Abstract
Access to safe drinking water remains a fundamental issue in rural areas of Ethiopia. This study aimed to evaluate the physicochemical and bacteriological quality of drinking water at protected sources in the Farta district, South Gondar Zone, Ethiopia. The study covered 16 rural Kebeles and was conducted on 75 protected dug wells with hand pumps (HDWs) and 17 protected springs (PSs). Data were collected during the wet and dry season, and field measurement were conducted on water samples pH, turbidity, electrical conductivity, and temperature, while laboratory analysis focused on E. coli prevalence. Additionally, sanitary risk assessment was also performed. The result showed that, the pH values ranged from 5.4 to 8.1, turbidity levels varied between 0 to 100 nephelometric turbidity unit (NTU), electric conductivity ranged from 62 to 584 µS/cm, and temperature ranged from 12.1 to 27 °C. Among all the samples, 39.1% had a pH below the minimum standard value of 6.5, close to 50.5% did not meet the turbidity requirement (5NTU), and all samples were safe against electric conductivity levels. The E. coli contamination was widespread, and only a small percentage of water sources, such as 21.7% HDWs, 6.7% PSs during dry season, and 13% HDWs during wet season were negative to E. coli detection. A significant proportion of water sources, such as 18% HDWs and 13% PSs during dry season, as well as 44.9% HDWs and 46.7% PSs during wet season, fell into the high microbial health risk category. Sanitary inspections revealed that only 16.7% of water sources were classified as low sanitary risk. This study revealed that majority of water sources were unfit to drinking and may endanger the public health. To ensure safe water availability frequent cleaning and disinfection of water sources, implementation of household water treatment, and improvement of WASH (water, sanitation and hygiene) infrastructure is needed.
1. Introduction
According to the WHO/UNICEF joint monitoring program report [1], in 2022, approximately 2.2 billion people still lacked safely managed drinking water services, with 292 million having limited services, 296 million with unimproved access, and 115 million relying on surface water for drinking. The same report indicated that around 38.6% of Ethiopia’s urban areas have access to safely managed drinking water services, compared to only 5.8% of its rural areas. Shallow ground water is the main source of drinking water for rural communities in sub-Sahara African countries. However, regular studies to check whether these water sources are safe or polluted are limited [2].
Water quality has recently become just as important as water quantity, although until recently, people in developing countries were only concerned with the quantity of water, and the available water was automatically considered to be potable water [3]. Water quality is a term used to describe the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water that influence the congruity of water for human consumption and ecosystem health [4]. Since water is often collected directly from the source without proper treatment, the drinking water quality in rural regions is largely dependent on the source water quality [5]. Making informed decisions about the management and protection of drinking water source requires a fundamental understanding of the status of drinking water quality and related health hazards [6].
Drinking water quality is one of the significant factors affecting the consumer’s health, especially in developing countries [6]. The biggest threat to the safety of drinking water is microbial contamination brought on by fecal contamination. Unsafe water supply and improper sanitation practice are among the main factors that contributed to diarrhea disease.. Although it can be enormously reduced with the provision of adequate water supply and sanitation, the problem still exists [7]. In 2016, diarrhea caused the deaths of 1.6 million people, including 26.3% of children under the age of five, and 90% of these deaths happened in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa [8]. Consumption of contaminated water causes health risks to the public, and the situation is serious in rural areas. There is a higher prevalence of diarrhea, fever, and cough in households with less access to improved water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) facilities [9]. Regardless of the water protection measures in place, flooding remains the primary cause of exposure to fecal contamination, highlighting its potential as a significant pollutant of drinking water sources in rural regions [10]. Because it releases agrochemicals, nutrients, organic matter, drug residues, sediments, and pathogens into the environment, agriculture is also one of the main causes of water pollution [11].
Contamination of drinking water in Ethiopia is a persistent issue due to factors such as rapid population growth, industrial expansion, intensive agriculture, improper disposal of waste, open defecation, and chemical effluents into water sources [12]. Many studies in Ethiopia have shown that drinking water sources have a high percentage of fecal contamination. For instance, in the Boloso Sore district, 60% of protected hand-dug wells (HDWs) and 25% of protected springs (PSs) were found E. coli-positive [13]; in the Guto Gida district, all HDWs and 62.5% of PSs were positive for E. coli [14].
The Farta district is predominantly comprised of rural communities engaged in agriculture and livestock raising. Access to safe drinking water is a crucial concern for these communities. Numerous complaints have been raised regarding issues such as odor, unpleasant taste, cloudy water color, and the presence of insects in the drinking water, all of which could be indicative of pollution. In addition, there is a lack of routine water treatment at the source, regular maintenance and cleaning of existing water schemes, and proper sanitary inspections, leaving the drinking water sources vulnerable to contamination. As per the district health bureau’s findings, drinking water contamination is associated with four out of the top ten diseases reported. Amoebiasis, typhoid fever, diarrhea, and helminthiasis have been identified as among the leading diseases linked to drinking water contamination. Despite the recognized vulnerability of water sources to contamination, there is limited knowledge regarding the status of drinking water quality at water points. Therefore, the aim of this work was to assess protected drinking water source quality in the Farta district and provide recommendations to safeguard the drinking water sources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
The Farta district, which is found in the Amhara regional state, is located approximately 597 km away from the capital city of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa. It is situated in the northwest highlands of Ethiopia between the coordinates 11°40′ and 12°2′ North and 37°50′ and 38°18′ East as shown on Figure 1. The total land area of Farta district is 805.76 km2, and it is divided into 32 administrative units or wards, which are known in Ethiopia as Kebeles. The district receives an annual rainfall between 1097 and 1954 mm, with a long-term average of 1248 mm [15]. The mean maximum temperature is 21 °C, encountered from February to May, and the minimum temperature is 9.6 °C, from June to January, whereas the average annual temperature is 15.5 °C. The central statistics agency projected that the population of Farta Woreda would reach 234,143 in 2022, with the majority (80%) living in rural areas [16].
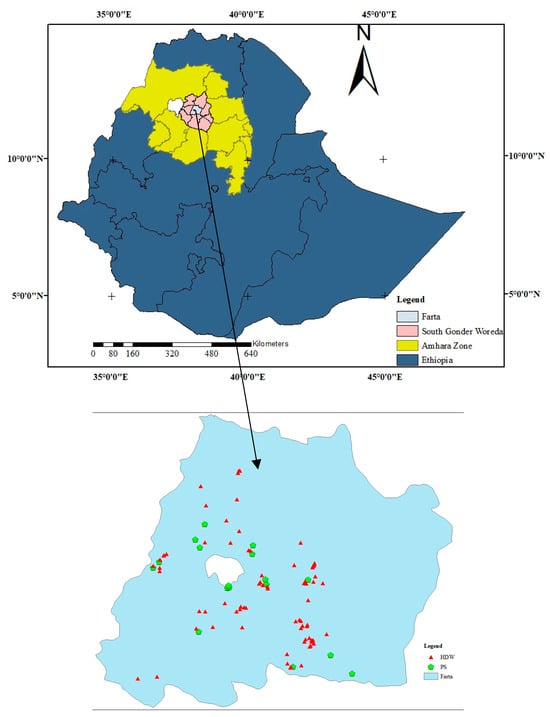
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area and sampled HDW and PS water sources.
As per the water and energy office of Farta district the rural areas within the district have a water coverage of 51.98%. Out of this, 30% of the population has access to basic drinking water services, while 21.98% have limited-service access. The remaining 48.02% of the population relies on unimproved water sources, including unprotected springs, unprotected hand-dug wells, and surface water, for their domestic water needs. Despite efforts from the government and development partners (NGOs) to enhance access to improved water sources, the drinking water supply situation remains critical challenge.
2.2. Sampling Site and Size
The selection of sampling sites primarily relied on the enumeration area (EA), which has been delineated by the national statistical service specifically for conducting house and population censuses. For this study, 16 out of the district’s 32 rural kebeles were selected using the probability proportion to size sampling technique [17]. Then, each rural kebele was represented by one EA. The study encompassed all protected water sources that provide service to the community within the selected EA. A total of 75 protected dug well with hand pumps (HDWs) and 17 protected springs (PSs) were included in the study from the 16 selected EAs.
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
The survey and sample collection from community drinking water sources were carried out; during the wet season, from 5 July to 10 August in 2022, and during the dry season, from 23 January to 8 February in 2023. The collected samples were analyzed for E. coli and physicochemical parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity, and temperature. The survey was performed using the mWater (Version: 67.0.0) mobile application (data management platform for WASH). The Whirl-Pak provided with sodium thiosulphate for dichlorination, which was used to collect the samples needed for the E. coli test. For the test, 100 mL of sample water was vacuum filtered through a 45-micron sterile millipor s-pack type HA membrane filters (HACH, Manchester, UK), and the filter was placed in a petri dish with membrane pad saturated with culture media (membrane lauryl sulfate broth) that was selective for E. coli. The plates were incubated at 44 °C for 24 h, and yellow colonies were counted. When it was difficult to filter the full 100 mL sample due to high turbidity, a lesser volume was filtered, and results were subsequently adjusted with a corresponding dilution factor. E. coli counts were performed up to 100 CFU/100 mL. If the number of E. coli exceeded 100 CFU/100 mL, the sample was recorded as 101, meaning “Too Numerous To Count” (TNTC). All physicochemical parameters were tested in situ. The turbidity was tested using LaMotteTM Turbidity (Lamotte, Chestertown, MD, USA). Temperature, pH, and electric conductivity were all measured using a Hanna Instruments HI98129 Meter (Hanna Instruments Ltd., Leighton Buzzard, UK).
The level of E. coli present in a 100 mL sample was used to determine the associated health risk for consuming the water. To facilitate understanding, a color code system was implemented. A blue color code indicated no E. coli detection (0 CFU/100 mL) and represented a safe category. Green (1–10 CFU/100 mL) represented low risk, yellow (11–100 CFU/100 mL) represented intermediate risk, orange (101–1000 CFU/100 mL) represented high risk, and red (>1000 CFU/100 mL) represented very high risk. This color code system visually represented the health risk categories associated with different E. coli contamination levels, aiding in the understanding and communication of the potential health risks of consuming the water [18,19].
A sanitary inspection was carried out for all sampled water sources. The sanitary inspection forms utilized during the process were adapted from reputable organizations such as the Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) and the World Health Organization (WHO). The sanitary risk levels were categorized into four classifications based on the scores obtained: a score of ≥9 indicated a very high risk level, a score of 6–8 indicated a high risk level, a score of 3–5 indicated a medium risk level, and a score of ≤2 indicated a low risk level.
2.4. Quality Control
By analyzing duplicate samples and blank samples with known parameter values, the accuracy of the analysis procedure was verified. This ensured that any variability in the results obtained was not due to errors in the laboratory analysis or sample collection procedures. Every Wednesday, a field blank sample was taken from a sealed water bottle and tested for E. coli to ensure the sample collection procedure was free from contamination. To ensure the field test procedure and equipment accuracy, a duplicate sample was taken every Friday from the water point, where samples were taken. A laboratory blank was examined daily during the E. coli test to ensure the quality of the membrane lauryl sulfate broth (MLSB) and the integrity of analysis techniques. As part of the quality control measures, field test instruments were calibrated once a week and verified daily. If the equipment failed verification, standard solutions were used for calibration. Furthermore, training sessions were conducted for data collectors and laboratory technicians to ensure the data quality.
2.5. Data Analysis
To determine if the water quality complied with standards, the measured E. coli count and physicochemical quality parameters of the water samples were compared to national and international drinking water standards. The Ethiopian drinking water quality standard [20], the World Health Organization guidelines for drinking water quality [21] and the Council of the European Union Standard [22] were used to evaluate the drinking water quality.
All data manipulation and analysis were performed using R programming language (R 4.2.3, RStudio 2023.12.1). Graphical visualizations, including histograms, kernel distribution estimation, and whisker-and-box plots, were employed to assess the normality of the data distribution. Additionally, the Shapiro–Wilk test, known for its high power in detecting non-normality in continuous data, was utilized for this purpose [23]. Instead of discarding outliers, outlier-resistant statistical analysis methods were utilized to account for their presence. Descriptive statistics such as median, minimum and maximum, were employed to provide an overview of the data’s fundamental characteristics. The Mann–Whitney U test was utilized to assess significant differences between any two groups. The chi-squared test was used to know the independence of explanatory variable in the contingency table. All tests used a significant level of 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Water Points Survey
The survey was carried out to collect information about the extent of water points protection and water samples was taken to test pH, electrical conductivity, turbidity, temperature, and E. coli The study included 75 protected dug wells with hand pumps (HDWs) and 17 protected springs (PSs). Overall, 27.5% of the sources had chlorine dispensers, and their ages ranged from 2 to 23 years. About 57.1% of the sources were constructed by the government, and 35.2% by NGOs. During the wet season, approximately 57.6% of water sources had quality issues, with cloudy water color being predominantly reported, followed by smell and bad taste. However, during the dry season, this percentage decreased to 35.9%, with bad taste being majorly reported, followed by cloudy water color and smell. According to the sanitary risk assessment, 57.3% of HDWs were at a medium risk level, followed by high risk (24%), low risk (17.3%), and very high risk (1.3%). A substantial proportion of protected springs, comprising 58.8% classified as high risk, 17.6% as medium risk, 11.8% as very high risk, and 11.8% as low risk.
3.2. Physicochemical Quality Characteristics of Drinking Water
The physicochemical parameters analysis results are summarized in Table 1. During the dry season, the median pH was 6.52 (ranging from 5.4 to 7.5), while in the wet season, it rose to 6.8 (ranging from 5.6 to 8.1). About 33.7% of samples had a pH below the minimum standard 6.5 during the wet season, and this percentage increased to 44.6% in the dry season. Overall, 39.1% of the water sources fell below the minimum pH standard. The Mann–Whitney U test confirmed that the pH was significantly varied across the seasons (p < 0.05), with lower pH levels observed during the dry season, as shown in Figure 2a. The median pH for HDWs was 6.6, with 32.7% of samples falling below the recommended level. For PSs, the median pH was 6.4, and a higher percentage, 67.6%, fell below the recommended level. The Mann–Whitney U test confirmed a significant pH variation between HDWs and PSs (p < 0.05), as illustrated in Figure 2a, where HDWs displayed higher pH values compared to PSs.

Table 1.
The minimum, maximum, and median values in bracket for water quality parameters based on different water source types and across seasons.
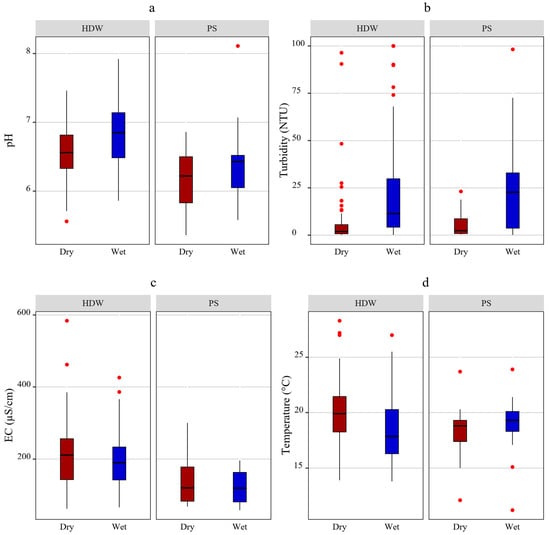
Figure 2.
Variation of physicochemical parameters values across seasons and water source types: (a) pH, (b) turbidity, (c) electrical conductivity, (d) temperature.
During the dry season, the median turbidity was 2 (ranging from 0 to 96.4 NTU), while in the wet season, it was 182.6 (ranging from 0.1 to 100 NTU). In the dry season, approximately 29.3% of samples had turbidity levels that exceeded the maximum recommended level of 5 NTU. However, during the wet season, this percentage increased significantly to 71.7%. Overall, 50.5% of samples did not conform to the national standard for turbidity. A significant difference in turbidity was observed between the wet and dry seasons, as indicated by the Mann–Whitney U test (p < 0.05). This is shown in Figure 2b, where the box plot for the dry season is positioned lower than that of the wet season, indicating higher turbidity levels during the wet season. HDWs and PSs exhibited median turbidity values of 4.9 NTU and 6.8 NTU, respectively. The percentage of samples that did not conform to the turbidity standard was 50% for HDWs and 52.9% for the PSs. The Mann–Whitney U test indicated no significant differences in turbidity between HDWs and PSs.
According to the regulations set by the European Union, the maximum permissible electrical conductivity in drinking water should not exceed 2500 µS/cm [22]. During the dry season, the range of electrical conductivity (EC) was 62 to 584 µS/cm, with a median of 211 µS/cm. In the wet season, EC ranged from 66 to 426 µS/cm, with a median value of 190 µS/cm. All samples had EC values below the threshold of 2500 µS/cm. The Mann–Whitney U test indicated no significant variation in EC between the wet and dry seasons (p = 0.27). The median EC values of HDWs and PSs were 202.5 µS/cm and 119.5 µS/cm, respectively. The Mann–Whitney U test demonstrated a significant variation in EC between HDWs and PSs (p < 0.05). This is shown in the Figure 2c, where the box plots for HDWs are positioned above of the PSs, suggesting higher EC values for the former.
The temperature of drinking water should be below 25 °C to limit the growth of Legionella pneumophila [21]. During the dry season, the temperature ranged from 12.1 to 28.3 °C, with a median temperature of 19.4 °C. In the wet season, the temperature ranged from 11.2 to 27 °C, with a median temperature of 18.5 °C. Only 5 samples were above 25 °C. The Mann–Whitney U test indicated that there was significant difference in temperature between the two seasons (p < 0.05). The median temperature of HDWs and PSs were 19 °C and 18.9 °C, respectively. The Mann–Whitney U test indicated no significant variation in temperature among the types of water sources (p = 0.44).
3.3. Bacteriological Quality of Drinking Water Sources
In all waters directly intended for drinking, E. coli must not be detected [21]. In each season, E. coli testing was conducted on 69 protected dug wells with hand pumps (HDWs) and 15 protected springs (PSs). The results revealed a significant proportion of water sources were contaminated with E. coli, as illustrated in Figure 3a. During the dry season, 21.7% of samples from HDWs and 6.7% of samples from PSs were negative for E. coli detection, whereas 18.8% of HDW samples and 13.3% of PS samples fell into the high health risk category. In contrast, during the wet season, the percentages of samples with no E. coli decreased to 13% for HDWs and none for PSs, whereas the percentage of samples fell into the high health risk category increased to 44.9% for HDWs and 46.7% for PSs samples, as shown in Figure 3a. The chi-squared test indicated that the E. coli result was significantly varied across seasons, with a considerable increase of fecal contamination during the wet season. The chi-squared test did not find a statistically significant variation in E. coli results between HDWs and PSs. However, as shown in Figure 3a, HDWs had a higher proportion of samples, with no E. coli compared to PSs.
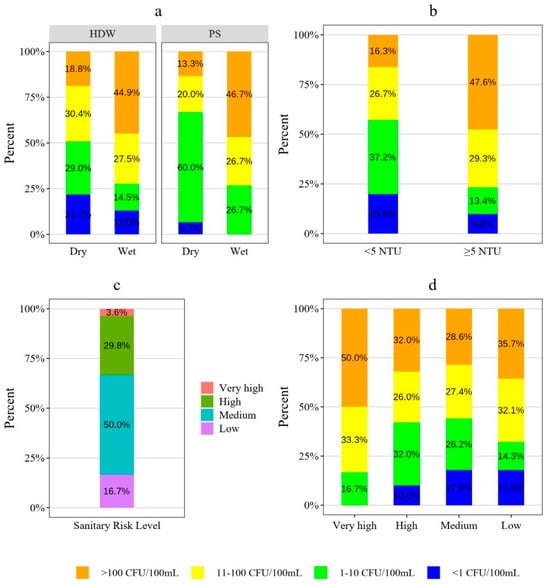
Figure 3.
(a) E. coli load variation among water sources and across seasons, (b) E. coli load variation with respect to the water sources turbidity, (c) sanitary risk level of water sources, and (d) E. coli load variation among water points sanitary risk level.
Water points reported by users as having quality issues were found to have a higher E. coli contamination load. Water sources that maintained turbidity levels within the recommended standard showed a higher percentage (19.8%) of samples with no E. coli detected compared to water sources not conformed to turbidity level requirement (9.8%), as shown in Figure 3b. Additionally, water sources with turbidity levels exceeding the standard had a higher proportion (47.6%) of samples falling into the high health risk category compared to water sources that complied with the turbidity level requirement (16.3%). The chi-squared test indicated the existence of significant variation in E. coli contamination between water sources with turbidity within the recommended level and those exceeding it. Figure 3c illustrates sanitary risk level of all the water sources: 18.3% were categorized as low risk, 49% as medium risk, 29.8% as high risk, and 2.9% as very high risk. Although the presence of E. coli did not show significant variation across different sanitary risk levels according to chi-squared test, there was an observable trend in the samples E. coli detection, as shown in Figure 3d. Water samples from sources with low and medium sanitary risk exhibited the highest percentage of samples negative to E. coli detection, followed by high and very high sanitary risk level.
4. Discussion
The water quality assessment in the Farta district, South Gondar zone, Ethiopia revealed that a significant proportion of water sources used for drinking had an acidic nature, were objectionable in terms of turbidity, and were heavily contaminated with fecal matter.
The pH levels of water sources were found to be lower during dry season, and protected springs (PSs) were found acidic compared to protected dug wells with hand pumps (HDWs). A similar observation was made on the research conducted in the Jimma zone, which reported that 47.7% of samples deviated from the pH standard, with springs had the lowest mean pH value [24]. Additionally, different studies have found springs with lower pH values compared to dug wells [12,25]. A study in the Guto-Gida district found that approximately 60% of water samples had pH readings below the standard [14], and in Guinea-Bissau, 83% of water sources had pH levels below the standard, with no significant variation across seasons [26]; this is larger than the percentage found in this study. In a study conducted in a rural community in Nigeria, HDWs exhibited acidic pH levels ranging from 6 to 6.5, with the highest values recorded during the wet season [27]. The pH of natural waters is primarily controlled by the carbon dioxide-bicarbonate carbonate equilibrium system, with an increase in carbon dioxide concentration leading to a decrease in pH [28]. Additionally, the composition of the soil can affect the pH of the water as it interacts with the surrounding environment [24]. pH is an important operational parameter for water treatment and corrosion control in metal pipes.
Half of the water sources sampled had turbidity exceeding the recommended level, with a severe condition during the wet season due to the intrusion of surface runoff water into the water sources. Similar studies in the Jimma zone [24] and Mecha district [29] found that 60% and 61.5% of the samples exceeded the turbidity limit, respectively. The findings from a study conducted in the Bona district revealed that a higher proportion of samples from HDWs (83%) and PSs (67%) conformed to the turbidity standard [30], indicating relatively clearer water compared to the samples analyzed in this study. The study conducted in a rural community in Nigeria did not detect any turbidity in the HDWs [27]. The differences in findings could be attributed to various factors, such as variations in geographical location, hydrological conditions, water source management practices, local environmental factors, public awareness, and seasons when samples were collected. High turbidity is often associated with elevated levels of suspended organic debris and microorganisms in the water source. The presence of these particles can hinder the effectiveness of disinfection processes, requiring higher doses of disinfectants and longer contact times to ensure adequate disinfection [31]. Therefore, even though the water may not present immediate health risks, it is crucial to address turbidity issues to maintain the aesthetic quality and consumers’ confidence in the drinking water supply. The high turbidity observed in wells may result from the wells’ vulnerability, shallowness, and lack of adequate lining. Due to their poor protection, the wells are highly susceptible to both inorganic and organic particles being washed into the well [32]. Implementing appropriate water sources protection measures and monitoring the turbidity levels can ensure that the water meets the desired aesthetic standards and maintains the required disinfection efficacy.
The electrical conductivity (EC) of sampled water sources was generally low, and HDWs had higher EC compared to the PSs. In the Mecha [29] and Ankober districts [33], an EC range from 34 to 304 µS/cm was found, which aligns with this study’s findings. Furthermore, a wider range of EC values from 30.8 to 727.7 µS/cm in the Jimma zone was documented [24]. In a Nigerian rural community, HDWs had EC ranging from 6 to 71.3 µS/cm [27], indicating the potential for greater variability across different regions. The EC of water is typically increased by the presence of minerals such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, and others, which are primarily derived from the geological characteristics of the soil [27]. The water sources in the Farta district were found to be fresh based on the results obtained from the EC measurements. Studies have observed higher EC values in protected hand-dug wells compared to springs water sources [14,23]. However, the study conducted in the Mbarara municipality, Uganda, reported higher EC values in springs compared to other water sources [34], which contradicts our findings. The differences in EC values across different regions could be attributed to variations in geological factors, such as the mineral composition of the surrounding soil and rock formations and human activities. One potential explanation for the higher EC values observed in protected water sources, such as HDWs, could be the accumulation of metals resulting from metal corrosion. These metals may originate from the pipes or other infrastructure components used in protected water sources, and their corrosion over time can release dissolved metals into the water, elevating the EC levels [14].
The majority of water sources sampled had a temperature of less than 25 °C. A study conducted in the Mecha [29] and Ankober [33] districts reported temperature recordings ranging from 15 to 27 °C, showing consistency with the findings of this research. In the study conducted in the Guto Gida district, no significant variation in temperature was found between different types of water sources. However, it was observed that unprotected sources had higher temperatures compared to other sources [14]. In a study conducted in Uganda, in the Mbarara municipality, significant variations in temperature among different water sources were found, with springs exhibiting the highest temperatures [34]. Water’s acceptability, chemical pollutants, and microbial proliferation are all impacted by temperature [21].
The water sources tested for E. coli indicated heavy fecal contamination with severe conditions during the wet season. The contamination of E. coli was higher during the wet season, which could be attributed to the intrusion of surface runoff into the water sources [35]. Rainfall plays a role in mobilizing soil particles with associated organisms by facilitating their infiltration and percolation, leading to their eventual arrival in subsurface groundwater. The previous studies conducted in the same area found that only 10% of samples were able to conform to the standard [36], consistent with this study. The study conducted in the Mecha district revealed that 92.3% of samples had fecal contamination [29]. A study conducted in Guinea-Bissau found that 83% of the sampled water sources did not meet the microbiological requirement, and the contamination level was significantly higher during the wet season [26]. A study conducted in the Ankober district found that most of the samples from protected springs were free from contamination [33], in contrary to this study. In the Jimma zone, 26.7% of samples from protected wells and 60% of samples from protected springs were free from fecal contamination [24]. Whereas a study conducted in District Bajaur, Pakistan [37], found that all samples taken from springs, HDWs, and open dug wells tested positive for E. coli, indicating widespread fecal contamination.
The findings from this study support the association between E. coli load and the turbidity of water sources, which is consistent with the findings of the study in Guinea-Bissau [26]. The influential factors for the variation of E. coli among samples include the protection status of water sources, proximity to latrines, presence of open defecation, and the prevalence of unhygienic practices [10]; furthermore, freely wandering domestic animals also play an important role [26]. Strong attention should be given to the disposal of fecal solids and wastewater as they are significant sources of groundwater contamination [38]. It is important to address these factors through appropriate interventions such as improving water source protection, promoting proper sanitation practices, and enhancing hygiene behaviors to mitigate the risk of fecal contamination in water sources. Additionally, the findings suggest a relationship between sanitary risk levels and the likelihood of E. coli contamination, highlighting the importance of ensuring proper protection practices and maintenance of water sources to minimize fecal contamination and promote public health. Nonetheless, despite the low level of sanitary risk level of water sources, there was still a substantial and consistent presence of E. coli throughout different seasons, suggesting groundwater pollution. Continuous engagement in improper sanitation practices, such as the persistent use of pit latrines, contributes to the ongoing contamination of the aquifer in the area [39].
Considering the water quality analysis results obtained from this study, it is imperative to implement immediate interventions to safeguard public health. The following remedial methods can be promptly applied:
- Eliminate the current latrines and any other sources of contamination located within a 30 m radius of the water source, as well as prevent the construction of new latrines within this proximity. It is possible to disinfect latrines using quicklime [38].
- To ensure the safety of HDWs, either wall lining must be installed for those lacking it, or significant maintenance work should be undertaken to prevent the infiltration of subsurface water around the upper section of the well. Additionally, consistent desludging, cleaning, and disinfection should be carried out.
- Encouraging household drinking water treatment is crucial for reducing both turbidity and microbial load [26]. Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam and Moringa peregrina) has demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity against E. coli, Salmonella typhi, and Shigella dysenteriae. Additionally, the water treatment process based on Moringa is cheap and straightforward, making it suitable for regions where extensive water treatment or piped water infrastructure are lacking [40]. Compared the raw Moringa seed, raw seed extract, and de-oiled seed extract, it was observed that the raw Moringa seed exhibited superior performance [41]. A study conducted in Ethiopia demonstrated that Moringa seed powder exhibits a substantial reduction in both turbidity and E. coli without a significant effect on the pH of water [42]. The Moringa powder can be prepared by collecting mature, dry Moringa seeds, removing the brown seed coat, and then crushing the seeds into a powder. The resulting white seed powder should be sieved through a strainer, and the fine seed fraction should be stored in an airtight container until needed. To use the Moringa seed powder, add it to the water and agitate thoroughly to mix it. Then, allow the bottle to settle overnight, and decant the clear water for an additional 6 h SODIS (solar disinfection) treatment process to further enhance the water quality [43].
- The enhanced implementation of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) is necessary to mitigate groundwater contamination from on-site sanitation systems [44].
5. Conclusions
The study was conducted in the Farta district, where water samples were collected from 75 protected dug wells with hand pumps (HDWs) and 17 protected springs (PSs) during both the wet and dry seasons. The findings revealed that around four out of ten water sources had a pH below the minimum recommendation set by the WHO, and half of the water sources did not conform to the national standard for turbidity. These results indicate that a considerable proportion of the water sources are aesthetically unsuitable for drinking purposes. However, all water sources had lower electrical conductivity, indicating their freshness. Furthermore, nearly nine out of ten HDWs and all PSs were found to have fecal contamination during wet season, posing a significant threat to public health in terms of waterborne diseases. The deteriorated drinking water sources quality condition was persistent throughout the entire year but worsened significantly during the wet season, coinciding with elevated water turbidity levels. In our findings, the majority of the water sources were deemed unsuitable for drinking purposes, highlighting the need for immediate intervention in WASH infrastructure to establish a sustainable and single health solution where multiple sectors must engage and work together to solve the public health problem. To determine the specific reasons for the reduction in pH of water sources in the study area, further investigations and studies are recommended.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F. and E.A.; methodology, M.F. and E.A.; software, M.F.; validation, M.F., E.A., D.A., A.T., and E.J.; formal analysis, M.F.; investigation, M.F. and E.A.; resources, Hilton Foundation; data curation, M.F. and E.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.F.; writing—review and editing, M.F., E.A., D.A., A.T., and E.J.; visualization, M.F., E.A., and D.A.; supervision, D.A.; project administration, E.A.; funding acquisition, D.A. and E.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Conrad N. Hilton Foundation grant number 27064 and the APC was funded by Norwegian Directorate for Higher Education and Skills, University of South-Eastern Norway (grant number WASH4ONEHEALTH/NORPART-2021/10070).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Notwithstanding that, the datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the Aquaya Institute for their invaluable assistance in designing the data collection procedure, establishing protocols, conducting trainings, and providing ongoing support throughout the entire process. We extend a special thanks to Anna Murray and Meseret Dessalegne for their unwavering support in ensuring the publication of this paper. Their assistance during data collection and data cleaning was truly invaluable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP). Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2022: Special Focus on Gender; United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and World Health Organization (WHO): New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liddle, E.S.; Mager, S.M.; Nel, E.L. The suitability of shallow hand dug wells for safe water provision in sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons from Ndola, Zambia. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 57, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S. Water Quality Indices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Migliaccio, K. Water Quality Concepts, Sampling, and Analyses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheili, A.; Delpla, I.; Sadiq, R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Impact of raw water quality and climate factors on the variability of drinking water quality in small systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2703–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J. Drinking water quality and public health. Expo Health 2019, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Zimsen, S.R.; Albertson, S.B.; Stanaway, J.D.; Deshpande, A.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, M.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Aboyans, V.; Adetokunboh, O.; Afshin, A.; Agrawal, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Bishwajit, G.; Zou, D.; Yaya, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Y. Burden of common childhood diseases in relation to improved water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) among Nigerian children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwimbi, P.; George, M.; Ramphalile, M. Bacterial contamination of drinking water sources in rural villages of Mohale Basin, Lesotho: Exposures through neighbourhood sanitation and hygiene practices. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.E.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Qadir, M.; Boelee, E.; Ippolito, A. Agricultural water pollution: Key knowledge gaps and research needs. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitotaw, B.; Melkie, E.; Temesgen, D. Bacteriological and physicochemical quality of drinking water in Wegeda Town, Northwest Ethiopia. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 6646269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizachew, M.; Admasie, A.; Wegi, C.; Assefa, E. Bacteriological Contamination of Drinking Water Supply from Protected Water Sources to Point of Use and Water Handling Practices among Beneficiary Households of Boloso Sore Woreda, Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 5340202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, M.T.; Midekssa, M.J. Quality and Safety of Rural Community Drinking Water Sources in Guto Gida District, Oromia, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 5568375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneyew, B.G. Drivers of the decline of indigenous land management technologies in Farta Woreda, Northwestern Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 79, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA, Central Statistics Agency. The 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Statistical Report at Country Level. 2007. Available online: http://www.csa.gov.et (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Skinner, C.J. Probability proportional to size (PPS) sampling. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Z.H.; Islam, M.S.; Imran, K.M.; Hakim, S.A.I.; Worth, M.; Ahmed, A.; Hossan, S.; Haider, M.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, F.; et al. Occurrence of Escherichia coli and faecal coliforms in drinking water at source and household point-of-use in Rohingya camps, Bangladesh. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Mahami, T. Escherichia coli as a tool for disease risk assessment of drinking water sources. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 2534130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethiopian Standard Agency (ESA). Ethopian Drinking Water Quality Standard—2013; Ethiopian Standard Agency: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2013.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Union (EU). Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1998; pp. 865–878. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31998L0083&from=EN (accessed on 1 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power comparisons of shapiro-wilk, kolmogorov-smirnov, lilliefors and anderson-darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.; Ketema, T.; Bacha, K. Physico-chemical and bacteriological quality of drinking water of different sources, Jimma zone, Southwest Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylamicheal, I.D.; Moges, A. Assessing water quality of rural water supply schemes as a measure of service delivery sustainability: A case study of WondoGenet district, Southern Ethiopia. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.; Amorim, E.; Bordalo, A.A. Spatial and Seasonal Drinking Water Quality Assessment in a Sub-Saharan Country (Guinea-Bissau). Water 2022, 14, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owamah, H.I. A comprehensive assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in a Nigerian rural Niger delta community. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). pH in Drinking Water; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lewoyehu, M. Evaluation of Drinking Water Quality in Rural Area of Amhara Region, Ethiopia: The Case of Mecha District. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9911838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Hailu, D. Bacteriological and physicochemical quality of drinking water sources and household water handling practice among rural communities of Bona District, Sidama Zone-Zouthern, Ethiopia. Sci. J. Public Health 2015, 3, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Water Quality and Health-Review of Turbidity: Information for Regulators and Water Suppliers; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, A.E.; Peprah, M.O.; Marfo, M.O. Unregulated hand dug wells and their quality threat: A case study in Cape Coast Metropolis. Open Access Libr. J. 2020, 7, e6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassegne, A.B.; Leta, S. Assessment of physicochemical and bacteriological water quality of drinking water in Ankober district, Amhara region, Ethiopia. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 1791461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukubye, B.; Andama, M. Physico-chemical quality of selected drinking water sources in Mbarara municipality, Uganda. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2017, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.E.; Mureithi, M.; Mboya, J.; Campolo, J.; Swarthout, J.M.; Pajka, J.; Null, C.; Pickering, A.J. Effects of high temperature and heavy precipitation on drinking water quality and child hand contamination levels in rural Kenya. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6975–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genet, G.K.; Desta, H.H. Bacteriological quality of drinking water from source to point of use among rural communities of Farta Woreda in North West, Ethiopia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Nafees, M.; Muhammad, N.; Ullah, U.; Hussain, R.; Bilal, M. Assessment of drinking water sources for water quality, human health risks, and pollution sources: A case study of the district Bajaur, Pakistan. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordalo, A.A.; Savva-Bordalo, J. The quest for safe drinking water: An example from Guinea-Bissau (West Africa). Water Res. 2007, 41, 2978–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterodt, G.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Hoiting, Y.; Kamara, A.K.; Oduro-Kwarteng, S.; Foppen, J.W.A. Microbial groundwater quality status of hand-dug wells and boreholes in the Dodowa area of Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancessi, A.; Pinto, M.M.F.; Duarte, E.; Catarino, L.; Nazareth, T. The antimicrobial properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. for water treatment: A systematic review. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsergany, M. The Potential Use of Moringa peregrina Seeds and Seed Extract as a Bio-Coagulant for Water Purification. Water 2023, 15, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delelegn, A.; Sahile, S.; Husen, A. Water purification and antibacterial efficacy of Moringa oleifera Lam. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.B.; Elmusharaf, K.; Borde, P.; Guigan, K.G.M. Evaluation of the natural coagulant Moringa oleifera as a pretreatment for SODIS in contaminated turbid water. Sol. Energy 2017, 158, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twinomucunguzi, F.R.B.; Nyenje, P.M.; Kulabako, R.N.; Semiyaga, S.; Foppen, J.W.; Kansiime, F. Reducing Groundwater Contamination from On-Site Sanitation in Peri-Urban Sub-Saharan Africa: Reviewing Transition Management Attributes towards Implementation of Water Safety Plans. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).