Abstract
Controlling the water level in irrigation channels is important for the efficient management of irrigation and water delivery. In this study, the proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controller was implemented in both the HEC-RAS boundary condition, as an internal model, and MATLAB, as an external model. In the latter, the Hydrologic Engineering Center’s (HEC) River Analysis System (HEC-RAS) model was automated for irrigation canals by coding in the MATLAB script. To test the new models, E1R1 (first right bank branch of the first eastern canal in the Dez irrigation network, Khuzestan Province, Iran) irrigation canal data were prepared in HEC-RAS. A flow pattern was provided to simulate the canal water levels. The results showed efficient control of the water level for both models. The maximum and average water depth deviations from the target value were 13% and 4%, respectively, which fall in the good agreement range. The fewer these indicators, the better the performance is. The efficiency and adequacy were close to the ideal value and in the good agreement classes. The equity indicator was 0.013, which is very close to its ideal value of zero, showing efficient water distribution in the tested system. According to the literature for the equity indicator, a range of 0–0.10 is good, a range of 0.11–0.25 is fair, and a range of greater than 0.25 is poor. The results showed that simple and fast implementation is the main advantage of the internal model; however, it is not suitable for implementing complex controllers. Conversely, the external model can be implemented for complicated algorithms without any limitations.
1. Introduction
Various hydraulic and hydrodynamic software have their own sets of advantages and disadvantages [1]. There are several specialized hydraulic software to calculate water depth or hydraulic energy level, including HEC-RAS (Hydrologic Engineering Center’s River Analysis System), SWMM (Storm Water Management Model), and ICSS (Irrigation Conveyance Simulation System) [2].
They are designed to solve the complete form of the Saint-Venant equations, which are fundamental in the field of open-channel hydraulics. By using these software, engineers and researchers can accurately model and analyze the hydraulic behavior of water systems, leading to better-informed decision-making for water resource management and infrastructure design [3].
Among these models, HEC-RAS has gained popularity with recent improvements and is used for various applications [4,5,6,7,8]. Various studies have assessed the effectiveness of the direct use of HEC-RAS in different study areas [9,10,11,12,13].
There are various boundary conditions in HEC-RAS, e.g., flow and stage hydrographs, normal depth, rating curve, etc., that can be utilized for the planning and management of different hydraulic structures. In addition to the usual boundary conditions, there are some advanced boundary conditions. One of these is the elevation-controlled gate boundary condition that allows the user to open and close the gate according to the elevation of the water surface, which is used to control the inline structure gates in the E1R1 canal located in the Dez irrigation network in the north of Khuzestan Province (Iran) whose water is supplied using the E1 main canal. These boundary conditions allow the user to effectively regulate the water level in response to the different flow conditions [14]. Another programmable advanced boundary condition, allows the user to control inline gate structures by iteratively solving the energy equation taking into account this boundary condition for gradually varied flow [15].
Additionally, integration with other models or simulation techniques is possible with HEC-RAS [16,17]. HEC-RAS is utilized for the calibration and selection of the most appropriate Manning’s roughness coefficient using common boundary conditions [18]. The Manning’s roughness coefficient in the Euphrates River was calibrated using the common boundary conditions of HEC-RAS by manually simulating water surface elevations. The optimal Manning’s roughness coefficients of 0.045 and 0.047 were obtained for the main channel and floodplain, respectively, showing strong agreement between observed and simulated water surface elevations [19].
A similar method was used to calibrate the Manning’s roughness coefficient in the Thiba main canal reach in the Mwea irrigation scheme in Kenya [20]. Shahverdi and Talebmorad [21] automated the HEC-RAS using the HECRAS controller and linked it with the particle swarm optimizer to calibrate the Manning’s roughness coefficient in the Asad-Abad plain of Hamedan province in Iran.
Canal control algorithms have been widely used to control water depth and flow in irrigation canals. A study was conducted on predictive control for cascade irrigation canals in the southern irrigation region of Changma in Gansu Province, China. The study compared model predictive control with the classical proportional–integral method. The findings showed that while proportional–integral is ineffective in controlling canal water depth, model predictive control proved to be effective in managing the canal system when faced with known demand changes, and it maintained water levels at the control points successfully [22].
Regarding classic controllers, a simple, commonly used, and straightforward method for control is the proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controller [23]. The use of a hierarchical proportional–integral (H-PI) control approach for water level regulation in open channel systems was studied [24].
In [25], the application of dynamic reinforcement learning (RL) to achieve an optimal speed of DC motors using the proportional–integral controller was studied. They found that the reinforcement learning-based proportional–integral controller tuning method outperformed both integer and fractional order proportional–integral controllers. The effects of canal automation on the improvement of water distribution and delivery systems of irrigation canals were investigated [26]. For this purpose, a decentralized and a centralized control system were designed. The results indicated that the decentralized control system did not demonstrate significant operational improvements.
In a study, a proportional–integral–derivative controller was employed with a specific set of parameters, utilizing a newly modified gray wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm for water level management [27]. Subsequently, the proportional–integral–derivative controller was implemented on an ESP32 microcontroller module, and an android-based application was created using the Blynk platform for the monitoring and control of the IoT plant. A proportional–integral–derivative controller with a conventional model-free adaptive controller (MFAC) to develop a modified model-free adaptive controller (MMFAC) to enhance the control performance of the proportional–integral–derivative controller and MFAC in regulating the water level of a reservoir through rate adjustments was combined [28]. There are many other studies regarding the employment of the proportional–integral–derivative controller for regulating water levels in open channel systems and water tanks [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
As shown above, there are numerous studies on HEC-RAS and proportional–integral–derivative controllers. However, they need to be coupled to repeatedly and consequently regulate and simulate irrigation canals’ structures. To the best of our knowledge, there are only a handful of such studies for irrigation canals. Thus, the novelties of this study are: (i) automating the HEC-RAS model for irrigation canals to run without a user interface, (ii) coupling HEC-RAS with the proportional–integral–derivative controller and developing an advanced irrigation canal control system as an external model, and (iii) implementing the proportional–integral–derivative controllers using the advanced boundary conditions available in HEC-RAS (internal model). The objectives of this study are: (i) improving irrigation canal performance using the new control systems developed in this research, (ii) testing the models for the E1R1 Dez irrigation canal in Iran, and (iii) comparing the results of the two developed models.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Area
The E1R1 irrigation canal is situated in the Dez irrigation network in the north of Khuzestan Province (Iran). Water is diverted from the E1 main canal with a maximum flow of 2.47 (m3/s), supplying the E1R1 secondary canal. The geometric data of the canal and its hydraulic characteristics were obtained from the Khuzestan Water and Power Organization. As can be seen in Figure 1, three inline check gates (CH1-CH3) control water depth upstream so that the flow is delivered to the six online turnout gates (TO1-TO6). There are two online turnout gates upstream of each inline check gate. The cross-section along the concrete E1R1 canal is trapezoidal and is 2830 km long with a bottom slope of 0.00012–0.0015 and a bottom width of 1 m (from upstream of the canal to CH1) to 1.5 m (between CH1-CH3) [37]. The hydraulic model of the canal was provided in HEC-RAS using geometric data and an unsteady flow data editor.
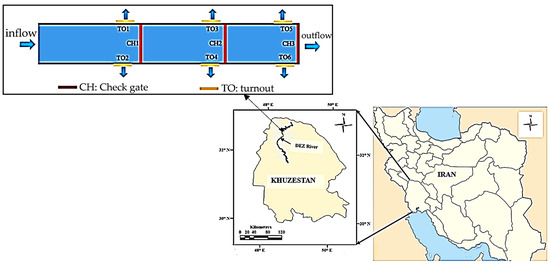
Figure 1.
The E1R1 irrigation canal in the Dez irrigation network in the north of Khuzestan Province (Iran).
2.2. Simulation Model
This study aimed to control the water levels upstream of inline check gates using the proportional–integral–derivative controller. For this purpose, the HEC-RAS hydraulic model was used along with the proportional–integral–derivative controller employing two methods.
In the first one, named external controller, HEC-RAS was automated to be opened, run, and closed by MATLAB, the controller is therefore apart from HEC-RAS and provided in MATLAB. In this case, the time series of gate opening (TSGO) boundary condition in HEC-RAS was used. In the second one, the proportional–integral–derivative water surface controller was developed inside HEC-RAS and defined in the rule operation (RO) boundary condition. In this regard, the controller was coded within RO boundary conditions in HEC-RAS (internal controller). Regardless of the method, HEC-RAS uses continuity and momentum equations to solve unsteady flow defined as:
where : wetted area (m2), : flow (m3/s), : gravity acceleration (m/s2), : canal slope (-), : friction slope (-), : time (S), and : length (m). The geometry parameters in the equations are known, and the friction slope is calculated using the Manning equation. The computational length and time are specified by the user. Consequently, there are two unknown parameters in Equations (1) and (2), which are water depth and velocity. HEC-RAS divides the canal into several cross-sections, where water depth and velocity are unknown. It uses an implicit finite difference solution scheme for calculations of both one-dimensional and two-dimensional unsteady flows.
2.3. Design of the Proportional–Integral–Derivative Controllers
The proportional–integral–derivative controller is simple and robust and has three terms, proportional, integral, and derivative, which are combined to calculate the amount of change in gate opening necessary to bring the water depth to the corresponding target value when deviations occur. The control block diagram of the proportional–integral–derivative controller is presented in Figure 2. As shown, the depth errors are calculated using the summation of the target and actual water depth from the hydraulic model. Next, the gate openings related to the proportional, integral, and derivative controllers are separately calculated and summed to reach the final gate openings. In the next step, the gate openings are applied and this process is continued until reaching the total simulation time step of . Note that this control block diagram could differ a bit depending on the type of model, either the external or internal model that will be described in the next subsections.
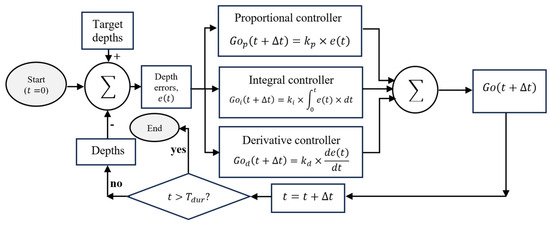
Figure 2.
Control block diagrams of the proportional–integral–derivative controller.
The gate opening proportional , integral , and derivative terms at the time step of are calculated as:
where , , and are the proportional, integral, and derivative gains, respectively, is the time, is the time step, and is the water depth minus the target depth (depth error). The gains were determined by trial and error according to the water depth variations. The final amount of change in gate opening at each time is calculated as:
where are respectively the gate openings at time steps of and . Usually, the total simulation time and the time step in irrigation canals are 24 h and 0.01 h, respectively.
2.4. External Controller
To develop the external controller, two calculation routines were used in MATLAB’s editor. The first routine was the proportional–integral–derivative controller, and the second one was automating and handling HEC-RAS and coupling it with the controller (Figure 3). In the proportional–integral–derivative controller, variables including the total simulation time, time step, target depths, and gains are first introduced. Note that the target depths 1–3 in the E1R1 canal are all 1.2 m. Then, the target and calculated water depths are summed, and the depth errors are calculated. Next, the gate openings are calculated using the proportional, integral, and derivative controllers and summed to find the final gate openings. In the next step, the gate openings are applied to HEC-RAS. To this end, the automated HEC-RAS is called to be run using new gate openings.
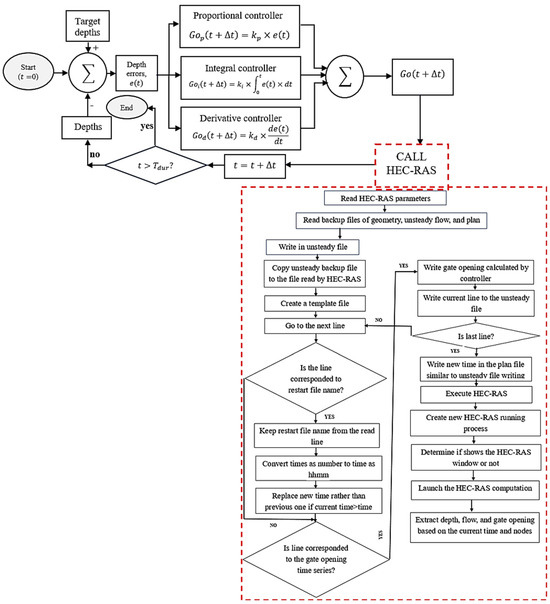
Figure 3.
Schematic of the external controller process.
As HEC-RAS is called by MATLAB, some useful and required information, including the HEC-RAS version and the project directory are read. HEC-RAS needs three files, geometry, unsteady, and plan, to carry out the simulation. These files and related backup files for the E1R1 canal were prepared. The main process here is to update the gate openings by creating new gate openings and simulating new situations. Note that HEC-RAS is called at each time step and closed after performing the simulation.
To update the unsteady file, the unsteady backup data from the backup file are copied to the unsteady file. Next, a template file is created, and the data in the unsteady file are pasted within it line by line. Each line that corresponds to the time and gate opening is updated with new values. When the steady file is updated, the plan file is updated similarly, and the new time replaces the old value. Then, HEC-RAS is executed by creating a new run and determining prerequisites. Then, the computation is launched. Finally, new depths and flows are extracted from the controller. The time is increased by and this process is continued until the total simulation time step of is reached.
2.5. Internal controller
To develop an internal controller in HEC-RAS, the rule operation (RO) was used, where the controller may be programmed using the tools incorporated. In RO, there is a programming window with two columns. The first column shows the line number of the program, and the second one shows the operation written using the available tools, including “new variable”, “get sim value”, “set operational param”, “branch (if/else)”, “math”, etc. (Figure 4).
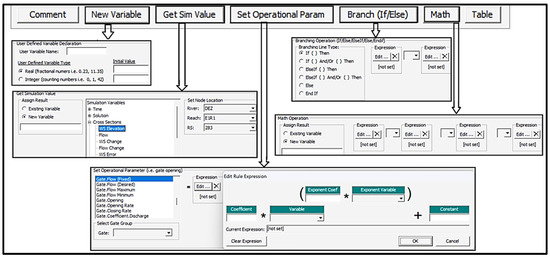
Figure 4.
Structure and buttons of the internal controller to develop the controller in HEC-RAS.
Any real or integer variable and constant are created using the “new variable” button. By the “get sim value” button, the value of any parameters simulated by HEC-RAS, such as depth, flow, time, etc., in the considered cross-section can be found. Operation parameters, such as new gate opening, flow, etc. may be defined by the “set operational param” button. Furthermore, any conditional and mathematical formulas are written in RO.
The controller process developed in RO is presented in Figure 5. As shown, it is similar to Figure 2, but it is not in a loop. In the internal model, the controller is called at each time step. As called, it calculates the gate openings of each separate controller using depth errors and gains. Then, the new gate openings are calculated, and the process is terminated. It is worth noting that the feedback loop of the proportional–integral–derivative controller is not executed in the boundary condition directly; rather, it is executed based on the operational parameter values of the previous and penultimate steps. This causes the feedback processes in the controller to be carried out correctly.
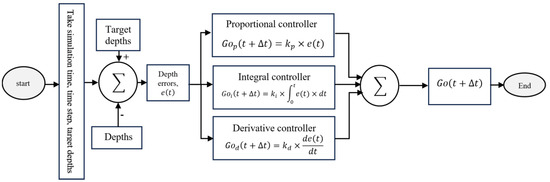
Figure 5.
The developed controller in RO in HEC-RAS (note: the previous and penultimate data in each time step is called using operational parameters, causing the feedback process to be executed correctly).
2.6. Indicators and Evaluation
To test the developed models, a flow pattern was generated and employed that included flow variations by 50% containing both increasing and decreasing changes in the online turnouts of 3–6. The first two turnouts were closed throughout the operation. The changes affect all the inline and online structures. The controller should distribute the water among reaches efficiently, adequately, and equitably while stabilizing water depth at the target value with minimum deviations from the corresponding target values.
To measure water depth and flow deviations, measure indicators of maximum absolute error (MAE) and integral absolute error (IAE) were used [38]. To measure the flow delivery accuracy, efficiency, equity, and adequacy indicators were used. In Table 1, each indicator with its corresponding description, equation, range, and class (desirability) are presented. The notations used in Table 1 are: is the target depth, is the real water depth received from HEC-RAS, is the number of turnouts, is delivered discharge, is requested discharge, is the coefficient of spatial variation of discharge, is the simulation time step, is the total simulation time, and is the number of time steps in a total simulation period, defined as . It should be noted that a core i5 computer with 8 G RAM was used in this research. The total times elapsed to run the external and internal models were 10 min and 1 h, respectively.

Table 1.
Standard performance assessment indicators.
3. Results and Discussion
The flow pattern applied to the canal to assess the external and internal models is given in Figure 6. The flow pattern was defined based on data received from the water authority of the Dez Irrigation and Drainage Operation Company. Both increasing and decreasing flows were considered. The inflow to the canal varied between 1 and 1.5 m3/s. It was 1 m3/s initially and increased to 1.5 m3/s, changing by 50%. Then, it was decreased to 20% and reached 1.2 m3/s from 1.5 m3/s. The flow delivering turnouts 3–6 (TO3-TO6) ranged from 0 to 0.2 m3/s with steps shown in the figure. Having defined such a flow pattern for the turnouts made it possible to deliver flow to all turnouts up to 0.2 m3/s simultaneously or successively, meaning that both smooth and severe changes were applied. The range of the outflow from the canal was from 0.6 to 1.5 m3/s, whose value is dependent on the flow delivering to the turnouts. Notice that TO in the figure is the abbreviation of the turnout, e.g., TO3 refers to turnout number 3.
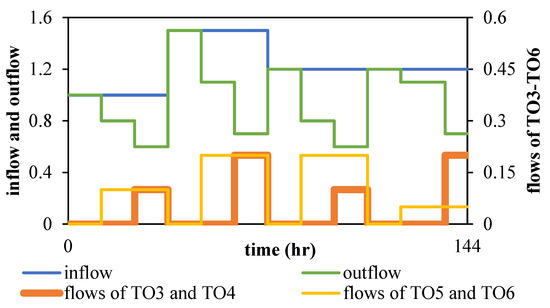
Figure 6.
Flow pattern used in the simulations (m3/s).
To test the proportional–integral–derivative controller, the gains must be precisely specified, herein performed by trial and error. To this end, various values of gains were separately tested, and a value that causes the indicators’ desirability to be in the good class was chosen as a desired value. To determine appropriate , the gains of the integral and derivative controllers were set to zero, meaning that the proportional controller was active and others were inactive. Next, different values of 0.1–5 were tested and evaluated. For example, was assumed to be 0.1, 0.1, and 0.1 for check gates 1–3, and the external model was run. In the next step, the MAE indicators were calculated based on the external model results. This process was carried out for different values of . Eventually, the values that resulted in the least MAEs were considered as final values, which were 5, 4.5, and 1 for the inline check gates of 1–3, respectively.
To find suitable values of , the final values of were employed in the proportional controller, and gains were set to zero, meaning that the proportional and integral controllers were active and the derivative controller was inactive. Different values between 0.1 and 0.0001 were tested while calculating IAE. Eventually, the best gains were obtained as 0.001 which had fewer IAEs. The gains were determined to be similar to the gains. The final values of the and gains were set in the proportional and integral controllers, and different values between 0.1 and 0.0001 were tested. The best gains cause smooth water surface fluctuations, which were obtained as 0.0001 for all inline check gates 1–3. It should be mentioned that the results presented hereafter are based on these gains.
In Figure 7, a sample of the coding in RO for the HEC-RAS boundary condition for the inline check gate 1 is illustrated. Lines 1, 10, and 22 are just comments written using the “comment” button (see Figure 4). In lines 1–5, the simulation values are extracted from computations. For example, the water surface elevation (WS EL 0) at cross-section 183.05 of the reach E1R1 of the DEZ river at the previous time step is extracted in line 2. In line 5, the value of gate opening in the inline structure of cross section 183.01 was extracted. The target elevation with an initial value of 151.52 m was defined in line 6, and then, the values of the gains were defined. In lines 11–21, several mathematical operations are written to calculate the final position of the inline check gate 1. For example, the water surface error from the target value is calculated in line 14 and by multiplying it by the proportional gain, the proportional term is calculated in line 18. As mentioned, the operational parameters are extracted from previous and penultimate time steps and used in the controller; therefore, its feedback originality holds despite starting and ending in a time step.
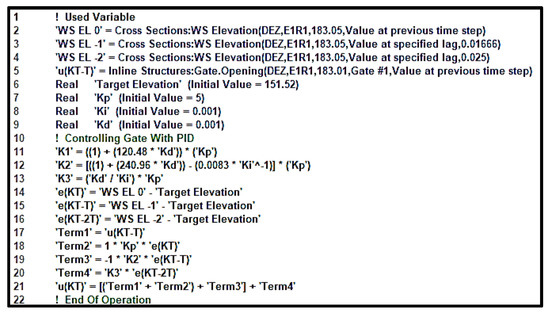
Figure 7.
Programming lines in the internal controller using RO in HEC-RAS.
Note that the coding with the RO boundary condition of HEC-RAS is simple; however, the coding of complex algorithms is not as simple as coding with external programming languages like MATLAB.
In Figure 8, the water depth error variations upstream of inline check gates 1–3 are presented. “Ch” is the abbreviation of the check gate, and the depth error is the difference between the water depth simulated with HEC-RAS and the associated target value. Note that these changes correspond to the flow pattern considered in this research. As shown, the variations after each operation are firstly large, and then they converge to the target value. The target is reached when the water depth deviation from the target value is zero, i.e., depth error equals zero. In most of the operation time, the water depth is fixed at the corresponding target value. The water depth error throughout the operation ranged from −0.1 m to 0.14 m. Note that the large variations are related to the proportional term, which instantly reacts to the flow changes. In other words, the proportional term is a feedback controller with a closed loop; therefore, it receives the depth error and calculates the corresponding gate-opening error afterward. This process continues until the variations decrease and the water depth is fixed at the target value.
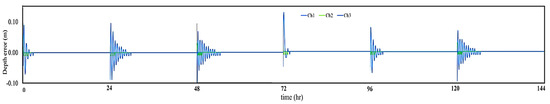
Figure 8.
Water depth error variation upstream of the inline check gates 1–3 (Ch1–Ch3) as a result of the internal controller (m).
Comparing the results in different operation times, it can be seen that the largest changes are related to the operation time of 72 h. It is because, at this time, the inflow is suddenly decreased by 20% and turnouts 3 and 4 are both closed simultaneously, making remarkable changes in the water surface.
The average variations are controlled using the integral term, which decreases the average error. Finally, the speed of changes is controlled using the derivative term since this is calculated by differentiating the error between the water depth and the corresponding target value.
The maximum values of the water depth indicators of MAE and IAE for the external and integral models are shown in Figure 9. The MAE indicators of inline check gates 1–3 were obtained as 3%, 12%, and 12%, respectively, when using the external model and respectively obtained as 2%, 3%, and 12% for the internal model. As can be seen, the MAE values of both models in inline check gate 1 are very close, and those for inline check gate 3 are the same. Although they are different in inline check gate 2; all values are reasonable, showing that both external and internal models reach the same results and have the same accuracy. Therefore, it is better to use the RO boundary condition wherever and whenever possible. Regarding the desirability, both model results fall in the range of 0–0.15 (0–15%) of the standard performance criteria according to Table 1, which shows a “good” performance class.
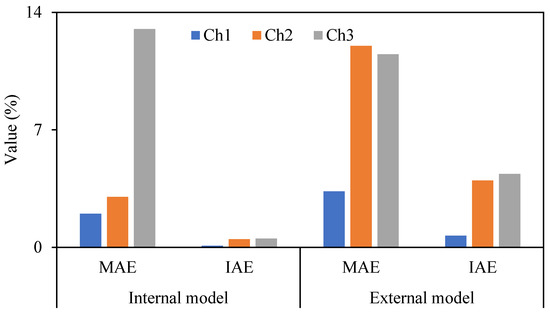
Figure 9.
MAE and IAE obtained using the internal and external controllers.
The same results as MAE were obtained for the IAE indicator; however, the internal model resulted in a somewhat smaller value than the external model, meaning that the average error by the internal model is less than the external model. According to the performance criteria of IAE, the desirability is good since all IAE values fall in the range of 0–0.15 (0–15%).
The efficiency, adequacy, and equity obtained based on the results of the external and internal models are presented in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively. A comparison of the results shows that the efficiency of both models is almost similar. The efficiency of the external model varies from 0.998 to 1, which has a “good” desirability class since they fall in the range of 0.85–1. The efficiency of the internal model varies from 0.993 to 0. 998, which again has a “good” desirability class since they fall in the range of 0.85–1. These results showed that the flow was efficiently distributed among the online turnout gates, and the loss of water was not much.
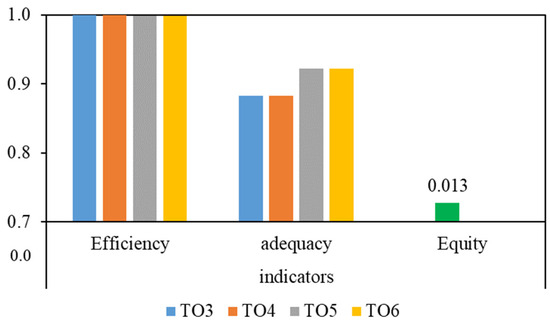
Figure 10.
Efficiency, adequacy, and equity obtained using the external controller.
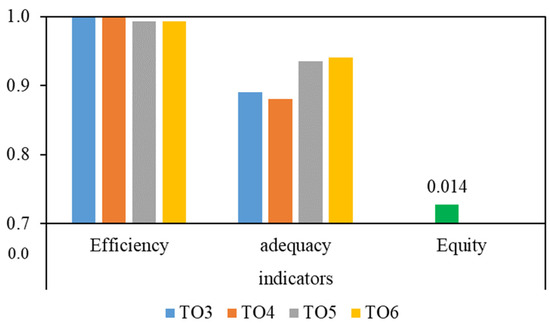
Figure 11.
Efficiency, adequacy, and equity obtained using the internal controller.
Regarding adequacy, the internal model, ranging from 0.880–0.941, is a bit better than the external model, ranging from 0.882–0.922; however, some of the values fall in the “good” desirability range and the others fall in the “fair” desirability range. The adequacy shows the amount of water deficiency. The further the adequacy from 1, the poorer it is. As for the equity, it shows how equitable the water distribution is. Here, the equity was obtained at 0.013 and 0.014 for the external and internal models, respectively, falling in the range of 0–0.1, which corresponds to the “good” desirability class. The equity results for both models are similar too. Note that the equity indicator is calculated using all flows delivered to the online turnout gate. In summary, the results of the two models are similar and there is no preference for one model over the other.
It is worth noting that the performance of the external and internal models is similar; however, there are some significant differences when running the two models. In the internal model, the HEC-RAS is run with a smaller computational burden. In the external model, the computational burden is much larger since, at each time step, the HEC-RAS model should load, perform the computations, and finally close. This is repeated at each time step. Conversely, the advantage of the external model is that it can handle more complex canal systems while the internal model is simpler. Another important point is that MATLAB controls HEC-RAS in the external model and the controller operates as it originally does. However, in HEC-RAS, the controller runs at each time step since it is provided in an advanced boundary condition. This is why the speed of computations of the internal model is less than that of the external model.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a proportional–integral–derivative controller was used to adjust inline check gates in the E1R1 Dez canal. To simulate the canal water level, the HEC-RAS model was implemented. Two models defined as internal and external models were developed. In the internal model, the controller was defined as a boundary condition in HEC-RAS. In the external model, the controller was implemented in MATLAB, and the HEC-RAS model was automated and coupled with MATLAB to perform calculations.
The proportional gain was determined as 5, 4.5, and 1 for the inline check gates 1–3, respectively. The integral gains were obtained as 0.001, and the derivative gains were obtained as 0.0001 for all inline check gates. The water depth error throughout the operation ranged from −0.1 to 0.14 m with a maximum MAE and IAE of 13% and 4%, respectively, which fall in the good desirability range. The efficiency was close to its desired value of 1 and the performance was in the good desirability range. The maximum value of the equity was obtained as 0.014, meaning that the water was distributed equitably. The adequacy desirability was in both good and fair range. In summary, the results of the two models are similar and there is no remarkable preference for one model over another. In the internal model, the HEC-RAS calculates the water levels and the controller computations are not heavy. On the other hand, in the external model, the computational burden is much larger since in each time step the HEC-RAS model should load, perform the computations, and finally close.
Author Contributions
K.S.: Conceptualized, coded, tested, and analyzed the model results and wrote the manuscript. A.N.: assisted in writing, conceptualizing, and analyzing the results and reviewed the manuscript, H.G. and R.B.: assisted in conceptualizing and analyzing the results, reviewed the manuscript, and gave constructive suggestions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the first corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from the Strategic Research Area: The Middle East in the Contemporary World (MECW) at the Centre for Advanced Middle Eastern Studies, Lund University, Sweden.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fassoni-Andrade, A.C.; Fan, F.M.; Collischonn, W.; Fassoni, A.C.; Paiva, R.C.D.d. Comparison of numerical schemes of river flood routing with an inertial approximation of the Saint Venant equations. Rbrh 2018, 23, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshfaraz, R.; Dasineh, M.; Ghaderi, A. Evaluation of scour depth around bridge piers with HEC-RAS (case study: Bridge of Simineh Rood, Miandoab, Iran). Environ. Water Eng. 2019, 5, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, A.M.A. Evaluation of local scour around bridge piers for various geometrical shapes using mathematical models. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, A.I.; Agnihotri, P.G.; Patel, D.; Prieto, C. Mesh grid stability and its impact on flood inundation through (2D) hydrodynamic HEC-RAS model with special use of Big Data platform—A study on Purna River of Navsari city. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, A.I.; Agnihotri, P. Application of new HEC-RAS version 5 for 1D hydrodynamic flood modeling with special reference through geospatial techniques: A case of River Purna at Navsari, Gujarat, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuri, R.; Raja, Y.S.; Raju, K.S.; Punith, B.S.; Manoj, K. Urban flood risk analysis of buildings using HEC-RAS 2D in climate change framework. H2Open J. 2021, 4, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Shafy, M.; Mostafa, A. Flash Flood Modeling Using HEC-RAS (2D) model on Wadi Reem in the western region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Egypt. Acad. Soc. Environ. Dev. D Environ. Stud. 2021, 22, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, I.R.; Hassan, Z.F.; Abdullah, H.H.; Alwan, I.A. 2D-HEC-RAS modeling of flood wave propagation in a Semi-Arid Area due to dam overtopping failure. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilali, A.E.; Taleb, I.; Nafii, A.; Taleb, A. A practical probabilistic approach for simulating life loss in an urban area associated with a dam-break flood. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 76, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. Measuring and modeling event-based environmental flows: An assessment of HEC-RAS 2D rain-on-grid simulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.F.; Yin, D.; Bakhtyar, R.; Moftakhari, H.; Xue, Z.; Mandli, K.; Ferreira, C. Inter-model comparison of Delft3D-FM and 2D HEC-RAS for total water level prediction in coastal to inland transition zones. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C.; Ferraro, D.; Barca, P. Is HEC-RAS 2D accurate enough for storm-event hazard assessment? Lessons learnt from a benchmarking study based on rain-on-grid modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Szydłowski, M. Application of different building representation techniques in HEC-RAS 2-D for urban flood modeling using the Toce River experimental case. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollazeynali, H.; Shahverdi, K. Application of Controlled Gates Boundary Condition in HEC-RAS in Water Conveyance and Distribution Systems. J. Water Irrig. Manag. 2022, 12, 847–858. [Google Scholar]
- Nourozirad, Z.; Shahverdi, K.; Ghodousi, H. Check Structure Level Regulation in Water Supply Canals using RBO in HEC-RAS. Water Irrig. Manag. 2023, 13, 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Papaioannou, G.; Markogianni, V.; Loukas, A.; Dimitriou, E. Remote sensing methodology for roughness estimation in ungauged streams for different hydraulic/hydrodynamic modeling approaches. Water 2022, 14, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyanova, F.; Ongdas, N.; Zinabdin, N.; Karakulov, Y.; Nazhbiyev, A.; Mussagaliyeva, Z.; Atalikhova, A. Operation of Gate-Controlled Irrigation System Using HEC-RAS 2D for Spring Flood Hazard Reduction. Computation 2023, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohani, E. Estimating the Manning’s Roughness Coefficient in Rivers by Experimental Method. Foot 2019, 1, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, Z.N.; Almansori, N.J.H. Estimation of manning coefficient for the section between Al-Hindiya barrage and Al-Kufa barrage utilizing HEC-RAS. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 2595–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serede, I.J.; Mutua, B.M.; Raude, J.M. Calibration of channel roughness coefficient for Thiba Main Canal Reach in Mwea irrigation scheme, Kenya. Hydrology 2015, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, K.; Talebmorad, H. Automating HEC-RAS and linking with particle swarm optimizer to calibrate manning’s roughness coefficient. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, H. Constrained model predictive control algorithm for cascaded irrigation canals. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucho, I.; De Paula, M.; Acosta, G.G. Double Q-PID algorithm for mobile robot control. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 137, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y. Improved Proportional Integral (PI) controller for water level control in open channel systems: A case study of the Middle Route Project for South-to-North Water Transfer. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufenkci, S.; Alagoz, B.B.; Kavuran, G.; Yeroglu, C.; Herencsar, N.; Mahata, S. A theoretical demonstration for reinforcement learning of PI control dynamics for optimal speed control of DC motors by using Twin Delay Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Jolfan, M.; Hashemy Shahdany, S.M.; Javadi, S.; Mallakpour, I.; Neshat, A. Effects of canal automation on reducing groundwater extraction within irrigation districts: Case study of Qazvin irrigation district. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhookya, J.; Kumar, M.V.; Kumar, J.R.; Rao, A.S. Implementation of PID controller for liquid level system using mGWO and integration of IoT application. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 28, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Mohammed, Y.; Karam, E.H.; Kadhim, N.N. Controlling Water Level by Using Modified Model Free Adaptive Controller. J. Eng. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 27, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, S.; Parvaresh Rizi, A.; Isapoor, S. The effect of design parameters of an irrigation canal on tuning of coefficients and performance of a PI controller. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, S.C.; Susanto, E.; Wibowo, A.S. Design and implementation of water level control using gain scheduling PID back calculation integrator Anti Windup. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications (ICCEREC), Bandung, Indonesia, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Getu, B.N. Water level controlling system using PID controller. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 11223–11227. [Google Scholar]
- Arain, B.A.; Shaikh, M.F.; Harijan, B.L.; Memon, T.D.; Kalwar, I.H. Design of PID controller based on PSO algorithm and its FPGA synthesization. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2018, 8, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Saddam, G.; Batlle, V.F. Robust Fractional Order Control of a Pool of a Main Irrigation Canal in Submerged Flow Condition. IFAC-Pap. 2020, 53, 16611–16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiastra, I.N.; Pemayun, A. Prototype Design of Water Level Control System Based on PID Controller in PLTMH. J. Electr. Electron. Inform. 2020, 4, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Principle and Simulation PID Controller of Liquid Level System. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012187. [Google Scholar]
- Prastiyo, D.; Aji, W.S. Irrigation Sluice Control System Using Algorithm Based DC Motor PID And Omron PLC. Control Syst. Optim. Lett. 2023, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Negenborn, R.R.; van Overloop, P.-J.; Maestre, J.M.; Sadowska, A.; van de Giesen, N. Efficient multi-scenario model predictive control for water resources management with ensemble streamflow forecasts. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 109, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmens, A.J.; Kacerek, T.F.; Grawitz, B.; Schuurmans, W. Test cases for canal control algorithms. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1998, 124, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).