Abstract
Water is a fundamental and crucial natural resource for human survival. However, the global demand for water is increasing, leading to a subsequent decrease in water availability. This study addresses the critical need for improved water resource forecasting models amidst global water scarcity concerns exacerbated by climate change. This study uses the best weather and water resource forecasting model for sustainable development. Employing a Recurrent Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory (RNN-LSTM) approach, the research enhances drought prediction capabilities by integrating secondary data of the rainfall, temperature, and ground and surface water supplies. The primary objective is to forecast water resources under changing climatic conditions, facilitating the development of early warning systems for vulnerable regions. The results from the LSTM model show an increased trend in temperature and rainfall patterns. However, a relatively unstable decrease in rainfall is observed. The best statistical analysis result was observed with the LSTM model; the model’s accuracy was 99%, showing that it was quite good at presenting the obtained precipitation, temperature, and water data. Meanwhile, the value of the root mean squared error (RMSE) was about 13, 15, and 20, respectively. Therefore, the study’s results highlight that the LSTM model was the most suitable among the artificial neural networks for forecasting the weather, rainfall, and water resources. This study will help weather forecasting, agriculture, and meteorological departments be effective for water resource forecasting.
1. Introduction
Climate change poses a significant global challenge in the 21st century, manifesting as glacier melting, temperature variability, and diminishing freshwater resources [1,2]. The rise in global average temperatures by 0.87 degrees Celsius has resulted in sea level increases ranging from 52 to 98 cm. Water, essential for sustaining life, has historically played a crucial role in developing advanced societies, exemplified by ancient civilizations like Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Indus Valley [1]. With the exponential growth of the world population, there has been a nearly sixfold rise in global water demand compared to the previous century, reflecting the escalating pressures on water resources [1]. According to NOAA 2023 data, the average surface temperature worldwide (including land and ocean) was 0.86 °C in 2022, making it the sixth warmest year since records began in 1880. If current trends persist due to human activities, global warming will increase by 1.5 °C between 2030 and 2052 [3,4,5]. Elevated temperatures disturb the hydrological cycle by accelerating the evaporation of water into the atmosphere, resulting in droughts in certain regions [6,7,8]. The worldwide precipitation over terrestrial areas has grown by 0.1 inches per decade [2]. In addition to long-term changes, scientists have associated climate change with extreme and combined phenomena, such as floods and droughts, which adversely affect society and pose challenges to water security [9,10,11]. The depletion of natural resources and increased demand for water are contributing to the reduction of water supplies, particularly in emerging nations such as Pakistan. Eighty percent of Pakistan’s 21.5 million hectares of arable land are irrigated mainly through the Indus River System (IRS) [3,4].
The primary river system in Pakistan is experiencing increasing strain due to population growth and diminished snowfall in the Himalayas and Karakorum Mountain ranges. Pakistan uniquely combines water resources, encompassing glaciated mountains, the Indus Basin River Water System (IRS), and an intricate network of canals and distributaries. Pakistan is experiencing a rapid transition from water stress to water scarcity [12]. This transition can be attributed to various factors, including population growth, the inadequate management of water resources, inefficient water distribution systems, and a need for more public awareness regarding water conservation [13]. Pakistan, boasting an annual growth rate of 1.75%, ranks as the fifth most populous nation globally. Accurate evaluation of water shortage constitutes the initial measure in tackling the challenges associated with water scarcity. Most prior studies on water scarcity have predominantly concentrated on blue water, which refers to accessible freshwater sources. Groundwater, streams, and lakes are sources of water [5]. Anticipated climatic changes, notably shifts in precipitation, will impact renewable water supplies, resulting in fluctuations in water shortages [6]. Climate change has caused rising temperatures, leading to sudden shifts in the rainfall patterns strongly connected to agricultural production, water availability, and forest resources [14,15,16,17]. The distribution and intensity of rainfall have significantly changed, leading to catastrophic droughts and destructive floods that harm fertile areas and infrastructure. Like many nations relying on agriculture in semiarid regions, Pakistan must implement climate-smart crop management practices to ensure food security [18,19,20]. Implementing climate change mitigation solutions should be a high policy priority. Climate change impacts both the intensity and quantity of annual rainfall. Several regions in the country were experiencing yearly rainfall below 250 mm, necessitating agricultural and irrigation infrastructure improvements such as irrigation channels, canals, and dams for water retention. Water-saving techniques and the most advanced irrigation scheduling technologies must be implemented. Livestock accounts for almost 41% of greenhouse gas emissions in Pakistan [7,8].
The Indus Basin covers 566,000 square kilometers, and 80% of Pakistan’s population resides in this area. Pakistan has become water-stressed in the past decade [21,22]. The United Nations (UN) has calculated that Pakistan’s per capita water availability has reached 1090 m3. Pakistan’s water supplies are facing significant strain because of the constantly increasing population. An increase in population necessitates increased food production, although no additional water resources are available for this purpose [23,24]. The Government of Pakistan has highlighted water shortage as the most problematic issue since the water needed for agriculture is crucial for developing the agriculture industry and, as a result, for reducing poverty [25]. The Ministry of Water Resources released the National Water Policy in April 2018 to tackle Pakistan’s existing water resource management challenges and set specific goals to be accomplished by 2030. The focus was on promoting the sustainable use of water resources and introducing the idea of maximizing crop yield per water unit [26,27,28].
Extensive research has investigated the difficulties linked to water resource management in Pakistan. Society is grappling with the significant challenge of water scarcity, which is mainly caused by population growth, urban expansion, and the impacts of climate change. Water supplies are further strained due to ineffective irrigation techniques and insufficient distribution infrastructure [29,30]. Pakistan’s water resource management is hindered by inadequate storage capacity and poorly maintained dams and reservoirs, emphasizing the necessity for infrastructure development [30]. The lack of appropriate infrastructure for wastewater treatment worsens the issue, intensifying contamination and the use of technologies in water management [31]. Prioritizing and evaluating prospective climate change and land-use change trends is crucial before initiating any water resource projects [32].
Nevertheless, the escalating population, agricultural activities, and other domestic needs have propelled Pakistan into water scarcity [33]. Furthermore, there exists an imbalance in the accessibility of water for drinking, irrigation, and other applications [34]. Pakistan is physically advantageous due to its location in rain-prone regions and diverse temperature zones, encompassing four distinct climates and experiencing consistent rainfall throughout the year. According to a survey conducted by the World Bank, Pakistan experiences an average precipitation of 200 mm throughout the period spanning from July to September. Regrettably, most precipitation is directed into the Arabian Sea due to flooding and inadequate water storage and drainage infrastructure [35,36,37,38].
The research article has been meticulously developed, considering the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) about providing safe drinking water across Pakistan. Additionally, it addresses the various dimensions of water storage, management, fair distribution, and the application of technology for wastewater recycling. The article offers a comprehensive compilation of recommendations to attain the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030. It serves as a valuable policy input for the relevant governmental entities in Pakistan [39]. The research findings indicate that the forecast results produced by the LSTM model exhibit strong concordance with the actual observed values.
Furthermore, the LSTM model demonstrates notable flexibility and efficiency [40,41,42]. In recent years, there has been a noteworthy progression and innovation in developing water quality and water management forecast models utilizing the LSTM model. Specifically, the LSTM deep learning model and other data-driven techniques have substantially improved. Notably, using the LSTM hybrid model and gradient-boosting decision tree has shown promise in predicting dissolved oxygen concentration (DO) in aquaculture and water management [43]. The research introduces a continuous hourly rainfall–runoff model designed for forecasting the next 24 h. It incorporates advanced deep learning techniques such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) learning, a Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function, dropout regularization, mini-batch training, and GPU acceleration. In addition to these deep learning methods, other machine learning approaches, such as multivariate linear regression, Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and Gaussian processes, were considered [44]. This paper illuminates a significant gap in the current body of research concerning the sustainable management of water resources in Pakistan. While most studies have traditionally leaned on theoretical frameworks to address water sustainability, a gap exists in leveraging advanced predictive models, particularly Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) capabilities. The LSTM model, renowned for its proficiency in forecasting through sequential data analysis, holds untapped potential in predicting key factors such as rainfall, temperature, groundwater levels, surface water availability, and the overall status of water resources under the specter of climate change. Our endeavor seeks to bridge this gap by deploying the LSTM model to project the future of Pakistan’s water resources, offering a novel approach through which policymakers can anticipate and strategize for the challenges. This paper aims to forecast Pakistan’s water resources, rainfall, and temperature during climate change using the LSTM model. This paper highlights the current research shortfall and proposes a forward-thinking approach to resource management in the face of evolving global climatic.
- The paper’s main objective is to find the forecasting of water resources under climate change using the RNN-LSTM model;
- The other aim is to forecast the ground and surface water resources under climate change using the LSTM model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Pakistan is situated within the geographical coordinates of 24° to 37° north latitude and 61° to 75° east longitude (Figure 1). Pakistan’s climate is characterized as subtropical and semiarid. Pakistan exhibits notable yearly variability in precipitation patterns, where the southern plains receive an average of 125 mm of rainfall [45,46,47,48]. In comparison, the sub-mountainous regions and northern plains range from 500 to 900 mm. Around 70% of Pakistan’s overall rainfall occurs during the summer, from July to September. In contrast, the winter season accounts for the remaining 30% of the total rainfall in Pakistan [49].
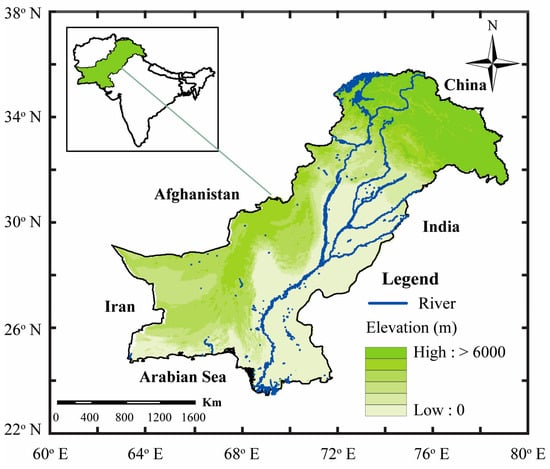
Figure 1.
Study area of the map of Pakistan along with elevation.
2.2. Datasets
This study utilizes time series rainfall and temperature data from the Pakistan Meteorological Department [50,51,52]. The dataset incorporates historical data spanning from 1901 to 2020 (https://www.pmd.gov.pk/en/, accessed on 15 April 2024). The water resources department, planning and development division, and Indus River System Authority provided data on groundwater, surface water, and water availability published in the statistical yearbook 2022 (https://www.pbs.gov.pk/sites/default/files/other/yearbooks/Pakistan_Statistical_Year_Book_2022.pdf, accessed on 15 April 2024) [21].
2.3. Methodology
This study’s research approach uses Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to predict annual precipitation, temperature patterns, surface ground, and water resources [53]. First, a normalization method was applied to the dataset, which was assumed to have variables for ‘Year’, ‘Rainfall’, ‘Temperature’, ‘surface, groundwater and overall water resources of Pakistan’. By guaranteeing data consistency, this phase was essential for adjusting the scale of the rainfall measurements and enabling a more efficient training procedure for the LSTM model [54,55,56,57,58]. After normalization, the data were turned into sequences, and a min–max scalar was used. The number of steps (n_steps, 1) in each sequence was predetermined; in this case, three was selected as the critical hyperparameter that affected the model’s capacity to recognize temporal dependencies. The LSTM network could thus learn from the patterns in rainfall over time by using this sequential data as input. The exact process was carried out for the temperature, surface, ground, and overall water resources [52,59,60,61,62,63].
2.4. LSTM Model Architecture and Training
The architecture of the LSTM model included:
- An LSTM layer with 50 neurons;
- Utilizing an ReLU activation function to introduce non-linearity;
- Allowing the model to learn complex patterns in the data.
This was followed by a dense layer that predicted the annual rainfall amount. The model was compiled with the Adam optimizer and root mean square error (RMSE) loss function, focusing on minimizing the prediction error. Training was conducted over 200 epochs, a deliberate choice to balance adequate learning and avoiding overfitting. This phase was critical for adjusting the model’s internal weights based on the error gradient, optimizing its predictive performance on unseen data and the model training loss shown in Figure 2 below.
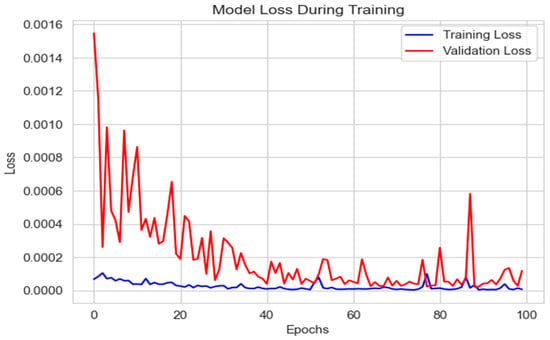
Figure 2.
Model loss during training.
2.5. Model Evaluation Criteria
Root mean square error (RMSE) is a widely used statistical technique in hydrology. It assesses the accuracy of forecasting models by comparing predicted values to observed values. The RMSE is commonly employed to determine data accuracy, considering its relative range, and to assess the degree of similarity between the expected values and the observed values.
RMSE = sn1 i∑ = n1(Y − Yi)2
In Equation (1), Y represents the actual discharge at time t, whereas Yi represents the anticipated discharge simultaneously. Y was the average of all actual discharges, and n was the total number of observations. The proposed framework are shown in the Figure 3.
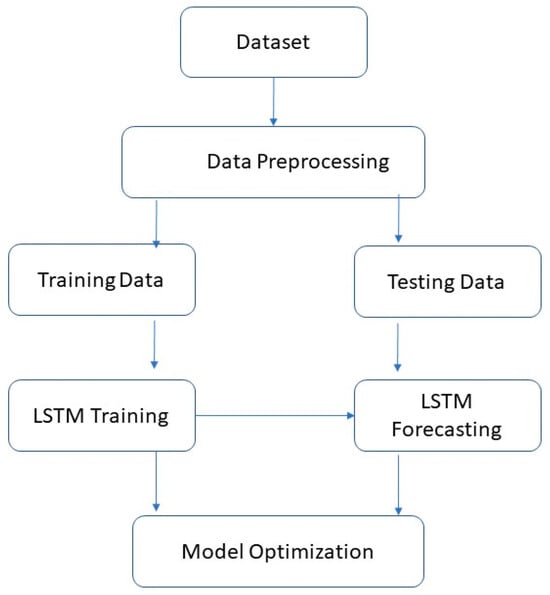
Figure 3.
Proposed theoretical framework.
2.6. LSTM Model Mathematical Equation
An artificial neural network (NN) known as a recurrent neural network (RNN) is commonly employed for time series prediction. Elman networks are a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) that comprises one or more hidden layers [64]. The initial layer possesses the weight derived from the input layer, and the preceding layer determines the weight of each layer. Typically, this network employs the activation function. The hidden layer uses a sigmoid bipolar function, while the output layer employs a linear function (purlin). The Elman network possesses activation functions that pertain to both continuation and cessation. It features a delay in the link between the input layer and the first hidden layer in the preceding time (t − 1), which can be utilized in the present time (t). The distinguishing characteristic of the recurrent neural network is its feedback connection, which transmits interference information (noise) from the previous input to the subsequent input.
LSTM is a specialized architecture of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) specifically developed to represent temporal sequences. LSTM has extensive interdependencies, rendering it more precise than traditional RNNs. The backpropagation algorithm in the NNRNN design leads to the issue of erroneous backflow [65]. LSTM, in contrast to RNN, incorporates memory blocks as distinct units inside the recurrent hidden layer. The memory blocks consist of memory cells that possess self-connections, enabling them to store the temporal state of the network.
Additionally, these blocks incorporate specialized multiplicative units known as gates, which regulate the flow of information. In the original architecture, every memory block that encompassed three distinct types of gates was studied. Specifically, the input gate regulates how input activations are directed into the memory cell. The output gate is responsible for regulating the transmission of cell activations to the other components of the network. The forget gate is responsible for scaling the cell’s internal state before its incorporation as input into the cell via the self-recurrent link. This process adaptively enables the cell to forget or reset its memory [66].
Given the input time series x(t) and output time series y(t), with connection weight matrices W_[I], W_[II], and W_[III] and activation functions f_I and f_H, the behavior of the recurrent network can be expressed through the following equations:
The state of the system at time t + 1, denoted as h(t + 1), is determined by the following:
h(t + 1) = f_I(W_{I}x(t) + W_[II]h(t))
And the output at time t + 1, y(t + 1), is obtained by the following:
y(t + 1) = f_H(W_[II]h(t + 1))
Here, h(t) represents the state of the dynamical system at time t, encapsulating all pertinent information about its past behavior, essential for predicting its future behavior as shown in Figure 4 [23].
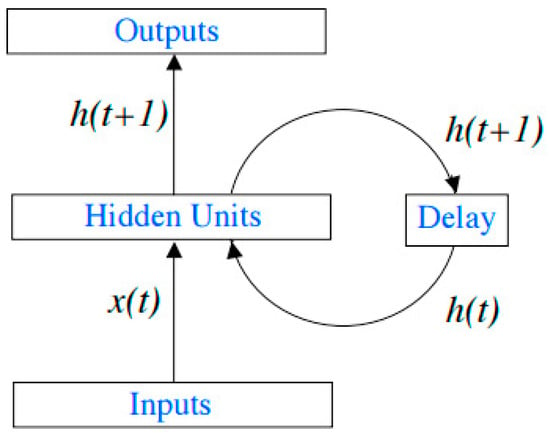
Figure 4.
Recurrent neural network model (LSTM).
3. Results
The forecasting models were validated and tested using separate datasets. During the validation and testing phase, the RMSE values were utilized to assess the qualitative and quantitative aspects when comparing the actual data and anticipated values. The number of training datasets varied based on the specific scenario. The training phase utilized a dataset covering 80% of the dataset, whereas the testing phase employed a dataset covering 20% of the dataset. Additionally, a separate dataset covering some years was used for prediction.
The RMSE of the prediction model, both during testing and training, can be observed in Table 1. The training’s LSTM model percentage score is 99%, and the testing phase percentage score is 99%, which is quite good.

Table 1.
Model evaluation.
3.1. Climate Change and Water Resources in Pakistan
Figure 5 shows historical data and forecasts of male and female populations since 1950, utilizing an LSTM model. The trend represents the current population, while the data forecast represents future estimates. These lines demonstrate an increased trend for both genders, with a steeper incline observed in the female demographic. A comprehensive understanding of these demographic changes is crucial for formulating robust water management policies, which are essential for achieving sustainability and climate action (SDG) objectives.
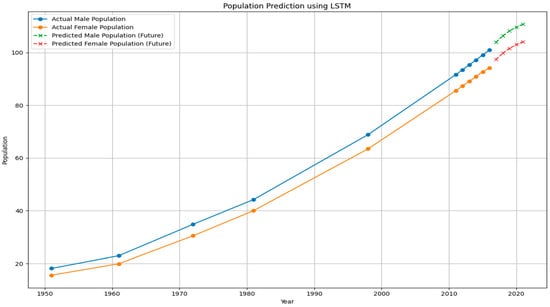
Figure 5.
Representing the population’s actual vs. predicted value across Pakistan.
Similar to many other South Asian countries, Pakistan possesses a diverse range of water resources. These resources include surface water sources such as rivers, lakes, coastal basins, and big and small water reservoirs. Additionally, Pakistan also has subsurface water resources. Primary sources encompass precipitation and descent, which contribute to the creation of glaciers. Pakistan possesses a total of 143 water storage reservoirs, encompassing both large and small facilities. Notably, the Tarbela, Mangla, and Chashma reservoirs have significant prominence, boasting a storage capacity of 18.92 million acre feet (MAF) [1]. Pakistan has experienced a substantial decrease in its water supplies over time, which can be attributed to various factors. The escalating population can be attributed to the growing need for freshwater supply. According to the Human Development Report 2001, published by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), the increase in population has led to a situation where over 12% of the population lacks access to clean drinking water (UNDP and United Nations, 2001).
Moreover, a decrease in the mean yearly precipitation has added to the strain on water supplies due to diminished replenishment on an annual basis [67]. Global warming has impacted Pakistan, resulting in yearly temperature increases [28,63,64]. The primary obstacles in water management in Pakistan arise from the per capita water usage disparity between urban and rural regions. The public sector’s investment in water supply and sanitation is insufficient [68].
3.2. Change in Groundwater and Surface Water Resources of Pakistan
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the LSTM neural network to forecast water availability in Pakistan, specifically for surface and groundwater during the Kharif and Rabi agricultural seasons. The Kharif season, which coincides with the monsoon rains, often entails the cultivation of crops that are planted at the onset of the monsoon period and subsequently harvested at its conclusion. In contrast, the Rabi season crops are shown after the monsoon and harvested throughout spring. These two seasons ensure Pakistan’s food security and economic stability within its agricultural economy.
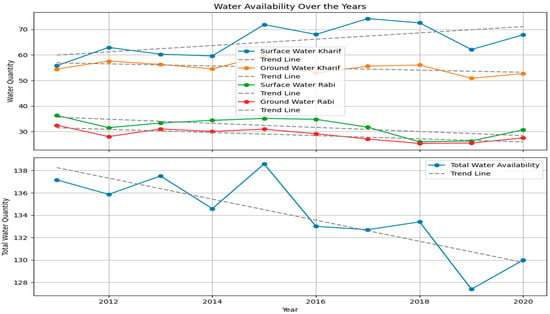
Figure 6.
Seasonal (Kharif and Rabi) variability and its predicted surface water availability across Pakistan.
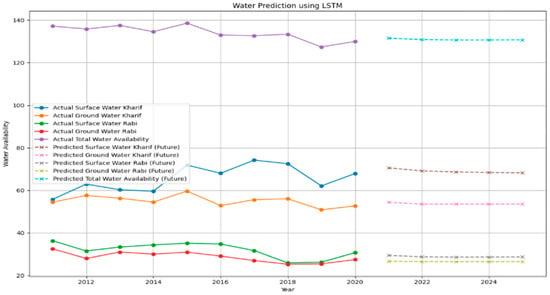
Figure 7.
Overall water resources in Pakistan.
Based on the historical data from Table 2, the Kharif season has the most significant actual surface water availability compared to other seasons. The result is consistent with the impact of the monsoon season, which helps to replenish reservoirs and rivers. As indicated in Figure 6, the groundwater level in Kharif is comparatively lower than the surface water, suggesting a dependence on monsoon rains for the water supply during this particular season. During the Rabi season, when rainfall is less, the historical data in Table 2 indicate that the natural surface water is lower compared to the Kharif season. Groundwater levels play a vital role in supporting crops. Considering the nation’s dependence on groundwater during the Rabi season, the anticipated decrease necessitates an urgent focus on groundwater management strategies.

Table 2.
Surface water, groundwater, and overall water resource data.
The future surface water predictions, represented in Figure 7, show some variations but no substantial alteration. This suggests that monsoon patterns stay stable, although this may not adequately offset the decrease in groundwater. According to the projected future, there is an anticipated decline in the total water supply, potentially worsening water stress in Pakistan. Given the anticipated decline in groundwater usage for agricultural purposes, it may be necessary for Pakistan to undertake water usage policy reforms, allocate resources towards water conservation technologies, and formulate sustainable water management plans to address the potential challenges water shortages pose. The LSTM model’s forecasts provide a mathematical foundation for Pakistan’s water resource planning, highlighting the importance of integrated approaches considering surface and groundwater resources. This is particularly crucial given the evolving climatic patterns and growing agricultural requirements.
3.3. Future Changes in Precipitation and Temperature
Figure 8 shows the overall and trend data through the year, plotted on the graph. Most of the rainfall occurred from June to August, the three months where most of the rainfall occurs. Figure 9 depicts the past and projected precipitation in Pakistan over around 40 years, as represented by a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are well-suited for time series forecasts due to their ability to effectively capture long-term dependencies in data. This characteristic is crucial for comprehending intricate patterns in weather-related events like rainfall.
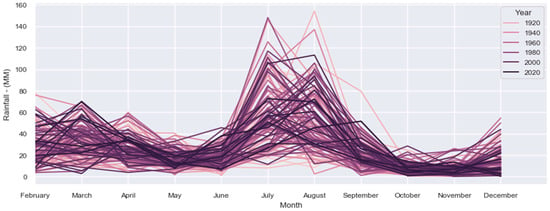
Figure 8.
Rainfall data from 1960 to 2020.
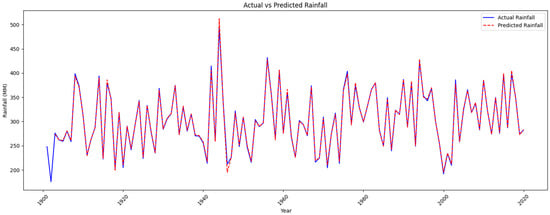
Figure 9.
Actual vs. predicted rainfall.
Based on the graphical representation in Figure 9, it is evident that the Rainfall data demonstrate notable annual variations indicative of the climatic variability in Pakistan. Figure 10, shown below, shows the rainfall forecasted by the LSTM model. The model firmly adheres to historical data, indicating its capacity to acquire knowledge from previous rainfall patterns. It is essential to acknowledge that although the LSTM model exhibits a general pattern, it performs well and has an accuracy of up 99 percent. The RMSE value is 13 below 100, which is quite good. The LSTM model is a good fit for the prediction of rainfall in the future, so it is pretty helpful for weather forecasters to prepare for protective measurements.
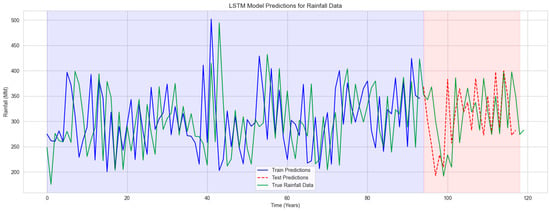
Figure 10.
LSTM model prediction of rainfall data. Whereas, blue background color represents the actual data and red background predicted data.
The consistent alignment between the anticipated values and the actual rainfall until about 2010 indicates that the model has successfully acquired knowledge of the fundamental pattern in the historical data. After 2010, there was a minor rise in the difference between the actual and anticipated values. The background color represents the actual data and predicted data shown on the graph blue color represent the actual data and the red color represent the predicted data as shown in Figure 10.
The years in which the projected precipitation exhibits more pronounced deviations from the observed values warrant additional scrutiny, as they could align with atypical weather occurrences or alterations in climatic patterns. These findings may have significant ramifications for managing Pakistan’s water resources, agriculture, and disaster preparedness.
The LSTM model’s capacity to predict rainfall patterns is crucial for Pakistan, a nation heavily reliant on agriculture, and where water resources are closely tied to the monsoon season. The model’s ability to provide predictive insights can facilitate decision-making processes related to agricultural planning, the allocation of water resources, and the formulation of adaptation strategies in the face of climate change.
3.4. Historical Temperature and Forecasting
Figure 11 shows the trend of the temperature, which is high from May to August and low from December to January. The presented Figure 12 and Figure 13 provide a graphical representation that facilitates comparison between observed temperatures over time and those projected by a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network. LSTMs are well-suited for forecasting due to their proficiency in comprehending sequences, such as temporal weather patterns. Accurate temperature predictions are essential for Pakistan’s agriculture and water management sectors. Additionally, they play a critical role in preparing for natural disasters. The model performs well, and accuracy is up 99 percent. The RMSE value is 15 below 100, which is quite good. The LSTM model is a good fit for the prediction of rainfall in the future, so it is quite helpful for weather forecasters to prepare for protective measurements.
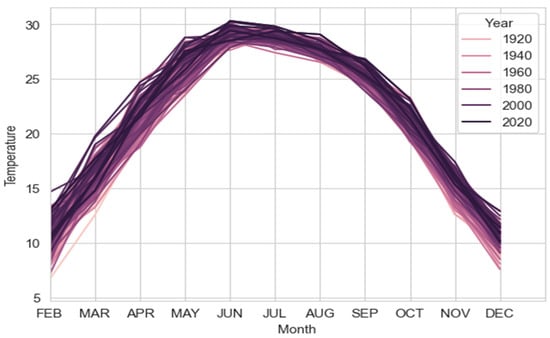
Figure 11.
Temperature data from 1960 to 2020.
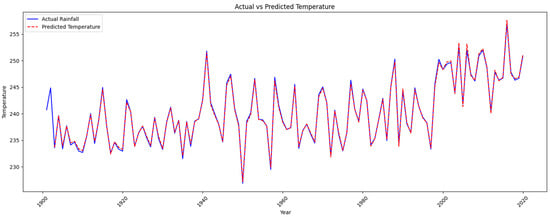
Figure 12.
Actual vs. predicted temperature from 1960 to 2020.
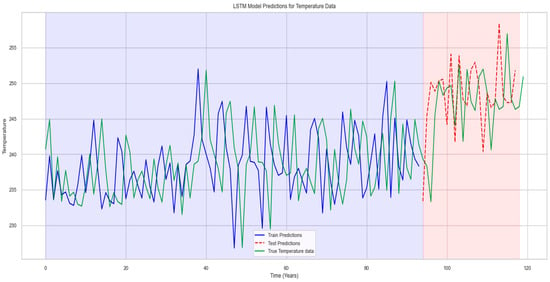
Figure 13.
LSTM model of temperature data. Whereas, blue background color represents the actual data and red background predicted data.
Upon careful analysis of the graph, a consistent pattern was observed that implied the occurrence of seasonal variations annually. Figure 11 shows a consistent pattern with the observed temperatures, indicating that the LSTM model can detect and replicate past temperature patterns.
Figure 12 and Figure 13 cover the period from approximately 1901 to slightly beyond 2020, providing a comprehensive overview of the performance of the LSTM model throughout the years. The fluctuations in observed temperature data may indicate recurring climate patterns that influence the meteorological conditions in Pakistan, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation. The LSTM’s capacity to forecast these patterns exhibits potential, although it also implies the possibility of refining the model to enhance accuracy. The data trend represents the increase in temperature over the past few years; it indicates that the global temperature is rising, which could affect water resources, rainfall, and temperature. Continuous progress of this nature is crucial for generating more precise temperature forecasts in Pakistan, enabling the government to anticipate and address climate fluctuations effectively. The background color represents the actual data and predicted data shown on the graph blue color represent the actual data and the red color represent the predicted data as shown in Figure 13.
4. Discussion
Using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models to assess climate change impacts on water resources underscores their capacity to predict forthcoming scarcities, providing valuable insights for developing adaptive management methods. The success of the models depends on the quality of the input data, indicating the necessity for comprehensive datasets. The comparative analysis demonstrates a superiority over conventional models in effectively managing intricate temporal sequences. The results highlight the possibility of informing policy decisions and promoting the integration of LSTM-based predictions in water resource planning to reduce the adverse effects of climatic variability. The predominant approach in modeling surface water quality parameters in published work involves using traditional and standalone models such as ANN, GEP, SVM, DT, RF, and regression. Using standard artificial intelligence approaches for modelling and predicting water management metrics did not yield the intended results. Hence, it is imperative to utilize modelling techniques in conjunction with optimization algorithms to provide accurate and efficient modelling results [29,30]. Using an optimization method could enhance the model’s competency in modelling water management parameters. The current study’s findings show that employing the input optimization procedure may achieve modelling accuracy, optimal structure, decreased computational time, optimized inputs, and reduced modelling complexity. In addition, the integrated optimization methods are highly effective in generating robust models with improved output compared to standalone ANN, SVM, GEP, RF, and other regression models [31,32,33,69,70]. As the population of Pakistan has risen over the past decade and the water resources of Pakistan have continuously declined, the result of the model shows that a serious issue needs to be addressed. The result aligns with the previous study, which indicates that Pakistan has experienced a significant decrease in its water supplies over time, which can be attributed to various factors. The escalating population can be attributed to the growing need for freshwater supply. According to the Human Development Report 2001 published by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), the increase in population has led to a situation where over 12% of the population lacks access to clean drinking water.
The precipitation data for Pakistan also declined. Climate change affects the precipitation pattern and rainfall pattern changes. This is a severe issue for countries such as Pakistan to take action because it affects water resources, which are already scarce, and the result aligns with the previous research [34].
Pakistan has a heightened susceptibility to climate-related challenges, as evidenced by its ranking as the twelfth most severely affected nation in terms of the adverse effects of climate change on agricultural sectors and livelihoods [7,35]. The primary factor contributing to greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) is believed to be the massive utilization of fossil fuels, as it has a significant impact on the retention of heat in the upper atmosphere. The increase in global temperature has exacerbated the phenomena of global warming and has initiated climate change impacts that are experienced worldwide. Pakistan’s economy is mainly focused on agriculture, which serves as a source of employment for about 25 million individuals.
Furthermore, Pakistan ranks sixth in terms of size and is the most densely populated nation globally, seeing an annual population growth rate of around 2 percent [35]. Currently, the majority of cultivable land in Pakistan is being utilized for agricultural purposes as the nation attempts to achieve the sustainable food security threshold in response to its fast-expanding population. The rise in temperatures has led to sudden alterations in rainfall patterns, strongly associated with agricultural production, water availability, and forest resources. The distribution and intensity of rainfall have undergone significant changes, as demonstrated by severe droughts and destructive floods that cause harm to both fertile areas and infrastructure. Like many other countries that rely on arable food production in semiarid climates, Pakistan must develop and implement climate-smart crop management practices to attain food security.
The results show that future surface water predictions suggest stable monsoon patterns, yet they fail to offset declining groundwater levels. Anticipated decrease in overall water supply could worsen Pakistan’s water stress. Urgent water usage policy reforms, conservation tech investment, and sustainable management plans are necessary. LSTM model forecasts provide a vital mathematical framework for Pakistan’s water resource planning, which is crucial amidst evolving climate patterns and agricultural demands. The research results resonate with the findings presented in the current body of literature. The harmful impact on the quantity and quality of groundwater resources in Pakistan is attributed to rapid population increase, urbanization, and inconsiderate water distribution and consumption practices [67,68,69].
Furthermore, the region cannot maintain its freshwater supplies sustainably and is already susceptible to significant water scarcity [10]. The replenishment is facilitated by the inflow of river water, primarily resulting from substantial precipitation during the monsoon period. The shallow aquifer is refilled through water infiltration from lakes, rivers, and irrigation canals, potentially carrying groundwater contaminants [36,70]. The researchers employed a geographical information system (GIS) to measure groundwater depressions quantitatively. A depression zone was seen in the groundwater level below 38 m, and its extension was determined to occur at an average annual pace of 24.5 km2 [37].
5. Conclusions
This research addressed the critical challenge of water scarcity and management due to rising global demand and declining availability. While numerous models exist for rainfall, temperature, and water data prediction, there remains a need for a more robust and accurate solution. The aim of this research is to identify shortfalls and propose a forward-thinking approach to forecasting the rainfall, temperature, and water resources under climate change. Our research study investigated classical statistical models with deep learning approaches, focusing on the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model. The model achieved a remarkable accuracy of 99%, demonstrating its exceptional capability in this domain. Our findings suggest that the LSTM model is a feasible and highly recommended approach for predicting not only the temperature, rainfall, and water resources but also intermediate data points to enhance overall accuracy further. The model’s impressive performance, reaching 99% accuracy with RMSE values of 13, 15, and 20 for rainfall, temperature, and water data, respectively, underscores the reliability of deep learning algorithms in weather and water resource prediction. This translates to a valuable tool for strategic water resource planning and management. The LSTM model’s ability to forecast future ground and surface water demand, coupled with its weather-forecasting capabilities, holds immense value for countries facing water shortage and water management problems, like Pakistan. This research paves the way for the further exploration and refinement of deep learning models to optimize water resource management and ensure sustainable water management and water scarcity.
Limitations and Recommendations
- This study relied solely on the LSTM model, and comparisons with other advanced deep learning architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or transformers, could provide valuable insights;
- While this research employed average annual data for rainfall, temperature, and water resources, further investigation using daily and monthly data may lead to even more precise results;
- Future research should investigate the effectiveness of combining LSTM with other deep learning architectures to achieve even higher accuracy potential;
- Further research could explore integrating the LSTM model with existing water resource management frameworks to evaluate its real-world implementation and potential benefits;
- It is recommended that policymakers invest in the further development of the LSTM model for water resource prediction and weather forecasting;
- Exploring the integration of the LSTM model with existing water management frameworks and weather forecasting frameworks is recommended for achieving the best prediction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S. and J.C.; methodology, W.S.; software, W.S.; validation, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1), M.H.S. and W.S.; formal analysis, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1) and M.H.S.; investigation, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1); resources, J.C.; data curation, W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S.; writing—review and editing, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 2), M.H.S. and I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1); visualization, I.U. ((Irfan Ullah 1); supervision, J.C.; project administration, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1); funding acquisition, I.U. (Irfan Ullah 1). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Fund for International Scientists under Grant No: 42350410438 and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant No: 2023M730928.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in the present study are available to the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tehsin, M.; Khan, D.; Ali, S. Water Resource Management in Pakistan. Margalla Pap. 2019, 23, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sadiq, R.; Zhu, Y. Climate change impacts on water resources and sustainable water management strategies in North America. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 2771–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramay, S.A. A Profile of Pakistan’s Development Status and Green Economy in Pakistan; Working Paper; SDPI: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque, W.; Mukhtar, M.; Tanvir, R. Pakistan’s water resource management: Ensuring water security for sustainable development. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1096747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present, and future. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moursi, H.; Kim, D.; Kaluarachchi, J.J. A probabilistic assessment of agricultural water scarcity in a semiarid and snowmelt-dominated river basin under climate change. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Raza, T.; Bhatti, T.T.; Eash, N.S. Climate Impacts on the agricultural sector of Pakistan: Risks and solutions. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Judging Rainfall Intensity from Inter-Tip Times: Comparing ‘Straight-Through and Syphon-Equipped Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge Performance. Water 2024, 16, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Sarwar, G.; Shah, S.H.; Muhammad, S. Soil salinity research in 21st century in Pakistan: Its impact on availability of plant nutrients, growth and yield of crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, A.; Murtiza, G.; Yousaf, A.; Hussain, M.; Al Jbawi, E. A critical analysis of legal responses to water pollution in Pakistan. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2023, 9, 2254944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab, A. Pakistan: Institutional Transformation of the Punjab Irrigation Department to a Water Resources Department; Asian Development Bank: Sydney, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Watto, M.A.; Mitchell, M.; Akhtar, T. Pakistan’s water resources: Overview and challenges. In Water Resources of Pakistan: Issues and Impacts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bamurigire, P.; Vodacek, A.; Valko, A.; Ngoga, S.R. Simulation of internet of things water management for efficient rice irrigation in Rwanda. Agriculture 2020, 10, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, D.; Rais, M.N.; Ahmed, W.; Bano, R.; Burian, S.J.; Ijaz, M.W. Future water demand modeling using water evaluation and planning: A case study of the Indus Basin in Pakistan. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Ragab, R. Drought risk under climate and land use changes: Implication to water resource availability at catchment scale. Water 2019, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, D. Pakistan’s national water policy. The Express Tribune, 29 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.; Wang, F.; Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Wang, X.; Hong, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y. The asymmetric impacts of international agricultural trade on water use scarcity, inequality and inequity. Nat. Water 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Qamar, U. Pakistan’s Water Economy: Running Dry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Than, N.H.; Ly, C.D.; Van Tat, P. The performance of classification and forecasting Dong Nai River water quality for sustainable water resources management using neural network techniques. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Demir, I. A rainfall-runoff model with LSTM-based sequence-to-sequence learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Lei, H.; Khan, A.; Muhammad, I.; Javeed, T.; Khan, A.; Huo, X. Yield gap analysis of major food crops in Pakistan: Prospects for food security. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7994–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Majeed, M.D.; Zaman, M.; Shahid, M.A.; Zhang, D.; Zahra, S.M.; Safdar, M.; Sabir, R.M.; Maqbool, Z. Artificial Neural Networks and Regression Modeling for Water Resources Management in the Upper Indus Basin. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.G.; Heryadi, Y.; Abdurahman, E.; Suparta, W. Single layer & multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) model with intermediate variables for weather forecasting. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 135, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, I.A.; Bhatti, S.S. Lahore, Pakistan–Urbanization challenges and opportunities. Cities 2018, 72, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dai, L.; Chin, T.; Rafiq, M. Understanding the role of psychological capital in humorous leadership-employee creativity relations. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naheed, G.; Rasul, G. Projections of crop water requirement in Pakistan under global warming. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2010, 7, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Qamar-uz-Zaman, C.; Mahmood, A.; Rasul, G.; Afzaal, M. Climate Change Indicators of Pakistan; Pakistan Meteorological Department: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2009.
- Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124670. [Google Scholar]
- Kilinc, H.C.; Yurtsever, A. Short-term streamflow forecasting using hybrid deep learning model based on grey wolf algorithm for hydrological time series. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.I.; Javed, M.F.; Khan, M.I.; Rasheed, S.; El-Shorbagy, M.A.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Malik, M.Y. Application of random forest for modelling of surface water salinity. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismani, G.; Pisinaras, V.; Arampatzis, G. Water Governance for Climate-Resilient Agriculture in Mediterranean Countries. Water 2024, 16, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Jiao, Y.; Ji, P.; Li, C.; An, X. Ensemble Forecasts of Extreme Flood Events with Weather Forecasts, Land Surface Modeling and Deep Learning. Water 2024, 16, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J. Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China. Water 2024, 16, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.G.; Yaseen, G. Global climate change and its impact on agriculture sector in Pakistan. Am. J. Trade Policy 2017, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, H.; Khan, S. Climate responsive urban groundwater management options in a stressed aquifer system. In 10th Kovacs Colloquium 2010; IAHS Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; pp. 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, K.; Rana, A.D.; Tariq, S.; Kanwal, S.; Ali, R.; Haidar, A. Groundwater levels susceptibility to degradation in Lahore metropolitan. Depression 2011, 150, 8.01. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Ullah, W.; Liu, M.; Ullah, I. Performance Evaluation of ERA-5, JRA-55, MERRA-2, and CFS-2 Reanalysis Datasets, over Diverse Climate Regions of Pakistan. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 1003, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Ullah, W.; Ali, G.; Ullah, S.; Liu, M.; Shahzaman, M.; Ullah, I. Evaluation of GPM-IMERG and TRMM-3B42 Precipitation Products over Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Shao, D.; Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Ullah, I. Investigation of the Drainage Loss Effects with a Street View Based Drainage Calculation Method in Hydrodynamic Modelling of Pluvial Floods in Urbanized Area. J. Hydrol. 1273, 2022, 60565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F.; Zhang, W.; Hina, S.; Zeng, X.; Ullah, I.; Bibi, T.; Nnamdi, D.V. Population Exposure Changes to Mean and Extreme Climate Events over Pakistan and Associated Mechanisms. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Taha Bakheit Taha, A.; Tian, F.; Yuan, X.; Ajmal, M.; Ullah, I.; Ahmad, M. Flood Modelling and Risk Analysis of Cinan Feizuo Flood Protection Area, Huaihe River Basin. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hina, S.; Saleem, F.; Arshad, A.; Hina, A.; Ullah, I. Droughts over Pakistan: Possible Cycles, Precursors and Associated Mechanisms. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1638–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokossi, K.; Jin, S.; Mazhar, U.; Molina, I.; Calabia, A.; Ullah, I. Monitoring the Drought in Southern Africa from Space-Borne GNSS-R and SMAP Data. Nat. Hazards 2024, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Arshad, M.; Ma, X.; Ullah, I.; Wang, J.; Shao, W. Evaluating Observed and Future Spatiotemporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature across China Based on CMIP6-GCMs. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 7703–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Ullah, I.; Arshad, M. Non-stationary Frequency Analysis of Extreme Streamflow Disturbance in a Typical Ecological Function Reserve of China under a Changing Climate. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khan, J.; Ullah, I.; Khan, F.; Lee, Y. Investigating Drought and Flood Evolution Based on Remote Sensing Data Products over the Punjab Region in Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khan, J.; Ullah, I.; Khan, F.; Lee, Y. Assessing Impacts of Flood and Drought over the Punjab Region of Pakistan Using Multi-Satellite Data Products. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.M.; Wang, J.; Abbas, H.; Ullah, I.; Khan, R.; Ali, F. Impact of Climate and Land-Use Change on Groundwater Resources, Study of Faisalabad District, Pakistan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie Sein, Z.M.; Ullah, I.; Saleem, F.; Zhi, X.; Syed, S.; Azam, K. Interdecadal Variability in Myanmar Rainfall in the Monsoon Season (May–October) Using Eigen Methods. Water 2021, 13, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Ullah, I.; Syed, S.; Zhi, X.; Azam, K.; Rasool, G. Interannual Variability of Air Temperature over Myanmar: The Influence of Enso and Iod. Climate 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Zhi, X.; Ullah, I.; Azam, K.; Ngoma, H.; Saleem, F.; Xing, Y.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Hina, S.; et al. Recent Variability of Sub-seasonal Monsoon Precipitation and Its Potential Drivers in Myanmar Using In-situ Observation during 1981–2020. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 3341–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sein, Z.M.M.; Ullah, I.; Iyakaremye, V.; Azam, K.; Ma, X.; Syed, S.; Zhi, X. Observed Spatiotemporal Changes in Air Temperature, Dew Point Temperature and Relative Humidity over Myanmar during 2001–2019. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2022, 134, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzaman, M.; Zhu, W.; Bilal, M.; Habtemicheal, B.; Mustafa, F.; Arshad, M.; Ullah, I.; Ishfaq, S.; Iqbal, R. Remote Sensing Indices for Spatial Monitoring of Agricultural Drought in South Asian Countries. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzaman, M.; Zhu, W.; Ullah, I.; Mustafa, F.; Bilal, M.; Ishfaq, S.; Nisar, S.; Arshad, M.; Iqbal, R.; Aslam, R.W. Comparison of Multi-Year Reanalysis, Models, and Satellite Remote Sensing Products for Agricultural Drought Monitoring over South Asian Countries. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zeng, X.-M.; Wang, N.; Ullah, I.; Lv, H. Attribution of Moisture Sources for Summer Precipitation in the Upstream Catchment of the Three Gorges Dam. J. Hydrometeorol. 2024, 25, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Saleem, F.; Syed, S.; Omer, A.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Liu, M.; Arshad, M. Observed Changes in Seasonal Drought Characteristics and Their Possible Potential Drivers over Pakistan. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 1576–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Asfaw, T.G.; Azam, K.; Syed, S.; Liu, M.; Arshad, M.; Shahzaman, M. Evaluating the Meteorological Drought Characteristics over Pakistan Using in Situ Observations and Reanalysis Products. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 4437–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.; Hina, S.; Syed, S.; Ma, X.; Iyakaremye, V.; Yin, J.; Singh, V. Recent and Projected Changes in Water Scarcity and Unprecedented Drought Events over Southern Pakistan. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Asfaw, T.G.; Yin, J.; Iyakaremye, V.; Saleem, F.; Xing, Y.; Azam, K.; Syed, S. Projected Changes in Increased Drought Risks Over South Asia Under a Warmer Climate. Earth’s Futur. 2022, 10, e2022EF002830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Saleem, F.; Iyakaremye, V.; Yin, J.; Ma, X.; Syed, S.; Hina, S.; Asfaw, T.G.; Omer, A. Projected Changes in Socioeconomic Exposure to Heatwaves in South Asia Under Changing Climate. Earth’s Futur. 2022, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.; Mukherjee, S.; Aadhar, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Syed, S.; Ayugi, B.O.; Iyakaremye, V.; Lv, H. Future Amplification of Multivariate Risk of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events on South Asian Population. Earth’s Futur. 2023, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Ren, G.; Yin, J.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Lu, K.; Xing, Y.; Singh, V. Recent Changes in Drought Events over South Asia and Their Possible Linkages with Climatic and Dynamic Factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Omer, A.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Saleem, F.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Arshad, M.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Meteorological Drought Variability and Trends (1981–2020) over South Asia and the Associated Large-Scale Circulation Patterns. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 2261–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyakaremye, V.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Ullah, I.; Gahigi, A.; Vuguziga, F.; Asfaw, T.G.; Ayugi, B. Increased High-Temperature Extremes and Associated Population Exposure in Africa by the Mid-21st Century. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 1481, 79062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyakaremye, V.; Zeng, G.; Ullah, I.; Gahigi, A.; Mumo, R.; Ayugi, B. Recent Observed Changes in Extreme High-Temperature Events and Associated Meteorological Conditions over Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 4522–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwimbabazi, J.; Jing, Y.; Iyakaremye, V.; Ullah, I.; Ayugi, B. Observed Changes in Meteorological Drought Events during 1981–2020 over Rwanda, East Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, M.; Ullah, I. Characteristics and Propagation of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts in Eastern Gansu, a Typical Semiarid Region, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 5327–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Mukherjee, S.; Syed, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Ayugi, B.O.; Aadhar, S. Anthropogenic and Atmospheric Variability Intensifies Flash Drought Episodes in South Asia. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-Z.; Liu, S.-J.; Zeng, X.-M.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Zhu, J.; Ullah, I. A Study of Precipitation Forecasting for the Pre-Summer Rainy Season in South China Based on a Back-Propagation Neural Network. Water 2024, 16, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).