Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Environmental Drivers in Chinese Mitten Crab Aquaculture Ponds: Highlighting the Need for Cyanobacteria Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Location
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
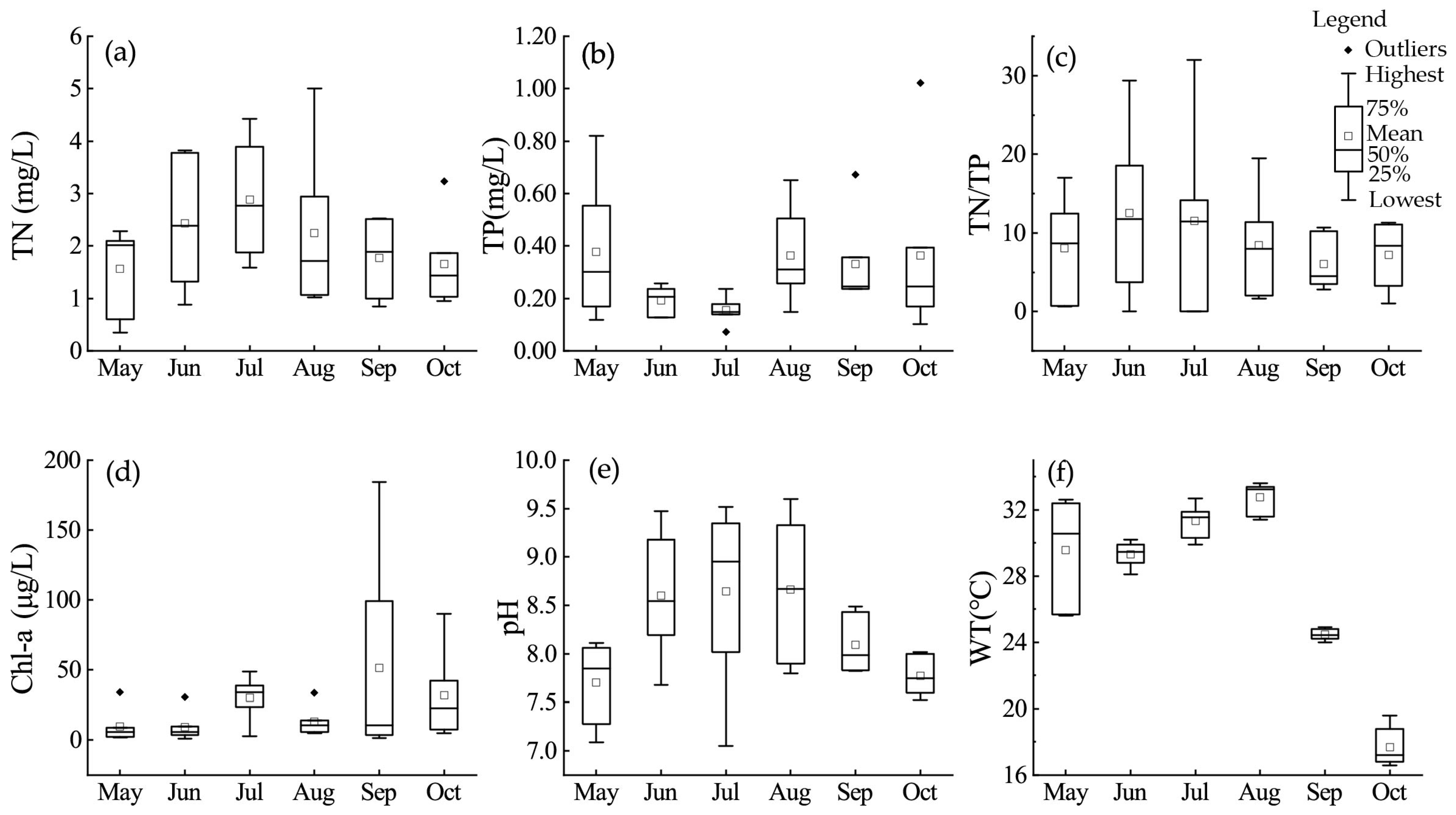
3.1. Physical and Chemical Parameters
3.2. Phytoplankton Species
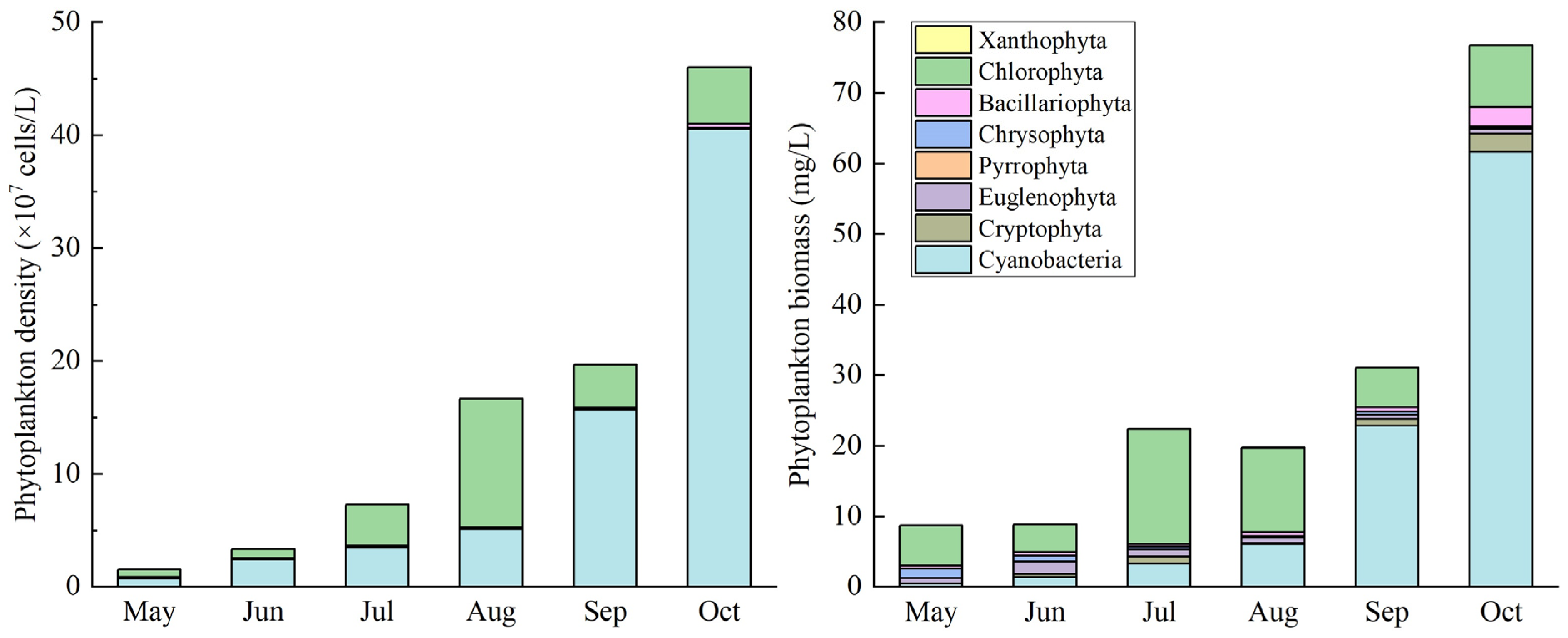
3.3. Dynamics of Phytoplankton Cell Density and Biomass
3.4. Changed in Phytoplankton Diversity Index
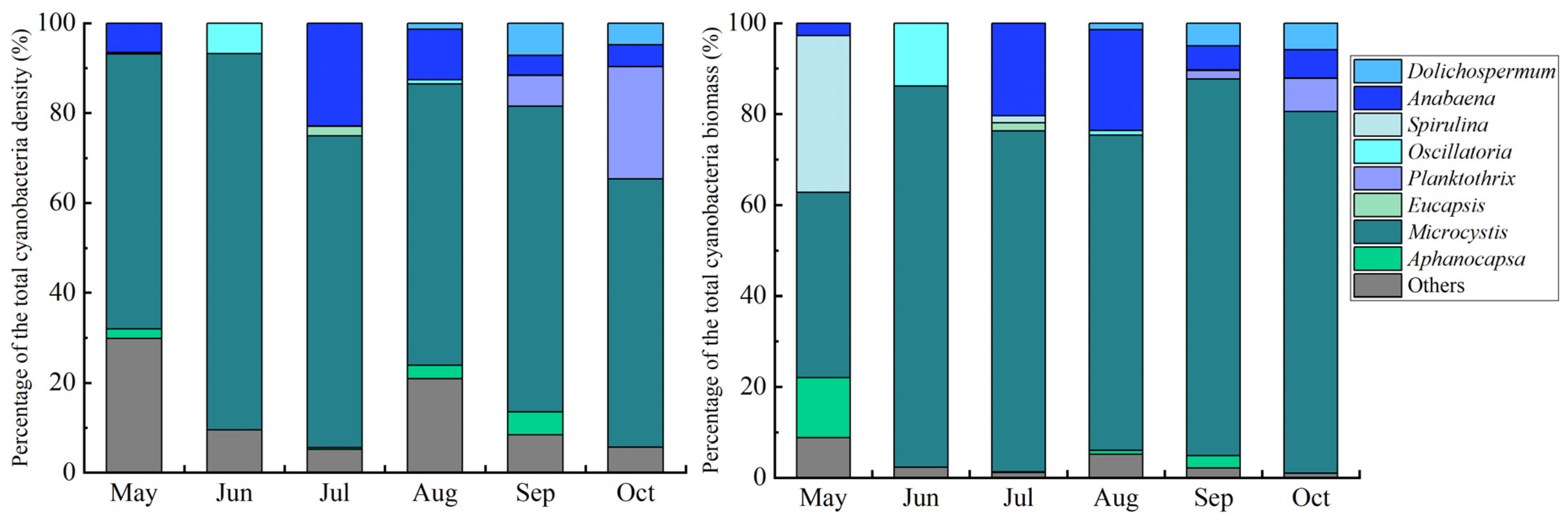
3.5. Shifts in Phytoplankton Community Dynamics
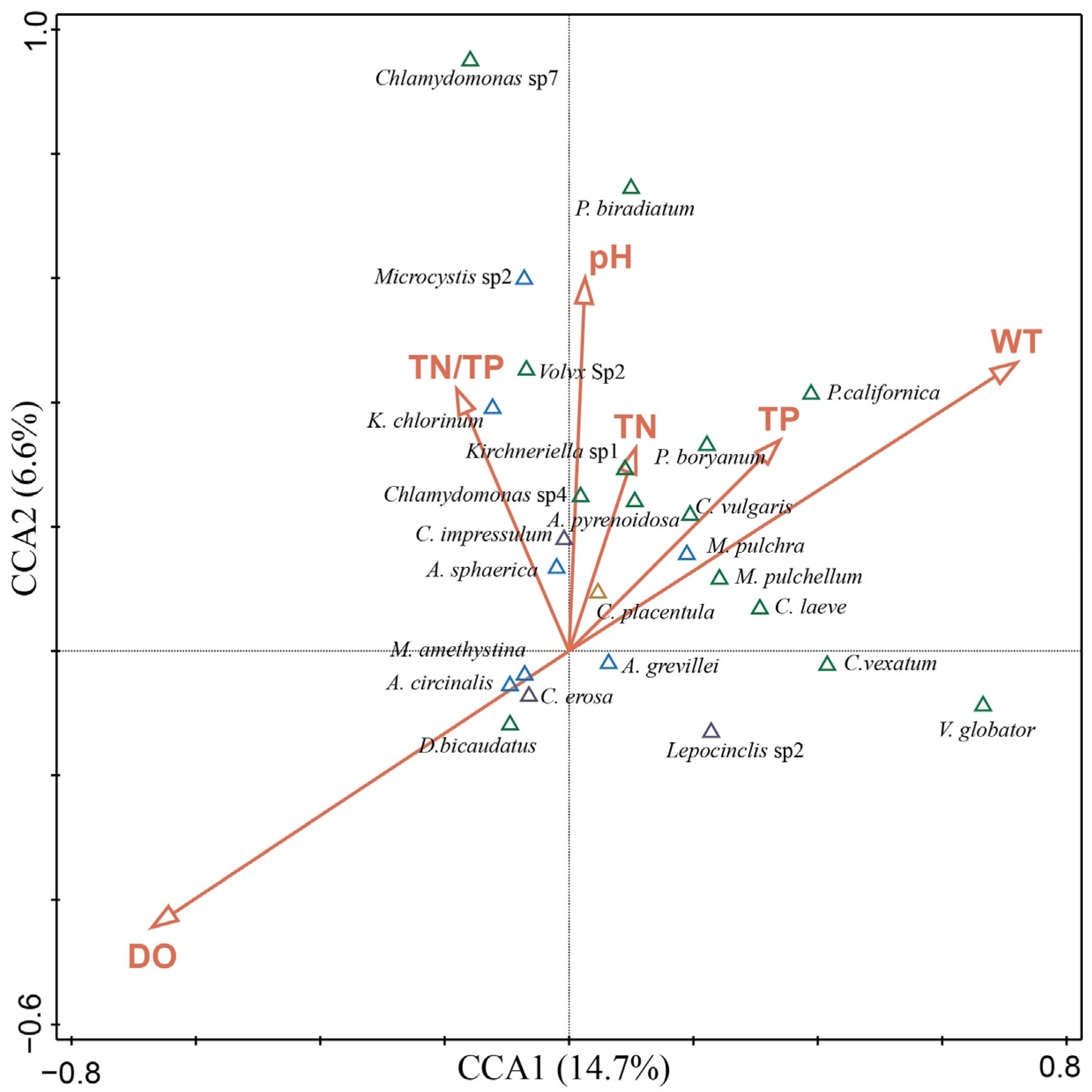
3.6. Relationship between Phytoplankton and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2021 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Wang, S.; Zuo, J.; Luo, Y.; Gan, N. Research and Prospects of Eco-toxicity of Anatoxins. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 17, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, P.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sandrini, G.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Davis, T.W.; Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. How rising CO2 and global warming may stimulate harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, W.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Lan, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Long-term variation of phytoplankton community and driving factors in Qiandaohu Reservoir, southeast China. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Chen, G.; Bi, X.; Zhong, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Lv, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, N. Light limitation inducing overcompensatory growth of cyanobacteria and function of serine/threonine kinase (STK) genes involved. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.-D.; Zhang, S.-L.; Dai, W.; Xing, K.-Z.; Yang, F. Effects of lead(II) on the extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) production and colony formation of cultured Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2013, 67, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of nutrients, temperature and their interactions on spring phytoplankton community succession in Lake Taihu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Visser, P.M. Harmful Cyanobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.S.; Hosper, S.; Meijer, M.L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative Equilibria in Shallow Lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Díaz, R.J.; Levin, L.A.; Turner, R.E.; Gilbert, D.; Zhang, J. Dynamics and distribution of natural and human-caused hypoxia. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 585–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriluoto, J.; Spoof, L.; Codd, G.A. Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastner, J.; Beulker, C.; Geiser, B.; Hoffmann, A.; Kroger, R.; Teske, K.; Hoppe, J.; Mundhenk, L.; Neurath, H.; Sagebiel, D.; et al. Fatal Neurotoxicosis in Dogs Associated with Tychoplanktic, Anatoxin-a Producing Tychonema sp. in Mesotrophic Lake Tegel, Berlin. Toxins 2018, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrao-Filho, A.D.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, B.; Potts, M. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Fastner, J.; Bormans, M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Ecology, prevention, mitigation and control: Editorial to a CYANOCOST Special Issue. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Tiwari, D.N.; Rai, A.N. Cyanobacteria: From Basic Science to Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Havens, K.E.; Hall, N.S.; Otten, T.G.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B. Mitigating a global expansion of toxic cyanobacterial blooms: Confounding effects and challenges posed by climate change. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Eshetu, F.; Faassen, E.J.; Kosten, S.; Huszar, V.L.M. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 58, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Phytoplankton; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Xie, S.; Feng, J. Interactive effects of temperature and nutrients on the phytoplankton community in an urban river in China. Env. Monit. Assess 2019, 191, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, N.; Tolotti, M. Phytoplankton and anthropogenic changes in pelagic environments. Hydrobiologia 2020, 848, 251–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Yuan, J.-l.; Liu, M.; Gu, Z.-M. Assessment of water quality and phytoplankton community of Limpenaeus vannamei pond in intertidal zone of Hangzhou Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Mao, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Ding, H. Dynamics of Cyanobacteria and Related Environmental Drivers in Freshwater Bodies Affected by Mitten Crab Culturing: A Study of Lake Guchenghu, China. Water 2019, 11, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremona, F.; Tuvikene, L.; Haberman, J.; Noges, P.; Noges, T. Factors controlling the three-decade long rise in cyanobacteria biomass in a eutrophic shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayele, H.S.; Atlabachew, M. Review of characterization, factors, impacts, and solutions of Lake eutrophication: Lesson for lake Tana, Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14233–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D. Recent Advances in the Understanding and Management of Eutrophication. Limnol. Ocean. 2006, 51, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.; Paerl, H.; Howarth, R.; Boesch, D.; Seitzinger, S.; Havens, K.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G. Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, G.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Salmaso, N.; Zingone, A.; Bergami, C.; Flaim, G.; Accoroni, S.; Basset, A.; Bastianini, M.; Belmonte, G.; et al. Plankton dynamics across the freshwater, transitional and marine research sites of the LTER-Italy Network. Patterns, fluctuations, drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.E.; Wu, X.; Hao, H.L.; He, Z.L. Mechanisms and assessment of water eutrophication. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.; Dunstan, W. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Eutrophication in the Coastal Marine Environment. Science 1971, 171, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karydis, M. Eutrophication Assessment of Coastal Waters based on Indicators: A Literature Review. Glob. Nest J. 2009, 11, 373–390. [Google Scholar]
- Downing, J.A. Marine nitrogen: Phosphorus stoichiometry and the global N:P cycle. Biogeochemistry 1997, 37, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, S.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Ge, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Effect of submerged plant coverage on phytoplankton community dynamics and photosynthetic activity in situ. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lili, H.; Yunsheng, Z.; Hu, X.; Bailu, T.; Suqin, W. Functional groups and trophic evaluation of phytoplankton in subtropical aquaculture lakes around Dongting Lake in summer. Chin. J. Fish. 2023, 36, 79–87+121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Duan, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Phytoplankton community structure in nansi lake and its influencing factors. Wetl. Sci. 2022, 20, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haohao, L.; Kun, H.; Zhilong, X.; Xugan, W.; Jiamei, J.; Hongbo, P. Plankton community succession and its influencing factors on earthen pond cultivation of Eriocheir sinensis larvae. J. Fish. Sci. China 2023, 30, 723–734. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kirchman, D.L.; Cottrell, M.T.; Chen, R.; Wang, K.; Ouyang, Z.; Xu, Y.Y.; Chen, B.; Yin, K.; et al. Biological regulation of pH during intensive growth of phytoplankton in two eutrophic estuarine waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 609, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Deng, L.; Song, Y.; Qi, W.; Hu, C. Nutrient Thresholds Required to Control Eutrophication: Does It Work for Natural Alkaline Lakes? Water 2022, 14, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise Middelboe, A.; Juel Hansen, P. Direct effects of pH and inorganic carbon on macroalgal photosynthesis and growth. Mar. Biol. Res. 2007, 3, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Xue, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, L. Temporal patterns of phyto- and bacterioplankton and their relationships with environmental factors in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Inoue, T.; Suzuki, R.; Kashiwazaki, H.; Wada, S.; Sasano, D.; Kosugi, N.; Ishii, M. Response of a phytoplankton community to nutrient addition under different CO2 and pH conditions. J. Oceanogr. 2015, 72, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterwick, C.; Heaney, S.I.; Talling, J.F. Diversity in the influence of temperature on the growth rates of freshwater algae, and its ecological relevance. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 50, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Kremer, C.T.; Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E. A global pattern of thermal adaptation in marine phytoplankton. Science 2012, 338, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, M. Growth of several diatom species isolated from various environments to temperature. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, J.; Jones, R. Effect of Temperature on Photosynthesis-light Response and Growth of Four Phytoplankton Species Isolated from a Tidal Freshwater River. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JÖHnk, K.D.; Huisman, J.E.F.; Sharples, J.; Sommeijer, B.E.N.; Visser, P.M.; Stroom, J.M. Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 14, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatwell, T.O.M.; Köhler, J.A.N.; Nicklisch, A. Warming promotes cold-adapted phytoplankton in temperate lakes and opens a loophole for Oscillatoriales in spring. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Hitchcock, J.N.; Davie, A.W.; Ryan, D.A. Growth responses of Cyclotella meneghiniana (Bacillariophyceae) to various temperatures. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincon-Leite, B.; Casenave, C. Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markensten, H.; Moore, K.; Persson, I. Simulated lake phytoplankton composition shifts toward cyanobacteria dominance in a future warmer climate. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2010, 20, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.C.; Tu, Q.Y. Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication, 2nd ed.; Chinese Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.J.; Wei, Y.X. The Freshwater Algae of China-Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhu, H.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Shi, Z.X. The Freshwater Algae of China; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.B.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State EPA of China. Monitoring and Analysis Methods for Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environmental Sscience Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal variation of driving factors of algal proliferation in a large river-connected lake. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 64–71+128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, X.; Yu, H.; Otte, M. Interactions between Fe and light strongly affect phytoplankton communities in a eutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bi, S.; Lyu, H.; Cai, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J. Spatial and temporal distribution analysis of dominant algae in Lake Taihu based on ocean and land color instrument data. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, H.; Song, X. Effects of Macrophyte Species and Density on Algae Inhibition and Water Purification in Submerged Macrophyte Ponds. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3451–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Wang, N.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Niu, L.; Ma, B.; Yang, F.; et al. Temporal patterns of algae in different urban lakes and their correlations with environmental variables in Xi’an, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 133, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Huang, T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Shang, P.; Feng, J.; Jia, J. Water Quality and Diversity of Denitrifier Community Structure of Typical Scenic Water Bodies in Xi’an. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 38, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zong, R.; He, H.; Liu, K.; Yan, M.; Miao, Y.; Ma, B.; Huang, X. Biogeographic distribution patterns of algal community in different urban lakes in China: Insights into the dynamics and co-existence. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 100, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V. Eutrophication of Freshwater and Coastal Marine Ecosystems: A Global Problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2003, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.; Davis, T.; Burford, M.; Gobler, C. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2013, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Panosso, R.; Lürling, M. Consequences of acclimation to Microcystis on the selective feeding behavior of the calanoid copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Pagano, M.; Troussellier, M. Effects of a cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) on bacteria and zooplankton communities in Ingazeira reservoir (northeast Brazil). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 25, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panosso, R. Effect of grazing by a neotropical copepod, Notodiaptomus, on a natural cyanobacterial assemblage and on toxic and non-toxic cyanobacterial strains. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Paerl, H.W. Nutrient enrichment and selective predation by zooplankton promote Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) bloom formation. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, R.W. 16—Intracellular pH Regulation. In Cell Physiology Source Book; Sperelakis, N., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.A. Nutrient transport in microalgae. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1980, 21, 47–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taraldsvik, M.; Myklestad, S. The effect of pH on growth rate, biochemical composition and extracellular carbohydrate production of the marine diatomSkeletonema costatum. Eur. J. Phycol. 2000, 35, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, G.L.L.; Moura da Rosa, C.; Yunes, J.S.; Luquet, C.M.; Bianchini, A.; Monserrat, J.M. Toxic effects of microcystins in the hepatopancreas of the estuarine crab Chasmagnathus granulatus (Decapoda, Grapsidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 135, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.; Bargu, S.; Dash, P.; Rabalais, N.; Sutor, M.; Morrison, W.; Walker, N. Evaluating the potential risk of microcystins to blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) fisheries and human health in a eutrophic estuary. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shang, K.; Da, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, A. Synergetic Effect of Combined CaO2 and Microwave Treatment on Waste Active Sludge Dewaterability and Organic Contaminants’ Removal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 734277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
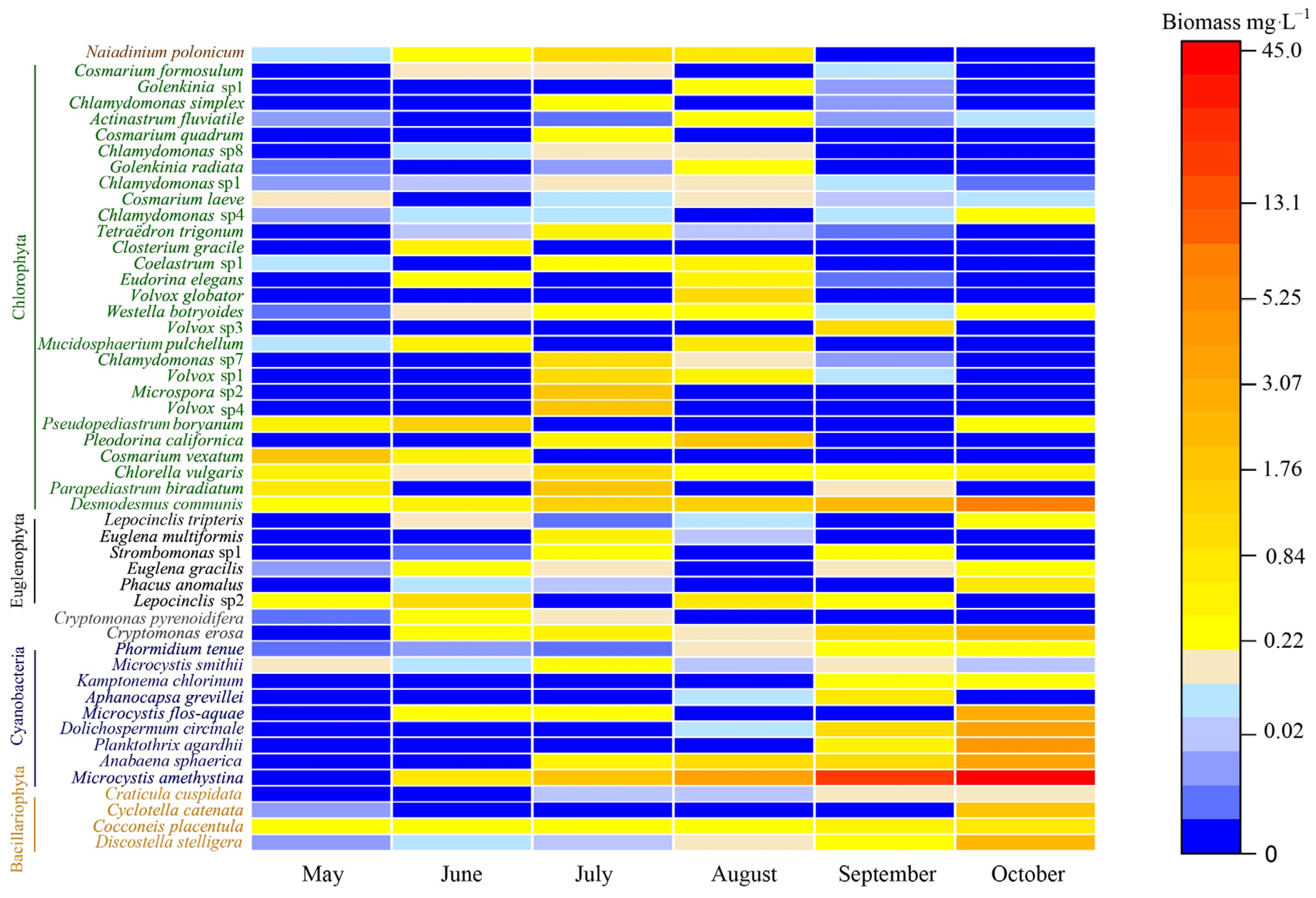


| May | June | July | August | September | October |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcystis smithii | M. smithii | M. amethystina | M. amethystina | M. amethystina | M. amethystina |
| Cocconeis placentula | M. amethystina | M. smithii | Anabaena sphaerica | Aphanocapsa grevillei | D. circinalis |
| Lepocinclis sp2 | C. placentula | C. erosa | C. placentula | Kamptonema chlorinum | A. sphaerica |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Cryptomonas erosa | P. biradiatum | C. erosa | A. sphaerica | M. flos-aquae |
| Parapediastrum biradiatum | Lepocinclis sp2 | Auxenochlorella pyrenoidosa | Lepocinclis sp2 | M. smithii | M. aeruginosa |
| Pseudopediastrum boryanum | Mucidosphaerium pulchellum | Microspora sp2 | D. bicaudatus | Dolichospermum circinalis | Planktothrix agardhii |
| Cosmarium vexatum | Kirchneriella sp1 | D. bicaudatus | Pleodorina californica | C. placentula | C. placentula |
| Desmodesmus bicaudatus | Chlamydomonas sp4 | C. vulgaris | V. globator | C. erosa | Cyclotella catenata |
| Kirchneriella sp1 | C. impressulum | Volvox sp2 | Kirchneriella sp1 | D. bicaudatus | C. erosa |
| C. laeve | C. vulgaris | Chlamydomonas sp7 | M. pulchellum | Kirchneriella sp1 | D. bicaudatus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Ding, A.; Lin, J.; Wu, X.; Ji, G. Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Environmental Drivers in Chinese Mitten Crab Aquaculture Ponds: Highlighting the Need for Cyanobacteria Control. Water 2024, 16, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121688
Jin L, Ding A, Lin J, Wu X, Ji G. Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Environmental Drivers in Chinese Mitten Crab Aquaculture Ponds: Highlighting the Need for Cyanobacteria Control. Water. 2024; 16(12):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121688
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Luqi, Anjie Ding, Jianwei Lin, Xugan Wu, and Gaohua Ji. 2024. "Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Environmental Drivers in Chinese Mitten Crab Aquaculture Ponds: Highlighting the Need for Cyanobacteria Control" Water 16, no. 12: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121688
APA StyleJin, L., Ding, A., Lin, J., Wu, X., & Ji, G. (2024). Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Environmental Drivers in Chinese Mitten Crab Aquaculture Ponds: Highlighting the Need for Cyanobacteria Control. Water, 16(12), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121688







