Abstract
Blooms of the harmful dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on the West Florida Shelf (WFS), Gulf of Mexico, are hypothesized to initiate in association with the colonial cyanobacterium Trichodesmium spp. and benefit from dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) release derived from N2-fixation by the cyanobacteria. Previous studies have detected DON release using direct experimental measurements, but there have been few studies that have followed nutrient release by in situ blooms of Trichodesmium and the associated plankton community. It was determined that long-term Trichodesmium spp. and Karenia brevis abundances on the WFS were related, following a 2-month lag. A separate Eulerian study of a Trichodesmium erythraeum bloom event was conducted over 9 days on the Great Barrier Reef. Concentrations of T. erythraeum increased over the course of the study, with coincident increases in dinoflagellate abundance and decreases in diatom abundance. Inside the bloom, concentrations of NH4+, PO43−, and DON increased significantly. The copepod grazer Macrosetella gracilis also increased in abundance as T. erythraeum numbers increased, contributing to nutrient release. Copepod grazing rates were measured, and N release rates estimated. Together, these studies show that Trichodesmium blooms have consequences for dinoflagellate abundance at both seasonal and ephemeral scales via direct and indirect N release.
1. Introduction
The open ocean pelagic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium has a pan-global distribution in tropical and subtropical oceanic regions. It was first recorded in Australian waters of the Great Barrier Reef (GBR) during the 1770 voyage of Captain Cook [1,2] and remains the most conspicuous phytoplankter in the region [3,4]. It is also frequently noted in the Gulf of Mexico [5,6]. Trichodesmium is truly a “globally significant marine cyanobacterium” [7], with blooms occurring in tropical and subtropical regions around the world’s oceans, including the Red Sea [8,9,10], the Caribbean [11], the western Atlantic (off the coast of Brazil) [12,13], the Eastern Atlantic (off coastal Africa) [14,15,16], western regions of the Pacific Ocean [17,18,19], the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea [20,21,22], as well as the South China Sea [23], amongst other locations. In recent years, the relationship between Trichodesmium blooms and dinoflagellate blooms has been of considerable interest due the long-term (>50 year) monitoring records that show blooms of Trichodesmium tend to precede or co-occur with blooms of the toxic “red-tide” dinoflagellate Karenia brevis in the eastern Gulf of Mexico and West Florida Shelf [5,6]. The dinoflagellates are hypothesized to benefit from the fixed nitrogen (N) that is released by Trichodesmium, providing an important nutrient source to initiate blooms [24,25]. During the past decade, the West Florida Shelf has experienced numerous massive and devastating K. brevis blooms [26], increasing the need to further understand how these blooms are initiated and/or maintained.
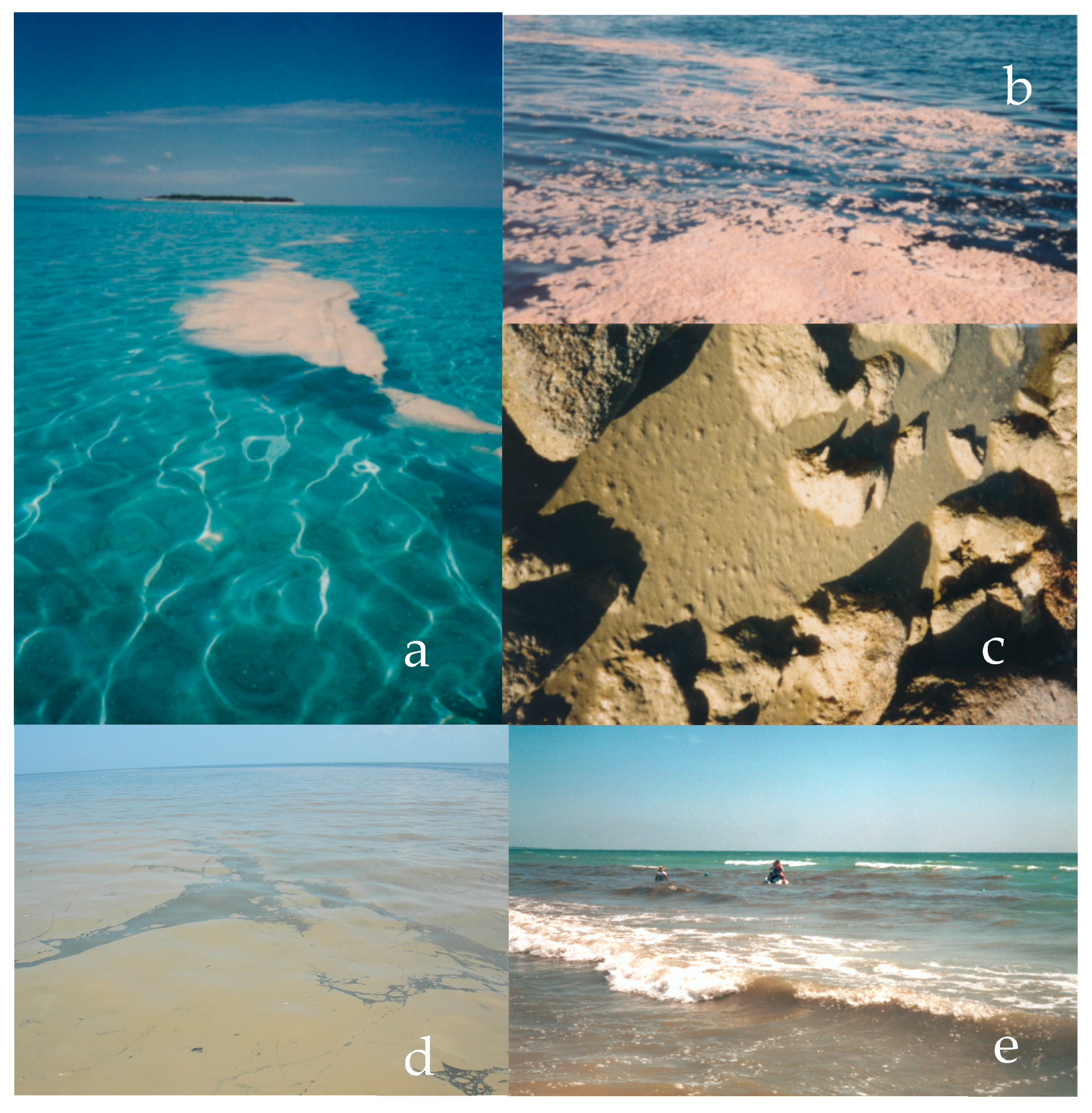
Trichodesmium episodically occurs in dense surface aggregations (Figure 1a,b), very large examples of which have been photographed from the Space Shuttle [4,27] and satellites [28,29,30,31,32,33]. Recent estimates using multi-band satellite imagery and deep learning techniques investigated Trichodesmium abundance around Australia from 2012–2021 during peak months (September–November) and found that it was ubiquitous around the continent, except the Southern Coast. It was estimated to have a “cumulative footprint exceeding 4.6 million km2” in area [33], which demonstrates how significant Trichodesmium biomass can be and why its impacts can be consequential. In shallow areas, such as lagoons of the Great Barrier Reef, blooms may be deposited by receding tides on the reef flat that are exposed and may periodically smother corals and other substrates [34] (Figure 1c). Beaches can also be impacted (Figure 1e). Trichodemsium is also known to produce compounds that cause skin irritation [35] and ciguatera-like toxic effects [36,37]. They can also produce several neurotoxic compounds [38,39] that are associated with asthma-like symptoms and headaches [40,41,42,43], as well as producing toxins that deter copepod grazing [38,44]. Trichodesmium can exist as single filaments (also known as trichomes [45] or as colonies comprising a few to several hundred trichomes, with dimensions ranging from 100 s to 1000 s of µm. These large surface aggregations, or slicks, tend to occur during warm, calm periods, when the water column is stable and stratified [33,46,47] (Figure 1a,d).

Figure 1.
Trichodesmium blooms. (a) Surface slicks of T. erythraeum present during the early stages of bloom development, with Heron Island in the background; (b) degenerating surface slicks of T. erythraeum during the later stage of a bloom; (c) T. erythraeum slicks deposited on coral and rock along the edge of Heron Island during the later stages of a bloom; (d) surface slicks of Trichodesmium spp. in the Gulf of Mexico; and (e) Trichodesmium spp. accumulations reaching the beaches of Florida. Photos (a–c) by P. Glibert. Photo (d) by Sara Klass, Mote Marine Laboratory, and photo (e) by C. Heil.
Whatever the surface concentrating mechanism may be (e.g., an increase in biomass resulting from growth, langmuir cell windrows, or other physical features), the dense surface accumulations of Trichodesmium biomass are ecologically significant in nutrient-poor tropical shelf and oceanic waters, as it is the most abundant pelagic organism confirmed to fix significant amounts of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) [46,48,49].
As an N2 fixer, Trichodesmium produces and biologically packages “new” N [50] into forms potentially available to other marine organisms [51,52,53,54,55] and may have impacts on the food web at multiple levels [56,57]. There have been some efforts to understand the fate of this N within Trichodesmium-dominated assemblages. It has been shown, for example, that Trichodesmium may release a significant fraction of its newly fixed N in the form of dissolved organic N (DON) [58,59,60], consisting largely of a small molecular weight size class (<10,000 Da) and primarily composed of amino acids, glutamine, and glutamate [58,59]. It has also been demonstrated that 15N2-labelled DON produced by Trichodesmium N2 fixation can be directly taken up by other organisms, particularly dinoflagellates, including the dinoflagellate K. brevis in the Gulf of Mexico [61]. Yet, the extent to which this DON or other forms of released N (e.g., NH4+) may support other components of the food web is unknown.
Motivated by the perceived notion that Trichodesmium spp. play an important role in nutrient cycling in oligotrophic waters via both direct and indirect pathways, this study aimed to (1) demonstrate the relationship between Trichodesmium abundance and the severity of K. brevis blooms on the West Florida Shelf on a seasonal basis, (2) explore previously unpublished data sets in which nutrient concentrations and plankton community changes were monitored closely in a Trichodesmium erythraeum bloom on the Great Barrier Reef, and (3) estimate N release from copepod grazing of Trichodesmium spp. based on grazing rates of Trichodesmium erythraeum by its common harpacticoid copepod grazer, Macrosetella gracilis [62,63,64]. The hypothesis tested is that the relationship between Trichodesmium spp. and K. brevis—and with dinoflagellates more generally—is mediated by the change in nutrient concentration and quality, and thus this relationship plays a key role in K. brevis bloom initiation. Using the rates measured therein, contemporary trends in Trichodesmium spp. occurrence were examined in the Gulf of Mexico and interpreted with available copepod grazing data to provide new estimates of the potential role of Trichodesmium in nutrient supply for blooms of Karenia brevis in the Gulf of Mexico. Collectively, these data sets provide a more comprehensive estimate of the nutrient cycling associated with Trichodesmium blooms in the Gulf of Mexico than has been previously possible and show that blooms of this important cyanobacteria have lasting consequences for the food web. Discerning these interactions may be of particular importance, given the hypothesis that Trichodesmium blooms may be increasing with climate change [33,65,66,67,68,69].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gulf of Mexico: Interannual Comparisons of Trichodesmium spp. and Karenia brevis
Georeferenced data on Trichodesmium were obtained by request from the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s Fish and Wildlife Research Institute’s (FWC-FWRI) HAB Monitoring Database. This database, which supports the Florida state K. brevis monitoring program, is described in Haverkamp [70]. The data set focused on the period from 2007 to the present, because although Trichodesmium spp. records date from 1960 to current, it was only after 2006 that abundances of Trichodesmium spp. were regularly monitored in conjunction with the monitoring of Karenia brevis. For this study, Trichodesmium spp. refers to all Trichodesmium species identified within a sample and includes both T. erythraeum and T. thiebautii.
A bloom severity index (BSI) was recently developed for K. brevis [20]. This index is specific for the southwest region within 5 km of the coast, not including estuarine sites, and categorizes blooms into 5 bins: <5000 cells L−1, >5000 cells L−1, > 50,000 cells L−1, >100,000 cells L−1, and >1,000,000 cells L−1. Although reported values of BSI date back decades, these authors caution that earlier data are less reliable due to inconsistent and under-sampling. The index reports severity on a scale of 0 (<5000 cells L−1) to 10 (maximum extent of coastline impacted by a bloom present for any month during the time series assessed thus far). Herein, the reported BSI values of Stumpf et al. [20] for blooms > 100,000 cells L−1 were compared to those of Trichodesmium spp. for the period of 2007–2019, a period with data that are considered robust and consistently reported. Trichodesmium spp. data were first log transformed (log (cells L−1 + 1)). The bloom severity index was applied for blooms >100,000 cells L−1 [20] and averaged by month. After removing all years for which bloom severity was <−1.0, regressions of bloom severity with Trichodesmium spp. abundance were calculated. Comparisons were made with coincident reported values and for K. brevis indices lagged by 1 and 2 months.
2.2. Great Barrier Reef: The Eularian Study
Previously unreported data were explored for an intensive Eularian study of a Trichodesmium bloom on a reef edge southwest of Heron Island, in the Wistari Channel, on 2–11 October 1996. Heron Island (23°26′ S; 151°55′ E) is a coral cay situated on a platform reef located ~70 km offshore in the Mackay Capricorn Region of the southern Great Barrier Reef, Queensland, Australia. Sampling was initiated during a period when T. erythraeum abundance had been low (<20 colonies L−1) for several weeks, but over the course of the study, a bloom of the cyanobacterium occurred. Daily wind speeds and temperature were recorded at the University of Queensland’s Heron Island Research Station.
Water samples for nutrient analyses were collected daily (between 900 and 1100 h) from surface water with a modified Van Dorn bottle deployed from a small boat. Samples were collected both “inside” and “outside” areas having high concentrations of T. erythraeum, with the designation of these sampling area types made by visual inspection of the sea surface (Figure 1a) and confirmed by subsequent counting of the samples. Surface water temperature was determined with a Horiba Water Quality Sampler. Duplicate surface samples were immediately syringe-filtered through pre-combusted (550 °C, 2 h) Whatman GF/F filters and frozen. Subsequently, samples were frozen for later analysis. Inorganic nutrients (PO43−, NH4+, NO2+3) were measured by the Queensland Government Chemical Laboratories, Australia, using standard colorimetric methods [71]. Concentrations of DON were analyzed according to Bronk et al. [72].
Phytoplankton and zooplankton were sampled daily with 64 (0.5 m diameter) and 20 (0.25 m diameter) μm mesh nets, respectively, within and outside the T. erythraeum bloom. For enumeration of the cyanobacteria, surface water samples (1 L) were also taken, and replicate samples were filtered through GF/F filters and colonies counted using a dissecting microscope. Under bloom conditions, samples were stirred and subsampled as necessary, for accurate enumeration.
Phytoplankton populations were sampled using a 20 μm net towed behind the boat at slow speed for 2 min and preserved with Lugol’s preservative. During the initial sampling, 250 mL of water was collected from both inside and outside the bloom and immediately preserved with Lugols’ preservative for enumeration of the total phytoplankton community present. Phytoplankton species in these initial samples were counted the same day by settling 50 mL according to the Utermöhl method [73] and identifying diatom and dinoflagellates to the species level, where possible, according to Tomas [74] and Wood [75]. The resulting phytoplankton concentrations outside the bloom were so low that the cell concentration data from whole water sample was not considered representative of the community present. To enable daily samples from inside and outside blooms to be treated in a similar manner, phytoplankton were subsequently sampled with short quantitative timed tows as described above, with 10–25 mL of each tow settled and counted as previously described. Although the use of quantitative 20 μm tows to sample the phytoplankton community present only allowed for the sampling of the larger “net” phytoplankton fraction, given the highly disparate Trichodesmium and phytoplankton biomass inside and outside the bloom, these short tows were the only method available to make a quantitative comparison of phytoplankton populations and species present in these regions. The diversity of phytoplankton communities inside and outside the Trichodesmium bloom was determined using a Shannon–Weaver Diversity Index according to the following formula:
where H’ is the Shannon–Weaver Species Diversity Index, s is the number of species, Pi is the proportion of each species in a sample and ln Pi is the natural logarithm of this proportion [76]. Statistically significant differences between populations were determined using a Student’s t-test using the Statistical Analysis ToolPak in Microsoft Excel (2019).
Phytoplankton from the >20 µm size fraction was analyzed for community composition by counting duplicate aliquots from each tow using a Sedgewick Rafter Counting chamber and a BH-2 Olympus microscope. Cells were allowed to settle for 5 min within the chamber, and then all cells were counted and identified to species level where possible.
Duplicate tows for determination of zooplankton concentrations were conducted immediately after collection of surface water samples. Flow rates were measured using a General Oceanics (Miami, FL, USA) flow meter with a standard rotor. Under peak bloom conditions, clogging of the zooplankton net occurred after the first of the replicate tows, and accurate flow meter readings were not obtained for the replicates. Therefore, in these instances only the first tow is shown in the analyses. Plankton samples were returned to the lab within 30 min of sampling, and both T. erythraeum and zooplankton populations were immediately counted live.
Zooplankton tows were concentrated to a known volume and dispensed into Bogorov trays for counting in 5 mL subsamples using a Stempel pipette. Generally, 20 subsamples from each replicated tow were counted for abundance of the copepod Macrosetella gracilis and life stage assessment. No other harpacticoid copepod species known to graze Trichodesmium were observed in any samples. The proportion of the total tow counted was determined, and numbers of M. gracilis were calculated per cubic meter of water from flow meter measurements. The proportion of total individuals counted for a given sample was characterized as nauplii, copepodites, and adults.
2.3. Great Barrier Reef: Trichodesmium Grazing Study
In a study conducted independently from the study described above, but at the same time of year and conducted in the same locale, rates of grazing of Trichodesmium spp. by the M. gracilis were determined using incorporation of 14C-labelled Trichodesmium into the copepod M. gracilis [52,77,78]. Colonies of T. erythraeum of uniform size were sorted, using a plastic inoculating loop, and placed into polycarbonate vials of filtered seawater, to which 25 μCi H14CO3 was added. The T. erythraeum was incubated with the isotope for a period of 2.5 h under neutral density screening in ambient light with a flow-through incubator to maintain ambient sea temperature (23–24 °C).
Adult M. gracilis were picked from the 64 µm mesh plankton tows using a wide-bore pipette and held temporarily in GF/F-filtered seawater. Three copepods were then placed in each of 4 replicate polycarbonate test tubes with 30 mL filtered (Whatman GF/F) seawater. There were 4 test tubes for each of the 3 sacrificial time points. Three colonies of the 14C-labelled Trichodesmium were added to each of the 12 test tubes. The bottles containing both the Trichodesmium and the copepods were returned to the incubator for periods of 0, 0.5, and 1 h. At each time point, 4 replicated test tubes were filtered onto pre-weighed 12 µm polycarbonate membrane filters (Poretics, Livermore, CA), and rinsed with an isotonic solution of 6% ammonium formate as well as 10% HCl to remove any unincorporated 14C. Using a hypodermic needle, the copepods were then individually removed and placed onto clean pre-weighed 12 μm f,ilters. The filters were dried, and the weight of copepods were obtained using a microbalance. These filters were placed in 5 mL scintillation fluid (Aquasol- New England Nuclear Corporation Boston, MA, USA), and disintegrations per minute (DPM) were determined using a Beckman scintillation counter. Ingestion rates were determined using linear regression of C ingested by the copepods over the time course and converted to a carbon (C)-specific rate using the average C content of Trichodesmium and M. gracilis. Ingestion rates were expressed as μg C copepod μg C−1 h−1 [52]. The C content of the copepods and the T. erythraeum was determined using a CHN analyzer (Control Data Corporation, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
Nitrogen flux from M. gracilis grazing on Trichodesmium spp. was then calculated based on a M. gracilis NH4+ release rate of 7.7 nmol N copepod−1 h−1 [78] and 12 h of daylight. Calculations of the potential N flux from adult M. gracilis grazing on Trichodesmium spp. to the West Florida Shelf were then based upon Trichodesmium abundance data from 2007 to April 2024 (see above rationale for this data window). As the window for K. brevis bloom initiation generally begins in August [79], mean colony concentration was calculated for combined June to July samples for 2007 to the present from cell concentrations, assuming 50–100 cells trichome−1 and 100 trichomes colony−1. This value was then subsequently converted to copepods L−1 based on a 100 trichome colony−1 average for Gulf of Mexico Trichodesmium spp. (unpub. data) and a copepod abundance of one M. gracilis L−1 [78].
3. Results
3.1. Gulf of Mexico: Interannual Comparisons of Trichodesmium spp. and Karenia brevis
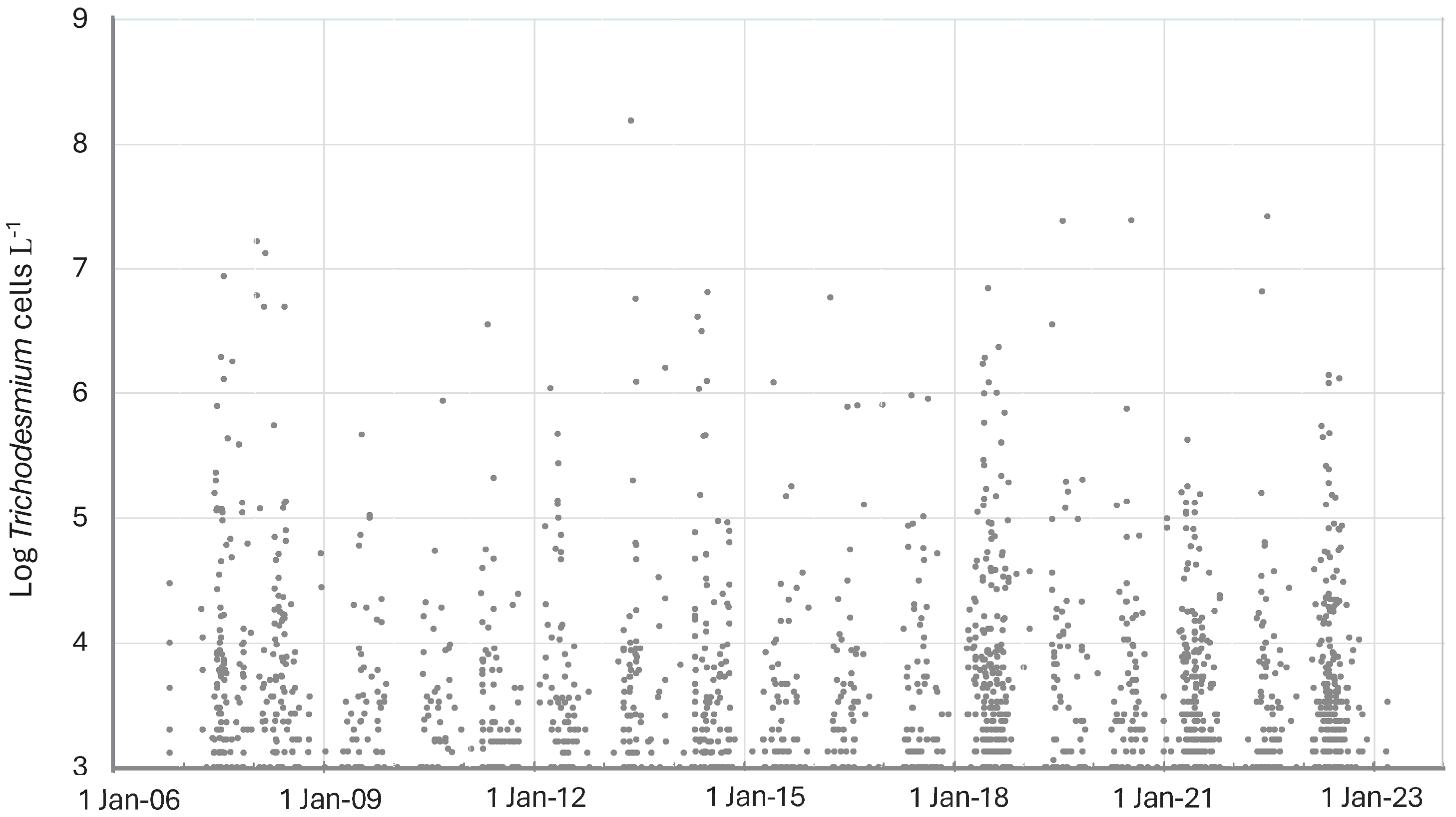
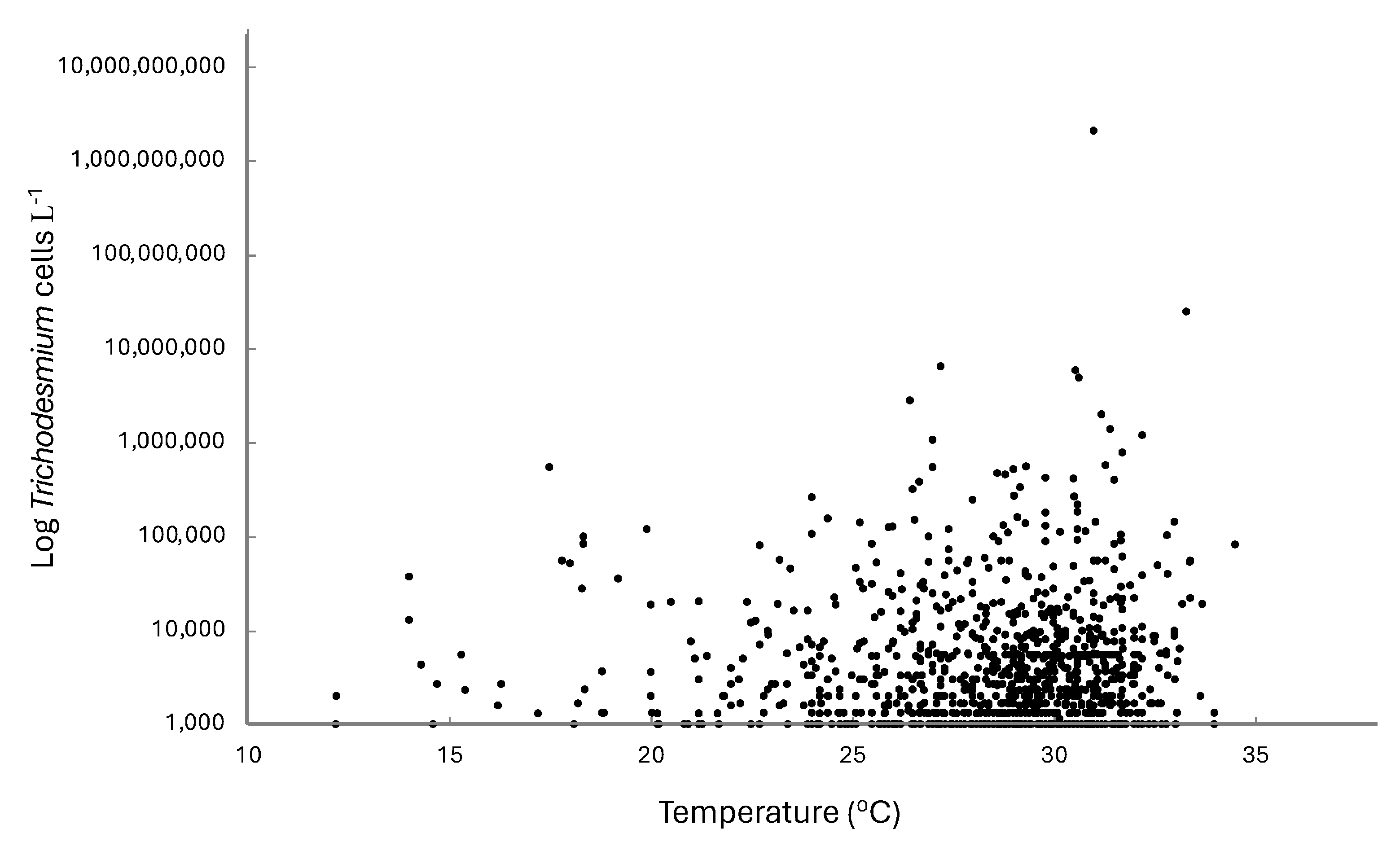
In the eastern Gulf of Mexico, Trichodesmium spp., while generally always present at low concentrations, exhibited a strong seasonal abundance (Figure 2). Maximum abundance tended to occur from May to July, although several years exhibited maximum abundances earlier in the year between January and March (e.g., 2008, 2016). The temperature range for Trichodesmium spp. in the eastern Gulf of Mexico was 12.2 to 34.5 °C, with maximum concentrations occurring between 26.4 and 35.3 °C (Figure 3). The average temperature of all samples with Trichodesmium spp. present was 28.1 °C.
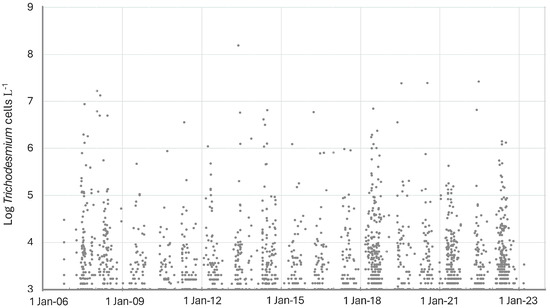
Figure 2.
Occurrence of Trichodesmium spp. in Florida HAB monitoring samples in the eastern Gulf of Mexico from 2007 to 2024. Data from Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Fish and Wildlife Research Institute (FWC-FWRI) HAB Monitoring Database.
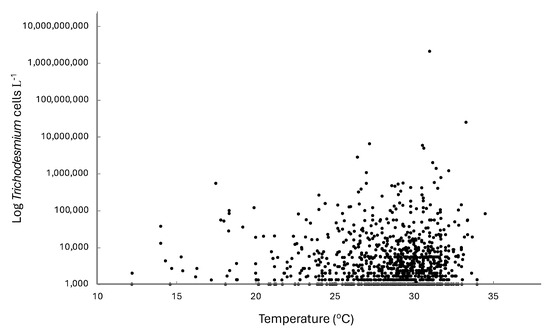
Figure 3.
Relationship between Trichodesmium spp. and water temperature in the eastern Gulf of Mexico from 2007 to the present. Data from Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Fish and Wildlife Research Institute (FWC-FWRI) HAB Monitoring Database.
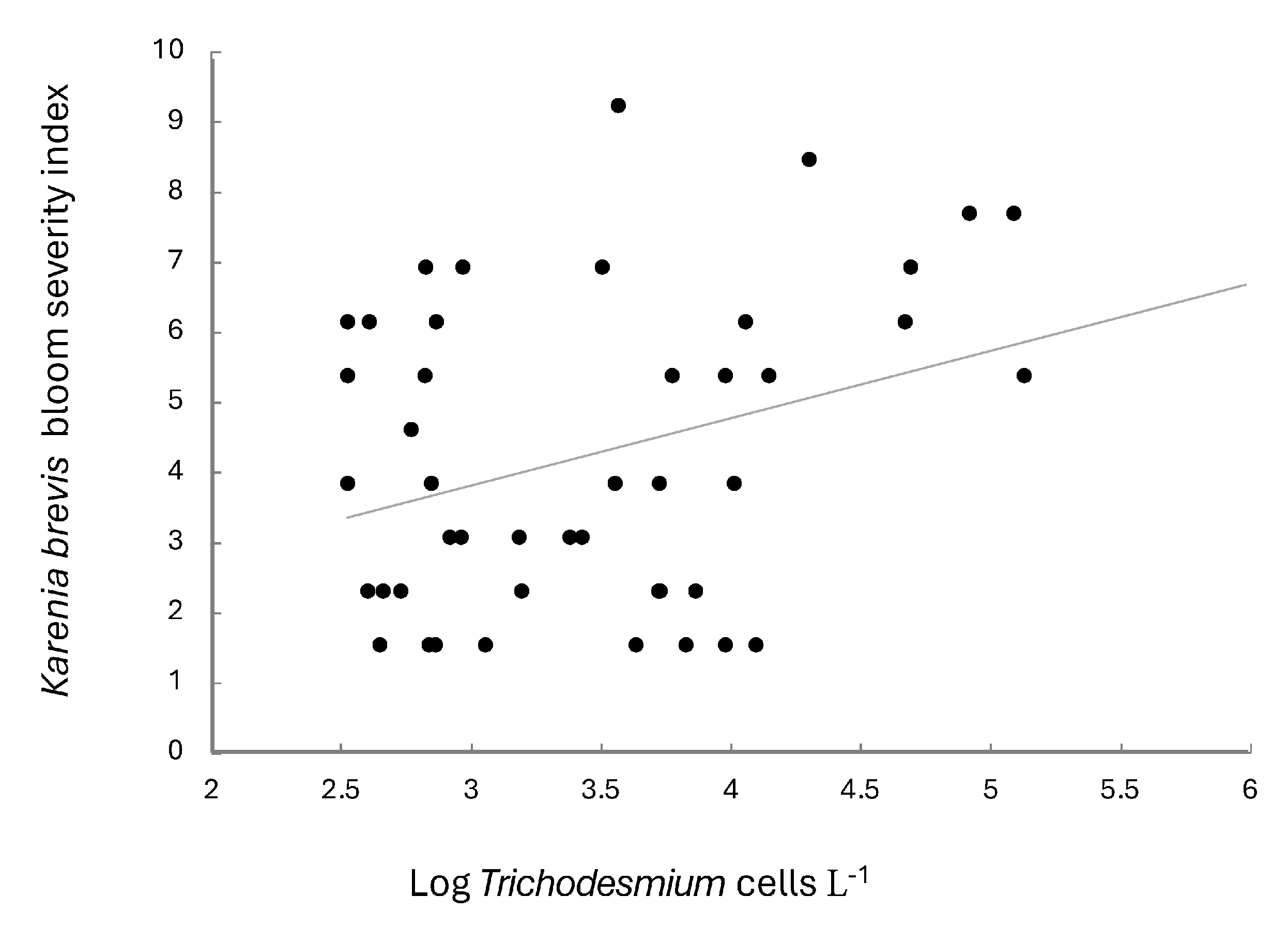
Abundances of Trichodesmium spp. were significantly related to K. brevis bloom severity when the dinoflagellate data were lagged by two months (r = 0.320, n = 53, p = 0.02; Figure 4). No significant relationships were found when coincident data were compared or when data were lagged by 1 month.
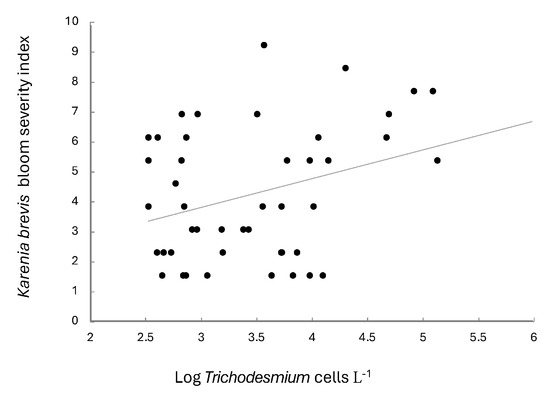
Figure 4.
Log Trichodesmium (cell L−1) and bloom severity index of Karenia brevis (for blooms with abundances >100,000 cells L−1). Data encompass the time period 2007–2019. All data are averaged monthly. Bloom severity index data obtained from Stumpf et al. [26].
3.2. Great Barrier Reef: The Eularian Study
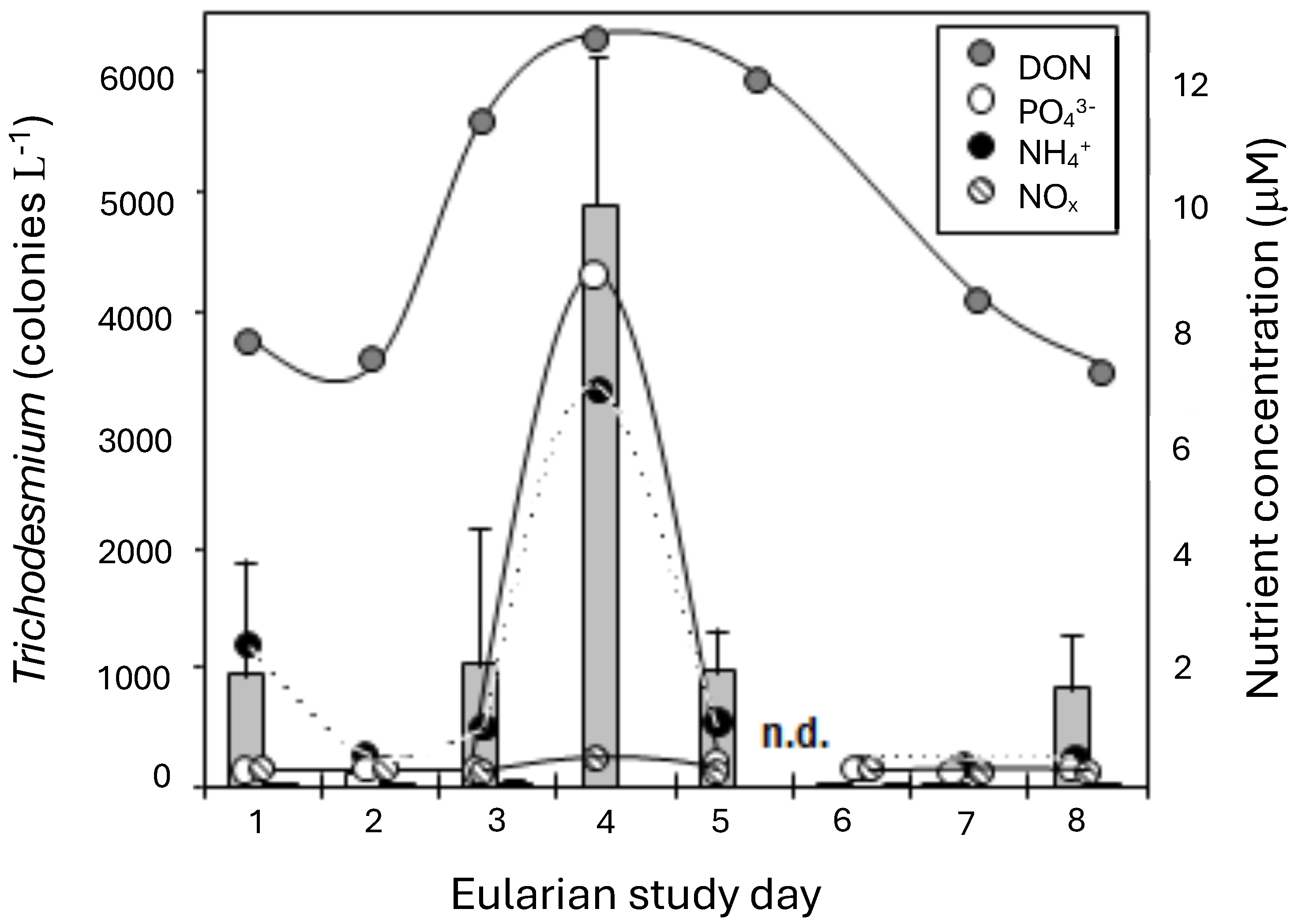
The T. erythraeum bloom developed and then dissipated in the waters off Heron Island over the course of the 9-day study (Figure 5). The first 2 days of sampling were during the developmental phase of the cyanobacterial bloom and occurred during a period of weak wind speeds (3.5–8 knots; i.e., 1.8–4.1 m s−1) and constant 24.5 °C water temperatures. The abundance of T. erythraeum was low during this initial period, at <20 colonies L−1, in the areas sampled surrounding Heron Island. By day 3, elevated concentrations of T. erythraeum were observed (up to 1000 colonies L−1), and areas could be designated as “inside” or “outside” of the bloom. A maximum T. erythraeum abundance of 5000 colonies L−1 was observed by day 5, coincident with the lowest wind speeds and highest water temperatures measured during the study. A gradual increase in wind speed to a maximum of 16.5 knots (8.5 m s−1) and a decline in water temperature to 22.1 °C coincided with a decrease in T. erythraeum concentrations. There was a substantial decline in colony numbers after this mixing event. Although T. erythraeum was present in the waters off Heron Island throughout the study period, concentrations in areas outside the bloom rarely exceeded 50 colonies L−1.
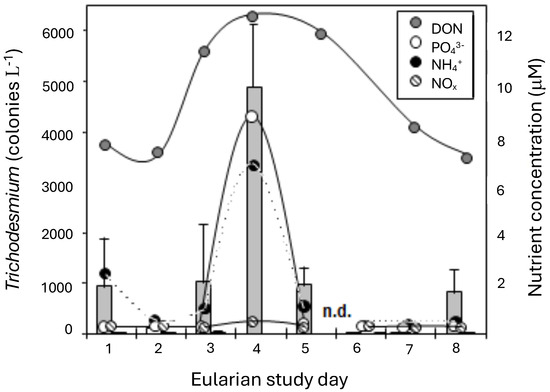
Figure 5.
Trichodesmium erythraeum abundance (colonies L−1) off Heron Island over the course of the study (bar graph). Values are the mean of two replicates (±S.D.). Concentrations (μM, ±S.D.) of NOx (Nitrate + Nitrite; hatched circle); NH4+ (black circle); PO43− (white circle), and dissolved organic nitrogen (grey circle) at the time of each sampling of the eularian study.
The increase in Trichodesmium colony numbers over the first days of the study was associated with changes in both inorganic and organic nutrient concentrations in the water column (Figure 5). Concentrations of PO43− were lower prior to the bloom, at <0.2 μM, but increased to >8 μM during peak T. erythraeum abundance. A similar trend was evident with NH4+, which increased from 0.3 μM to a maximum concentration of 6 μM. Nitrate and nitrite (NO2+3) values were below detection (0.14 μm) during all sampling, except on day 5, when the average increased to 0.5 µm (Figure 5). Concentrations of DON ranged from 6 to 7 μM during the development stages of the bloom. Values at peak T. erythraeum abundance varied from 11 to 12 μM. The highest concentrations of all nutrients measured coincided with maximum T. erythraeum abundance.
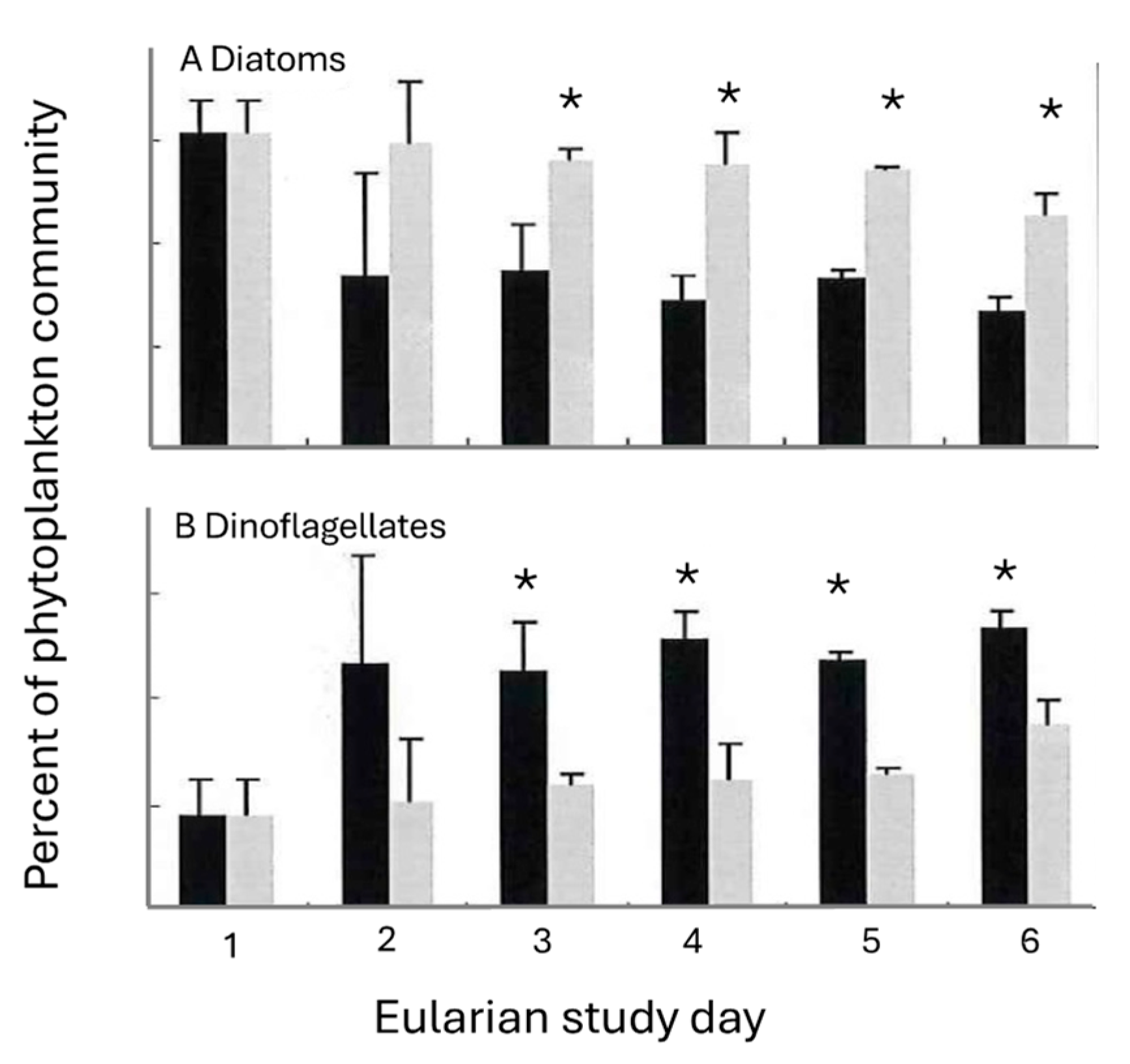
Changes in both phytoplankton and copepod numbers accompanied the T. erythraeum bloom. Diatoms dominated the phytoplankton community at the start of the study (Figure 6).
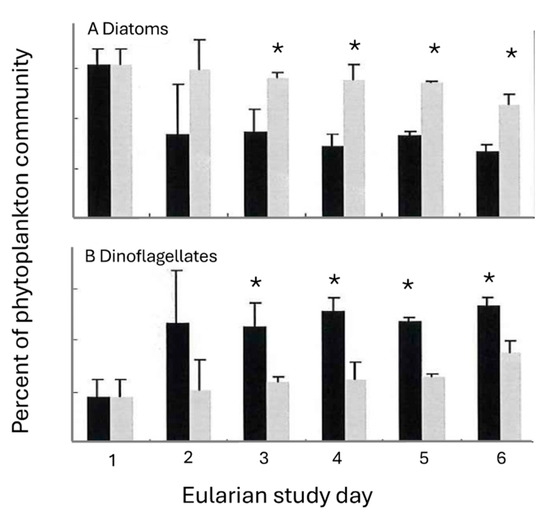
Figure 6.
Changes (±S.D.) in the percent contribution of (A) diatoms and (B) dinoflagellates to the phytoplankton community inside (black bars) and outside (grey bars) of the Trichodesmium bloom. All values exclude Trichodesmium erythraeum from total phytoplankton abundance. Differences within and outside of the T. erythraeum bloom were apparent by the second day of the study. (A statistically significant difference (<0.05) between values is indicated by the presence of an *).
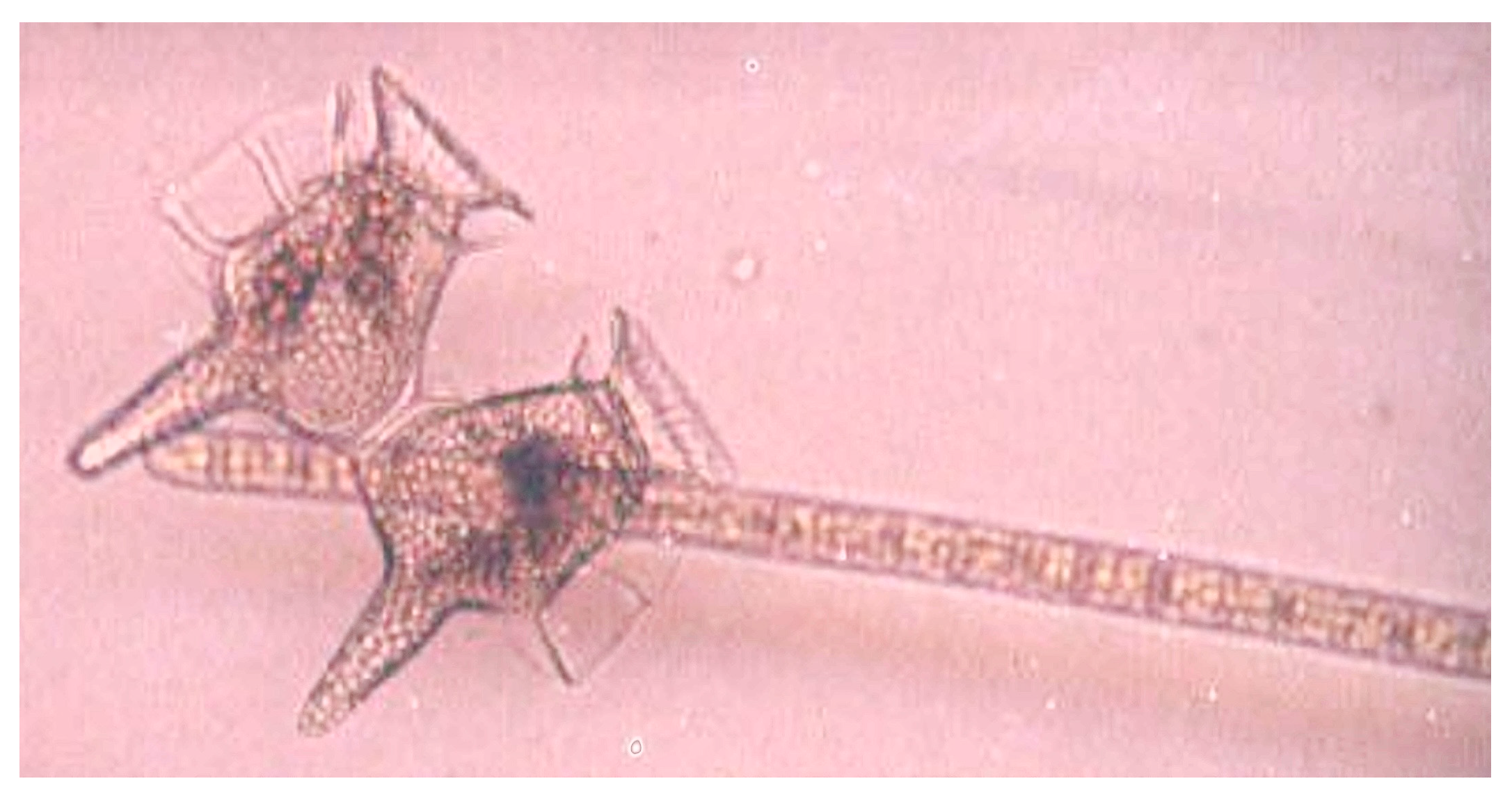
Dinoflagellates, primarily Protoperidinium spp. and Dinophysis caudata, (Figure 7), comprised an increasing proportion of the population within the T. erythraeum bloom (from 56–66%), while diatom abundance decreased within the bloom, to a minimum of 33% of the total population at the peak of the bloom (Figure 6). In the area outside the bloom, the percent of diatoms and dinoflagellates within the total phytoplankton community remained relatively constant until mid-bloom, when diatom and dinoflagellate populations decreased and increased, respectively. Additionally, the increase in Trichodesmium abundance was coincident with a decrease in the total phytoplankton diversity. At the beginning of the bloom, the Shannon–Weaver diversity index H’ was ~1.2; at the peak of the bloom the diversity decreased to 0.54. Statistically significant (p < 0.005) differences between dinoflagellate and diatom community abundances were observed on days 3–4 (Figure 6).
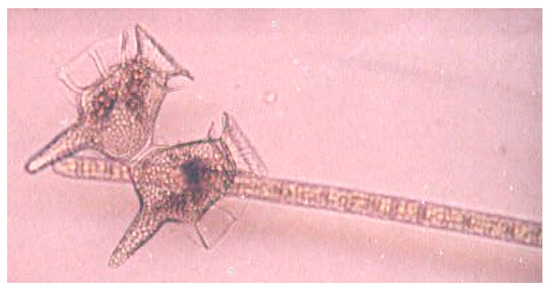
Figure 7.
Microscopic image of a dividing cell of the dinoflagellate Dinophysis caudata and a single Trichodesmium erythraeum trichome, from the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. Dinophysis caudata was one of the species of dinoflagellates that increased in abundance in relation to T. erythraeum colony increase (Photo: C. Heil).
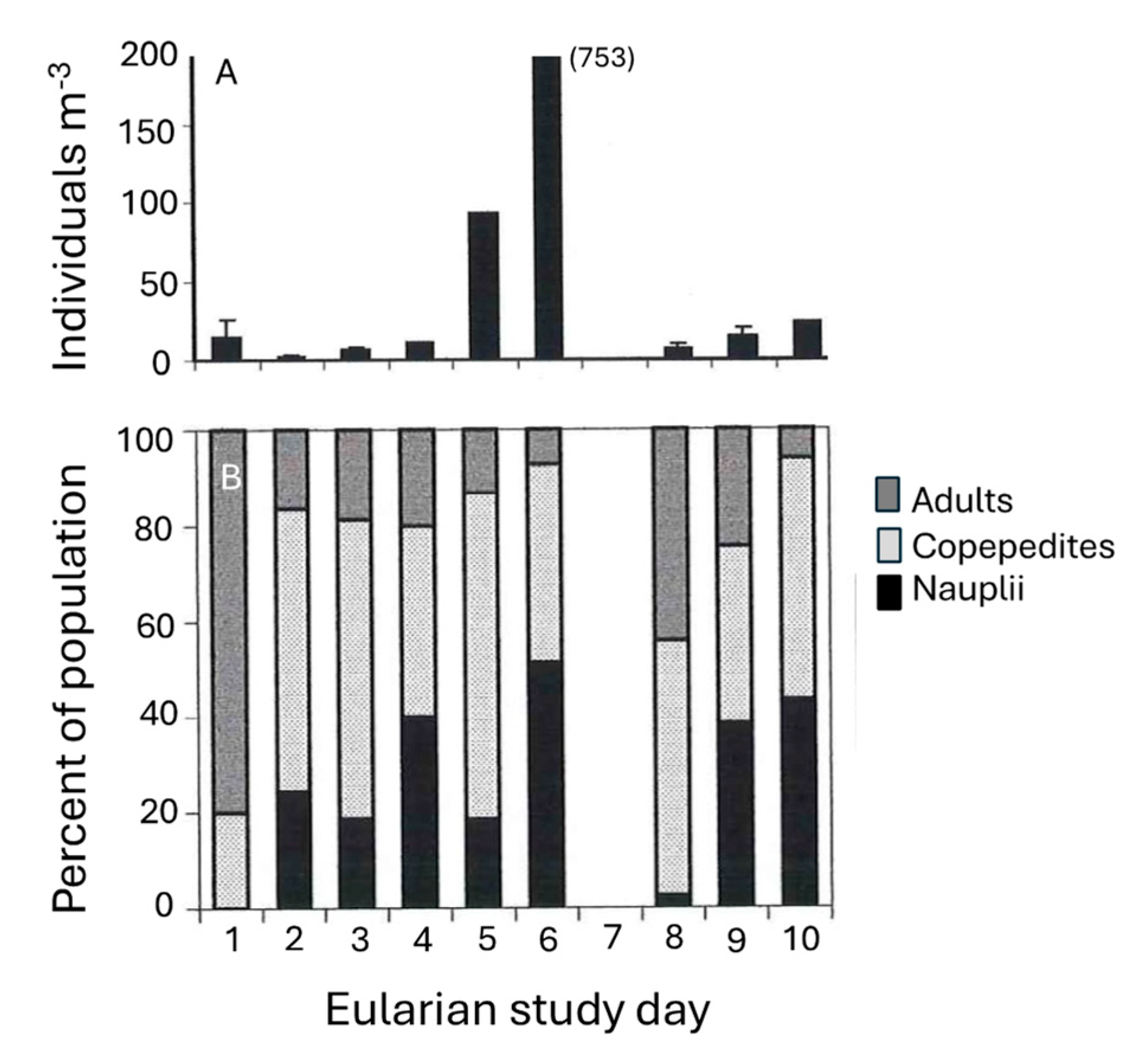
Concentrations of the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis were related to T. erythraeum abundance (Figure 8). During the initial stages of the bloom, <15 M. gracilis m−3 was found within the developing bloom. Maximum M. gracilis abundance increased ~50-fold (750 individuals m−3) a day after maximum T. erythraeum concentrations were observed (compare Figure 8A with Figure 5. A front moved through on day 7 of the Eularian study, with increased wind speed and a slight decrease in water temperature. After this event, T. erythraeum numbers as well as M. gracilis abundances decreased. The proportion of the population made up by nauplii, having increased (from 0% at the start of the study) over the build-up of the bloom, declined sharply after the storm event (Figure 8B) from a peak of ~50% on day 6 to <5% on day 8 (Figure 8B). The proportion of the community comprising adults decreased as juvenile stages dominated during peak T. erythraeum abundances.
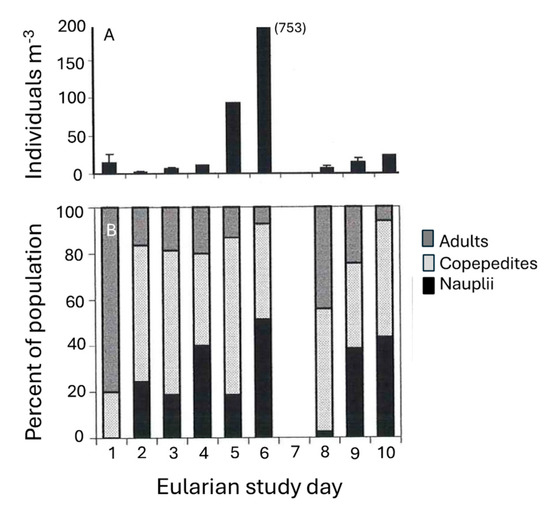
Figure 8.
(A) Top panel; Abundance of the copepod Macrosetella gracilis (individuals m−3) within the T. erythraeum bloom during the course of the study. (B) Bottom panel; Life stage (nauplii, copepodite, or adult) of M. gracilis population as percentage of total number of individuals counted over course of the bloom. (N.B.: On Day 7, no sampling occurred due to a front that passed through the study area, with increased wind speed increases, which curtailed boating.)
3.3. Great Barrier Reef: Grazing Study
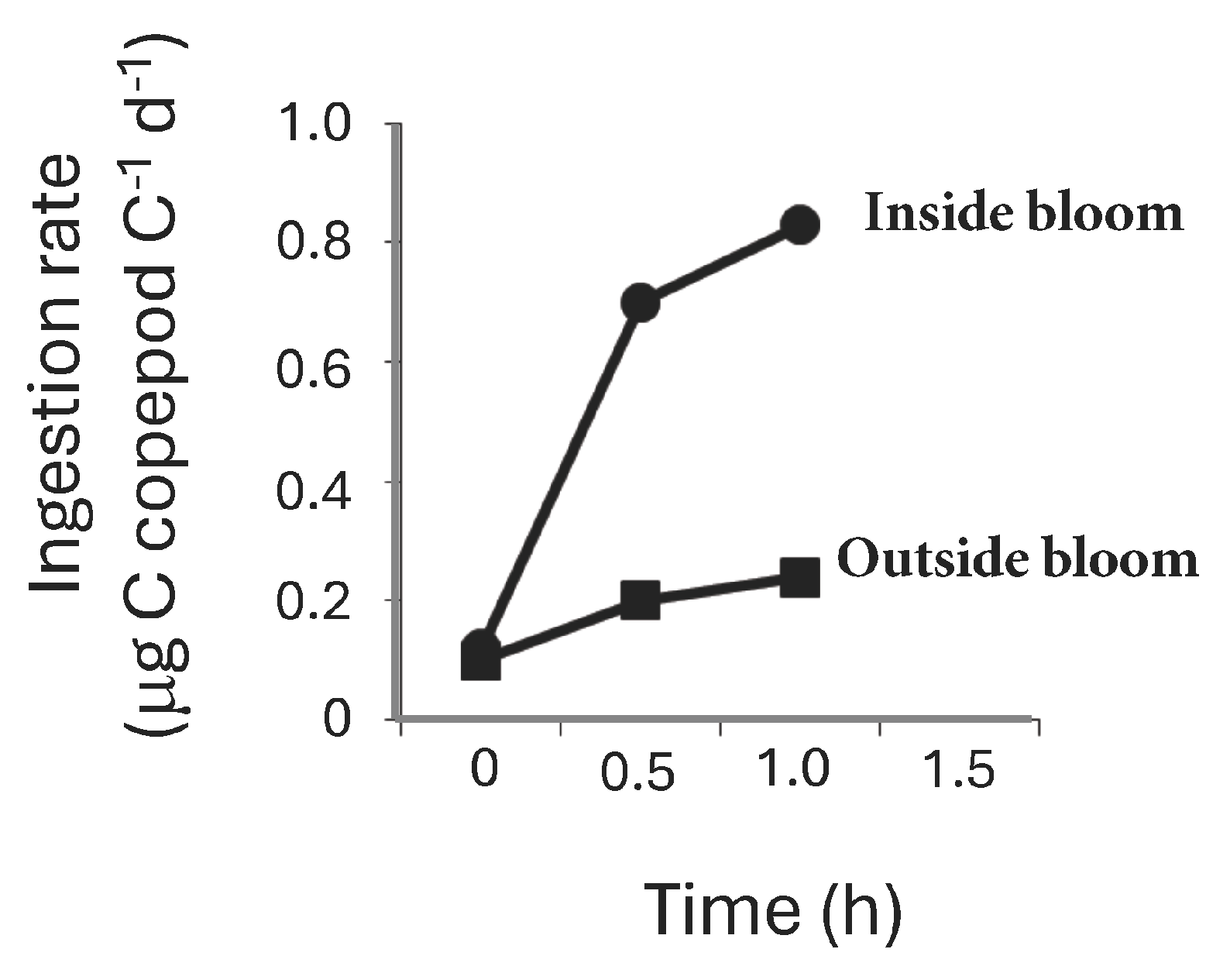
Rates of grazing measured during a similar bloom in the same location at the same time of year showed a significant (p < 0.05 ANOVA) increase in Macrosetella gracilis ingestion rates of T. erythraeum within the bloom compared with outside the bloom (Figure 9). The average ingestion rate of M. gracilis inside the T. erythraeum bloom was 0.68 (±0.36 s.e., n = 4) μg C copepod C−1 d−1 compared to 0.17 (±0.04 s.e., n = 4) μg C copepod C−1 d−1 outside the bloom (Figure 9).
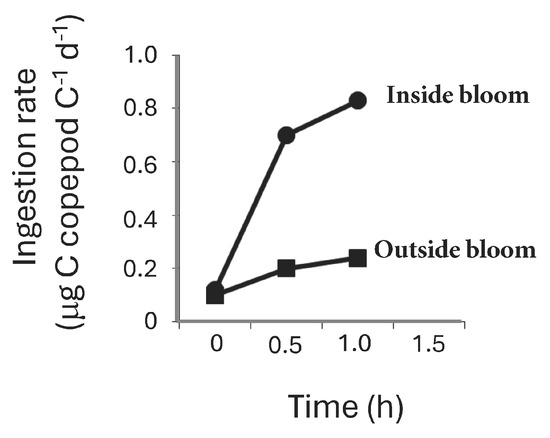
Figure 9.
Trichodesmium erythraeum ingestion rates (μg C μg copepod C−1 h−1) by adult Macrosetella gracilis inside (black circles) and outside (black squares) of a T. erythraeum bloom measured on Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef. Each value is the mean of 3–4 replicates (±standard error).
4. Discussion
Massive blooms of Trichodesmium that can extend > 150 km and are of sufficient area to be observed from space [27] are frequently observed in oligotrophic waters of the world. Blooms of this magnitude have significant impacts on ecosystems [33,49]. As blooms develop and decay, there may be direct toxicity effects [80,81,82], as well as indirect effects due to oxygen depletion. Both the nutrient and plankton changes within a bloom may be significantly different compared to ambient, non-bloom conditions. Large aggregations or blooms of Trichodesmium have been hypothesized to provide significant input of “new” nitrogen from nitrogen fixation into these oligotrophic environments [7,83,84]. It has also been hypothesized that with warming waters due to climate change, cyanobacterial blooms, including Trichodesmium [33], as well as concomitant blooms of harmful dinoflagellates, will also increase [65,66,85,86,87]. With recent increases in K. brevis blooms in the Gulf of Mexico [26,88,89,90] and the need to understand offshore nutrient sources supporting these blooms in comparison to land-based nutrient sources [91,92], this study applied previously unpublished data from the Great Barrier Reef to understand how Trichodesmium spp. can shape plankton communities via direct and indirect pathways. This study was uniquely able to determine nutrient fluxes from these cyanobacteria associated with copepod grazing on the cyanobacteria.
Direct fluxes of N release by Trichodesmium have previously been quantified using 15N tracer techniques [58], leaving no doubt that at least some of the DON accumulated during blooms is from the Trichodesmium itself. In addition to direct release, cell surface oxidation of amino acids has been shown to be associated with Trichodesmium development in non-bloom conditions [93,94]. Additional mechanisms by which nutrients, both organic and inorganic, may be released within Trichodesmium-dominated communities include cell death and decay (particularly in surface blooms exposed to high light and UV), copepod grazing and excretion, microzooplankton regeneration, and viral and/or bacterial degradation [95]. Although Trichodesmium colonies have been observed to be microhabitats for a variety of organisms, such as cyanobacteria, bacteria, phytoplankton, and microzooplankton [51,96,97], freshly formed blooms are not as enriched with the diversity of organisms as older colonies or blooms (J. O’Neil, pers. obvs.).
4.1. Grazing on Trichodesmium
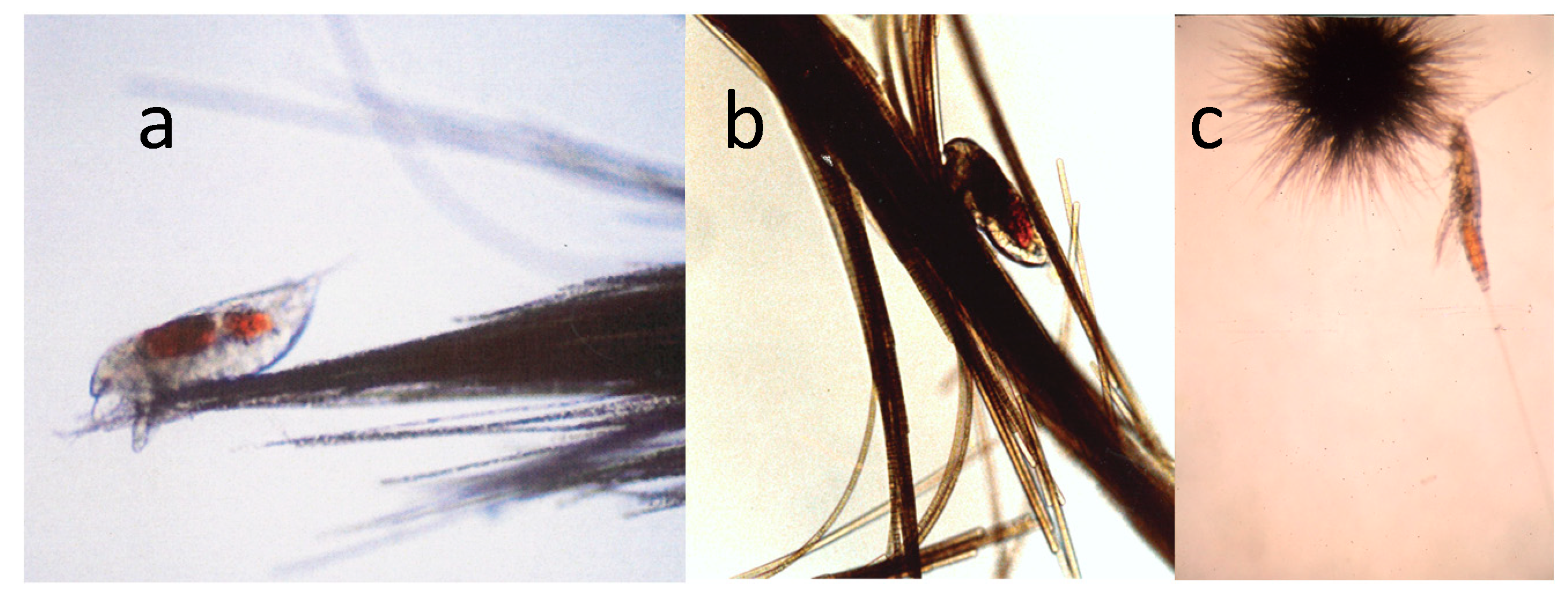
Although Trichodesmium has few known grazers, given the presence of toxins [44,80], there is one family (Miraciidae) of harpacticoid copepods that can graze on this cyanobacterium and pass utilizable nutrients from Trichodesmium into the food web. Macrosetella gracilis is the most abundant member of group and is the most specific grazer of Trichodesmium [51,52,62,63,98,99]. It uses Trichodesmium colonies as a physical substrate for the development of non-swimming juvenile stages [53,62] (Figure 10).
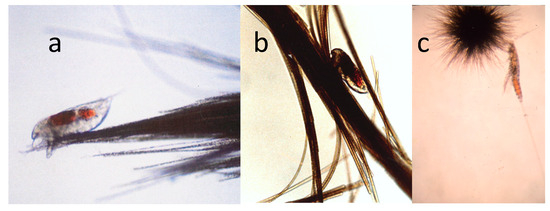
Figure 10.
(a) A nauplius of the copepod Macrosetella gracilis on a Trichodesmium colony; (b) another M. gracilis between the filament of a tuft colony of Trichodesmium; (c) an adult M. gracilis with a puff colony of T. thiebautii. Photos by J.M. O’Neil.
Other Miraciidae copepods (Miracia efferata and Oculosetella gracilis) are also able to graze Trichodesmium but are much less abundant and do not have the specific life-cycle connection to the cyanobacterium [52]. Macrosetella gracilis is a ubiquitous, pan-global associate of Trichodesmium spp., and through grazing, sloppy feeding, and excretion and remineoralization can make “new” N from Trichodesmium, available in the form of NH4+ and DON [54,78]. The rate of NH4+ regeneration has been shown to increase directly as a function of the number of Trichodesmium on which M. gracilis is grazing [78].
The rates of Trichodesmium grazing by M. gracilis presented here, with copepods fed equal numbers of Trichodesmium colonies from either inside or outside a bloom, showed that Trichodesmium ingestion rates within the bloom were higher. This suggests that some cue other than quantity alone, perhaps food quality, may indicate this potential “bloom” status to the adult M. gracilis. This cue may be linked to an increased reproductive capacity during bloom events, as well as increased food quality (e.g., increase in likelihood of mate encounter in a surface bloom), resulting in an optimal foraging strategy for this dilute oligotrophic environment. Macrosetella gracilis nauplii are unable to swim, and the peak in nauplii abundance with peak Trichodesmium abundance appears to be an adaptive strategy for this harpacticoid’s existence in the pelagic zone [53,54].
Based upon measured NH4+ excretion rates of M. gracilis feeding upon T. thiebautii [78] and measured M. gracilis abundance at the peak of this bloom, M. gracilis may have been capable of contributing 0.14 µM NH4+ L−1 d−1 to the measured 7 µM NH4+ pool on the Great Barrier Reef. As M. gracilis tends to feed by breaking Trichodesmium filaments [62], Trichodesmium cell lysis is another pathway by which both inorganic and organic N may be released. While not quantified in this study, N could be further added to the system by micrzooplankton grazing or by mixotrophic activity by the dinoflagellates and other protists [56,57,99]. Once blooms are trapped in the micro-surface layer and exposed to high amounts of light and UV radiation, the lysis of cell contents as well as viral and bacterial degradation [95,100] will undoubtedly add to the large increase in nutrient levels.
The N fluxes due to M. gracilis grazing in the Gulf of Mexico were herein estimated to be 0.95 to 1.91 μmol N L−1 d−1. Estimates of N regeneration due to pelagic zooplankton excretion in the eastern Gulf of Mexico are highly variable and range from a low of 0.71 μmol N L−1 d−1 [101] to 4.99 μmol N L−1 d−1 [102]. Estimates of N2 fixation only for this region range from 0.03–0.16 μmol N L−1 d−1 [101] to 0.18 [24] but increase to 1.70–788.30 μmol N L−1 d−1 when Trichodesmium seasonal N decay and regeneration are included with N2 fixation estimates [6].
These new estimated rates of N fluxes due to M. gracilis grazing represent an average value based on Trichodesmium average abundance during summer months when both abundance and N2 fixation rates are greatest. These values are the same order of magnitude as more recently reported rates for other zooplankton (i.e., grazers of K. brevis) in the Gulf, at 1.70–14.9 μmol N L−1 d−1 [102,103], suggesting that during the summer months when Trichodesmium is abundant, M. gracilis grazing is a significant N source for Gulf of Mexico shelf surface waters. These rates are sufficient to meet up to 100% of the N requirements of a small (105 cells L−1) offshore K. brevis bloom [104], especially during initiation and early growth phases. Lenes and Heil [6] reported that, collectively, N2 fixation, N regeneration, and seasonal biomass decay can range broadly from 1.7 to 787 μmol N L−1 d−1, with an average of 153.9 μmol N L−1 d−1. Given the relatively shallow (~50 m) nature of the west Florida shelf where K. brevis blooms initiate and the range of vertical buoyancy and sinking of Trichodesium (~70 m) [105,106], this N would be available to K. brevis throughout the water column.
4.2. Trichodesmium Effects on Phytoplankton Community Structure
Phytoplankton (>20 μm) composition inside and outside the Trichodesmium blooms studied on Heron Island was significantly different as compared with the Gulf of Mexico and also was decreased in diversity. In the Great Barrier Reef study, higher overall abundances of dinoflagellates were associated with higher Trichodesmium colony numbers relative to diatoms, compared with the sampled area outside the bloom, or with lower Trichodesmium abundances. In the West Florida Shelf study, higher Trichodesmium abundances were associated with greater values of bloom severity, although these lagged by 2 months. Similar associations of dinoflagellates with Trichodesmium have been noted for the west coast of Florida, as well as for the Arabian Sea. Walsh and Steidinger [5] and Lenes and Heil [6] showed that the initiation and growth stages of Karenia brevis blooms on the eastern Gulf of Mexico shelf are temporally correlated with the development of Trichodesmium blooms. Other dinoflagellates species, including Dinophysis caudata, are also common in these shelf waters [107]. In the Arabian Sea, where massive blooms of Trichodesmium also develop and dissipate, Dinophysis has been observed to increase in abundance during and after these blooms (A.R. Al-Muftah, University of Qatar, pers. comm.), and D. caudata was one of the more abundant dinoflagellate species that was observed during this Great Barrier Reef Trichodesmium bloom (Figure 7). This is of significance, as similarly to Karenia-producing brevetoxins that can cause neurologic shellfish poisoning (NSP) [108], Dinophysis spp. can produce the toxin okadaic acid, which is responsible for Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) [109] and can therefore cause concerns for both human and ecosystem health. Other studies in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Brazil have shown increases in the abundance of the dinoflagellates Neoceratium spp. and Protoperidinium in relation to increases in Trichodesmium spp. colonies [13]. This suggests that an increase in potentially harmful algal bloom species may be favored after blooms of Trichodesmium spp. and specifically may be due to DON uptake by dinoflagellates. This pattern fits into the phytoplankton-functional-type model for diatoms and dinoflagellates outlined in Glibert [110], with dinoflagellates dominating in the very specific conditions that existed in the Heron Island peak of Trichodesmium abundance occurring at the peak of DON concentration, peak of temperature, and lowest wind speed, with a stable water column.
The temporal offset in K. brevis relative to Trichodesmium observed in the Gulf of Mexico appears to contradict the immediate effect of Trichodesmium on dinoflagellate abundance in the Great Barrier Reef study. It is of note that the Great Barrier Reef study considered all dinoflagellates, and Karenia spp. is not a common dinoflagellate of the warm Great Barrier Reef waters [111,112]. Trichodesmium has a higher temperature optimum than that of K. brevis, which is considered to prefer waters in the range of 22–28 °C [101,113,114]. Thus, maximum Trichodesmium blooms develop during the summer months, while K. brevis generally reaches bloom intensity after the summer. It is hypothesized that the enhanced nutrient flux from Trichodesmium “primes the pump” for K. brevis initiation, which is then able to flourish with numerous nutrient sources when it is transported close to the coast [25,104]. Chen et al. [115] recently showed that a different type of nutrient pulse, in this case, release from a former phosphate mine waste, led to a succession of species from diatoms to K. brevis, as summer remineralization of DON provided sufficient regenerated N to support the slow-growing K. brevis. Similarly, a prolonged sewage leak, high in DON and P, in the southeastern Mediterranean Sea caused a large increase in Trichodesmium erythraeum and subsequent changes in the microbial and plankton community, including an increase in dinoflagellates [116].
Concentrations of NH4+, DON, and PO43− within the T. erythraeum bloom from Heron Island studied here were enriched up to 30, 100, and 2-fold, respectively, relative to water collected from outside the bloom aggregations. Previously reported enrichment factors for the same nutrients in blooms off Hawaii and in the Gulf of Mexico are highly variable but also show considerable enrichment of these nutrients within blooms (Table 1). The concentration of NH4+ and DON outside the Trichodesmium patch at Heron Reef remained roughly constant from one day to the next, and showed higher enrichment than previously reported values from the Northern Great Barrier Reef [117]. On a significantly longer time scale, Karl et al. [10] observed roughly a 30% increase in DON in surface waters of the North Pacific subtropical gyre (hydrostation ALOHA) from summer 1991 through 1992 following the appearance of large aggregations of Trichodesmium spp. with concentrations up to 6.50 µM (650 mmol m−2), indicating just how significant a source of DON these events can be for these oligotrophic ecosystems in multiple regions. Lenes et al. [118] noted a three-fold enrichment in DON in June and July of 1999 in west Florida Shelf waters, co-incident with increased Trichodesmium abundance. These impacts of Trichodesmium blooms on community structure, including the promotion of potentially harmful dinoflagellate species, are likely to increase in area and duration due to climate change effects in the tropical and subtropical regions where they proliferate [33,69,119,120,121].

Table 1.
Summary of nutrient concentrations (µM) and enrichment factors associated with blooms of Trichodesmium spp. Values given for the mean values inside and outside the bloom for the current study are the average (+ S.D.) of all daily measurements made during the course of the study.
5. Conclusions
This study showed that Trichodesmium spp. blooms provide enhanced nutrient cycling, via direct and indirect release, and that such blooms alter the plankton community composition, with immediate (as shown for the Great Barrier Reef) and long-term impacts (as shown for the Gulf of Mexico). Nutrient release from Trichodesmium spp. is not only due to the release associated with “new” nitrogen into the system from N2 fixation [50] from various degradative pathways, but also may be due to the regenerated nitrogen release associated with feeding and excretion of its common grazer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; methodology, J.M.O., P.M.G., C.A.H., J.G.G., J.G. and C.M.S.; formal analysis, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; investigation, J.M.O., P.M.G., C.A.H., J.G.G., J.G. and C.M.S.; resources, J.M.O., P.M.G., C.A.H. and J.G.G.; data curation, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; writing—review and editing J.M.O., P.M.G., C.A.H., J.G.G., J.G. and C.M.S.; visualization, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; supervision, J.M.O.; project administration, J.M.O., P.M.G. and C.A.H.; funding acquisition, J.M.O., J.G.G., P.M.G. and C.A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this project was provided by a University of Queensland External Support Enabling Grant (ESEG) to J.G. Greenwood and J.M. O’Neil and NOAA ECOHAB grant #NA19NOS4780183 to C. Heil and P. Glibert.
Data Availability Statement
The authors will store the associated data from this project on our UMCES backup servers and lab computers for up to 5 years after publication. Some supporting data will also be available on institutional websites.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff of the University of Queensland’s Heron Island Research Station. We would like to thank W. Dennison for assistance in the field and comments on the manuscript, the Horn Point Analytical Services Laboratory, Queensland Health, Government Chemical Laboratory for nutrient analyses, and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s Fish and Wildlife Research Institute for the provision of the FWC-FWRI HAB database. This is contribution number 6383 for the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science and ECOHAB publication #1104.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cook, J. The journals of Captain James Cook on his voyages of discovery. In The voyage of the Endeavour 1768–1771; Beaglehole, J.C., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1955; Volume 1, 684p. [Google Scholar]
- Cribb, A.C. Sea sawdust. Qld. Nat. 1969, 19, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Furnas, M.J. Pelagic Trichodesmium (= Oscillatoria) in the Great Barrier Reef region. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Brando, V.E.; Lønborg, C.; Leahy, S.M.; Dekker, A.G. Phenology of Trichodesmium spp. blooms in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon, Australia, from the ESA-MERIS 10-year mission. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.J.; Steidinger, K.A. Saharan dust and Florida red tides: The cyanophyte connection. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 11597–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenes, J.M.; Heil, C.A. A historical analysis of the potential nutrient supply from the N2 fixing marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium spp. to Karenia brevis blooms in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. J. Plank. Res. 2010, 32, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, D.G.; Zehr, J.P.; Paerl, H.W.; Bergman, B.; Carpenter, E.J. Trichodesmium, a globally significant marine cyanobacterium. Science 1997, 276, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.F.; Dedej, Z.; Gottlieb, R.; Li, H.; Thomas, D.N.; El-Absawi, M.; El-Naggar, A.; El-Gharabawi, M.; Sommer, U. Spatial and temporal distribution of Trichodesmium spp. in the stratified Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 239, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Koedooder, C.; Zhang, F.; Kessler, N.; Eichner, M.; Shi, D.; Shaked, Y. Colonies of the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium optimize dust utilization by selective collection and retention of nutrient-rich particles. iScience 2022, 25, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koedooder, C.; Landou, E.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Basu, S.; Berman-Frank, I.; Shaked, Y.; Rubin-Blum, M. Metagenomes of Red Sea subpopulations challenge the use of morphology and marker genes to assess Trichodesmium diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 879970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Bernhardt, P.W.; Heil, C.A.; Bronk, D.A.; O’Neil, J.M. Nitrogen fixation and release of fixed nitrogen by Trichodesmium spp. in the Gulf of Mexico. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1762–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Sônia, M.; Gianesella, F.; Flávia, M.; Saldanha-Corrêa, P. Trichodesmium erythraeum bloom on the continental shelf off Santos South East, Brazil. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2008, 56, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bif, M.B.; de Souza, M.S.; Costa, L.D.F.; Yunes, J.S. Microplankton community composition associated with toxic Trichodesmium aggregations in the Southwest Atlantic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugomela, C.; Lymo, T.J.; Bryceson, I.; Semesla, K. Trichodesmium in coastal waters of Tanzania: Diversity, seasonality, nitrogen and carbon fixation. Hydrobiol. 2002, 477, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, R.R.; Coles, V.J.; Capone, D.G. Modeling the distribution of Trichodesmium and nitrogen fixation in the Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, C06006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.G.; Martel, A.; Codd, G.A.; Soler, E.; Coca, J.; Redondo, A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S.; Ojeda, A.; Suárez, S.; et al. Bloom of the marine diazotrophic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum in the northwest African upwelling. Mar. Ecol. 2005, 301, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, D.M.; Letelier, R.; Hebel, D.F.; Bird, D.F.; Winn, C.D. Trichodesmium blooms and new nitrogen in the North Pacific Gyre. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 219–238. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, D.M.; Letelier, R.; Tupas, L.; Dore, J.; Christian, J.; Hebel, D. The role of nitrogen fixation in biogeochemical cycling in the subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Nature 1997, 388, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.; Berthelot, H.; Duhamel, S.; Raimbault, P.; Bonnet, S. Dissolved organic matter uptake by Trichodesmium in the Southwest Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devassy, V.P.; Bhattathiri, P.M.A.; Qasim, S.Z. Trichodesmium phenomenon. Ind. J. Mar. Sci. 1978, 7, 68–186. [Google Scholar]
- D’Silva, M.S.; Anil, A.C.; Naik, R.K.; D’Costa, P.M. Algal blooms: A perspective from the coasts of India. Nat. Hazards 2012, 63, 1225–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothibabu, R.; Karnan, C.; Jagadeesan, L.; Arunpandi, N.; Pandiarajan, R.S.; Muraleedharan, K.R.; Balachandran, K.K. Trichodesmium blooms and warm-core ocean surface features in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fu, F.X.; Sun, J.; Thangaraj, S.; Pujari, L. Nitrogen Fixation by Trichodesmium and unicellular diazotrophs in the northern South China Sea and the Kuroshio in summer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Bernhardt, P.W.; Ozmon, I.; Procise, L.A.; Garrett, M.; O’Neil, J.M.; Heil, C.A.; Bronk, D.A. Contribution of diazotrophy to nitrogen inputs supporting Karenia brevis blooms in the Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 2014, 38, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, C.A.; Bronk, D.A.; Dixon, L.K.; Hitchcock, G.L.; Kirkpatrick, G.J.; Mulholland, M.R.; O’Neil, J.M.; Walsh, J.J.; Weisberg, R.; Garrett, M. The Gulf of Mexico ECOHAB: Karenia Program 2006-2012. Harmful Algae 2014, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Li, Y.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Litaker, R.W.; Hubbard, K.A.; Currier, R.D.; Harrison, K.K.; Tomlinson, M.C. Quantifying Karenia brevis bloom severity and respiratory irritation impact along the shoreline of Southwest Florida. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchler, D.A.; Jupp, D.L.B. Shuttle photograph captures massive phytoplankton bloom in the Great Barrier Reef. Int. J. Rem. Sens. 1988, 9, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupouy, C. Discoloured waters in the Melanesian archipelago (New Caledonia and Vanuatu). The value of the NIMBUS-7 Coastal Zone Colour Scanner observations. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Borstad, G.A.; Gower, J.F.R.; Carpenter, E.J. Development of algorithms for remote sensing of Trichodesmium blooms. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 193–210. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, A.; Brown, C.W.; Hood, R.R.; Carpenter, E.J.; Capone, D.G. Detecting Trichodesmium blooms in SeaWiFS imagery. Deep Sea Res. 2002, 49 Pt II, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hardy, R. Remote detection of Trichodesmium blooms in optically complex coastal waters: Examples with MODIS full-spectral data. Rem. Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementson, L.A.; Oubelkheir, K.; Ford, P.W.; Blondeau-Patissier, D. Distinct Peaks of UV-Absorbing Compounds in CDOM and Particulate Absorption Spectra of Near-Surface Great Barrier Reef Coastal Waters, Associated with the Presence of Trichodesmium spp. (NE Australia). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Capone, D.G.; Subramaniam, A.; Carpenter, E.J.; Xie, Y. Trichodesmium around Australia: A view from space. Geophys. Res. Let. 2023, 50, e2023GL104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endean, R. Chapter 7—Destruction and recovery of coral reef communities. In Biology and Geology of Coral Reefs; Jones, O.A., Endean, R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1976; Volume III, pp. 343–369. [Google Scholar]
- Villareal, T.A. Abundance and photosynthetic characteristics of Trichodesmium spp. along the Atlantic Barrier Reef at Carrie Bow Cay, Belize. P.Z.S.N.1. Mar. Ecol. 1995, 16, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, S.T.; Capra, M. The cyanobacterium Oscillatoria erythraea—A potential source of toxin in the ciguatera food-chain. Food Addit. Contam. 1992, 9, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endean, R.; Monks, S.A.; Griffith, J.K.; Llewellyn, L.E. Apparent relationships between toxins elaborated by the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum and those present in the flesh of the narrow-barred Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus commersoni. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawser, S.P.; Codd, G.A.; Capone, D.G.; Carpenter, E.J. A neurotoxic factor associated with bloom-forming cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Toxicon 1991, 3, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudek, S.; Haygood, M.G.; Youssef, D.T.; Schmidt, E.W. Structure of trichamide, a cyclic peptide from the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum, predicted from the genome sequence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4382–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, I.; Schluter, P.J.; Shaw, G.R. Cyanobacterial lipopolysaccharides and human health—A review. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2007, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proença, L.A.O.; Tamanaha, M.S.; Fonseca, R.S. Screening the toxicity and toxin content of blooms of the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum (Ehrenberg) in northeast Brazil. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2009, 15, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Kerbrat, A.S.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. Detection of ciguatoxin-like and paralysing toxins in Trichodesmium spp. from New Caledonia lagoon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 61, 60–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbrat, A.S.; Amzil, Z.; Pawlowiez, R.; Golubic, S.; Sibat, M.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. First evidence of palytoxin and 42-hydroxy-palytoxin in the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Mar. Drugs. 2011, 9, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Tester, P.A. Toxic effect of the bloom-forming Trichodesmium sp. (Cyanophyta) to the copepod Acartia tonsa. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, P.J.A.; Carpenter, E.J.; Bergman, B. Trichodesmium: Ultrastructure and protein localization. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 9–28. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Capone, D.G. Nitrogen fixation in Trichodesmium blooms. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, B.; Sandh, G.; Lin, S.; Larsson, J.; Carpenter, E.J. Trichodesmium—A widespread marine cyanobacterium with unusual nitrogen fixation properties. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.J. Nitrogen fixation by marine Oscillatoria (Trichodesmium) in the world’s oceans. In Nitrogen in the Marine Environment; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ani, C.J.; Smithers, S.G.; Lewis, S.; Baird, M.; Robson, B. eReefs modelling suggests Trichodesmium may be a major nitrogen source in the Great Barrier Reef. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 285, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugdale, R.C.; Goering, J.J. Uptake of new and regenerated forms of N in primary production. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 21, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Roman, M.R. Grazers and associate organisms of Trichodesmium. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Roman, M.R. Ingestion of the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium spp. by the pelagic harpacticoid copepods Macrosetella, Miracia and Oculosetella. Hydrobiologia 1994, 292-293, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M. The colonial cyanobacterium Trichodesmium as a physical and nutritional substrate for the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis. J. Plankt. Res. 1998, 20, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M. Grazer interactions with nitrogen-fixing marine cyanobacteria: Adaptation for N-acquisition? Bull. Inst. Oceanogr. Monaco 1999, 19, 293–317. [Google Scholar]
- Holl, C.M.; Villareal, T.A.; Payne, C.D.; Clayton, T.D.; Hart, C.; Montoya, J.P. Trichodesmium in the western Gulf of Mexico: 15N2-fixation and natural abundance stable isotope evidence. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, B.J.; Steinberg, D.K.; Stukel, M.R.; Goes, J.I.; Coles, V.J. Meso- and microzooplankton grazing in the Amazon River plume and western tropical North Atlantic. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 825–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Conroy, B.J.; Steinberg, D.K.; Song, B.; Kalmbach, A.; Carpenter, E.J.; Foster, R.A. Mesozooplankton Graze on Cyanobacteria in the Amazon River Plume and Western Tropical North Atlantic. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibert, P.M.; Bronk, D.A. Release of dissolved organic nitrogen by the marine diazotroph Trichodesmium spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3996–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, D.G.; Ferrier, D.M.; Carpenter, E.J. Amino acid cycling in colonies of the planktonic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium thiebautii. Appl. Env. Microb. 1994, 60, 3989–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Capone, D.G. N2 fixation, N uptake and N metabolism in natural and cultured populations of Trichodesmium spp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 188, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk, D.A.; Sanderson, M.P.; Mulholland, M.R.; Heil, C.A.; O’Neil, J.M. Organic and inorganic nitrogen uptake kinetics in field populations dominated by Karenia brevis. In Harmful Algae 2002; Steidinger, K., Vargo, G.A., Heil, C.A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Florida Institute of Oceanography and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Björnberg, T.K.S. Observations on the development and the biology of the Miracidae Dana (Copepods: Crustaceae). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1965, 15, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, M.R. Ingestion of the blue-green algae Trichodesmium by the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1978, 23, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger-Schnack, R.; Schnack, D. Vertical distribution and population structure of Macrosetella gracilis (Copepoda: Harpacticoida) in the Red Sea in relation to the occurrence of Oscillatoria (Trichodesmium) spp. (Cyanobacteria). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 52, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, A.D.; Richardson, A.J.; Burford, M.A.; Furnas, M.J. Chapter 06: Vulnerability of Great Barrier Reef plankton to climate change. In Climate Change and the Great Barrier Reef: A Vulnerability Assessment; Johnson, J.E., Marshall, P.A., Eds.; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, Australia, 2007; pp. 121–152. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11017/539 (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2007, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Fu, F.X. Microorganisms and ocean global change. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 2, 17508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Capone, D.G. The ocean nitrogen cycle: New developments and global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Tagliabue, A. Feedbacks between phytoplankton and nutrient cycles in a warming ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, D.; Steidinger, K.A.; Heil, C.A. HAB Monitoring and Databases: The Karenia brevis example. In Harmful Algae Management and Mitigation; Hall, S., Etheridge, S., Anderson, D., Kleindinst, J., Zhu, M., Zou, Y., Eds.; Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation: Singapore, 2004; APEC Publication#204-MR-04.22004. [Google Scholar]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Trussell, R.R. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bronk, D.A.; Lomas, M.W.; Glibert, P.M.; Schukert, K.J.; Sanderson, M.P. Total dissolved nitrogen analysis: Comparisons between the persulfate, UV and high temperature oxidation methods. Mar. Chem. 2000, 69, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermöhl, H. Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Mitt. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1958, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tomas, C.R. (Ed.) Identifying Marine Diatoms and Dinoflagellates; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E.F. Dinoflagellates in the Australian region. Mar. Freshwat. Res. 1954, 5, 171–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry; W.H. Freeman Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1981; 561p. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, M.R.; Rublee, P.A. A method to determine in situ grazing rates on natural particle assemblages. Mar. Biol. 1981, 65, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Metzler, P.M.; Glibert, P.M. Ingestion of 15N2− labeled Trichodesmium spp. and ammonium regeneration by the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis. Mar. Biol. 1996, 125, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, C.A.; Amin, S.A.; Glibert, P.M.; Hubbard, K.A.; Li, M.; Martinez-Martinez, J.; Weisberg, R.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y. Termination patterns of Karenia brevis blooms in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Harmful Algae, La Paz, Mexico, 10–15 October 2021; Band-Schmidt, C.J., Rodríguez-Gómez, C.F., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algal Blooms: La Paz, Mexico, 2022. 365p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawser, S.P.; O’Neil, J.M.; Roman, M.R.; Codd, G. AToxicity of blooms of cyanobacterium Trichodesmium to zooplankton. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Bunter, O.; Jones, B.; Llewellyn, L. Effects of the bloom-forming alga Trichodesmium erythraeum on the pearl oyster Pinctada maxima. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, N.; Burford, M.; Stenzel, D. Effects of Trichodesmium spp. blooms on penaeid prawn larvae. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, P.R.F.; Elemtri, I.; Uwins, P. Nitrogen fixation of Trichodesmium spp. in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon-importance to the overall nitrogen budget. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 186, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, P.R.F. Analysis of satellite imagery using a simple algorithm supports evidence that Trichodesmium supplies a significant new nitrogen load to the GBR lagoon. Ambio 2021, 50, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Envir. Microb. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J. Global warming and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, T.; Stumpf, R.; Tomlinson, M.; Ransibrahmanakul, V.; Villareal, T. Detecting Karenia brevis blooms and algal resuspension in the Western Gulf of Mexico with Satellite Ocean Color Imagery. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, L.E.; Compton, A. Long-term increase in Karenia brevis abundance along the Southwest Florida Coast. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, I.M.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hu, C.; Wolny, J. Characterization of Karenia brevis blooms on the West Florida Shelf using ocean color satellite imagery: Implications for bloom maintenance and evolution. J. App. Rem. Sens. 2016, 11, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Huffaker, R.; Jawitz, J.W.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Seasonal dynamics of terrestrially sourced nitrogen influenced Karenia brevis blooms off Florida’s southern Gulf Coast. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.; Kaplan, D.; Milbrandt, E.C.; Tomasko, D.; Huffaker, R.; Angelini, C. Nitrogen-enriched discharges from a highly managed watershed intensify red tide (Karenia brevis) blooms in southwest Florida. Sci. Tot. Envir. 2022, 827, 154149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Glibert, P.M.; Berg, G.M.; Van Heukelem, L.; Pantoja, S.; Lee, C. Extracellular amino acid oxidation by phytoplankton and cyanobacteria: A cross-ecosystem comparison. Aq. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 15, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; O’Neil, J.M. Dissolved organic nitrogen release and amino acid oxidase activity by Trichodesmium spp. Bull. Inst. Oceanogr. Monaco 1999, 19, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hewson, I.; Govil, S.R.; Capone, D.G.; Carpenter, E.J.; Fuhrman, J.A. Evidence of Trichodesmium viral lysis and potential significance for biogeochemical cycling in the oligotrophic ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, K.G. Trophodynamics of marine cyanobacteria blooms. In Marine pelagic cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, C.C.; Steinberg, D.K.; Kling, G.W. The microbial and metazoan community associated with colonies of Trichodesmium spp.: A quantitative survey. J. Plank. Res. 2002, 24, 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Calef, G.W.; Grice, G.D. Relationship between the blue-green alga Trichodesmium thiebautii and the copepod Macrosetella gracilis in the plankton off of South America. Ecology 1966, 47, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandel, V.; Kiko, R.; Brandt, P.; Dengler, M.; Stemmann, L.; Vandromme, P.; Sommer, U.; Hauss, H. Nitrogen Fueling of the Pelagic Food Web of the Tropical Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; LaBarre, B.A.; Hewson, I. Characterization of Trichodesmium-associated viral communities in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2013, 84, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vargo, G.A.; Heil, C.A.; Fanning, K.A.; Dixon, L.K.; Neely, M.B.; Lester, K.; Ault, D.; Murasko, S.; Havens, J.; Walsh, J.; et al. Nutrient availability in support of Karenia brevis blooms on the central West Florida Shelf: What keeps Karenia blooming? Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, B.M. Zooplankton Population Dynamics in Relation to the Red Tide Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on the West Florida Shelf of the Gulf of Mexico. Master of Science Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2012; 152p. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, B.M.; O’Neil, J.M. Zooplankton community composition and copepod grazing on the West Florida Shelf in relation to blooms of Karenia brevis. Harmful Algae 2014, 38, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, C.A.; Dixon, L.K.; Hall, E.; Garrett, M.; Lenes, J.M.; O’Neil, J.M.; Walsh, B.M.; Bronk, D.A.; Killberg-Thoreson, L.; Hitchcock, G.L.; et al. Blooms of Karenia brevis (Davis) G. Hansen & Ø. Moestrup on the West Florida Shelf: Nutrient sources and potential management strategies based on a multi-year regional study. Harmful Algae 2014, 38, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsby, A.E. The properties and buoyancy-providing role of gas-vacuoles in Trichodesmium Ehrenberg. Brit. Phycol. J. 1978, 13, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villareal, T.A.; Carpenter, E.J. Buoyancy regulation and the potential for vertical migration in the oceanic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steidinger, K.A.; Williams, J. Dinoflagellates. Memoirs of the Hourglass Cruises. Tech. Ser. Fla. Dep. Nat. Resour. Mar. Res. Lab. 1970, 2, 1–251. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, R.H.; Henry, M.S. Harmful algal toxins of the Florida red tide (Karenia brevis): Natural chemical stressors in South Florida coastal ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis Toxins: Causative Organisms, Distribution and Fate in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibert, P.M. Margalef revisited: A new phytoplankton mandala incorporating twelve dimensions, including nutritional physiology. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revelante, N.; Gilmartin, M. Dynamics of phytoplankton in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. J. Plankt. Res. 1982, 4, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelante, N.; Williams, W.T.; Bunt, J.S. Temporal and spatial distribution of diatoms, dinoflagellates and Trichodesmium in waters of the Great Barrier Reef. J. Exper. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1982, 63, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidinger, K.A. Historical perspective on Karenia brevis red tide research in the Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña, H.A.; Villareal, T.A. The effect of environmental factors on the growth rate of Karenia brevis (Davis) G. Hansen and Moestrup. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Glibert, P.M.; Heil, C.A. MurKy waters: Modeling the succession from r to K strategists (diatoms to dinoflagellates) following a nutrient release from a mining facility in Florida. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 2288–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahav, E.; Bar-Zeev, E. Sewage outburst triggers Trichodesmium bloom and enhance N2 fixation rates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.B. Effect of Trichodesmium bloom on water quality in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Rueter, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 273–287. [Google Scholar]
- Lenes, J.M.; Darrow, B.P.; Cattrall, C.; Heil, C.A.; Callahan, M.; Vargo, G.A.; Byrne, R.H.; Prospero, J.M.; Bates, D.E.; Fanning, K.A.; et al. Iron fertilization and the Trichodesmium response on the West Florida shelf. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, K.; Gao, P.; Wang, P.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Was dissolved nitrogen regime driving diatom to dinoflagellate shift in the Bohai Sea? Evidences from microcosm experiment and modeling reproduction. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2001, 127, e2021JG006737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.B.E.; Biswas, H.; Schulz, K.G.; LaRoche, J.; Riebesell, U. Effect of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide on the marine nitrogen fixer Trichodesmium. Glob. Biogeochem Cycl. 2007, 21, mGB2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.R.; Garnett, C.M.; Moore, M.; Florian, P. The Predicted Impact of Climate Change on Toxic Algal (Cyanobacterial) Blooms and Toxin Production in Queensland. Environ. Health 2001, 1, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).