Zeolites for Nitrogen Recovery from the Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Permeate: Zeolite Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- (a)
- Prepared ammonium aqueous solutions with deionized water and NH4Cl
- (b)
- Tap water fortified with NH4Cl
- (c)
- Tap water fortified with NH4Cl and enriched with PO4 at the same concentration found in the AnMBR permeate
- (d)
- Tap water fortified with NH4Cl and with organic components (glucose and methanol) to study the effect of organic matter.
- (e)
- Permeate of AnMBR process.
2.2. Kinetic Batch Sorption Studies
2.3. Equilibrium Studies
3. Results and Discussion
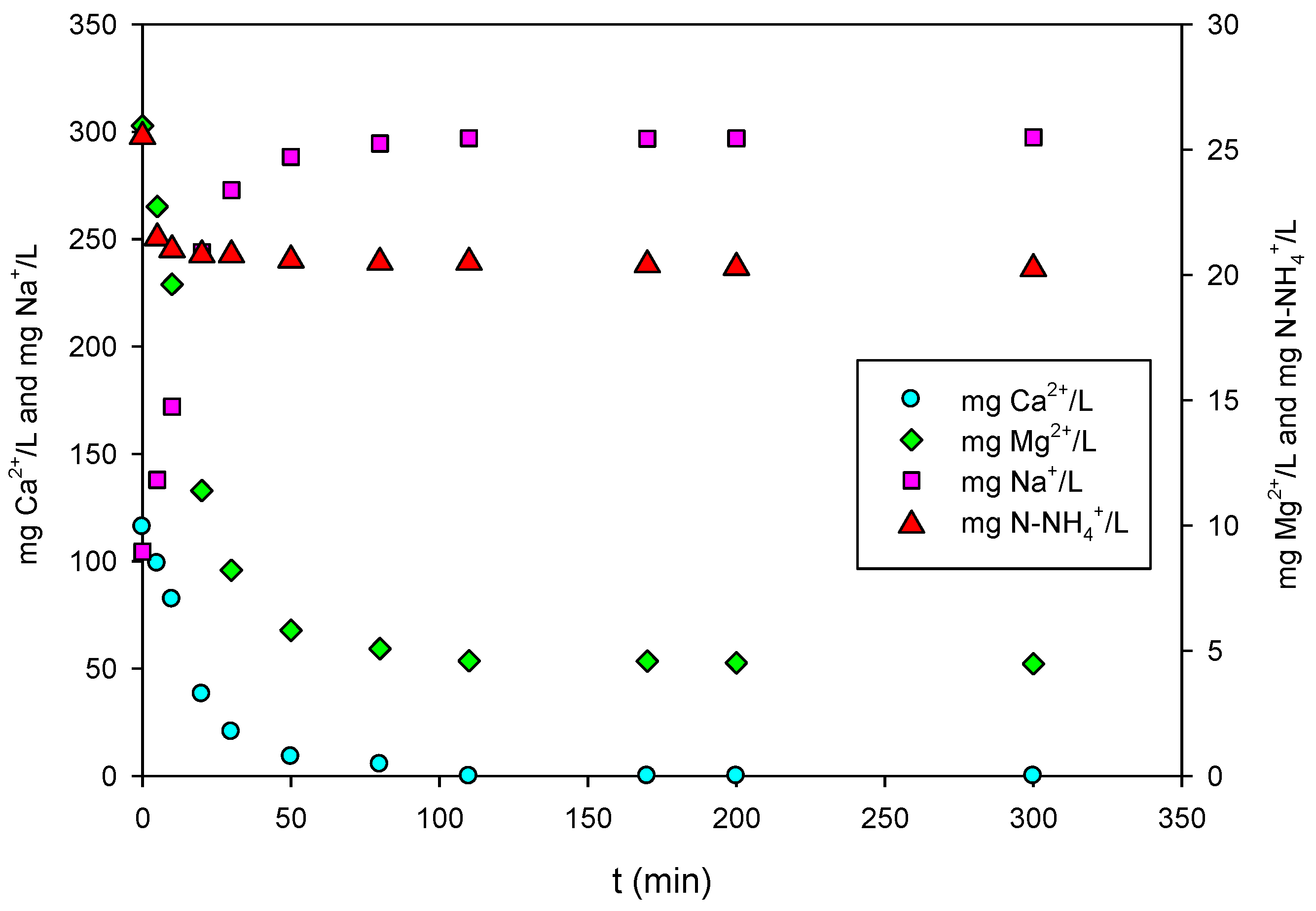
3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
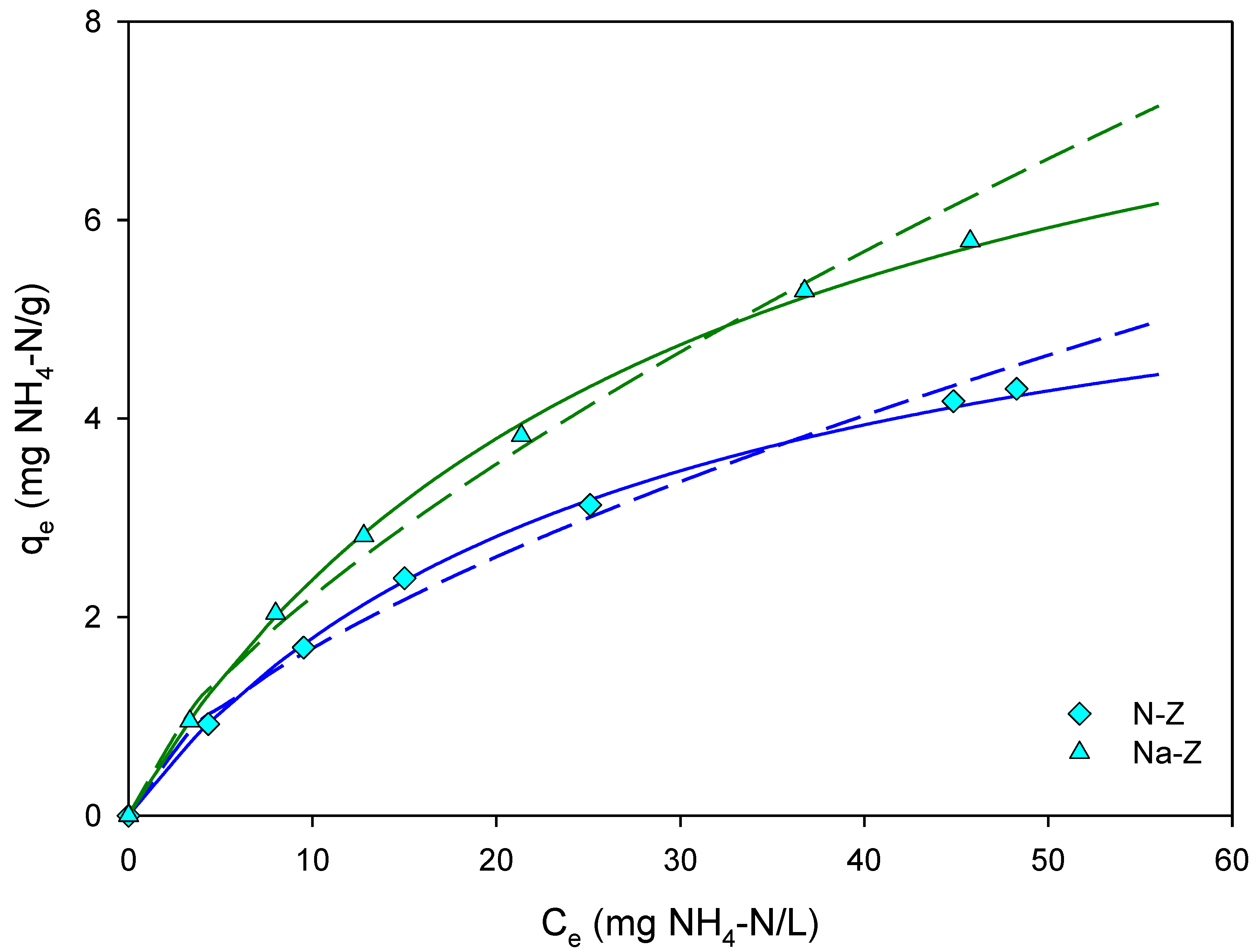
3.2. Effect of Zeolite Activation and Particle Size
3.3. Competing Ions
3.4. Effect of Organic Matter
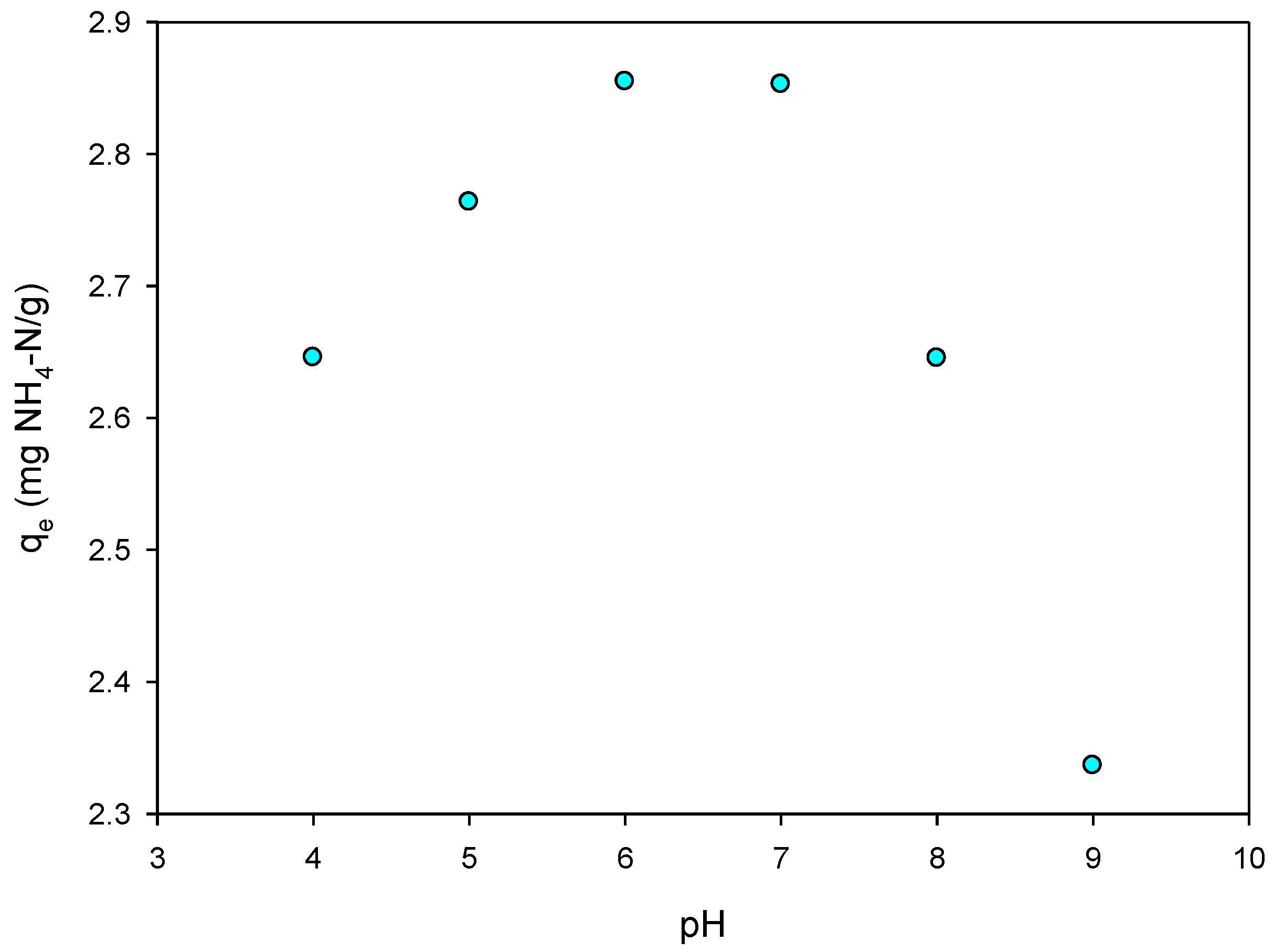
3.5. pH Effect
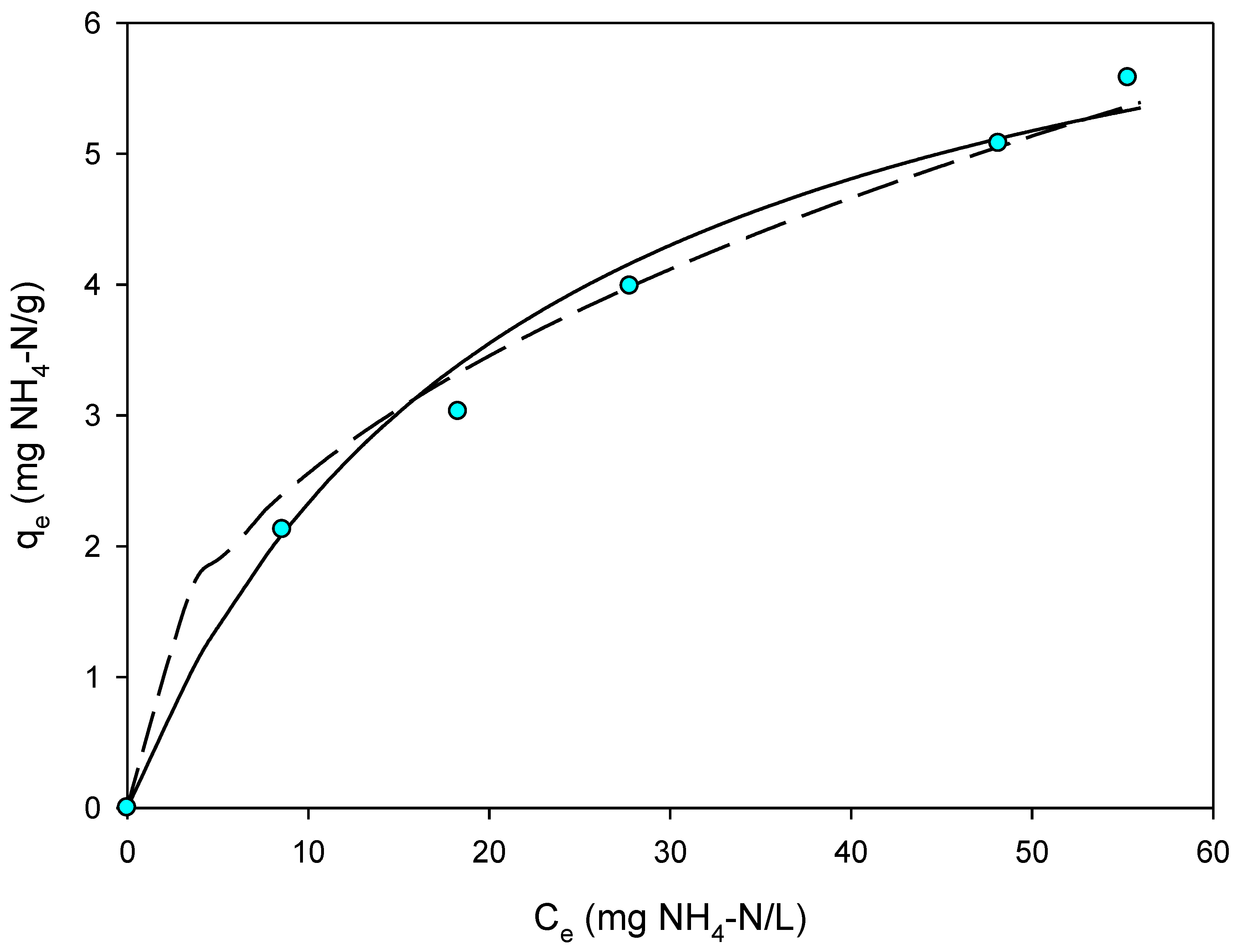
3.6. Effect of AnMBR Permeate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B.; Love, N.G.; Skerlos, S.J.; Raskin, L. Perspectives on anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Liao, B. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: Challenges and opportunities. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, T.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y. Insights into the carbon neutrality for the treatment process engineering of municipal wastewater by anaerobic membrane bioreactor integrated with partial nitritation-anammox: CO2 reduction and energy recovery. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, A.; Aparicio, S.; González-Camejo, J.; Benítez, A.L.J.; Mateo, O.; Mora, J.F.; Noriega-Hevia, G.; Sanchis-Perucho, P.; Serna-García, R.; Zamorano-Lopez, N.; et al. Resource recovery from sulphate-rich sewage through an innovative anaerobic-based water resource recovery facility (WRRF). Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Dhar, B.R.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Lee, H.-S. Ammonium nitrogen removal from the permeates of anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Economic regeneration of exhausted zeolite. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Huang, F.; Zhang, J. Removal of phosphorus from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent by ion exchange resin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guida, S.; Jefferson, B.; Soares, A. Economic evaluation of ion-exchange processes for nutrient removal and recovery from municipal wastewater. Npj Clean Water 2020, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; An, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Tang, J.; Ye, J.; Zhou, Z. Inhibitory effects of Ca2+ on ammonium exchange by zeolite in the long-term exchange and NaClO–NaCl regeneration process. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K. Organics and nitrogen recovery from sewage via membrane-based pre-concentration combined with ion exchange process. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Han, T.; Chuan, S.; Zhu, T. Ammonia removal from leachate solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheikh, F.; Moralejo, C.; Pritzker, M.; Anderson, W.A.; Elkamel, A. Batch adsorption study of ammonia removal from synthetic/real wastewater using ion exchange resins and zeolites. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmayai, A.; Hermassi, M.; Alouani, R.; Cortina, J.L.; Amara, A.B.H. Characterization of natural Yemeni zeolites as powder sorbents for ammonium valorization from domestic waste water streams using high rate activated sludge processes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornton, A.; Pearce, P.; Parsons, S. Ammonium removal from solution using ion exchange on to MesoLite, an equilibrium study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions using microwave-treated natural Chinese zeolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 58, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, M. Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from eutrophic waters using natural calcium-rich attapulgite-based versatile adsorbent. Desalination 2014, 351, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Assabri, A.M.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, C. The investigation into the ammonium removal performance of Yemeni natural zeolite: Modification, ion exchange mechanism, and thermodynamics. Powder Technol. 2014, 258, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Armijos, C.; Cortina, J.L. Simultaneous phosphate and ammonium removal from aqueous solution by a hydrated aluminum oxide modified natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xing, Z. Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen in low temperature domestic wastewater by modification bentonite. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavi, G.; Talebi, S.; Farrokhi, M.; Sabouti, R.M. The investigation of mechanism, kinetic and isotherm of ammonia and humic acid co-adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Cabezas, M.; Sanchez-Arévalo, C.M.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Vincent-Vela, M.C.; Álvarez-Blanco, S. Recovery of phenolic compounds from olive oil washing wastewater by adsorption/desorption process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing ammonium from water and wastewater using cost-effective adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Ho, Y.; Xie, S.; Tang, X. Mechanism of the Adsorption of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solution by a Chinese Natural Zeolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3485–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; Winnett, A.; Thompson, T.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Equilibrium studies of ammonium exchange with Australian natural zeolites. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Circular economy-driven ammonium recovery from municipal wastewater: State of the art, challenges and solutions forward. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Ni, J. Improving the ammonium ion uptake onto natural zeolite by using an integrated modification process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Q.-L.; Dong, Y.-B.; He, Y.-H.; Wang, L. Physicochemical properties and mechanism study of clinoptilolite modified by NaOH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 218, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; He, Y. Anion Effect and Mechanism of Sodium Modified Clinoptilolite for Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, T.; Xu, L.; Lee, S.S. Ammonium removal using a calcined natural zeolite modified with sodium nitrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, K.; Xia, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhang, M.; An, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z. Up-concentration of nitrogen from domestic wastewater: A sustainable strategy from removal to recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, N.P.; Pliankarom, S.; Hilal, N. Removal of NH4+ ion from NH4Cl solution using clinoptilolite: An equilibrium ion exchange study on the removal of NH4+ ion from aqueous effluent using clinoptilolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 3639–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, G.; Huang, H.; Tian, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Facile preparation of polyethylenimine-tannins coated SiO2 hybrid materials for Cu2+ removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by natural Iranian zeolite in the presence of organic acids, cations and anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Pang, R.; Han, C.; Ding, L. Simultaneous removal of nutrients from simulated swine wastewater by adsorption of modified zeolite combined with struvite crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherley, L.; Miladinovic, N. Comparison of the ion exchange uptake of ammonium ion onto New Zealand clinoptilolite and mordenite. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Lebedynets, M.; Terzyk, A.P.; Kowalczyk, P.; Namieśnik, J.; Buszewski, B. Ammonium sorption from aqueous solutions by the natural zeolite Transcarpathian clinoptilolite studied under dynamic conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Hermassi, M.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Recovery of ammonium and phosphate from treated urban wastewater by using potassium clinoptilolite impregnated hydrated metal oxides as N-P-K fertilizer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3519–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Simultaneous nutrients (N,P) removal by using a hybrid inorganic sorbent impregnated with hydrated manganese oxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.; Weatherley, L. Ammonia removal from wastewater by ion exchange in the presence of organic contaminants. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, M.; Duta, A.; Teodosiu, C.; Draghici, C. Thermodynamic and kinetic study on ammonium removal from a synthetic water solution using ion exchange resin. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Influent | Deionized Water | Tap Water | AnMBR Permeate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+(mg Ca2+/L) | N.D. | 116 | 119 |
| Mg2+ (mg Mg2+/L) | N.D. | 29.7 | 32.3 |
| Na+ (mg Na+/L) | 0.16 | 287 | 109 |
| K+ (mg K+/L) | N.D. | 12.1 | 14.4 |
| NH4+ (mg NH4+-N/L) | N.D. | N.D. | 28.8 |
| Cl− (mg Cl−/L) | 2.2 | 122.8 | 194 |
| NO3− (mg NO3−-N/L) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| PO43− (mg PO43−-P/L) | N.D. | N.D. | 3.3 |
| mg COD/L | N.D. | N.D. | 68.2 |
| mg BOD/L | N.D. | N.D. | 19.5 |
| pH | 7.6 | 7.3 | 7.2 |
| K | qeth | qexp | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | N-Z | 0.0105 | 1.67 | 2.68 | 1.11 |
| Purolite SSTC60 | 0.1086 | 1.51 | 1.925 | 0.89 | |
| PSO | N-Z | 0.0149 | 2.80 | 2.68 | 0.11 |
| Purolite SSTC60 | 0.1559 | 1.93 | 1.92 | 0.07 |
| Particle Size (µm) | qe (mg N-NH4/g) |
|---|---|
| 500–1000 | 2.86 |
| 600–1800 | 2.69 |
| 1000–2500 | 2.57 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | qmax | RMSE | Kf | 1/n | RMSE | |
| Distilled water N-Z | 0.037 | 6.56 | 0.058 | 0.396 | 0.629 | 0.195 |
| Distilled water Na-Z | 0.033 | 9.44 | 0.078 | 0.459 | 0.682 | 0.268 |
| qe (mg/g) | |
|---|---|
| Distilled water N-Z | 3.42 |
| Distilled water Na-Z | 4.66 |
| Tap water Na-Z | 3.63 |
| Tap water + PO4 Na-Z | 3.66 |
| Tap water + methanol Na-Z | 4.53 |
| Tap water + glucose Na-Z | 4.59 |
| AnMBR permeate | 4.06 |
| Adsorbent | Influent | Maximum Ammonium Concentration (mg NH4-N/L) | Adsorption Capacity (mg NH4-N/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite-Na | Synthetic | 70 | 9.44 | This study |
| Clinoptilolite-Na | AnMBR permeate | 70 | 7.44 | This study |
| Bentonite | Synthetic | 311 | 6.72 | [24] |
| Bentonite-Na | Synthetic | 311 | 10.40 | [24] |
| Purolite C150H | Synthetic | 150 | 28.23 | [40] |
| Clinoptilolite | Synthetic | 5000 | 51.8 | [12] |
| Clinoptilolite-Na | Real wastewater | 22.7 | 1.2 | [11] |
| Clinoptilolite-Na | Synthetic | 250 | 11.18 | [16] |
| Clinoptilolite-Mn | Synthetic | 5000 | 23 | [38] |
| Clinoptilolite | Synthetic | 40 | 10.39 | [33] |
| Clinoptilolite | Synthetic + Cations | 40 | 8.51 | [33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godifredo, J.; Ferrer, J.; Seco, A.; Barat, R. Zeolites for Nitrogen Recovery from the Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Permeate: Zeolite Characterization. Water 2023, 15, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061007
Godifredo J, Ferrer J, Seco A, Barat R. Zeolites for Nitrogen Recovery from the Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Permeate: Zeolite Characterization. Water. 2023; 15(6):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061007
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodifredo, Jesús, José Ferrer, Aurora Seco, and Ramón Barat. 2023. "Zeolites for Nitrogen Recovery from the Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Permeate: Zeolite Characterization" Water 15, no. 6: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061007






