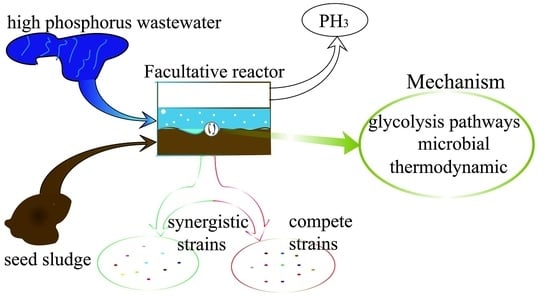
High Concentration Organic Wastewater with High Phosphorus Treatment by Facultative MBR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Quality
2.2. Seed Sludge
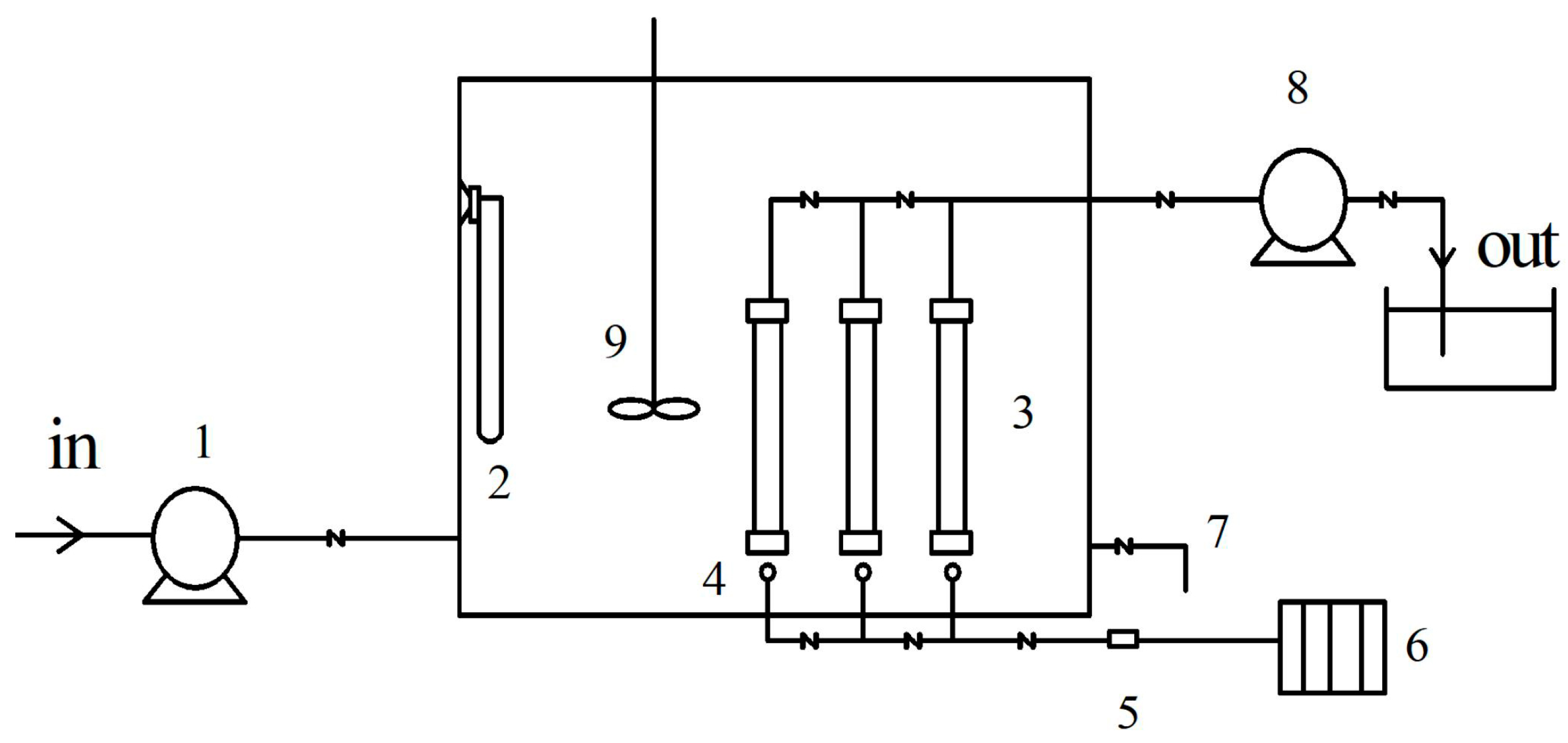
2.3. Facultative MBR
2.4. Analysis Methods
2.4.1. Phosphine Analysis
2.4.2. COD Analysis
2.4.3. P Analysis
2.4.4. Microbial Community Analysis
Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing
Microbial Analysis
Imputed Metagenomic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
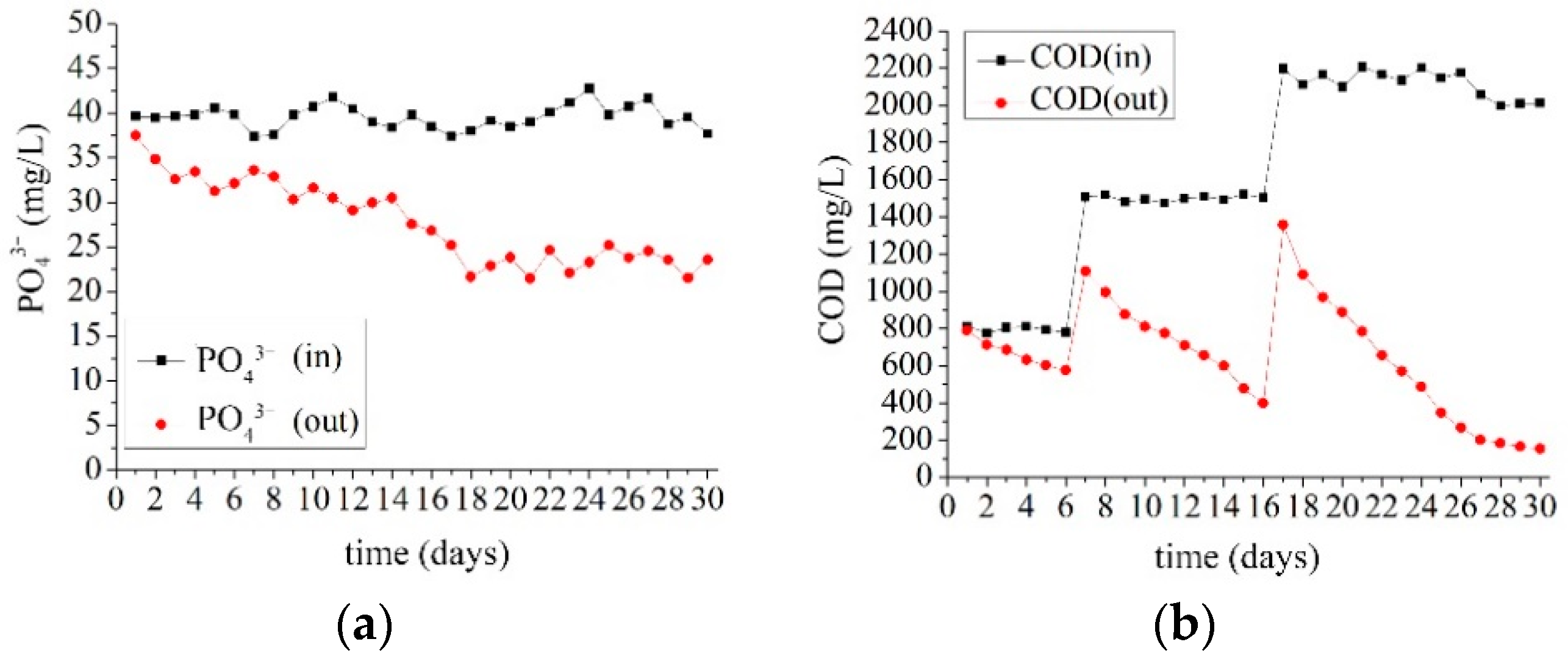
3.1. Operation Effect of Start-Up Period (Sludge Domestication Process in Facultative Phosphorus Removal System)
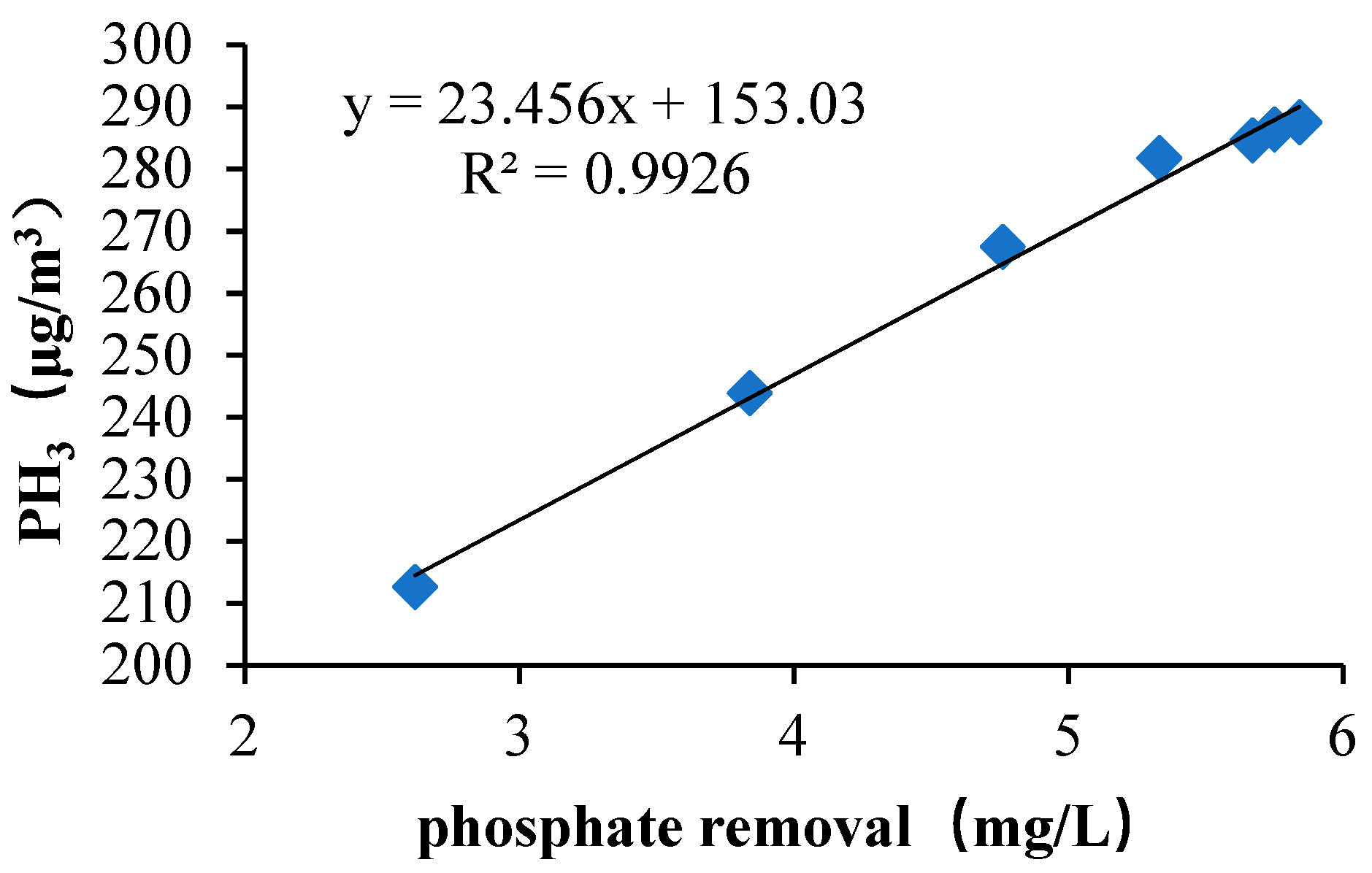
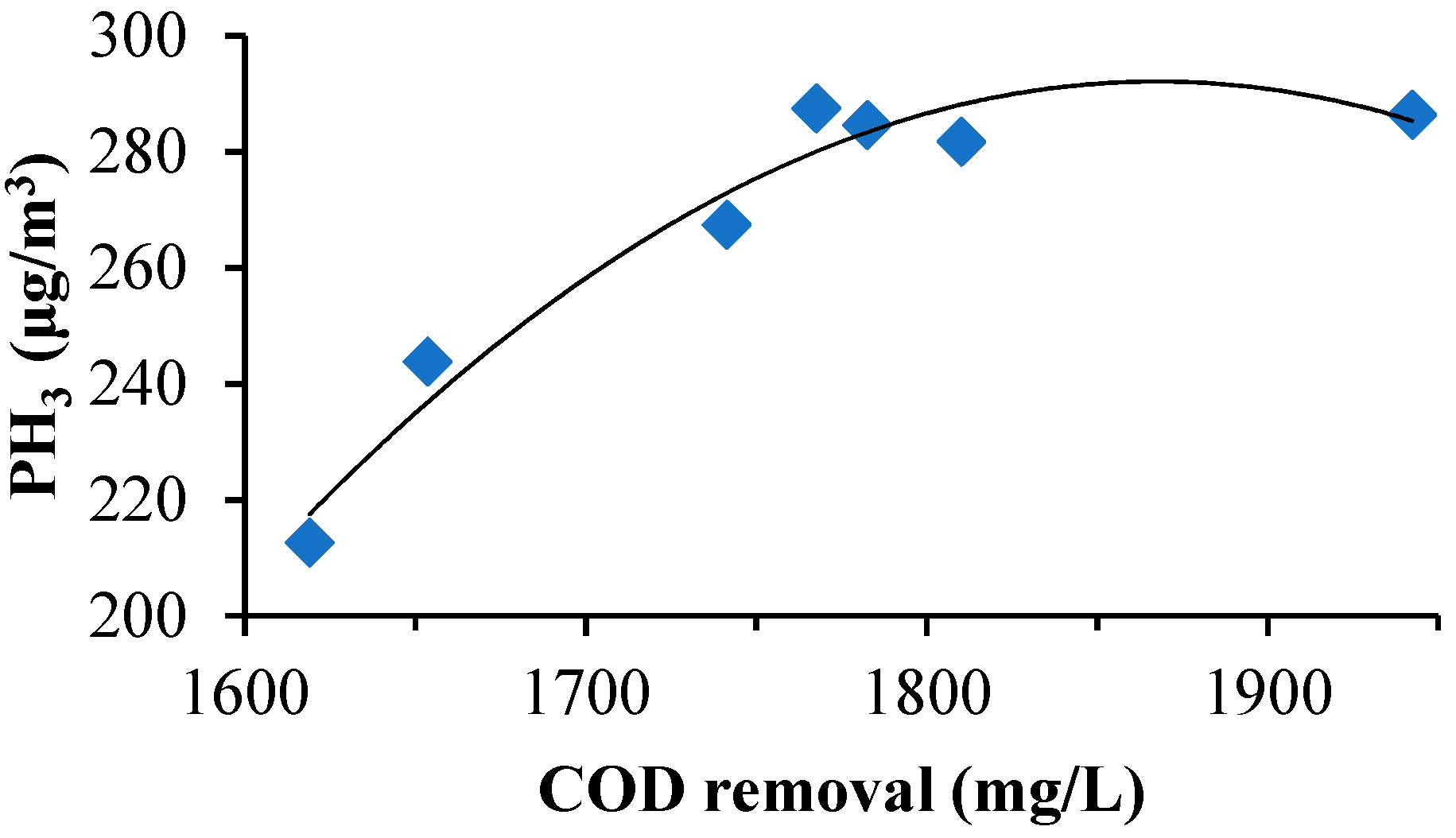
3.2. Gasification and Phosphorus Removal in the Facultative MBR
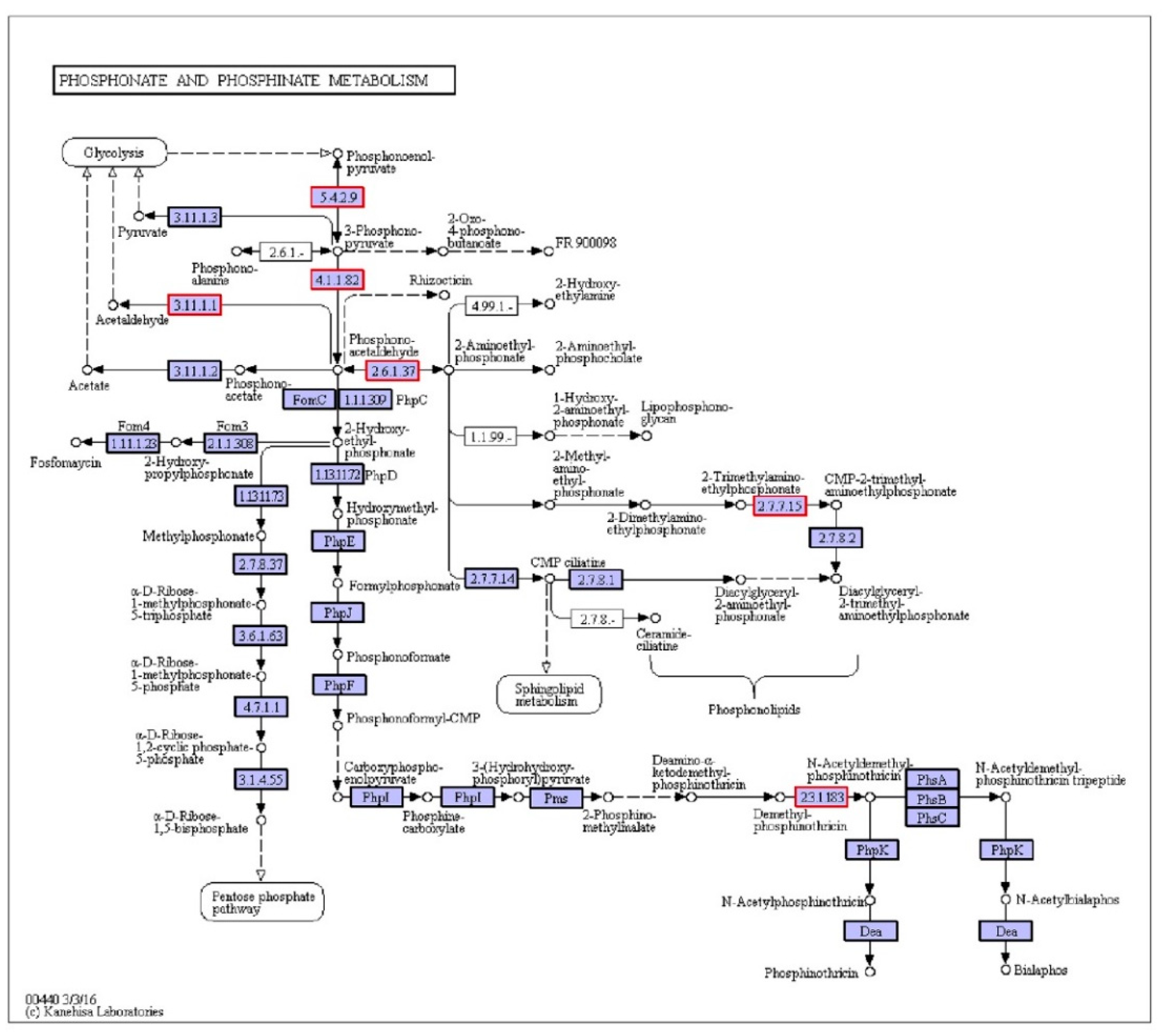
3.3. The Microbial Mechanism in the Facultative MBR
3.4. The Microbial Mechanism Combined with Thermodynamic
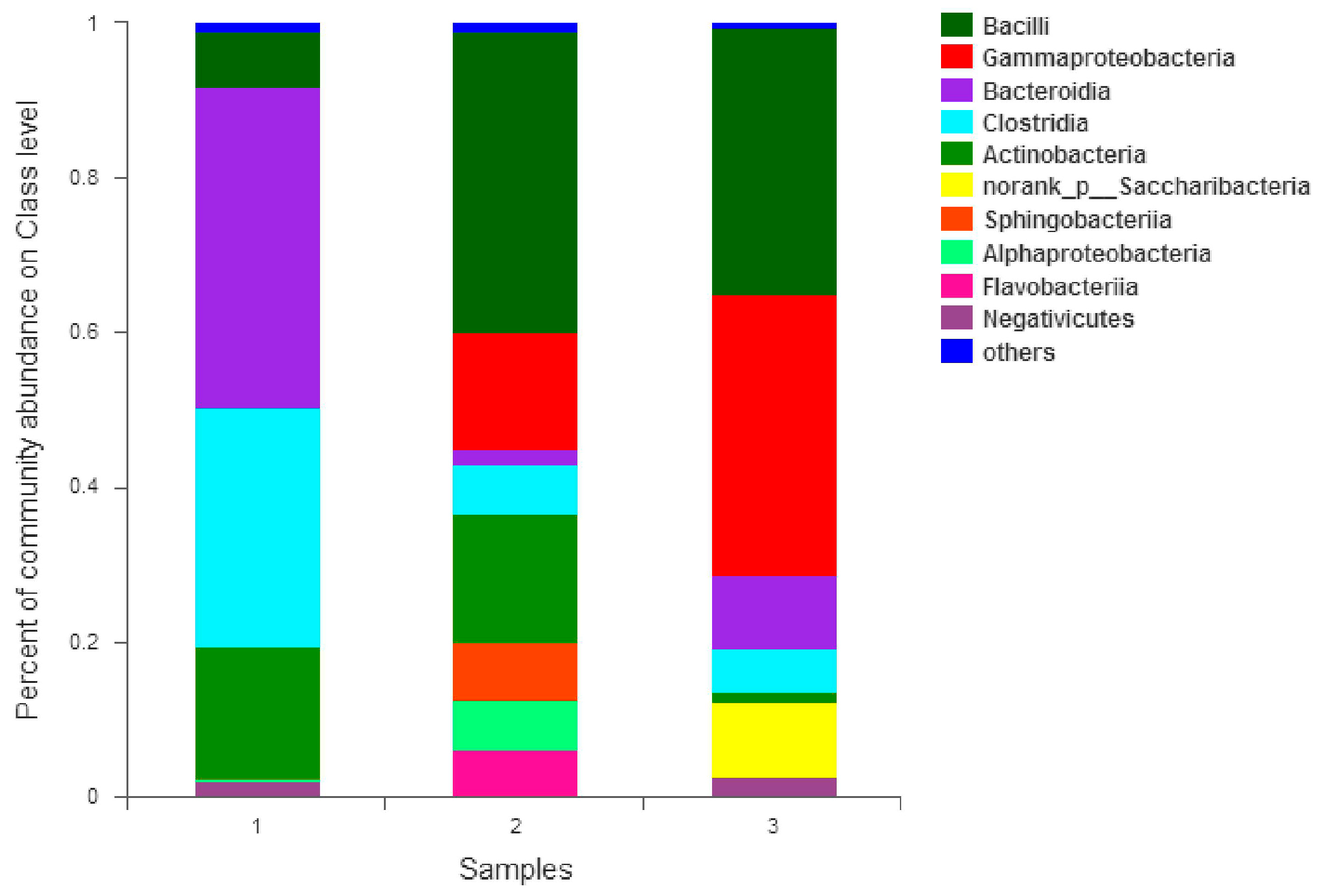
3.5. The Community of the Facultative MBR
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roels, J.; Huyghe, G.; Verstraete, W. Microbially mediated phosphine emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, L.; Geng, J. Stimulation of gaseous phosphine production from Antarctic seabird guanos and ornithogenic soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.J.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.M.; Lin, X.; Liu, M. Occurrence of matrix-bound phosphine in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Glindemann, D.; Kong, D.; Sun, L.; Geng, J.; Wang, X. Phosphine in the marine atmosphere along a hemispheric course from China to Antarctica. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M.; Zhou, S. Analysis of the characteristics of phosphine production by anaerobic digestion based on microbial community dynamics, metabolic pathways, and isolation of the phosphate-reducing strain. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, J.; Verstraete, W. Biological formation of volatile phosphorus compounds. Bioresour Technol. 2001, 79, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.O.; Morris, T.A.; Craig, P.J.; Ritchie, A.W.; Ostah, N. Phosphine generation by mixed- and monoseptic-cultures of anaerobic bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 250, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, W.; Petkowski, J.J.; Sousa-Silva, C.; Seager, S. New environmental model for thermodynamic ecology of biological phosphine production. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.M.; Lv, M.Y.; Niu, X.J.; Ma, J.L.; Song, Q. Evidence and mechanism of biological formation of phosphine from the perspective of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 146, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, P.; Ma, X.; Sun, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M. Pilot-scale multi-level biological contact oxidation system on the treatment of high concentration poultry manure wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 120, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- YU, X.; Gao, J.; LI, Y.; LI, J. Transcriptome Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana and Changes of Glucosinolates Metabolism Pathway Induced by Flg22. China Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Fang, H. Recent Progress and Application of KEGG Database in the Research of Bioinformatics. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 19, 535–539. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Jia, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, S. Differences in phosphine contents of various environment samples and the effecting factors. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2004, 24, 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, C.; Wei, W.; Rong, H.; Liu, T. Phosphine Release in Aerobic Sequencing Reactor Process and Anaerobic/Aerobic Sequencing Reactor Process. Environ. Eng. 2011, 29, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Marietou, A. Nitrate reduction in sulfate-reducing bacteria. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L. Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher, J.; Ake, F.M.; Derkaoui, M.; Zebre, A.C.; Cao, T.N.; Bouraoui, H.; Kentache, T.; Mokhtari, A.; Milohanic, E.; Joyet, P. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system: Regulation by protein phosphorylation and phosphorylation-dependent protein-protein interactions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plumbridge, J. Expression of ptsG, the gene for the major glucose PTS transporter in Escherichia coli, is repressed by MIc and induced by growth on glucose. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 29, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppenfeld, T.; Larisch, C.; Lengeler, J.W.; Jahreis, K. Glucose transporter mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with changes in substrate recognition of IICBGlc and induction behavior of the ptsG gene. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 4443–4452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roels, J.; Verstraete, W. Occurrence and origin of phosphine in landfill gas. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 327, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.A.; Lange, N.A. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]



| Nutrient | Concentration/g·L−1 | Nutrient | Concentration/g·L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.330 | CoD2·6H2O | 0.440 |
| NaMoO4·2H2O | 0.290 | NiCl2·6H2O | 0.290 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.290 | H3BO4 | 0.024 |
| MnCl12·4H2O | 0.990 |
| Source | Calculation Project | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Waste water | ||
| 30-day average influent TP | 39.58 mg/L | |
| 30-day average effluent TP | 23.71 mg/L | |
| Average phosphorus removal | 15.88 mg/L | |
| Daily influent volume | 12 L | |
| Total phosphorus removal in 30 days | 5716.8 mg | |
| Sludge | ||
| Initial sludge concentration | 7102 mg/L | |
| TP in initial sludge | 12.09 mg/g | |
| Final sludge concentration | 9811 mg/L | |
| TP in final sludge | 27.71 mg/g | |
| Reactor volume | 19 L | |
| Increased P in sludge | 3534 mg | |
| Difference | 2183 mg |
| Pathway | 1 | 2 | 3 | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ko00440 | 6471 | 17,203 | 28,541 | Phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism |
| ko02060 | 67,286 | 149,148 | 499,389 | Phosphotransferase system (PTS) |
| ko04070 | 11,283 | 23,155 | 29,763 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system |
| ko00030 | 121,303 | 191,449 | 311,269 | Pentose phosphate pathway |
| Serial Number | Reaction |
|---|---|
| (1) | |
| (2) | |
| (3) | |
| (4) | |
| (5) |
| Substance | Physical State | ΔfHmθ (kcal·mol−1) | ΔfGmθ (kcal·mol−1) | Sθ (cal·mol−1·°C−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH3 | g | 1.29 | 2.79 | 50.24 |
| H2PO4− | aq | −309.82 | −270.17 | 21.6 |
| HCO3− | aq | −165.39 | −140.26 | 21.8 |
| H+ | aq | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O | l | −68.315 | −56.687 | 16.71 |
| C3H4O3 | l | −139.7 | −110.75 | 42.9 |
| C6H12O6 | c | −304.26 | −217.6 | 50.7 |
| CO2 | g | −94.05 | −94.26 | 51.07 |
| H2 | g | 0 | 0 | 31.211 |
| CH3CHOHCOO− | l | −161.21 | −123.85 | 45.91 |
| Reaction | ΔrHmθ (kcal·mol−1) | ΔrSθ (cal·mol−1·K−1) | 25 °C, ΔrGmθ (kcal·mol−1) | 30 °C, ΔrGmθ (kcal·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | 91.78 | 165.68 | 41.72 | 41.55 |
| (2) | 257.88 | 166.02 | 204.85 | 207.55 |
| (3) | 266.96 | 303.96 | 172.79 | 174.81 |
| (4) | 42.06 | −29.36 | 49.52 | 50.96 |
| (5) | 103.94 | 42.06 | 70.69 | 91.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Alvarez, P.; Crittenden, J.C.; Sun, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Ran, Z. High Concentration Organic Wastewater with High Phosphorus Treatment by Facultative MBR. Water 2021, 13, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202902
Wang B, Liu Y, Zhang S, Zhang K, Alvarez P, Crittenden JC, Sun B, Yang L, Liu S, Ran Z. High Concentration Organic Wastewater with High Phosphorus Treatment by Facultative MBR. Water. 2021; 13(20):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202902
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bing, Yunlong Liu, Siyu Zhang, Kaihang Zhang, Pedro Alvarez, John C. Crittenden, Bing Sun, Lin Yang, Su Liu, and Zhilin Ran. 2021. "High Concentration Organic Wastewater with High Phosphorus Treatment by Facultative MBR" Water 13, no. 20: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202902
APA StyleWang, B., Liu, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, K., Alvarez, P., Crittenden, J. C., Sun, B., Yang, L., Liu, S., & Ran, Z. (2021). High Concentration Organic Wastewater with High Phosphorus Treatment by Facultative MBR. Water, 13(20), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202902