Abstract
Agricultural water serves various functions, including public interest purposes, beyond its primary role in agricultural production. In order to evaluate the various public interest purposes of agricultural water, a quantified study of the effect of agricultural water on river flow, water quality, and aquatic ecosystems is needed. Therefore, this study quantified the impact of agricultural water on the environmental and ecological maintenance function of downstream rivers, taking into account the return flow of agricultural water in rural areas. To this end, first, the effect of agricultural return flow on river maintenance function was evaluated by comparing the return flow quantity calculated using the reservoir supply data with the simulated river flow rate through the SWAT model. Second, the effect of the agricultural return flow on the downstream river environmental ecological function was analyzed using the optimal flow rate results calculated through the PHABSIM model. The lastly, the effect of agricultural water by farming period on the water quality of downstream rivers was analyzed. As a result of the analysis, it was found that the return flow of agricultural water had a large effect on the river flow rate in the case of the non-rainy season, but the optimal ecological flow rate was not satisfied. In the case of river water quality, it was confirmed that the effect of agricultural water (mainly considered as a pollutant) was not significant, except for the drainage duration of rice paddies. Therefore, it can be understood that agricultural water is not only used for the purpose of production but can also have a positive impact on the aquatic ecology of downstream rivers.
1. Introduction
Agricultural water holds significant importance not merely in terms of its primary function for crop production and irrigation but also plays a crucial role from a broader public interest standpoint. This encompasses aspects such as maintaining the ecosystem balance, supporting biodiversity, and contributing to the landscape’s aesthetic and recreational value. Additionally, it serves as a vital resource for sustaining rural communities and their economies, thereby underlining its multifaceted value beyond mere agricultural productivity. From this perspective, it is necessary to secure agricultural water and re-evaluate its value (in terms of water quantity, quality, and aquatic ecology). In Korea, the demand for agricultural, domestic, and industrial water is continuously increasing [1]. However, the development of new water sources for securing the water supply is facing considerable restrictions due to environmental protection concerns, leading to a growing interest in identifying alternative water resources [2,3]. In addition, efficient water resource use is subject to integrated project management policies and the demands of the times [4,5]. Recently, changes in farming practices and the industrialization of rural areas have led to an increased demand for agricultural water in these regions [6]. Additionally, the frequency of droughts and floods, exacerbated by climate change, has heightened the need for the rational and efficient management of agricultural water to ensure a stable water supply [7,8,9]. Therefore, the reasonable and efficient management of agricultural water is required to ensure a stable water supply [10]. Agricultural water, which accounts for 41% of Korea’s total water resources, is broadly defined as water used for agricultural activities ranging from livestock production to irrigation water for crop cultivation and has social and environmental functions, such as atmospheric circulation, groundwater recharge, provision of river maintenance water, and amenity and ecosystem conservation [11,12,13]. In particular, the agricultural return water drained from rice paddies flows into nearby rivers (rapid return flow) and groundwater (delayed return water), greatly affecting the river ecosystem and performing a multidisciplinary function in the agricultural environment [14,15].
Recently, there has been an increasing interest in the multifunctional aspects of agricultural water [16,17]. The perception of agricultural water, previously understood solely as irrigation water necessary for crop growth, is shifting towards a more inclusive concept that encompasses various environmental and ecological uses, such as improving rural living environments and supporting the environmental flow for ecosystems. Return flows from agricultural water play a crucial role in efficient water use and the maintenance of the environmental flow for ecosystems. They are significantly important for watershed water supply planning, predicting river flow conditions, determining irrigation water usage, preventing river dry-up, protecting aquatic ecosystems, and ensuring biodiversity. These processes underscore the importance of managing agricultural water not just for agricultural productivity but also for broader environmental and ecological health [18,19].
In Korea, according to previous studies [20], the return rate of agricultural water greatly varies from 38.1% to 70.5%, depending on the regional characteristics and crop cultivation methods used. Accurate calculation of the return rate of agricultural water is required for rational and economical water resource use and water management. Song et al. [21] calculated the amount of irrigation return during 2011–2012 for the irrigation district of the Idong Reservoir. They found that, the higher the supply of agricultural water, the higher the irrigation return rate and the return rate of agricultural water and that agricultural return water was the main component contributing to the river flow rate. Also, as part of a survey on river water use, a systematic survey of the return flow rate of agricultural water was conducted; based on the results, approximately 35% of the supply of agricultural water is expected to return to rivers.
Recent changes in rivers, including the installation of hydraulic structures for water diversion and flood control, water quality deterioration from various pollution sources, and alterations to the water cycle system due to industrialization and urbanization, have led to river contamination. Therefore, restoring river functions to conserve river ecosystems and create environmentally stable rivers requires the efficient management of environmental flows [22,23]. To recover the self-purification capability and normal functions of rivers, various conditions are needed, including creating habitats for aquatic organisms, blocking sources of pollution, and maintaining appropriate river flow levels, with the maintenance of ecological flows in rivers serving as a fundamental component for other habitat formations. The Ministry of Environment in Korea defines environmental ecological flow as the minimum flow necessary to maintain the health of aquatic ecosystems. The Water Environment Conservation Act mandates consideration of the environmental ecological flow when announcing river maintenance flows, allowing for the announcement of such flows at representative points in small streams, dried-up tributaries, or branches [24]. For larger rivers, like national rivers, maintenance flows have often been established based on drought flows rather than calculated flows considering the aquatic ecosystem, necessitating the determination and development of necessary flow measures to protect habitats of endangered species in these rivers [25].
Although recent studies on calculating the return flows of agricultural water and estimating ecological flows have been actively carried out [26,27,28], research on the impact of agricultural water on the quantity and quality of water in downstream rivers and its effects on aquatic ecosystems remains insufficient. In the past, the management of water resources in rivers focused on quantity and quality [29], but as interest in the environment has increased, the aspect of aquatic ecology has been emphasized in river flow management [30,31]. Furthermore, agricultural water is often perceived as a potential source of pollution in downstream rivers from an environmental perspective. However, there is still a lack of seasonal and quantitative studies conducted on this matter. From this view, the calculation of the environmental and ecological flow rates of rivers can be of great significance, and the integrated management of river quantity, water quality, and aquatic ecology is needed.
Therefore, in this study, the effect of agricultural water on the water quantity and quality and the ecology in downstream rivers were evaluated considering agricultural water return in a rural basin. This research assessing the effective impact of agricultural water return flows not only in terms of quantity and quality but also from an aquatic ecology perspective can serve as fundamental data for quantitatively assessing the public benefits of agricultural water. This information can be foundational for decision-making in policy and institutional development aimed at the efficient management of agricultural water.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, the river flow and water quality were monitored in the main stream and inflow streams of the reservoir irrigation district (this study site), and aquatic health was evaluated using data from the National Biometric Network and previous studies [32,33]. In addition, the return flow for agricultural water was calculated using the reservoir supply data, and the long-term flow rate of downstream rivers was simulated using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model to evaluate the impact of the return water on river function maintenance. Using the simulation results of the optimal ecological flow, the impact of return water for agricultural use on the environmental ecological function of the downstream rivers was evaluated (Figure 1).
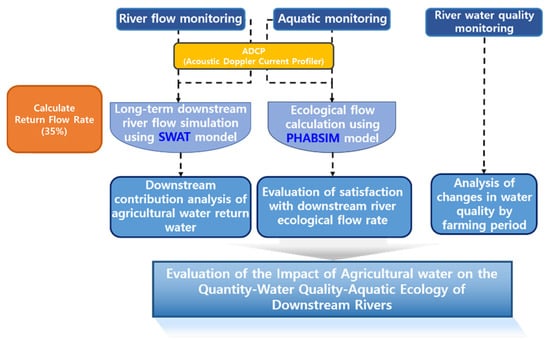
Figure 1.
Flowchart of this study.
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted in the Heungeop Reservoir irrigation district located in Maeji-ri, Heungeop-myeon, Wonju-si, Gangwon-do, Korea, where it is possible to analyze the contribution of agricultural water to downstream river pollution. The Heungeop Reservoir was built to supply agricultural water, and the irrigation area is approximately 165 ha. The water volume of the reservoir is 1,098,000 tons, the basin area is 1750 ha, and the full water area is 25 ha. The reservoir is managed by the Wonju Branch of the Rural Community Corporation.
There are six weather stations in Wonju, where the Heungeop Reservoir is located. The Wonju weather station was selected as a representative observatory for this study. The average annual precipitation (2011–2020 years) was 1209.9 mm, which is less than the national average precipitation (1397.7 mm). The total annual precipitation in Wonju-si shows a decreasing trend; it decreased significantly from 2011 to 2014, then gradually increased until 2020, except in 2019. In particular, in 2020, the precipitation was approximately 545 mm higher than in 2019. The total annual precipitation was 1063.6 mm in 2017, 1229.2 mm in 2018, and 771.9 mm in 2019. Rainfall occurrences of 30 mm or more occurred 10 times in 2017, 14 times in 2018, and 3 times in 2019 and, thus, were the most prevalent in 2018.
2.2. Monitoring for Analysis of the Contribution of Agricultural Return Flow to Downstream Rivers
2.2.1. River Flow Monitoring
To assess the quantitative and aquatic ecological impact of agricultural water on downstream rivers, precise investigations into the river flow are essential. This necessitates accurate cross-sectional surveys and ongoing flow measurements. In this study, the water level gauges were installed at monitoring points selected during a preliminary field survey to measure the river flow rate and to monitor the long-term water-level and flow rate changes (Figure 2a). River flow monitoring was conducted at two points: Bonghyeon Bridge (H1), located downstream in the benefiting area, and Heongeop 2 Bridge (H2), where the Majicheon (MJ) and Seogokcheon (SG) tributaries converge. For flow monitoring at each point, a float level meter and river gauge were installed on the bridge piers, and flow rates were measured using the velocity-area method. In addition, tributaries inflowing from downstream areas other than the Seogok Stream were identified, and at the inflow point (H3), regular on-site flow measurements were conducted instead of using a water gauge. The primary aim of this study is to analyze the contribution of agricultural return flows to the flow rates in the downstream rivers at the extents of the Heungeop Reservoir beneficiary areas. Consequently, monitoring sites were selected to assess the proportion of agricultural return flows compared to the total flow originating from the Heungeop Reservoir watershed, including the beneficiary regions. The final downstream location, H1, was chosen, and other specific points such as Seogok Stream (H2) entering at the middle part of the Heungeop Reservoir beneficiary area and a downstream tributary (H3) were selected to exclude their flows. In addition, the flow rate change before the Seogok Stream was measured by monitoring the flow rate in the Maeji Stream at point H4. The river flow monitoring data were used as correction data for the basin model used for the long-term river flow simulation. The river flow rate was measured using the velocity-area method, in which the average flow rate and the flow rate in a cross-section of a small section are calculated by dividing the flow channel into several small sections and measuring the depth of the water in each small section using a flow meter. In this study, the water flow and water quality were monitored at 11 time points during rainfall and non-rainfall periods.
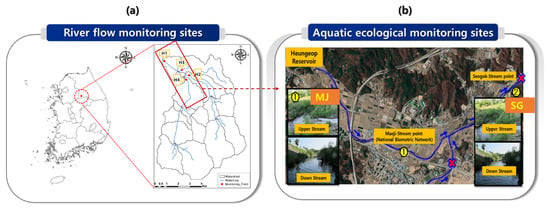
Figure 2.
(a) River flow, water quality, and (b) aquatic ecological monitoring points. Red box means the irrigated area as shown in (b). Arrows mean the flow direction. H1~H3 means flow monitoring sites. MJ(MaeJi) and SG(SeoGok) are the aquatic ecological monitoring sites.
2.2.2. Aquatic Ecological Monitoring
In this study, monitoring was conducted to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems in a downstream river of a district receiving agricultural water, utilizing methods such as the Trophic Diatom Index (TDI), Benthic Macroinvertebrate Index (BMI), and Fish Assemblage Index (FAI) at selected aquatic ecological monitoring sites. Additionally, representative fish species were selected based on fish surveys, and their optimal ecological flow was calculated to evaluate the impact of agricultural water on the downstream river’s aquatic ecology. Monitoring was conducted on downstream rivers directly affected by agricultural return flows from the Heungeop Reservoir (Figure 2b), and the investigation point was selected to reflect the current operating aquatic ecological monitoring sites (operated by the Ministry of Environment) to verify aquatic ecosystem monitoring data. The SG monitoring site was selected for its suitability for aquatic ecological monitoring, including fish surveys, due to adequate space available near the downstream flow and water quality monitoring sites conducted in this study. For the MJ site, located upstream, a currently operating national biometric network site was chosen, allowing for comparative validation of the aquatic monitoring performed in this study. Therefore, we selected point MJ, which was, to some extent, secured from the upstream flow, and we selected the point SG near the Bonghyeon Bridge located at the end of the beneficiary area as the branch.
Considering the physical water system and seasonal characteristics, the major habitat characteristics and cluster structures (including species diversity, wind patterns, and uniformity) were analyzed, and aquatic health was analyzed and evaluated. The monitoring was conducted twice at two points (MJ and SG) on 30 May and 21 September 2020 (once a month for each site), before and after the flood season, to exclude the effects of rainfall and typhoons in the summer. The field survey followed the “Guidelines for Surveying and Evaluating River Ecosystem Health” by the Ministry of Environment. As outlined in the guidelines, surveys were conducted once each in the spring and autumn annually. Monitoring was conducted in a relatively uniform condition, without any issues such as rainfall, and all biotas were investigated considering the hydraulic and hydrologic parameters, such as river width, water depth, and flow rate. In addition, data of the site from the National Biometric Network were collected and used to evaluate the aquatic ecology health. The health of the river aquatic ecosystems at each branch was evaluated using three indices:
- –
- Fish Assessment Index (FAI),
- –
- Tropic Diatom Index (TDI),
- –
- Benthic Macroinvertebrate Index (BMI).
In the case of fish, the species composition, population, share, dominant species, and least dominant species were analyzed for the fish collected through monitoring. In this study, fish communities were collected along a 50–100 m stretch of the water system around the survey points using a throw net (mesh size 7 × 7 mm) and a dip net (mesh size 5 × 5 mm). To ensure the quantification of fish communities between locations, collections with the throw net were repeated 10 times, and those with the dip net were conducted over 50 min. The collected fish were preserved in a 10% formalin solution. In addition, the distribution of legally protected species, such as rare and endangered species of classes I and II and foreign, introduced species, was analyzed. Tolerance guilds and feeding guilds of fish were analyzed. Tolerance guilds were classified into sensitive species, intermediate species, and tolerant species, respectively, and feeding guilds were classified into insectivores, omnivores, carnivores, and herbivores, according to their feeding characteristics. The FAI was calculated based on the scores for eight metrics (total number of domestic species; number of riffle-benthic species, sensitive species; proportion of the population of tolerant species; proportion of omnivores; proportion of domestic insectivores; total number of domestic species collected; and proportion of individuals with disease, tumors, fin damage, and other anomalies), and the end score (0–100) was classified as very good, good, normal, bad, or very bad. Cluster analysis was used to calculate the likelihood, variety, uniformity, and abundance of species based on the species and populations collected quantitatively at each survey point [34,35].
In the case of epilithic diatoms, the total taxonomic groups, species composition, density, dominant species, subdominant species, and cumulative dominant frequency of epilithic diatoms were analyzed, and cluster analysis was conducted. The dominant species was determined as the species with the largest population in each survey section. The epilithic algae collection was conducted in riffle areas of the streambed, ideally located near the center of the river with average flow rates between 10 and 50 cm/s and composed primarily of substrates larger than gravel size. The substrate chosen for algae collection was the most stable and solid natural material available within the river, specifically flat-surfaced rocks. Approximately 250 cm2 of the collection area was brushed off to gather samples. The collected material was preserved on-site in 10% formalin and later identified in the laboratory. The health of the aquatic ecosystem at each point was evaluated using the TDI.
In the case of benthic macroinvertebrates, the total taxonomic groups, species composition, density, dominant species, and subdominant species of benthic macroinvertebrates were analyzed, and the dominance, diversity, abundance, and evenness indices of small benthic macroinvertebrates were calculated for each monitoring point. Collection was conducted at each survey site using a Surber net (30 × 30 cm2, 1 mm mesh size), taking into account the flow and environment of each location. Quantitative collection was performed once at riffle and pool areas at each site. The collected samples were preserved on-site in 10% formalin, transported to the laboratory, and then sorted using a sieve (1 mm mesh). Finally, the samples were stored in 75% ethanol. Aquatic ecosystem health was evaluated by calculating the BMI based on benthic macroinvertebrates for each survey section and calculating scores based on the evaluation criteria. In addition, we calculated the ecological score of the benthic macroinvertebrate community (ESB), which is another biological index widely used for rivers, wetlands, and lakes. The ESB is used to evaluate the water environment by assigning an environmental quality score (Qi) to each benthic macroinvertebrate species according to the National Natural Environment Survey Guidelines issued by the Ministry of Environment. The calculation method of each index is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Calculation method for each index.
2.2.3. Monitoring of River Water Quality
To assess the impact of agricultural water discharge on downstream river water quality during the farming season, additional monitoring of the river water quality was conducted at point H1 (Bonghyeon Bridge) located at the outlet of the basin. In this study, biological oxygen demand (BOD5) and total phosphorus (T-P) were chosen as indicators to evaluate the quality of agricultural water. BOD5 was selected because it measures the level of organic matter contamination and is widely used in water pollution assessments. T-P was chosen as it represents non-point source pollutants such as agricultural and livestock wastewater and serves as an indicator of eutrophication in rivers and lakes. Moreover, in Korea, the current Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) program sets and manages water quality targets for the BOD5 and T-P. The BOD5 was measured using the method that involves collecting a water sample, measuring its initial dissolved oxygen (DO) level, incubating it at 20 °C in the dark for five days, remeasuring the DO, and calculating the oxygen depletion to determine the organic pollution level. Total phosphorus (TP) was measured by digesting the water sample with acid to convert all phosphorus forms to orthophosphate, which was then quantified using a spectrophotometer after reacting with a color reagent, typically resulting in a blue color. Water quality monitoring was conducted on the same dates as the river flow monitoring, including 14 May, 16 June, 25 June, 14 July, 29 July, 10 August, 27 August, 11 September, 25 September, 8 October, and 26 October, totaling 11 sessions. Water quality analysis was performed by collecting samples and transporting them to a laboratory, where they were analyzed according to the water pollution testing standards. According to the management manual for each crop (agricultural day management schedule) proposed by the Rural Development Administration, the management schedule varies depending on the climate characteristics and temperature of the year, but the rice field is usually drained completely for 30–35 days from the end of September to October. From November to December, the rice straw is ploughed to prepare for farming activities in the following year. In this study, the effect of agricultural water discharge on the water quality of downstream rivers during rainy periods was evaluated in different farming management periods.
2.3. Modeling for the Analysis of the Contribution of Agricultural Water to Downstream River Parameters
2.3.1. Determining Long-Term Flow Rate Fluctuations Using the SWAT Model
Long-term river flow was simulated using the SWAT model to identify long-term flow rate fluctuations in the basin. The SWAT model can simulate the behavior of agricultural chemicals based on soil properties, land use, and land management status, as well as the water quality of basins with complex characteristics, using similar principles [42]. The predictive ability of the SWAT model was assessed based on the coefficient of determination (R2) and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) between the simulated and measured results. R2 is a statistical measure that indicates the correlation between simulated and measured values and takes a value between 0 and 1, with 1 indicating a completely linear relationship. NSE is a normalized statistic that indicates the relative magnitude of the residual variance between measured and simulated values. It takes a value from −∞ to 1, with 1 indicating a perfect match between measured and simulated values [43]. The interpretation of these parameters for model evaluation is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Statistic interpretation guidance for model assessment.
The parameters of the SWAT model for long-term river flow simulation were optimized based on the measured results of the river flow rate monitoring at points H1 and H2, using the SWAT-CUP calibration and uncertainty program. SWAT-CUP was developed for model calibration and validation and sensitivity and uncertainty analyses of SWAT models. In this study, the parameters were optimized using the SUFI2 algorithm, which can quantify and represent parameter uncertainty. The parameters calibrated in this study are described in Table 3.

Table 3.
Definition and scope of the parameters for SWAT model calibration.
2.3.2. Evaluation of the Contribution of Return Water to Downstream River Parameters
The agricultural return water quality varies greatly depending on the natural environment, crop cultivation method, and regional characteristics. According to long-term comprehensive water resource planning, rationalization of rural water use planning, and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport in Korea, approximately 35% of the agricultural water supply is expected to return to rivers (rapid and delayed returns) in Korea [24]. In this study, the environmental preservation function of agricultural water return was indirectly evaluated using the available data, and the return was quantified by setting the return rate of agricultural water to 35%. The effect of the agricultural water return quantity on the river was evaluated using the calculated return quantity results and the river flow rate data simulated with the SWAT model.
2.3.3. Environmental Ecological Flow Estimation Using the Physical Habitat Simulation System (PHABSIM) Model
The ecological flow rate in rivers downstream of the Heungeop Reservoir was calculated using the PHABSIM model, which was developed to evaluate the effect of agricultural water return on the aquatic ecology of downstream rivers. The PHABSIM model predicts the physical habitat of aquatic species according to their growth stage based on changes in the flow characteristics (e.g., flow rate and water depth) and calculates the optimal flow rate required for the aquatic species of interest in relation to the available habitat area (weighted available area). This model can calculate the ecological flow rate for representative fish species in the simulated area and was used to quantitatively evaluate the environmental conservation function of agricultural water return based on the environmental ecological flow rate (Figure 3). The PHABSIM model uses river cross-section data, flow rate data by depth, and flow rate data by water level as the input data. In this study, we utilized Habitat Suitability Indices (HSI) for the depth and velocity for key fish species as presented through field surveys in the existing literature [46]. Additionally, river cross-section data for the targeted research area were sourced from the River Maintenance Basic Plan for point H1. River sections and depth-specific velocities were also measured on-site using Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) equipment and incorporated into the model (Figure 4). Following the collection of this baseline data, the PHABSIM model was employed to calculate the relationship curves between Weighted Usable Area (WUA) and the flow rate based on the Instream Flow Incremental Methodology (IFIM). These curves were then used to estimate environmental ecological flows corresponding to the physical habitats. The effect of agricultural water on downstream rivers was evaluated by calculating the optimal ecological flow rate for representative fish species in the Seogok Stream, a terminal river in the study area. Ecological flow satisfaction was analyzed by comparing the simulation results of the long-term outflow of the rivers at the end of the beneficiary area downstream of the Heungeop Reservoir obtained with the SWAT model and the optimal ecological flow results calculated using the PHABSIM model.
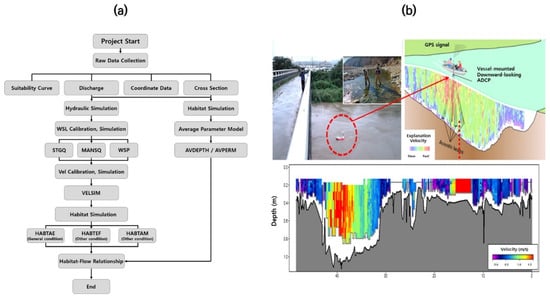
Figure 3.
PHABSIM modeling process and river sections/depth-specific velocity measurements using ADCP (a,b). Red dotted circle means the ADCP equipment in operation on site.
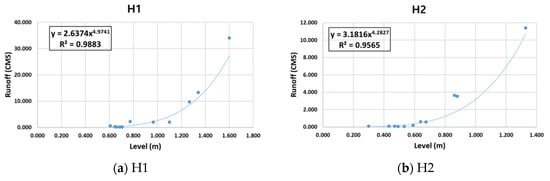
Figure 4.
Water level-flow curves for monitoring sites H1 (Bonghyeon Bridge) and H2 (Heongeop 2 Bridge).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quantity and Water Quality Monitoring Results
3.1.1. River Flow Monitoring Results
The flow rate at point H1 showed the largest change after rainfall and was the lowest, at 0.170 m3/s, in May, the dry season. Similarly, the flow rate at point H2 was the highest, at 3.641 m3/s, in July, and the lowest, at 0.059 m3/s, in May. At point H3, the basin area was small, and the flow rate was 1.206 m3/s in August, the flood season. At point H4, the flow rate was 0.527 m3/s at the 9th measuring time point but only 0.055 m3/s at the 11th measuring time point after a relatively long period of rainless days (26 days). The water level flow curves for H1 and H2 were calculated to be y = 2.6374 × 4.9741 (R2 = 0.988) and y = 3.1816 × 4.2827 (R2 = 0.956), respectively, using flow rate data obtained from river flow monitoring and water level data at H1 and H2, where water level gauges were installed (Figure 4).
3.1.2. River Water Quality Monitoring Results
To evaluate the effect of agricultural water return on the aquatic ecological health of downstream rivers, which was the purpose of this study, long-term aquatic ecology monitoring at the Seogok Stream point at the end of the beneficiary area downstream of the Heungeop Reservoir was conducted. River water quality monitoring at point H1 (at the outlet of the basin) revealed an average BOD5 value of 1.3 mg/L (0.6–2.6 mg/L), indicating a river living environment standard of Ia (very good) to II (slightly good) (Table 4). The average T-P value was 0.067 mg/L (0.034–0.135 mg/L), representing Ib (good) to III (normal).

Table 4.
River living environment standards.
The factors that affect river water quality vary widely depending on the characteristics of the watershed and of the pollution source. In the rural basin, we considered that pollutants running off from crop fields flow into the river depending on farming activities and affect the river water quality; therefore, the river water quality was analyzed in different farming periods. In the rice transplanting period in May, the BOD5 value was 1.7 mg/L, and in the active tillering stage in early June, it was 2.3 mg/L. In late June and early July, the water quality was good, as indicated by BOD5 values of 0.7 mg/L and 1.2 mg/L, respectively. At the end of July, when the water was drained, the water pollutant concentration was the highest, with a BOD5 value of 2.6 mg/L. After the water was drained, the water pollutant concentration decreased, and it increased again in October.
The T-P value was 0.088 mg/L at the end of May, and it decreased from the end of June to mid-July but was the highest, at 0.135 mg/L, around the end of July, when the water was drained. Then, the T-P value decreased, but it increased again during the complete draining period from late September to October, showing a similar tendency to the BOD5 parameter. The average BOD5 value during the water draining period was 1.5 mg/L, which was 1.6 times higher than that in other periods (1.0 mg/L). The average T-P value during the water draining period was 0.081 mg/L, which was 1.9 times higher than the average value in other periods (0.043 mg/L) (Figure 5).
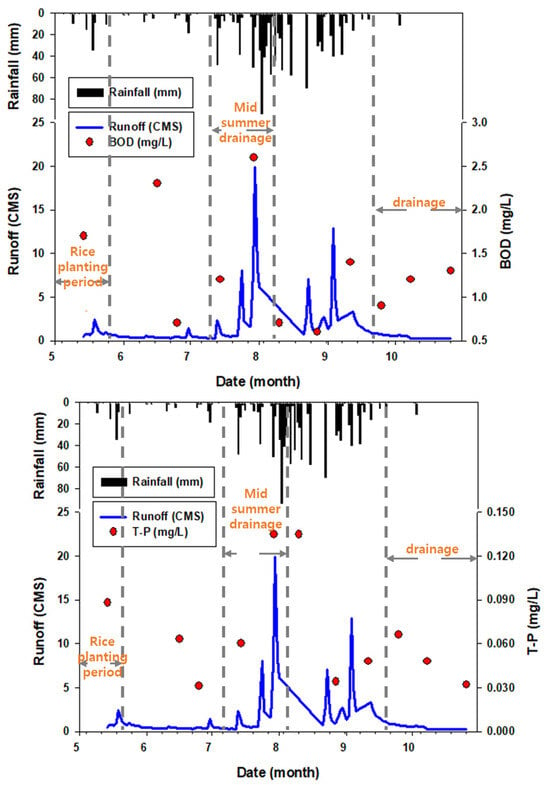
Figure 5.
Analysis of the water quality(BOD and T-P) according to the farming period at point H1.
The agricultural land area in the irrigation district of the Heungeop Reservoir is 815.2 ha, accounting for 14.5% of the total basin area (Figure 6). The fertilizers used for soil amendment and agricultural activities during rainy periods, including the end of May, the end of July to early August, and the end of September to October, were found to affect water pollution in the river. The effect of agricultural water discharge on the river water quality was limited, except for run-off during intensive farming periods. Therefore, appropriate measures should be taken to reduce pollutant runoff during water drainage periods. In addition, the target water quality for small basins in the future should be set according to the characteristics of the basin and in agricultural areas, considering the characteristics of the different farming periods. However, as this study did not account for the effect of prior precipitation and analyzed only short-term monitoring data, it is necessary to analyze long-term river water flow and quality and account for prior rainfall in future studies.
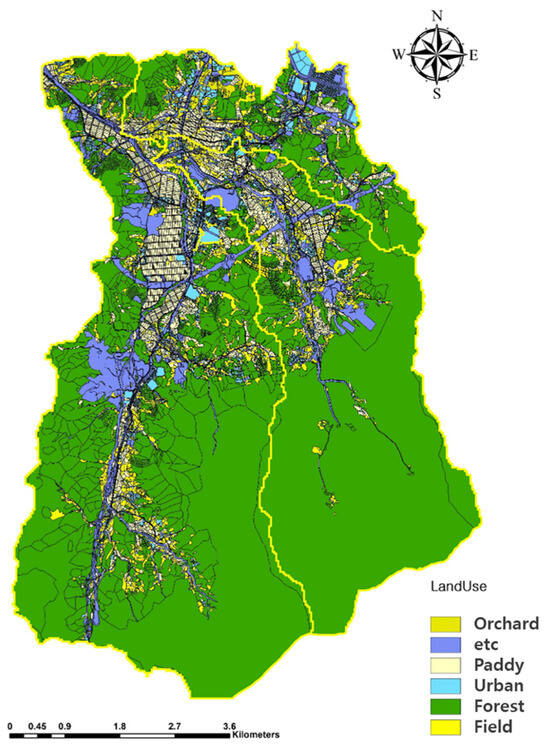
Figure 6.
Land use in the study area.
3.2. Aquatic Ecology Monitoring Results
In the case of fish, a total of six families and 10 species of freshwater fish were surveyed at the aquatic ecological monitoring sites (Table 5). A total of 100 freshwater fish from three families and six species were detected at the MJ site, and 188 fish from five families and eight species were detected at the SG site. No legally protected species (rare and endangered species) were detected. One specimen of Odontobutis interrupta was found in each of the MJ and SG sites, respectively, and Micropterus salmoides, an ecosystem disturbance species, was detected at the SG site in the autumn. In terms of comparative abundance according to family, at the MJ site, carps were the most abundant, at 66.6%, and the Korean dark sleeper and Gobiidae each had an abundance of 16.7%. At the SG site, carps were the most abundant, at 50.0%, while loach, catfish, black rockfish, and Korean dark sleeper each had an abundance of 12.5%. These results indicate that carps were predominant in both streams. At the species level, Chinese minnow was the most abundant, at 45.0%, at the MJ site, followed by the striped shiner, pale chub, Korean spotted sleeper, and Amur goby. At the SG site, the striped shiner was the most abundant, at 40.4%, followed by the pale chub, Chinese minnow, Korean spotted sleeper, and dojo loach. Thus, striped shiner was the most abundant, followed by pale chub, Chinese minnow, Korean spotted sleeper, and Amur goby.

Table 5.
Fish species results collected in this study for each site.
We next calculated the clustering index for each stream. The dominance index was 0.36–1.00 for the MJ site and 0.71–0.86 for the SG site, and the diversity index was 0.44–1.49 for the MJ site and 1.06–1.40 for the SG site. The abundance index was higher for the SG site (0.88–1.34) than for the MJ site (0.34–1.09). The evenness index for the MJ site was 0.63–0.83 and, for the SG site, was 0.66–0.78. The FAI for freshwater fish was evaluated as normal (grade C), with an average value of 46.9 for the MJ site and 53.2 for the SG site. In the first survey conducted in May, the FAI for the MJ site was 68.8, which is considered good (grade B), whereas, in the second survey conducted in September, it was 25.0, which is interpreted as bad (grade D). The MJ site has various flow rates and various riverbed structures; however, numerous fish were lost due to flooding caused by excessive rainfall, and the FAI was low because the fish population did not recover in the second survey. In contrast, the SG site was located downstream, and due to the influence of various pollutants, such as drainage of the surrounding agricultural land and soil, the FAI was evaluated as normal (grade C).
In the case of epilithic diatoms, a total of 2 order, 3 suborders, 8 families, 20 genera, and 54 species were identified. For the MJ site, the average cluster index was 0.39, the diversity index (H′) was 1.93, the abundance index (R) was 2.31, and the evenness index (J) was 0.58. In the first survey, the diversity, abundance, and evenness indices were found to be high, and in the second survey, the dominance index was high. For the SG site, the dominance index was 0.44, the diversity index was 3.51, the abundance index was 1.96, and the evenness index was 1.10. In the first survey, the dominant species, diversity, abundance, and evenness indices were all high. The abundance index for the MJ site was higher than that for the SG site, whereas the dominance, diversity, and evenness indices for the SG site were higher than those for the MJ site. The TDI for epilithic diatoms was normal (grade C) for the MJ site, with an average of 58.7, and bad (grade D), based on a value of 35.8, for the SG site.
In the case of benthic macroinvertebrates, a total of 5 phyla, 6 classes, 13 orders, 31 families, and 41 species were identified at each of the two points at the MJ and SG sites. The analysis according to season revealed that relatively many species were present in both rivers in autumn. The average population density per unit area was 137 for the MJ site and 188, which was relatively high, for the SG site. On average, insects accounted for 69.8% of the population of benthic macroinvertebrates, with percentages of 56.2% at the MJ site and 79.7% at the SG site. In the cluster index analysis, the dominance index was 0.52–0.59 for the MJ site and 0.49–0.66 for the SG site, the diversity index was 2.00–2.15 for the MJ site and 1.85–2.26 for the SG site, the abundance index was 2.60–3.72 for the MJ site and 3.23–4.22, which was higher, for the SG site, and the evenness index was 0.68–0.82 for the MJ site and 0.64–0.72 for the SG site.
The BMI values of 63.2 for the MJ site and 59.4 for the SG site in the first survey were evaluated as normal (grade C). In the second survey at the MJ site in autumn, the BMI of 65.3 was evaluated as good (grade B). The BMI values for the MJ site were higher than those for the SG site, likely because the MJ site has various habitat environments, various flow rates, and various riverbed structures, whereas, at the MJ site, land use, including agricultural land use and soil sedimentation, is higher. An environmental quality evaluation based on the ESB revealed that, in the first survey, the MJ site showed a grade II, whereas, in other surveys, the MJ site, and the SG site in all the surveys, showed a grade II.
The TDI was evaluated as normal (grade C), based on an average value of 58.7, for the MJ site and as bad (grade D), based on an average value of 35.8, for the SG site. We believe this is because the proportion of saproxenous taxa, which are more tolerant to relatively polluted water, was higher at the SG site than at the MJ site.
As a result of the two times of monitoring, the average BMI and FAI at both points were evaluated as normal (grade C). However, in the autumn survey, the FAI for the MJ site was evaluated as bad (grade D). We believe this temporal low was observed because numerous fish were lost due to flooding caused by excessive rainfall and the fish population had not yet recovered.
According to the analysis of the data from 2010 to the present, at the MJ site, the TDI had little effect on flow fluctuations and tended to gradually improve (Figure 7). The BMI tended to decrease, but we reason that this was a temporal phenomenon due to low flow rates because of drought damage in 2015 and 2016. The FAI has been improving, and in 2020, we reasoned that the lower rating was because numerous fish were lost due to flooding caused by excessive rainfall.
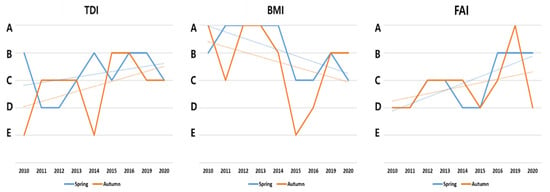
Figure 7.
Analysis of past aquatic health evaluation data (TDI, BMI, FAI) of the MJ site.
3.3. Analysis of the Agricultural Return Flow Contribution to Downstream Rivers through Stream Flow and Ecological Modeling
3.3.1. Identification of Long-Term Flow Rate Variation Using the SWAT Model
Simulation of the river flow rate using the SWAT model revealed R2 = 0.737, NSE = 0.706 at point H1 and R2 = 0.749, NSE = 0.673 at point H2, all of which were rated as good, indicating that the model well simulated reality (Figure 8). Although model optimization was limited by a slight difference between the precipitation data collected at the weather station and flow measurement data obtained through monitoring, the results of the river flow measurements and simulation showed similar trends, as shown in Figure 9.
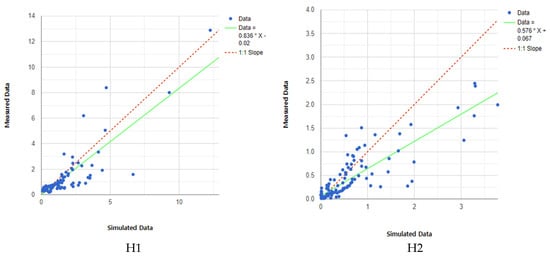
Figure 8.
Correlation between river monitoring data and SWAT model simulation results (* mark means multiplication).
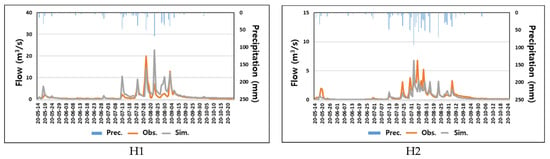
Figure 9.
Comparison of river monitoring results and simulation results.
3.3.2. Evaluation of River Contribution of the Return Water
To evaluate the effect of agricultural water return on downstream rivers, we used data on the supply volumes from Rural Community Corporation reports to calculate the return quantity. The return quantity was calculated setting the return rate of agricultural water to 35%. The return quantity in the downstream beneficiary area of the Heungeop Reservoir was calculated to be approximately 45,000 tons (0.02 m3/s) to 498,000 tons (0.19 m3/s) from April to October 2017, 46,000 tons (0.02 m3/s) to 465,000 tons (0.17 m3/s) in 2018, and 63,000 tons (0.02 m3/s) to 754,000 tons (0.28 m3/s) in 2019. The flow rate of the main stream at the end of the beneficiary area downstream of the Heungeop Reservoir calculated by the hydrological model was calculated to be 0.17–7.66 m3/s from April to October 2017, 1.20–3.24 m3/s in 2018, 0.16–2.33 m3/s in 2019, and 0.23–2.28 m3/s in 2020 (Figure 10).
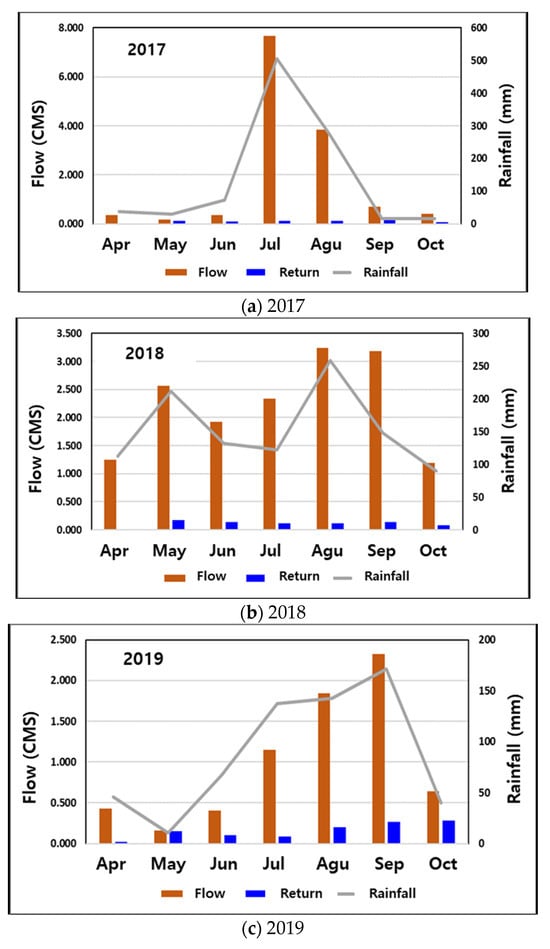
Figure 10.
Comparative analysis of the total flow and return flow in rivers at the outlet of the watershed.
The ratio of return water to main stream flow was 1.5–77.8% in 2017, 1.4–7.0% in 2018, and 5.7–96.5% in 2019. Therefore, it differed depending on the rainfall, ranging from a minimum of 1.4% to a maximum of 96.5%. The ratio of return water to main stream flow, excluding the inflow tributary flow at the end of the beneficiary area downstream of the Heungeop Reservoir, was 1.4–100.0% in 2017, 2.3–15.4% in 2018, 10.7–100.0% in 2019, and 6.5–35.9% in 2020. This ratio also differed depending on the rainfall, ranging from a minimum of 1.4% to a maximum of 100.0%. Comparison of the flow rate and return water by season for each year revealed that the fiver flow significantly increased during summer rainfall; therefore, the effect of the return water was generally small, but during the rainy season (April–June), it was significant.
3.3.3. Results of Environmental Ecological Flow Rate Calculation Using the PHABSIM Model
The optimal ecological flow rate for a representative fish species, striped shiner, was calculated considering the performance of river and aquatic ecology monitoring using the PHABSIM model and was approximately 1.2 m3/s, as shown in Figure 11. Furthermore, according to the literature review [46], the optimal ecological flow for striped shiner was found to be 1.0 m3/s, which is similar to the results of this study. It also indicates that the optimal ecological flow rate for striped shiner is 1.2 m3/s, which implies that the habitat area for striped shiner is the most widely distributed
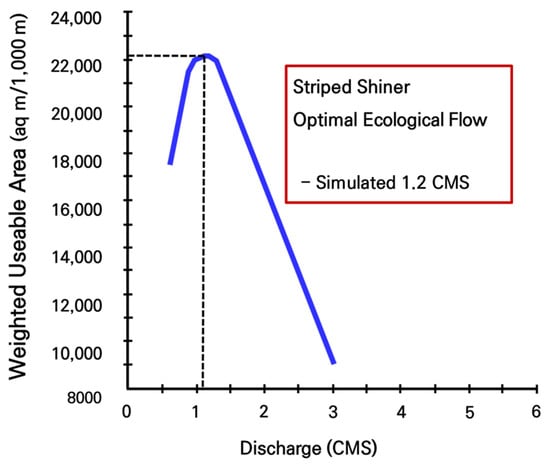
Figure 11.
Result of the calculation of the optimal ecological flow for striped shiner.
A comparison of the long-term runoff simulation results with the optimal ecological flow rate of the river at the outlet of the basin revealed that it differed by year depending on the difference in rainfall. In general, in the summer months of July–September—except in 2018, when the rainfall was higher than normal—the flow rate of the main stream was in line with the optimal ecological flow rate (1.2 CMS). In contrast, in April–June, which are non-rainy months, the optimal ecological flow rate was not reached. Therefore, the ratio of return water for agricultural use is not small during rainy periods, and the return water can play an important role in securing the optimal ecological flow rate of the river.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the Heungeop Reservoir located in Wonju-si, Gangwon-do, was monitored to evaluate the impact of agricultural water on the downstream river quantity, quality, and ecology, considering the agricultural return water quantity in the rural watershed. Analysis of the aquatic ecology monitoring results and data from 2010 to the present for the Maeji Stream Branch revealed that the TDI was not substantially affected by flow rate fluctuations and gradually improved. The BMI tended to decrease, but we reasoned this was because of a temporal low due to a decrease in the flow rate because of drought in 2015 and 2016. The FAI showed an improving trend, except in 2020, when there was a temporary loss of fish due to floods caused by heavy rainfall. The results revealed that the average water pollutant concentration as reflected by the BOD5 and T-P was 1.6–1.9 times higher than the average during autumn, when paddy water is drained to prepare for farming activities in the following year. The effect of discharged agricultural water on the water quality of downstream rivers was found to be very limited, except during the autumn farming season. As a result of calculating the optimal ecological flow rate for the representative fish species (striped shiner) using the PHABSIM model, it was found to be about 1.2 m3/s. As a result of comparing the optimal ecological flow rate calculation with the stream flow rate simulated by the SWAT model and comparing the flow rate and return water for each period, the river flow significantly increased during the summer rainy period. The effect of return water was small, but during the rainy period (April–June), it was significant. Comparison of the flow rate of long-term runoff simulation results and the optimal ecological flow rate (1.2 m3/s) revealed that, at the outlet of the watershed, the optimal ecological flow rate was achieved in July–September, except in 2018, when the rainfall was higher than usual. In contrast, the optimal ecological flow rate was not achieved in April–June, which are non-rainy months. Thus, the ratio of return water for agricultural use was not small during rainstorms, and return water may play an important role in securing the optimal ecological flow rate of the river.
According to the results of this study, it is necessary to reduce the loss of agricultural water supplied from agricultural reservoirs and to secure river maintenance water by managing the ecological flow rate in downstream rivers. To secure the ecological flow rate in the dry season, it is necessary to secure the reservoir water volume and create a sufficient flow rate, and to secure the minimum flow rate for normal river function and river ecosystem conservation, the agricultural return water volume has to be secured. The optimal ecological flow rate calculated in this study can be used to evaluate the environmental function of agricultural return water and can be expected to reevaluate agricultural water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K. and K.J.L.; methodology, Y.S.; investigation, M.S. and T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, T.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.S., D.L. and K.J.L.; supervision, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through the Agricultural Foundation and Disaster Response Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (322081-3).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Taesung Kang was employed by the company EM Research Institute. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Shen, X.; Yuan, G.; Wang, J. Water environment management and performance evaluation in central China: A research based on comprehensive evaluation system. Water 2019, 11, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachova, N.I.; Nakayama, M.; Jansky, L. International Water Security; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan; New York, NY, USA; Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, C.; Bakker, K. Water security: Debating an emerging paradigm. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenmark, M.; Molden, D. Wake up to realities of river basin closure. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2008, 24, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Hydrologic alteration at the upper and middle part of the Yangtze river, China: Towards sustainable water resource management under increasing water exploitation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fraiture, C.; Wichelns, D. Satisfying future water demands for agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J.; Dronin, N.; Endejan, M.; Golubev, G.; Kirilenko, A. A new assessment of climate change impacts on food production shortfalls and water availability in Russia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2007, 17, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Qureshi, M.E. Global water crisis and future food security in an era of climate change. Food Policy 2010, 35, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turral, H.; Burke, J.; Faurès, J.-M. Climate Change, Water and Food Security; FAO Water Reports 36; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, W.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hong, E.M.; Kim, J.T. Assessment of irrigation efficiencies using smarter water management. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 55, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.M.; Reeder, R.J. Farm-Based Recreation: A Statistical Profile; Economic Research Service ERR-53: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley, C. Evaluating the benefits of peri-urban agriculture. J. Plan. Lit. 2012, 27, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellerstein, D.; Nickerson, C.; Cooper, J.C.; Feather, P.; Gadsby, D.; Mullarkey, D.; Tegene, A. Farmland Protection: The Role of Public Preferences for Rural Amenities; Economic Research Service AER-815: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zoebl, D. Is water productivity a useful concept in agricultural water management? Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 84, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinton, S.M.; Lupi, F.; Robertson, G.P.; Hamilton, S.K. Ecosystem services and agriculture: Cultivating agricultural ecosystems for diverse benefits. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-C.; Gim, U.-S.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.-S. The multi-functionality of paddy farming in Korea. Paddy Water Environ. 2006, 4, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kwon, H.; Kim, S.; Jun, B. Identification of landscape multifunctionality along urban-rural gradient of coastal cities in South Korea. Urban Ecosyst. 2020, 23, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnino, M.; Ward, F.A. Economics of agricultural water conservation: Empirical analysis and policy implications. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2012, 28, 577–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Nam, W.-H.; Mun, Y.-S.; Bang, N.-K.; Kim, H.-J. Estimation of irrigation return flow on agricultural watershed in Madun reservoir. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 63, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Moon, J.-P. Estimation of return flow rate of irrigation water in Daepyeong pumping district. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 52, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.H.; Song, I.; Kim, J.-T.; Kang, M.S. Characteristics of irrigation return flow in a reservoir irrigated district. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 57, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-K.; Kim, G.-H.; Ko, I.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Seo, J.-W.; Jang, C.-L. Environmental Flow Assesment for Sustainable River Management in Guem River. In Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, 17 May 2007; pp. 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, D.S.; Brändle, J.M.; Seliger, C.; Zeiringer, B.; Ferreira, T.; Schmutz, S. Advancing towards functional environmental flows for temperate floodplain rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Ecological Flows in the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive; CIS Guidance Document, No. 31; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Hur, J.W. Comparative Analysis of Environmental Ecological Flow Based on Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) in Miho stream of Geum river system. Ecol. Resilient Infrastruct. 2022, 9, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L.; Richter, B.D.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Naiman, R.J.; Kendy, E.; Acreman, M.; Apse, C.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Freeman, M.C. The ecological limits of hydrologic alteration (ELOHA): A new framework for developing regional environmental flow standards. Freshwater Biol. 2010, 55, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerten, D.; Hoff, H.; Rockström, J.; Jägermeyr, J.; Kummu, M.; Pastor, A.V. Towards a revised planetary boundary for consumptive freshwater use: Role of environmental flow requirements. Current Opinion in Environ. Sustainability 2013, 5, 551–558. [Google Scholar]
- Grantham, T.; Mezzatesta, M.; Newburn, D.; Merenlender, A. Evaluating tradeoffs between environmental flow protections and agricultural water security. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H. Assessing water scarcity by simultaneously considering environmental flow requirements, water quantity, and water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Singha, P. Linking river flow modification with wetland hydrological instability, habitat condition, and ecological responses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 11634–11660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Assessment of multiple dam-and sluice-induced alterations in hydrologic regime and ecological flow. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Nam, W.-H.; Mun, Y.-S.; An, H.-U.; Kim, J.; Shin, Y.; Do, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Estimation of irrigation return flow from paddy fields on agricultural watersheds. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, C.; Lim, K.J.; Kim, J.; Ji, B.; Yeon, J. Web-based agricultural infrastructure digital twin system integrated with GIS and BIM concepts. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 215, 108441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, S.J. Relationships among functional properties of Californian grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. Shannon’s formula as a measure of specific diversity: Its use and misuse. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfah, M.; Fajri, S.N.; Nasir, M.; Hamsah, K.; Purnawan, S. Diversity, evenness and dominance index reef fish in Krueng Raya Water, Aceh Besar. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 348, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzian, P.; Erfanifard, S. The efficiency of indices of richness, evenness and biodiversity in the investigation of species diversity changes (case study: Migratory water birds of Parishan international wetland, Fars province, Iran). Biodivers. Int. J. 2017, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Park, Y.; Jeon, Y. Revision of Ecological Score of Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 251–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M. Use of the trophic diatom index to monitor eutrophication in rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.; Marvan, P. Zur präzisierung der biologischen klassifikation der reinheid fliessender grewässer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1961, 57, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, D.J. Fish Field and Laboratory Methods for Evaluating the Biological Integrity of Surface Waters; Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Office of Modeling, Monitoring Systems, and Quality Assurance, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttlah, R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, C.; Oh, C.; Hwang, S. Watershed-scale Hydrologic Modeling Considering a Detention Effect of Rice Paddy Fields using HSPF Surface-Ftable. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 60, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, P.B.; Hummel, P.R.; Donigian, A.S., Jr.; Imhoff, J.C. BASINS/HSPF: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1523–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Son, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, P.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Min, J.K.; Kim, A.R. Estimation of Habitat Suitability Index of Fish Species in the Gapyeong stream. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2011, 33, 626–639. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).