Application of the Improved K-Nearest Neighbor-Based Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Runoff Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodologies
2.1. Benchmark Model
2.1.1. Model Input Selection
2.1.2. Benchmark Model Establishment
2.2. The Improved K-Nearest Neighbors Method
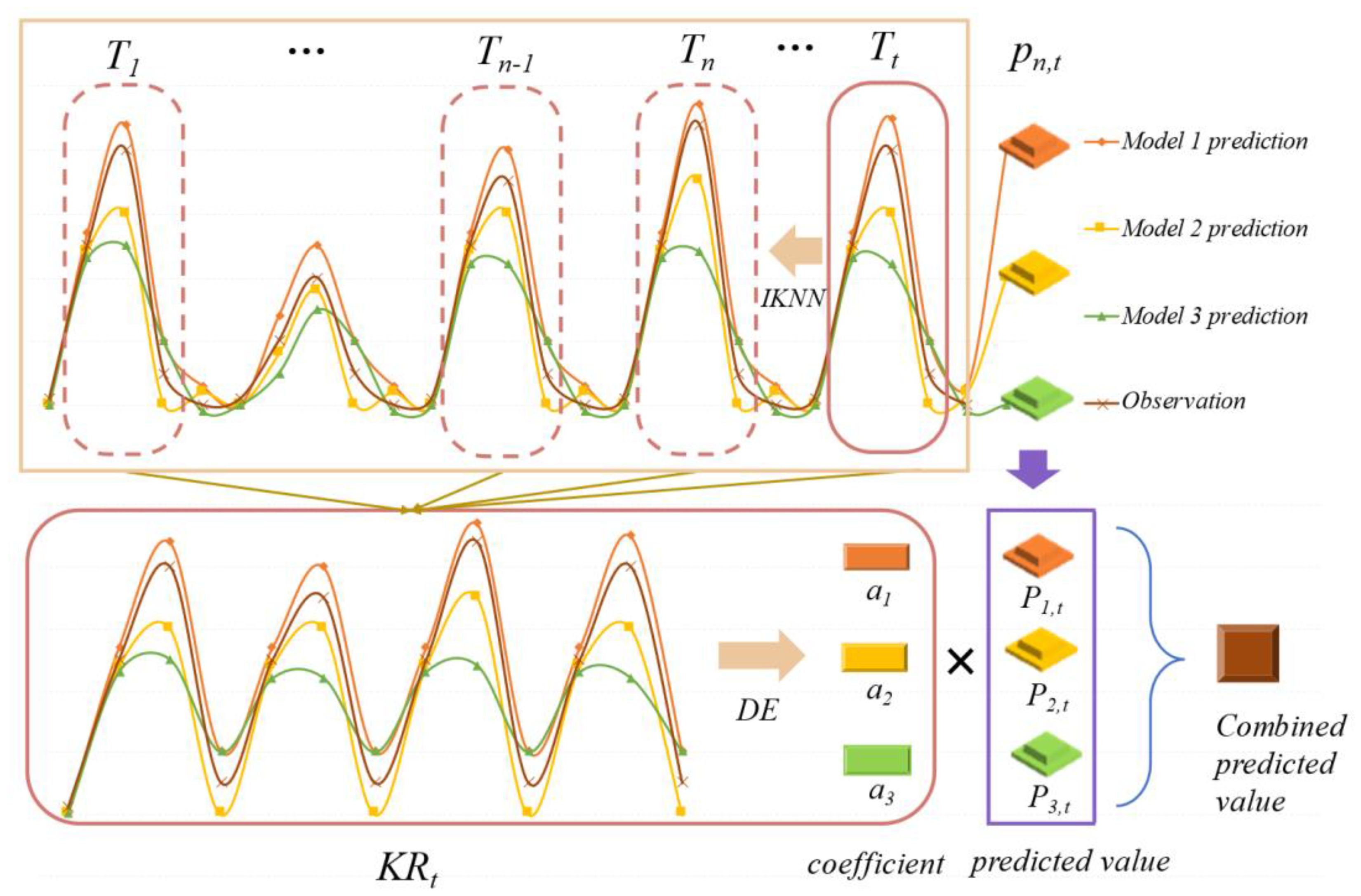
2.3. The Multi-Model Ensemble Method Based on the Improved KNN Algorithm
2.4. Method Evaluation Metric
3. Case Study
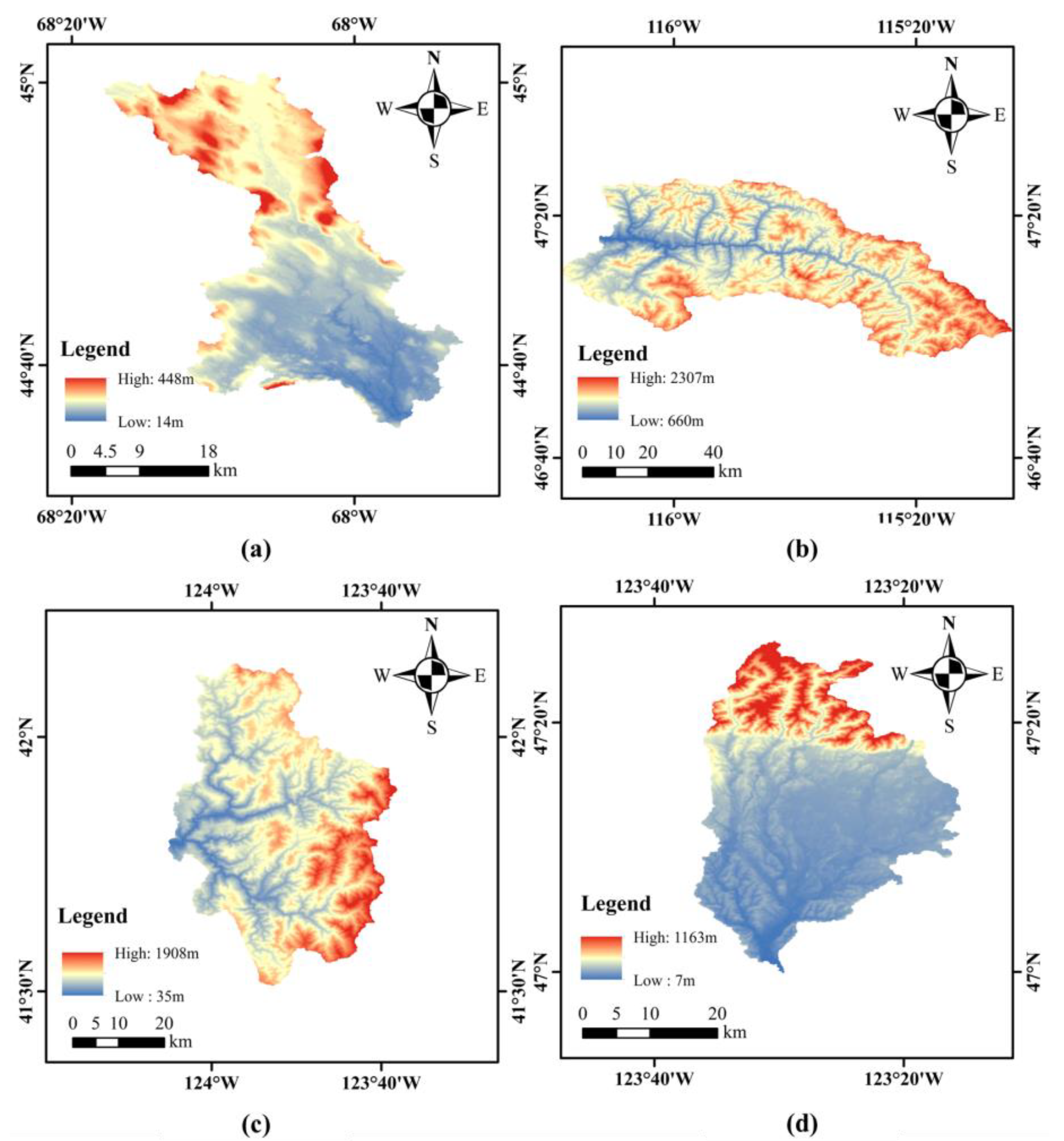
3.1. Study Area and Data
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Runoff Prediction Results of Benchmark Model
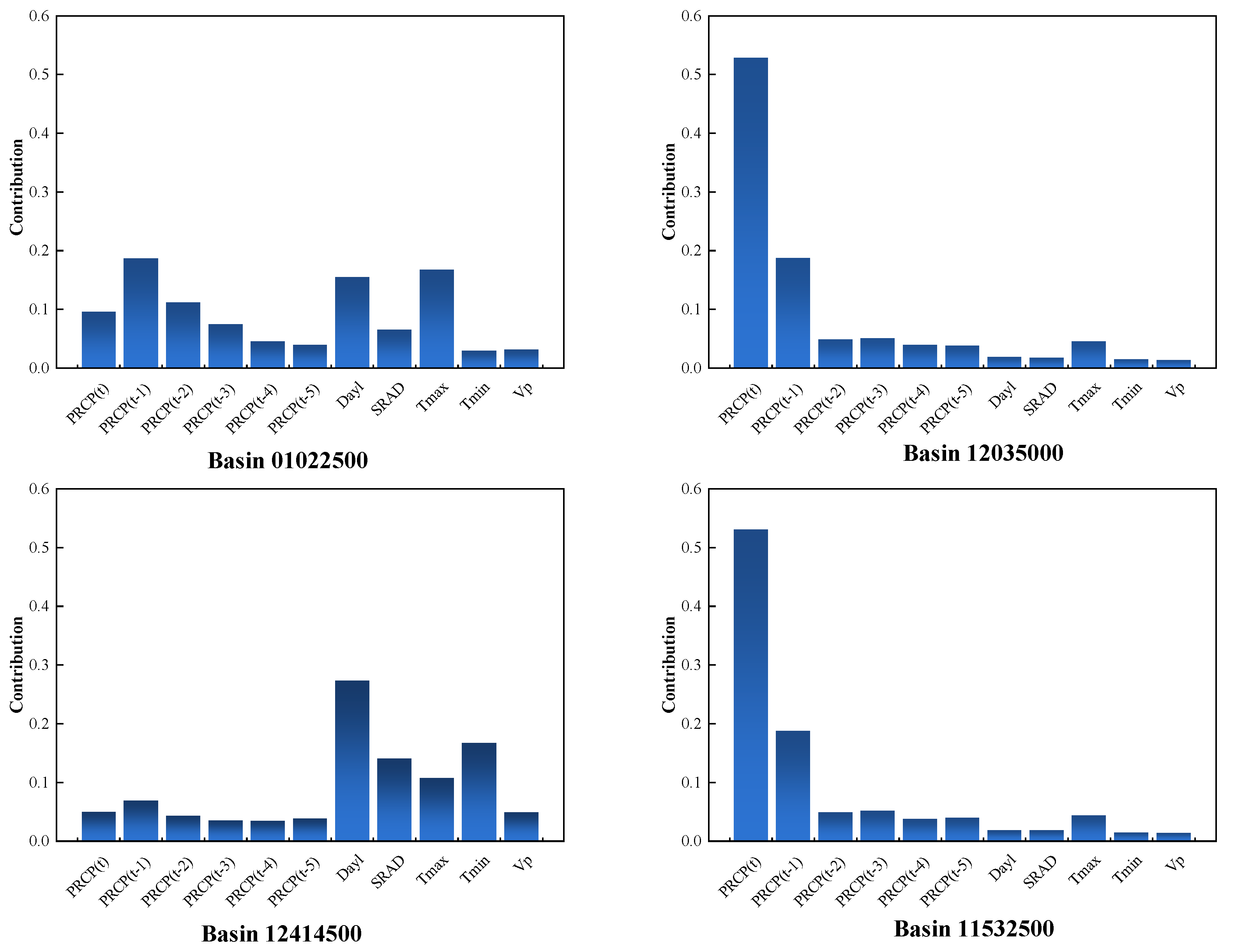
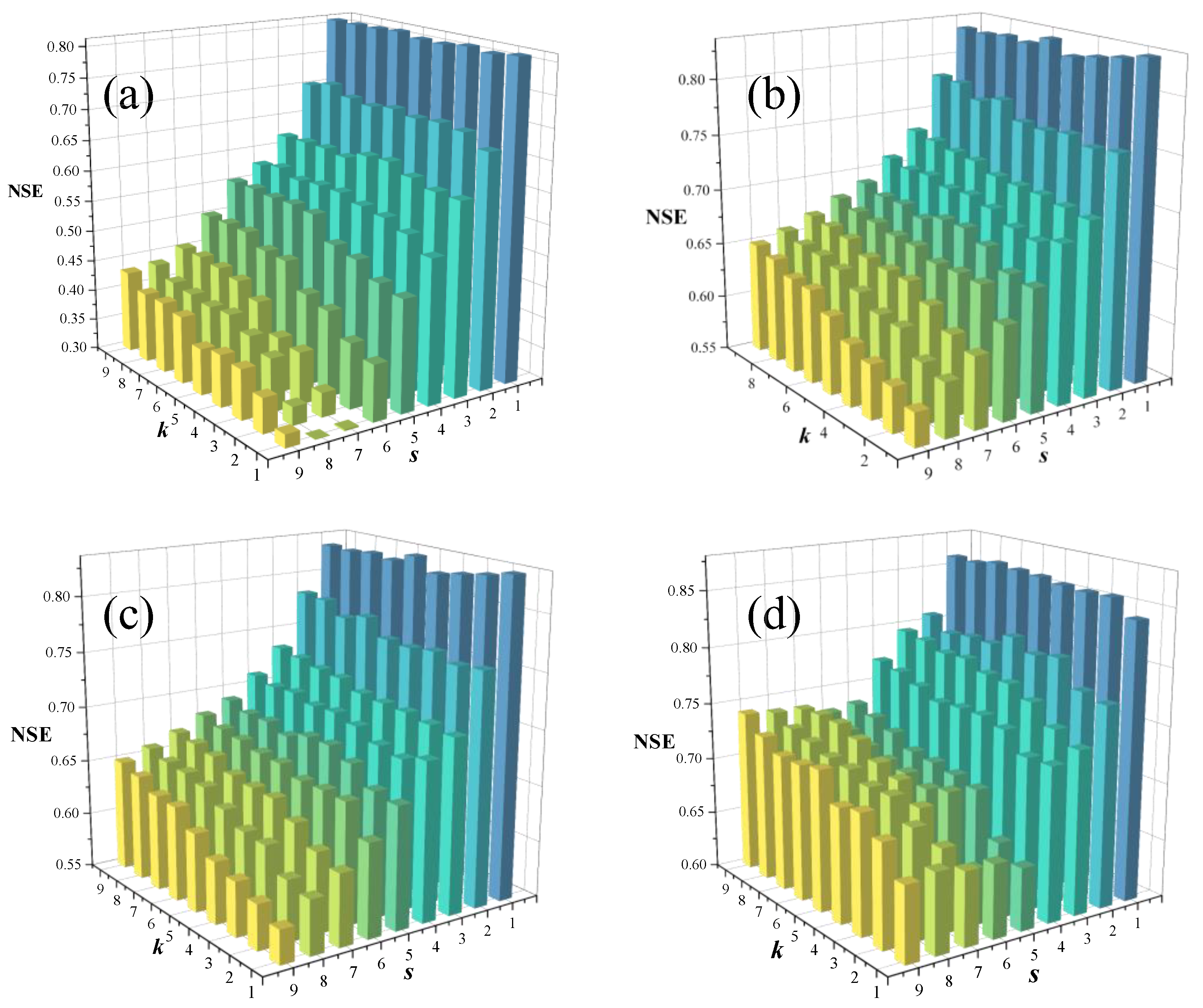
4.2. Parameters Preferences
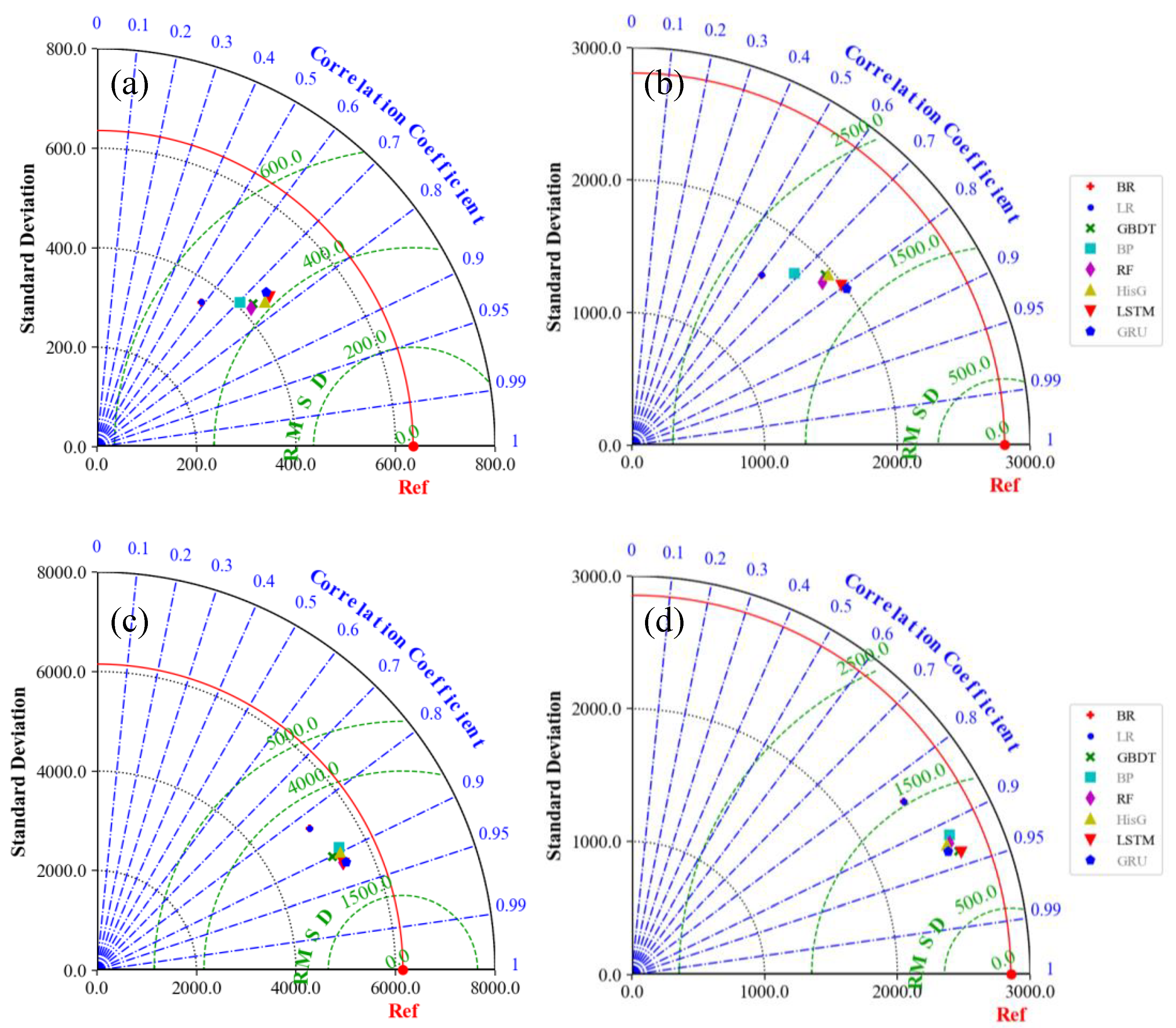
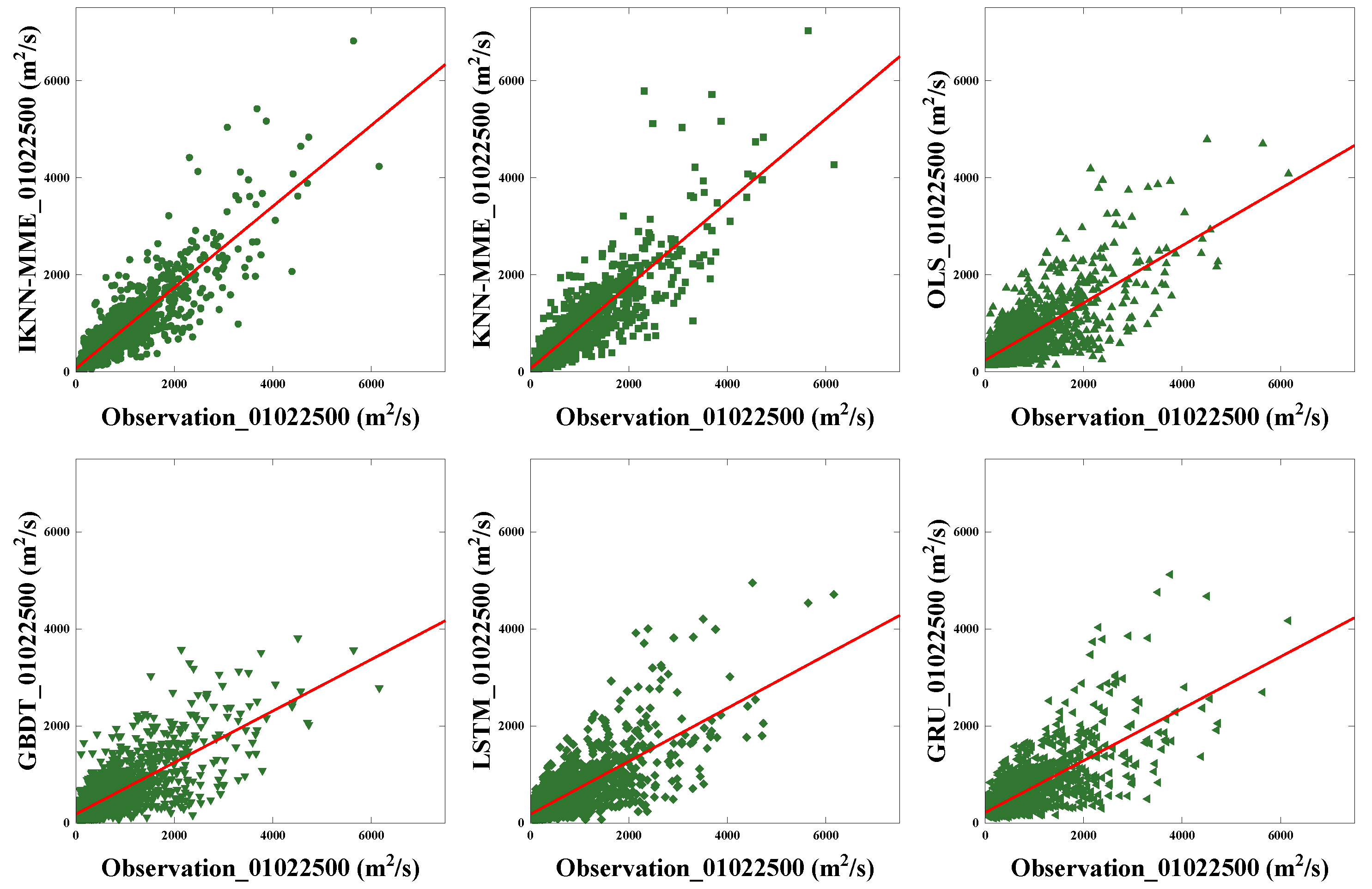
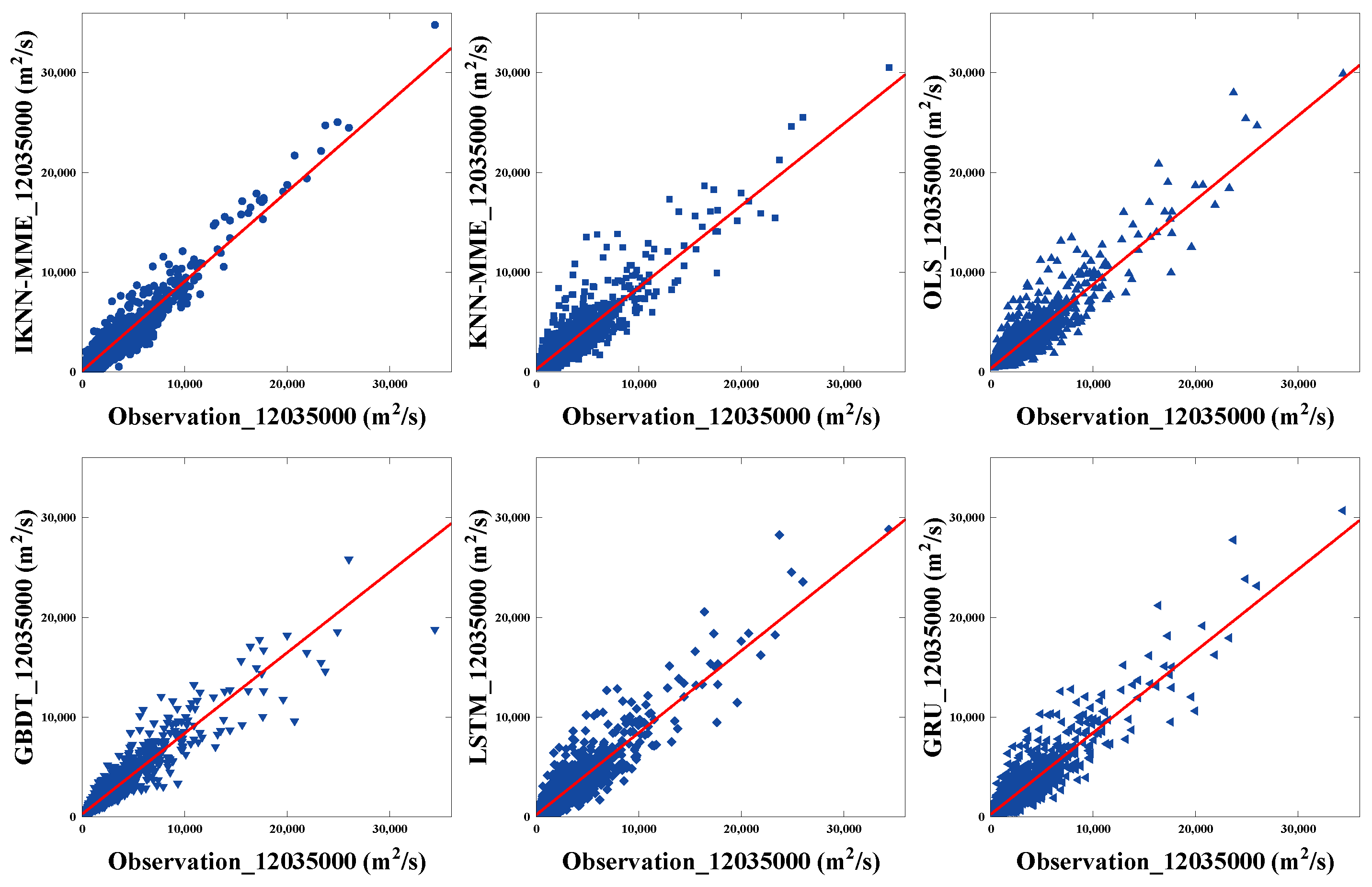
4.3. Comparisons of Multi-Model Ensemble Forecasting Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, H. Risk Analysis of Water Supply-Hydropower Generation-Environment Nexus in the Cascade Reservoir Operation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Singh, V.P.; Jiang, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Qiu, H. A Time-Varying Distributed Unit Hydrograph Method Considering Soil Moisture. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5269–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Moosavi, V.; Leitão, J.P. Data-Driven Rapid Flood Prediction Mapping with Catchment Generalizability. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tang, Z.; Qin, H.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, J. Short-Term Runoff Prediction Using Deep Learning Multi-Dimensional Ensemble Method. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.H.; Shahid, S.; Sammen, S.S. Chapter 25—Runoff Modeling Using Group Method of Data Handling and Gene Expression Programming. In Handbook of Hydroinformatics; Eslamian, S., Eslamian, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 353–377. ISBN 978-0-12-821962-1. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Fang, K.; Shen, C. Enhancing Streamflow Forecast and Extracting Insights Using Long-Short Term Memory Networks with Data Integration at Continental Scales. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganna, S.R.; Marulasiddappa, S.B.; Balreddy, M.S.; Yaseen, Z.M. Daily Scale Streamflow Forecasting in Multiple Stream Orders of Cauvery River, India: Application of Advanced Ensemble and Deep Learning Models. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.H.R.; Lall, U. Climate Informed Monthly Streamflow Forecasts for the Brazilian Hydropower Network Using a Periodic Ridge Regression Model. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Gupta, H.V.; Bao, W.; Jiang, P.; Wang, W. Improved Dynamic System Response Curve Method for Real-Time Flood Forecast Updating. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Kim, T.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Q. A Large-Scale Comparison of Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining (AI&DM) Techniques in Simulating Reservoir Releases over the Upper Colorado Region. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Rangan, D.M.; Ramasastri, K.S. Short-Term Flood Forecasting with a Neurofuzzy Model. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W04004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K. Flood Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Luo, S.; Zhao, G.; Wu, H. Predicting Hard Rock Pillar Stability Using GBDT, XGBoost, and LightGBM Algorithms. Mathematics 2020, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall–Runoff Modelling Using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldin, A.Y.; O’Connor, K.M.; Liang, G.C. Methods for Combining the Outputs of Different Rainfall–Runoff Models. J. Hydrol. 1997, 197, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Singh, V.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Real-Time Error Correction Method Combined with Combination Flood Forecasting Technique for Improving the Accuracy of Flood Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2014, 521, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Ye, L. Coupling Forecast Methods of Multiple Rainfall–Runoff Models for Improving the Precision of Hydrological Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5091–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevuturi, A.; Tanguy, M.; Facer-Childs, K.; Martínez-de la Torre, A.; Sarkar, S.; Thober, S.; Samaniego, L.; Rakovec, O.; Kelbling, M.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; et al. Improving Global Hydrological Simulations through Bias-Correction and Multi-Model Blending. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Khare, Y.P. Multi-Parameter Approaches for Improved Ensemble Prediction Accuracy in Hydrology and Water Quality Modeling. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhong, P.; Zhu, F.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Real-Time Error Correction for Flood Forecasting Based on Machine Learning Ensemble Method and Its Uncertainty Assessment. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 1557–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Wood, E.F. Improved Sub-Seasonal Meteorological Forecast Skill Using Weighted Multi-Model Ensemble Simulations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Shen, K.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, J. Probabilistic Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Wind Speed Based on Multi-Network Deep Ensembles Method. Renew. Energy 2023, 209, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Schepen, A.; Robertson, D.E. Merging Seasonal Rainfall Forecasts from Multiple Statistical Models through Bayesian Model Averaging. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5524–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X. Applying a Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Long-Term Runoff Prediction under Climate Change Scenarios for the Yellow River Basin, China. Water 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian Model Averaging to Calibrate Forecast Ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bao, W.; Xiao, Z.; Si, W. Multi-Model Integrated Error Correction for Streamflow Simulation Based on Bayesian Model Averaging and Dynamic System Response Curve. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán, J.F.; Cea, L. Improving the Predictive Skills of Hydrological Models Using a Combinatorial Optimization Algorithm and Artificial Neural Networks. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajirahimi, Z.; Khashei, M. Weighting Approaches in Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery: A Review. Neural Process Lett. 2023, 55, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Amorim, R.C. A Survey on Feature Weighting Based K-Means Algorithms. J. Classif. 2016, 33, 210–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; van Overloop, P.J.; Afshar, A. Clustered K Nearest Neighbor Algorithm for Daily Inflow Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Cui, Y.; Xiang, K.; Song, Y. Improved Runoff Forecasting Based on Time-Varying Model Averaging Method and Deep Learning. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Saifullah, M. Coupling the K-Nearest Neighbor Procedure with the Kalman Filter for Real-Time Updating of the Hydraulic Model in Flood Forecasting. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delima, A.J.P. An Enhanced K-Nearest Neighbor Predictive Model through Metaheuristic Optimization. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2020, 10, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, G. GECA Proposed Ensemble–KNN Method for Improved Monthly Runoff Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukey, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W. Survey on Exact kNN Queries over High-Dimensional Data Space. Sensors 2023, 23, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.; Afshar, A. Similarity-Based Error Prediction Approach for Real-Time Inflow Forecasting. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 45, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaresi, F.; Araghinejad, S. A Comparative Assessment of Support Vector Machines, Probabilistic Neural Networks, and K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithms for Water Quality Classification. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4095–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Yakowitz, S. Nearest-Neighbor Methods for Nonparametric Rainfall-Runoff Forecasting. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, L.; She, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zou, L. Sensitivity and Interaction Analysis Based on Sobol’ Method and Its Application in a Distributed Flood Forecasting Model. Water 2015, 7, 2924–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauhar, N.; Das, S.; Moury, K.S. Prediction of Flood in Bangladesh Using K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 January 2021; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Ali, S.; Li, T.; Cui, S. Measurement and Analysis of Regional Flood Disaster Resilience Based on a Support Vector Regression Model Refined by the Selfish Herd Optimizer with Elite Opposition-Based Learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Yi, B.; Leng, Z.; Zheng, J.; Song, Q. A Method for Monthly Extreme Precipitation Forecasting with Physical Explanations. Water 2023, 15, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttinaovarat, S.; Horkaew, P. Flood Forecasting System Based on Integrated Big and Crowdsource Data by Using Machine Learning Techniques. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 5885–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Al Mehedi, M.A.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Kumar, R. Development of Machine Learning Flood Model Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) at Var River. Liquids 2022, 2, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, G.; Yao, X.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Duan, H.; Xie, Z.; Fan, R.; Yang, Y. Simulation and Reconstruction of Runoff in the High-Cold Mountains Area Based on Multiple Machine Learning Models. Water 2023, 15, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Li, S.; Leng, Z. Influences of the Runoff Partition Method on the Flexible Hybrid Runoff Generation Model for Flood Prediction. Water 2023, 15, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Leng, Z.; Gan, X.; Xie, T.; Mei, Z. Hydrological Modelling with an Improved Flexible Hybrid Runoff Generation Strategy. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Gippel, C.J.; Shan, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, W. Uncertainty of Flood Forecasting Based on Radar Rainfall Data Assimilation. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, e2710457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Peng, T.; Sun, N.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shahzad Nazir, M. Metaheuristic Evolutionary Deep Learning Model Based on Temporal Convolutional Network, Improved Aquila Optimizer and Random Forest for Rainfall-Runoff Simulation and Multi-Step Runoff Prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 229, 120616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldin, A.Y.; O’Connor, K.M. A Nearest Neighbour Linear Perturbation Model for River Flow Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 1996, 179, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Yang, G. Comparative Study of Three Updating Procedures for Real-Time Flood Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2111–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Shourian, M. River Flow Prediction Using Dynamic Method for Selecting and Prioritizing K-Nearest Neighbors Based on Data Features. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 04020010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Chau, K.-W.; Cheng, C.-T.; Qiu, L. A Comparison of Performance of Several Artificial Intelligence Methods for Forecasting Monthly Discharge Time Series. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R. Differential Evolution—A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addor, A.N.; Mizukami, M.; Clark, M.P. Catchment Attributes for Large-Sample Studies; UCAR/NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Sampson, K.; Clark, M.P.; Bock, A.; Viger, R.J.; Blodgett, D. A Large-Sample Watershed-Scale Hydrometeorological Dataset for the Contiguous; UCAR/NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.J.; Clark, M.P.; Sampson, K.; Wood, A.; Hay, L.E.; Bock, A.; Viger, R.J.; Blodgett, D.; Brekke, L.; Arnold, J.R.; et al. Development of a Large-Sample Watershed-Scale Hydrometeorological Data Set for the Contiguous USA: Data Set Characteristics and Assessment of Regional Variability in Hydrologic Model Performance. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addor, N.; Newman, A.J.; Mizukami, N.; Clark, M.P. The CAMELS Data Set: Catchment Attributes and Meteorology for Large-Sample Studies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5293–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, A.P.; Liniger, M.A.; Appenzeller, C. Can Multi-Model Combination Really Enhance the Prediction Skill of Probabilistic Ensemble Forecasts? Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Abbreviation | Model Type |
|---|---|---|
| Bayesian Ridge Regression | BR | Statistical Model 1 |
| Linear Regression | LR | Statistical Model 2 |
| Gradient Boosting Decision Tree | GBDT | Machine Learning Model 1 |
| Back Propagation Neural Network | BP | Machine Learning Model 2 |
| Random Forest | RF | Machine Learning Model 3 |
| HistGradient Boosting Regressor | HistG | Machine Learning Model 4 |
| Long Short-Term Memory | LSTM | Deep Learning Model 1 |
| Gate Recurrent Unit | GRU | Deep Learning Model 2 |
| Variable Name | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| PRCP | Precipitation | mm/day |
| SRAD | Solar radiation | W/m2 |
| Tmax | Maximum temperature | °C |
| Tmin | Minimum temperature | °C |
| Vp | Vapor pressure | Pa |
| Dayl | Day length | s |
| Basin Code | Size (km2) | Elevation (m) | Slope (m_km−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01022500 | 620.38 | 92.68 | 17.79 |
| 12414500 | 2660.37 | 1381.41 | 104.38 |
| 11532500 | 1590.16 | 725.07 | 112.11 |
| 12035000 | 768.98 | 149.30 | 29.35 |
| Basin Code | 01022500 | 12414500 | 11532500 | 12035000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | Training | |||
| MAXIMUM (m3/s) | 6790.00 | 33,900.00 | 91,200.00 | 51,800.00 |
| MINIMUM (m3/s) | 12.00 | 105.00 | 172.00 | 147.00 |
| MEAN (m3/s) | 487.53 | 2239.04 | 3640.09 | 2086.57 |
| Standard Deviation (m3/s) | 577.97 | 2692.87 | 6247.83 | 2918.35 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 1.19 | 1.20 | 1.72 | 1.40 |
| Statistics | Testing | |||
| MAXIMUM (m3/s) | 6160.00 | 22,000.00 | 76,900.00 | 34,400.00 |
| MINIMUM (m3/s) | 37.00 | 140.00 | 190.00 | 204.00 |
| MEAN (m3/s) | 593.45 | 2428.78 | 3462.30 | 2104.60 |
| Standard Deviation (m3/s) | 635.49 | 3222.77 | 5741.19 | 2585.62 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 1.07 | 1.33 | 1.66 | 1.23 |
| Area | Model | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01025000 | BR | 0.32 | 523.1 | 323.0 |
| LR | 0.32 | 523.1 | 323.0 | |
| GBDT | 0.52 | 441.6 | 258.0 | |
| BP | 0.47 | 464.8 | 272.7 | |
| RF | 0.52 | 439.9 | 253.3 | |
| HistG | 0.55 | 425.8 | 245.5 | |
| LSTM | 0.55 | 426.3 | 248.0 | |
| GRU | 0.54 | 431.3 | 255.8 | |
| average | 0.47 | 459.5 | 272.4 | |
| 12414500 | BR | 0.38 | 2530.0 | 1576.8 |
| LR | 0.38 | 2529.9 | 1577.1 | |
| GBDT | 0.53 | 2221.5 | 1228.7 | |
| BP | 0.50 | 2274.9 | 1288.0 | |
| RF | 0.55 | 2162.8 | 1170.7 | |
| HistG | 0.57 | 2122.2 | 1161.1 | |
| LSTM | 0.58 | 2095.4 | 1127.4 | |
| GRU | 0.58 | 2094.3 | 1120.9 | |
| average | 0.51 | 2253.9 | 1281.4 | |
| 11532500 | BR | 0.67 | 3297.7 | 1866.4 |
| LR | 0.67 | 3297.8 | 1866.7 | |
| GBDT | 0.78 | 2687.8 | 1536.7 | |
| BP | 0.78 | 2689.3 | 1561.4 | |
| RF | 0.79 | 2637.0 | 1535.1 | |
| HistG | 0.78 | 2718.7 | 1543.3 | |
| LSTM | 0.80 | 2557.7 | 1524.3 | |
| GRU | 0.79 | 2626.9 | 1534.6 | |
| average | 0.76 | 2814.1 | 1621.1 | |
| 12035000 | BR | 0.70 | 1425.9 | 928.8 |
| LR | 0.70 | 1425.9 | 928.9 | |
| GBDT | 0.83 | 1069.4 | 669.7 | |
| BP | 0.82 | 1096.3 | 723.2 | |
| RF | 0.82 | 1098.5 | 674.4 | |
| HistG | 0.82 | 1099.9 | 670.8 | |
| LSTM | 0.84 | 1034.5 | 653.8 | |
| GRU | 0.84 | 1047.2 | 658.7 | |
| average | 0.79 | 1162.2 | 738.5 |
| Basin Code | Model | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01022500 | IKNN-MME | 0.81 | 274.7 | 137.4 |
| KNN-MME | 0.80 | 281.2 | 138.7 | |
| OLS | 0.56 | 419.7 | 262.9 | |
| HistG | 0.55 | 425.8 | 245.5 | |
| LSTM | 0.55 | 426.3 | 248.0 | |
| GRU | 0.54 | 431.3 | 255.8 | |
| 12414500 | IKNN-MME | 0.84 | 1290.2 | 553.6 |
| KNN-MME | 0.83 | 1337.3 | 561.6 | |
| OLS | 0.56 | 2149.0 | 1262.7 | |
| HistG | 0.57 | 2122.2 | 1161.1 | |
| LSTM | 0.58 | 2095.4 | 1127.4 | |
| GRU | 0.58 | 2094.3 | 1120.9 | |
| 11532500 | IKNN-MME | 0.89 | 1939.3 | 808.3 |
| KNN-MME | 0.88 | 2030.1 | 822.3 | |
| OLS | 0.80 | 2583.3 | 1505.2 | |
| RF | 0.79 | 2637.0 | 1535.1 | |
| LSTM | 0.80 | 2557.7 | 1524.3 | |
| GRU | 0.79 | 2626.9 | 1534.6 | |
| 12035000 | IKNN-MME | 0.89 | 875.8 | 372.0 |
| KNN-MME | 0.87 | 925.2 | 382.5 | |
| OLS | 0.84 | 1047.9 | 669.4 | |
| GBDT | 0.83 | 1069.4 | 669.7 | |
| LSTM | 0.84 | 1034.5 | 653.8 | |
| GRU | 0.84 | 1047.2 | 658.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, T.; Chen, L.; Yi, B.; Li, S.; Leng, Z.; Gan, X.; Mei, Z. Application of the Improved K-Nearest Neighbor-Based Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Runoff Prediction. Water 2024, 16, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010069
Xie T, Chen L, Yi B, Li S, Leng Z, Gan X, Mei Z. Application of the Improved K-Nearest Neighbor-Based Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Runoff Prediction. Water. 2024; 16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Tao, Lu Chen, Bin Yi, Siming Li, Zhiyuan Leng, Xiaoxue Gan, and Ziyi Mei. 2024. "Application of the Improved K-Nearest Neighbor-Based Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Runoff Prediction" Water 16, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010069
APA StyleXie, T., Chen, L., Yi, B., Li, S., Leng, Z., Gan, X., & Mei, Z. (2024). Application of the Improved K-Nearest Neighbor-Based Multi-Model Ensemble Method for Runoff Prediction. Water, 16(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010069







