Monthly Runoff Prediction for Xijiang River via Gated Recurrent Unit, Discrete Wavelet Transform, and Variational Modal Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
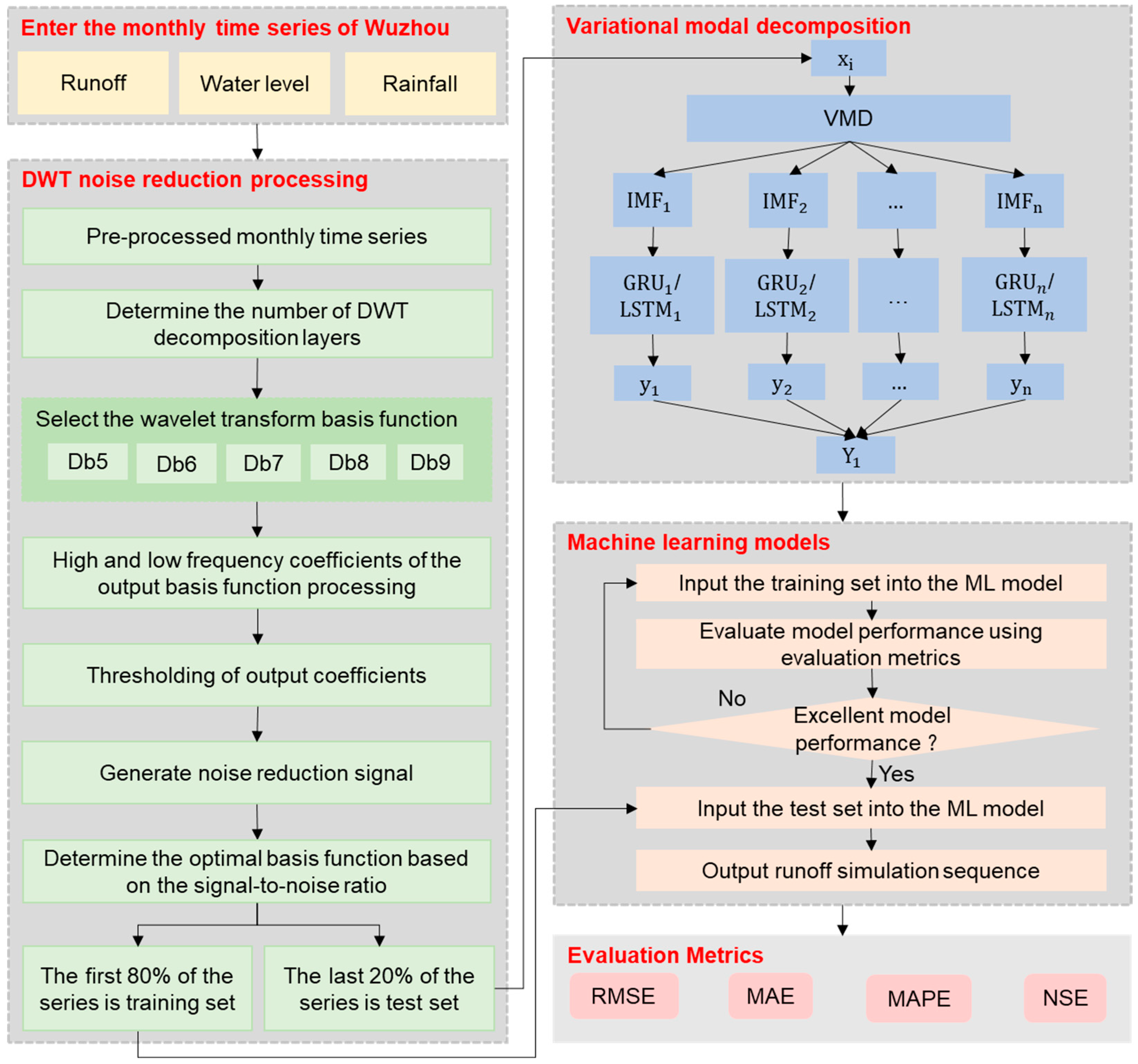
3. Methods
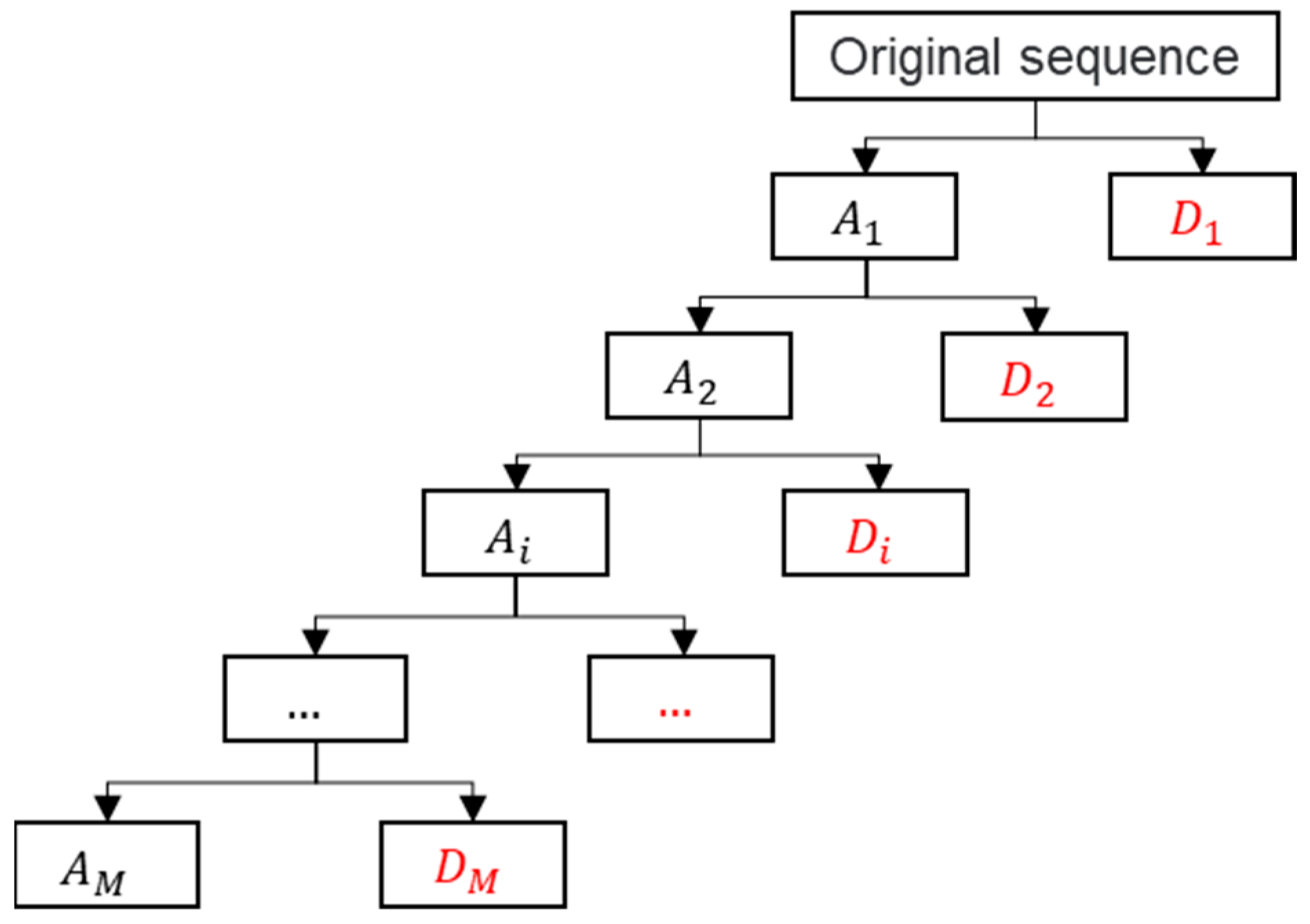
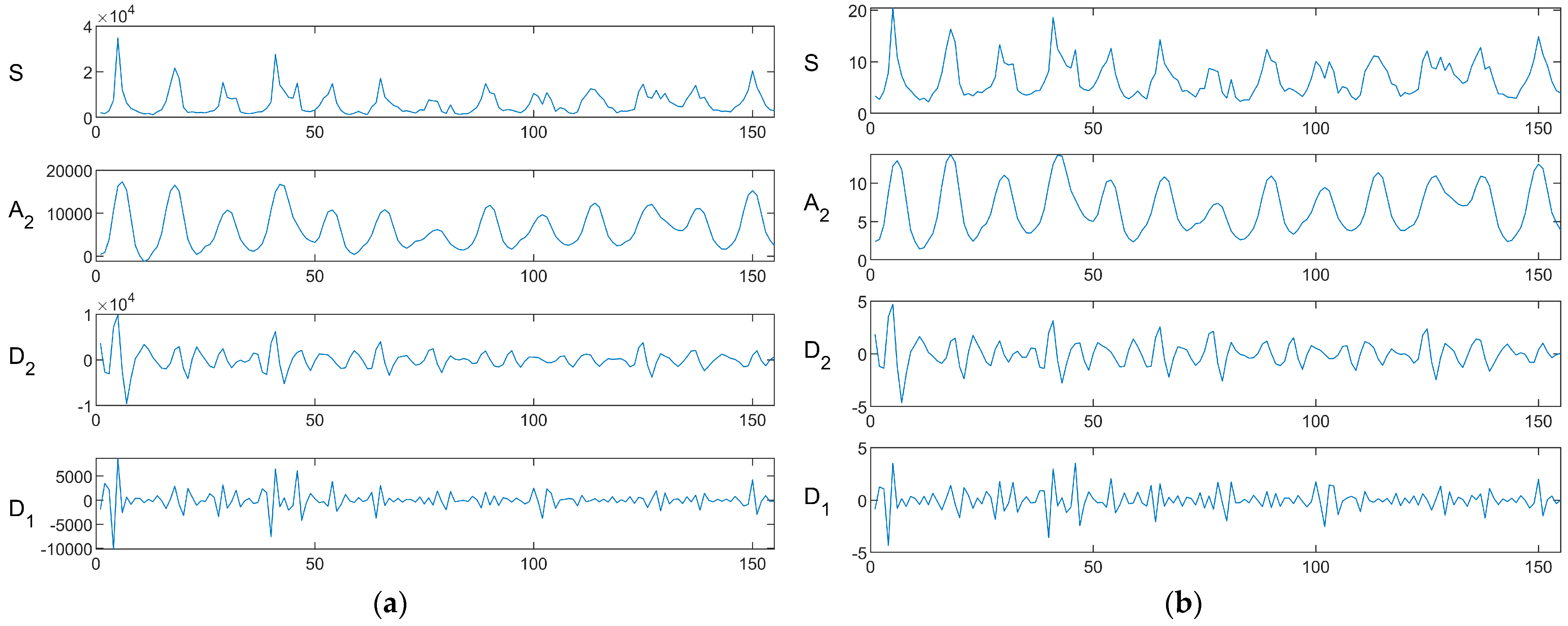
3.1. Discrete Wavelet Transform
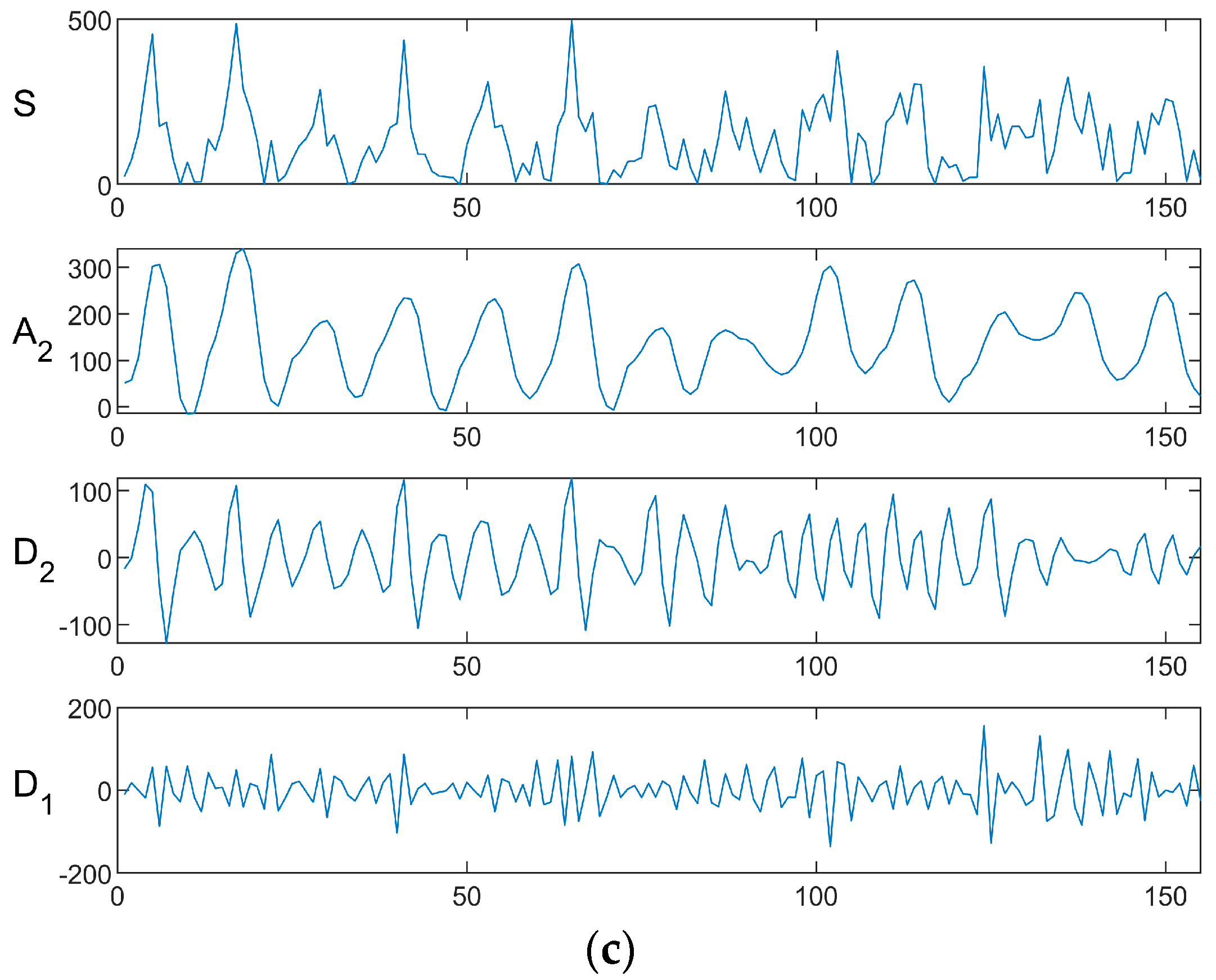
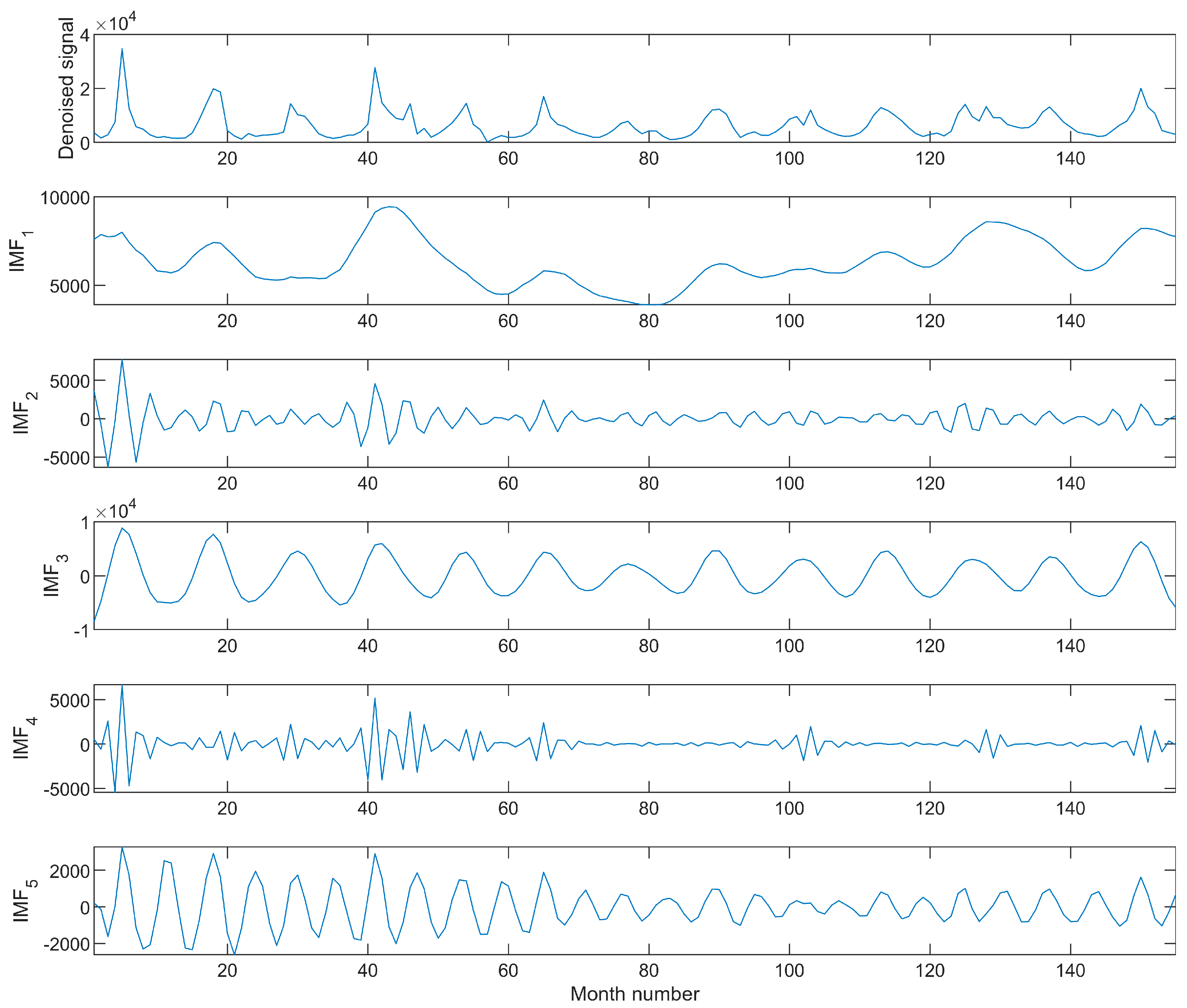
3.2. Variational Modal Decomposition
3.3. Recurrent Neural Network
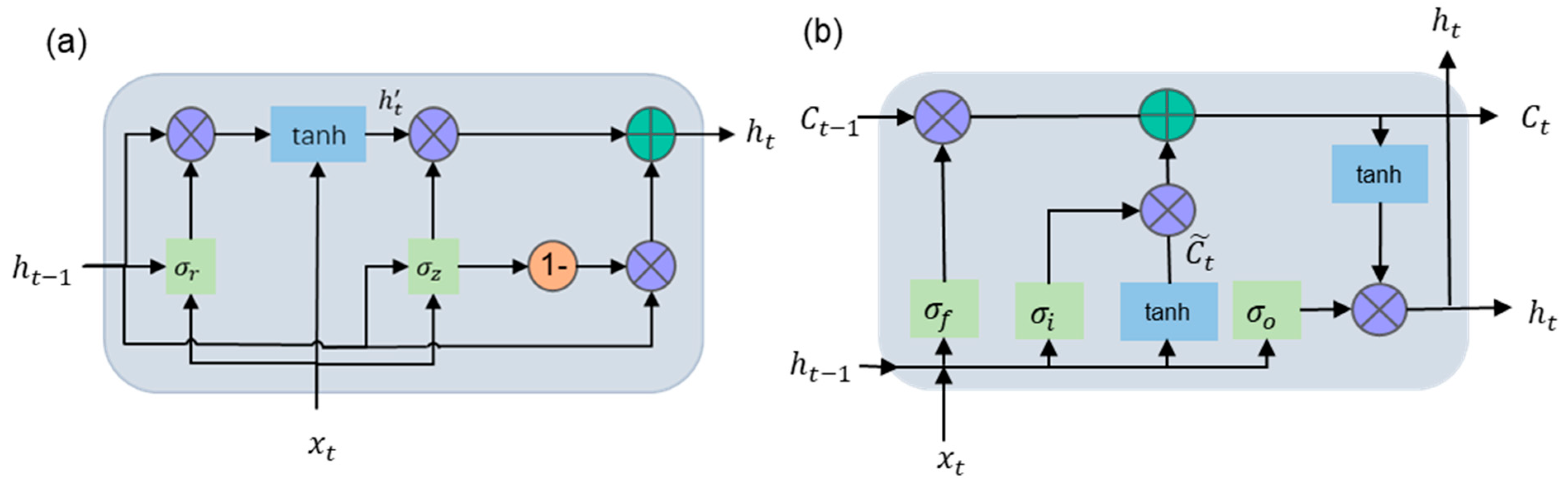
3.3.1. Gated Recurrent Unit
3.3.2. Long Short-Term Memory
3.4. Model Development
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
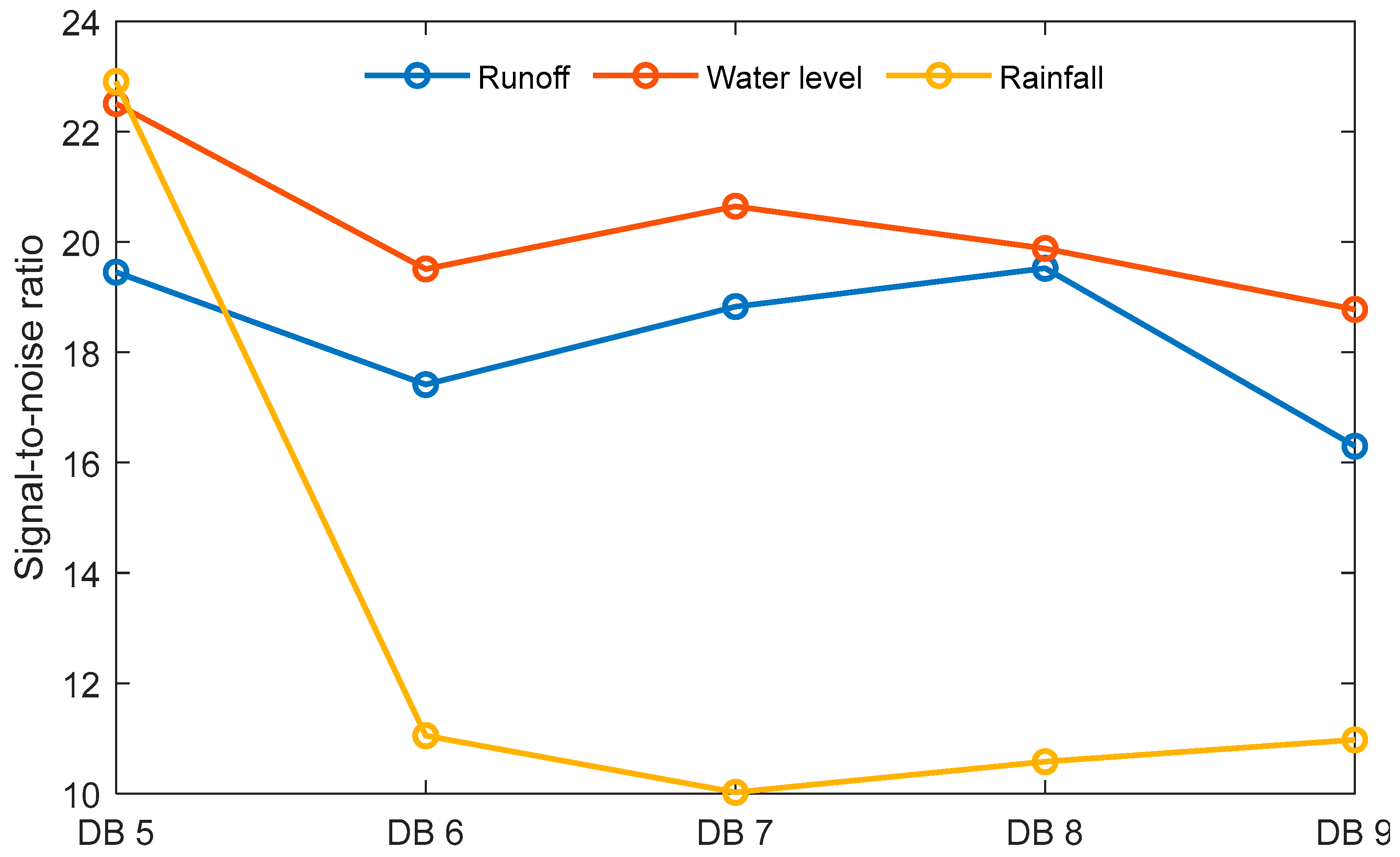
4.1. Performance of Discrete Wavelet Transform
4.2. Performance of Variational Modal Decomposition
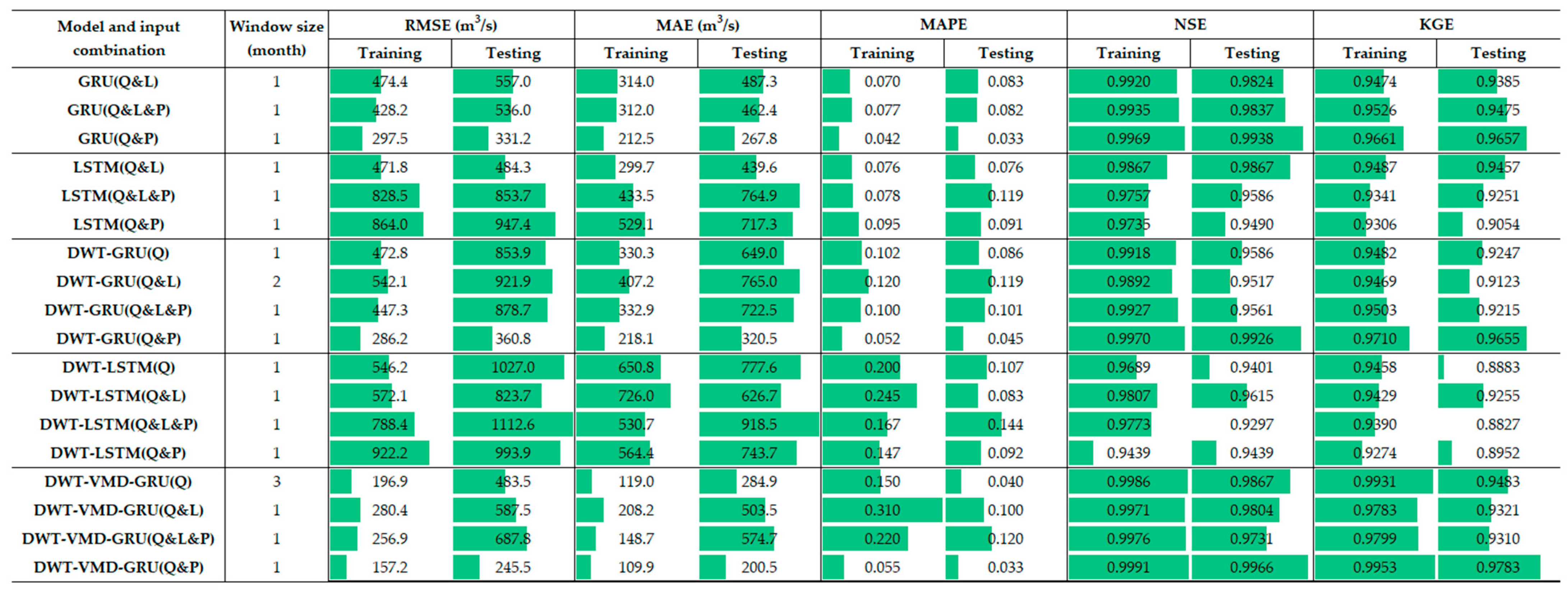
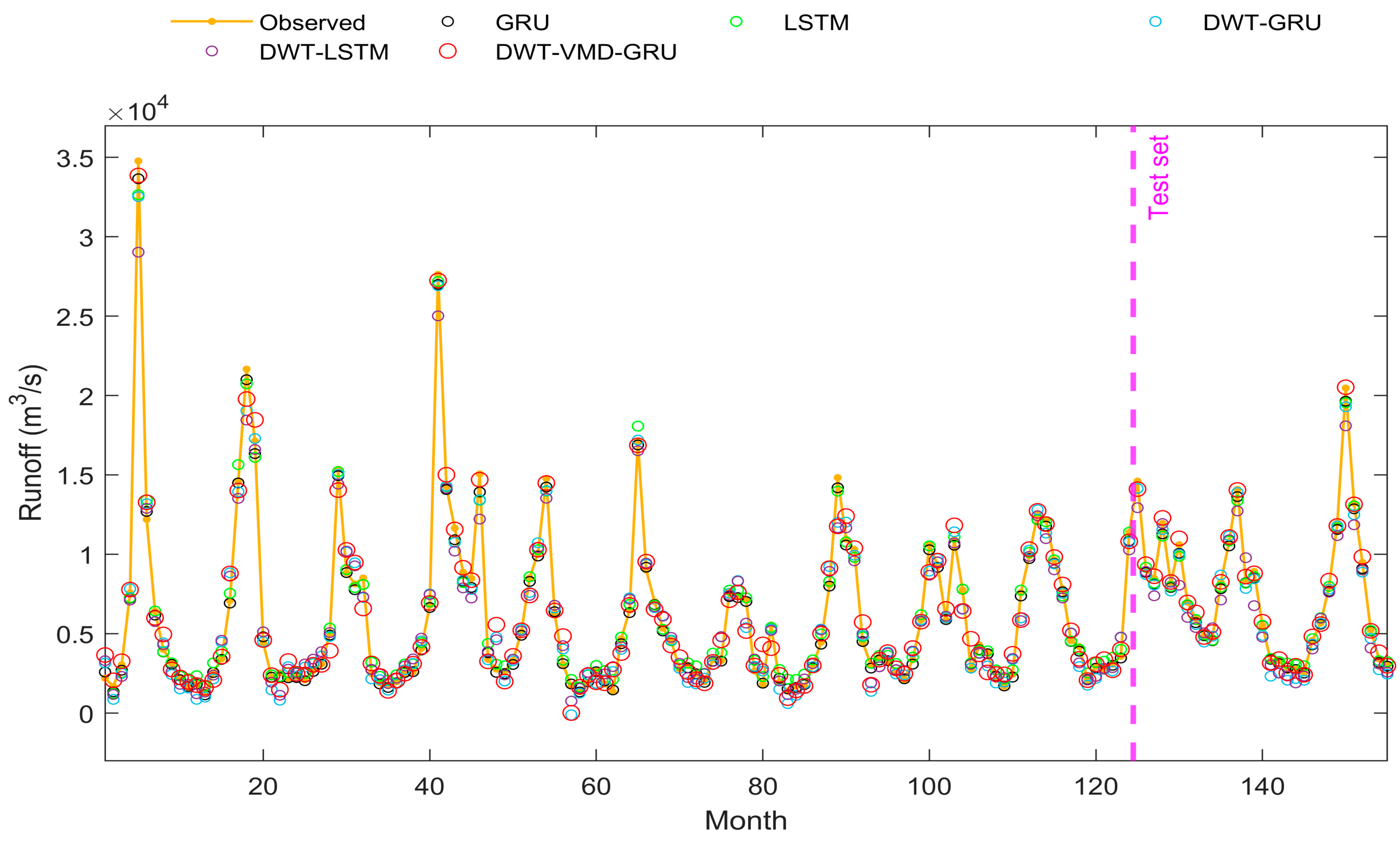
4.3. Performance of Neural Network Models
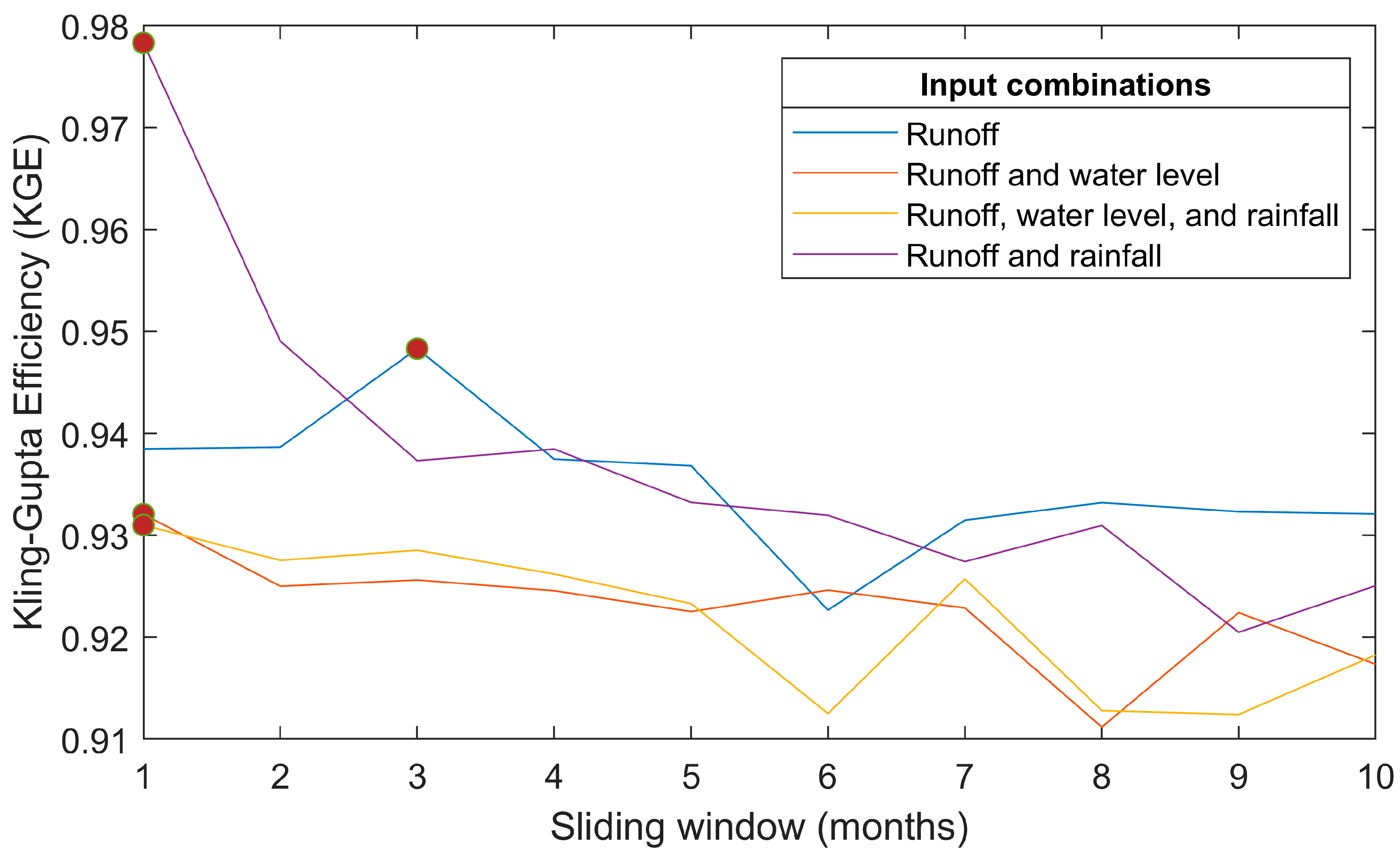
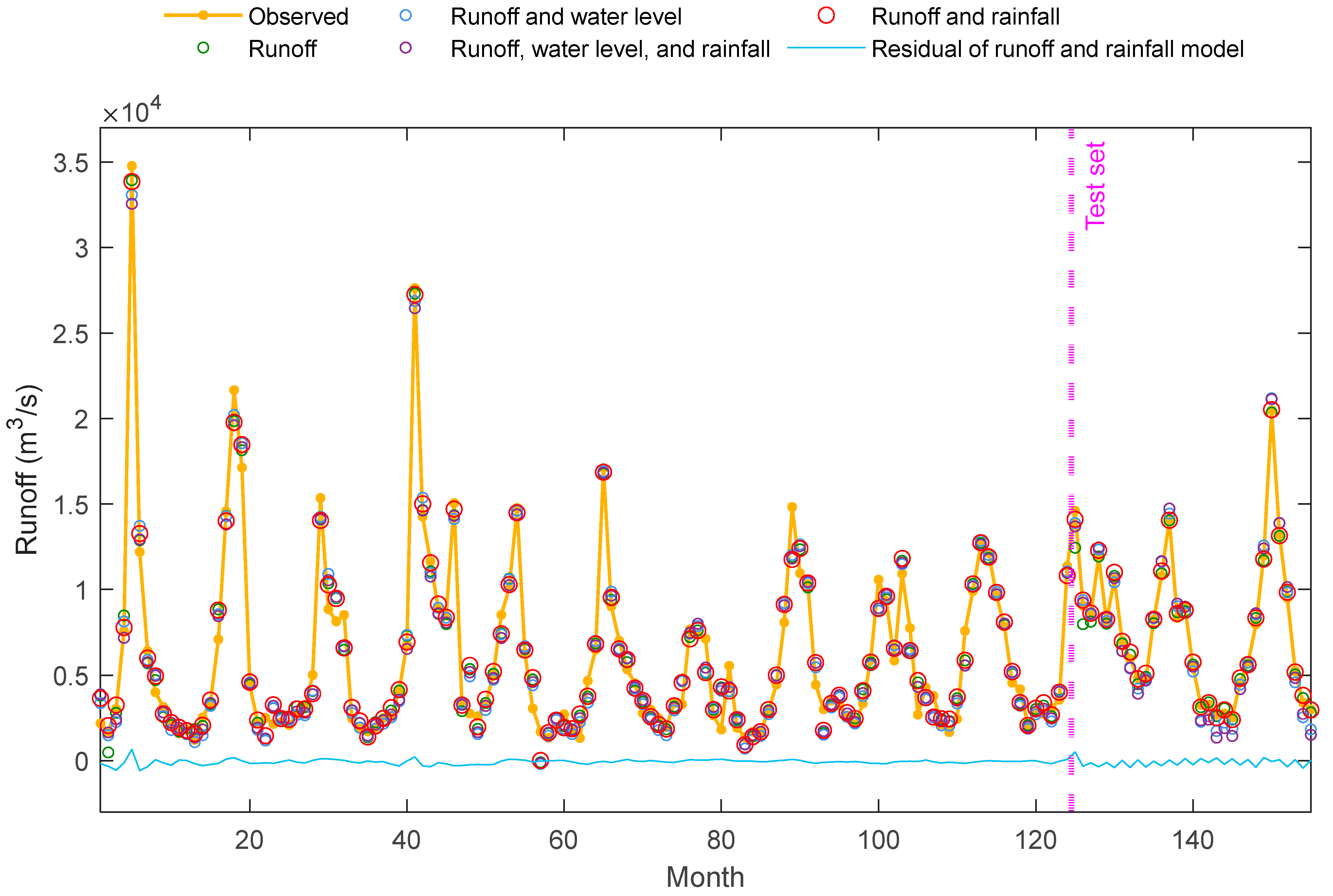
4.4. Window Size and Input Combinations of DWT–VMD–GRU
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, K.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Han, D.; Wang, G.; Shen, C. Physics-guided deep learning for rainfall-runoff modeling by considering extreme events and monotonic relationships. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.P.; Chen, H.; Gu, H.; Xie, J. AI-based techniques for multi-step streamflow forecasts: Application for multi-objective reservoir operation optimization and performance assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 5951–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.L.; Guo, Z.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, Y.N. RR-Former: Rainfall-runoff modeling based on Transformer. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.L.; Wang, F.D.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.N.; Chen, J.J.; Xia, R.L.; Jin, J. Rainfall-runoff modeling using long short-term memory based step-sequence framework. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.C.J.; Xiong, L.H.; Chen, H. A framework of integrating heterogeneous data sources for monthly streamflow prediction using a state-of-the-art deep learning model. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, A.; Sahoo, B.; Chatterjee, C. Two novel error-updating model frameworks for short-to-medium range streamflow forecasting using bias-corrected rainfall inputs: Development and comparative assessment. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Cheng, Q.; Chau, K.W.; Hu, H.; Zang, H.F.; Xu, D.M. An enhanced monthly runoff time series prediction using extreme learning machine optimized by salp swarm algorithm based on time varying filtering based empirical mode decomposition. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.H.; Lv, H.F.; Lv, S.J.; Sang, Y.T.; Wei, Y.Z.; Zhu, X.P. Enhancing robustness of monthly streamflow forecasting model using gated recurrent unit based on improved grey wolf optimizer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Yang, J.X.; Luo, Q.Y.; Wang, W.C.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhong, L.; Sun, G.-L. A Hybrid Model of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Sparrow Search Algorithm-Based Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks for Monthly Runoff Forecasting. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 909682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.G.; Luo, J.G.; Wang, N.; Lian, Y.N.; He, X.X. Decomposition ensemble model based on variational mode decomposition and long short-term memory for streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, S.F.; Kang, C.X.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.F.; Tang, M.; Huang, B.B. Can sampling techniques improve the performance of decomposition-based hydrological prediction models? Exploration of some comparative experiments. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, B.; He, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, D. A new precipitation forecast method based on CEEMD-WTD-GRU. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4120–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, H.; Liu, L.; Tian, F. Mid-long term forecasting of reservoir inflow using the coupling of time-varying filter-based empirical mode decomposition and gated recurrent unit. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 87200–87217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, G.; Hou, J.; Xie, J.; Lv, M.; Liu, F. Hybrid forecasting model for non-stationary daily runoff series: A case study in the Han River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibtain, M.; Li, X.; Azam, M.I.; Bashir, H. Applicability of a Three-Stage Hybrid Model by Employing a Two-Stage Signal Decomposition Approach and a Deep Learning Methodology for Runoff Forecasting at Swat River Catchment, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.C.; Chen, J.L.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, Q.S. Study on NO2 concentration prediction in Tianjin based on DWT-GRU model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Mo, L.; Jia, B.; Yang, Y.; Fang, W.; Qin, Z. A Novel Runoff Forecasting Model Based on the Decomposition-Integration-Prediction Framework. Water 2021, 13, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Cui, X.; Pei, R. A Novel Runoff Prediction Model Based on Support Vector Machine and Gate Recurrent Unit with Secondary Mode Decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.C.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Lin, Q.S. Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, H.; Sibtain, M. A multivariate streamflow forecasting model by integrating improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with additive noise, sample entropy, Gini index and sequence-to-sequence approaches. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, S.A.; Qin, T.L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, D.H. Wavelet transform-based trend analysis of streamflow and precipitation in Upper Blue Nile River basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, F.; Gharamaleki, A.F.; Jalilzadeh, M.; Akhoundzadeh, A. Prediction of River Stage-Discharge Process Based on a Conceptual Model Using EEMD-WT-LSSVM Approach. Water Resour. 2020, 47, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Hu, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y. Monthly Runoff Forecast of the Three Gorges Reservoir Based on Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network Model. Water Resour. Power 2022, 40, 10–13+49. [Google Scholar]
- Amininia, K.; Saghebian, S.M. Uncertainty analysis of monthly river flow modeling in consecutive hydrometric stations using integrated data-driven models. J. Hydroinformatics 2021, 23, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Singh, V.P. Machine Learning Models Coupled with Variational Mode Decomposition: A New Approach for Modeling Daily Rainfall-Runoff. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.; Kim, H.S. Case Study: Reconstruction of Runoff Series of Hydrological Stations in the Nakdong River, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.S.; Wang, J.; Lei, P.; Li, Y. A novel multi-step ahead forecasting model for flood based on time residual LSTM. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Yang, J. Comprehensive Analysis for Long-Term Hydrological Simulation by Deep Learning Techniques and Remote Sensing. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 875145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.S.; Liu, X.F.; Li, W.D. Daily suspended sediment concentration forecast in the upper reach of Yellow River using a comprehensive integrated deep learning model. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Jung, Y.; Seong, Y.; Lee, S. Development of Deep Learning Models to Improve the Accuracy of Water Levels Time Series Prediction through Multivariate Hydrological Data. Water 2022, 14, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, H.; Jian, H.; Zha, W.; Wang, J.; Shu, Z.; Yao, S.; Han, H. A combined hydrodynamic model and deep learning method to predict water level in ungauged rivers. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S. A novel Interval Decomposition Correlation Particle Swarm Optimization-Extreme Learning Machine model for short-term and long-term water quality prediction. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Technical note: Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash-Sutcliffe and Kling-Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chen, X.H.; Wu, P.; Jin, H.Y. Combining time varying filtering based empirical mode decomposition and machine learning to predict precipitation from nonlinear series. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C. Jiyu VMD-LSTM de heliu liuliang yuce fangfa [River flow prediction method based on VMD-LSTM]. Water Resour. Hydropower Northeast. China 2024, 42, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, P.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Time-series generative adversarial networks for flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Chen, X.H.; Khan, A.; Zhang, Y.K.; Kuang, X.X.; Liang, X.Y.; Taccari, M.L.; Nuttall, J. Daily runoff forecasting by deep recursive neural network. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Tiwari, H.L.; Nateriya, R. Runoff modeling in Kolar river basin using hybrid approach of wavelet with artificial neural network. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of IMFs (K) 1 | Center Frequency | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | IMF6 | IMF7 | IMF8 | |
| 1 | 0.0261 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 2 | 0.0120 | 0.2794 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 3 | 0.0043 | 0.3565 | 0.1297 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 4 | 0.0038 | 0.2324 | 0.1142 | 0.4163 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 5 | 0.0035 | 0.2426 | 0.1149 | 0.4197 | 0.1376 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 6 | 0.0035 | 0.2237 | 0.1143 | 0.4252 | 0.1389 | 0.3253 | n/a | n/a |
| 7 | 0.0034 | 0.2241 | 0.1144 | 0.4252 | 0.1379 | 0.3324 | 0.0577 | n/a |
| 8 | 0.0034 | 0.2224 | 0.1144 | 0.4186 | 0.1363 | 0.3352 | 0.0448 | 0.4617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, D. Monthly Runoff Prediction for Xijiang River via Gated Recurrent Unit, Discrete Wavelet Transform, and Variational Modal Decomposition. Water 2024, 16, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111552
Yang Y, Li W, Liu D. Monthly Runoff Prediction for Xijiang River via Gated Recurrent Unit, Discrete Wavelet Transform, and Variational Modal Decomposition. Water. 2024; 16(11):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111552
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuanyuan, Weiyan Li, and Dengfeng Liu. 2024. "Monthly Runoff Prediction for Xijiang River via Gated Recurrent Unit, Discrete Wavelet Transform, and Variational Modal Decomposition" Water 16, no. 11: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111552
APA StyleYang, Y., Li, W., & Liu, D. (2024). Monthly Runoff Prediction for Xijiang River via Gated Recurrent Unit, Discrete Wavelet Transform, and Variational Modal Decomposition. Water, 16(11), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111552








