Analysis of Water Temperature Variations in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches in the Context of Cascade Hydropower Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
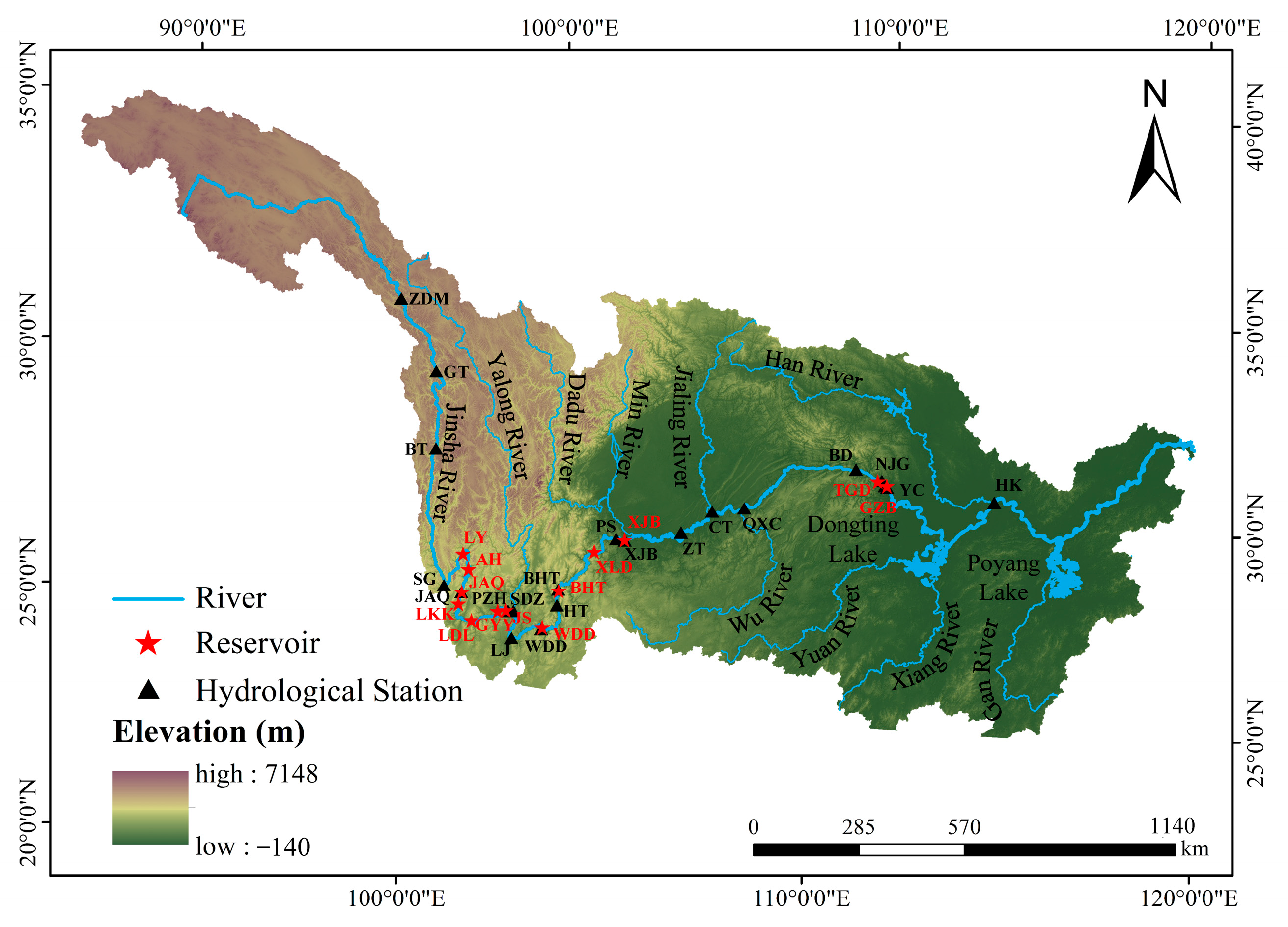
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
2.2.2. The Temperature-Increasing Index
2.2.3. The Extreme Fluctuation Index
2.2.4. The Baseline Deviation Indicator
2.2.5. The Phase Offset Time Index
3. Results
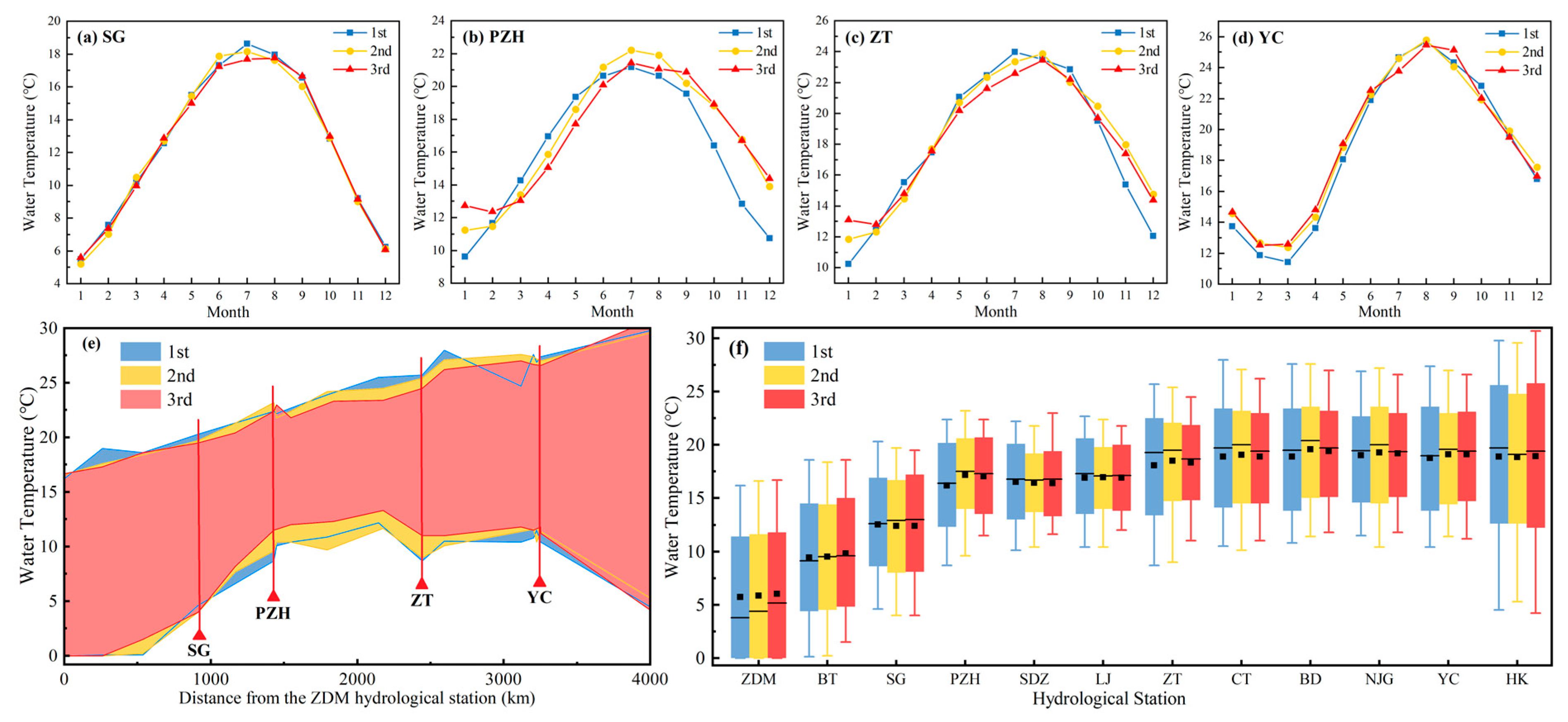
3.1. Influencing Factors of Water Temperature in the Mainstream of the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River
3.2. The Temperature-Increasing Index
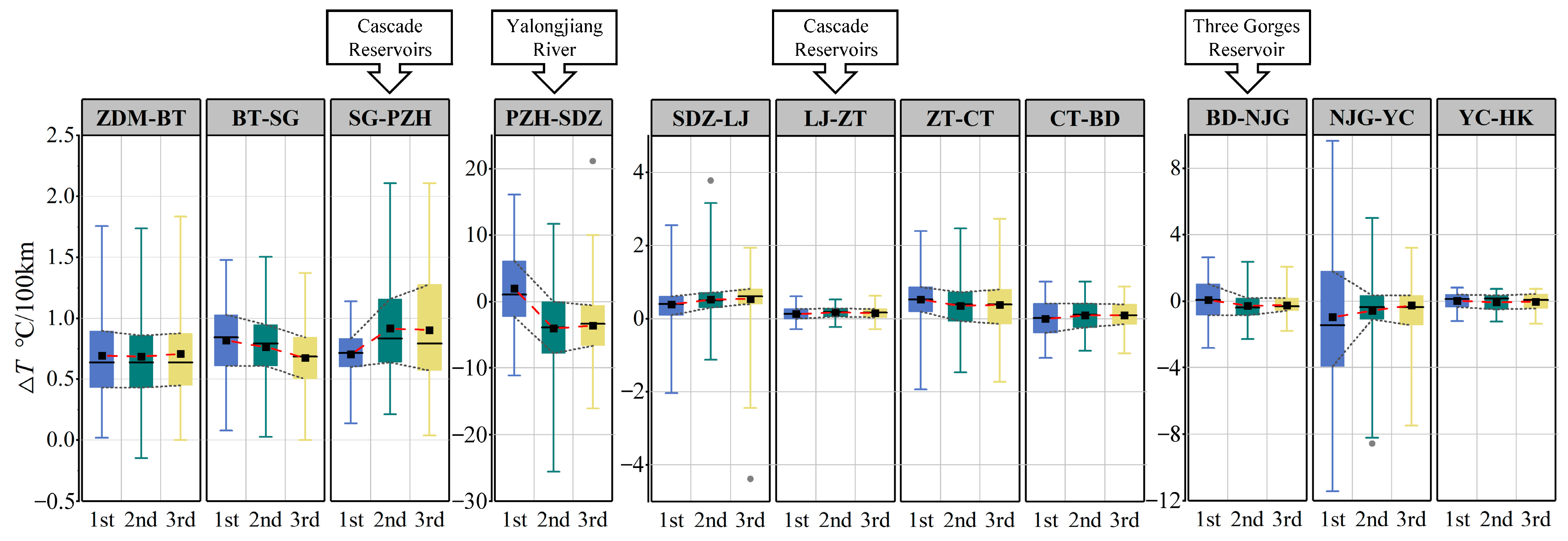
3.3. The Extreme Fluctuation Index
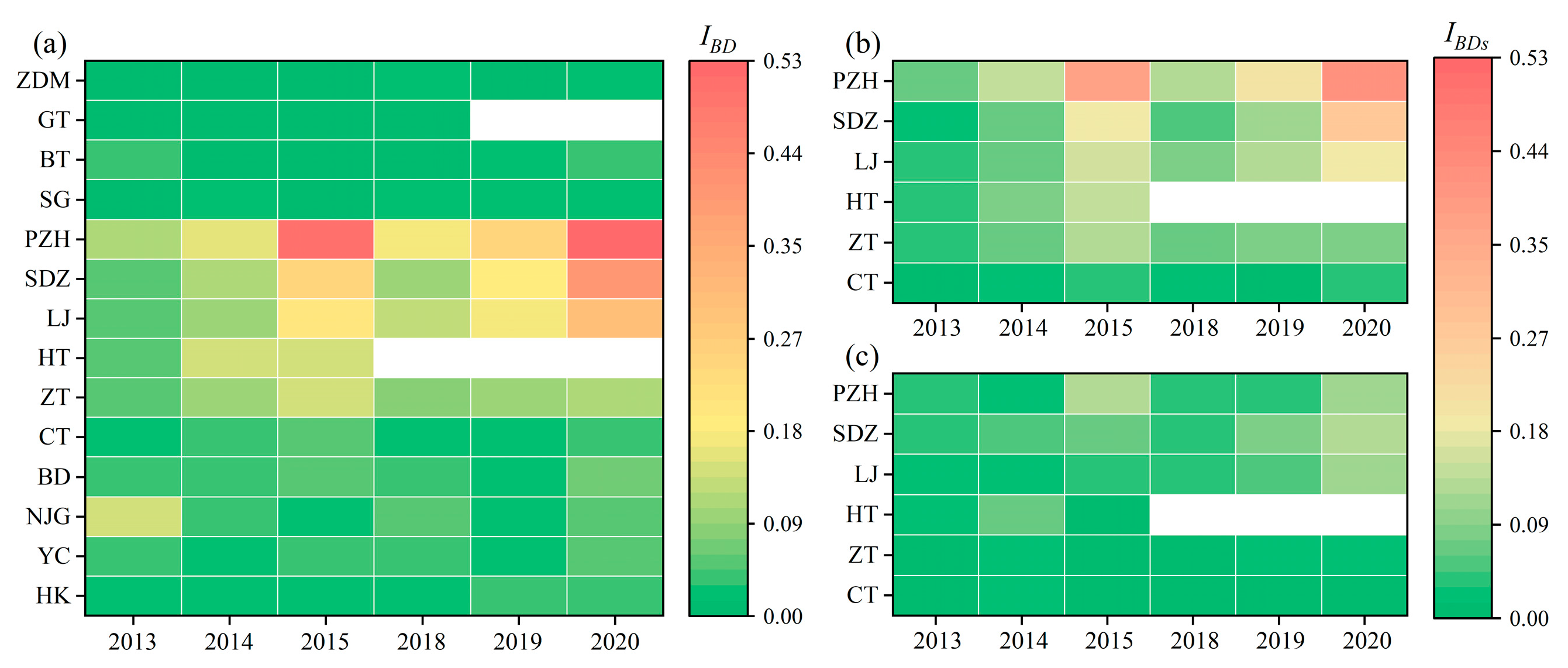
3.4. The Baseline Deviation Index
3.5. The Phase Offset Time Index
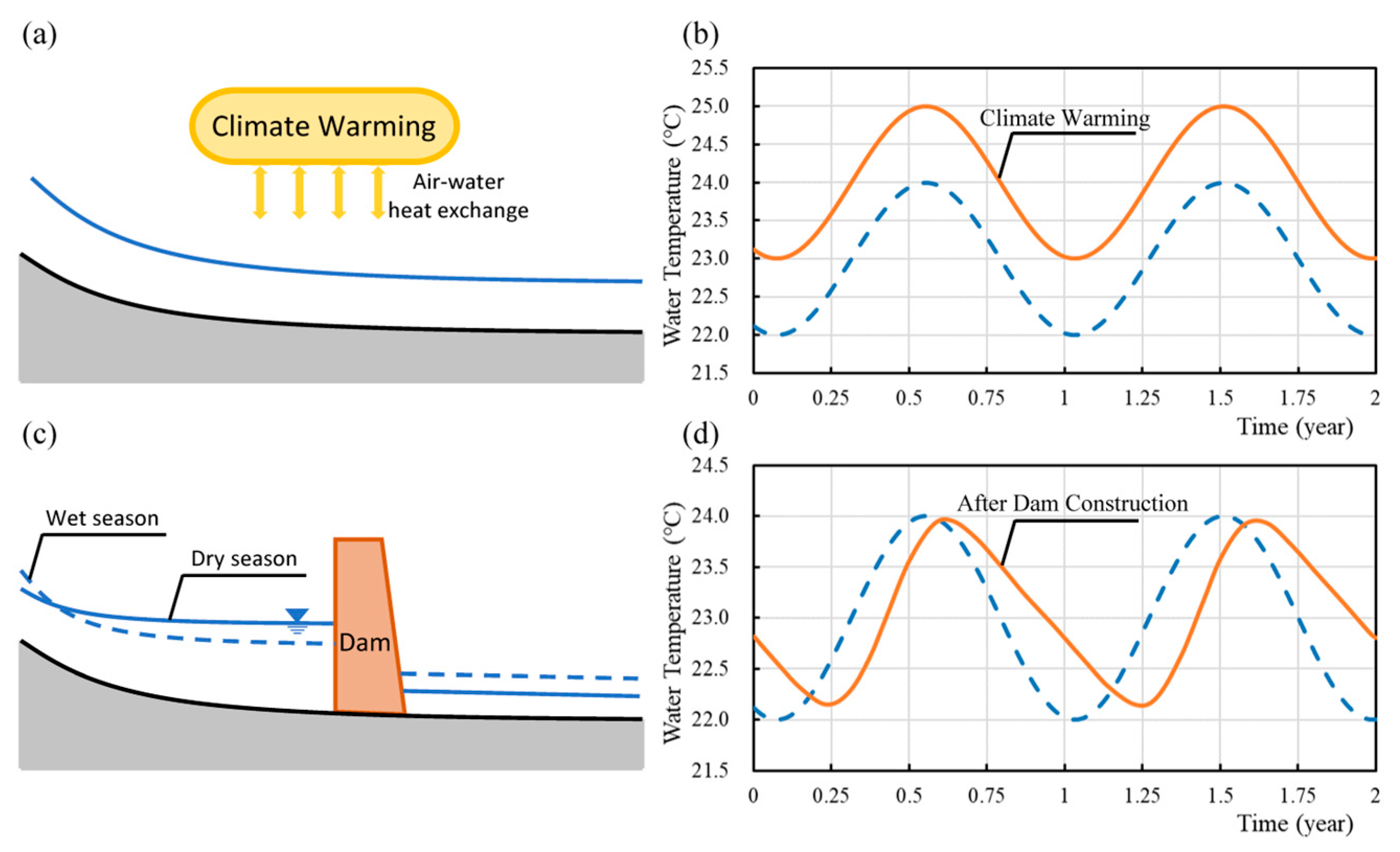
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Water Temperature Distribution in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches
4.2. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Water Temperature Evaluation Indexes
5. Conclusions
- The construction and operation of cascade reservoirs in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River have weakened the synchronization of water temperature and air temperature in the lower reaches. For instance, with an increase in the number of dams and their extended operation time of cascade reservoirs in the middle reaches of Jinsha River, there was a decline in the Pearson correlation coefficient between water temperature and air temperature at the PZH hydrology station from 0.850 in the first period to 0.823 in the second period, further decreasing to 0.723 in the third period, indicating a significant weakening of synchronization between water temperature and air temperature.
- The construction and operation of cascade reservoirs in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River have significantly altered the distribution law of river water temperature. The of the BD to NJG section decreased from −0.85~1.04 °C/100 km in the first period to −0.57~0.19 °C/100 km in the third period. The of the NJG to YC section decreased from −3.93~1.79 °C/100 km in the first period to −1.43~0.36 °C/100 km in the third period. The operation of the TGD and GZB gradually reduced the difference in water temperature between the upper and lower reaches.
- The construction and operation of cascade reservoirs in the mainstream of the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River caused homogenization and lagging effect of water temperature in the lower reaches, and there was a cumulative effect, which can be quantified by the , and . For example, the of the PZH hydrology station decreased year by year from 0.78 in 2015 to 0.68 in 2020, and the increased year by year in the second and third periods, reaching 0.502 and 0.528 in 2015 and 2020, respectively. The were 19.7 days in the second period and 28.1 days in the third period, respectively. These results indicated that cascade reservoir construction in the middle reaches of the Jinsha River had a cumulative effect on the water temperature in the lower reaches.
- The homogenization and lagging effect of water temperature in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River were more significant in the cold season than in the warm season. In the lower reaches of the Jinsha River, the mean value of in the cold season was about 0.15 lower than that in the warm season, the degree of baseline deviation in the cold season accounted for 49~93%, and the were 4.42~14.97 days higher than the .
- The inflow of tributaries has a significant impact on the water temperature of the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River. After the Yalong River was refluxing, the of the PZH to SDZ section ranged from −25.56 to 16.11 °C/100 km, and the fluctuation in water temperature was significantly greater than that of other sections. The of the SDZ hydrology station decreased by about 50% compared with that of the PZH hydrology station, and the decreased by 4.1 days. At the same time, the decreasing effect of the Yalong River on the homogenization of water temperature of the mainstream was stronger in the warm season.
- The process of water–air heat exchange can mitigate the impact of cascading reservoirs on the thermal regime of the river in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River. According to the calculation results of , and , the homogenization and lagging effects of water temperature in the PZH to HT section and the ZT to BD section were weakened along the way. This suggests that natural heat exchange mechanisms play a critical role in lessening the alterations imposed by reservoirs on the river’s temperature dynamics.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webb, B.W.; Walling, D.E. Temporal Variability in the Impact of River Regulation on Thermal Regime and Some Biological Implications. Freshw. Biol. 1993, 29, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.B.; Schladow, S.G.; Reuter, J.E. Forecasting Stream Water Temperature Using Regression Analysis, Artificial Neural Network, and Chaotic Non-Linear Dynamic Models. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Nyarko, E.K.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M. Modelling Daily Water Temperature from Air Temperature for the Missouri River. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Zarfl, C. River Dam Impacts on Biogeochemical Cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.T.; Xiang, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.M.; Yu, Q. Impact of Spatial Variations in Water Quality and Hydrological Factors on the Food-Web Structure in Urban Aquatic Environments. Water Res. 2019, 153, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Du, J.; Han, Y.; Hu, H. Identifying Major Contributors to Algal Blooms in Lake Dianchi by Analyzing River-Lake Water Quality Correlations in the Watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Wu, J. Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Yangtze River Water Temperature: Assessment and Ecological Implications. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, Y.; Teng, J.; Wang, X.; Song, J. Characteristics of Spatial Distribution for Microbial Ecology inside and Outside Source Water Reservoir. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yao, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Dahlgren, R. Water Temperature and Organic Carbon Control Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Particle-attached and Free-living Bacterial Communities in a Hypereutrophic Urban River Network. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, J.; Xie, Z.; Jia, B.; Qin, P.; et al. Global River Water Warming Due to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Heat Emission. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2020, 193, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, S.; Shi, X.; Guo, J.; Ke, S.; Hu, C.; Asad, M.; Jalbani, S.; Zwain, H.M.; Khan, P.; Boota, M.W. Are Global Influences of Cascade Dams Affecting River Water Temperature and Fish Ecology? Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caissie, D. The Thermal Regime of Rivers: A Review. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, D.M.; Garner, G. River Water Temperature in the United Kingdom Changes over the 20th Century and Possible Changes over the 21st Century. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 39, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Piotrowski, A.P. River/Stream Water Temperature Forecasting Using Artificial Intelligence Models: A Systematic Review. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaak, D.J.; Wollrab, S.; Horan, D.; Chandler, G. Climate Change Effects on Stream and River Temperatures across the Northwest U.S. from 1980-2009 and Implications for Salmonid Fishes. Clim. Chang. 2012, 113, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Psaris, M. Local Landscape Predictors of Maximum Stream Temperature and Thermal Sensitivity in the Columbia River Basin, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, M.T.H.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Yearsley, J.R.; Ludwig, F.; Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Kabat, P. Global River Discharge and Water Temperature under Climate Change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, K. A Global Boom in Hydropower Dam Construction. Aquat. Sci 2015, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, M.E.; Danner, E.M. The Drivers of River Temperatures Below a Large Dam. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, H.; Ma, Y.; Hong, F.; Wang, H. Multi-Scale Impact of Climate Change and Cascade Reservoirs on Hydrothermal Regime Alteration in Regulated Rivers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, D.K.; Ali, R.; Bhat, S.A.; Elbeltagi, A.; Kushwaha, N.L.; Kumar, R.; Rajput, J.; Heddam, S.; Kuriqi, A. Pre- and Post-Dam River Water Temperature Alteration Prediction Using Advanced Machine Learning Models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83321–83346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic Stresses on the World’s Big Rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Jin, C.; Jijun, X.; Zeng, G.; Lianhai, S.; Liu, Q.; Qiang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhengjie, Y.; et al. Effects of Dam Construction on Biodiversity: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the World’s Free-Flowing Rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Chen, L.; Zhu, D.Z.; Zhu, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, X. Impact of the Three Gorges Reservoir on the Hydrologic Regime of the River-Lake System in the Middle Yangtze River. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 121004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Finlayson, B.L.; Wei, T.; Sun, Q.; Webber, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. Changes in Monthly Flows in the Yangtze River, China—With Special Reference to the Three Gorges Dam. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Fenicia, F.; Peng, H.; Xu, G. Hydrologic Impacts of Cascading Reservoirs in the Middle and Lower Hanjiang River Basin under Climate Variability and Land Use Change. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Assessment of Multiple Dam- and Sluice-Induced Alterations in Hydrologic Regime and Ecological Flow. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Qian, X.; Han, B.-P.; Luo, L.; Luo, L.-C.; Hamilton, D.P. Effects of Local Climate and Hydrological Conditions on the Thermal Regime of a Reservoir at Tropic of Cancer, in Southern China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2591–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton, R.S.; Calamita, E.; Wehrli, B. Reviews and Syntheses: Dams, Water Quality and Tropical Reservoir Stratification. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Naiman, R.J. Incorporating Thermal Regimes into Environmental Flows Assessments: Modifying Dam Operations to Restore Freshwater Ecosystem Integrity. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędra, M.; Wiejaczka, Ł. Disturbance of Water-Air Temperature Synchronisation by Dam Reservoirs. Water Environ. J. 2016, 30, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Ji, D.; Liu, D.; Yang, Z.; Lorke, A. Effect of Cascading Reservoirs on the Flow Variation and Thermal Regime in the Lower Reaches of the Jinsha River. Water 2019, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.; Song, K.; Zhang, X. Cascade Dam-Induced Hydrological Disturbance and Environmental Impact in the Upper Stream of the Yellow River. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Cumulative Effects of Cascade Dams on River Water Cycle: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yi, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, Z. Effects of a Cascade Reservoir System on Runoff and Sediment Yields in a River Basin of Southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Liu, P.; Pan, H. Prospects of Hydropower Industry in the Yangtze River Basin: China’s Green Energy Choice. Renew. Energ. 2019, 131, 1168–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Wang, D. A Transitional Region Concept for Assessing the Effects of Reservoirs on River Habitats: A Case of Yangtze River, China. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Ni, M. Influences of Land Use Metrics at Multi-Spatial Scales on Seasonal Water Quality: A Case Study of River Systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chang, F.; He, X.; Yang, Q.; Ma, W. Influence of Cascade Hydropower Development on Water Quality in the Middle Jinsha River on the Upper Reach of the Yangtze River. Water 2022, 14, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Deng, Y.; Tuo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Naisheng, L. Impact of the Dam Construction on the Downstream Thermal Conditions of the Yangtze River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bruce, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, D.Y.; Ni, L.; Wu, J. Quantifying the Impacts of the Three Gorges Reservoir on Water Temperature in the Middle Reach of the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, C. Quantitative Assessment of Climatic and Reservoir-Induced Effects on River Water Temperature Using Bayesian Network-Based Approach. Water 2022, 14, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolon, M.; Piccolroaz, S. A Hybrid Model for River Water Temperature as a Function of Air Temperature and Discharge. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Lin, B.; Xu, H. Dam-Influenced Seasonally Varying Water Temperature in the Three Gorges Reservoir. River Res. Appl. 2021, 37, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Jaworski, N.A.; Pace, M.L.; Sides, A.M.; Seekell, D.; Belt, K.T.; Secor, D.H.; Wingate, R.L. Rising Stream and River Temperatures in the United States. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedrist, G.H. Substantial Warming of Central European Mountain Rivers under Climate Change. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2023, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheu, A.; St-Hilaire, A.; Caissie, D.; El-Jabi, N.; Bourque, G.; Boisclair, D. A Regional Analysis of the Impact of Dams on Water Temperature in Medium-Size Rivers in Eastern Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 1885–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidel, P.A.; Roy, A.H.; Houle, K.M.; Lambert, B.; Letcher, B.H.; Nislow, K.H.; Smith, C. Impacts of Small Dams on Stream Temperature. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Spatiotemporal Variation and Hotspots of Climate Change in the Yangtze River Watershed during 1958–2017. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xing, B. Spatio-Temporal Variability in Hydroclimate over the Upper Yangtze River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhou, X.; Tang, W. Evaluation Indicators for Assessing the Influence of Reservoirs on Downstream Water Temperature. Adv. Water Sci. 2012, 23, 419–426. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Long, L.; Ji, D.; Yang, Z. Spatio-Temporal Variations Characteristics and Differences of Water Temperature in Upper and Middle Reaches of Lancang-Nujiang River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 2186–2196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Tao, Y.; Wu, J. Influence of the Impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir on Hydrothermal Conditions for Fish Habitat in the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 10995–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.C.; Kelly, O.M.; Maloney, K.O.; Schmid, M.; McKenna, J.E. Developing and Testing Temperature Models for Regulated Systems: A Case Study on the Upper Delaware River. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędra, M.; Wiejaczka, Ł. Climatic and Dam-Induced Impacts on River Water Temperature: Assessment and Management Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 626, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficklin, D.L.; Barnhart, B.L.; Knouft, J.H.; Knouft, J.; Stewart, I.T.; Maurer, E.P.; Letsinger, S.L.; Whittaker, G. Climate Change and Stream Temperature Projections in the Columbia River Basin: Habitat Implications of Spatial Variation in Hydrologic Drivers. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4897–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Xiong, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Q. Stream Temperature Response to Climate Change and Water Diversion Activities. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Yin, J.; Paw, U.K.T.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, G.; Liu, Z. How the Three Gorges Dam Affects the Hydrological Cycle in the Mid-Lower Yangtze River: A Perspective Based on Decadal Water Temperature Changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qian, Y. Annual Distribution Features of Precipitation in China and Their Interannual Variations. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2003, 17, 146–163. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Su, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Interannual Runoff Distribution Based on Degree and Time of Concentration for Rivers. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 791–795. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Babaousmail, H.; Ayugi, B.O.; Onyutha, C.; Kebacho, L.L.; Ojara, M.; Ongoma, V. Analysis of Changes in Rainfall Concentration over East Africa. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hette-Tronquart, N.; Roussel, J.-M.; Dumont, B.; Archaimbault, V.; Pont, D.; Oberdorff, T.; Belliard, J. Variability of Water Temperature May Influence Food-Chain Length in Temperate Streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 718, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarova, P.; Halmova, D.; Miklanek, P.; Onderka, M.; Pekar, J.; Skoda, P. Is the Water Temperature of the Danube River at Bratislava, Slovakia, Rising? J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, M.T.H.; Ludwig, F.; Zwolsman, J.J.G.; Weedon, G.P.; Kabat, P. Global River Temperatures and Sensitivity to Atmospheric Warming and Changes in River Flow. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W02544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-González, M.A.; Quílez, D.; Isidoro, D. Factors Controlling the Changes in Surface Water Temperature in the Ebro River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Z.J.; Xin, Y.; Qu, M. Comparative Study on Temperature Response of Hydropower Development in the Dry-Hot Valley. GeoHealth 2021, 5, e2021GH000438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, B.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, H. Attribution Analysis of Runoff in the Upper Reaches of Jinsha River, China. Water 2022, 14, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wang, D.; Wu, J. A Framework for Assessing River Thermal Regime Alteration: A Case Study of the Hanjiang River. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; He, X.; Sun, L.; Sun, T.; Zhong, R.; Duan, X.; Chen, L. Impacts of Watershed Hydropower Development on Social-Ecological Systems in Hot-Dry Valleys. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 5639–5647. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Dan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y. Impact of Cascade Reservoirs on Continuity of River Water Temperature: A Temperature Trend Hypothesis in River. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Long, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, D.; Song, L. Advances in Study on Cumulative Effects of Construction of Cascaded Reservoirs on Water Environment. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2017, 37, 7–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, J.; Val, R.; Armengol, J.; Dolz, J. Temporal Variability in the Thermal Regime of the Lower Ebro River (Spain) and Alteration Due to Anthropogenic Factors. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Xu, H.; Ji, D.; Cui, Y.; Liu, D.; Song, L. Characteristic of the Water Temperature Lag in Three Gorges Reservoir and Its Effect on the Water Temperature Structure of Tributaries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Yuan, B.; Lin, B.; Zhang, X. Roles of Dam and Climate Change in Thermal Regime Alteration of a Large River. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 094016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reservoirs | Abbreviation | Normal Water Level (m a.s.l.) | Dead Water Level (m a.s.l.) | Total Storage Capacity (108 m3) | Regulating Storage Capacity (108 m3) | Regulation Performance | Operation Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liyuan | LY | 1618 | 1605 | 8.05 | 1.73 | week | 2014 |
| Ahai | AH | 1504 | 1492 | 8.82 | 2.38 | day | 2011 |
| Jinanqiao | JAQ | 1418 | 1398 | 8.47 | 3.46 | week | 2010 |
| Longkaikou | LKK | 1298 | 1290 | 5.58 | 1.13 | day | 2012 |
| Ludila | LDL | 1223 | 1216 | 17.18 | 3.76 | day | 2013 |
| Guanyinyan | GYY | 1134 | 1122 | 20.72 | 5.5 | week | 2014 |
| Jinsha | JS | 1022 | 1020 | 1.08 | 0.112 | day | 2020 |
| Wudongde | WDD | 975 | 945 | 74.08 | 24.4 | year | 2020 |
| Baihetan | BHT | 825 | 765 | 206.27 | 104.35 | year | 2021 |
| Xiluodu | XLD | 600 | 540 | 126.7 | 64.6 | season | 2013 |
| Xiangjiaba | XJB | 380 | 370 | 51.63 | 9 | season | 2012 |
| Three Gorges Dam | TGD | 175 | 155 | 393 | 221 | year | 2003 |
| Gezhouba | GZB | 66 | 63 | 7.11 | 0.86 | —— | 1981 |
| Period | Year | Hydrological Condition | Dams |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2009 | dry | JAQ, TGD, GZB |
| 2010 | wet | ||
| 2nd | 2013 | dry | LY, AH, JAQ, LKK, LDL, GYY, XLD, XJB, TGD, GZB |
| 2014 | normal | ||
| 2015 | wet | ||
| 3rd | 2018 | dry | LY, AH, JAQ, LKK, LDL, GYY, JS, WDD, XLD, XJB, TGD, GZB |
| 2019 | normal | ||
| 2020 | wet |
| Water Temperature and Air Temperature | ||||||
| Period | ZDM | BT | SG | PZH | SDZ | LJ |
| 1st | 0.876 | 0.946 | 0.895 | 0.850 | 0.910 | 0.892 |
| 2nd | 0.873 | 0.931 | 0.890 | 0.827 | 0.816 | 0.848 |
| 3rd | 0.883 | 0.941 | 0.912 | 0.723 | 0.677 | 0.791 |
| Period | ZT | CT | BD | NJG | YC | HK |
| 1st | 0.939 | 0.930 | 0.809 | 0.760 | 0.784 | 0.915 |
| 2nd | 0.923 | 0.921 | 0.779 | 0.745 | 0.775 | 0.919 |
| 3rd | 0.928 | 0.923 | 0.823 | 0.781 | 0.782 | 0.941 |
| Water Temperature and Discharge | ||||||
| Period | ZDM | BT | SG | PZH | SDZ | LJ |
| 1st | 0.700 | 0.760 | 0.736 | 0.627 | 0.598 | —— |
| 2nd | 0.544 | 0.659 | 0.639 | 0.654 | 0.594 | —— |
| 3rd | 0.695 | 0.742 | 0.713 | 0.786 | 0.707 | —— |
| Period | ZT | CT | BD | NJG | YC | HK |
| 1st | 0.700 | 0.702 | —— | —— | 0.756 | 0.808 |
| 2nd | 0.707 | 0.713 | —— | —— | 0.735 | 0.828 |
| 3rd | 0.720 | 0.684 | —— | —— | 0.720 | 0.739 |
| (days) | ZDM | GT | BT | SG | PZH | SDZ | LJ |
| −0.3 | −1.0 | −0.3 | −1.8 | 19.7 | 15.6 | 14.2 | |
| 1.0 | −3.3 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 28.1 | 24.6 | 23.4 | |
| (days) | HT | ZT | CT | BD | NJG | YC | HK |
| 11.4 | 9.6 | 4.8 | 1.9 | −0.3 | −1.9 | −1.5 | |
| —— | 9.7 | 3.4 | −1.7 | −4.3 | −2.6 | −4.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Yu, S.; Xu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, R.; Wei, H.; Liu, D. Analysis of Water Temperature Variations in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches in the Context of Cascade Hydropower Development. Water 2024, 16, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121669
Wang Z, Ma J, Yu S, Xu Y, Tao Z, Zhang J, Xiao R, Wei H, Liu D. Analysis of Water Temperature Variations in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches in the Context of Cascade Hydropower Development. Water. 2024; 16(12):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhangpeng, Jun Ma, Shengde Yu, Yaqian Xu, Zeyi Tao, Jiaqi Zhang, Ran Xiao, Hao Wei, and Defu Liu. 2024. "Analysis of Water Temperature Variations in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches in the Context of Cascade Hydropower Development" Water 16, no. 12: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121669
APA StyleWang, Z., Ma, J., Yu, S., Xu, Y., Tao, Z., Zhang, J., Xiao, R., Wei, H., & Liu, D. (2024). Analysis of Water Temperature Variations in the Yangtze River’s Upper and Middle Reaches in the Context of Cascade Hydropower Development. Water, 16(12), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121669








