Comparative Assessment of the Application of Four Water Quality Indices (WQIs) in Three Ephemeral Rivers in Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection and Measurements
2.3. WQI Description and Application
2.3.1. NSF WQI
2.3.2. Oregon WQI
2.3.3. CCME WQI
2.3.4. Prati’s Index of Pollution
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quality Data of the Three Rivers
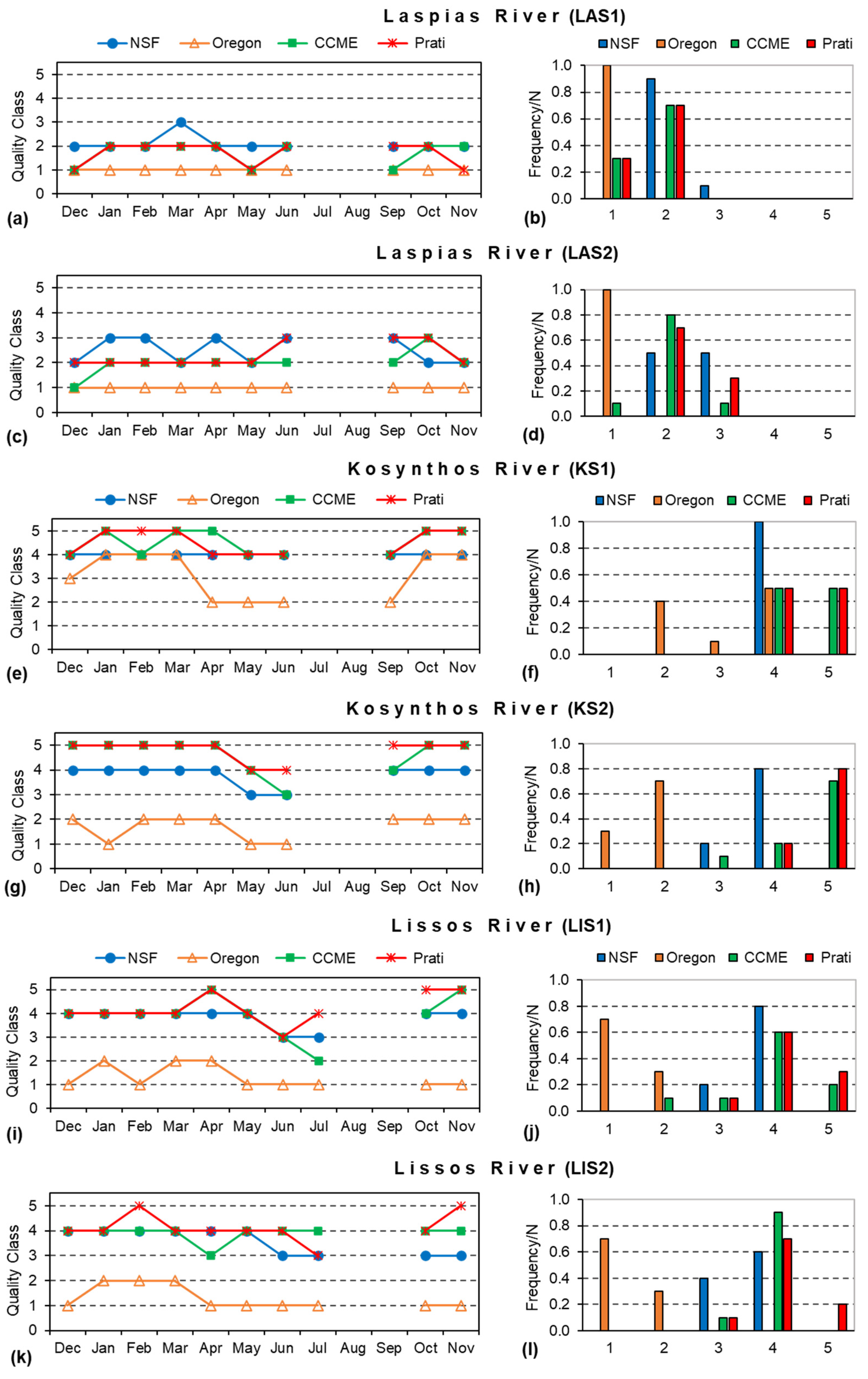
3.2. Water Quality Class in the Three Rivers according to the Four WQIs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kummu, M.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; De Moel, H.; Eisner, S.; Flörke, M.; Porkka, M.; Siebert, S.; Veldkamp, T.I.E.; Ward, P.J. The world’s road to water scarcity: Shortage and stress in the 20th century and pathways towards sustainability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, S.K. A critical review on water quality index tool: Genesis, evolution and future directions. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Water Quality Indices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Tsakiris, G.; Gikas, G.D. Suitability of water quality indices for application in lakes in the Mediterranean. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikoilidou, E.; Samiotis, G.; Tsikritzis, L.; Kevrekidis, T.; Amanatidou, E. Evaluation of water quality indices adequacy in characterizing the physico-chemical water quality of lakes. Environ. Process. 2017, 4 (Suppl. 1), 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and integrated interpretation with water quality index studies. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Ramal, M.M.; Diop, L.; Jaafar, O.; Demir, V.; Kisi, O. Hybrid adaptive neuro-fuzzy models for water quality index estimation. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2227–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Yuxin, Z.; Yuxiao, W.; Feng, Y. Can entropy weight method correctly reflect the distinction of water quality indices? Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Porta, D. Hydrogeochemical evaluation of water quality suitable for human consumption and comparative interpretation for water quality index studies. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, P.; Farooq, S.H. Application of water quality index and multivariate statistical analysis for assessing coastal water quality. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidzadeh, Z. An integrated approach of hydrogeochemistry, statistical analysis, and drinking water quality index for groundwater assessment. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 781–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, J. Environmental factors assisted the evaluation of entropy water quality indices with efficient machine learning technique. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2045–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Ma, K. An enhanced Beetle Antennae Search algorithm based comprehensive water quality index for urban river water quality assessment. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2685–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME). Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Water Quality Index 1.0, User’s Manual. In Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2001. Available online: http://www.mae.gov.nl.ca/waterres/quality/background/cwqi.html (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A Water Quality Index-Do We Dare? Water Sew. Works 1970, 17, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Cude, C.G. Oregon Water Quality Index: A Tool for Evaluating Water Quality Management Effectiveness. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Pavanello, R.; Pesarin, F. Assessment of Surface Water Quality by a Single Index of Pollution. Water Res. 1971, 5, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.S. Water quality variations and control technology of Yamuna River. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1985, 37, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinius, S.H. Design of an index of water quality. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1987, 23, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marselina, M.; Wibowo, F.; Mushfiroh, A. Water quality index assessment methods for surface water: A case study of the Citarum River in Indonesia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, G.; Kootenaei, F.G.; Ramezani, M.; Lotfi, E.; Asgharnia, H. Comparative investigation of river water quality by OWQI, NSFWQI, and wilcox indexes (case study: The Talar River—Iran). Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water quality indices: Challenges and application limits in the literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotou, I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Gikas, G.D. Performance of seven water quality indices (WQIs) in a Mediterranean river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotou, I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Gikas, G.D. Water quality evaluation of a lacustrine water body in the Mediterranean based on different water quality index (WQI) methodologies. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, A.; Akiner, M.E. Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: A case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlat, A.; Guidoum, A.; Koulala, I. Status and trends of water quality in the Tafna catchment: A comparative study using water quality indices. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2017, 7, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrin, J.L.; Salles, C.; Bancon-Montigny, C.; Raïs, N.; Chahinian, N.; Dowse, L.; Rodier, C.; Tournoud, M.G. Comparison of index systems for rating water quality in intermittent rivers. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, M.; Homaei, F.; Farhadi, H. Reliability assessment of water quality index based on guidelines of national sanitation foundation in natural streams: Integration of remote sensing and data-driven models. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 4619–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, M.; Ghaemi, A.; Emamgholizadeh, S. Prediction of water quality parameters using evolutionary computing-based formulations. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6377–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D. Water quantity and hydrochemical quality monitoring of Laspias River, North Greece. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Dimou, D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. River water quantity and quality monitoring in an agricultural basin in North Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gikas, G.D.; Yiannakopoulou, T.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Modeling of non-point source pollution in a Mediterranean drainage basin. Environ. Model. Assess. 2006, 11, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Yiannakopoulou, T.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Water quality trends in a coastal lagoon impacted by non-point source pollution after implementation of protective measures. Hydrobiologia 2006, 563, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisinaras, V.; Petalas, C.; Gikas, G.D.; Gemitzi, A.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Hydrological and water quality modeling in a medium-sized basin using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). Desalination 2010, 250, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFD, 2000. Directive of the European Parliament and of the council 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal C513 23/10/2000. 2000. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:5c835afb-2ec6-4577-bdf8-756d3d694eeb.0004.02/DOC_1&format=PDF (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Tsakiris, G. The status of the European waters in 2015: A review. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacharias, I.; Liakou, P.; Biliani, I. A Review of the status of surface European waters twenty years after WFD introduction. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA, AWWA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association & American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rusydi, A.F. Correlation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradilla-Hernández, M.S.; de Anda, J.; Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Montes, C.Y.; Barrios-Piña, H.; Ruiz-Palomino, P.; Díaz-Vázquez, D. Assessment of the water quality of a subtropical lake using the NSF-WQI and a newly proposed ecosystem specific water quality index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Lhamo, P.; Sahoo, N.K. Inconsistency of PCA-based water quality index—Does it reflect the quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA; RWS Publications International: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sutadian, A.D.; Muttil, N.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process to identify parameter weights for developing a water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Water Quality Assessments, A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK; Great Britain, University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; p. 559. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2006/44/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 6 September 2006 on the quality of fresh waters needing protection or improvement in order to support fish life. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 264, 20–31.
- Dodds, W.K. Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gikas, G.D.; Sylaios, G.K.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.; Boskidis, I. Comparative evaluation of river chemical status based on WFD methodology and CCME water quality index. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, C.; Soulis, K.; Bellos, V.; Ntoanidis, L.; Dimitriou, E. Estimation of a suitable range of discharges for the development of instream flow recommendations. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Mackay, E.B.; Cardoso, A.C.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Birk, S.; Blackstock, K.L.; Borics, G.; Borja, A.; Feld, C.K.; Ferreira, M.T.; et al. Protecting and restoring Europe’s waters: An analysis of the future development needs of the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.I.; Vidal, T.; Gonçalves, F.J.; Castro, B.B.; Pereira, J.L. Challenges to water quality assessment in Europe—Is there scope for improvement of the current Water Framework Directive bioassessment scheme in rivers? Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andricevic, R. Ecological quality assessment under uncertainty for transitional and coastal waters: Central Eastern Adriatic Sea study. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikidis, N.; Amaxidis, Y.; Bertahas, I.; Laschou, S.; Gritzalis, K. Analysis of factors driving stream water composition and synthesis of management tools—A case study on small/medium Greek catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Alexakis, D.E.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Laschou, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Dimitriou, E. Implementing the CCME water quality index for the evaluation of the physicochemical quality of Greek rivers. Water 2022, 14, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N.; Arpon, K.D.; Giakoumis, T. The EU Water Framework Directive: From great expectations to problems with implementation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, K.; Hao, Q.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Y. Hydrogeochemical insights into the signatures, genesis and sustainable perspective of nitrate enriched groundwater in the piedmont of Hutuo watershed, China. CATENA 2022, 212, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Giovanardi, F. Contribution of Richard A. Vollenweider toward understanding eutrophication of the coastal Adriatic Sea. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2011, 14, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
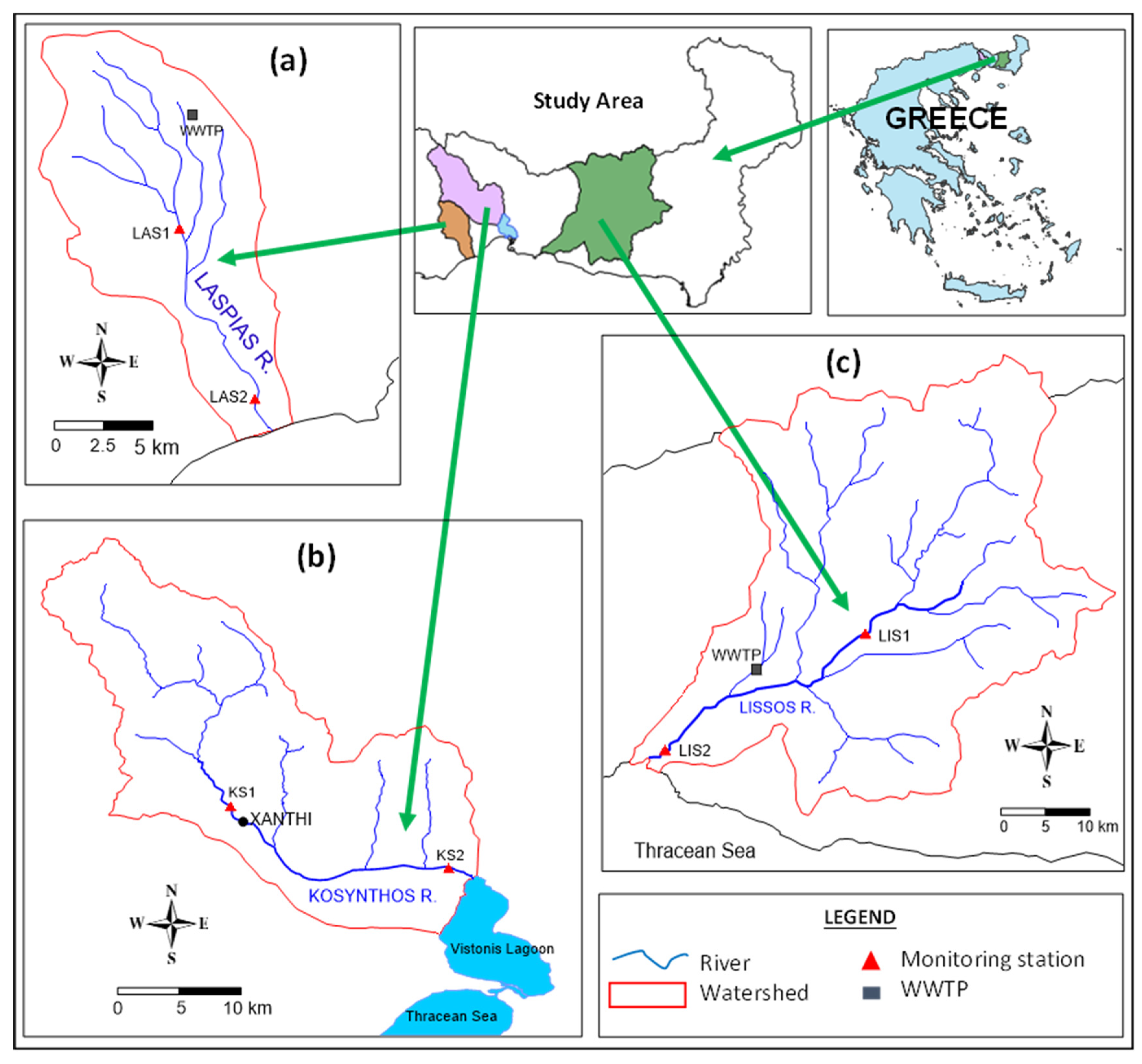
| Characteristics | Laspias | Kosynthos | Lissos |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 30 km | 52 km | 45 km |
| Watershed area and morphology | 221 km2; mountainous 14%, plain area 86% | 440 km2; mountainous 80%, plain area 20% | 1475 km2; mountainous 26%, hilly area 34%, plain area 40% |
| Cultivated area | 122 km2 | 65 km2 | 407 km2 |
| Nutrient quantities used in agricultural activities | Nitrogen 1358 tn/y Phosphorus 239 tn/y | Nitrogen 1190 tn/y Phosphorus 162 tn/y | Nitrogen 5186 tn/y Phosphorus 958 tn/y |
| Pollution sources | Effluents from the WWTP * of the city of Xanthi, light industry, agricultural runoff, livestock units | Untreated wastewater from small settlements, urban and agricultural runoff, livestock units | Effluents from the WWTP * of an industrial area, agricultural runoff |
| Index | Parameter (Unit) | Weight b | OV c | Aggregation Formula d | Range of WQI, Characterization | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSF WQI [3,18] | DO (%) pH BOD5 (mg/L) NO3 (mg/L) PO4 (mg/L) T (°C) TS (mg/L) | 0.224 0.144 0.144 0.132 0.132 0.132 0.092 | - | 91–100 = Excellent 71–90 = Good 51–70 = Medium 26–50 = Bad 0–25 = Very bad | 5 4 3 2 1 | |
| O-WQI [19] | DO (mg/L), pH, BOD5 (mg/L) NH4-N + NO3-N (mg N/L) TP (mg P/L), T (°C), TSS (mg/L) | - | - | 90–100 = Excellent 85–89 = Good 80–84 = Fair 60–79 = Poor 10–59 = Very poor | 5 4 3 2 1 | |
| CCME WQI [17] | DO (mg/L) pH BOD5 (mg/L) TSS (mg/L) NH4-N (mg N/L) NOx-N (mg N/L) a TP (mg P/L) | - | >6 6.5–9.0 <6.0 <25 <0.6 <10 <0.165 | F1: Scope F2: Frequency F3: Amplitude | 95–100 = Excellent 80–94 = Good 65–79 = Fair 45–64 = Marginal 0–44 = Poor | 5 4 3 2 1 |
| Prati’s index of pollution [20] | DO (mg/L), pH, BOD5 (mg/L) COD (mg/L) TSS (mg/L) NO3-N (mg N/L) NH4-N (mg N/L) TP (mg P/L) | - | - | 0–1 = Excellent 1–2 = Acceptable 2–4 = Slight pollution 4–8 = Pollution >8 = Heavy pollution | 5 4 3 2 1 |
| Parameter | LAS1 | LAS2 | KS1 | KS2 | LIS1 | LIS2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Τ (°C) | Mean | 11.8 | 13.0 | 12.1 | 15.8 | 14.5 | 14.5 |
| SD * (n *) | 5.7 (35) | 5.7 (35) | 6.1 (25) | 6.5 (25) | 6.0 (20) | 7.2 (20) | |
| Min *–Max * | 2.1–22.8 | 3.9–22.8 | 2.0–22.3 | 5.7–27.8 | 5.2–26.0 | 5.5–28.0 | |
| DO (mg/L) | Mean | 5.0 | 5.7 | 11.1 | 11.2 | 10.0 | 9.8 |
| SD (n) | 3.1 (35) | 3.2 (35) | 2.5 (25) | 2.4 (25) | 1.8 (20) | 1.9 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.7–10.6 | 0.2–10.6 | 5.4–16.4 | 5.7–15.2 | 7.1–12.7 | 6.7–12.8 | |
| pH | Mean | 8.0 | 7.8 | 8.5 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 8.1 |
| SD (n) | 0.2 (35) | 0.2 (35) | 0.3 (25) | 0.3 (25) | 0.3 (20) | 0.2 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 7.5–8.4 | 7.3–8.2 | 8.0–9.5 | 7.2–8.7 | 7.2–8.3 | 7.7–8.7 | |
| EC (mS/cm) | Mean | 1.67 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.55 |
| SD (n) | 0.36 (35) | 0.53 (35) | 0.05 (25) | 0.13 (25) | 0.09 (20) | 0.13 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.63–2.31 | 0.36–2.25 | 0.09–0.26 | 0.15–0.64 | 0.19–0.53 | 0.28–0.80 | |
| ΒOD5 (mg/L) | Mean | 14.4 | 12.0 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 |
| SD (n) | 15.6 (30) | 9.0 (31) | 2.5 (25) | 3.2 (25) | 3.7 (20) | 3.6 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.0–71.2 | 1.4–36.7 | 0.0–8.1 | 0.0–11.5 | 0.0–10.7 | 0.0–12.0 | |
| COD (mg/L) | Mean | 95.2 | 93.2 | 5.8 | 7.4 | 9.4 | 10.9 |
| SD (n) | 69.5 (30) | 67.4 (30) | 3.9 (25) | 5 (25) | 6.7 (20) | 16.0 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 14.1–334.9 | 6.0–301.8 | 0.0–14.3 | 0.0–21.6 | 0.0–22.6 | 0.0–75.6 | |
| NOx-N (mg-N/L) | Mean | 5.7 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 2.9 | 2.6 |
| SD (n) | 2.5 (25) | 1.6 (24) | 0.2 (25) | 0.8 (25) | 1.8 (20) | 1.9 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.7–10.3 | 0.1–5.2 | 0.1–0.8 | 0.8–3.6 | 0.9–7.0 | 0.4–7.1 | |
| NH4-N (mg-Ν/L) | Mean | 19.1 | 11.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| SD (n) | 19.1 (28) | 7.5 (28) | 0.2 (25) | 0.1 (25) | 0.7 (20) | 0.9 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 3.0–77.3 | 0.5–36.5 | 0.0–0.7 | 0.0–0.4 | 0.0–2.7 | 0.0–3.9 | |
| TP (mg-P/L) | Mean | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| SD (n) | 0.7 (35) | 0.5 (35) | 0.04 (25) | 0.02 (25) | 0.01 (20) | 0.06 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.0–3.2 | 0.0–1.7 | 0.0–0.19 | 0.0–0.09 | 0.01–0.09 | 0.05–0.31 | |
| TSS (mg/L) | Mean | 38.6 | 23.3 | 5.7 | 9.7 | 5.3 | 11.8 |
| SD (n) | 60.9 (34) | 27.2 (34) | 13.0 (25) | 18.1 (25) | 6.1 (20) | 20.0 (20) | |
| Min–Max | 0.2–276.4 | 0.3–121.0 | 0.0–65.7 | 0.4–89.7 | 0.2–23.7 | 0.3–74.2 |
| River | WQI | Quality Class | Monitoring Station | Quality Characterization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laspias | NSF-WQI | 2 | LAS1, LAS2 | Bad water quality |
| O-WQI | 1 | LAS1, LAS2 | Very poor water quality | |
| CCME-WQI | 1 | LAS1, LAS2 | Poor water quality | |
| Prati’s Index | 1 | LAS1 | Heavy pollution | |
| Kosynthos | NSF-WQI | 3 | KS2 | Medium water quality |
| O-WQI | 1 | KS2 | Very poor water quality | |
| CCME-WQI | 3 | KS2 | Fair water quality | |
| Prati’s Index | 4 | KS1, KS2 | Acceptable | |
| Lissos | NSF-WQI | 3 | LIS1, LIS2 | Medium water quality |
| O-WQI | 1 | LIS1, LIS2 | Very poor water quality | |
| CCME-WQI | 2 | LIS1 | Marginal water quality | |
| Prati’s Index | 3 | LIS1, LIS2 | Slight pollution |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gikas, G.D.; Lergios, D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Comparative Assessment of the Application of Four Water Quality Indices (WQIs) in Three Ephemeral Rivers in Greece. Water 2023, 15, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081443
Gikas GD, Lergios D, Tsihrintzis VA. Comparative Assessment of the Application of Four Water Quality Indices (WQIs) in Three Ephemeral Rivers in Greece. Water. 2023; 15(8):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081443
Chicago/Turabian StyleGikas, Georgios D., Dimitrios Lergios, and Vassilios A. Tsihrintzis. 2023. "Comparative Assessment of the Application of Four Water Quality Indices (WQIs) in Three Ephemeral Rivers in Greece" Water 15, no. 8: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081443






