Influence of Temperature on the Removal Efficiency of Organic Matter and Ammonia from Micro-Polluted Source Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Device
2.2. Inlet Water Quality
2.3. Test Methods
2.4. Detection Methods
3. Results and Discussion
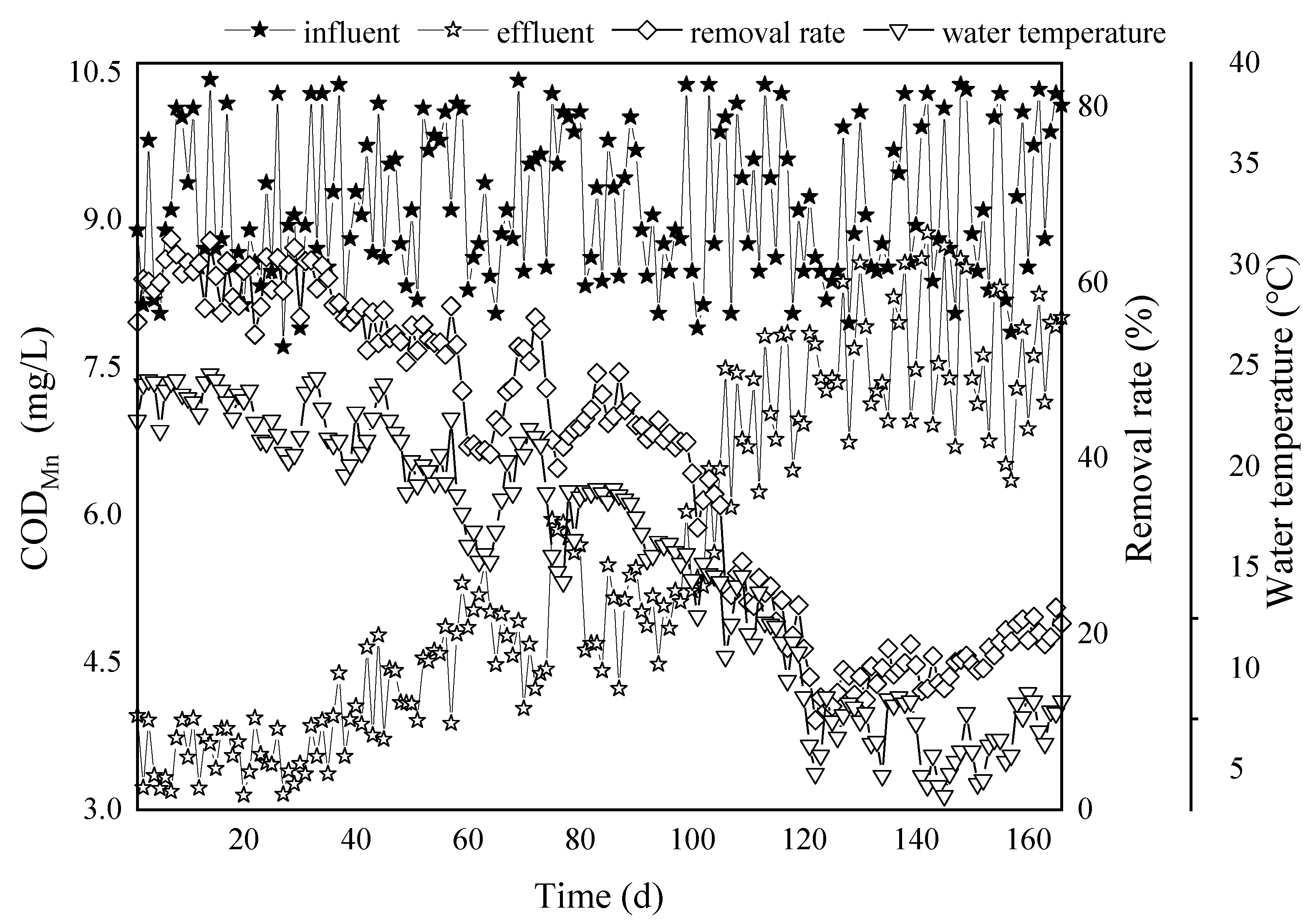
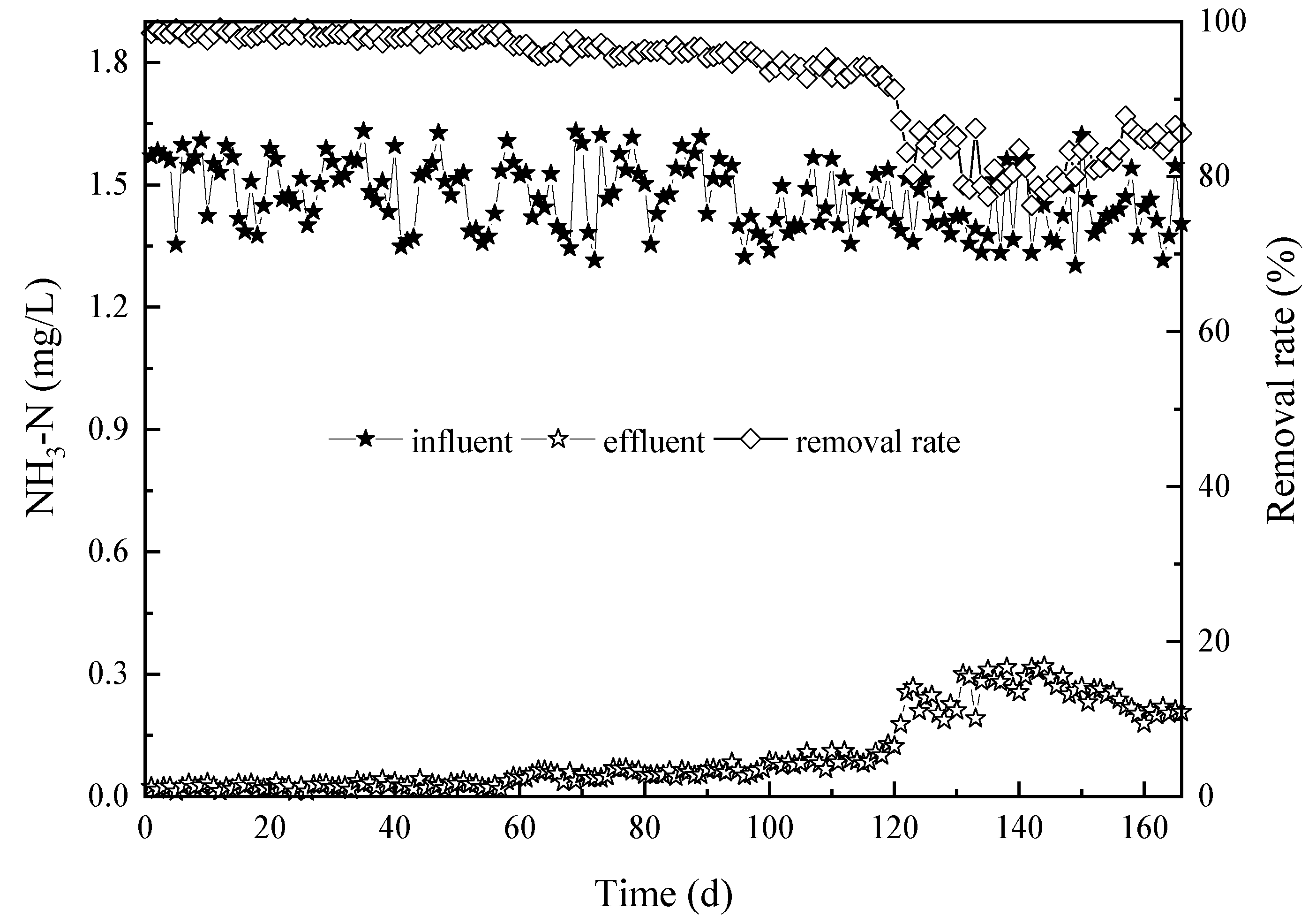
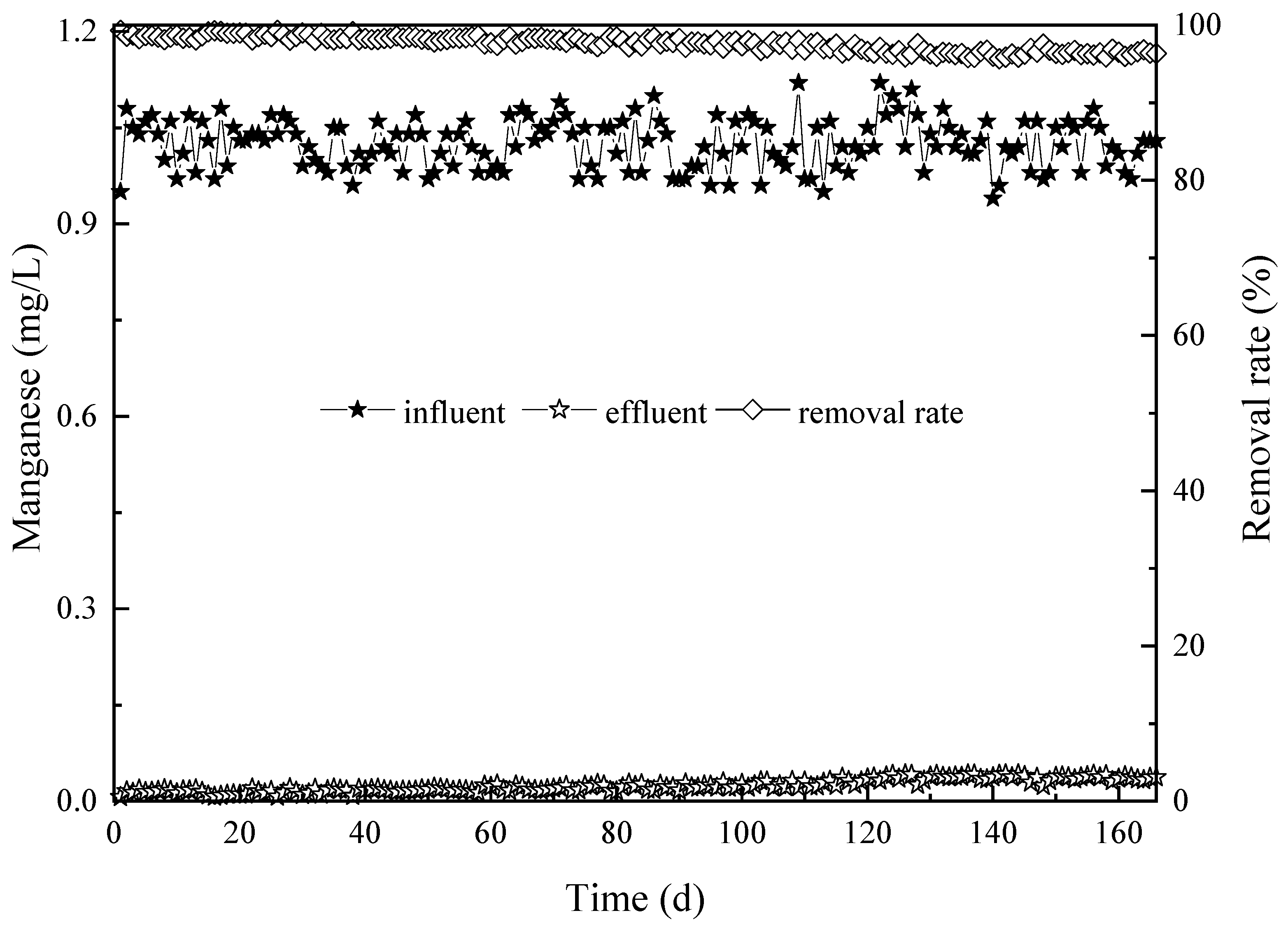
3.1. The Influence of Water Temperature on the Removal Efficiency with Respect to CODMn, Ammonia-N, and Manganese
3.1.1. Effect of Water Temperature on CODMn Removal Efficiency
3.1.2. Influence of Water Temperature on Ammonia-N Removal Efficiency
3.1.3. Influence of Water Temperature on Manganese Removal Efficiency
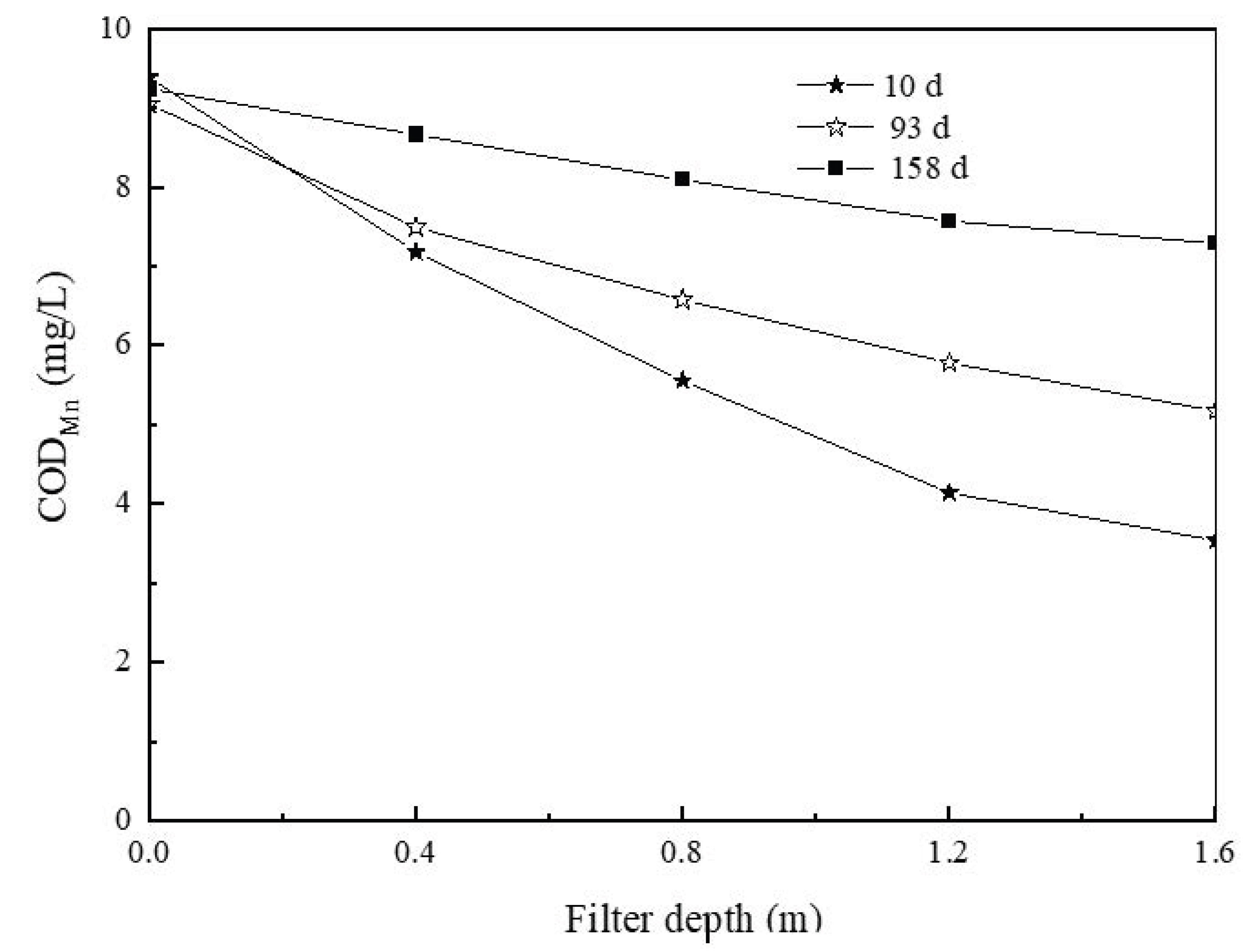
3.2. Change and Kinetic Analysis of CODMn, Ammonia-N, and Mn during the Experiment
3.2.1. Change in CODMn Levels along the Treatment Path and Kinetic Analysis
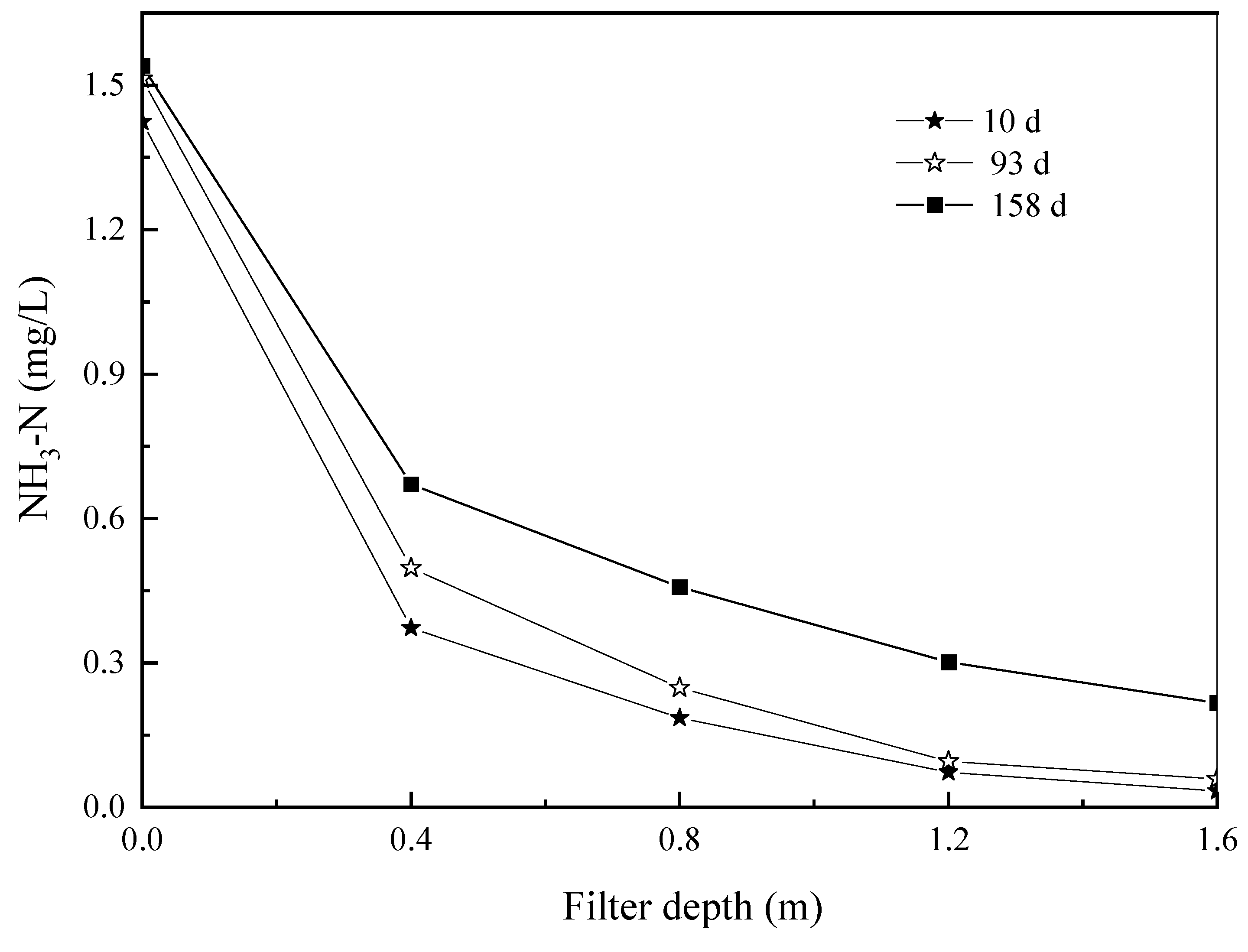
3.2.2. Change along the Treatment Path and Kinetic Analysis of Ammonia-N
3.2.3. Changes in Concentrations and Kinetic Characteristics of Manganese along the Treatment Path
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Sadat Mazari Moghaddam, N.; Masoomeh Rahimi, S.; Hajjizadeh, M.; Nasseh, N. Hexadecyltrimethylammonium-activated and zinc oxide-coated nano-bentonite: A promising photocatalyst for tetracycline degradation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, X.Y. Synthesis of magnetic CuO/MnFe2O4 nanocompisite and its high activity for degradation of levofloxacin by activation of persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Nengzi, L.-C.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X. Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole by CuCo LDH and LDH@fibers composite membrane activating peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, N.S.M.; Barikbin, B.; Al-Essa, E.M.; Khosravi, R.; Al-Musawi, T.; Nasseh, N. Application of magnetic activated carbon coated with CuS nanoparticles as a new adsorbent for the removal of tetracycline antibiotic from aqueous solutions (isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study). Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 280, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengzi, L.-C.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.-Z.; Zhang, W.-M.; Jiang, D.-A. Fabrication of SnS/TiO2 NRs/NSs photoelectrode as photoactivator of peroxymonosulfate for organic pollutants elimination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 117172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Nengzi, L.; Zhang, J. Influence of temperature on CODMn and Mn2+ removal and microbial community structure in pilot-scale biofilter. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengzi, L.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Qiu, G.; Li, H. Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water 2023, 15, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Z.; Dai, M.; Zhao, G. Combination of the endophytic manganese-oxidizing bacterium Pantoea eucrina SS01 and biogenic Mn oxides: An efficient and sustainable complex in degradation and detoxification of malachite green. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; He, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, J. Manganese dioxide supported on hollow graphitized carbon spheres for the catalytic oxidation of toluene: Improved adsorption and electron transfer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 321, 124203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Tian, H.; Guo, X.; Feng, S.; Du, E.; Peng, M.; Zhang, J. Advanced synergetic nitrogen removal of municipal wastewater using oxidation products of refractory organic matters in secondary effluent by biogenic manganese oxides as carbon source. Water Res. 2023, 241, 120163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Lv, W.; Hu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L. The mechanism of degradation polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by magnetic biogenic manganese oxides. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 191, 108803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengzi, L.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Ma, J.-H.; Li, H.-T.; Cheng, Q.; Cheng, X. Synthesis of silver bromide/graphene oxide composite and its enhanced visible light photocatalytic efficiency and mechanism for elimination of parachlorobenzoic acid. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 4279–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liao, C.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, G.; Liu, W.; Gao, P.; Sun, D.; Du, J. Combined Process of Biogenic Manganese Oxide and Manganese-Oxidizing Microalgae for Improved Diclofenac Removal Performance: Two Different Kinds of Synergistic Effects. Toxics 2022, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, J.; Sheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y. Performance, community structure, metabolic pathway, and mechanism in a three-dimensional electrocatalytic biofilter (3DEBF) for the degradation of multiple concentrations of clofibric acid (CA). Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-L.; Zhang, F.-Z.; Zhou, W.-W. Advanced Purification of Effluent from Micro-polluted Source Water Waterworks by Nanofiltration. China Water Wastewater 2019, 35, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.N.; Kim, D.G.; Ko, S.O. Efficient removal of 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol from secondary wastewater treatment effluent by a biofilm process incorporating biogenic manganese oxide and Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.F.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.H. Enhanced performance of tetracycline treatment in wastewater using aerobic granular sludge with in-situ generated biogenic manganese oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ruan, Z.Y.; Liu, J. Complete degradation of bisphenol A and nonylphenol by a composite of biogenic manganese oxides and Escherichia coli cells with surface-displayed multicopper oxidase CotA. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hambly, A.; Wang, G.; Tang, K.; Andersen, H. Engineered manganese redox cycling in anaerobic–aerobic MBBRs for utilisation of biogenic manganese oxides to efficiently remove micropollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.F.; Huang, Y.; Nengzi, L.C. Performance and microbial community profiles in pilot-scale biofilter for the simultaneous removal of ammonia, iron and manganese at different manganese concentrations. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.F.; Nengzi, L.C.; Bao, L.L. Interactions between ammonia, iron and manganese removal using pilot-scale biofilters. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2017, 66, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Meng, L.; Zhang, J. Influence of backwashing period on removal efficiency in a biological manganese removal filter. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Ou, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hou, X.; Yan, L.; Tian, L. Characterization of acetochlor degradation and role of microbial communities in biofilters with varied substrate types. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, D.; Li, X. Rapid Start-up of Bioflter Purifying Groundwater Containing High Concentrations of lron, Manganese and Ammonia Nitrogen. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, D.; Li, X. Raid start-up of iological purifying fiter of groundwater containing high concentration of iron and manganese associated ammonia nitrogen. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2013, 45, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nengzi, L.; Meng, L.; Qiu, Y.; Li, X.; Didi, K.; Li, H.; Qiu, G. Influence of Nitrite on the Removal of Organic Matter and Manganese Using Pilot-Scale Biofilter: A Kinetic Study. Water 2023, 15, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengzi, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of temperature on removal efficiency of ammonia, iron and manganese in biological purification biofilter. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2020, 39, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiao, H.; Deng, S.; Han, X.; Xia, F.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced performance of thallium(I) removal by in situ-generated manganese oxides during biogenic Mn(II) oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Feng, S.; Du, E.; Peng, M.; Zhang, J. Advanced nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure of a lab-scale denitrifying filter with in-situ formation of biogenic manganese oxides. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 17299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Project | CODMn (mg L−1) | NH4+-N (mg L−1) | Mn (mg L−1) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intake water quality | range | 7.71~10.43 | 1.30~1.63 | 0.94~1.12 | 6.87~7.43 |
| average value | 9.15 | 1.47 | 1.02 | 7.17 | |
| Water Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Reaction Half-Life t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23.4 | 0.0328 | 21.13 | y = −0.0328 × −0.00710 | 0.997 |
| 15.6 | 0.0167 | 41.51 | y = −0.0167 × −0.0522 | 0.999 |
| 8.3 | 0.00790 | 87.74 | y = −0.00790 × −0.00370 | 0.997 |
| Water Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Reaction Half-Life t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23.4 | 0.110 | 6.32 | y = −0.110 × −0.386 | 0.993 |
| 15.6 | 0.0995 | 6.97 | y = −0.0995 × −0.291 | 0.995 |
| 8.3 | 0.0513 | 13.51 | y = −0.0513 × −0.408 | 0.999 |
| Water Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Reaction Half-Life t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23.4 | 0.164 | 4.22 | y = −0.164 × +0.612 | 0.998 |
| 15.6 | 0.144 | 4.83 | y = −0.144 × +0.540 | 0.997 |
| 8.3 | 0.119 | 5.82 | y = −0.119 × +0.451 | 0.996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nengzi, L.; Li, H.; Ke, D.; Wu, X.; Meng, L.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Q. Influence of Temperature on the Removal Efficiency of Organic Matter and Ammonia from Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water 2023, 15, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152695
Nengzi L, Li H, Ke D, Wu X, Meng L, Fang Y, Hu Q. Influence of Temperature on the Removal Efficiency of Organic Matter and Ammonia from Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water. 2023; 15(15):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152695
Chicago/Turabian StyleNengzi, Lichao, Haitao Li, Dan Ke, Xiaofeng Wu, Lin Meng, Yin Fang, and Qiyuan Hu. 2023. "Influence of Temperature on the Removal Efficiency of Organic Matter and Ammonia from Micro-Polluted Source Water" Water 15, no. 15: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152695
APA StyleNengzi, L., Li, H., Ke, D., Wu, X., Meng, L., Fang, Y., & Hu, Q. (2023). Influence of Temperature on the Removal Efficiency of Organic Matter and Ammonia from Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water, 15(15), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152695







