Fate and Spatial–Temporal Variation of 23 Elements at 7 Wastewater Treatment Plants in Southeast City of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Concentration of Elements in WWTPs
3.2. Spatial Variation of Elements in Seven WWTPs
3.3. Removal Efficiency for Elements
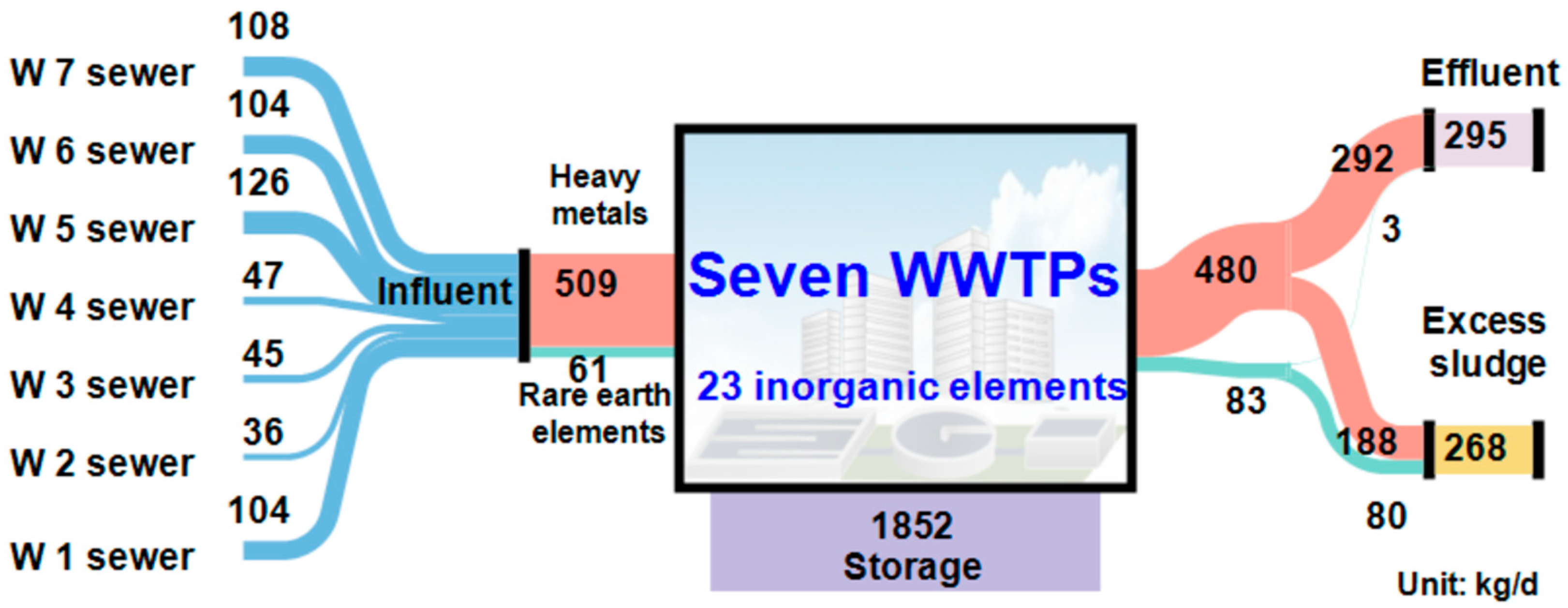
3.4. Elemental Flux
3.5. Annual Variations of Elements in Sludge
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvelas, M.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Samara, C. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busetti, F.; Badoer, S.; Cuomo, M.; Rubino, B.; Traverso, P. Occurrence and removal of potentially toxic metals and heavy metals in the wastewater treatment plant of Fusina (Venice, Italy). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 9264–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzier, R.; Tusseau-Vuillemin, M.-H.; dit Meriadec, C.M.; Rousselot, O.; Mouchel, J.-M. Trace metal speciation and fluxes within a major French wastewater treatment plant: Impact of the successive treatments stages. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, D.; Cheng, J. Effluent concentration and removal efficiency of nine heavy metals in secondary treatment plants in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17058–17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ÜStün, G.E. Occurrence and removal of metals in urban wastewater treatment plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iloms, E.; Ololade, O.O.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Selvarajan, R. Investigating industrial effluent impact on municipal wastewater treatment plant in Vaal, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- US EPA. Toxic and Priority Pollutants under the Clean Water Act /US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/toxic-and-priority-pollutants-under-clean-water-act (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Cobelo-García, A.; Filella, M.; Croot, P.; Frazzoli, C.; Du Laing, G.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Rauch, S.; Salaun, P.; Schäfer, J.; Zimmermann, S. COST action TD1407: Network on technology-critical elements (NOTICE)—From environmental processes to human health threats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15188–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaegi, R.; Gogos, A.; Voegelin, A.; Hug, S.J.; Winkel, L.H.E.; Buser, A.M.; Berg, M. Quantification of individual Rare Earth Elements from industrial sources in sewage sludge. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogos, A.; Wielinski, J.; Voegelin, A.; Kammer, F.v.d.; Kaegi, R. Quantification of anthropogenic and geogenic Ce in sewage sludge based on Ce oxidation state and rare earth element patterns. Water Res. X 2020, 9, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atinkpahoun, C.N.H.; Pons, M.-N.; Louis, P.; Leclerc, J.-P.; Soclo, H.H. Rare earth elements (REE) in the urban wastewater of Cotonou (Benin, West Africa). Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubert, J.M.; Pomiès, M.; Martin Ruel, S.; Coquery, M. Influent concentrations and removal performances of metals through municipal wastewater treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in municipal wastewater in Heilongjiang province, China: A monthly reconnaissance from 2015 to 2017. Water 2020, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vriens, B.; Voegelin, A.; Hug, S.J.; Kaegi, R.; Winkel, L.H.E.; Buser, A.M.; Berg, M. Quantification of element fluxes in wastewaters: A nationwide survey in switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10943–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, S.T.; Yaşa, İ.; Ali, S.F.; Eren, A.E.; Turky, A.N. Occurrence, seasonal changes and removal efficiency assessment of heavy metals in urban wastewater treatment plant. J. Asian Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanon, F.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Chi, Q.; Mulla, S.I.; Mama, D.; Yu, C.-P. Assessment of the occurrence, spatiotemporal variations and geoaccumulation of fifty-two inorganic elements in sewage sludge: A sludge management revisit. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPA. Method 3015A (SW-846): Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Aqueous Samples and Extracts; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- EPA. Method 3051A (SW-846): Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Oils; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Hassan, N.M.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Celo, V.; Chen, H. Analysis of environmental samples using microwave-assisted acid digestion and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Maximizing total element recoveries. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 178, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, F.J.; Sato, A.P.S.; Luz, M.S.; Fávaro, D.I.T.; Ferreira, F.J.; da Silva Paganini, W.; Olympio, K.P.K. The environmental impact of informal and home productive arrangement in the jewelry and fashion jewelry chain on sanitary sewer system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10701–10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarsiero, A.; Veschetti, E.; Donati, G.; Ottaviani, M. Heavy metal distribution in wastewater from a treatment plant. Microchem. J. 1998, 59, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MOEP). Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant (GB18918-2002); MOEP: Beijing, China, 2002; (In Chinese).
- Yang, J.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Gao, D.; Zheng, G.; Guo, G.; Lee, D. Current status and developing trends of the contents of heavy metals in sewage sludges in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Lee, S.; Yang, Y.; Gordon, G.W.; Hristovski, K.; Halden, R.U.; Herckes, P. Characterization, recovery opportunities, and valuation of metals in municipal sludges from U.S. wastewater treatment plants nationwide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9479–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkinahamira, F.; Suanon, F.; Chi, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, M.; Huang, X.; Yu, C.-P.; Sun, Q. Occurrence, geochemical fractionation, and environmental risk assessment of major and trace elements in sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, T.; Lester, J. Heavy metal behaviour during the activated sludge process I. Extent of soluble and insoluble metal removal. Sci. Total. Environ. 1987, 63, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Vale, P.; Whelan, J.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Cartmell, E. Mercury and antimony in wastewater: Fate and treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.-Q. The role of coagulation in water treatment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.; Polesel, F.; Kjos, M.; Carvalho, P.A.; Ciesielski, T.; Flores-Alsina, X.; Hansen, S.F.; Booth, A.M. Monitoring and modelling of influent patterns, phase distribution and removal of 20 elements in two primary wastewater treatment plants in Norway. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Qin, W.; Wen, X. Sludge retention time affects the microbial community structure: A large-scale sampling of aeration tanks throughout China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterritt, R.M.; Brown, M.J.; Lester, J.N. Metal removal by adsorption and precipitation in the activated sludge process. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1981, 24, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Cho, J.; Lim, B.-R.; Song, K.-G.; Ahn, K.-H. Effects of sludge retention time on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, M.; Bestani, B.; Said, A.H.; Benderdouche, N.; Guibal, E. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by a local dairy sludge as a biosorbant. Desalination 2010, 262, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, M. The abundance and distribution of the chemical elements in the earth’s crust. J. Chem. Educ. 1954, 31, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkinahamira, F.; Alsbaiee, A.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, T.-Y.; Cao, M.; Feng, M.; Sun, Q.; Yu, C.-P. Recovery and purification of rare earth elements from wastewater and sludge using a porous magnetic composite of β-cyclodextrin and silica doped with PC88A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Vela, N.; el Aatik, A.; Murray, E.; Roche, P.; Navarro, J.M. On the use of an IoT integrated system for water quality monitoring and management in wastewater treatment plants. Water 2020, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Chover, V.; Castellet-Viciano, L.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Cost analysis of the facilities deterioration in wastewater treatment plants: A dynamic approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Thunéll, S.; Lindberg, U.; Jiang, L.; Trygg, J.; Tysklind, M. Towards better process management in wastewater treatment plants: Process analytics based on SHAP values for tree-based machine learning methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağ, Y.; Tatar, B.; Kutsal, T. Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by activated sludge in batch and continuous-flow stirred reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, J. Evolution of environmental policy for China’s rare earths: Comparing central and local government policies. Resour. Policy 2020, 68, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsrud, B.; Nedland, K.T. Strategy for land application of sewage sludge in Norway. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, C.L.; Hui, Y.F.; Ou Yang, W.J. Study on Variation Trends of Heavy Metals Contents in Process of Sludge Energy Utilization. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 610–613, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jia, L.; Liu, Q.Z.; Chen, X.L.; Cheng, J.P. Source identification of heavy metals in sewage sludge and the effect of influent characteristics: a case study from China. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdova, J.; Raclavska, H.; Raclavsky, K.; Skrobankova, H. Heavy metals in domestic wastewater with respect to urban population in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Nkinahamira, F.; Adyari, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, A.; Sun, Q. Fate and Spatial–Temporal Variation of 23 Elements at 7 Wastewater Treatment Plants in Southeast City of China. Water 2023, 15, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061226
Guo S, Nkinahamira F, Adyari B, Zhang Y, Hu A, Sun Q. Fate and Spatial–Temporal Variation of 23 Elements at 7 Wastewater Treatment Plants in Southeast City of China. Water. 2023; 15(6):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061226
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shanshan, François Nkinahamira, Bob Adyari, Yiqing Zhang, Anyi Hu, and Qian Sun. 2023. "Fate and Spatial–Temporal Variation of 23 Elements at 7 Wastewater Treatment Plants in Southeast City of China" Water 15, no. 6: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061226
APA StyleGuo, S., Nkinahamira, F., Adyari, B., Zhang, Y., Hu, A., & Sun, Q. (2023). Fate and Spatial–Temporal Variation of 23 Elements at 7 Wastewater Treatment Plants in Southeast City of China. Water, 15(6), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061226






