Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration Using Remote Sensing and SEBAL Model in an Arid Environment of Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. MODIS Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
2.2.3. Other Data
2.3. SEBAL Model
2.3.1. Net Radiation Flux (Rn)
2.3.2. Soil Heat Flux (G)
2.3.3. Sensible Heat Flux (H)
2.3.4. Daily ET
2.4. Validation Methods
2.4.1. FAO P-M Equation
2.4.2. Pan Evaporation
2.4.3. MOD16 ET Product
2.5. Principal Component Regression
2.5.1. PCA
- (1)
- Extraction of the principal component (PC). To determine the number of PCs, the cumulative contribution of variance over 85% was used as the selection criterion herein.
- (2)
- Calculation of the PC score. It is expressed as:
2.5.2. MLR
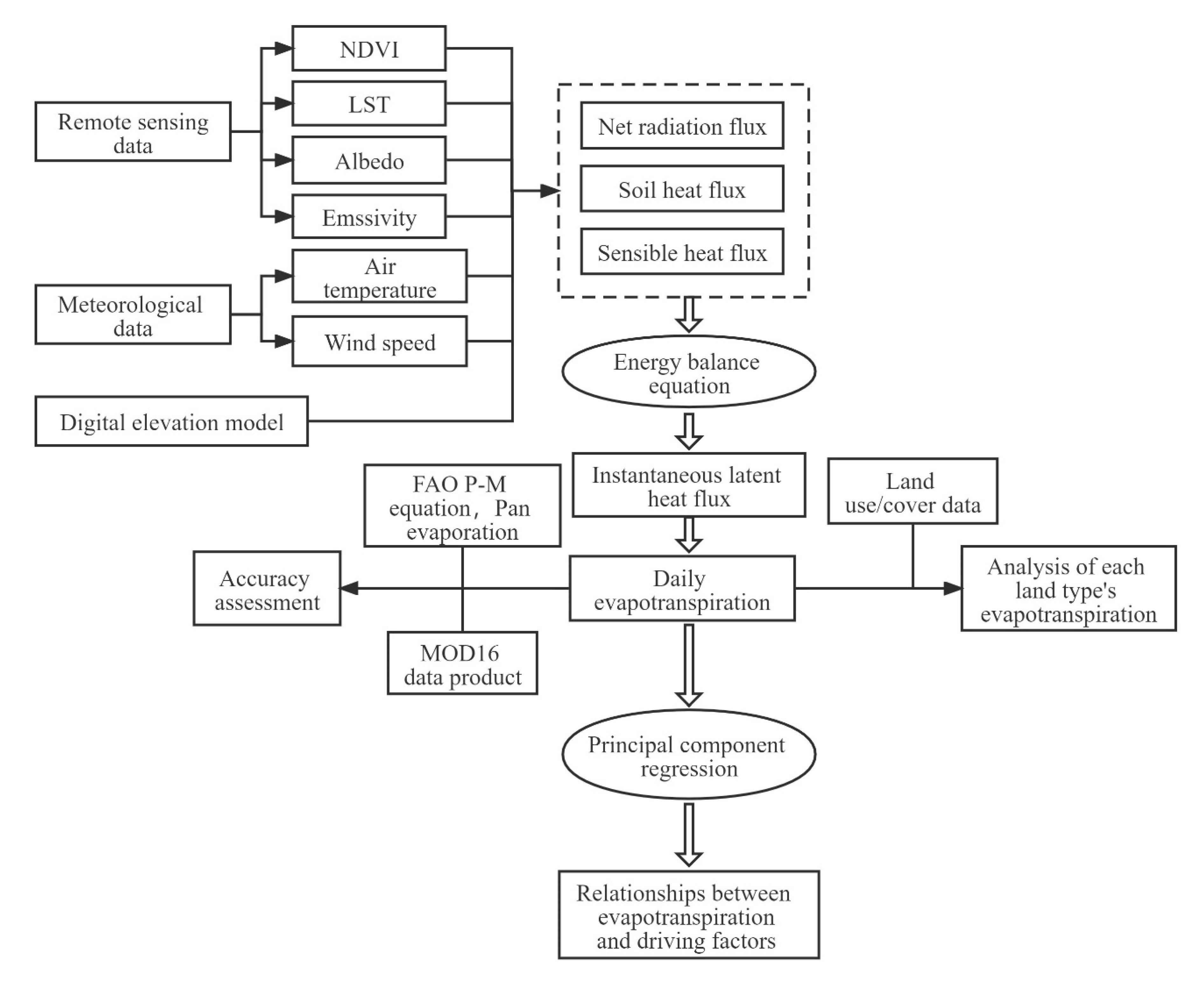
2.6. Technical Process
3. Results
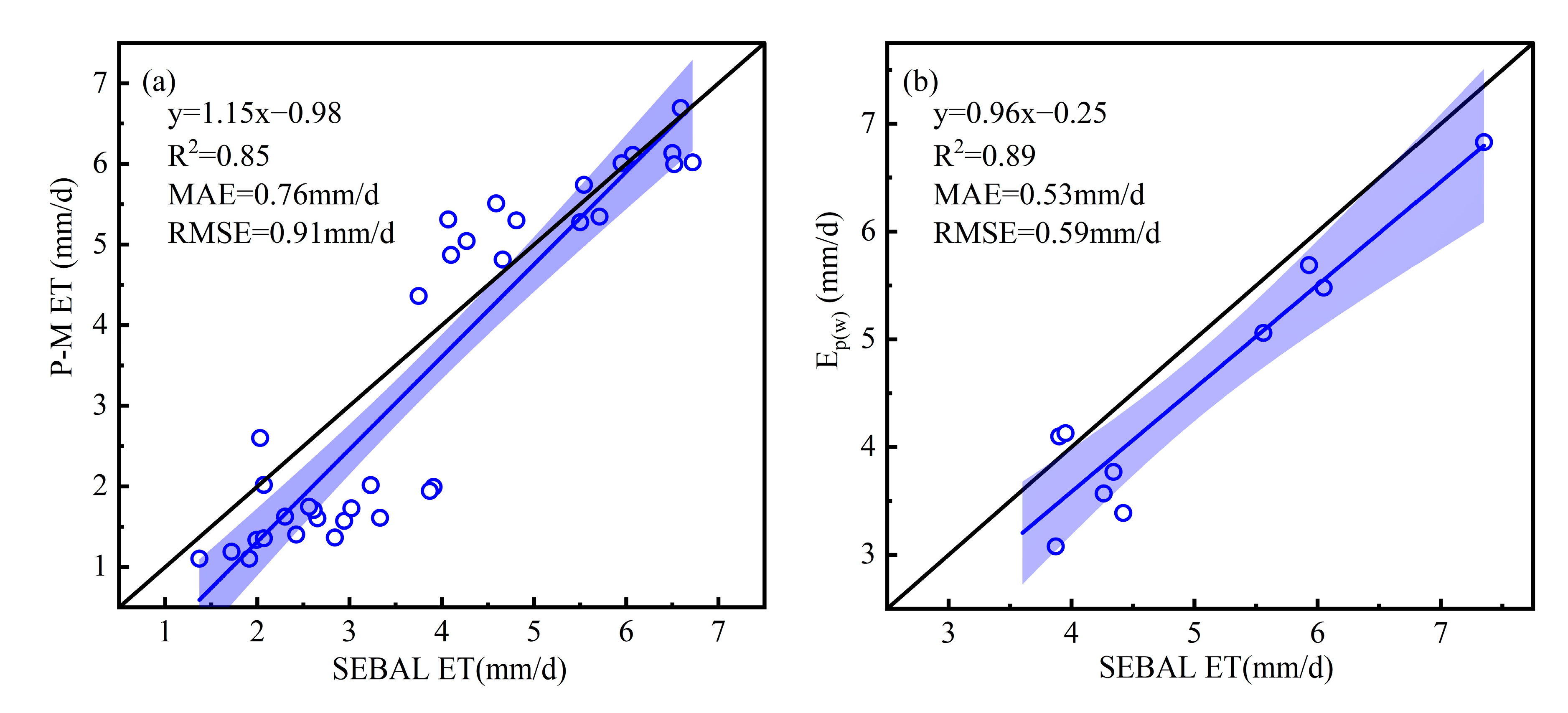
3.1. Accuracy Validation of SEBAL ET
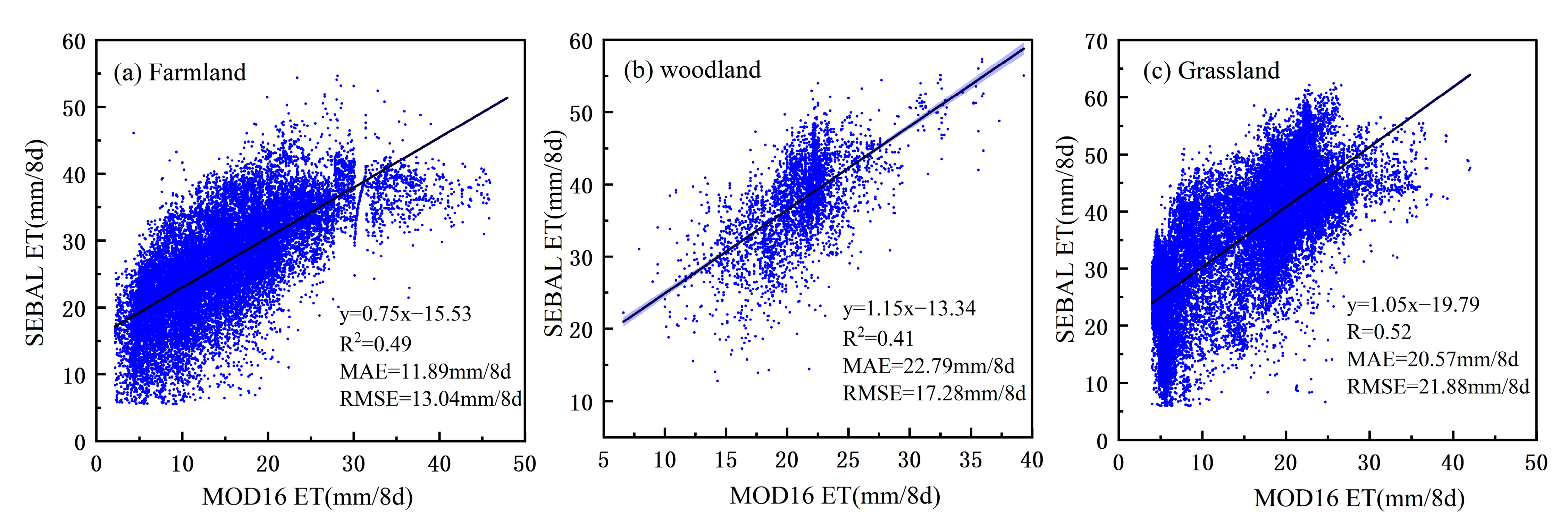
3.2. Comparison of SEBAL ET and MOD16 ET under Different Land Cover Types
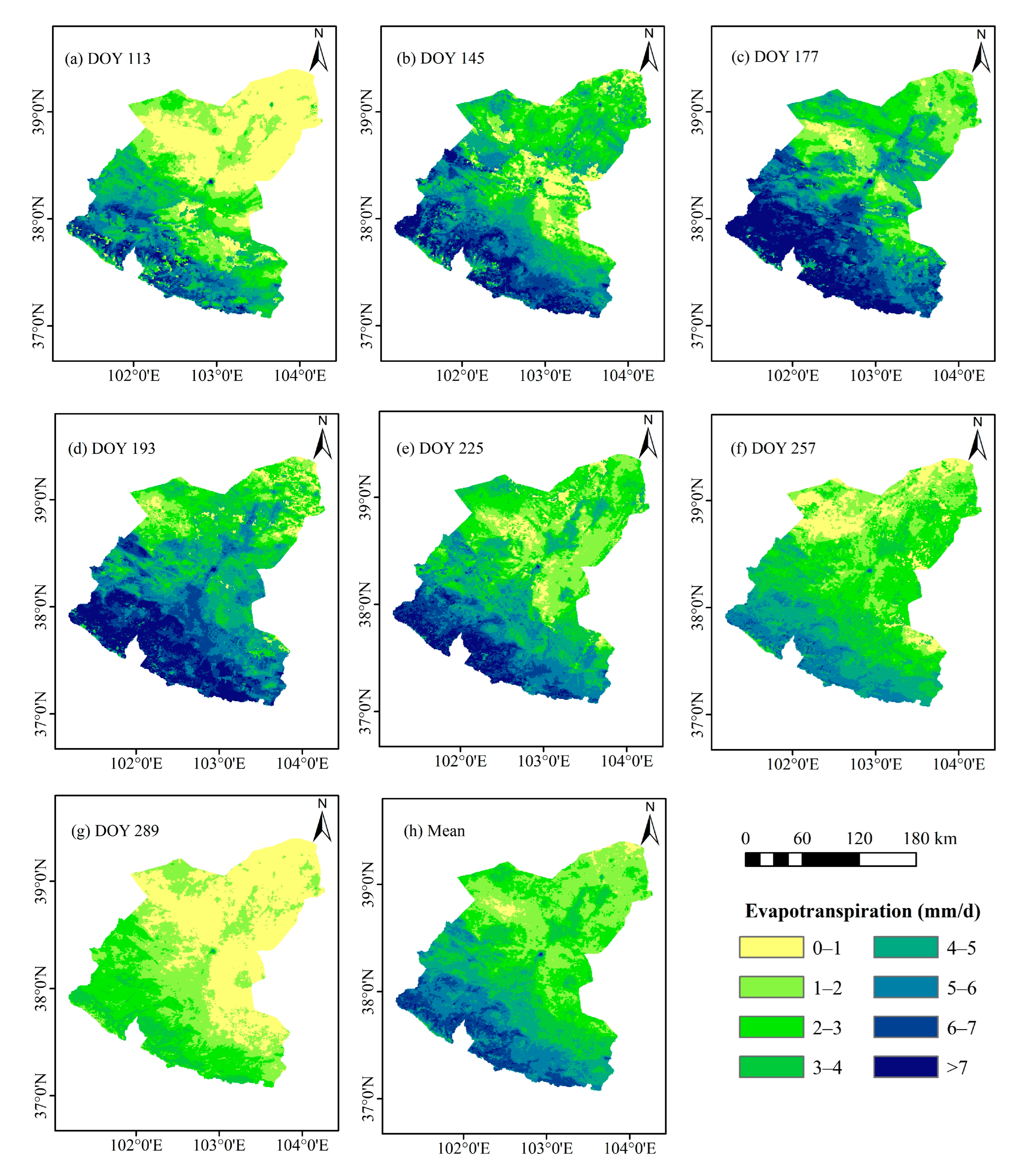
3.3. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Actual ETd
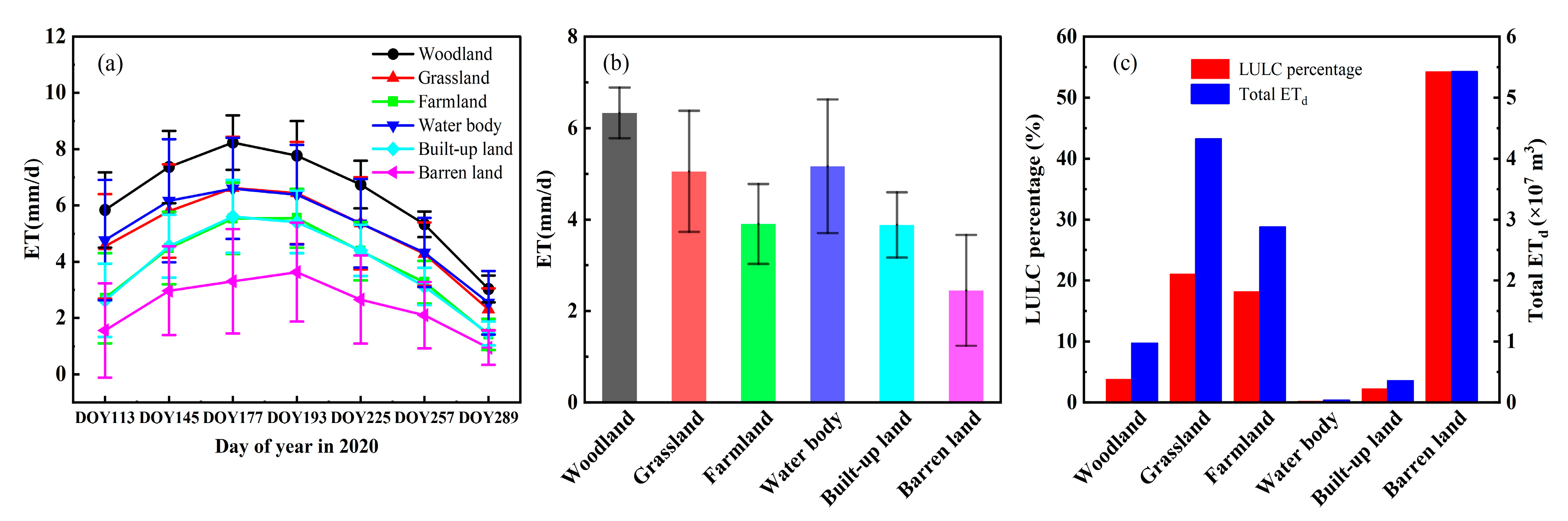
3.4. Comparison of ETd in Different LULC Types
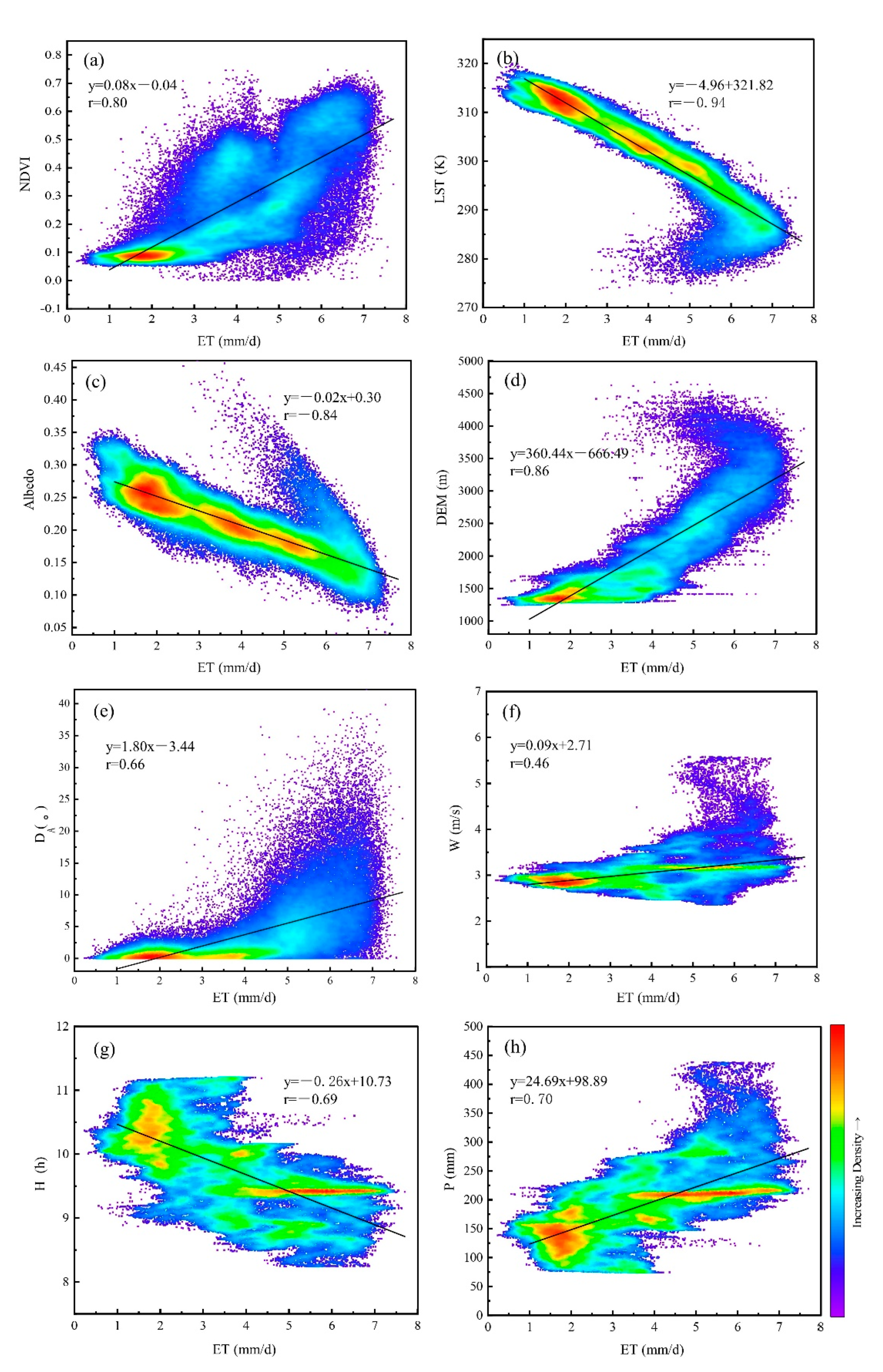
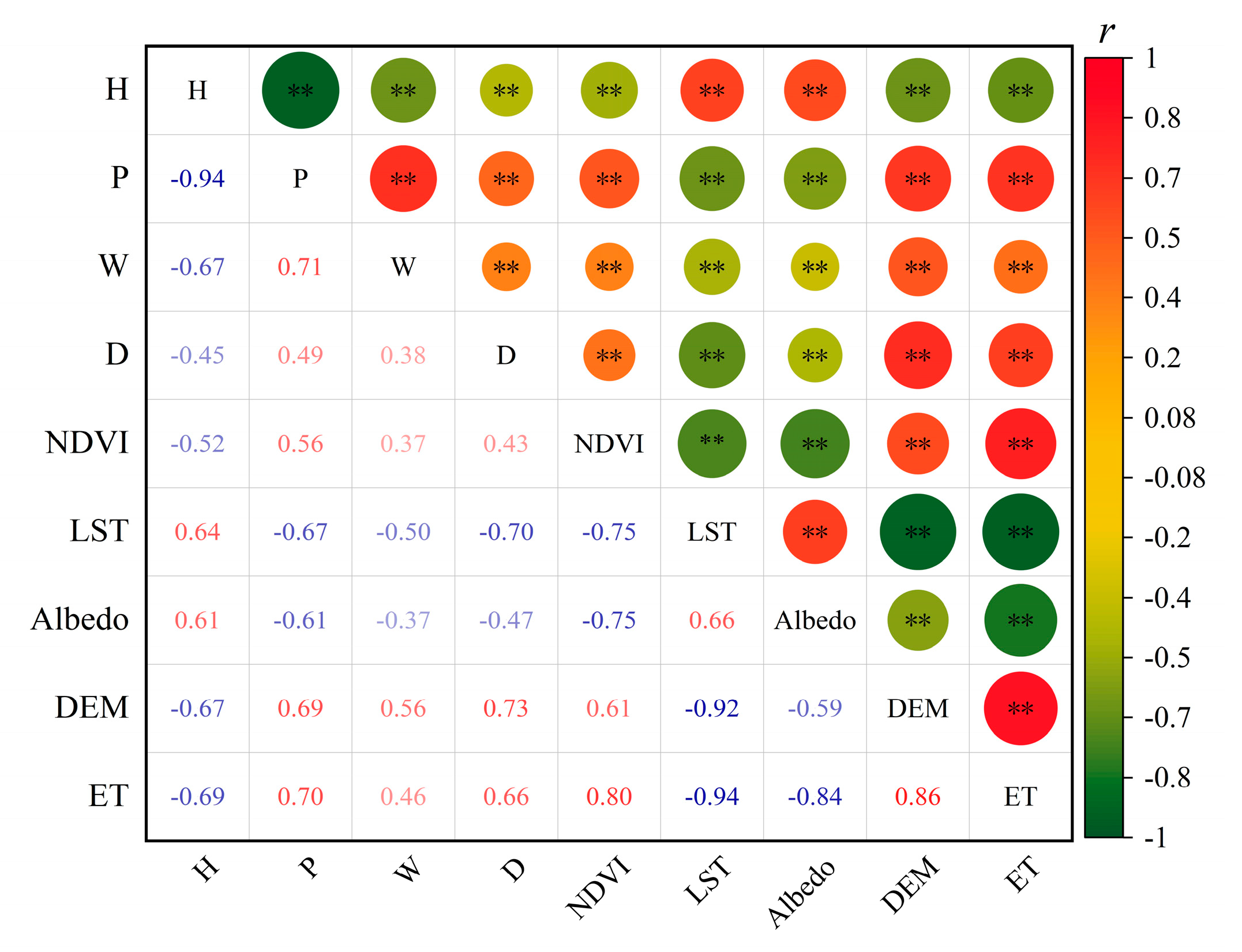
3.5. Analysis of Driving Factors for ET
3.5.1. Correlation Analysis
3.5.2. Principal Component Regression
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Assessment of ET Estimation Using SEBAL
4.2. Analysis of the ETd with Different LULC Types
4.3. Impact of Environmental Factors on ET
4.4. Limitations and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, Y.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Tian, F.; Qiu, G.Y. An evapotranspiration product for arid regions based on the three-temperature model and thermal remote sensing. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.K.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, X.N.; Wu, P.T. Evaluation of the mechanisms and performances of major satellite-based evapotranspiration models in Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.K.; Jia, L.; Fan, W.J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration and its components in an irrigated area by integrating the Shuttleworth-Wallace and surface temperature-vegetation index schemes using the particle swarm optimization algorithm. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 307, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kite, G. Using a basin-scale hydrological model to estimate crop transpiration and soil evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.Q.; Qiao, M.; Qiu, X.F.; Zeng, Y.; Hua, H.H.; Ye, X.Z.; Adamu, M. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration Distribution in the Huaihe River Upstream Basin Based on the Generalized Complementary Principle. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.W.; Sun, Z.C.; Zhao, K.Y.; Shi, F.S.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.S.; Shi, Z.M. A method for simultaneous estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration and inflow rates in the discharge area using seasonal water table fluctuations. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwasoka, D.T.; Gumindoga, W.; Gwenzi, J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration using the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) algorithm in the Upper Manyame catchment in Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, G.; Katerji, N. Measurement and estimation of actual evapotranspiration in the field under Mediterranean climate: A review. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.; Holzman, B. The determination of evaporation from land and water surfaces. Mon. Weather Rev. 1939, 67, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R. Vertical eddy flux of heat in the atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1948, 5, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Fao. Rome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Roerink, G.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.S.; Liu, S.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.W.; Xia, T.; Li, M.S. Application of remote sensing-based two-source energy balance model for mapping field surface fluxes with composite and component surface temperatures. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.; Holtslag, A. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnmer, A.; Khadr, M.; Kanae, S.; Tawfik, A. Mapping daily and seasonally evapotranspiration using remote sensing techniques over the Nile delta. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, P.; Gowda, P.H.; Northup, B.K. Dynamics of evapotranspiration over a non-irrigated alfalfa field in the Southern Great Plains of the United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Chen, X.; Ju, W.; Geng, X. Distributed hydrological model for mapping evapotranspiration using remote sensing inputs. J. Hydrol. 2005, 305, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Liedl, R.; Awan, U.K. Spatio-temporal estimation of consumptive water use for assessment of irrigation system performance and management of water resources in irrigated Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.d.C.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Ahmad, M.; Bos, M. Reviewing SEBAL input parameters for assessing evapotranspiration and water productivity for the Low-Middle Sao Francisco River basin, Brazil: Part A: Calibration and validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R.; Waters, R.; Bastiaanssen, W. SEBAL (Surface Energy Balance Algorithms for Land)—Advanced Training and Users Manual—Idaho Implementation (Version 1.0); The Idaho Department of Water Resources: Boise, ID, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.M.; Zhou, X.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Bi, S.J.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, D.L. Evaluating water-saving efficiency of plastic mulching in Northwest China using remote sensing and SEBAL. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 209, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.H.; Jiao, X.Y.; Li, B.B.; Yu, X.; Shao, M.C.; Jin, X.L. Long time series of daily evapotranspiration in China based on the SEBAL model and multisource images and validation. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3995–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.R.; Sun, M.; Luan, Q.H.; Zhao, X.N.; Wang, J.C.; He, G.H.; Zhao, Y. The spatial and temporal evolution of the actual evapotranspiration based on the remote sensing method in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D. Evapotranspiration estimation based on MODIS products and surface energy balance algorithms for land (SEBAL) model in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiptala, J.K.; Mohamed, Y.; Mul, M.L.; Van der Zaag, P. Mapping evapotranspiration trends using MODIS and SEBAL model in a data scarce and heterogeneous landscape in Eastern Africa. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8495–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.F.; Xiong, Y.J.; Tian, J.L.; Tan, Z.H. Spatiotemporal Changes in Evapotranspiration from an Overexploited Water Resources Basin in Arid Northern China and Their Implications for Ecosystem Management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal patterns of evapotranspiration, gross primary productivity, and water use efficiency of cropland in agroecosystems and their relation to the water-saving project in the Shiyang River Basin of Northwestern China. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 172, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.M.; Bi, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Tang, B.H.; Yan, G.J.; Zhang, X.Y. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starks, P.J.; Norman, J.M.; Blad, B.L.; Walter-Shea, E.A.; Walthall, C.L. Estimation of shortwave hemispherical reflectance (albedo) from bidirectionally reflected radiance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 38, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I: Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A. Satellite-based evapotranspiration by METRIC and Landsat for western states water management. In Proceedings of the US Bureau of Reclamation Evapotranspiration Workshop, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 8–10 February 2005; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G. SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Jackson, R.D. Assessing the spatial distribution of evapotranspiration using remotely sensed inputs. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, S.Y.; Tian, W.; Tian, J.; He, C.S. Assessing the Effects of Spatial Scales on Regional Evapotranspiration Estimation by the SEBAL Model and Multiple Satellite Datasets: A Case Study in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone, Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.; Gurney, R.; Hsu, A.; Ormsby, J. FIFE: The variation in energy partition at surface flux sites. IAHS Publ. 1989, 186, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Crago, R.D. Conservation and variability of the evaporative fraction during the daytime. J. Hydrol. 1996, 180, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guideline for computing crop water requirements. Irrig. Drain 1998, 56, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.L. New evapotranspiration crop coefficients. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1982, 108, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.J.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Liu, Q. Assessment of actual evapotranspiration in the Minjiang River Basin Based on the GLDAS-Noah model. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Bargaoui, Z.; Mannaerts, C.M. Remote-sensing estimation of the water stress coefficient and comparison with drought evidence. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4616–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Jiang, H.B.; He, X.L.; Ji, L.; Zhang, S.B. Research on characteristics and reduction technology ofwater surface evaporation in arid area. J. Water Res. Eng. 2014, 6, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.; Mu, Q.; Lee, S.O.; Choi, M. Validation of MODIS 16 Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Products in Various Climates and Land Cover Types in Asia. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Z.; Kimball, J.S.; Yi, Y.H.; Running, S.W.; Guan, K.Y.; Moreno, A.; Wu, X.C.; Maneta, M. Satellite data-driven modeling of field scale evapotranspiration in croplands using the MOD16 algorithm framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, S.; Lo Presti, S.; Martello, M.; Panunzi, L.; Berti, A.; Morari, F. Integrating SEBAL with in-Field Crop Water Status Measurement for Precision Irrigation Applications-A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.T.; Luo, Y.F.; Shen, Y.Y.; Han, Z.Z.; Cui, Y.L. Driving force analysis of irrigation water consumption using principal component regression analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.L.; Xing, W.; Akmalov, S.; Peng, J.B.; Pan, X.H.; Guo, C.Y.; Duan, Y.C. Water Balance Analysis Based on a Quantitative Evapotranspiration Inversion in the Nukus Irrigation Area, Lower Amu River Basin. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Yang, L.X.; Xu, X.F.; Tian, W.; He, C.S. Analysis of evapotranspiration pattern by SEBAL model during the growing season in the agro-pastoral ecotone in Northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.L.; Hu, Y.X.; Yang, L.Y.; Shan, Z.B.; Wang, Y.T. Estimation of evapotranspiration for the blown-sand region in the Ordos basin based on the SEBAL model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 1945–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Dasineh, M.; Shokri, M.; Abraham, J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration using the remote sensing method and SEBAL algorithm: A case study in Ein Khosh Plain, Iran. Hydrology 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadegan, M.; Janani, A. Estimating evapotranspiration of pistachio crop based on SEBAL algorithm using Landsat 8 satellite imagery. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Li, J.F.; Sun, Z.H.; Liu, J.B.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, T. Daily actual evapotranspiration estimation of different land use types based on SEBAL model in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northwest China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autovino, D.; Minacapilli, M.; Provenzano, G. Modelling bulk surface resistance by MODIS data and assessment of MOD16A2 evapotranspiration product in an irrigation district of Southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 167, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Sahoo, B.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R. Evaluation of Variable-Infiltration Capacity Model and MODIS-Terra Satellite-Derived Grid-Scale Evapotranspiration Estimates in a River Basin with Tropical Monsoon-Type Climatology. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Coupling SEBAL with a new radiation module and MODIS products for better estimation of evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, R.; Muller, J.-P.; Kharbouche, S.; Yin, F.; Woodgate, W.; Kitchen, M.; Roland, M.; Arriga, N.; Meyer, W.; Koerber, G.; et al. Validation of Space-Based Albedo Products from Upscaled Tower-Based Measurements Over Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Landscapes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.L.; Hou, J.L.; Gu, J.; Zhu, G.F.; Li, X. Mapping daily evapotranspiration based on spatiotemporal fusion of ASTER and MODIS images over irrigated agricultural areas in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 244, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Mei, X.R.; Huo, Z.G.; Yan, C.R.; Ju, H.; Zhao, F.H.; Liu, Q. Water consumption in summer maize and winter wheat cropping system based on SEBAL model in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Jiang, R.Z.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.D.; Yang, H.; CHEN, S. Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain in recent 20 years. Geol. China 2021, 48, 1392–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.J.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.M. Factors affecting evapotranspiration analyzed based on a structural equation model. J. Tsinghua Univ. 2022, 62, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoelo, A.; Majozi, N.; Mathieu, R.; Jovanovic, N.; Nickless, A.; Dzikiti, S. Validation of Global Evapotranspiration Product (MOD16) using Flux Tower Data in the African Savanna, South Africa. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7406–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Data Product | Satellite Imagery | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOD11A1/A2 | LST/Emissivity | Daily/8 d | 1 km |
| MOD13A1 | NDVI | 16 d | 0.5 km |
| MOD09A1 | Albedo | 8 d | 0.5 km |
| MOD16A2 | ET8d | 8 d | 0.5 km |
| Station | April | May | June | July | August | September | October |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minqin | 0.53 | 0.69 | 1.29 | 1.29 | 1.26 | 0.76 | 0.37 |
| Wuwei | 0.51 | 0.51 | 1.28 | 1.28 | 1.25 | 0.66 | 0.51 |
| Wushaoling | 0.38 | 0.86 | 1.12 | 1.13 | 1.08 | 0.97 | 0.48 |
| Gulang | 0.34 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 1.27 | 1.02 | 0.64 | 0.41 |
| Yongchang | 0.34 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 0.55 |
| Principal Components | Initial Eigenvalues and Variance Contribution Rates | Extracted Eigenvalues and Variance Contribution Rates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalues | Variance Contribution Rates/% | Cumulative Contribution Rates/% | Eigenvalues | Variance Contribution Rates/% | Cumulative Contribution Rates/% | |
| PC1 | 5.309 | 66.362 | 66.362 | 5.309 | 66.362 | 66.362 |
| PC2 | 0.967 | 12.085 | 78.448 | 0.967 | 12.085 | 78.448 |
| PC3 | 0.746 | 9.331 | 87.779 | 0.746 | 9.331 | 87.779 |
| PC4 | 0.379 | 4.741 | 92.52 | |||
| PC5 | 0.306 | 3.827 | 96.346 | |||
| PC6 | 0.191 | 2.390 | 98.736 | |||
| PC7 | 0.052 | 0.645 | 99.381 | |||
| PC8 | 0.05 | 0.619 | 100 | |||
| References | Study Area | Validation Methods | Temporal/ Spatial Resolution | Time | Accuracy Evaluation Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | MAE (mm/d) | RMSE (mm/d) | |||||
| Li et al. [50] | Agro-pastoral ecotone in northwest China | FAO P-M equation | Daily/1 km | 2015 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.94 |
| Kong et al. [51] | Ordos Basin in China | FAO P-M equation | Daily/30 m | 2015–2016 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.97 |
| Ghaderi et al. [52] | Ein Khosh Plain in Iran | FAO P-M equation | Daily/1 km | 2015 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.47 |
| Rahimzadegan and Janani [53] | A pistachio farm in Semnan Province, Iran | FAO P-M equation | Daily/30 m | 2013–2017 | 0.80 | 2.09 | 2.48 |
| Liu et al. [49] | Nukus irrigation area of Amu River Basin | Pan evaporation | Daily/30 m | 2019 | 0.81 | / | 1.76 |
| Yang et al. [54] | Agro-pastoral ecotone in northwest China | Pan evaporation | Daily/30 m | 2016–2017 | 0.81 | / | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration Using Remote Sensing and SEBAL Model in an Arid Environment of Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081555
Chen X, Yu S, Zhang H, Li F, Liang C, Wang Z. Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration Using Remote Sensing and SEBAL Model in an Arid Environment of Northwest China. Water. 2023; 15(8):1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081555
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xietian, Shouchao Yu, Hengjia Zhang, Fuqiang Li, Chao Liang, and Zeyi Wang. 2023. "Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration Using Remote Sensing and SEBAL Model in an Arid Environment of Northwest China" Water 15, no. 8: 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081555




