Employing Data Mining Algorithms and Mathematical Empirical Models for Predicting Wind Drift and Evaporation Losses of a Sprinkler Irrigation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Procedures for Sprinkler Tests
2.3. WDEL Mathematical Empirical Models
2.4. Details of the Data Mining Algorithms
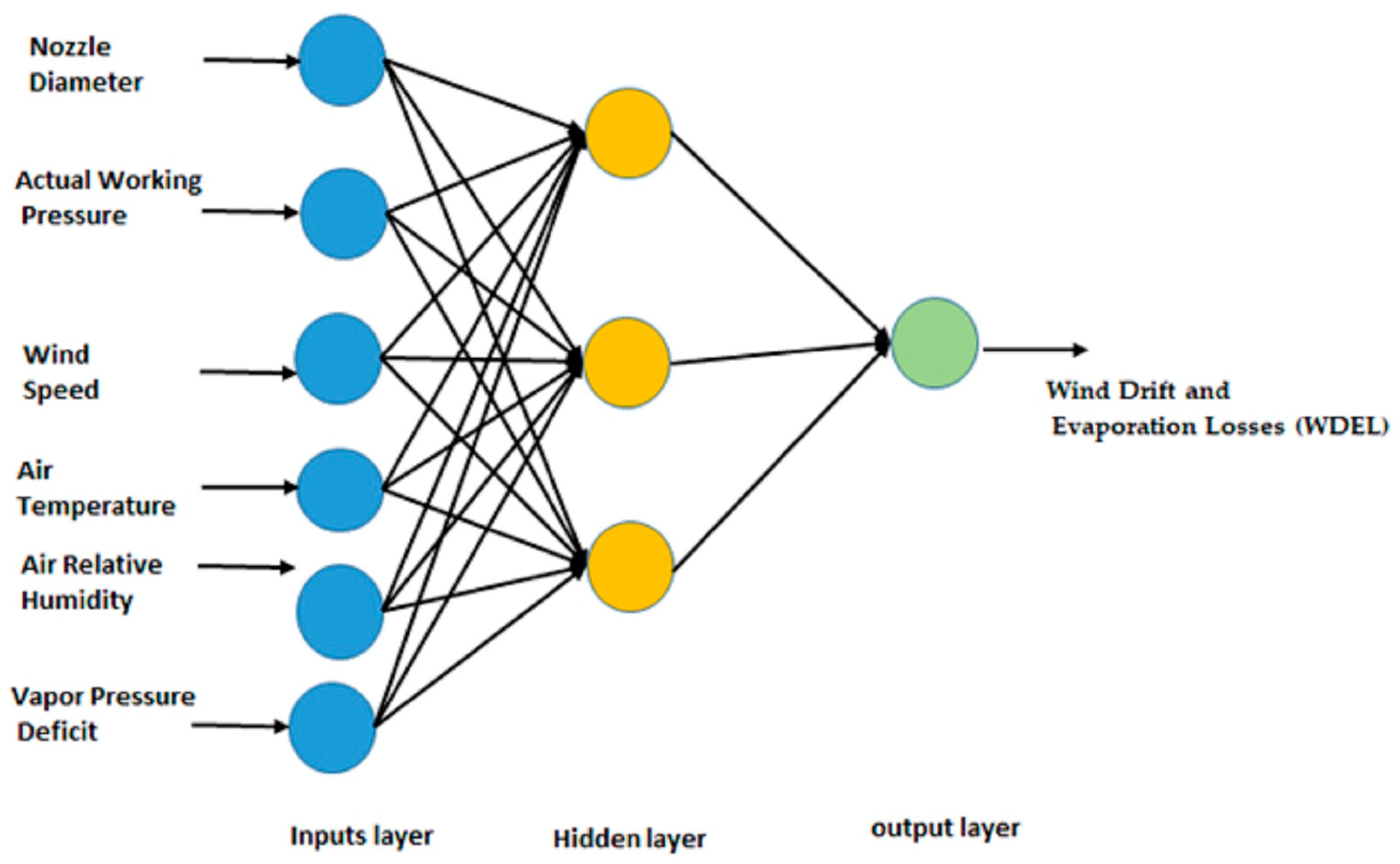
2.5. Multilayer Perceptron
2.6. REPTree
2.7. Prediction Performance of Fitted Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wind Drift and Evaporation Losses (WDEL)
3.2. Prediction of WDEL—Data Mining Models
3.3. Mathematical Empirical Models for WDEL Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatt, N.; Virparia, P.V. Survey based research for data mining techniques to forecast water demand in irrigation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Appl. 2015, 3, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Krupakar, H.; Jayakumar, A.; Dhivya, G. A Review of Intelligent Practices for Irrigation Prediction. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02893v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Su, D.; Wang, Y. Dynamics of water vapor content around isolated sprinklers: Description and validation of model. Water 2017, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Rana, T.; Dassanayake, D.; Abbas, A.; Blackwell, J.; Akbar, S.; Gabriel, H.F. Spatially distributed assessment of channel seepage using geophysics and artificial intelligence. Irrig. Drain. 2009, 58, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Islam, M.Z.; Hafeez, M. Irrigation water requirement prediction through various data mining techniques applied on a carefully pre-processed dataset. J. Res. Pract. Inf. Technol. 2011, 43, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- IWMI. Water for a food secure world. In International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Strategic Plan, 2009–2013; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; Available online: https://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/About_IWMI/PDF/Strategic_Plan_2009-2013.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K. Water footprints of nations: Water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishaw, D.; Olumana, M. Evaluating the effect of operating pressure and riser height on irrigation water application under different wind conditions in Ethiopia. Asia Pac. J. Energy Environ. 2015, 5, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.K.; Sriranjan, R.; Klassen, G. Spray evaporation losses from sprinkler irrigation system. Can. Agric. Eng. 2000, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yacoubi, S.; Zayani, K.; Slatni, A.; Playán, E. Assessing sprinkler irrigation performance using field evaluations at the Medjerda Lower Valley of Tunisia. Engineering 2012, 4, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Ortega, J.F.; Montero, J.; De Juan, J.A. Modeling evaporation and drift losses in irrigation with medium size impact sprinklers under semi-arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, G.; Yan, H. Development and validation of a modified model to simulate the sprinkler water distribution. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 111, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, E.M.; Sabreen, K.P. Investigation of riser height and operating pressure on sprinkler irrigation performance under different wind condition. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2016, 9, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, J.; Smith, R.J.; Hancock, N.H.; Foley, J.P. Evaporation and sapflow dynamics during sprinkler irrigation of cotton. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stambouli, T.; Martinez-Cob, A.; Faci, J.M.; Howell, T.; Zapata, N. Sprinkler evaporation losses in alfalfa during solid-set sprinkler irrigation in semiarid areas. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, J.; Bliesner, R.D. Sprinkler and Trickle Irrigation; Van Nestrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmat, A.V.; Boroomand, N.S.; Sakhaeerad, H.; Bavi, A. Evaporation and wind drift losses for two types of sprinklers with one and three nozzles in solid set systems in Ahwaz climate conditions. Iran. J. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 6, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Playán, E.; Salvador, R.; Faci, J.M.; Zapata, N.; Martinez-Cob, A.; Sánchez, I. Day and night wind drift and evaporation losses in sprinkler solid-sets and moving laterals. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazar, A. Evaporation and drift losses from sprinkler irrigation systems under various operating conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 1984, 8, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, W.L. Sprinkler evaporation loss equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1987, 113, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.F.; Tarjuelo, J.M.; Montero, J.; De Juan, J.A. Discharge efficiency in sprinkling irrigation: Analysis of evaporation and drift losses in semi-arid areas. Agric. Eng.Int. CIGR J. 2000, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Beskow, S.; Faria, L.C.; Colombo, A.; DeMoura, D.C.M. Modeling of evaporation and wind drift losses in medium-pressure sprinklers. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Environ. 2011, 15, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, G.S.; Bonomo, R.; De Souza, J.M. Evaporative water loss and wind drift in fixed sprinkler systems, North of the Espírito Santo. Rev. Bras. Agric. Irrig. 2013, 7, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaizy, R.; Simonet, D. Analysis of water evaporation and drift losses during irrigation in semi-arid areas of Sharjah (UAE) and Riyadh (KSA). Nat. Resour. Res. 2012, 21, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jumaily, K.; Abdul-Kader, S. Spray losses in sprinkler irrigation systems in Iraq. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Technology Conference, IWTC12, Alexandria, Egypt, 27–30 March 2008; pp. 717–727. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Calvo, I.; Roldan, J.; Lopez-Luque, R.; Gutierrez-Estrada, J.C. Demand forecasting for irrigation water distribution systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaiya, F.; Adeyemo, A.B. Application of data mining techniques in weather prediction and climate change studies. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2012, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabena, P.H.; Stadler, R.; Verhees, J.; Zanasi, A. Discovering Data Mining: From Concept to Implementation; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mirhashemi, S.H.; Tabatabayi, M. Evaluation ten models of Weka software to predict the potential evapotranspiration month for the next month in the synoptic weather station Arak. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2015, 8, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, S.; Guimarães, A.M.; Proença, C.A.; Da Rocha, J.C.F.; Caires, E.F. Data mining algorithms for prediction of soil organic matter and clay based on Vis-NIR Spectroscopy. Int. J. Agric. For. 2014, 4, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, O. Monthly rainfall estimation using data-mining process. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2012, 2012, 698071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, O. Estimating daily pan evaporation using data mining process. Sci. Iran. A 2013, 20, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Keskin, M.E.; Terzi, O.; Kucuksille, E.U. Data mining process for integrated evaporation model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, B.; Sattari, M.T.; Samadianfard, S. Performance evaluation of ANNs and an M5 model tree in Sattarkhan Reservoir inflow prediction. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 23, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, S.; Wang, Y.M.; Kerh, T. Artificial neural network for modeling reference evapotranspiration complex process in Sudano-Sahelian zone. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, M.M. Artificial neural network modeling for estimation of reference evapotranspiration at Nagpur. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Merriam, J.L.; Keller, J. Farm Irrigation System Evaluation: A Guide for Management; Department of Agricultural and Irrigation Engineering, Utah State University: Logan, Utah, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- ASAE. ASAE S398.1; Procedure for Sprinkler Testing and Performance Reporting. ASAE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 1 January 2001; pp. 880–882.
- Playán, E.; Zapata, N.; Faci, J.M.; Tolosa, D.; Lacueva, J.L.; Pelegrín, J.; Salvador, R.; Sanchez, I.; Lafita, A. Assessing sprinkler irrigation uniformity using a ballistic simulation model. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 84, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouazaa, S.; Burguete, J.; Zapata, N. Solid-set sprinklers irrigation of field boundaries: Experiments and modeling. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.S. Sprinkler performance as function of nozzle geometrical parameters. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 1996, 122, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Kawano, H. Sprinkler performance as affected by nozzle inner contraction angle. Irrig. Sci. 1998, 18, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Montero, J.; Valiente, M.; Honrubia, F.T.; Ortiz, J. Irrigation uniformity with medium size sprinklers part I: Characterization of water distribution in no-wind conditions. Trans. ASAE 1999, 42, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechmi, F.; Playán, E.; Cavero, J.; Faci, J.M.; Martanez-Cob, A. Wind effects on solid set sprinkler irrigation depth and yield of maize (Zea Mays). Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, I.; Zapata, N.; Faci, J.M. Combined effect of technical, meteorological and agronomical factors on solid-set sprinkler irrigation: I. Irrigation performance and soil water recharge in alfalfa and maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, J. On the computation of saturated vapour pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1967, 6, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques with Java Implementations; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.; Hinton, G.; Williams, R. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation, Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructures of Cognition; MIT Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Conceição, M.A.F.; Coelho, R.D. Simulating wind effect on microsprinkler water distribution. Sci. Agric. 2003, 60, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, P.A.; Sentelhas, P.C. Evaluation of the performance of different methods of estimation of potential evapotranspiration in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Braz. J. Agrometeorol. 1997, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Ghobar, M. Evaporation and drift losses from sprinkler irrigation systems under hot and dry conditions. J. King Saud Univ. 1993, 5, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jajoo, N.M. Improved equations for estimating spray losses of fixed sprinkler irrigation systems in Iraq. Al-Rafidain Eng. 2009, 17, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
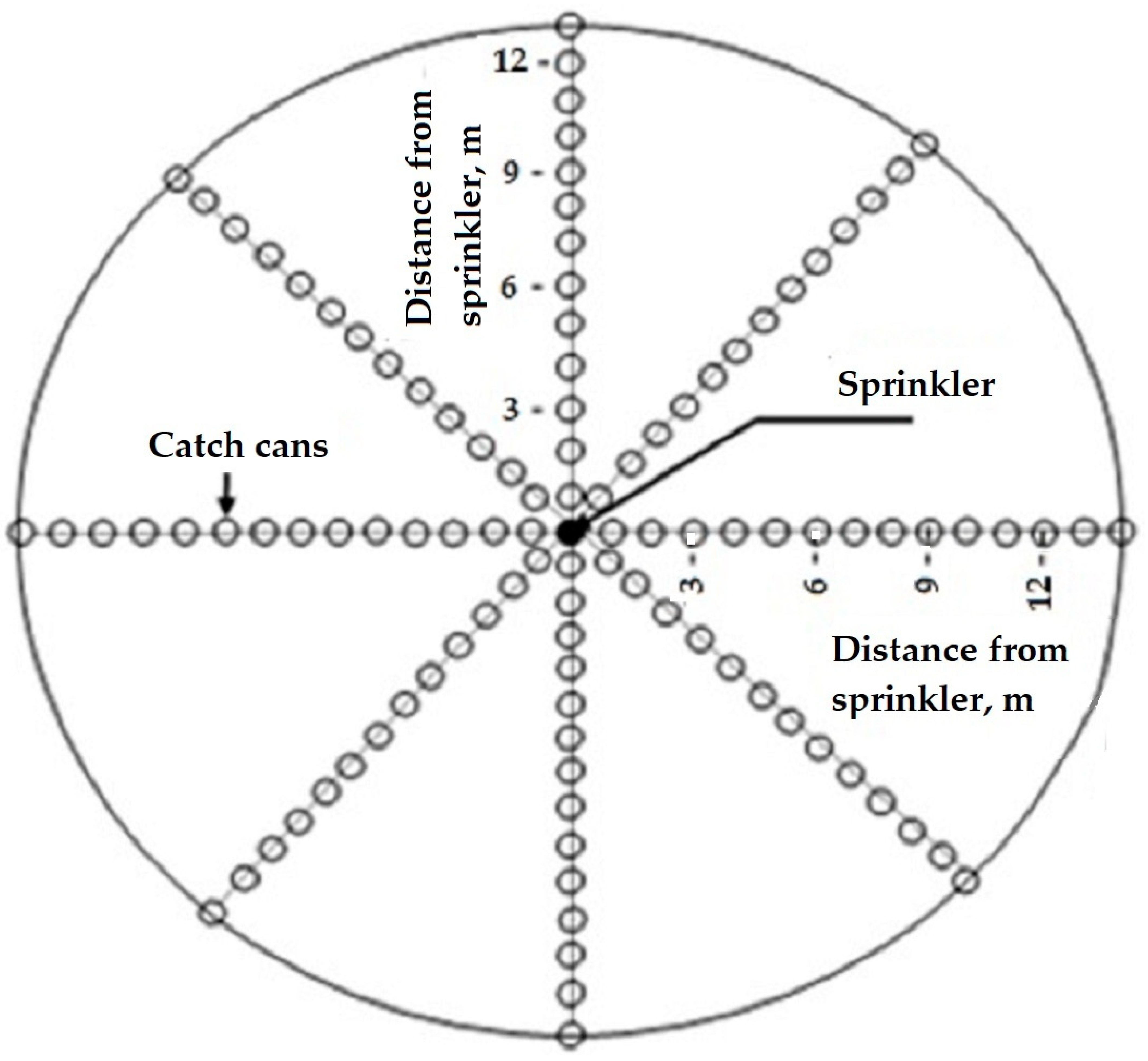
| Sprinkler Throw Distance (m) | Maximum Collector Distance between Centers (m) |
|---|---|
| 0.3–3 | 0.30 |
| 3–6 | 0.60 |
| 6–12 | 0.75 |
| >12 | 1.50 |
| Model | Empirical Equation |
|---|---|
| Trimmer [20] | |
| Yazar [19] | |
| Tarjuelo et al. [11] | |
| Playán et al. [18] |
| Nozzle Diameter | Actual Working Pressure | Wind Speed | Air Temperature | Air Relative Humidity | Vapor Pressure Deficit | WDEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (kPa) | (m/s) | (°C) | (%) | (kPa) | (%) |
| 4 | 188.1 | 0.82 | 14.93 | 57.11 | 0.73 | 11.60 |
| 4 | 286.6 | 1.07 | 19.12 | 47.89 | 1.16 | 14.85 |
| 4 | 379.4 | 1.27 | 21.59 | 40.56 | 1.54 | 18.49 |
| Overall mean | 1.05 | 18.55 | 48.52 | 1.14 | 14.98 | |
| 4.5 | 191.3 | 0.92 | 15.17 | 59.44 | 0.70 | 11.17 |
| 4.5 | 287.5 | 1.87 | 17.97 | 51.33 | 1.02 | 14.17 |
| 4.5 | 384.5 | 2.85 | 24.89 | 38.44 | 1.95 | 17.94 |
| Overall mean | 1.88 | 19.34 | 49.74 | 1.22 | 14.43 | |
| 5 | 190.4 | 0.87 | 10.83 | 59.22 | 0.53 | 10.61 |
| 5 | 287.3 | 1.82 | 14.73 | 49.11 | 0.86 | 13.68 |
| 5 | 379.8 | 2.58 | 16.71 | 35.67 | 1.23 | 16.25 |
| Overall mean | 1.76 | 14.09 | 48.00 | 0.87 | 13.52 | |
| The Tested Model | RMSE (%) | MAE (%) |
|---|---|---|
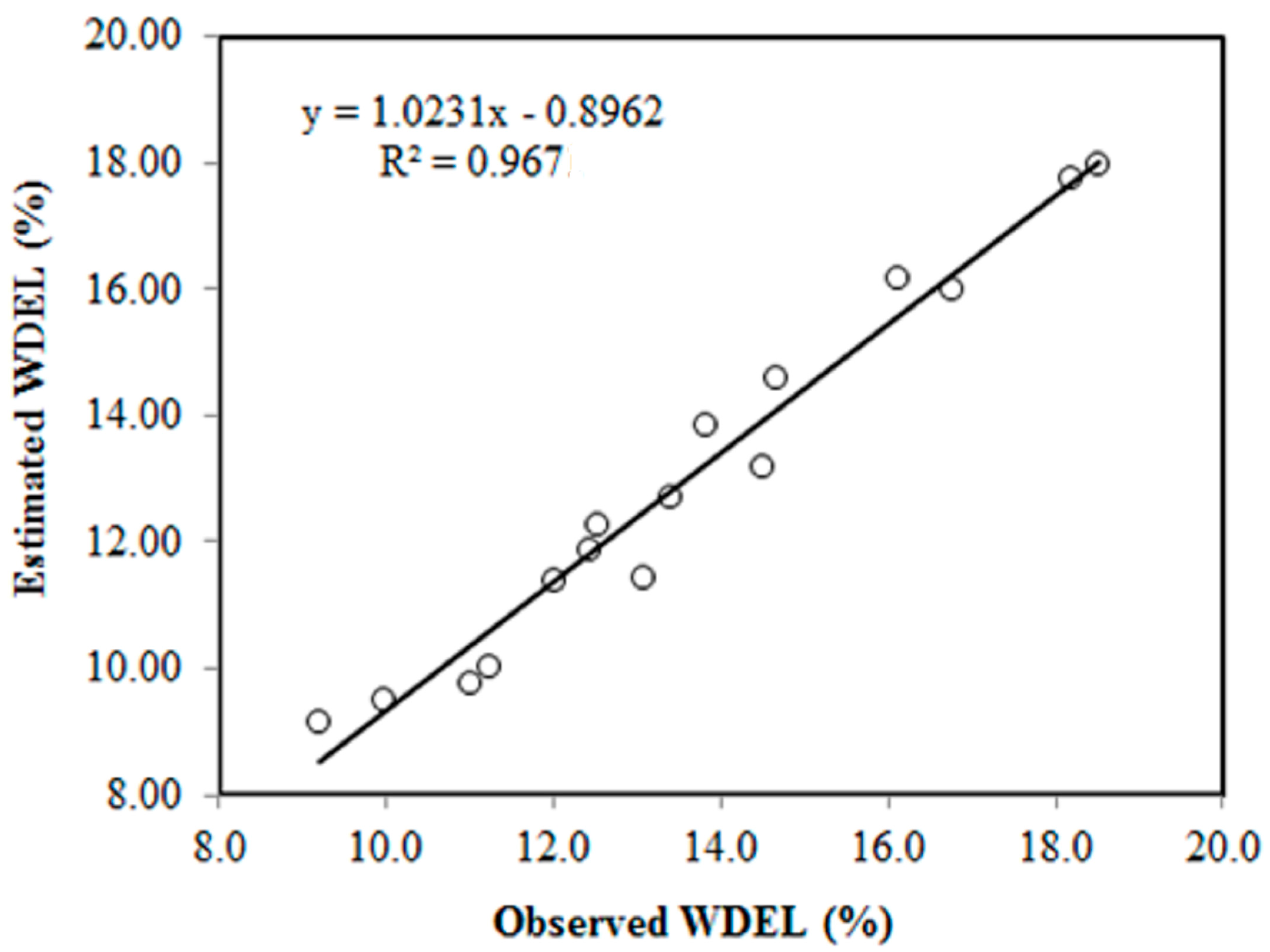
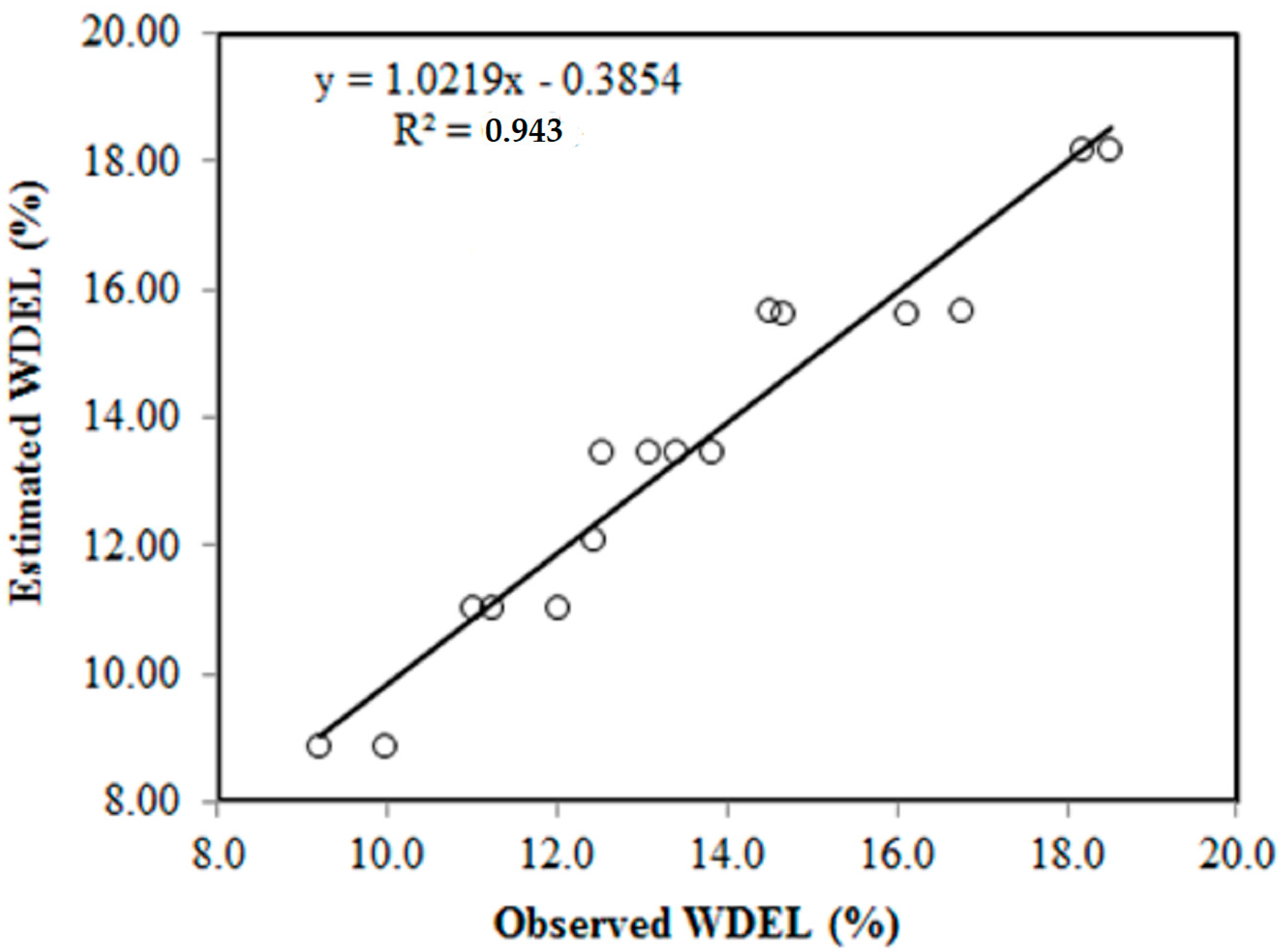
| ANN | 0.771 | 0.600 |
| REPTree | 0.679 | 0.544 |
| D | P | W | T | RH | Observed WDEL | Predicted WDEL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trimmer [20] | Yazar [19] | Tarjuelo et al. [11] | Playán et al. [18] | REPTree | ANN | |||||||
| (mm) | (kPa) | (m/s) | (°C) | (%) | (kPa) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| 4.5 | 193 | 1.20 | 15.40 | 56 | 0.77 | 12.44 | 1.99 | 3.75 | 8.84 | 13.43 | 12.104 | 11.91 |
| 4.5 | 288 | 1.98 | 19.11 | 49 | 1.13 | 14.65 | 3.99 | 8.16 | 11.53 | 15.64 | 15.638 | 14.63 |
| 4.5 | 195 | 0.47 | 14.30 | 64 | 0.59 | 9.20 | 1.35 | 2.49 | 7.42 | 10.97 | 8.885 | 9.18 |
| 5.0 | 272 | 1.43 | 14.63 | 51 | 0.82 | 12.51 | 2.43 | 5.23 | 9.78 | 14.78 | 13.473 | 12.30 |
| 4.5 | 194 | 1.18 | 14.50 | 58 | 0.69 | 12.00 | 1.90 | 3.49 | 8.50 | 12.89 | 11.037 | 11.42 |
| 4.0 | 186 | 0.80 | 16.90 | 56 | 0.85 | 13.08 | 2.17 | 3.41 | 8.77 | 13.26 | 13.473 | 11.45 |
| 5.0 | 388 | 2.57 | 16.81 | 36 | 1.23 | 16.76 | 5.57 | 12.10 | 13.06 | 18.75 | 15.683 | 16.03 |
| 5.0 | 189 | 0.93 | 10.51 | 60 | 0.51 | 11.01 | 1.26 | 2.47 | 7.37 | 12.24 | 11.037 | 9.80 |
| 4.5 | 299 | 1.89 | 17.50 | 52 | 0.96 | 13.81 | 3.77 | 7.35 | 10.92 | 14.87 | 13.473 | 13.86 |
| 5.0 | 195 | 0.95 | 11.24 | 59 | 0.55 | 11.23 | 1.33 | 2.68 | 7.63 | 12.52 | 11.037 | 10.05 |
| 4.0 | 379 | 1.30 | 22.10 | 41 | 1.57 | 18.50 | 6.18 | 9.91 | 13.00 | 16.81 | 18.204 | 17.98 |
| 4.0 | 376 | 1.28 | 20.50 | 40 | 1.45 | 18.18 | 5.86 | 9.21 | 12.59 | 16.99 | 18.204 | 17.79 |
| 4.0 | 290 | 1.02 | 19.10 | 53 | 1.04 | 13.40 | 3.59 | 5.80 | 10.42 | 14.09 | 13.473 | 12.71 |
| 4.0 | 285 | 0.87 | 19.46 | 49 | 1.15 | 14.50 | 3.53 | 5.84 | 10.65 | 14.96 | 15.683 | 13.20 |
| 4.5 | 190 | 0.52 | 14.70 | 62 | 0.64 | 9.96 | 1.40 | 2.62 | 7.65 | 11.56 | 8.885 | 9.52 |
| 5.0 | 379 | 2.43 | 16.32 | 34 | 1.23 | 16.10 | 5.26 | 11.35 | 12.87 | 18.92 | 15.638 | 16.19 |
| Average | 13.58 | 3.22 | 5.99 | 10.06 | 14.54 | 13.50 | 13.00 | |||||
| Minimum | 9.20 | 1.26 | 2.47 | 7.37 | 10.97 | 8.89 | 9.18 | |||||
| Maximum | 18.50 | 6.18 | 12.10 | 13.06 | 18.92 | 18.20 | 17.98 | |||||
| Standard deviation | 2.75 | 1.75 | 3.30 | 2.11 | 2.40 | 2.89 | 2.86 | |||||
| Prediction Method | Index of Agreement | Correlation Coefficient | Confidence Index | Performance Based on Confidence Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The model described by Trimmer [20] | 0.325 | 0.966 | 0.314 | Terrible |
| The model described by Yazar [19] | 0.437 | 0.898 | 0.393 | Terrible |
| The model described by the model described by Tarjuelo et al. [11] | 0.650 | 0.949 | 0.617 | Average |
| Playán et al. [18] | 0.913 | 0.908 | 0.829 | Very good |
| REPTree model | 0.984 | 0.971 | 0.956 | Optimal |
| ANN model | 0.980 | 0.983 | 0.964 | Optimal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Dosary, N.M.N.; Maray, S.A.; Al-Hamed, S.A.; Aboukarima, A.M. Employing Data Mining Algorithms and Mathematical Empirical Models for Predicting Wind Drift and Evaporation Losses of a Sprinkler Irrigation Method. Water 2023, 15, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050922
Al-Dosary NMN, Maray SA, Al-Hamed SA, Aboukarima AM. Employing Data Mining Algorithms and Mathematical Empirical Models for Predicting Wind Drift and Evaporation Losses of a Sprinkler Irrigation Method. Water. 2023; 15(5):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050922
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Dosary, Naji Mordi Naji, Samy A. Maray, Saad A. Al-Hamed, and Abdulwahed M. Aboukarima. 2023. "Employing Data Mining Algorithms and Mathematical Empirical Models for Predicting Wind Drift and Evaporation Losses of a Sprinkler Irrigation Method" Water 15, no. 5: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050922







