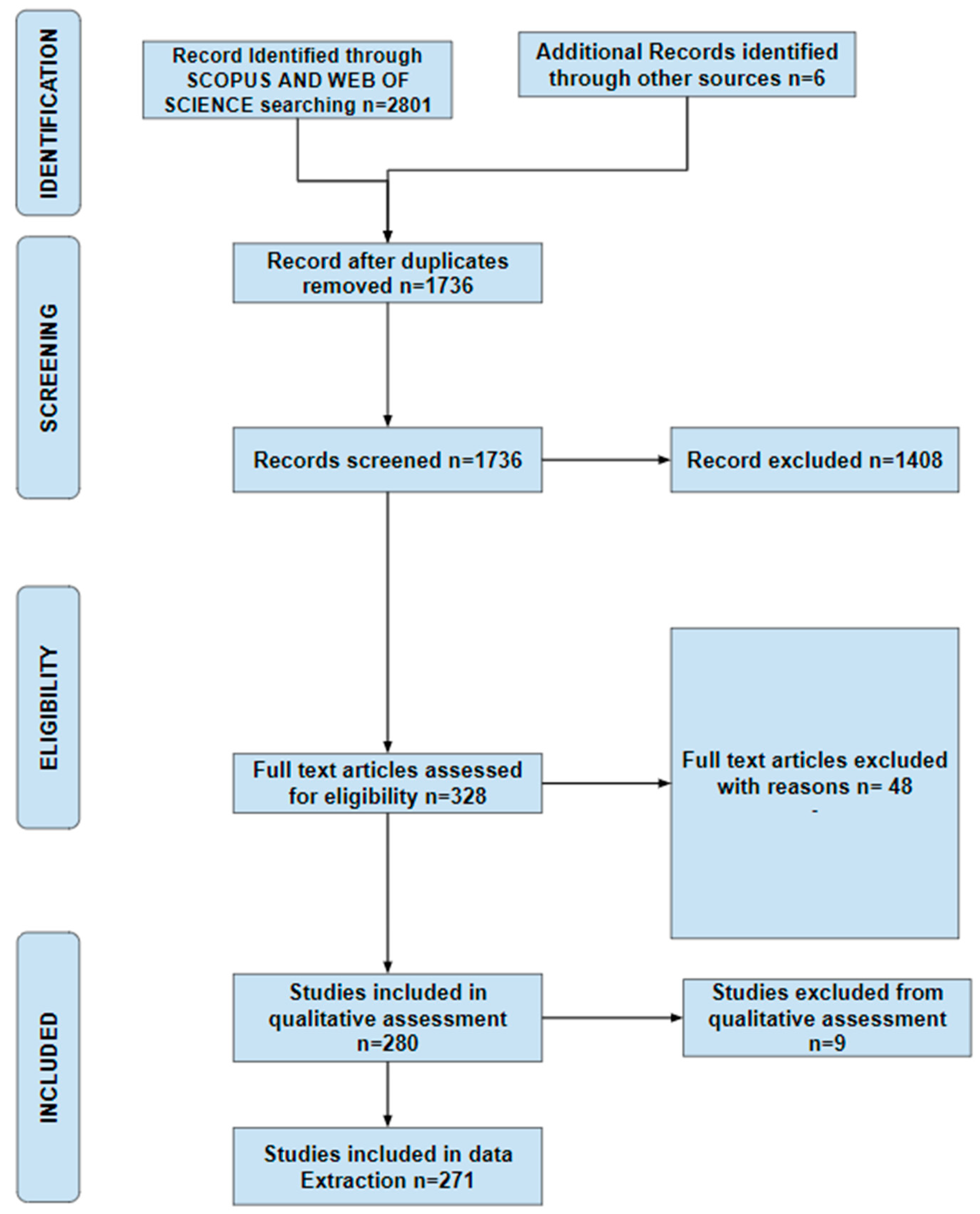
In the identification phase, a systematic approach based on the PRISMA approach [26] was formulated to identify relevant publications pertaining to this study. The relevant publications search was limited to Scopus and Web of Science databases. After a trial of several keywords and strings, a Boolean string used was: “Flood Early Warning System” OR “Flood Prediction” OR “Flood Forecasting” because it returned the most relevant and highest number of publications related to flood prediction and foresting models. All searches spanned from 1993 until 2023 and included journal articles, conference papers, and peer-reviewed book chapters from all over the world, written in English only. The main purpose of this identification phase was to retrieve all relevant existing publications on flood forecasting models employed in flood early warning systems in the fields of Environmental Science, Earth and Planetary Sciences, Engineering, Hydrology, Computer Science, Mathematics, Decision Science, and Multidisciplinary fields. The above fields were selected because they contained more relevant articles on flood early warning systems with an element of modelling rather than the social aspects. A total of two thousand eight hundred and one (2801) documents were originally identified from both Scopus and Web of Science and imported.
In the screening phase, duplicate publications were deleted, and one thousand seven hundred and thirty-six (1736) documents were retrieved from the database after a thorough evaluation of each title and abstract to determine their relevance to this study and remove any irrelevant papers that did not contain forecasting models. Hence, one thousand four hundred and eight (1408) records were eliminated, and only three hundred and twenty-eight (328) records passed the eligibility assessment.
During the eligibility phase, a criterion was established to include only fully accessible materials for the final articles to be assessed for eligibility. Forty-eight (48) publications were not fully accessible and hence were eliminated. Two hundred and eighty (280) publications were considered for the quality assessment phase.
During the qualitative assessment, nine (9) publications were excluded after reading the full articles as there were no relevant data pertaining to the study. Two hundred and seventy-one (271) articles were included in the study because they met the following criteria: they are original papers published in peer-reviewed journals or peer-reviewed book chapters and conference papers, written in English, and belong to the fields of Environmental Science, Earth and Planetary Sciences, Engineering, Hydrology, Computer Science, or Mathematics. Two hundred and sixty-three (263) of these articles were journal articles, five (5) conference papers, and three (3) were book chapters. These articles were published between 1993 and 2023 and sourced from various locations worldwide. A flow chart of the study selection procedure is presented in Figure 2.
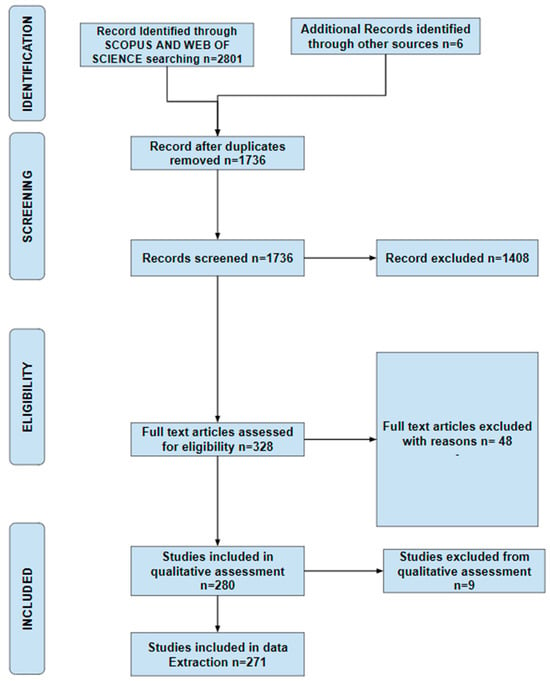
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the study selection procedure.
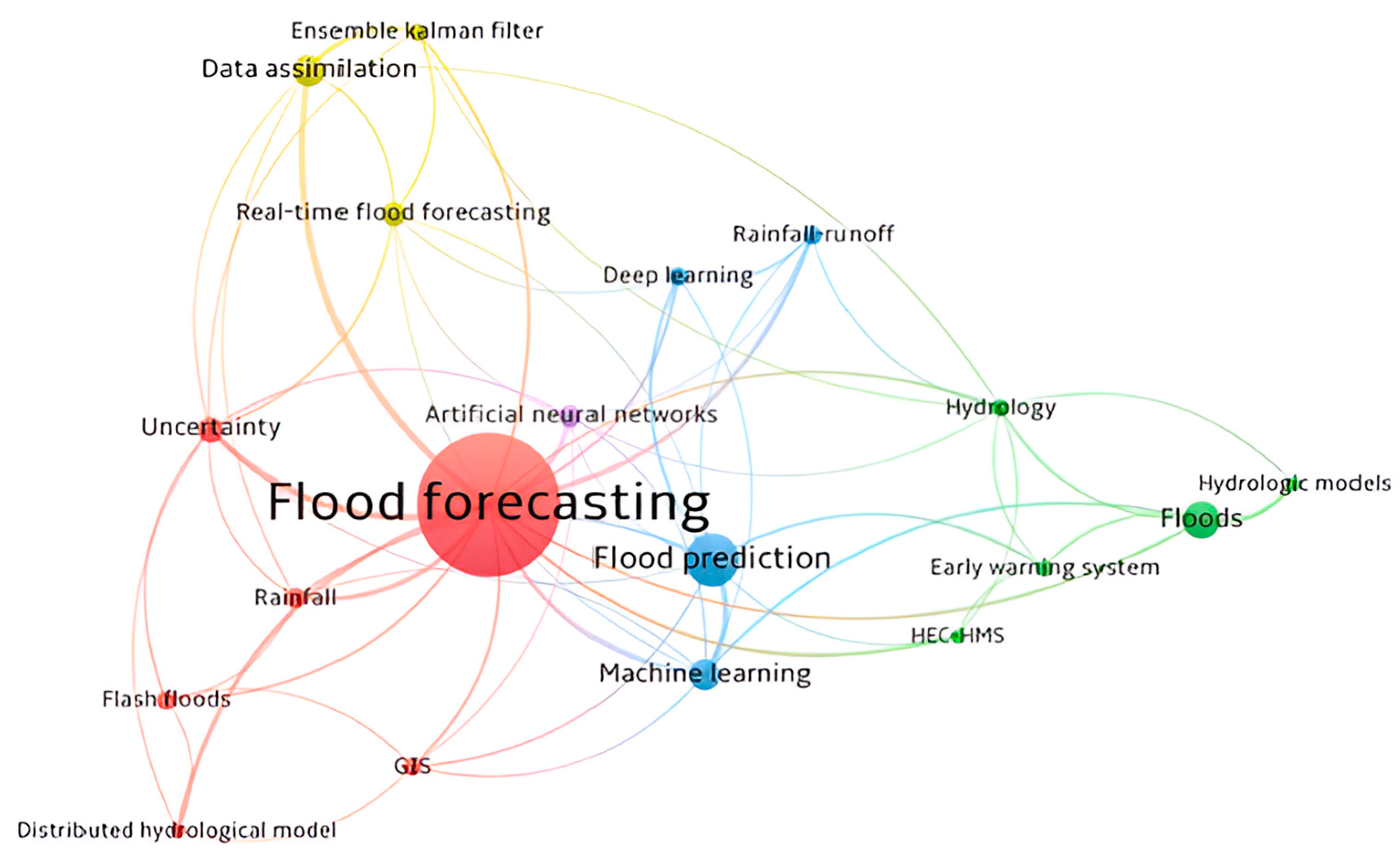
Using VOSviewer version 1.6.20 (a software tool for constructing and visualising bibliometric networks), a bibliometric analysis of the final two hundred and seventy-one (271) documents was carried out for co-occurrence of authors’ submitted keywords. A network of twenty (20) most common keywords was created indicating that floods, flood forecasting, and flood prediction were the most submitted keywords by the authors. Other main keywords included artificial neural network, deep learning, hydrology, and rainfall runoff, among others, as shown in Figure 3. The size of nodes indicates the frequency of occurrence. The curves between the nodes represent their co-occurrence in the same publications. The shorter the distance between two nodes, the larger the number of co-occurrences of the two keywords. VOSviewer uses clustering algorithms to group similar items in a network with a Red, Blue, and Green (RGB) spectrum. Colours range from Blue (lowest score) to Green (median score) to Red (highest score) in terms of occurrence and co-occurrence.
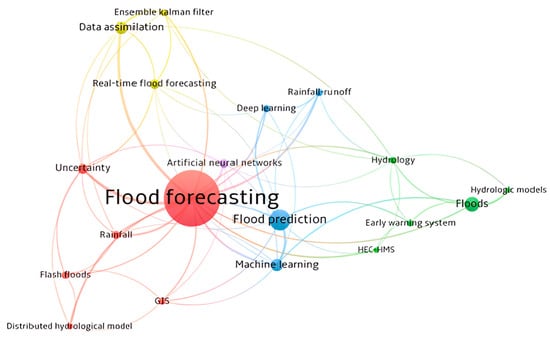
Figure 3.
Analysis of authors’ top keywords network (VOSviewer software).
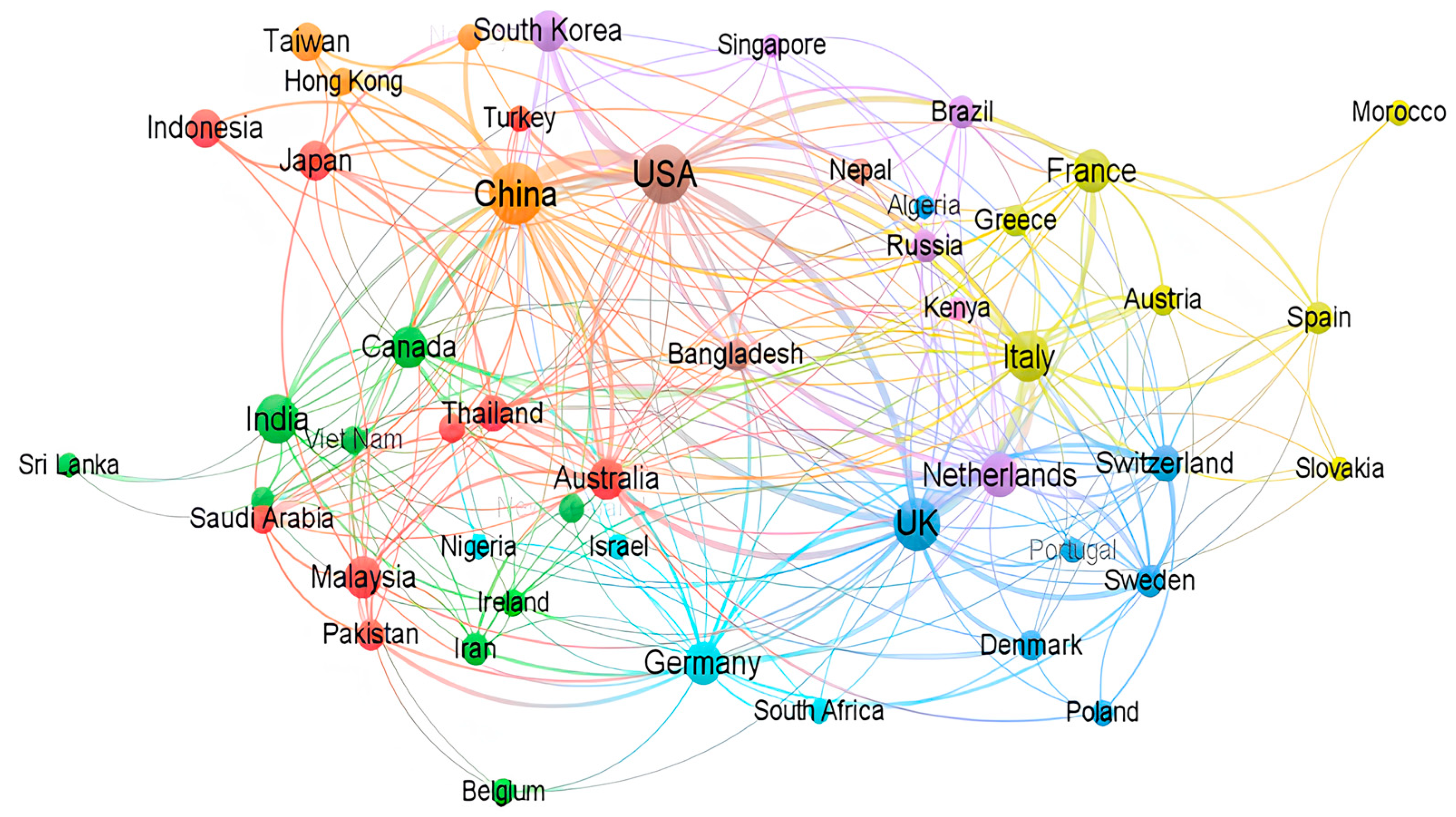
Additionally, a bibliometric co-authorship analysis network by country of the author was carried out using the VOSviewer application, indicating the strongest co-authorship between China, the United States (USA), the United Kingdom (UK), and Australia. From Africa, Algeria, Kenya, Morocco, Nigeria, and South Africa had the highest contribution of co-authorship, as shown in Figure 4. The size of nodes indicates the frequency of occurrence. The curves between the nodes represent their co-authorship in the same publication. The shorter the distance between two nodes, the larger the number of co-authorships of the two countries. VOSviewer uses clustering algorithms to group similar items in a network with a red, blue, and green (RGB) spectrum. Colours range from blue (lowest score) to green (median score) to red (highest score) in terms of co-authorship and countries. This network indicates a multi-institutional research effort towards developing flood early warning systems. Additionally, it indicates higher flood forecasting studies in high-income countries compared to developing countries.
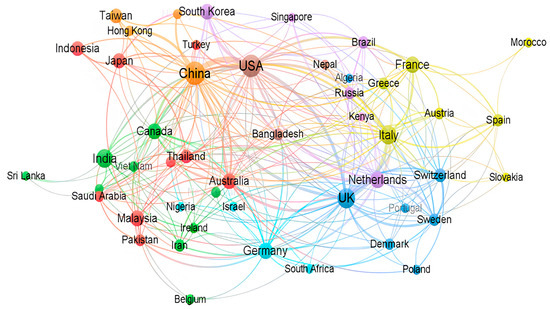
Figure 4.
Analysis of the co-authorship network for the reviewed articles.
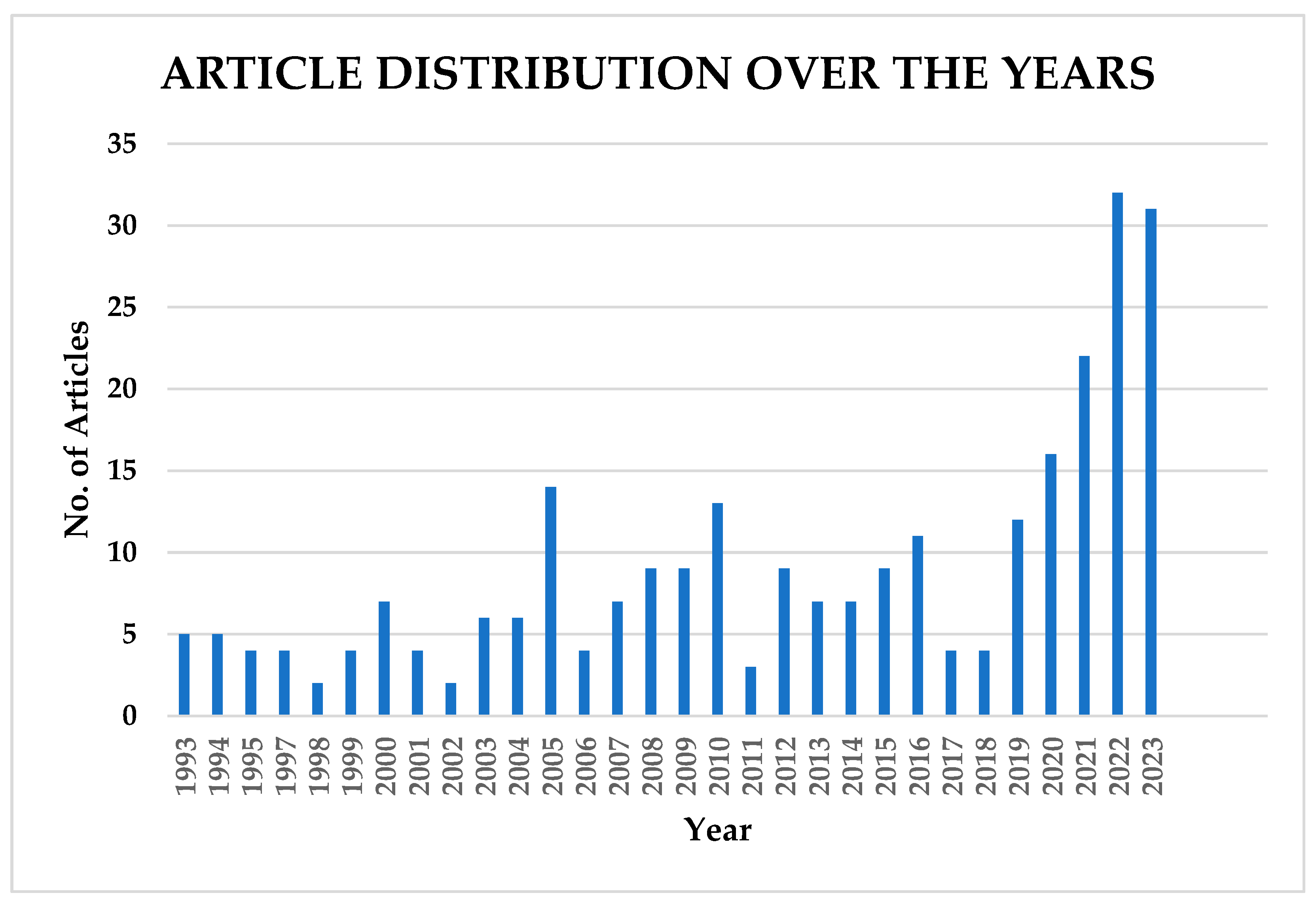
Figure 5 shows the distribution by year of the two hundred and seventy-one (271) articles from 1993 to 2023. Approximately 37% of the scientific papers included in the review were published in the last 4 years (2020–2023). This indicates that scientists are making significant advancements in flood forecasting for early warning systems, together with the increase in the number of open-access journals in recent years.
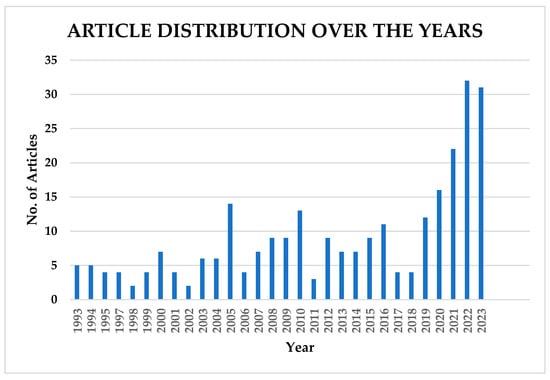
Figure 5.
Article distribution by year.
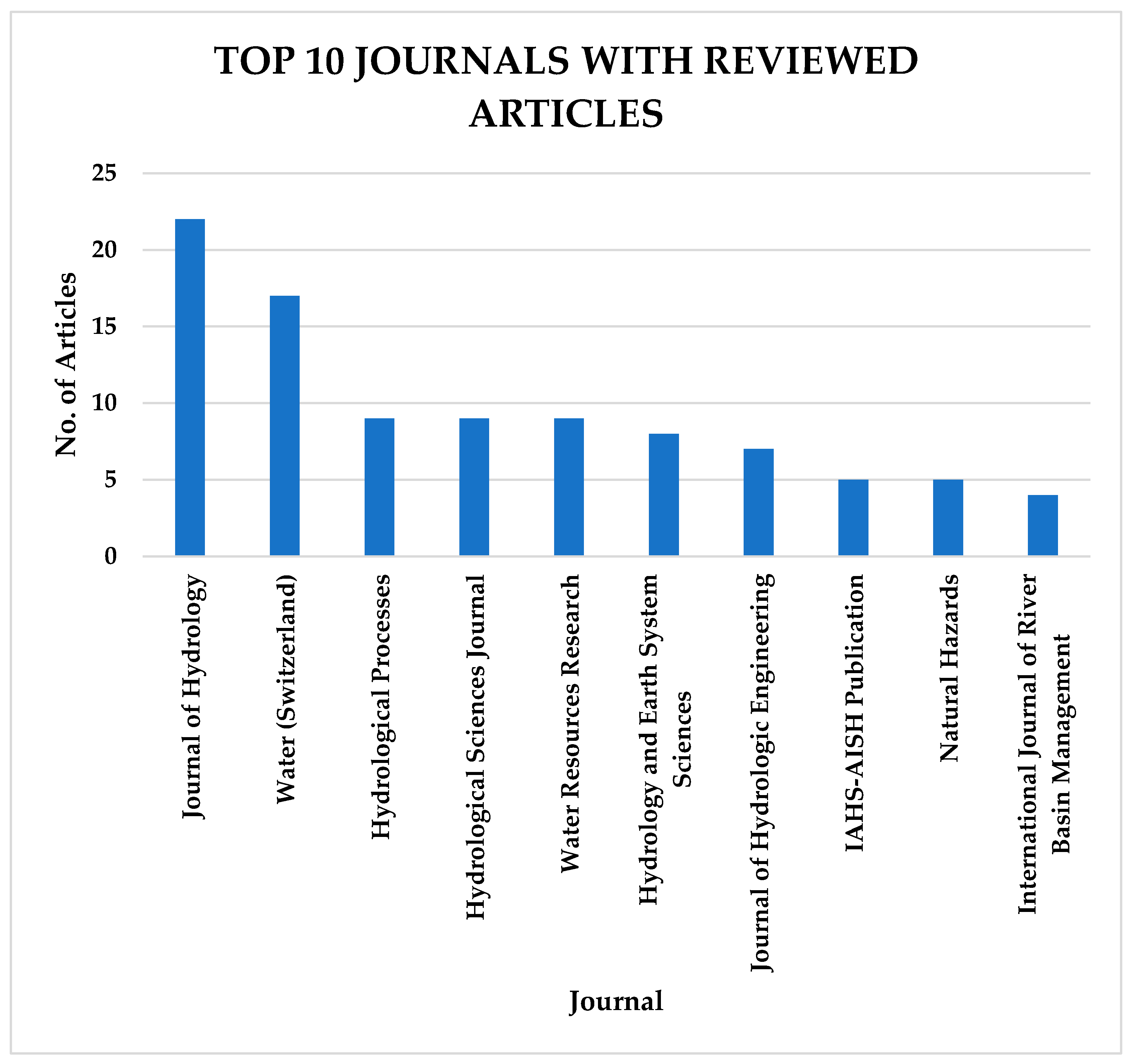
The data analysis indicates that the Journal of Hydrology has the highest number of articles included in this study, with twenty-two (22) articles, followed by Water (Switzerland) with seventeen (17) articles. These are the top journals where researchers in flood studies publish their research. The top 10 journals with the highest number of articles in this study are depicted in Figure 6.
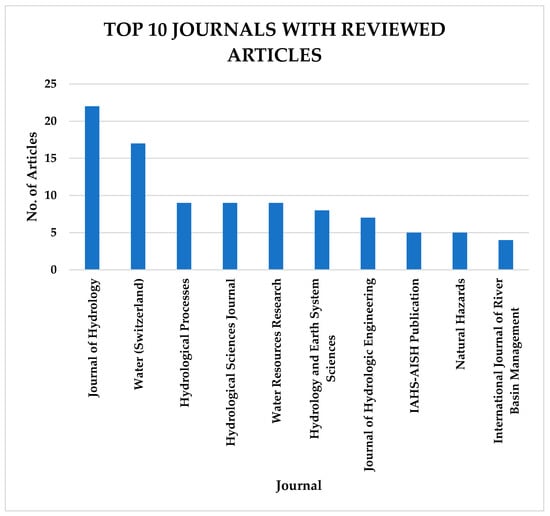
Figure 6.
Top 10 journals with the highest number of reviewed articles in this study.
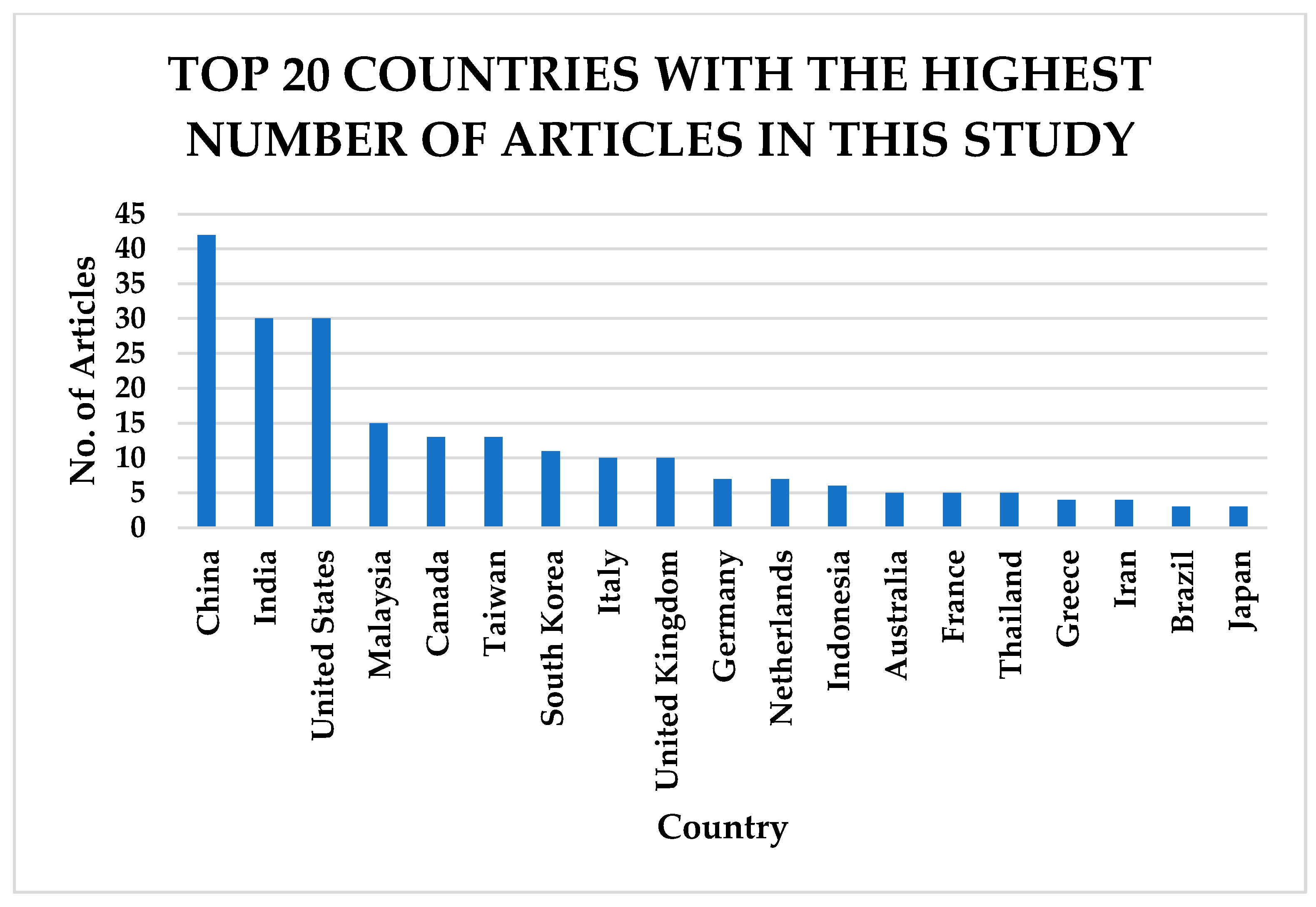
China, India, the United States, and Malaysia contributed the highest number of articles reviewed in this study, as indicated in Figure 7.
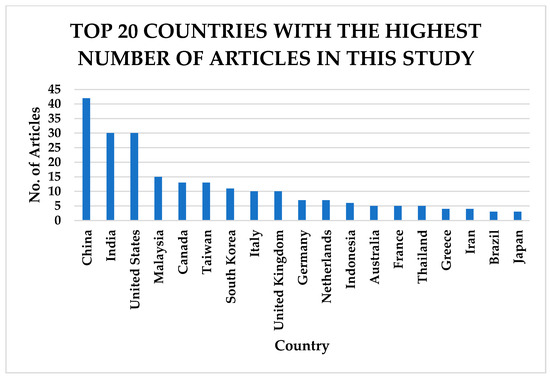
Figure 7.
Top 20 countries with the highest number of articles in this study based on institutional affiliation of the authors.
The above figure indicates that a large amount of research is conducted and published in peer-reviewed articles in developed economies compared to developing countries, which are more prone to data scarcity.
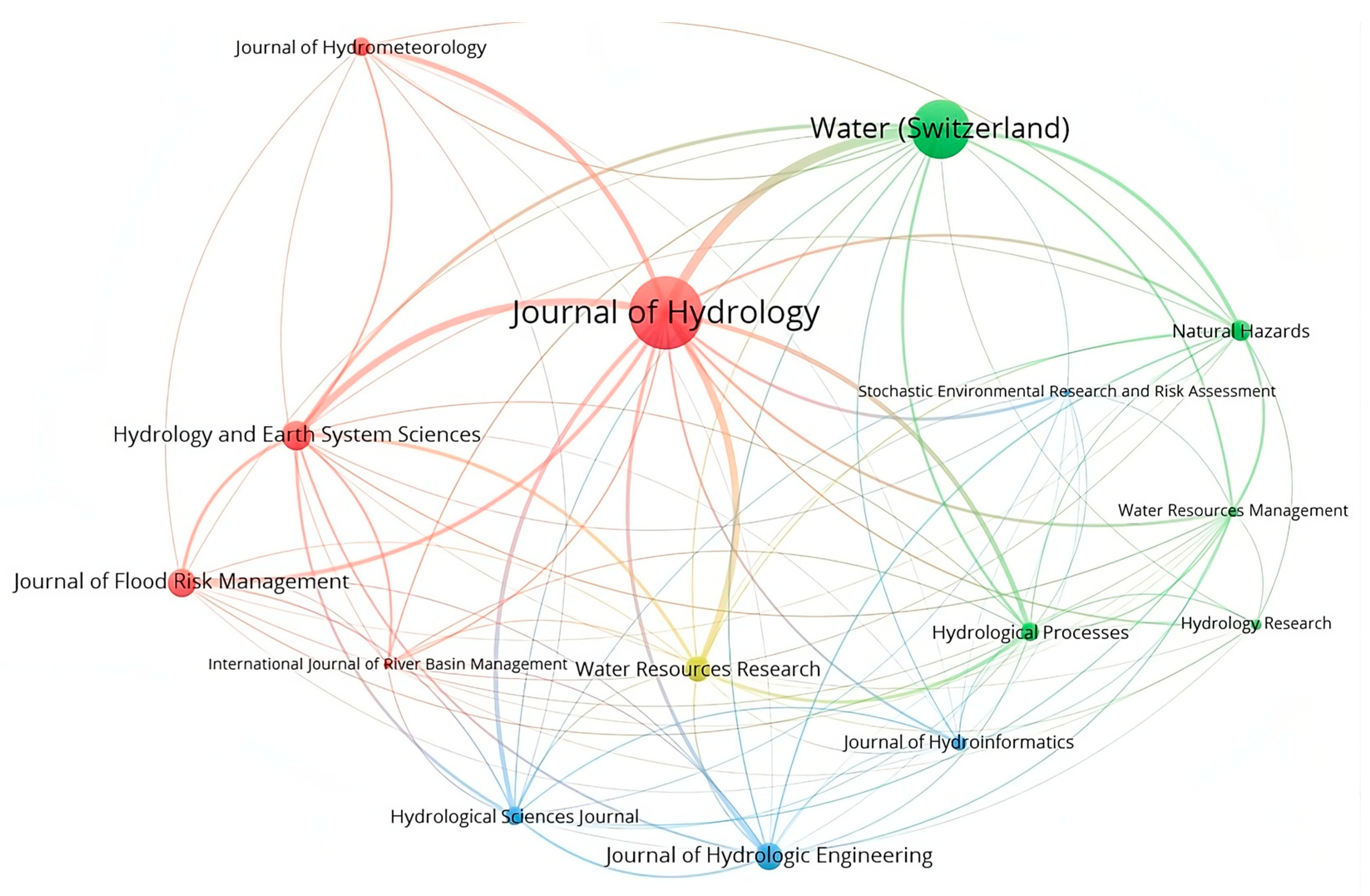
Water (Switzerland), the Journal of Hydrology, the Journal of Hydrologic Engineering and the Journal of Water Research were some of the most cited articles used for this review, as indicated in Figure 8. The size of nodes indicates the frequency of citations. The curves between the nodes represent their citations in the same publication. The shorter the distance between two nodes, the larger the number of citations of the two sources (journals). VOSviewer uses clustering algorithms to group similar items in a network with a red, blue, and green (RGB) spectrum. Colours range from blue (lowest score) to green (median score) to red (highest score) in terms of citations and journals.
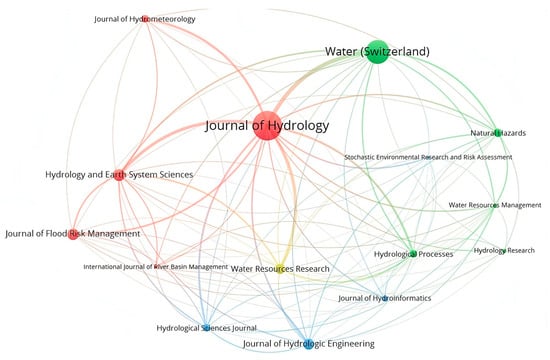
Figure 8.
Mapping journals with the most cited articles used in this study.
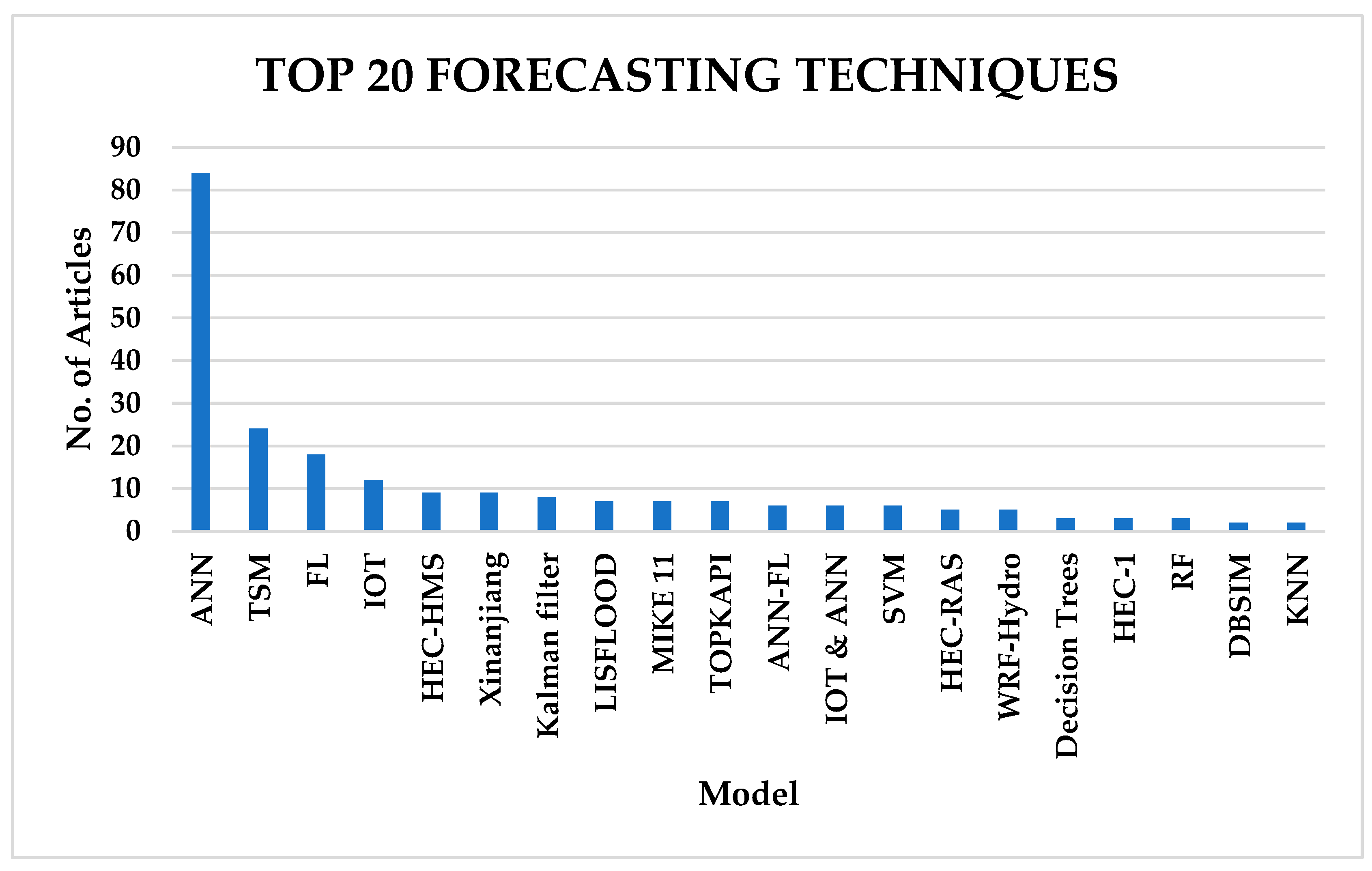
As per the analysis of the results, the most frequent flood forecasting technique for FEWSs was ANNs, followed by TSM and FL, as indicated in Figure 9.
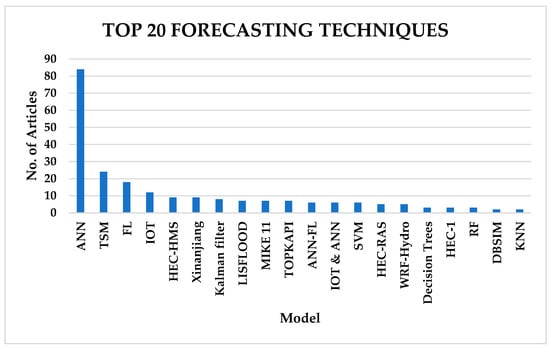
Figure 9.
Top 20 flood forecasting technique distribution by count (1993–2023).
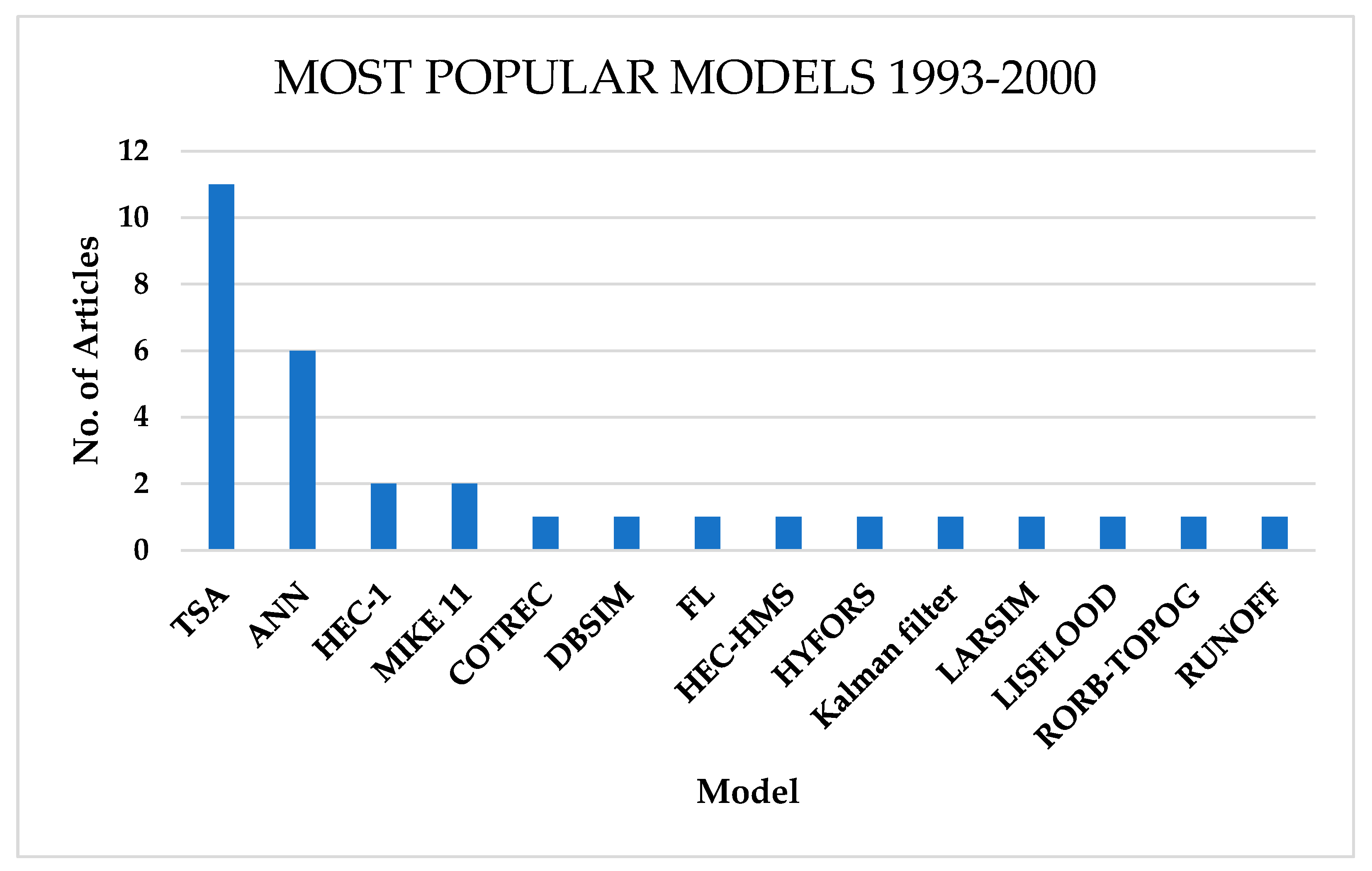
Seventy-two (72) studies indicated the use of artificial neural networks (ANNs), which account for 40% of the techniques used in flood forecasting. This shows the huge part that machine learning (ML) plays in flood early warning systems. Time series models (TSM) come second. The Fuzzy Logic (FL) technique comes third, and in some articles, two or more models are coupled together, for example, FL and ANN or TSM and ANN, to form hybrid deep learning models. However, machine learning techniques like ANN started becoming very popular at the end of the 1990s as time series models (TSM) became less used than ANNs. TSM models like ARIMA and seasonal ARIMA (SARIMA) were the most popular forecasting models between 1993 to the start of 2000, as indicated in Figure 10.
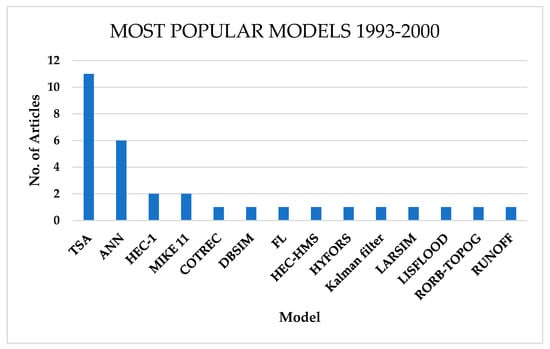
Figure 10.
Most popular flood forecasting techniques for FEWSs from 1993 to 2000.
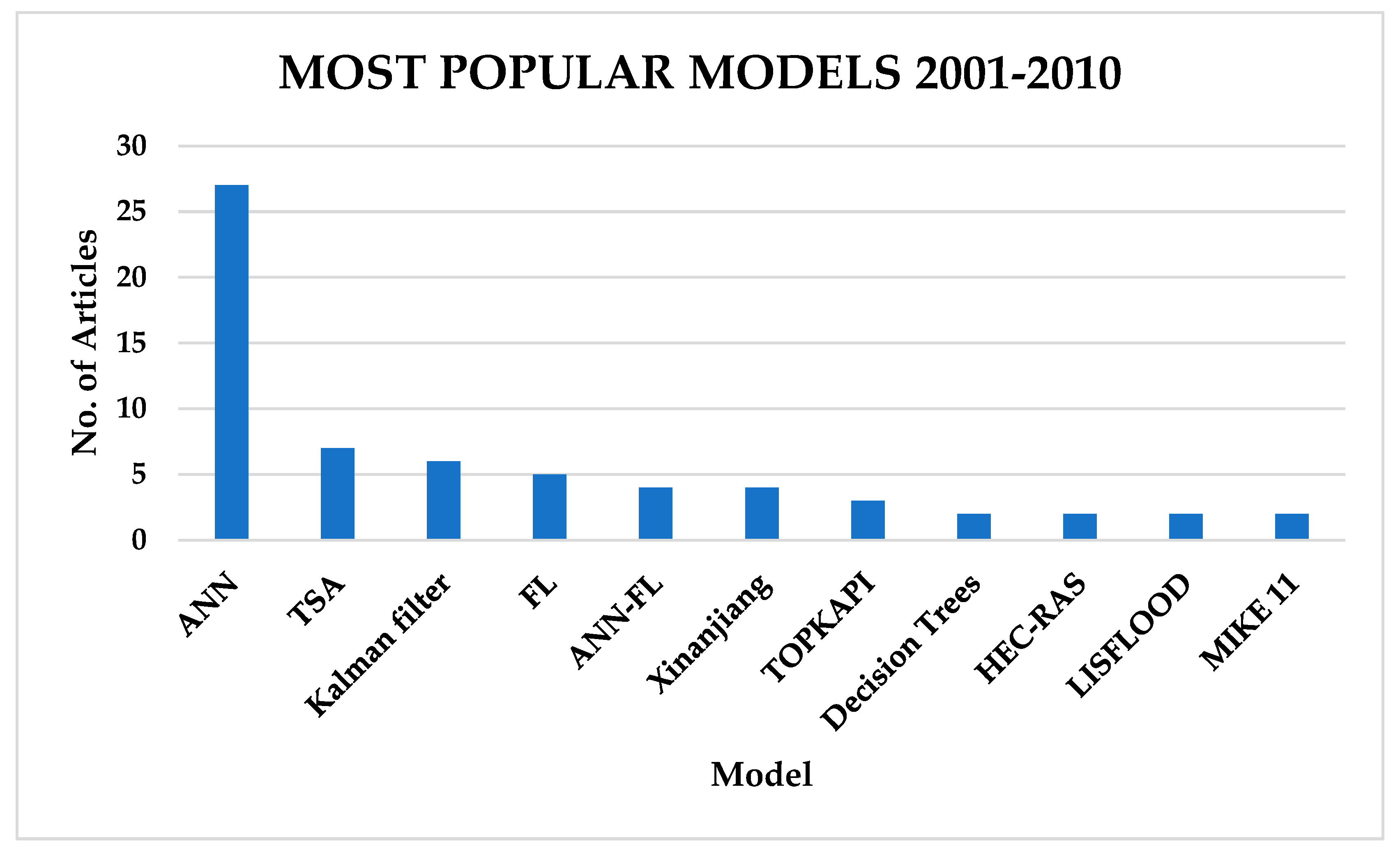
However, between 2001 and 2010, machine learning through ANNs became the most popular technique, with TSM becoming second and hybrid models ANN-FL becoming as frequently used as TSM, as indicated in Figure 11.
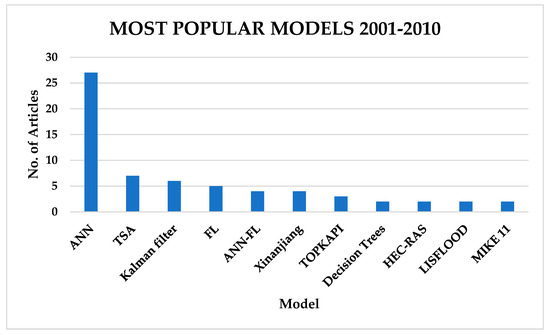
Figure 11.
Most popular flood forecasting techniques for FEWSs from 2001 to 2010.
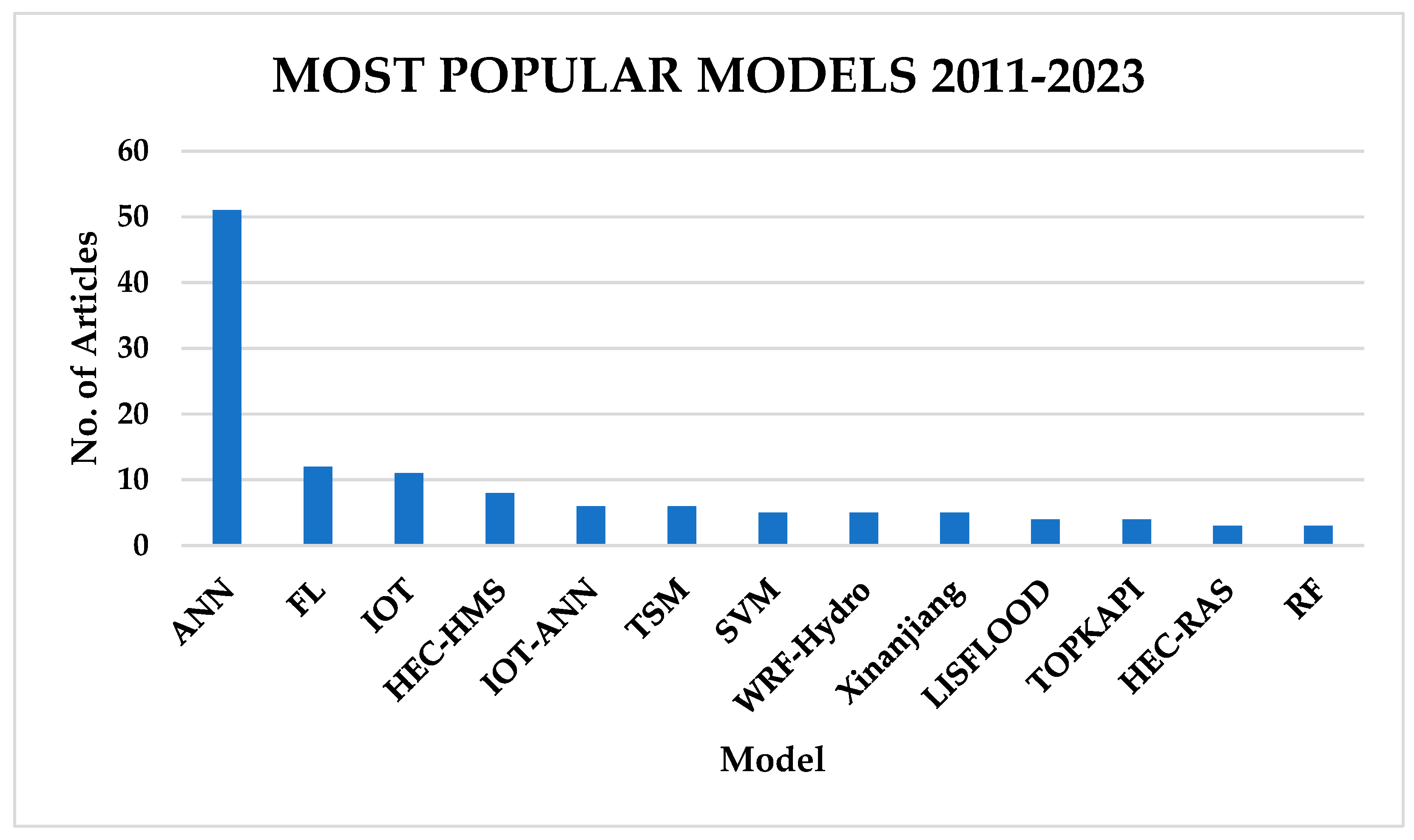
Between 2011 and 2023, there has been a tremendous rise in the application of ANNs, Fuzzy Logic, the Internet of Things (IoT), and HEC-HMS. TSMs still hold a huge space in flood forecasting, although they have dropped down the pecking order, as indicated in Figure 12.
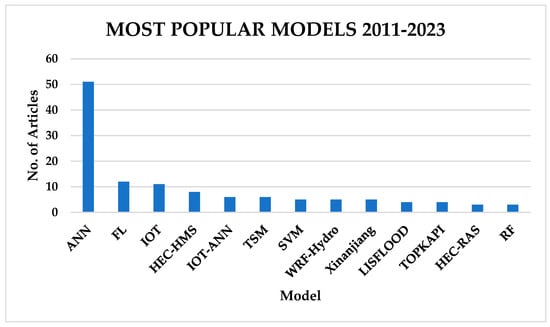
Figure 12.
Most popular flood forecasting techniques for FEWSs from 2011 to 2023.
4. Discussion
This section has been organised to discuss results in a logical flow that starts with an overview of FEWSs in literature, then reviews the flood monitoring and forecasting component of FEWSs, and discusses flood forecasting models in FEWSs. Finally, the section then analyses flood forecasting models employed for data-scarce regions and concludes with a discussion of challenges and opportunities associated with the development of FEWSs in data-scarce regions.
4.1. Overview of Flood Early Warning Systems (FEWSs) in the Context of Information Systems
An early warning system in geophysical hazards is described by [27] as an integrated framework that combines disaster monitoring, forecasting, prediction, risk assessment, communication, and preparedness activities that enable individuals, communities, governments, and businesses to take prompt action to reduce disaster risks before they occur. In contrast to flood hazard and risk assessment, which only determines the risk of flooding, a flood early warning system serves to assess risk and carry out all the functions mentioned above in addition to issuing warnings when a flood is about to happen or when it is already happening [28]. Early warning systems are effective non-structural techniques that are beneficial to populations lacking the physical structures to combat the risk of flood disasters [29]. These measures serve to mitigate economic losses and save the lives and property of a community. This versatile system increases community awareness of hazards and proper responses, as well as adaptation to extreme weather events like floods [30].
The flood early warning system architecture consists of intricate procedures that are interconnected to establish the necessary structure for the prompt distribution of information regarding natural catastrophes [31]. The framework’s core principle consists of a risk assessment model, a monitoring and forecasting model, a communication strategy, and an emergency plan to handle natural catastrophes effectively [31]. The system needs various data collected from various disciplines. Hydrometeorological data collected from multiple sources like meteorological stations, river and channel flow data gathered by hydrologists, GIS and remotely sensed data from earth observatory centres, and social-economic data like population and infrastructure in the area for risk assessments are collected by social scientists and engineers. The design and implementation of the systems are carried out by integrated disciplines of hydrologists, software engineers, systems analysts, and government funding agencies. Flood risk and warning dissemination is carried out by various organs of disaster management in governments and media. This demonstrates the integration of multidisciplinary knowledge among scientists, researchers, and stakeholders to develop efficient FEWSs models for flood disaster management.
A brief discussion of modelling approaches available in the literature is discussed below.
4.2. Flood Monitoring and Forecasting in FEWSs
This is the element of the FEWSs that entails the process of detecting, monitoring, analysing, and forecasting floods and their possible consequences. A flood forecast is a prediction of the forthcoming condition of a flood occurrence, such as the total volume, inundation level, extent of flooding, or average speed of water flow at a specific geographic location or portion of a channel [18]. The anticipation of flood forecasting capabilities regarding deliverables such as extent and timing has highly increased with the current appreciation of the critical role flood warning plays in flood management [32]. Most importantly, the game changer has been the growth of computational capabilities over the past three decades [33]. Ref. [34] emphasised how cloud computing with enormous speeds in computations is growing every day, and the lead times in flood forecasting have become longer, coupled with improved accuracy. In FEWSs, the phrase “short term” is defined as a period ranging between two and six hours, while “long term” refers to durations that are more than one day. “Nowcasting” is a kind of forecasting with a lead time of just a few minutes to maximally two hours. Nowcasting primarily focuses on extrapolating the most recent recorded patterns as some geographical locations require flash-flood forecasting. Flash-flood forecasting refers to predicting floods that happen shortly after a storm [35].
Ref. [30] noted that the most valuable outputs from FEWSs are river levels, inundation extent, and peak discharge timings with enough lead time for authorities and impacted communities to respond appropriately. The achievable forecast lead time is dependent on the characteristics of the catchment. Nevertheless, the fundamental criterion for evaluating lead time is the shortest duration of prior notice needed to carry out preparation measures properly. Factors that determine the lead time of a flood forecast during a FEWSs development include the basin’s topography and hydrometeorological features, the response dynamics of the basin, and the availability of data [36]. Additionally, the restrictions on the extent of services, such as the frequency of forecast issuance and updates or dependability, are mostly determined by the expenses associated with data collecting, limits in modelling, the availability of skilled specialists, the infrastructure for FEWSs, cross-border concerns, and institutional considerations [19]. However, flood inundation depth, extent forecasting, and warning services represent the most sophisticated form of flood early warning systems. Securing this degree of early warning service across the entire nation has so far been unattainable, even in the most developed nations, due to reasons like cost, the complexity of modelling involved, and the maintenance of technical services required [35].
4.3. Flood Forecasting Models in FEWSs
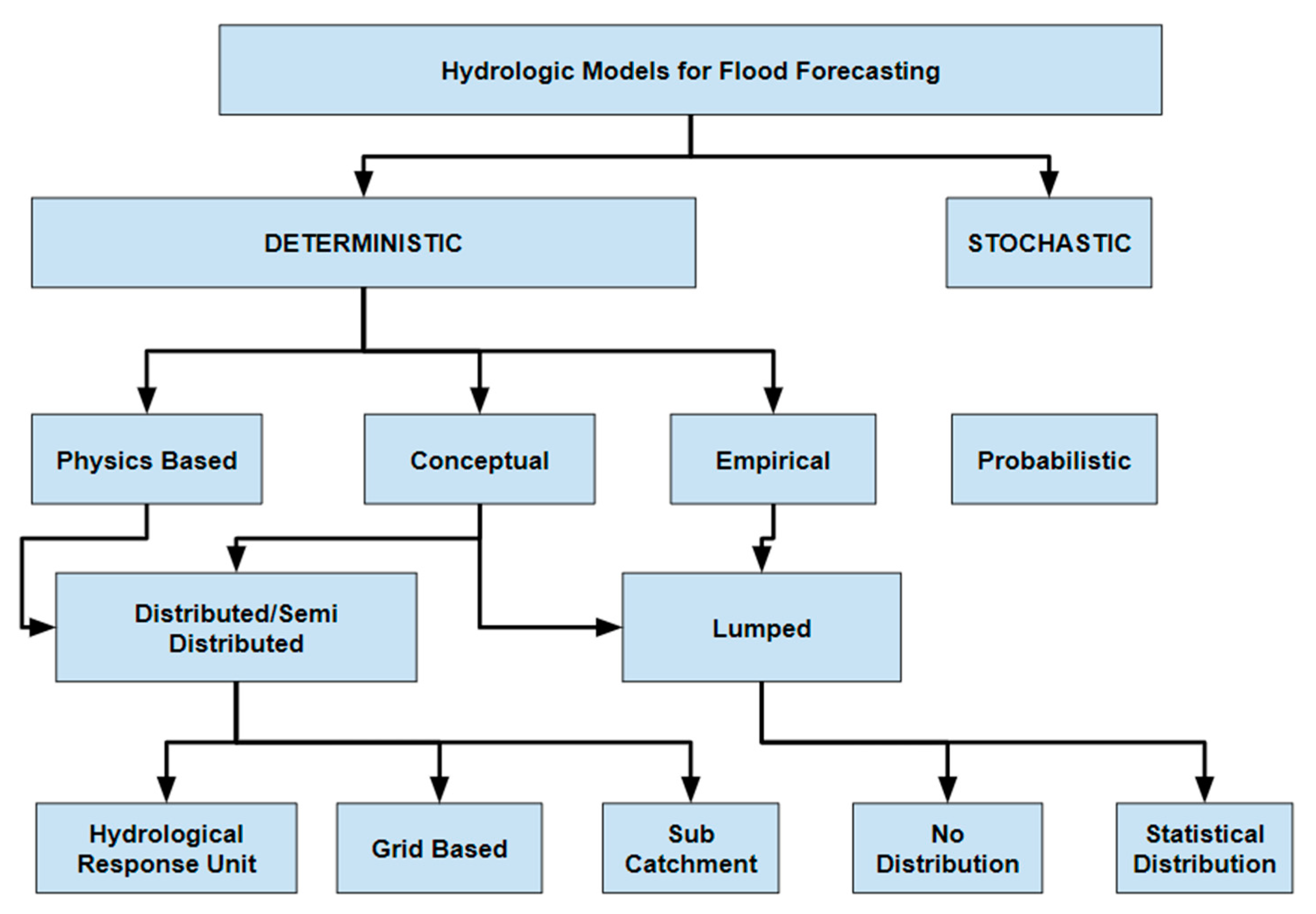
The selection of a model for a specific application is primarily influenced by the main runoff generation processes, the geographical and temporal scale, the area of coverage, and the spatio-temporal resolution of the data present in addition to the characteristics of the catchment [37]. The geographical distribution of input variables and their designated parameters is highly important in model selection. For example, lumped models depict catchments as storage tanks, while distributed models divide catchments into hydrologic response units [38]. Distributed models reproduce hydrological processes more accurately, although the uncertainties can generate significant errors, as in other models [39,40]. Ref. [41] provided a review of the characteristics of hydrological models considering their spatial representation.
There are different classes of catchment models based on lead time rainfall estimates, referred to as the “look-back window” [42]. These classes include updating and non-updating models. The updated models use recent real-time data and quantitative precipitation forecasts (QPFs), hence having enhanced accuracy and reliability [43,44,45]. Non-updating uses rainfall input only based on observed data without any updates. Errors in rainfall data, however, cast doubt on the accuracy of the meteorological inputs [18]. Forecasting can be improved by using weather radar and rain gauges for QPFs, but using QPFs themselves improves predictions and increases forecast lead time since they provide climatological precipitation patterns in real-time. Forecasting models need to adhere to stakeholder and end-user requirements to achieve their goals [19]. The amount of data that accessible should dictate the level of complexity. There is no justification for adding complexity. Most FEWSs use multi-model consensus or distributed models based on physical principles because they are highly predictive and accurate [46]. Resolving issues with inaccurate data, inadequate structure, and inefficient parameter estimates is of utmost importance when it comes to prediction uncertainty [47]. Categories of the catchment models employed in flood forecasting are depicted in Figure 13.
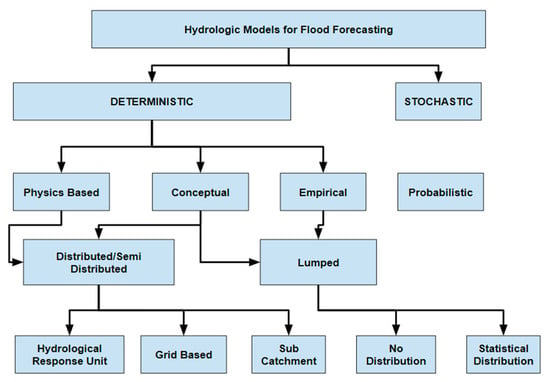
Figure 13.
The categories of the catchment models employed in flood forecasting (adapted from [35]).
4.3.1. Deterministic Models
The deterministic models require two very important components, which include the flood-producing process and flood routing. The flood-producing process includes the modelling of precipitation and catchment runoff modelling executed through hydrologic models [48]. Rainfall–runoff (RR) models represent the catchment hydrological processes like rainfall, water infiltration, soil moisture changes, evapotranspiration, runoff, and streamflow routing [49]. In brief, the RR models are a simplified representation of the real catchment system [50]. The runoff generation process is categorised into saturation-excess runoff generation and infiltration-excess runoff generation [51]. The main products of these models are basically runoff and flow depth [51]. The hydrometeorological inputs and topographic properties of the catchment are incorporated into the rainfall–runoff model to produce river flow characteristics and river depth at a given time during the process [52]. The RR models operating on a sub-basin level (distributed models) produce better results for large catchments, although they may not give the best results for small basins like the lumped models [53]. It is noted that these modes produce a longer lead time compared to models that operate on a catchment as a whole. Time and topographic attributes of the catchment affect the ability of rainfall to be transformed into runoff in the RR model [54]. Proper RR models must consider constant parametric changes in the catchment, including dynamic land use and other physical processes [54]. As much as AI is becoming more embraced in flood forecasting models, physics-based, deterministic (distributed and semi-distributed) models play a crucial role in flood simulation and forecasting. In this study, the top models in the literature include LISFLOOD, MIKE11, HEC-RAS, HEC-RAS 2D (HR2D), SWAT, Xinanjiang, and HEC-HMS. As per the results of this SLR, the Hydrologic Engineering Centre–Hydrologic Modelling System (HEC-HMS) as a hydrological model ranks highest among non-AI models for flood forecasting and has been used numerous times with great success [55,56,57,58,59,60].
HEC-HMS is very efficient and reliable, with low costs [61]. HEC-HMS has often been coupled with HEC-RAS for effective flood risk analysis and forecasting in the literature. Ref. [62] conducted hydrological modelling in the Sironko region, Uganda, using HEC-HMS via HEC GeoHMS in ArcGIS environment and hydraulic modelling using HEC-RAS to simulate 10, 50, 100, 250, and 500-year design floods, respectively. Flood hazard maps were generated and processed via ArcGIS to identify the flood-prone areas. Ref. [63] evaluated the extent of the floodplain in the copper slough watershed (CSW) in Champaign, Illinois, utilising the known precipitation and land use with HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS to develop runoff and floodplain inundation evaluation while incorporating ArcGIS extensions-HEC-GeoRAS and HEC-GeoHMS for the spatial analysis. The transformed runoff from HEC-HMS was used for floodplain mapping with HEC-RAS to generate inundation maps for the peak flow of 2015. Ref. [64] utilised HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS to simulate the flood inundation behaviour of Ain Sefra city during extreme flood events for return periods of 10, 100, and 1000 years, highlighting the region most affected by the flood as the downtown area.
HEC-HMS has also been coupled with AI models to provide higher accuracy and longer lead times in ungauged catchments [65,66,67].
LISFLOOD is mostly used to simulate flood forecasting in Europe but on a small spatial scale, as it works best at higher resolutions since it is grid-based [68]. It has been used in numerous studies in Europe and is the main hydrological model in the European Flood Awareness System (EFAS) [37]. LISFLOOD has also been coupled with other storm water management models (SWMMs) [69]) and The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) [70] for flood prediction.
In Asia, especially China, Xinanjiang is the most dominant non-AI model for flood forecasting [71,72,73,74] and, at times, it is coupled with AI algorithms like ANNs for superior accuracy [75,76].
Another fully distributed, physically based hydrological model that is popularly used for flood forecasting and is seventh-ranked by number in this study is the Topographic Kinematic Approximation and Integration (TOPKAPI) model. TOPKAPI is used mostly in data-scarce regions to provide probabilistic risk assessment [77,78].
4.3.2. Data-Driven Models
Data-driven models, also known as black-box models, do not take into account the physical processes behind the correlations and the interactive nature of the variables at hand [79]. These models are fully numerical and lessen the computation time associated with physical modelling [80]. There are different kinds of data-driven models, including stochastic models and nonlinear time series models. Mainstream TSMs like Auto-Regressive Moving Averages (ARMA) are examples of stochastic data-driven models. TSMs are frequently employed in hydrology because they have straightforward mathematical formulations as they are based on the principles of hydrology, for example, the temporal distribution of variables [80]. These models operate without the extensive calibration of parameters that physical models face, in addition to their low processing demands, and can accurately replicate hydrographs [81]. Nonlinear time series models are exemplified by ANNs that necessitate large amounts of high-quality hydrologic data. ANNs have been successfully used in modelling rainfall–runoff processes and flood forecasting [82]. ANNs can acquire knowledge from incoming data, make generalisations about the behaviour of the data, and effectively handle noise [83]. An intriguing use of data-driven approaches is enhancing real-time predictions generated by deterministic RR models. Significant enhancements were observed by combining ARMA models with other data-driven models for predicting rainfall and updating discharge [84]. Nevertheless, the use of ANNs in operational flood warning systems has been hindered by practical challenges, including lengthy training durations, the risk of overfitting, phase-shift problems, and the absence of clear guidelines for design and parameter selection [33]. Fuzzy Logic and fuzzy set theory are data-driven models that employ an “IF-THEN” principle, and they have been employed in flood prediction for FEWSs [85,86,87]. Hybrid data-driven models have been created through the application of fuzzy optimisation approaches and fuzzy-rule-based systems with other data-driven models like ANNs. The hybrid adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is a product of this integration [88]. Nevertheless, ref. [89] stated that data-driven models fail to accurately depict the fundamental principles of the basin’s physics as it evolves, and their parameters rely on the specific range of data employed for calibration [89,90,91].
This study found that data-driven models are on an upward trajectory as a main tool for flood prediction in FEWSs due to involving less parametrisation compared to deterministic models [92]. These models are gaining more popularity because they are purely numerical and lessen the computation time associated with physical modelling [80]. Various machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed in flood forecasting models of FEWSs, as indicated by the results of this study. These algorithms include Linear Regression (LR) [93,94], Decision Trees ([95]), Random Forest (RF) [96], Bayesian linear regression and XGBoost [97], K mean clustering, Hierarchical clustering, Support Vector Machine (SMV), and Logistic Regression (LR). Ref. [22] reviewed the above algorithms in detail with examples. However, it is the deep learning part of machine learning algorithms, ANNs, that has gained the most popularity in recent years, as depicted in the results of this study. The advancement in the application of ANNs has been tremendous in the past two decades.
ANNs are now incorporated with TSMs and other techniques to form powerful hybrid data-driven forecasting models with high accuracy in predictions [43,94,98,99,100]. As results indicated, between 2011 and 2023, there was a high rise in the incorporation of IoT and ANN, and this combination came in sixth position of all forecasting techniques used during that period [101,102,103,104,105]. It should also be noted that, between 2000 and 2010, ANN was frequently combined with FL to form the fifth highest-used forecasting model, as shown by the following studies: [106,107,108,109]. ANN-Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) [110] and ANN-Hydrologic Gray Model (HGM) [111] are two other forecasting models used. There are different types of ANN applied for flood forecasting in the reviewed literature, like radial basis function neural networks [112,113,114], back-propagation neural networks [115,116], and the most used ANNs in the studies completed between 2011 and 2023, the recurrent neural networks (RNNs) like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) [117,118]. A Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) is like LSTM but with a gating mechanism to push through some inputs or eliminate certain features, resulting in lessened features than LSTM has. In multi-dimensional hydrometeorological time series data, a type of CNN called Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) has been used in the literature with a Long Short Term Memory Network (LSTM), (ConvLSTM), to extract spatio-temporal features of hydrological information and provide flood forecasts [119,120,121].
Support vector machine (SVM), a supervised machine learning algorithm that employs data transformations to classify, regress, and detect outliers, has also been a growing machine learning algorithm in flood prediction between 2010 and 2023 [122,123,124]. In some cases like [125], SVMs have outperformed ANNs due to ANNs’ issues with generalisations that are not inherent in SVMs.
Fuzzy Logic (FL) has been implemented by various researchers for flood forecasting and has gained momentum over the past few years [126,127,128]. Fuzzy Logic is a mathematical method that allows for multiple truth values to be processed through the same variable [129]. Additionally, Fuzzy Logic has been combined with other techniques for hybrid flood forecasting, for example with ANN [130] or with TSM [86].
Additionally, GIS and remote sensing development has highly aided hydrologic and hydraulic modelling for flood mapping and forecasting by simplifying data collection. Digital elevation models combined with Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) and state-of-the-art satellite imagery provide data to computer systems that simulate catchments and their physical attributes with great accuracy. This makes the forecasting of future states possible without physically collecting data. There is a growing use of WSNs powered by the Internet and creating systems popularly known as the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT has been applied in various studies with successful flood predictions [131,132,133,134]. WSN-IoT has also evolved to involve AI-based algorithms like ANNs to produce powerful forecasts [135,136,137,138].
4.3.3. Chronological Evolution of Flood Forecasting Models in FEWSs
This study was undertaken for flood forecasting models between 1993 and 2023, and analysis was carried out for three time periods: 1993–2000, 2001–2010, and 2011–2023. From the results of this study, the following can be deduced about the chronological evolution of forecasting models used in FEWSs.
Between 1993 and 2000 (Figure 10), time series models (TSMs) were the most popular models in flood forecasting, especially the Autoregressive Moving Average (ARMA), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), and Transfer Function-Noise models. These statistical models provided a simplified mechanism away from physical-based models as they needed mostly precipitation data and flood indices to forecast flood occurrences. The second-most commonly used models were the catchment physics-based models HEC suite and MIKE suite. However, towards the end of the 1990s, machine learning became popular, with artificial neural networks coming close to the numbers of TSM use, overtaking physics-based models.
Between 2001 and 2010 (Figure 11), ML models were the most popular models, overtaking TSMs. Increased data volume due to GIS and RS, a rise in computational efficiency, cloud computing, and data storage revolutionised forecasting modelling in the 2000s. Various algorithms of ML became widely used in forecasting and artificial neural networks surpassed the traditional TSMs. However, the limitations of these data-driven models meant that they could not effectively reproduce catchment characteristics; hence, physics-based models were still in use independently or coupled with machine learning to a smaller extent.
Between 2001 and 2023 (Figure 12), due to higher computational capabilities, ML models were much more popular, due to increased accuracy. These models were coupled with TSMs, and an ensemble of ML and physics-based models with GIS and RS came into place to reproduce catchment characteristics and to increase forecasting accuracy while minimising model uncertainties. Hybrid models have become more popular in the past 10 years, attributed to AI development, easy access to scientific knowledge through journals, cloud computing, advancement in GIS and RS data collection, and rapid capacity development through higher learning institutions.
This study shows that AI, through enhanced machine learning capabilities, is the future of environment systems to forecast floods, as all responsible factors mentioned above are on the rise.
4.3.4. Ensemble Predictions
Ref. [139] stated that, due to the limitations of single deterministic models, a new form of combined models called ensemble modelling has been built by researchers. Ref. [140] described in detail how ensemble forecasting may provide a range of potential future outcomes for a given variable by experimenting with multiple initial circumstances, physical process representations, parameter settings, and problem-solving approaches. The system has a high capability to predict several hydrological factors, like streamflow and river levels, which enhances the output of the most probable outcome [141]. When meteorological and hydrological modelling capabilities are integrated with advancements in data collection, satellite observations, land-surface hydrology models, and increasing computational capacity, the capacity to develop an ensemble that forecasts on a worldwide level is realised [52]. Currently, forecasting systems in operation like the Global Flood Monitoring System (GFMS) developed by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the University of Maryland, Disaster AWARE Pro by NASA, Met Office Global and Regional Ensemble Prediction System (MOGREPS) by the United Kingdom (UK) government, Global Flood Awareness System (GloFAS) developed by European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), and the pre-operational stages like The THORPEX Interactive Grand Global Ensemble (TIGGE) commonly use ensemble weather predictions as inputs [142]. This inclusion enhances the accuracy and reliability of flood forecasts, enabling early flood warnings with more certainty. Ensemble Prediction Systems (EPSs) face several major problems, such as improving Numerical Weather Predictions (NWPs) and understanding the overall source of errors and biases in the system. Other issues associated with EPSs arise from the complexity associated with complex data integration techniques and not having enough case studies for validation [143]. Putting EPSs into operational settings and telling end users about uncertainty and probabilistic forecasts in a clear way are other challenges that EPSs face. Operational ensemble prediction systems, such as the Hydrologic Ensemble Prediction Service (HEFS) in the USA, ECMWF in Europe, and the European Flood Awareness System (EFAS), are perfect examples [144]. Inaccuracies in input datasets easily and significantly affect any flood forecasting model. There needs to be synchronisation between the forecasting model framework and the physical attributes of the basin and catchment as a whole to improve the model accuracy [145]. The model should be comprehensively calibrated, and accurate catchment attributes should be fed into the model. The main factors contributing to volumetric mistakes arise from the inadequate model framework, erratic input data or a delay in the assimilation of data from the model’s routing component in addition to spatio-temporal parameterisation [146]. Shape inaccuracies occur because the model converts rainfall to runoff. Therefore, all models require updating and verification.
4.4. Flood Forecasting in Data Scarce Regions
4.4.1. Challenges of Data-Scarce Regions and FEWSs
Data scarcity in flood forecasting can be attributed to the scarcity of conventional gauging systems for river, stream flow, and precipitation. In flood modelling, both gauged and meteorological data at an excellent spatial-temporal resolution are critically important to provide accurate forecasts. The main goal in the data-scarce regions is to find a solution to the lack of consistent long-recorded hydrometeorological data. Most developing countries started river flow gauging post-World War II, and this was mostly through either statistical or conceptual models mainly carried out on main transboundary rivers like the River Nile, River Niger, and Congo River, with a concentration on annual moving averages [147]. Ref. [148] noted that, apart from Algeria and South Africa, the modern rainfall gauging stations barely covered a century; Europe, America, and Asia have datasets extending to one or two centuries. The spatial variability in precipitation requires a well-developed gauging network to capture data at a local scale which can be used for training forecasting models [149,150]. Ref. [151] noted the lack of the decrease of gauging networks in developing networks, attributing this to the lack of funding priorities for these networks due to these countries having more pressing economic issues. To overcome these data challenges, at the local scale, various methods have been applied in flood forecasting, as illustrated in this section. From missing stream flow and precipitation data, the methodologies have been changing over the past 20 years from purely statistical simulation and derived distribution techniques to probabilistic algorithms and currently incorporating advanced ML algorithms and GIS and Remote Sensing (RS) products. However, GIS and RS products do pose various challenges for research organisations as they depend on satellite technology from developed nations’ organisations.
4.4.2. Solutions of Data-Scarce Regions and FEWSs
Various statistical methods may be applied to individual sites or regional areas in data-scarce regions. A few of these methods are presented below as potential solutions to improve data availability in data-scarce regions. Ref. [152] evaluated six methods for estimating peak flow from ungauged watersheds in coastal British Columbia. They included the British Columbia (B.C.) Ministry of Environment and Parks method, a statistical method based on the Bayes theorem, a physically based stochastic-deterministic procedure, a regional method, the Index Flood method, the method of Direct Regression of Quantiles, and the method of Regression of the Distribution Parameters. The study’s findings demonstrated that the Bayesian method, the British Columbia Environment method, and the stochastic-deterministic technique all produced respectable results. It also concluded that the stochastic-deterministic procedure only needs a very small amount of information, which is readily available from topographical maps and a rainfall atlas. The Index Flood method was also applied by [153,154,155] in flood analysis in data-scarce regions, with mixed results.
Models that use probability distributions have been instrumental in flood susceptibility analyses in data-scarce regions. These models in the literature mostly include The Multi Criteria Decision Models (MCDMs) and the Bayesian methods. MCDM prevalent in the literature for flood forecasting included Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [156], Combinative Distance-based Assessment (CODAS) [157], Complex Proportional Assessment (COPRAS) [158], Evaluation Based on Distance from Average Solution (EDAS) [159], and Multi-Objective Optimisation by Ratio Analysis (MOORA) [160]. The above MCDMs were analysed briefly by [22], and they noted that some AHP is highly biased as it does not consider some uncertainties. These models use satellite images for flood mapping, risk assessment, and flood forecasting. It should be noted that the above models are often coupled with a Fuzzy Logic Inference system for superior decision analysis and to enhance the accuracy of the forecasts.
For areas where there is scarce precipitation data, the use of Satellite Precipitation Products (SPP) becomes highly paramount in the flood analysis and forecasting phases. The SPPs include Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement) (IMERG) [161], TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) [162], Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) [163], Climate Prediction Centre (CPC) MORPHing technique (CMORPH) [164], Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station (CHIRPS) [165], and Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using artificial neural networks (PERSIANN) [166]. Ref. [167] evaluated TRMM products in hydrological modelling and found that these SPPs can provide data with a temporal resolution of an hour and a few square meters. SPP-derived hydrographs are comparable to rain gauge data-derived hydrographs and hence can be used to replace missing rain gauges [168], although the performance of SPP-forced hydrological models hugely depends on precipitation type, seasonality, hydrological model formulation, and topography [168]. Additionally, the superiority of SPPs in accuracy varies, and numerous studies have already been conducted to compare these SPPs. Ref. [169] evaluated IMERG, GSMaP, and CHIRPS statistically and hydrologically in the sparsely gauged Chenab River basin of Pakistan, with results indicating that GSMaP was superior to CHIRPS and IMERG. Ref. [168] compiled several assessments of SPPs all over the world, and, in agreement with [169], they both noted that bias was a significant issue in SPPs, and bias correction, such as quantile mapping and model recalibration, is very essential for systems that use SPPs to minimise errors.
Recent research has especially focused on the use of soft computing-based approaches that include ML, SPP with GIS, and RS to forecast floods in data-scarce areas. Ref. [170] used the satellite precipitation product and wavelet-based machine learning models in the flood-prone Vamsadhara river basin, India, where validation results showed that the proposed method has the potential to forecast extreme flood events with longer lead times in comparison with the other benchmark models. Ref. [171], utilising IMERG’s one-hour resolution rainfall data, four machine learning-based real-time flood forecasting models that included feed-forward neural network (FFNN), extreme learning machine (ELM), wavelet-based feedforward neural network, and wavelet-based extreme learning machine, were able to predict the water level at the Bagmati River’s Hayaghat gauging station with lead times ranging from one hour to ten days. The likelihood of detection of 85.42% indicated a strong association between the observed data and IMERG in the results. Wavelet-based models performed better overall than their singular counterparts. The FFNN model outperformed the ELM model among the singular models, achieving satisfactory forecasts with a lead time of up to five days. Only wavelet-based FFNN performed well, with a 7-day lead time; for a 10-day lead time, no model yielded sufficient results.
ML is instrumental in data-scarce areas to forecast floods due to various reasons that include faster and more reliable forecasts than traditional flood modelling methods in predicting local floods in addition to overcoming the challenge of scaling flood forecasting from local to regional levels [20]. However, the challenge here is that the most proven powerful ML techniques in the literature, such as ANNs, require a large historical dataset to provide accurate results. A small number of data will lead to either overfitting or model underfitting; hence, the algorithm chosen must consider dataset size [172]. This study found that in data-scarce regions, the following types of machine learning are essential: Transfer Learning (TL), which utilises pre-trained models and fine-tunes them for local flood forecasting. Ref. [173] used TL through a standard recurrent neural network in the form of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) to fit on a sufficiently large source domain dataset from the US and reutilised the learned weights to a significantly smaller similar target domain dataset from Kenya, which showed generalisation performance with results indicating the effective predictive skill of forecasting streamflow responses when knowledge transferring and static descriptors are used to improve hydrologic model generalisation in data-sparse regions.
Ensemble methods combine multiple models to improve prediction accuracy. Ref. [174] integrated multiple satellite-based precipitation and soil-moisture products using Random Forest (RF) and bias correction techniques in ungauged Andean-Amazon sub-basins that suffer frequent flash flood events where precipitation estimates derived from the Bias-Corrected Random Forest Precipitation framework (BC-RFP) showed a high ability to reproduce the intensity, distribution, and occurrence of hourly events while simulations of flash flood events by coupling the GR4H model with BC-RFP presented satisfactory performances with Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE) between 0.56 and 0.94.
Hybrid models integrated physical and machine learning models to leverage the strengths of both. Ref. [175] integrated a hydrodynamic model to simulate several compound flooding scenarios with three ML algorithms to model water level dynamics in data-scarce regions of Pontianak, Indonesia. ML algorithms used were Random Forest (RF), Multiple Linear Regression (MLR), and support vector machine, with RF providing the best results in the study, where it predicted 11 out of 17 compound flooding events during the implementation phase.
Active learning selectively samples data to maximise learning efficiency, and meta-learning trains models adapt quickly to new scarce data. Ref. [176] recommended deep active learning to overcome the time-consuming and labour-intensive data labelling process in supervised learning during flood inundation mapping using deep learning.
Graph Neural Networks utilise graph structures to model complex relationships. Ref. [177] used Flood GNN, which is a GNN for flood prediction, stating its advantages as it operates on both spatial and temporal dimensions and processes the water flow velocities as vector features instead of scalar features. The study produced promising results outperforming a Recurrent neural network (RNN).
Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) incorporate physical laws and constraints into neural networks. Ref. [178] used Physics Informed Neural Network for Spatial-Temporal Flood Forecasting with results showing that the PINN model performs better than the ANN models and is suitable for flood inundation forecasting.
Bayesian neural networks quantify uncertainty and provide probabilistic predictions. Ref. [179] used the Bayesian network (BN) model to estimate flood peaks from atmospheric ensemble forecasts (AEFs) and simulate historic storms. The BN model was trained to compute flood peak forecasts from AEFs and hydrological preconditions, with results showing a mean absolute relative error of 0.076 for validation data compared to 0.39 for ANN, indicating that BN is less sensitive to small data sets than ANN, thus being more suited for flood peak forecasting than ANN in data-scarce regions.
Overall, if historical hydrometeorological data are available and can be used to calibrate the SPPs, then, with the use of GIS and Remote Sensing data as well as machine learning algorithms, flood forecasting with superior accuracy is possible for the poorly gauged or ungauged regions of a catchment.
4.5. Challenges and Opportunities
This study has revealed that the new developments in AI algorithms require big data for training to achieve superior accuracy of the forecasts, but most developing countries do not have hundreds of years of hydrometeorological data to feed into these models for training. However, with the advancement in SPPs and global ensemble meteorological forecasts that can provide access to real-time meteorological forcing model input data with less data latency, this challenge can be overcome, although at least a few years of data need to be present from gauges for model recalibration and bias correction. Another opportunity here is that, in case there is completely no gauged data, machine learning algorithms like Transfer Learning can be used for data in similar climate regions for model enforcement, although these may need to be recalibrated.
Comprehensive hydrological and hydraulic models developed by commercial tech firms are costly, with any adjustments or customisations adding an extra cost. These models are provided through a business model known as Software as a Service (SaaS) with monthly or annual subscriptions, and base codes are not available to the user. These models are cloud-based most of the time. The authors advise taking the opportunity to use the freely available models like HEC suites where base codes are fully available for customisation and adjustments by the end user for the model to fit the catchment characteristics and to be coupled with other models through coding easily. Using multi-hydrological model systems enhances system accuracy and dependability as it brings out uncertainties. Additionally, the feasibility of model implementation is as important as the cost of the model’s development.
This research has limitations stemming from limited access to information from operational flood early warning systems worldwide. The models and architectural frameworks are protected information by governments or parastatal bodies, and there is limited publication of information directly into scientific journals; hence, almost all information in this study is obtained from academic institutions published in various journals.
5. Conclusions
The rise in technological development has produced very advanced information systems, and disaster warning systems like flood early warning systems have taken a new shape through an increased ability to integrate several models and assimilate various data inputs. In this study, a scoping literature review process known as Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) was conducted to uncover how flood forecasting models in the FEWSs have evolved over the past three decades, 1993 to 2023, and to find challenges and opportunities to assist in model selection for FEWSs in data-scarce regions. Available academic literature critically and systematically reviewed the flood early warning systems forecasting model components to establish and organise the chronological evolution of the flood forecasting techniques of flood early warning systems.
This study found that, between 1993 to 2020, time series models (TSMs) were the most used models in flood forecasting, and machine learning (ML) models have been the most dominant forecasting models from 2011 to the present.
AI tools, especially machine learning non-linear time series models like artificial neural networks, have become part and parcel of today’s forecasting and disaster warning systems. Models have become more complex and data-driven with greater accuracy and dependability but, on the other side, with greater final costs and high technical capacity requirements with a requirement for greater computational power.
This study found that coupling hydrological, hydraulic, and AI has proved to be the ideal ensemble for flood forecasting in FEWSs due to superior accuracy, longer lead times, and ability to bring out uncertainties in FEWSs.
Due to advances in global ensemble meteorological forecasts and access to real-time meteorological forcing model input data with less data latency, “Nowcasting” is now possible with FEWSs, flash floods are easy to detect, and warning information is disseminated in time to save lives. This SLR has played a crucial role in shedding light on current global trends of models used in flood risk detection and guiding the potential model selection for flood forecasting in FEWSs, even in data-scarce regions.
From this SLR, it can be deduced that model framework, input data, catchment characteristics, and parameterisation greatly affect the model’s uncertainty. Using multi-hydrological model systems enhances system accuracy and dependability as it brings out uncertainties. Additionally, the feasibility of model implementation is as important as the cost of the model’s development. The technical ability of the team required, input data, and spatial or temporal resolution of the model greatly affect the system’s output accuracy and dependability, and hence should always be put into consideration. A further study on model performances under the variables above to assess performance is highly recommended by this study. Therefore, further study is recommended to assess the cost of the models and model ensembles in relation to catchment size, prediction accuracy, and dependability.
The findings of the SLR recommend interdisciplinary, institutional, and multisectoral collaborations towards the development of FEWSs, as the expertise required spans all sectors and the development of FEWSs is multidisciplinary. Hence, it is recommended that institutional collaborations with governments are embraced to bridge this gap so that knowledge is shared for a faster-paced advancement of flood early warning systems.
Additionally, more model integrations are recommended, especially importing machine learning into physical models to improve accuracy, for example, where data are lacking due to poor gauging network or lack of gauging network.
Lastly, this SLR recommends adopting both in situ data collection and processing of remotely sensed or derived data using cloud computing techniques, because heavy data processing and model integrations are moving to cloud computing for faster processing time and higher computational capabilities.
This study should be adopted by researchers and technical experts in governments and the private sector working to develop flood early warning systems for regions and countries to assess and select the best flood forecasting models for their systems depending on the availability of appropriate temporal-spatial hydrometeorological data, expertise, funds, and other success factors as elaborated by this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, N.B. and D.K.; methodology, N.B., D.K. and G.M.; software, N.B. and G.M.; validation, N.B., D.K., G.M. and S.G.; formal analysis, N.B. and D.K.; investigation, N.B. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.B.; writing—review and editing, D.K. and S.G.; visualisation, N.B. and D.K.; supervision, D.K. and S.G.; project administration, D.K.; funding acquisition, D.K. and S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Water Research Commission (WRC) of South Africa, grant number C2023-2024-01256.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of WRC and the Centre for Water Resources Research (CWRR) at the University of KwaZulu Natal, South Africa.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Perera, D.; Seidou, O.; Agnihotri, J.; Rasmy, M.; Smakhtin, V.; Coulibaly, P.; Mehmood, H. Flood Early Warning Systems: A Review of Benefits, Challenges and Prospects; UNU-INWEH: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EM-DAT. Inventorying Hazards & Disasters Worldwide. 2023. Available online: https://www.emdat.be (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Milly, P.C.D.; Wetherald, R.T.; Dunne, K.; Delworth, T.L. Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature 2002, 415, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global flood risk under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Modi, P.; Mishra, V. Increased flood risk in Indian sub-continent under the warming climate. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2019, 25, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, N.; Devineni, N. Recent trends in the frequency and duration of global floods. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 757–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Chen, H. Implementing the Sendai Framework for disaster risk reduction 2015–2030: Disaster governance strategies for persons with disabilities in Taiwan. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 41, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhamo, L.; Matchaya, G.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Nhlengethwa, S.; Nhemachena, C.; Mpandeli, S. Cereal production trends under climate change: Impacts and adaptation strategies in southern Africa. Agriculture 2019, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, R.; Engelbrecht, F. Climate impacts in southern Africa during the 21st Century. In Report for Earthjustice and the Centre for Envrionmental Rights; Global Change Instiute, University of Witwatersrand: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bedeke, S.B. Climate change vulnerability and adaptation of crop producers in sub-Saharan Africa: A review on concepts, approaches and methods. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1017–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.-P.; Pretorius, T.B.; Kramers-Olen, A.L.; Padmanabhanunni, A.; Stiegler, N. Global warming and psychotraumatology of natural disasters: The case of the deadly rains and floods of April 2022 in South Africa. Ann. Médico-Psychol. Rev. Psychiatr. 2023, 181, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busayo, E.T.; Kalumba, A.M.; Afuye, G.A.; Olusola, A.O.; Ololade, O.O.; Orimoloye, I.R. Rediscovering South Africa: Flood disaster risk management through ecosystem-based adaptation. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 14, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzivhandila, T.S.; Maserumule, M.H. The Irony of a “Fire Fighting” Approach towards Natural Hazards in South Africa: Lessons from Flooding Disaster in KwaZulu-Natal; South African Association of Public Administration and Management (SAAPAM): Soshanguve, South Africa, 2022; Volume 57, pp. 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H. Global freshwater resources: Soft-path solutions for the 21st century. Science 2003, 302, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, O.; Brooks, D.B.; Gurman, S. Making the Most of the Water We Have: The Soft Path Approach to Water Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jamasy, O.; Siagian, E.; Movianto, G.E.; Pranoto, Y.; Nisa, K. Impact Analysis of Structural and Non-Structural Program and Collaboration of Stakeholder to Productivity of Sustainable Flood Mitigation Management. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Res. Rev. 2023, 6, 698–709. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, E.; Alabbad, Y.; Demir, I. Non-structural Flood Mitigation Optimization at Community Scale: Middle Cedar Case Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 119025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapuarachchi, H.; Wang, Q.; Pagano, T. A review of advances in flash flood forecasting. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 2771–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Mani, P.; Jain, S.K.; Prakash, P.; Singh, V.P.; Tullos, D.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, S.; Dimri, A. A Brief review of flood forecasting techniques and their applications. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2018, 16, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.-W. Flood prediction using machine learning models: Literature review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, F.H.; Alkhodre, A.B.; Sen, A.A.A.; Ramazan, M.S.; Alzahrani, B.; Siddiqui, M.S. Flood Prediction using Hydrologic and ML-based Modeling: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Agyakwa, K.T.; Afenyo, M.K.; Angnuureng, D.B. Know to predict, forecast to warn: A review of flood risk prediction tools. Water 2023, 15, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, D.C.; Costache, R.; Popa, M.C. An overview of flood risk analysis methods. Water 2021, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.; Waller, S.T. Remote sensing methods for flood prediction: A review. Sensors 2022, 22, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.R.; Coulibaly, P. Review of Recent Developments in Hydrologic Forecast Merging Techniques. Water 2024, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulwarty, R.S.; Sivakumar, M.V. Information systems in a changing climate: Early warnings and drought risk management. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 3, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, D.; Menoni, S.; Ballio, F. Flood Early Warning Systems: Knowledge and Tools for Their Critical Assessment; Wit Press: Southampton, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhwani, V.; Gyamfi, B.A.; Zhang, R.; AlHinai, A.M.; Shaw, R. Understanding the barriers restraining effective operation of flood early warning systems. Int. J. Disaster Risk Manag. 2019, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Khanal, N.R.; Nepal, P.; Rai, S.K.; Ghimire, P.K.; Pradhan, N.S. Community assessment of flood risks and early warning system in Ratu Watershed, Koshi Basin, Nepal. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.; Seidou, O.; Agnihotri, J.; Mehmood, H.; Rasmy, M. Challenges and technical advances in flood early warning systems (FEWSs). In Flood Impact Mitigation and Resilience Enhancement; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, S.; Aziz, N.A.; Husaif, N.; Sidek, L.M.; Shakirah, A.; Hanum, F.; Basri, H. Application of stochastic flood forecasting model using regression method for Kelantan catchment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil, Offshore & Environmental Engineering 2018 (ICCOEE 2018), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 August 2018; p. 07001. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Sharma, K.V.; Mehta, D.J.; Maharaj, K.T. The state of the art in deep learning applications, challenges, and future prospects: A comprehensive review of flood forecasting and management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yu, M.; Hu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y. Utilizing cloud computing to address big geospatial data challenges. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 61, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Manual on Flood Forecasting and Warning; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 1072. [Google Scholar]
- Lavers, D.A.; Ramos, M.-H.; Magnusson, L.; Pechlivanidis, I.; Klein, B.; Prudhomme, C.; Arnal, L.; Crochemore, L.; Van Den Hurk, B.; Weerts, A.H. A vision for hydrological prediction. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffeldt, A.; Wetterhall, F.; Pappenberger, F.; Salamon, P.; Thielen, J. Technical review of large-scale hydrological models for implementation in operational flood forecasting schemes on continental level. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiria, E.; Okazawa, H.; Noda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yamazaki, Y. A Comparative Evaluation of Lumped and Semi-Distributed Conceptual Hydrological Models: Does Model Complexity Enhance Hydrograph Prediction? Hydrology 2022, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Mission Report, WMO Fact-Finding and Needs-Assessment Mission to Pakistan. 2000. Available online: https://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/dra/rap/documents/PakistanMissionReport.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Sidle, R.C. Strategies for smarter catchment hydrology models: Incorporating scaling and better process representation. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. A concise review on introduction to hydrological models. Glob. Res. Dev. J. Eng. 2018, 3, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Girihagama, L.; Naveed Khaliq, M.; Lamontagne, P.; Perdikaris, J.; Roy, R.; Sushama, L.; Elshorbagy, A. Streamflow modelling and forecasting for Canadian watersheds using LSTM networks with attention mechanism. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 19995–20015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Saifullah, M. Coupling the k-nearest neighbor procedure with the Kalman filter for real-time updating of the hydraulic model in flood forecasting. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Yang, G. Comparative Study of Three Updating Procedures for Real-Time Flood Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2111–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grini, N.; Montanari, A. Real Time Flood Forecasting for the Reno River (Italy) through the TOPKAPI Rainfall-Runoff Model. Master’s Thesis, Università di Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.K.; Rana, H.K.; Luo, D.; Sun, H. Estimating climate-induced ‘Nowhere to go’range shifts of the Himalayan Incarvillea Juss. using multi-model median ensemble species distribution models. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kim, W.; Oh, H.; Youn, B.D.; Kim, N.H. Review of statistical model calibration and validation—From the perspective of uncertainty structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2019, 60, 1619–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Blöschl, G. A process typology of regional floods. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.; Lerat, J.; Pipunic, R.; Frost, A.; Donnelly, C.; Griffiths, M.; Hudson, D.; Loh, S. Seasonal ensemble forecasts for soil moisture, evapotranspiration and runoff across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S. General Review of Rainfall-Runoff Modeling: Model Calibration, Data Assimilation, and Uncertainty Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, P. A hybrid runoff generation modelling framework based on spatial combination of three runoff generation schemes for semi-humid and semi-arid watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, M.; Khadka, D.B. Simulation of Rainfall-Runoff of Kankai River Basin Using SWAT Model: A Case Study of Nepal. Int J Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, S.; Mishra, V. Runoff sensitivity of Indian sub-continental river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. RR-Former: Rainfall-runoff modeling based on Transformer. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, S.R. Flood forecasting for the Buffalo Bayou using CRWR-PrePro and HEC-HMS. Tech. Rep. Univ. Tex. Austin Cent. Res. Water Resour. 1999, 1999, ii-139. [Google Scholar]
- Oleyiblo, J.O.; Li, Z.J. Application of HEC-HMS for flood forecasting in Misai and Wan’an catchments in China. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.T.; Tefera, F.T.; Rientjes, T. Flood forecasting in Niger-Benue basin using satellite and quantitative precipitation forecast data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Bakhsh, A.; Khaliq, T. Near real time flood forecasting in the transboundary chenab river using global satellite mapping of precipitation. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 57, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Ghimire, U.; Than, H.H.; Srinivasan, G.; Dash, I.; Shakya, N.; Oo, M.T. Operationalizing a flood forecasting decision support system for Ayeyarwady river, Myanmar. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Islam, A.S.; Lemans, M.; Hegnauer, M.; Sajib, A.R.; Pieu, N.M.; Das, M.K.; Shadia, N.; Haque, A.; Roy, B.; et al. An efficient flash flood forecasting system for the un-gaged Meghna basin using open source platform Delft-FEWS: Flash Flood Forecasting System using Delft-FEWS Platform. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 161, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Pyasi, S.; Galkate, R. A review on the HEC-HMS rainfall-runoff simulation model. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, O.; Rugumayo, A.; Ovcharovichova, J. Application of HEC HMS/RAS and GIS tools in flood modeling: A case study for river Sironko–Uganda. Glob. J. Eng. Des Technol. 2012, 1, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, B.; Parajuli, R.; Kalra, A.; Ahmad, S.; Gupta, R. Coupling HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS in precipitation runoff modelling and evaluating flood plain inundation map. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2017, Sacramento, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 240–251. [Google Scholar]
- Abdessamed, D.; Abderrazak, B. Coupling HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS in rainfall–runoff modeling and evaluating floodplain inundation maps in arid environments: Case study of Ain Sefra city, Ksour Mountain. SW of Algeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meresa, H. Modelling of river flow in ungauged catchment using remote sensing data: Application of the empirical (SCS-CN), artificial neural network (ANN) and hydrological model (HEC-HMS). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, V.; Khaleghi, M.R. A simulation of the rainfall-runoff process using artificial neural network and HEC-HMS model in forest lands. J. For. Sci. 2021, 67, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, A.; Naik, M.G. Urban Rainfall-Runoff Modeling Using HEC-HMS and Artificial Neural Networks: A Case Study. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2023, 8, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Caloiero, T.; Mehta, D.J.; Singh, K. Comprehensive overview of flood modeling approaches: A review of recent advances. Hydrology 2023, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Rubinato, M.; Goerke, M.; Hart, J. Assessing the performance of LISFLOOD-FP and SWMM for a small watershed with scarce data availability. Water 2022, 14, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajib, A.; Liu, Z.; Merwade, V.; Tavakoly, A.A.; Follum, M.L. Towards a large-scale locally relevant flood inundation modeling framework using SWAT and LISFLOOD-FP. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Qi, H.; Wang, J. Case Study on Extreme Flood Forecasting Based on Ensemble Precipitation Forecast in Qingjiang Basin of the Yangtze River. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 104, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, T. Flood forecasting using an improved narx network based on wavelet analysis coupled with uncertainty analysis by monte carlo simulations: A case study of taihu basin, china. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 2674–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yao, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tong, B. Improving the flood forecasting capability of the Xinanjiang model for small-and medium-sized ungauged catchments in South China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 2077–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q. Study of early flood warning based on postprocessed predicted precipitation and Xinanjiang model. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 42, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Ba, H.; He, S. A novel hybrid XAJ-LSTM model for multi-step-ahead flood forecasting. Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 1436–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Soomro, S.E.E.; Wu, Q.; Tan, B.; Hu, C. flood forecasting based on machine learning pattern recognition and dynamic migration of parameters. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, G.; Ceresa, P.; Bussi, G.; Denaro, S.; Bazzurro, P.; Martina, M.; Fagà, E.; Avelar, C.; Ordaz, M.; Huerta, B. Large-scale flood risk assessment in data scarce areas: An application to Central Asia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Rabba, Z.A. Flood frequency analysis with PyTOPKAPI model-simulated stream flows from Aweitu river in Jimma town, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchetta, A.; Manetti, S. A real time hydrological forecasting system using a fuzzy clustering approach. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Leitão, J.P.; Simões, N.E.; Moosavi, V. Data-driven flood emulation: Speeding up urban flood predictions by deep convolutional neural networks. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Chakravorty, B.; Chatterjee, C.; Pandey, N.G. An artificial neural network approach for flood forecasting. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Part CP Comput. Eng. Div. 2003, 84, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Govindaraju, R.S. Artificial neural networks in hydrology. I: Preliminary concepts. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, F.-F. Hybrid models combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-term streamflow forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikyilmaz, A.; Turksen, I.B. Modeling uncertainty with fuzzy logic. Stud. Fuzziness Soft Comput. 2009, 240, 149–215. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Jhong, Y.D.; Wu, W.Z.; Chen, S.T. Fuzzy time series for real-time flood forecasting. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janál, P.; Kozel, T. Fuzzy logic based flash flood forecast. In Electronic Book with Full Papers from XXVIII Conference of the Danubian Countries on Hydrological Forecasting and Hydrological Bases of Water Management: November 6–8, 2019, Kyiv, Ukraine; Ukrainian Hydrometeorological Institute: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2019; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, S.; Razak, H.A. Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and artificial neural networks (ANNs) for structural damage identification. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2013, 45, 779–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunge, J.A. Of data and models. J. Hydroinformatics 2003, 5, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, C.; Xie, J.; Fitzmorris, R.; Wen, X.-H. A physics-based data-driven model for history matching, prediction, and characterization of unconventional reservoirs. SPE J. 2018, 23, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Kan, G.; Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Cheng, D.; Guo, J.; Jiang, H. A Hybrid Theory-Driven and Data-Driven Modeling Method for Solving the Shallow Water Equations. Water 2023, 15, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhang, M.; Xia, X.; Hu, B.; Niu, Z. Comparison of deterministic and data-driven models for solar radiation estimation in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, K.; Kawaguchi, N. FloodEye: Real-time flash flood prediction system for urban complex water flow. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakiri, K.; Marsellos, A.; Kapetanakis, S. Artificial neural network and multiple linear regression for flood prediction in Mohawk River, New York. Water 2018, 10, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, P.; Gadge, A.; Lende, A.; Chordiya, H.; Gosavi, G.; Mishra, A.; Hooli, B.; Ingle, Y.S.; Shaikh, N. Flood forecasting using machine learning: A review. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Smart Computing and Communications (ICSCC), Kochi, Kerala, India, 1–3 July 2021; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Deo, R.C.; Adamowski, J.F. Short-term flood forecasting using artificial neural networks, extreme learning machines, and M5 model tree. In Advances in Streamflow Forecasting: From Traditional to Modern Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, S.A.A.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A. Machine learning algorithm for flash flood prediction mapping in Wadi El-Laqeita and surroundings, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brath, A.; Montanari, A.; Toth, E. Neural networks and non-parametric methods for improving realtime flood forecasting through conceptual hydrological models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Jiang, P.; Hu, J.; Qu, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xiao, Z. Application of BP neural network algorithm in traditional hydrological model for flood forecasting. Water 2017, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.M.; Asmai, S.A.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Abas, Z.A.; Emran, N.A. Flood Prediction using Deep Learning Models. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, P.D.; Sood, S.K. Energy efficient IoT-based cloud framework for early flood prediction. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 2053–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvia, J.M.A.; Rani, M.P.; Aremu, B. Analysis of IoT big weather data for early flood forecasting system. In Proceedings of the 2021 Fourth International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Erode, India, 15–17 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, G.; Vedashree, C.N.; Astha, R.; Bharath, T.R.; Sudha, G.T. Flood Prediction and Alert System using ML and Sensor Networks. Grenze Int. J. Eng. Technol. (GIJET) 2022, 8, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, L.A.; Meneguette, R.I.; De Grande, R.E.; Ranieri, C.M.; Ueyama, J. FLORAS: Urban flash-flood prediction using a multivariate model. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 16107–16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankappan, J.; Mary, D.R.K.; Yoon, D.J.; Park, S.H. Adaptive Momentum-Backpropagation Algorithm for Flood Prediction and Management in the Internet of Things. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 77, 1053–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liang, J.-M. Fuzzy clustering neural network as flood forecasting model. Hydrol. Res. 2002, 33, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corani, G.; Guariso, G. An application of pruning in the design of neural networks for real time flood forecasting. Neural Comput. Appl. 2005, 14, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wang, B.; Liang, Q.; Fu, G. Classified real-time flood forecasting by coupling fuzzy clustering and neural network. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 25, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Singh, V.P. Multistep-ahead flood forecasting using wavelet and data-driven methods. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indra, G.; Duraipandian, N. Modeling of Optimal Deep Learning Based Flood Forecasting Model Using Twitter Data. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 35, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Park, S.W.; Cai, X. Integration of hydrologic gray model with global search method for real-time flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Liang, J.M.; Chen, Y.C. Flood forecasting using radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2001, 31, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslan, F.A.; Zain, Z.M.; Adnan, R. Modelling flood prediction using Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN) and Inverse Model: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering, Penang, Malaysia, 29 November–14 December 2013; pp. 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi, B.K.; Nath, T.K.; Senapati, M.R. An application of local linear radial basis function neural network for flood prediction. J. Manag. Anal. 2019, 6, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardah, T.; Abu Bakar, S.H.; Bardossy, A.; Maznorizan, M. Use of geostationary meteorological satellite images in convective rain estimation for flash-flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Chen, C.S. Application of integrated back-propagation network and self organizing map for flood forecasting. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fang, F.; Pain, C.C.; Navon, I.M. Rapid spatio-temporal flood prediction and uncertainty quantification using a deep learning method. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yuk, G.M.; Moon, H.T.; Moon, Y.I. Integrated flood forecasting and warning system against flash rainfall in the small-scaled urban stream. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, C.; Mejias, L.; Maire, F.; Woodley, A. Flood mapping with convolutional neural networks using spatio-contextual pixel information. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Panahi, M.; Golkarian, A.; Keesstra, S.D.; Saco, P.M.; Bui, D.T.; Lee, S. Convolutional neural network approach for spatial prediction of flood hazard at national scale of Iran. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, J.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Pei, Q. A short-term flood prediction based on spatial deep learning network: A case study for Xi County, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Wei, G.; Song, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H. Flash flood forecasting using support vector regression model in a small mountainous catchment. Water 2019, 11, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shada, B.; Chithra, N.; Thampi, S.G. Hourly flood forecasting using hybrid wavelet-SVM. J. Soft Comput. Civ. Eng. 2022, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, M.W.; Awais, M.; Riaz, K.; Rasheed, M.B.; Waqar, M.; Rasheed, S. Artificial Intelligence Based Flood Forecasting for River Hunza at Danyor Station in Pakistan. Arch. Hydroeng. Environ. Mech. 2022, 69, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalnezhad, A.; Rahman, A.; Nasiri, N.; Vafakhah, M.; Samali, B.; Ahamed, F. Comparing performance of ANN and SVM methods for regional flood frequency analysis in South-East Australia. Water 2022, 14, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniyaningrum, E.; Limantara, L.M.; Suhartanto, E.; Sisinggih, D. Development of flood early warning system based on the geoinformatics system in the Krukut River, Jakarta, Indonesia. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Tabbussum, R.; Dar, A.Q. Modelling hybrid and backpropagation adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems for flood forecasting. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 519–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, A.; Sood, S.K.; Bhatia, M. Digital Twin-assisted Fuzzy Logic-inspired Intelligent Approach for Flood Prediction. IEEE Sens. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M. Fuzzy Logic Introduction; Université de Rennes: Rennes, France, 2001; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tareghian, R.; Kashefipour, S.M. Application of fuzzy systems and artificial neural networks for flood forecasting. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.; Yakub, F.; Fakhrurradzi, A.; Hui, C.; Najiha, A.; Fakharulrazi, N.; Harun, A.; Rahim, Z.; Azizan, A. Designing early warning flood detection and monitoring system via IoT. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012016. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, A.; Giman, J.P. Performance Analysis of IOT based Flood Monitoring Framework in Sub-urban. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 7th International Conference on Smart Instrumentation, Measurement and Applications (ICSIMA), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–25 August 2021; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, H.; Bahaman, N.; Shah, W.M.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Khalid, A.M.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, M.R. Real-time Monitoring IoT-based System for Early Flash Flood Notification in Melaka. Multidiscip. Appl. Res. Innov. 2022, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, M.I.; Jabbar, W.A.; Sulaiman, N. Development of a smart sensing unit for LoRaWAN-based IoT flood monitoring and warning system in catchment areas. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Qundus, J.; Dabbour, K.; Gupta, S.; Meissonier, R.; Paschke, A. Wireless sensor network for AI-based flood disaster detection. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 319, 697–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Ma, L.; Zhai, G.; He, J.; Chu, X.; Yan, H. Resilient routing mechanism for wireless sensor networks with deep learning link reliability prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 64857–64872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, M.; Alaskar, H.; Hussain, A.J.; Baker, T.; Maamar, Z.; Buyya, R.; Liatsis, P.; Khan, W.; Tawfik, H.; Al-Jumeily, D. IoT-enabled flood severity prediction via ensemble machine learning models. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 70375–70386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasan, M.; Muthu, B.; Sivaparthipan, C.; Sundarasekar, R.; Kadry, S.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Dasel, A.A. Detection of flood disaster system based on IoT, big data and convolutional deep neural network. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, A.P.; Liniger, M.; Appenzeller, C. Can multi-model combination really enhance the prediction skill of probabilistic ensemble forecasts? Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. A J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 134, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutbecher, M.; Palmer, T.N. Ensemble forecasting. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3515–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.S.M.H.; Huang, Y.F.; Ahmed, A.N.; Koo, C.H.; El-Shafie, A. A review of the hybrid artificial intelligence and optimization modelling of hydrological streamflow forecasting. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, M.; Ait-El-Fquih, B.; Hoteit, I. Calibrating land hydrological models and enhancing their forecasting skills using an ensemble Kalman filter with one-step-ahead smoothing. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Jin, Y.; Song, A. An ensemble prediction system based on artificial neural networks and deep learning methods for deterministic and probabilistic carbon price forecasting. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 740093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Wu, L.; He, M.; Regonda, S.; Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J. Verification of temperature, precipitation, and streamflow forecasts from the NOAA/NWS Hydrologic Ensemble Forecast Service (HEFS): 1. Experimental design and forcing verification. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2869–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigue, G.; Johannet, A.; Borrell, V.; Pistre, S. Flash flood forecasting in poorly gauged basins using neural networks: Case study of the Gardon de Mialet basin (southern France). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 3307–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Gleason, C.J.; Hagemann, M.W.; Beighley, E.; Allen, G.H.; Feng, D.; Lin, P.; Pan, M.; Andreadis, K.; Pavelsky, T.M. Combining optical remote sensing, McFLI discharge estimation, global hydrologic modeling, and data assimilation to improve daily discharge estimates across an entire large watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR027794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, J.; Knott, D. Historical variations in African water resources. Influ. Clim. Chang. Clim. Var. Hydrol. Regime Water Resour. 1987, 168, 463–476. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Klotter, D.; Dezfuli, A.K. Spatial reconstruction of semi-quantitative precipitation fields over Africa during the nineteenth century from documentary evidence and gauge data. Quat. Res. 2012, 78, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunilkumar, K.; Narayana Rao, T.; Satheeshkumar, S. Assessment of small-scale variability of rainfall and multi-satellite precipitation estimates using measurements from a dense rain gauge network in Southeast India. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1719–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Guan, Q.; Chen, N.; Tong, D.; Hu, C.; Peng, Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, C. Optimizing the configuration of precipitation stations in a space-ground integrated sensor network based on spatial-temporal coverage maximization. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D. Comparison of satellite rainfall data with observations from gauging station networks. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Quick, M.C. Comparison of six extreme flood estimation techniques for ungauged watersheds in coastal British Columbia. Can. Water Resour. J. 1995, 20, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kjeldsen, T.R.; Smithers, J.; Schulze, R. Flood frequency analysis at ungauged sites in the KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Water SA 2001, 27, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.L.; Burn, D.H.; Cunderlik, J.M. A comparison of index flood estimation procedures for ungauged catchments. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2002, 29, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, T.R.; Smithers, J.; Schulze, R. Regional flood frequency analysis in the KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa, using the index-flood method. J. Hydrol. 2002, 255, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, D.U.; Yusof, K.W.; Hashim, M.A.; Balogun, A.-L. Spatial analytic hierarchy process model for flood forecasting: An integrated approach. Proceedings of IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2014; p. 012029. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadifar, A.; Gholami, H.; Golzari, S. Novel integrated modelling based on multiplicative long short-term memory (mLSTM) deep learning model and ensemble multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) models for mapping flood risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoubi Ayoublu, S.; Vafakhah, M.; Pourghasemi, H. Flood risk assessment using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Models (MCDM) and data mining methods (case study: Shiraz District 4). JWSS-Isfahan Univ. Technol. 2022, 26, 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Das, P.P. Evaluation Based on Distance from Average Solution (Edas) Method. In Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods in Manufacturing Environments; Apple Academic Press: Point Pleasant, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kasiviswanathan, K.S.; He, J.; Tay, J.-H. Flood frequency analysis using multi-objective optimization based interval estimation approach. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Soe, K.M.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Applications of TRMM-and GPM-era multiple-satellite precipitation products for flood simulations at sub-daily scales in a sparsely gauged watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Rahman, S.; Hossain, F.; Yarborough, L.; Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Easson, G. Satellite-based flood modeling using TRMM-based rainfall products. Sensors 2007, 7, 3416–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachi, M. Overview of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP). In Proceedings of the 6th World Water Forum, March, Marseille, France, 12–17 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.-L.; Wang, J.; Lin, P.; Liang, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z. Improving flood simulation capability of the WRF-Hydro-RAPID model using a multi-source precipitation merging method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, S.; Sisinggih, D.; Dewi, I. Validation of climate hazard group infrared precipitation with station (CHIRPS) data in wonorejo reservoir, Indonesia. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012042. [Google Scholar]
- Alijanian, M.; Rakhshandehroo, G.R.; Mishra, A.; Dehghani, M. Evaluation of remotely sensed precipitation estimates using PERSIANN-CDR and MSWEP for spatio-temporal drought assessment over Iran. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collischonn, B.; Collischonn, W.; Tucci, C.E.M. Daily hydrological modeling in the Amazon basin using TRMM rainfall estimates. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Massari, C. On the performance of satellite precipitation products in riverine flood modeling: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.; Naveed, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nabi, G.; Kashif, H.M.; Jawad, M.; Mujtaba, A. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products for Estimation of Floods in Data-Scarce Environment. Adv. Meteorol. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeditha, P.K.; Kasi, V.; Rathinasamy, M.; Agarwal, A. Forecasting of extreme flood events using different satellite precipitation products and wavelet-based machine learning methods. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2020, 30, 063115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, V. Real-time flood forecasting using satellite precipitation product and machine learning approach in Bagmati river basin, India. Acta Geophys. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, A.P.; Napiorkowski, J.J. A comparison of methods to avoid overfitting in neural networks training in the case of catchment runoff modelling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruche, R.; Egede, L.; Baker, T.; O’Donncha, F. Transfer learning to improve streamflow forecasts in data sparse regions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03088. [Google Scholar]
- Chancay, J.E.; Espitia-Sarmiento, E.F. Improving hourly precipitation estimates for flash flood modeling in data-scarce andean-amazon basins: An integrative framework based on machine learning and multiple remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampurno, J.; Vallaeys, V.; Ardianto, R.; Hanert, E. Integrated hydrodynamic and machine learning models for compound flooding prediction in a data-scarce estuarine delta. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2022, 29, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Li, W. Improving interpretability of deep active learning for flood inundation mapping through class ambiguity indices using multi-spectral satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 309, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazadi, A.N.; Doss-Gollin, J.; Sebastian, A.; Silva, A. Flood prediction with graph neural networks. Climate Change AI. Climate Change AI 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, R.B.; Leandro, J.; Lin, Q. Physics informed neural network for spatial-temporal flood forecasting. In Climate Change and Water Security: Select Proceedings of VCDRR 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, L.; Banihabib, M.E.; Roozbahani, A.; Dietrich, J. Bayesian network model for flood forecasting based on atmospheric ensemble forecasts. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).