Assessment and Management of the Water Quality and Heavy-Metal Pollution of a Protected Hypersaline Wetland in the United Arab Emirates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
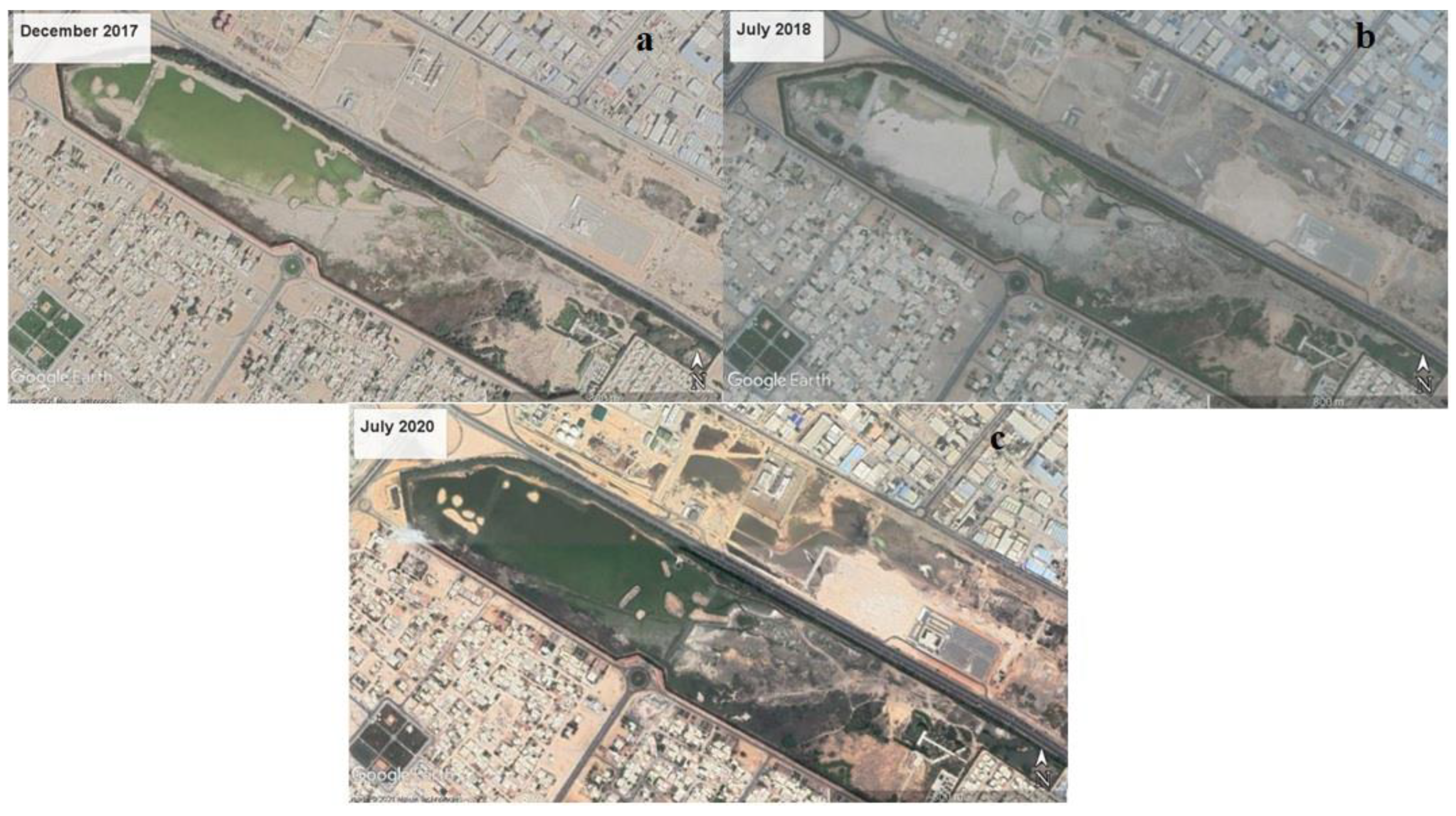
2.1. Site of Study
Sample Collection and On-Site Water-Quality Monitoring
2.2. Physical Water-Quality Parameters
2.3. Bacterial Analysis—Total Coliform and Escherichia coli (E. coli) E. coli Analysis (IDEXX)
2.4. Water Quality Index and Assessment of Hazard
- Calculate F1 which represents the number of variables whose objectives are not met
- Calculate F2 which represents the frequency by which the objectives are not met
- Calculate F3 representing the amount by which the objectives are not metFinally, all values are used for the equation
- The calculation of pollution load (PL)where C is the observed concentration of the specific parameter and S represents the standard or highest permissible limit.
- The calculation of the water pollution index (WPI)
2.5. Heavy Metal Analysis of Sediments
3. Results
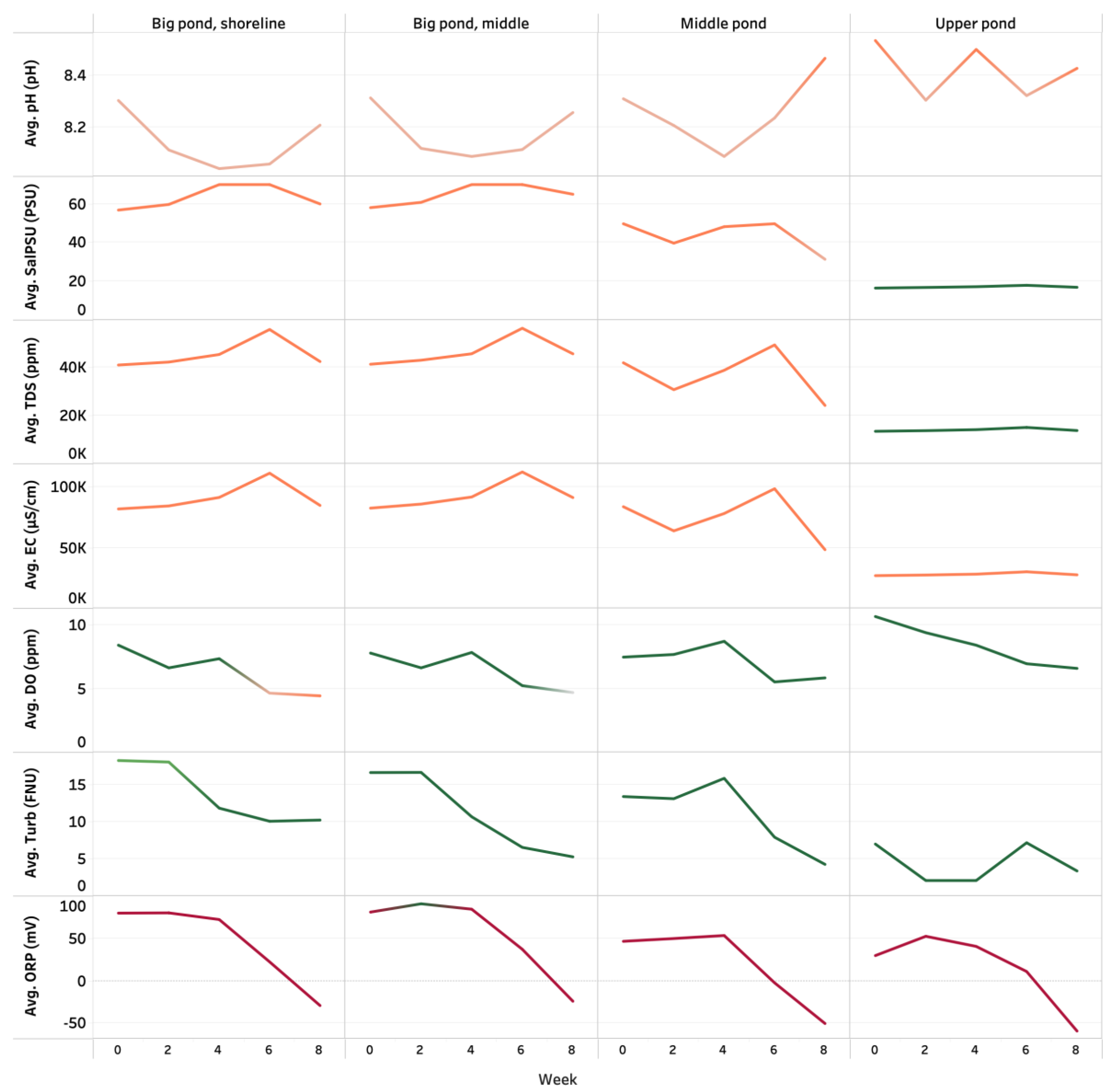
3.1. Water Quality Parameters
3.1.1. On-Site Measured Parameters
3.1.2. In-Lab Measured Parameters
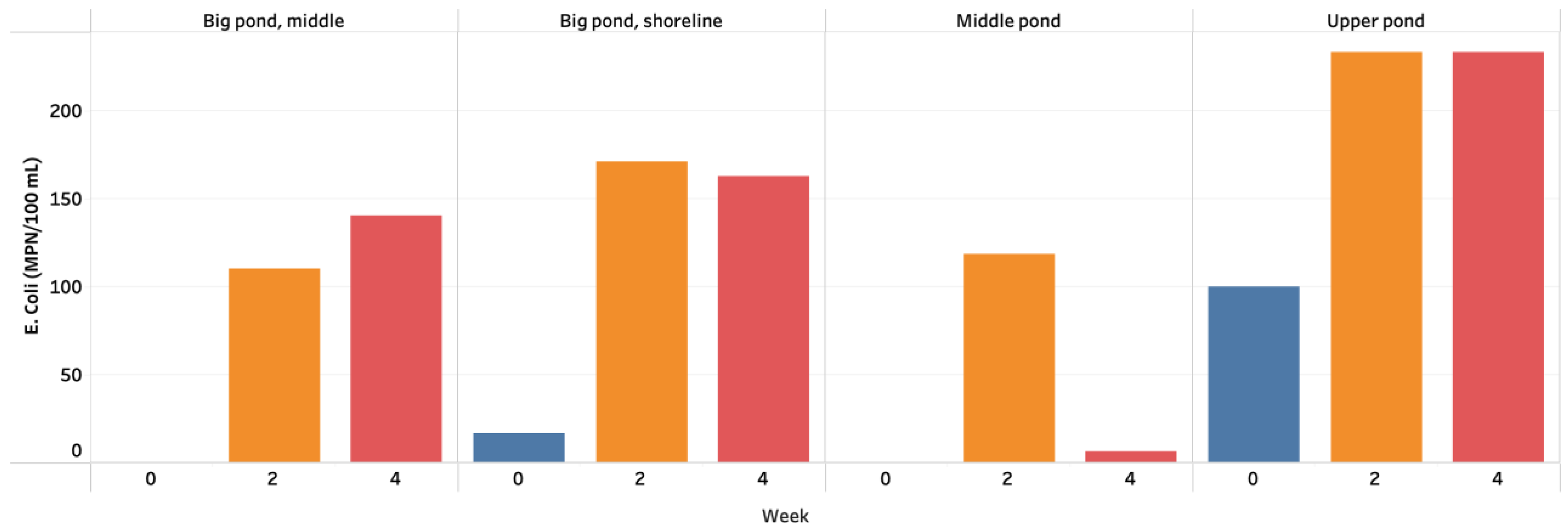
3.2. Bacterial Analysis—Total Coliform and E. coli Analysis (IDEXX)
3.3. Heavy Metal Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Water-Quality Parameters
4.2. Bacteria Analysis
4.3. Heavy Metals
4.4. Water-Quality Index and Hazard Assessment
| Sampling Locations | Heavy Metals in Sediments | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/kg) | ||||||||||
| Al | As | Cr | Cu | Fe | Pb | Ni | Zn | Hg | Cd | |
| Upper Pond | 3840 | 2.9 | 78.7 | 9.2 | 13,700 | 8.5 | 330 | 32.6 | 0.2 | ND |
| Middle Pond | 4990 | 2.9 | 30.3 | 10.5 | 7725 | 6.4 | 41.8 | 31.8 | 0 | ND |
| Big pond, middle | 4415 | 2.9 | 54.5 | 9.9 | 10,712.5 | 7.4 | 185.9 | 32.2 | 0.1 | ND |
| Big pond, shoreline | 521 | 1.1 | 6.5 | 1.2 | 590.3 | 1.9 | 6.2 | 10.4 | 0 | ND |
| Average | 3171.1 | 2.4 | 27.7 | 9.7 | 5599.3 | 5.6 | 54.1 | 52.3 | 0 | ND |
| Regional Parameter a | -- | 50 | 250 | 100 | -- | 200 | -- | 500 | 2 | 5 |
| Global Parameter b | -- | ND | 25–75 | 25–50 | 1.7–2.5 | 40–60 | 20–50 | 90–200 | ND | 6 |
| Average this study | 3171.1 | 2.4 | 27.7 | 9.7 | 5599.3 | 5.6 | 54.1 | 52.3 | 0 | ND |
| Hazard Quotient (HQ) | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 2239.72 | 0.03 | 1.08 | 0.10 | 0 | 0 | |
| UAE Mangroves (Samara et al., 2021) | 12,683.02 | -- | 17.31 | 1.99 | 1365.13 | 1.76 | 35.62 | 26.9 | -- | 0.08 |
| Hazard Quotient (HQ) | 0.07 | 0.02 | 546.05 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 0.05 | 0.02 | |||
4.5. Management of the Reserve
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsar Convention on Wetland. The Introductory Ramsar Brochure, 3rd ed.; Ramsar Convention on Wetland: Gland, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/about-the-convention-on-wetlands-0 (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- US EPA. What is a Wetland?|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wetlands/what-wetland (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Dorche, E.E.; Fathi, P.; Ofogh, A.E. Wetland water quality assessment in cold and dry regions (Case study: Choghakhor wetland, Iran). Limnol. Rev. 2019, 19, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, C.; Patel, V. Comparative Study of Seasonal Variation in Physicochemical Properties of Selected Wetlands of Mehsana Districts, North Gujarat. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2011, 4, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.A.; Nichols, S.J. The effects of water-level fluctuations on vegetation in a Lake Huron wetland. Wetlands 2008, 28, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaid, S.; Samraoui, B.; Thomas, J.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Schneider, W.; O’connell, M. An overview of wetlands of Saudi Arabia: Values, threats, and perspectives. AMBIO 2016, 46, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzinada, A. The role of protected areas in conserving biological diversity in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 54, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Arshad, M.; Hussain, M.; Batool, M.; Malik, M.F. Assessment of Avifauna and Water Quality Parameters of Mangla Wetland, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2021, 53, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. Wetlands Disappearing Three Times Faster Than Forests. 2018. Available online: https://unfccc.int/news/wetlands-disappearing-three-times-faster-than-forests (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Shiji, M.; Sabitha, A.R.; Prabhakar, K.; Harikumar, P.S. Water quality assessment of Kavvayi Lake of northern Kerala, India using CCME water quality index and biological water quality criteria. J. Environ. Biol. 2016, 37, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, M.; Sarkar, A. Development of Molecular Identification of Nitrifying Bacteria in Water Bodies of East Kolkata Wetland, West Bengal. J. Bioremediation Biodegradation 2014, 5, 1000211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Why are Wetlands Important: Wetlands and Nature? 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wetlands/why-are-wetlands-important (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Dahl, T. Status and Trends of Wetlands in the Conterminous United States 2004 to 2009; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: http://www.fws.gov/wetlands/Status-And-Trends-2009/index.html (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kükrer, S.; Mutlu, E. Assessment of surface water quality using water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses in Saraydüzü Dam Lake, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convention on Wetlands. Global Wetland Outlook: Special Edition 2021; Secretariat of the Convention on Wetlands: Gland, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, W.P.; Yu, L.H.; Yang, W.H.; Yin, Z.Y. Water quality assessment and analysis for rehabilitate and management of wetlands: A case study in Nanhai wetland of Baotou, China. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 60, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Weng, B.; Yan, D.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Bi, W.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y. Wetlands of International Importance: Status, Threats, and Future Protection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseena, M.; Malik, M.F.; Javed, A.; Arshad, S.; Asif, N.; Zulfiqar, S.; Hanif, J. Water pollution and human health. Environ. Risk Assess. Remediat. 2017, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J. Waterborne diseases. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 338–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, S.; Nummi, P.; Ojala, A. Urban Wetlands: A Review on Ecological and Cultural Values. Water 2021, 13, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabudin, M.M.; Musa, S. Occurrence of Surface Water Contaminations: An Overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 140, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L. Follow-On Assessment of Phase 1 Wetlands and Initial Assessment of Phase 2 Wetlands with Recommendations for their Rehabilitation and Sustainable Management; The Freshwater Consulting Group: Cape Town, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, I.; Marsalek, J.; Breil, P. (Eds.) Aquatic Habitats in Sustainable Urban Water Management: Urban Water Series—UNESCO-IHP, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Climate Change and Environment (MOCCAE). Status of Important Bird Areas in the UAE. 2018. Available online: https://www.moccae.gov.ae/en/reports-listing/28/4/2018/status-of-important-bird-areas-iba-in-the-uae-2018.aspx (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Dennehy, J. Climate Change a Serious Threat to the Emirates Wetlands. The National. 2019. Available online: https://www.pressreader.com/uae/the-national-news/20190308/281655371383484 (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Soorae, P.; Sakkir, S.; Saji, A.; Khan, S.B.; Al Zaabi, R.; Shah, J.N.; Ali, A.; Al Omari, K.; Al Dhaheri, A.; Javed, S.; et al. A Review of the Flora and Fauna in the Al Wathba Wetland Reserve in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Wetlands 2019, 40, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, F.; Ali, T.; Twyford, J.; Knuteson, S. Investigation of fecal contamination of groundwater and surface water at al wasit nature reserve, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 18, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shadrin, N. Hypersaline Lakes as the Polyextreme Habitats for Life. In Introduction to Salt Lake Sciences; Zheng, M., Deng, T., Oren, A., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ragnvaldsson, D.; Herting, G.; Jönsson, A.; Odnevall, I. Applying Generic Water Quality Criteria to Cu and Zn in a Dynamic Aquatic Environment—The Case of the Brackish Water Formation Strömmen-Saltsjön. Water 2022, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, N.; Anufriieva, E.; Latushkin, A.; Prazukin, A.; Yakovenko, V. Daily Rhythms and Oxygen Balance in the Hypersaline Lake Moynaki (Crimea). Water 2022, 14, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriieva, E.; Kolesnikova, E.; Revkova, T.; Latushkin, A.; Shadrin, N. Human-Induced Sharp Salinity Changes in the World’s Largest Hypersaline Lagoon Bay Sivash (Crimea) and Their Effects on the Ecosystem. Water 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar. Ramsar Information Sheet United Arab Emirates Wasit Nature Reserve. 2386. 2019. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris/2386 (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Mohammed, A.; Samara, F.; Alzaatreh, A.; Knuteson, S.L. Statistical Analysis for Water Quality Assessment: A Case Study of Al Wasit Nature Reserve. Water 2022, 14, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWO, World Weather Online. United Kingdom. Available online: https://www.worldweatheronline.com/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Saffran, K.; Cash, K.; Hallard, K. CCME Water Quality Index 1.0 User’s Manual. Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2001; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Climate Change and Environment (MOCCAE). Guiding Standards for Marine Water Properties in the United Arab Emirates. Ministry of Climate Change and Environment. 2020. Available online: https://www.moccae.gov.ae/assets/download/d6b99426/brand_%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%8A%D9%8A%D8%B1%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%B4%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%8A%D8%A9%20%D9%84%D8%AE%D9%88%D8%A7%D8%B5%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D9%8A%D8%A7%D9%87%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%8A%D8%A9_En[2].pdf.aspx (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Dubai Municipality. Environmental Standards and Allowable Limits of Pollutants on land, Water and Air Environment. In Information Bulleting, Dubai Municipality; Environment Protection & Safety Section: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Parameters of Water Quality: Interpretation and Standards; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.ie/pubs/advice/water/quality/Water_Quality (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Zamdayu, W.J.; Abdulkadir, S.A. Evaluating Water Quality of Lower River Gongola for Irrigation. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. 2021, 3, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katyal, D. Water Quality Indices Used for Surface Water Vulnerability Assessment by Deeksha Katyal: SSRN. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 2, 154–173. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2160726 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K. Water pollution index—A new integrated approach to rank water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11466:1995; Soil Quality—Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia. (n.d.). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/19418.html (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Telliard, W.A. Method 245.7 Mercury in Water by Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Revision 2.0.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Samara, F.; Solovieva, N.; Ghalayini, T.; Nasrallah, Z.A.; Saburova, M. Assessment of the Environmental Status of the Mangrove Ecosystem in the United Arab Emirates. Water 2020, 12, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabelkova, J.; Kominkova, D. Trace metals in the bed sediment of small urban streams. Open Environ. Biol. Monit. J. 2012, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Guidelines for the Pollution Classification of Great Lakes Harbor Sediments; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1977.
- Cowardin, L.M.; Carter, V.; Golet, F.C.; LaRoe, E.T. Classification of Wetlands and Deep-Water Habitats of the United States; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA; Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center Online: Jamestown, ND, USA, 1979. Available online: http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/wetlands/classwet/index.htm (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Naji, T.A.; Al-Jasim, A.A.N.; Shaban, A.H.; Abduljabbar, H.M. Spatial Analyzing of the Chemical Soil Properties for the Sanam Mountain-Al Zubair Region South of Basra Province and Diagnosis of its Effects on Soil Qualities Using Remote Sensing Technology and GIS. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1050, pp. 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Batayneh, A.; Nazzal, Y.; Ghrefat, H.; Elawadi, E.; Zaman, H. Status of trace metals in surface seawater of the Gulf of Aqaba, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Rashdan, M.; Nazzal, Y.; Howari, F.; Iqbal, J.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.; Al Bsoul, A.; Khashashneh, S. Evaluation of the Gulf of Aqaba Coastal Water, Jordan. Water 2020, 12, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, Z.Q.; Al-Madhhachi, A.-S.T.; Sachit, D.E. Evaluation of Water Quality Parameters in Shatt AL-Arab, Southern Iraq, Using Spatial Analysis. Hydrology 2020, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriadah, M. Water quality of two semi-closed areas in the United Arab Emirates coast along the Arabian Gulf: A comparative study. Pak. J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 11, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, M. Water Quality 101: What is ORP in Water Testing? Jenco. 2018. Available online: https://blog.jencoi.com/what-is-orp-in-water-testing (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Reineke, W.; Schlömann, M. Heavy Metals and Other Toxic Inorganic Ions. In Environmental Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Paul, T.T.; Sudheesan, D.; Sharma, S.K.; Suresh, V.R.; Das, B.K.; Manoharan, S.; Vijaykumar, M.E.; Samanta, S.; Jana, C. Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Changes in Water Quality of a Tropical River in Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India, Using Physicochemical Quality Indices and Multivariate Analysis. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 1375–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, H.; Rather, R.A.; Malik, S.; Bhat, M.A.; Khan, A.H.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Mir, I.A. Effect of Seasonal Variation on Pollution Load of Water of Hokersar Wetland: A Case Study of Queen Wetland of Kashmir, J&K, India. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. Chemical OXYGEN Demand in Influent Wastewater Monitoring. YSI. 2017. Available online: https://www.ysi.com/ysi-blog/water-blogged-blog/2017/01/chemical-oxygen-demand-in-influent-wastewater-monitoring (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Herlina, N.; Lubis, M.T.; Husin, A.; Putri, I. Studies on decreasing Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) on artificial laundry wastewater using anaerobic-aerobic biofilter dipped with bio ball media. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 276, 06015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Shafi, S.; Bandh, S.A.; Shameem, N. Impact of environmental changes and human activities on bacterial diversity of lakes. In Freshwater Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 105–136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, W.; Sun, Q.; Mortimer, R.J. Influence of salinity on COD measurements in coastal water management. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 18338–18345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redouane, F.; Mourad, L. Determination of the Sea Waters Quality of Arzew-Algeria Gulf. J. Pollut. Eff. Cont. 2017, 5, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.; Bange, H.W.; Dippner, J.W.; Middelburg, J.; Montoya, J.; Ward, B. The marine nitrogen cycle: Recent discoveries, uncertainties and the potential relevance of climate change. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bunn, S.E.; Burford, M.A. Effects of water level fluctuations on nitrogen dynamics in littoral macrophytes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 63, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriadah, M. Nutrient salts in the United Arab Emirates waters (the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman). Pak. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 15, 1–9. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/33722074.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Fadiran, A.; Dlamini, S.; Mavuso, A. A comparative study of the phosphate levels in some surface and ground water bodies of Swaziland. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2008, 22, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, D.S.; Simina, D. Water Stress Induced by Enrichment of Nutrient and Climate Change Factors. In Water Stress in Plants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Urmeneta, J.; Gascón, J.; Oubiña, A.; Pérez-Lezaun, A. Sensitivity of selected bacterial species to UV radiation. Curr. Microbiol. 1995, 30, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccò, M.; White, N.E.; Harrod, C.; Salazar, G.; Aguilar, P.; Cubillos, C.F.; Meredith, K.; Baxter, B.K.; Oren, A.; Anufriieva, E.; et al. Salt to conserve: A review on the ecology and preservation of hypersaline ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2828–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrin, N.; Anufriieva, E.; Gajardo, G. Ecosystems of Inland Saline Waters in the World of Change. Water 2023, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layalestani, S.S.S.; Shavandi, M.; Haddadi, A.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Dastgheib, S.M.M. Bacterial community structure in saline sediments from hypersaline wetland in south of Halghe Dare hills, Alborz province. J. Microb. World 2020, 13, 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Karbasdehi, V.N.; Dobaradaran, S.; Nabipour, I.; Ostovar, A.; Arfaeinia, H.; Vazirizadeh, A.; Mirahmadi, R.; Keshtkar, M.; Ghasemi, F.F.; Khalifei, F. Indicator bacteria community in seawater and coastal sediment: The Persian Gulf as a case. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Yoon, J.; Hovde, C. A brief overview of Escherichia Coli and its plasmid. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, W.; Marhaba, T. pH Effect on Heavy Metal Release from a Polluted Sediment. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7597640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klubi, E.; Samuel, A.; Akita, L. Assessment of hydrological pathway and water quality of the Songor wetland, Ghana. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjani, F.; Djidel, M.; Labar, S.; Bouchagoura, L.; Bara, C.R. Groundwater physico-chemical properties and water quality changes in shallow aquifers in arid saline wetlands, Ouargla, Algeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Zarei, M.; Keshavarzi, B.; Golshani, R.; Zafarani, S.G.G. Water quality stress to Amirkalayeh Wetland, Northern Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetaia, S.A.; Abu Khatita, A.M.; Abdelhafez, N.A.; Shaker, I.M.; El Kafrawy, S.B. Evaluation of Potential Health Risk, Heavy Metal Pollution Indices and Water Quality of Edku Lagoon-Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 265–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, S.; Cui, B.; Du, J. Responses of Urban Wetland to Climate Change and Human Activities in Beijing: A Case Study of Hanshiqiao Wetland. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UAE’s Wetlands Are a National Treasure that Deserve Our Care and Protection (n.d.). Available online: https://www.thenationalnews.com/opinion/comment/the-uae-s-wetlands-are-a-national-treasure-that-deserve-our-care-and-protection-1.785600 (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Bourhane, Z.; Cagnon, C.; Castañeda, C.; Rodríguez-Ochoa, R.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Duran, R. Vertical organization of microbial communities in Salineta hypersaline wetland, Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 869907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzi, M.; Mfarrej, B. Climate Change Patterns in the UAE: A Qualitative Research and Review. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. Int. Q. Sci. J. 2019, 18, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Climate Change and Environment (MOCCAE). National Climate Change Plan of the United Arab Emirates 2017–2050; Ministry of Climate Change and Environment: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2017; pp. 22–48.
- Assaf, H.; Idwan, S.; Jallad, A.H.; Ammari, M.Z.J.; Al Chaar, A.; Kouja, M. Public values regarding an urban mangrove wetland in the united arab emirates. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2022, 30, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudneva, I.I.; Gaisky, P.V.; Shaida, V.G.; Shaida, O.V. Assessing Climate and Human Activity Effects on Hypersaline Lake Ecosystem: Case Study of Saki Lake, Crimea. Water 2023, 15, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
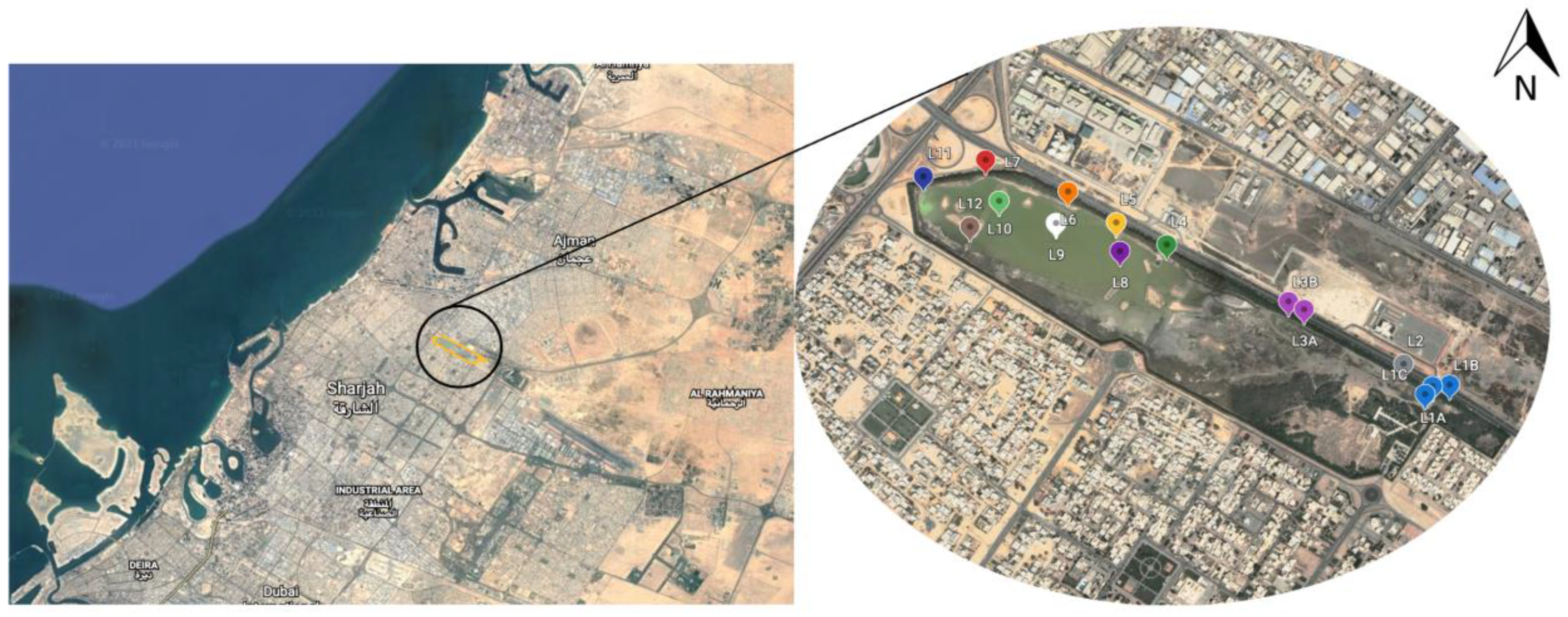






| Sampling Locations | Site Category |
|---|---|
| Loc 1A, 1B, 1C | Upper Pond |
| Loc 2, 3A, 3B | Middle Pond |
| Loc 8, 9, 10 | Big pond, middle |
| Loc 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12 | Big pond, shoreline |
| Sampling Categories | Temp | pH | Turbidity | TDS | ORP | D.O. | EC | Salinity | Chloride | Nitrates | Ammonia | COD | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (FNU) | (ppm) | (mV) | (ppm) | (µS/cm) | (psu) | (ppm) | (ppm) | (ppm) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | ||
| Upper Pond | 28.33 | 8.42 | 4.37 | 14,076.67 | 15.03 | 8.41 | 28,144.67 | 17.12 | 12,642.00 | 50.70 | 1.80 | 68.00 | 9.90 | 0.20 |
| Middle Pond | 31.17 | 8.25 | 10.80 | 36,009.00 | 17.30 | 7.02 | 72,601.00 | 42.85 | 33,990.00 | 57.10 | 0.40 | 1216.00 | 29.90 | 0.70 |
| Big pond, middle | 28.75 | 8.18 | 11.17 | 46,446.00 | 54.07 | 6.44 | 92,997.33 | 64.78 | 37,244.00 | 57.20 | 0.20 | 1412.00 | 21.00 | 0.70 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 29.14 | 8.14 | 13.68 | 44,031.50 | 45.25 | 6.30 | 88,205.83 | 63.32 | 35,442.00 | 57.60 | 0.20 | 1578.00 | 19.60 | 0.70 |
| Max | 31.17 | 8.42 | 13.68 | 46,446.00 | 54.07 | 8.41 | 92,997.33 | 64.78 | 37,244.00 | 57.60 | 1.80 | 1578.00 | 29.90 | 0.70 |
| Min | 28.33 | 8.14 | 4.37 | 14,076.67 | 15.03 | 6.30 | 28,144.67 | 17.12 | 12,642.00 | 50.70 | 0.20 | 68.00 | 9.90 | 0.20 |
| Average | 29.35 | 8.25 | 10.00 | 35,140.79 | 32.91 | 7.04 | 70,487.21 | 47.02 | 29,830.00 | 55.70 | 0.60 | 1068.00 | 20.10 | 0.50 |
| Stdev | 1.26 | 0.12 | 3.97 | 14,734.35 | 19.69 | 0.97 | 29,541.01 | 22.31 | 11,535.00 | 3.30 | 0.80 | 683.00 | 8.20 | 0.20 |
| Regional Permissible Limit a | 19–23 | 6.0–9.0 | <75 | <20,000 | - | <5 | <2000 | <45 | <250 | <50 | <0.06 | <40 | <2 | <0.05 |
| Global Permissible Limit b | 15–35 | 6.5–8.5 | <75 | <50,000 | 300–500 | <5 | <1000 | <40 | <250 | <50 | <0.04 | 1.2–30.2 | <0.3 | <0.3 |
| Site Category | Sampling Location | Total Coliforms (MPN/100 mL) | E. coli (MPN/100 mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| week 0 | week 2 | week 4 | week 0 | week 2 | week 4 | ||
| Upper pond | 1A | 3690 | 9139 | 13,786 | <100 | 345 | 170 |
| Upper pond | 1B | 2530 | 6893 | 11,496 | 200 | 122 | 362 |
| Upper pond | 1C | 1080 | 7915 | 5190 | 100 | 233 | 168 |
| Middle pond | 2 | 200 | 419 | <100 | <100 | 230 | <100 |
| Middle pond | 3A | 520 | 695 | 556 | <100 | 62 | <100 |
| Middle pond | 3B | - | 368 | 462 | - | 63 | 20 |
| Big pond, middle | 8 | <100 | 1014 | 618 | <100 | 98 | 126 |
| Big pond, middle | 9 | <100 | 479 | 456 | <100 | 52 | 104 |
| Big pond, middle | 10 | <100 | 860 | 758 | <100 | 181 | 192 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 4 | <100 | 2851 | 1366 | <100 | 206 | 82 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 5 | <100 | 1467 | 944 | <100 | 98 | 146 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 6 | <100 | 4160 | 1248 | <100 | 169 | 262 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 7 | <100 | 2282 | 1226 | <100 | 145 | 170 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 11 | <100 | 3441 | 2666 | <100 | 108 | 124 |
| Big pond, shoreline | 12 | 100 | 1904 | 1714 | 100 | 301 | 194 |
| Average | 1353 | 2925 | 3034 | 133 | 161 | 163 | |
| Acceptable Regional Parameter a | <1000 | <200 | |||||
| Acceptable Global Parameter b | <1000 | 30–35 | |||||
| Sampling Locations | Heavy Metals in Sediments (mg/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | As | Cr | Cu | Fe | Pb | Ni | Zn | Hg | |
| Loc 1 | 3840.0 | 2.9 | 78.7 | 9.2 | 13,700.0 | 8.5 | 330.0 | 32.6 | 0.2 |
| Loc 2 | 5480.0 | 2.9 | 29.6 | 13.0 | 7870.0 | 7.0 | 53.9 | 39.1 | 0.0 |
| Loc 3 | 4500.0 | 2.8 | 31.0 | 8.0 | 7580.0 | 5.7 | 29.7 | 24.5 | 0.0 |
| Loc 4 | 3740.0 | 2.2 | 22.0 | 5.1 | 5220.0 | 3.2 | 39.0 | 19.7 | 0.0 |
| Loc 5 | 3800.0 | 3.6 | 21.9 | 5.9 | 5690.0 | 2.8 | 38.0 | 15.1 | 0.0 |
| Loc 6 | 3090.0 | 1.0 | 18.3 | 5.6 | 3330.0 | 3.0 | 26.0 | 33.3 | 0.0 |
| Loc 7 | 4340.0 | 2.4 | 28.7 | 13.4 | 5750.0 | 8.2 | 42.5 | 218.0 | 0.0 |
| Loc 8 | 443.0 | 1.8 | 5.7 | 0.0 | 537.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 8.7 | 0.0 |
| Loc 9 | 404.0 | 1.5 | 5.4 | 0.0 | 437.0 | 1.8 | 4.8 | 8.2 | 0.0 |
| Loc 10 | 716.0 | 0.0 | 8.5 | 3.7 | 797.0 | 1.8 | 7.9 | 14.4 | 0.0 |
| Loc 11 | 4010.0 | 3.0 | 28.7 | 7.9 | 5880.0 | 4.0 | 23.8 | 52.8 | 0.0 |
| Loc 12 | 3690.0 | 4.4 | 53.3 | 44.5 | 10,400.0 | 19.5 | 48.1 | 161.0 | 0.0 |
| Max | 5480.0 | 4.4 | 78.7 | 44.5 | 13,700.0 | 19.5 | 330.0 | 218.0 | 0.2 |
| Min | 404.0 | 0.0 | 5.4 | 0.0 | 437.0 | 1.8 | 4.8 | 8.2 | 0.0 |
| Average | 3171.1 | 2.4 | 27.7 | 9.7 | 5599.3 | 5.6 | 54.1 | 52.3 | 0.0 |
| Stdev | 1698.6 | 1.2 | 20.8 | 11.7 | 4028.2 | 5.0 | 88.4 | 66.5 | 0.1 |
| Sampling Locations | Site Category | CCME WQI | Category | WPI | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loc 1A, 1B, 1C | Upper Pond | 19 | Poor | 8 | Highly Polluted |
| Loc 2, 3A, 3B | Middle Pond | 26 | Poor | 16 | Highly Polluted |
| Loc 8, 9, 10 | Big pond, middle | 26 | Poor | 18 | Highly Polluted |
| Loc 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12 | Big pond, shoreline | 21 | Poor | 18 | Highly Polluted |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samara, F.; Knuteson, S.L.; Abdulateef, T.A.; Yaghmour, F.; Whittington-Jones, B.; Al Abdalla, S.M.; Khalil, B.; Ahmed, N. Assessment and Management of the Water Quality and Heavy-Metal Pollution of a Protected Hypersaline Wetland in the United Arab Emirates. Water 2023, 15, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091766
Samara F, Knuteson SL, Abdulateef TA, Yaghmour F, Whittington-Jones B, Al Abdalla SM, Khalil B, Ahmed N. Assessment and Management of the Water Quality and Heavy-Metal Pollution of a Protected Hypersaline Wetland in the United Arab Emirates. Water. 2023; 15(9):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091766
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamara, Fatin, Sandra L. Knuteson, Tala A. Abdulateef, Fadi Yaghmour, Brendan Whittington-Jones, Sara Mohamed Al Abdalla, Baha Khalil, and Norhan Ahmed. 2023. "Assessment and Management of the Water Quality and Heavy-Metal Pollution of a Protected Hypersaline Wetland in the United Arab Emirates" Water 15, no. 9: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091766
APA StyleSamara, F., Knuteson, S. L., Abdulateef, T. A., Yaghmour, F., Whittington-Jones, B., Al Abdalla, S. M., Khalil, B., & Ahmed, N. (2023). Assessment and Management of the Water Quality and Heavy-Metal Pollution of a Protected Hypersaline Wetland in the United Arab Emirates. Water, 15(9), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091766






