Separation Zone Required to Buffer Hazardous Waste Landfills Impact on Scattered Water Supply Sources: From a Whole Lifespan Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Water Quality Criteria for Safe Drinking
2.2. Leachate Emission and Mitigation in Subsurface Media under Landfill Performance Degradation
2.2.1. HELP Model
2.2.2. Aging and Defect Evolution Model for HWL Engineering Materials
2.2.3. Simulation of the Leachate Migration Transformation Process
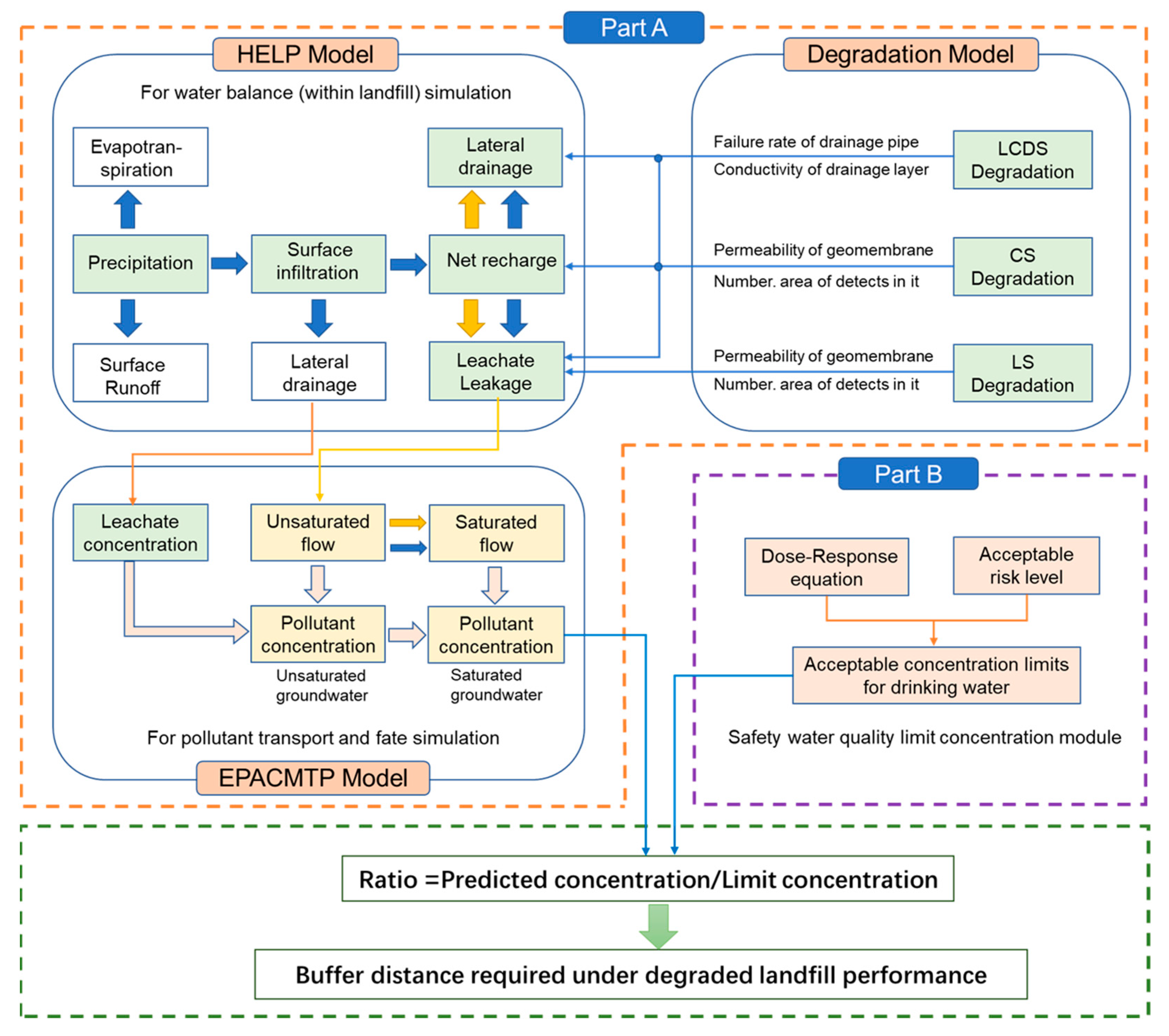
2.2.4. Articulation and Parameter Transfer of the Aging-HELP-EPACMTP Model
2.3. Calculation of BFD under Long-Term Aging Conditions
3. Case Studies
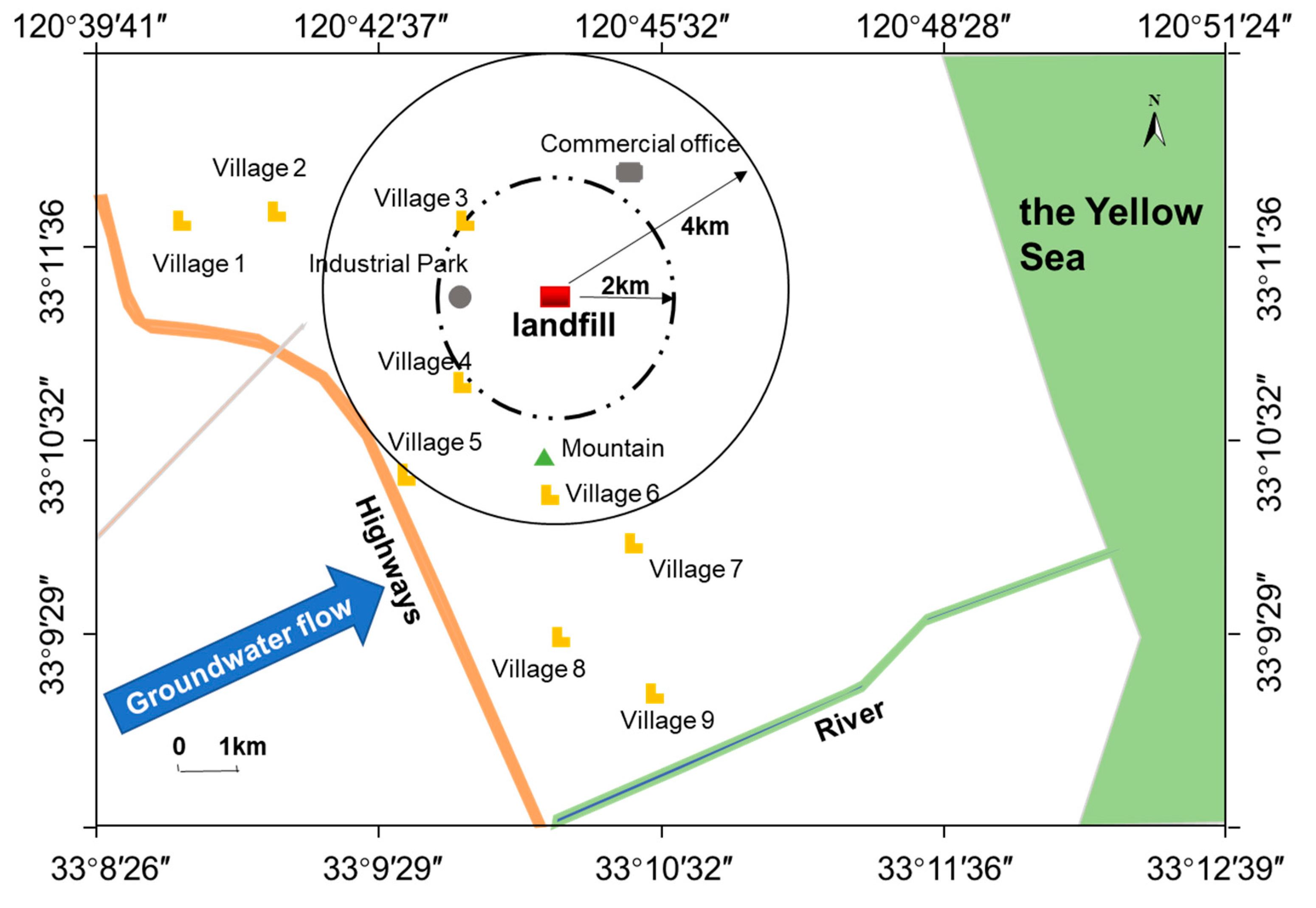
3.1. Site Description
3.2. Model Application and Parameter Setting
4. Results and Discussion
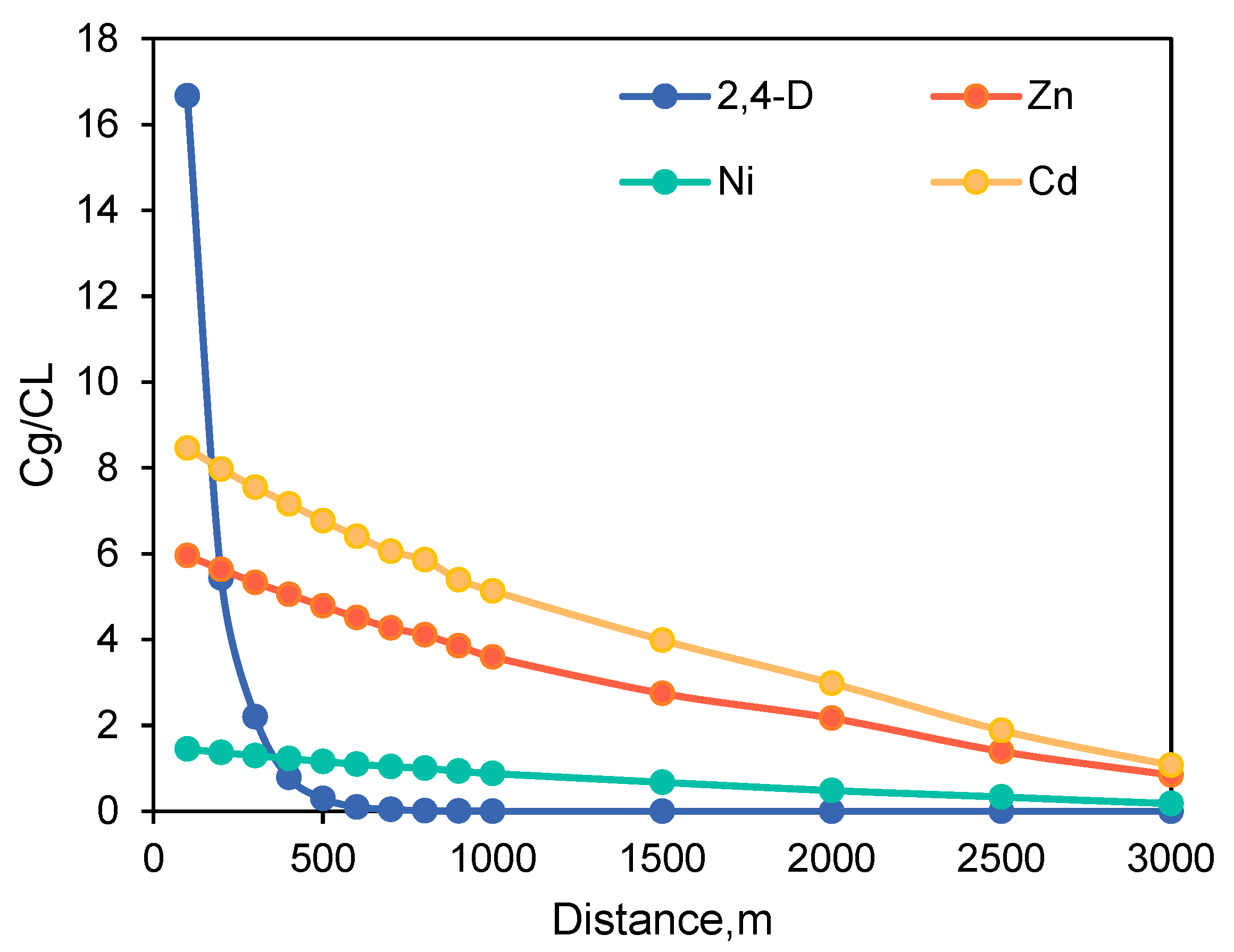
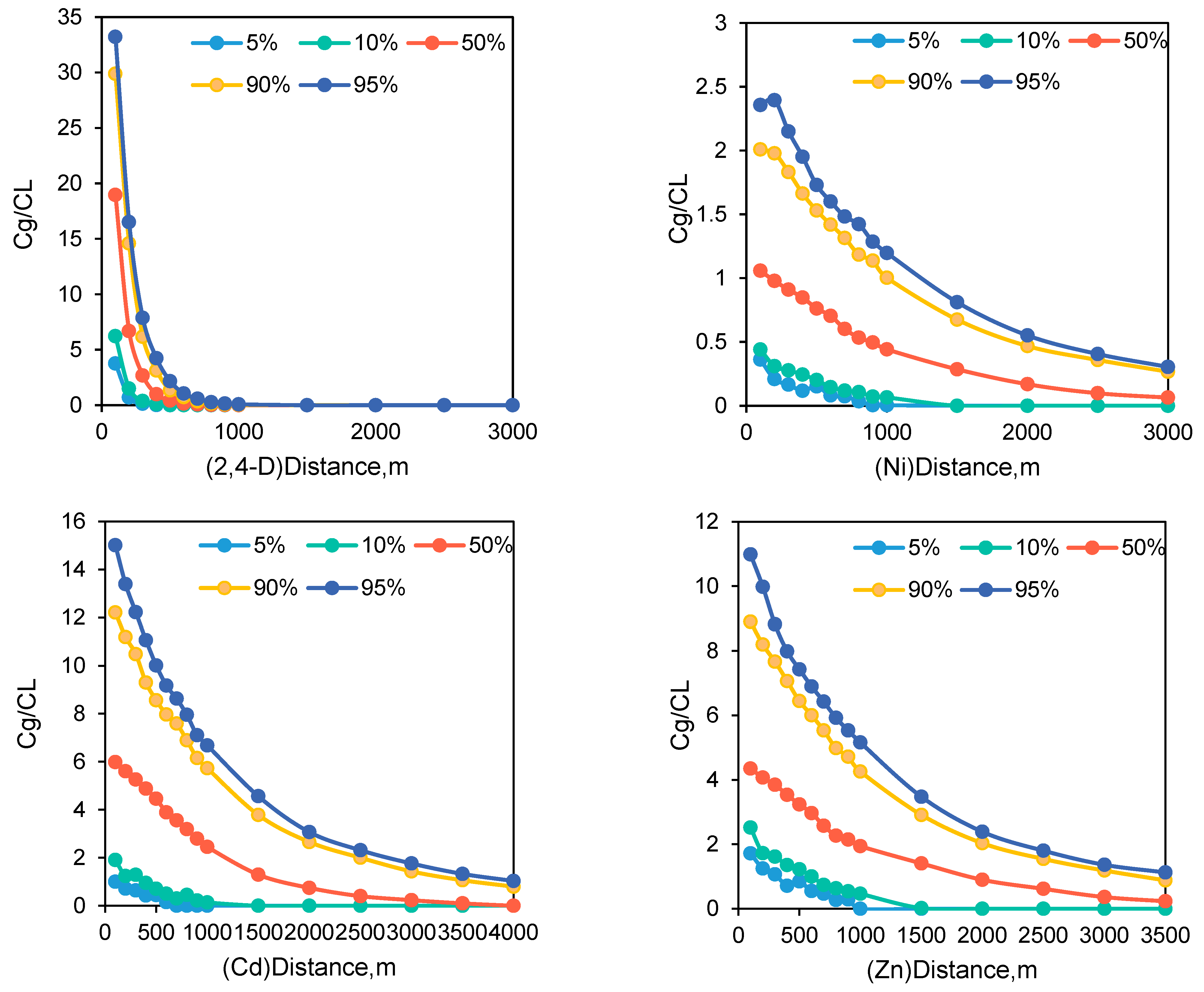
4.1. Different BFD of Dilution and Attenuation of Pollutants
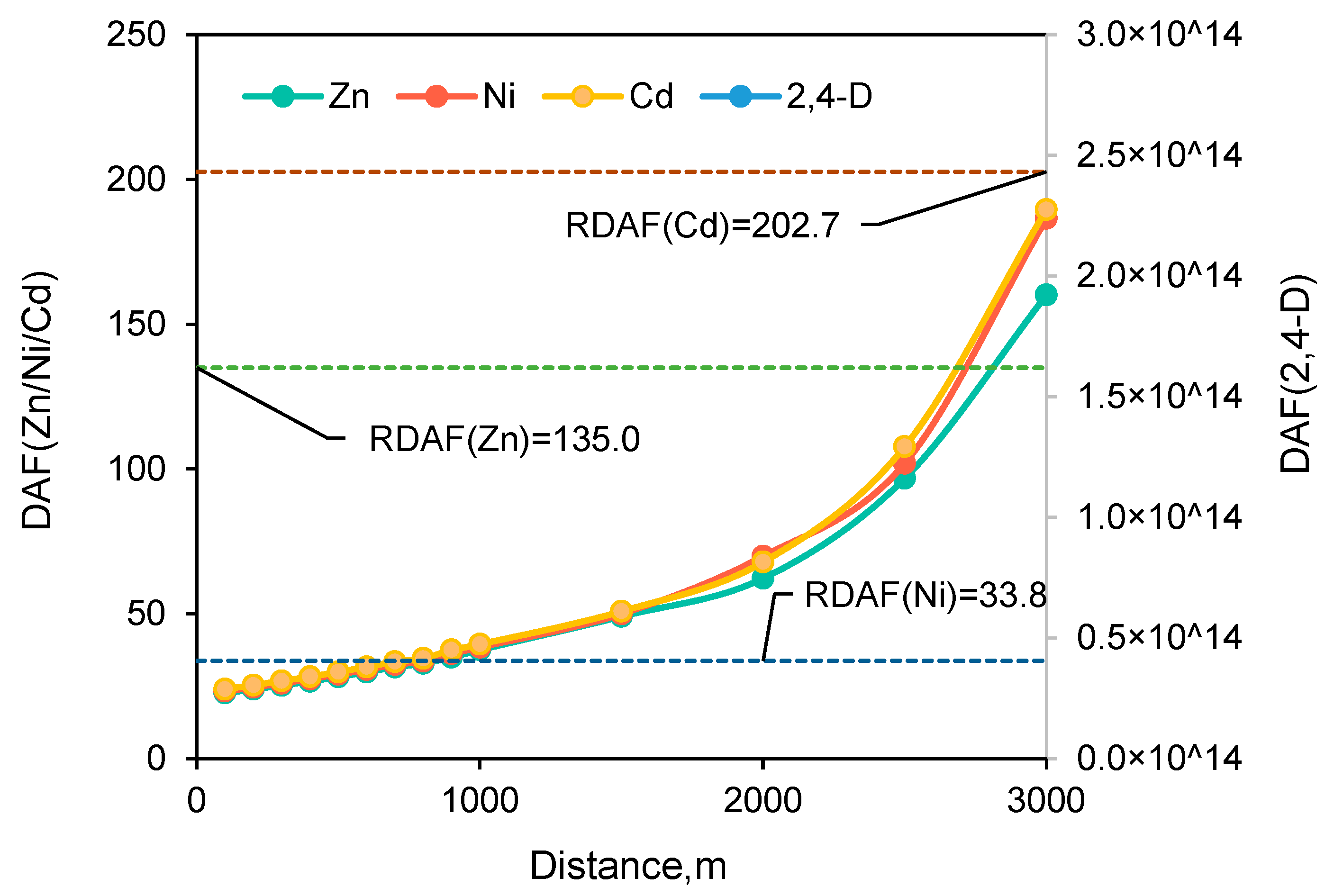
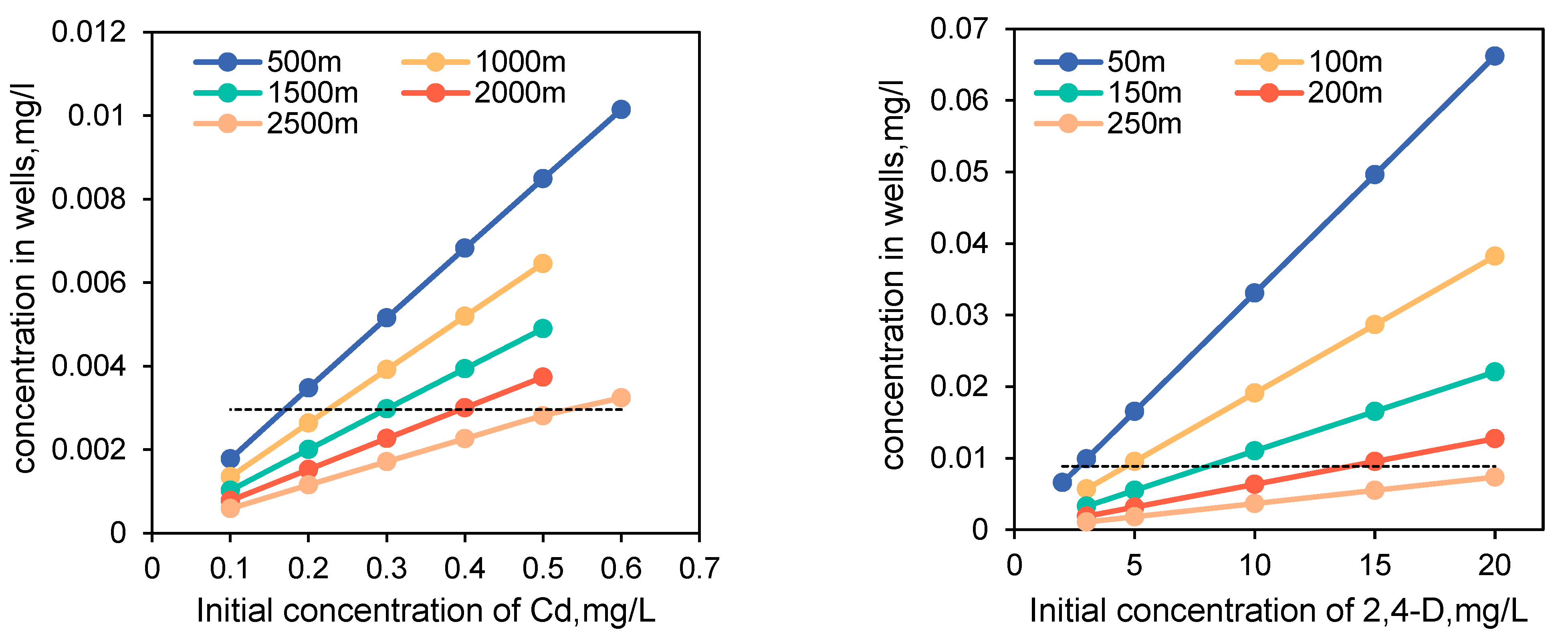
4.2. BFD Required under Long-Term Aging Conditions
4.3. Uncertainty of BFD under Aging Conditions
4.4. Management Strategies for BFD under Aging Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaverková, M.D.; Paleologos, E.K.; Adamcová, D.; Podlasek, A.; Pasternak, G.; Červenková, J.; Skutnik, Z.; Koda, E.; Winkler, J. Municipal solid waste landfill: Evidence of the effect of applied landfill management on vegetation composition. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X. A critical review of the central role of microbial regulation in the nitrogen biogeochemical process: New insights for controlling groundwater nitrogen contamination. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Paulraj, R. Leachate composition and toxicity assessment: An integrated approach correlating physicochemical parameters and toxicity of leachates from MSW landfill in Delhi. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaqout, A.; Hamoda, M.F. Long-term Temporal Variations in Characteristics of Leachates from a Closed Landfill in an Arid Region. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essien, J.P.; Ikpe, D.I.; Inam, E.D.; Okon, A.O.; Ebong, G.A.; Benson, N.U. Occurrence and spatial distribution of heavy metals in landfill leachates and impacted freshwater ecosystem: An environmental and human health threat. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimba, C.G.; Sivanesan, S.; Krishnamurthi, K. Mitochondrial dysfunctions elicited by solid waste leachates provide insights into mechanisms of leachates induced cell death and pathophysiological disorders. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros Engelmann, P.; dos Santos, V.H.J.M.; Moser, L.I.; do Canto Bruzza, E.; Barbieri, C.B.; Barela, P.S.; de Moraes, D.P.; Augustin, A.H.; Goudinho, F.S.; Melo, C.L.; et al. Environmental monitoring of water resources around a municipal landfill of the Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21398–21411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alslaibi, T.M.; Abunada, Z.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Abustan, I. Risk assessment of nitrate transport through subsurface layers and groundwater using experimental and modeling approach. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.M.; Santos, A.H.M.; Pereira, C.R.S.; Flauzino, B.K.; Pereira, A.C.O.S.; Nogueira, F.J.H.; Valverde, J.A.R. Spatially distributed potential of landfill biogas production and electric power generation in Brazil. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; Koks, E.E. A River Flood and Earthquake Risk Assessment of Railway Assets along the Belt and Road. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2021, 12, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehlmann, U.; Bumgardner, M.; Fluharty, T. Ban on landfilling of wooden pallets in North Carolina: An assessment of recycling and industry capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, X.; Dong, L.; Nai, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Long-term dynamics of leachate production, leakage from hazardous waste landfill sites and the impact on groundwater quality and human health. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, C.; Isch, A.; Bruand, A.; Azaroual, M.; Coquet, Y. Relationship between hydraulic properties and material features in a heterogeneous vadose zone of a vulnerable limestone aquifer. Vadose Zone J. 2021, 20, e20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, B.; Dwivedi, D.; Faybishenko, B.; Jana, R.B.; Wainwright, H.M. Understanding and Predicting Vadose Zone Processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2019, 85, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irhamni Pandia, S.; Purba, E.; Hasan, W. Heavy metal content in final disposal garbage site at Banda Aceh City. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1116, 042014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Caselles, C.; Desforges, J.-P.W.; Dangerfield, N.; Ross, P.S. A Risk-Based Characterization of Sediment Contamination by Legacy and Emergent Contaminants of Concern in Coastal British Columbia, Canada. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, X.; Jingcai, L.; Lu, D.; Yuqiang, L.; Weishi, L.; Changxing, N.; Qifei, H. Buffering distance between hazardous waste landfill and water supply wells in a shallow aquifer. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lei, G.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Huang, Q.F. Isolation distance between municipal solid waste landfills and drinking water wells for bacteria attenuation and safe drinking. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, D.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Huang, Z.Q.; Du, B.Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, F. Buffering Distance between Coastal Hazardous Waste Landfill and Water Source and Its Regulation Strategy. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhreddine, S.; Bourouss, M.; El-Fadel, M. A coupled groundwater transport and land use regression model for optimizing buffer zones around landfills. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, J. Optimal design of landfill buffer zones using groundwater modeling and multi-objective genetic algorithm: A case study in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 548–556. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, S.; Bhattacharjya, S.; Chakraborty, S. Geospatial analysis for assessing buffer zone requirement around a landfill in India. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, A.P.; Derx, J.; Zessner, M.; Kirnbauer, R.; Kavka, G.; Strelec, H.; Farnleitner, A.H.; Pang, L. Setback distances between small biological wastewater treatment systems and drinking water wells against virus contamination in alluvial aquifers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowe, R.K.; Rimal, S.; Sangam, H. Ageing of HDPE geomembrane exposed to air, water and leachate at different temperatures. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Kumar, G.; Kulkarni, H.S. Two-Phase Flow Modeling to Evaluate Effectiveness of Different Leachate Injection Systems for Bioreactor Landfills. Environ. Model. Assess. 2020, 25, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannou, C.; Ofrydopoulou, A.; Evgenidou, E.; Heath, D.; Heath, E.; Lambropoulou, D. Analytical strategies for the determination of antiviral drugs in the aquatic environment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 24, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yao, G.; Xiang, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Spatiotemporal difference of leachate production and its impact on the development and dynamics of LCS clogging. Waste Manag. 2023, 157, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Sabiiti, E.N.; Bukenya, B.; Namuddu, S. The Impact of Waste Disposal Sites on the Local Water Resources: A Case Study of the Kiteezi landfill, Uganda. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschan, J.; Pond, K.; Malcolm, R. Regulatory-driven risk assessment to improve drinking-water quality: A case study of private water supplies in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 140, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, S.; Wiegand, L.; Karges, U. 1,4-dioxane in German drinking water: Origin, occurrence, and open questions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 30, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.; Idris, K.M.; Abdullahi, B.A.; Darma, A.I. Bioaccumulation and health risks of some heavy metals in Oreochromis niloticus, sediment and water of Challawa river, Kano, Northwestern Nigeria. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics of groundwater quality and health risk assessment in Jinghe River Basin, Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Bjerg, P.L. Prioritization of potentially contaminated sites: A comparison between the application of a solute transport model and a risk-screening method in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.U. On the current state of the Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance (HELP) model. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, M. A review on settlement models of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Nai, C.-X.; Dong, L.; Liu, J.-C.; Huang, Q.-F. Evolution of geomembrane degradation and defects in a landfill: Impacts on long-term leachate leakage and groundwater quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, X.; Weishi, L.; Qifei, H.; Yuqiang, L.; Jingcai, L.; Li, L.; Dahai, Y. Long-term degradation characteristics of cyanide in closed monofills and its effects on the environment and human health: Evidence from nine landfill sites in northen China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallants, D.; Doble, R.; Beiraghdar, Y. Fate and transport modelling framework for assessing risks to soil and groundwater from chemicals accidentally released during surface operations: An Australian example application from shale gas developments. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Andrabi, S.M.; Raina, D.B.; Kumar, A. Three staged integrated community-based water filter system for potable water by effective removal of contaminants from ground water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, R.; Mallants, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Aghbelagh, Y.B.; Peeters, L.; Crosbie, R.; Marshall, S.K.; Evans, T. Upscaling a chemical screening approach to assess impacts of shale, tight and deep gas development on unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 45, 101296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Symbol | Parameter Definition | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters involved in concentration limit calculation | Cgw | the contaminant concentration in groundwater | mg/L |
| RfD0 | the reference oral intake dose | mg/(kg⸱d) | |
| WAF | the reference dose distribution proportion exposed to groundwater | - | |
| CGWERnc | groundwater exposure corresponding to drinking the affected groundwater (non-carcinogenic effects) | L/(kg∙d) | |
| GWCRa | the daily drinking volume of adults | L/d | |
| EFa | the adult exposure frequency | d/a | |
| EDa | the adult exposure period | a | |
| BWa | the adult human body mass | kg | |
| ATnc | the average time of non-carcinogenic effect | d | |
| CR | the carcinogenic risk of drinking groundwater | - | |
| SF | the cancer slope factor of the target pollutant | mg/(kg⸱d) | |
| CGWERca | groundwater exposure corresponding to drinking the affected groundwater (carcinogenic effects) | L/(kg⸱d) | |
| Parameters involved in aging module | Kgm(t) | the permeability coefficient of HDPE membrane at moment t | cm/s |
| N(t) | the number of defects per hectare in year t | Defects/Hectare | |
| N0 | the number of defects per hectare in the first year | Defects/Hectare | |
| Kd(t) | the hydraulic conductivity of the drainage layer at the moment t | cm/s | |
| Kd0 | the hydraulic conductivity of the drainage layer at the initial moment | cm/s | |
| wastes | the hydraulic conductivity of waste | cm/s |
| Parameter | Unit | Value | Data Sources | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Required parameters for the derivation of water quality indicator limits | Daily drinking volume of adults (GWCRa) | L/d | 1 | [17] | ||
| Adult Exposure Frequency (EFa) | d/a | 350 | ||||
| Adult Exposure Date (EDa) | a | 24 | ||||
| Adult Body Weight (BWa) | kg | 56.8 | ||||
| Average Time of Non-Carcinogenic Effect (ATnc) | d | 2190 | ||||
| Reference dose distribution ratio for exposure to groundwater (WAF) | 0.2 | |||||
| Oral Reference Dose (RfD (Ni)) | mg/(kg∙d) | 2 × 10−2 | ||||
| Oral Reference Dose (RfD (Zn)) | mg/(kg∙d) | 3 × 10−1 | ||||
| Oral Reference Dose (RfD (2,4-D)) | mg/(kg∙d) | 3 × 10−3 | ||||
| Oral Reference Dose (RfD (Cd)) | mg/(kg∙d) | 1 × 10−3 | ||||
| Parameters required by the HELP module | SCS curve number | 65 | Measured Data | |||
| Hole number in geomembrane | 0.1–5 mm2 | ha | 110 | |||
| 5–100 mm2 | ha | 5 | ||||
| 100–10,000 mm2 | ha | 10 | ||||
| Surface slope | - | 4% | ||||
| Thickness of geomembrane in capping system | mm | 1 | ||||
| Design infiltration | mm | 43.2 | ||||
| Infiltration under cap failure | mm | 321.8 | ||||
| Conductivity of geomembrane | cm/s | 1 × 10−12 | ||||
| Thickness of soil under geomembrane of capping system | mm | 600 | ||||
| Conductivity of soil under geomembrane of capping system | cm/s | 1 × 10−5 | ||||
| Final waste thickness | m | 4.5 | ||||
| Drainage layer thickness | mm | 300 | ||||
| The initial conductivity of the drainage layer | cm/s | 1 × 10−2 | ||||
| Landfill bottom slope | - | 1.15% | ||||
| Drainage pipe spacing | - | 10 | ||||
| Geomembrane thickness of liner system | mm | 2 | ||||
| Thickness of compacted soil under geomembrane | mm | 600 | ||||
| Conductivity of compacted soil under geomembrane | cm/s | 1 × 10−5 | ||||
| Parameters required by the aging module | Start of geomembrane degradation since fillingcommenced | years | 6 | Measured Data | ||
| Time for number of holes in geomembrane to double | years | 8 | ||||
| Probability of failure for a single pipe | - | 0.2 | ||||
| Parameters required by the EPACMTP module | Vadose zone thickness | m | 4 | Measured Data | ||
| Conductivity of vadose zone | cm/s | 1 × 10−5 | ||||
| longitudinal dispersity of vadose zone | 2,4-D | m | 0.6 | |||
| Cd/Zn/Ni | m | 0.042 | ||||
| Thickness of aquifer | m | 20 | ||||
| Conductivity of aquifer | cm/s | 1 × 10−3 | ||||
| Hydraulic gradient | - | 0.01 | ||||
| Longitudinal dispersity of aquifer | 2,4-D | m | 20.9 | |||
| Cd/Zn/Ni | m | 0.17 | ||||
| The initial concentration (C0(Ni)) | mg/L | 2 | ||||
| The initial concentration (C0(Zn)) | mg/L | 120 | ||||
| The initial concentration (C0(2,4-D)) | mg/L | 20 | ||||
| The initial concentration (C0(Cd)) | mg/L | 0.6 | ||||
| Unit | Value Range | Data Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design infiltration | mm | NORMAL (43.2, 2.1) | Site-measured value |
| Infiltration under cap failure | mm | NORMAL (321.8, 130.7) | |
| Vadose zone thickness | m | NORMAL (4, 1) | |
| Thickness of aquifer | m | NORMAL (30, 5) | |
| Regional Gradient | - | NORMAL (0.01, 0.003) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, P.; Yan, J.; Xu, Y.; Yao, G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, X. Separation Zone Required to Buffer Hazardous Waste Landfills Impact on Scattered Water Supply Sources: From a Whole Lifespan Perspective. Water 2023, 15, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081489
Qiu P, Yan J, Xu Y, Yao G, Liu Y, Huang Q, Li X. Separation Zone Required to Buffer Hazardous Waste Landfills Impact on Scattered Water Supply Sources: From a Whole Lifespan Perspective. Water. 2023; 15(8):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081489
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Panpan, Jianzhuo Yan, Ya Xu, Guangyuan Yao, Yuqiang Liu, Qifei Huang, and Xingrong Li. 2023. "Separation Zone Required to Buffer Hazardous Waste Landfills Impact on Scattered Water Supply Sources: From a Whole Lifespan Perspective" Water 15, no. 8: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081489
APA StyleQiu, P., Yan, J., Xu, Y., Yao, G., Liu, Y., Huang, Q., & Li, X. (2023). Separation Zone Required to Buffer Hazardous Waste Landfills Impact on Scattered Water Supply Sources: From a Whole Lifespan Perspective. Water, 15(8), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081489





