Abstract
The aim of the present study was to provide new knowledge regarding the effect of non-expansive inert material addition on anionic pollutant removal efficiency in Fe0-H2O system. Non-disturbed batch experiments and continuous-flow-through column tests were conducted using CrVI as a redox–active contaminant in three different systems: “Fe0 + sand”, “Fe0 only” and ”sand only”. Both experimental procedures have the advantage that formation of (hydr)oxide layers on Fe0 is not altered, which makes them appropriate proxies for real Fe0-based filter technologies. Batch experiments carried out at pH 6.5 showed a slight improvement of CrVI removal in a 20% Fe0 system, compared to 50, 80 and 100% Fe0 systems. Column tests conducted at pH 6.5 supported results of batch experiments, revealing highest CrVI removal efficiencies for “Fe0 + sand” systems with lowest Fe0 ratio. However, the positive effect of sand co-presence decreases with increasing pH from 6.5 to 7.1. Scanning electron microscopy—energy dispersive angle X-ray spectrometry and X-ray diffraction spectroscopy employed for the characterization of Fe0 before and after experiments indicated that the higher the volumetric ratio of sand in “Fe0 + sand” system, the more intense the corrosion processes affecting the Fe0 grains. Results presented herein indicate the capacity of sand at sustaining the efficiency of CrVI removal in Fe0-H2O system. The outcomes of the present study suggest that a volumetric ratio Fe0:sand = 1:3 could assure not only the long-term permeability of Fe0-based filters, but also enhanced removal efficiency of CrVI from contaminated water.
1. Introduction
Even though metallic iron (Fe0)-based water treatment technology was already applied for water potabilization in Europe around year 1890 at the water works of Antwerp (Belgium) [1], there has only been a growing interest in using Fe0 in remediation of contaminated water over the past three decades. Due to increasing industrial activities during the 20th century, water pollution has become a global issue of concern. Fe0 has been extensively applied, especially as reactive material in permeable reactive barriers (PRB), as a viable and cost-effective alternative for the conventional pump-and-treat technology, due to its low cost, widely availability and environmental friendliness; in addition, Fe0 is also very versatile and can be applied for the removal of various contaminants because it can act as adsorbent, reductant, as well as a generator of adsorbing, reducing and coagulation agents [2,3,4,5]. Both laboratory experiments and full-scale applications have warned that practical application (i.e., long-term operation) of Fe0-based filter treatment systems is impacted by the loss of filter hydraulic conductivity (caused by the expansive nature of iron corrosion products, mineral precipitation and gas formation that progressively fill the pore space within an Fe0-based filter) and loss of Fe0 efficiency caused by metal surface passivation, leading eventually to an incomplete utilization of Fe0 [6,7,8,9,10].
Theoretical studies published over the last several years concluded that mixing Fe0 with non-expansive additives (e.g., sand, pumice, etc.) could be a facile and efficient solution for sustainable Fe0-based treatment systems [11,12,13]. By amending the reactive Fe0 with sand, several positive effects could be achieved, including (1) delayed filter clogging, (2) better pH control, (3) increased adsorption surface for contaminants, and (4) saving costs of water treatment systems [14,15,16]. However, a problem that may arise from ”dilution” of Fe0 with sand is that, while having an undoubtful positive role on maintaining the long-term permeability of Fe0-based filters (i.e., enhancing the long-term sustainability), it may have a negative effect on pollutant removal percentages; to put it another way, while the “Fe0 only” filter can remove high percentages of pollutant (e.g., 100%), but only over a short time period (due to rapid clogging), the “Fe0 + sand” filter may have lower removal percentages (e.g., only 90%), but, instead, operates much longer (due to improved permeability). This behavior was observed at the very first Fe0-based PRB technology field demonstration, operated between 1991–1996 at Borden, Ontario, Canada [17], where constant removal efficiencies of only 90% and 86% were noticed over the duration of the test for trichloroethene and tetrachloroethene, respectively; not reaching 100% removal percentages was ascribed to the low mass ratio Fe0:sand in the reactive wall (22:78). However, it was presumed that the observed removal efficiency, although not being 100%, could have been maintained for at least another five years [16]. These results were later confirmed by continuous-flow experimental tests for CuII, NiII and ZnII removal using columns filled with reactive mixtures comprising a fixed amount of Fe0 and various amounts of pumice in order to give 0–100% volumetric proportions of Fe0 [18]; the outcomes of this study showed that: (1) pollutant removal percentages were higher in the “Fe0-only” system, but only for a short duration because of the rapid clogging (after 17 days), and (2) the “Fe0 + sand” system was more sustainable than the “Fe0-only” system, with highest operational duration (90 days) observed for the lowest Fe0 proportion (10%). Therefore, even though it showed slightly lower removal percentages than the “Fe0-only” system, the “Fe0 + sand” system was the most efficient with respect to the total amount of metal removed per gram of Fe0 [18]. Similar outcomes were reported in another study [8] investigating removal of methylene blue (MB) via column experiments in “Fe0 only” system, and “Fe0 + sand” system with 30% (volume) Fe0; higher removal percentages and reduced operating time were observed for the “Fe0 only” system compared with higher operational duration and higher total amount of metal removed for the “Fe0 + sand” system [8]. Therefore, it is clear that a proper design of Fe0-based filters implies the careful consideration of a balance between acceptable removal efficiency and acceptable long-term hydraulic performance [8,16].
It must be noted here, however, that the Fe0-H2O system is an ion-selective system with the highest affinity towards negatively charged pollutants [4,19]. The aforementioned studies have dealt with neutral [17] or cationic contaminants [8,18] with low affinity for the positively-charged (at circumneutral pH) iron (hydr)oxides covering the surface of Fe0. Thus, the question that arises is: what could be the influence of Fe0 “dilution” with sand on removal efficiency of anionic pollutants, and, particularly, of reducible anionic contaminants, in an Fe0-H2O system? To obtain a reliable answer, only data provided by relevant experimental procedures that may be transferred to real Fe0-based filtration systems should be considered. It is well-known that in real Fe0-based filtration systems (e.g., PRBs) no intense mixing of the contaminated water with Fe0 exists; thus, (hydr)oxide film formation at the surface of Fe0 occurs with no disturbance [20]. However, most previous works studying contaminant removal in Fe0-H2O systems were conducted under intensive mixing conditions (i.e., via well-mixed batch experiments), which result in mechanical abrasion of the surfaces and disturbance of (hydr)oxide film formation at the surface of Fe0 [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]; therefore, they will not be taken into further consideration in the present study, since they may report overestimated removal efficiencies of contaminants. As suggested by recent works [41,42], only non-disturbed (or very slowly) shaken batch experiments are appropriate for the investigation of contaminant removal in Fe0-H2O systems; unfortunately, as far as we know, there are no studies regarding anionic contaminant removal in Fe0-H2O systems conducted under such experimental conditions.
Even though well-designed batch experiments (i.e., non-disturbed or slowly shaken) can be useful in fine-tuning some relevant aspects at the laboratory scale, the most effective method of investigating the efficacy of Fe0 filtration systems, which delivers experimental data with the best transferability to real water treatment systems (e.g., PRBs, SONO filters), is via flow-through column experiments [14,43,44,45]. To the best of our knowledge, to date, there are only a few such studies which may be considered for finding an answer to the aforementioned question. From the work of Westerhoff and James [43], it seems that a column packed with a mixture of 50% Fe0 and 50% sand (w:w) (feed solution: 5–16 mg N/L; bed contact time: 1.5 h) was at least equally effective in removing NO3− as a column with 100% Fe0 (feed solution: 2–5 mg N/L; bed contact time: 1.1 h); however, this conclusion is questionable since experimental conditions were not equal for the two columns. The study of Kaplan and Gilmore [46] specifically investigated, under continuous-flow conditions, the effect of sand co-presence on kinetics of CrVI removal with Fe0, reporting that varying the Fe0 content in the column between 20 and 100% (weight) had no significant effect on the magnitude of the kobs.
Therefore, the present study is aimed at providing new knowledge regarding the effect of sand co-presence on the efficiency of anionic contaminant removal in an Fe0-H2O system. CrVI was selected as the model contaminant because, in addition to adsorption and co-precipitation which are the main mechanisms for neutral and cationic species removal in an Fe0-H2O system, it can also be removed via reduction (predominantly indirect at circumneutral pH, by dissolved/bound/adsorbed FeII) to CrIII followed by precipitation. To test the influence of sand co-presence on the efficiency of CrVI removal with Fe0, two experimental setups were employed: (1) non-disturbed batch experiments, and (2) continuous-flow-through column experiments. The extent of CrVI removal was comparatively discussed in three different systems: “Fe0 + sand”, “Fe0 only” and “sand only”; each system was characterized by the time-dependent changes of the CrVI, CrIII, FeII and FeIII concentration, as well as by the evolution of the pH.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Commercially available Fe0 from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA, USA, ≥99%, size range 1–2 mm) was used as received. Sand from a local aquifer was washed with distilled water, air-dried at room temperature and sieved in the particle size range of 0.5–1.2 and 1.2–2.0 mm. A stock solution of CrVI (10 g/L) was prepared by dissolving 28.29 g of AR grade K2Cr2O7 in 1000 mL of deionized water; then, working solutions of the desired initial CrVI concentration were prepared by diluting the stock solution. Natural (tap) water was used as background electrolyte to prepare the working solutions in order to simulate a freshwater contamination event; this was proven in numerous previous studies to be the best option for reproducing Fe0 corrosion in natural waters [20,43,47].
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Non-Disturbed Batch Experiments
Non-disturbed batch tests were carried out using working solutions with pH 6.5 and CrVI concentrations of 5 and 100 mg/L for an experimental duration of 40 days. The two concentrations were chosen because they are within the range of levels reported for natural water environments polluted with low [48] and high [49] CrVI concentrations. Experiments were initiated by adding 20 mL working solution in assay tubes containing either: (1) Fe0 + sand (1.2–2 mm), (2) Fe0 only, or (3) sand (1.2–2 mm) only. Assay tubes were kept in darkness, at room temperature (23 ± 2 °C), throughout the duration of experiments. The volume of Fe0 was fixed at 0.05 cm3 (0.2 g) and 1 cm3 (4 g) for tests with low (5 mg/L) and high (100 mg/L) CrVI concentration, respectively; this amount represented 100% of the reactive agent for the “Fe0 only” system. Three “Fe0 + sand” systems were tested: 20, 50 and 80% Fe0 (volumetric proportions), prepared by mixing the fixed masses of Fe0 with appropriate amounts of sand. The same mass ratios of CrVI:Fe0, CrVI:Fe0:sand and CrVI:sand were employed for both low and high CrVI concentration experiments.
2.2.2. Continuous-Flow-through Column Experiments
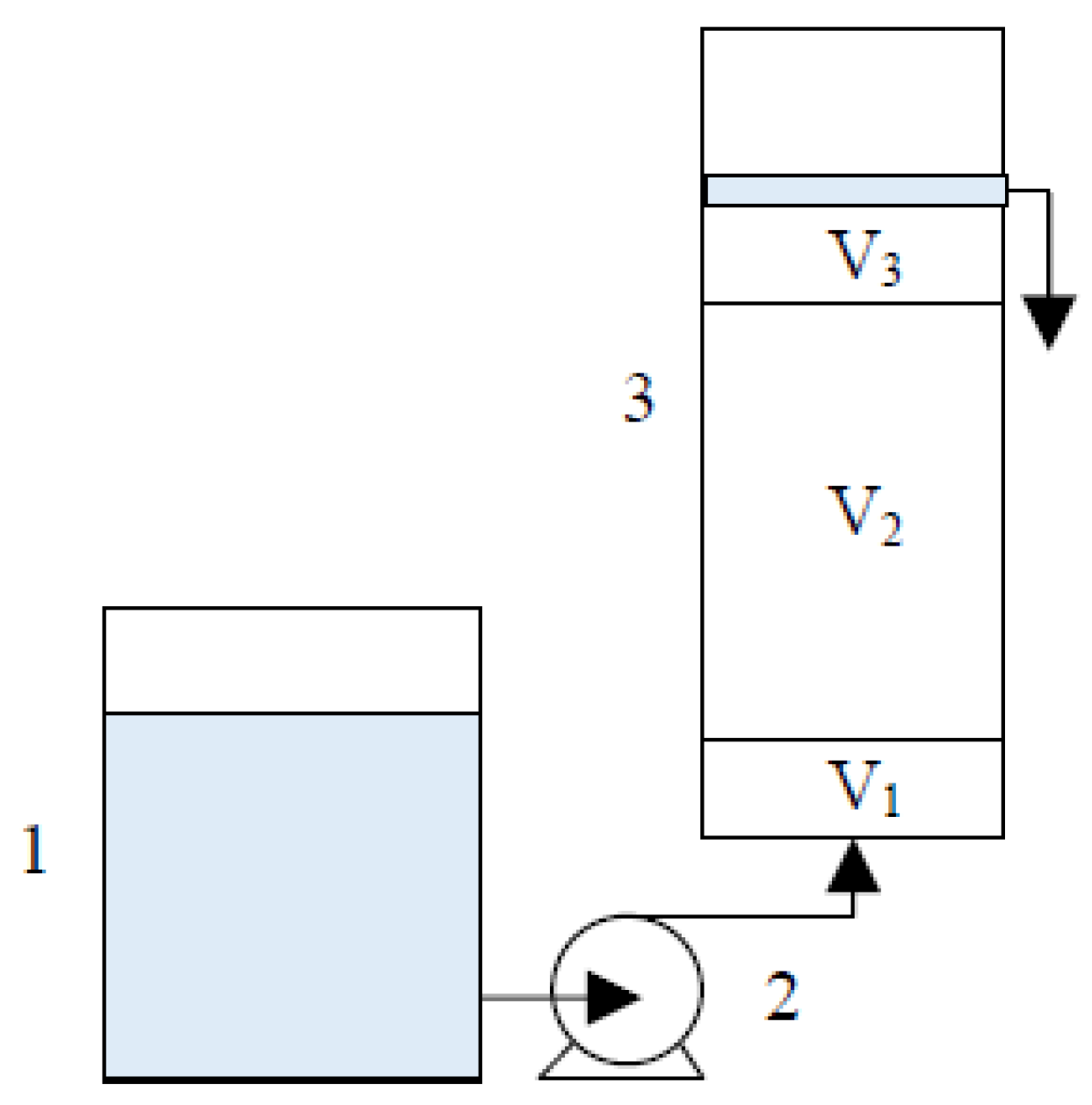
Column experiments were conducted in up-flow mode using vertical polyethylene columns of 12 cm height with 3 cm internal diameter. A 5 mg/L CrVI solution with pH 6.5 was pumped from the feed reservoir through the columns at a constant flow rate (30 mL/h) and room temperature (23 ± 2 °C) by an Ismatec IP08 peristaltic pump. From the bottom to the top, columns were packed with the following three layers (Figure 1): (1) sand (1.2–2.0 mm, V1 = 5.0 cm3), (2) reactive zone (V2), and (3) sand (0.5–1.2 mm, V3 = 5.0 cm3).
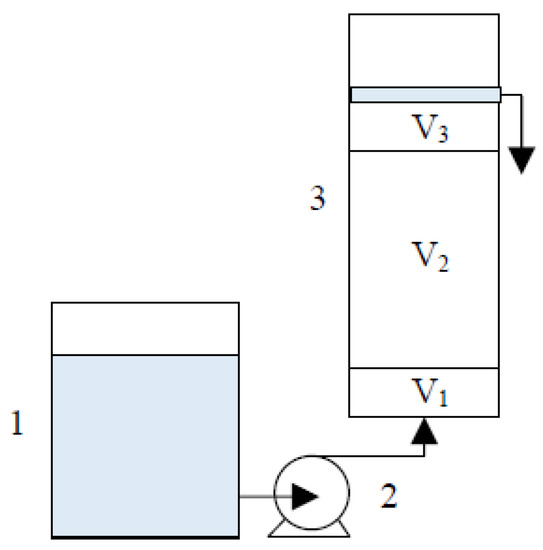
Figure 1.
Column experimental setup: (1) CrVI solution storage tank; (2) peristaltic pump; (3) column with V1 (sand 1.2–2.0 mm, 5.0 cm3), V2 (reactive zone) and V3 (sand 0.5–1.2 mm, 5.0 cm3) layers.
Three different systems were investigated: (1) Fe0 + sand (1.2–2 mm), (2) Fe0 only, and (3) sand only (1.2–2 mm). Two types of reactive zone (V2) containing Fe0 were explored:
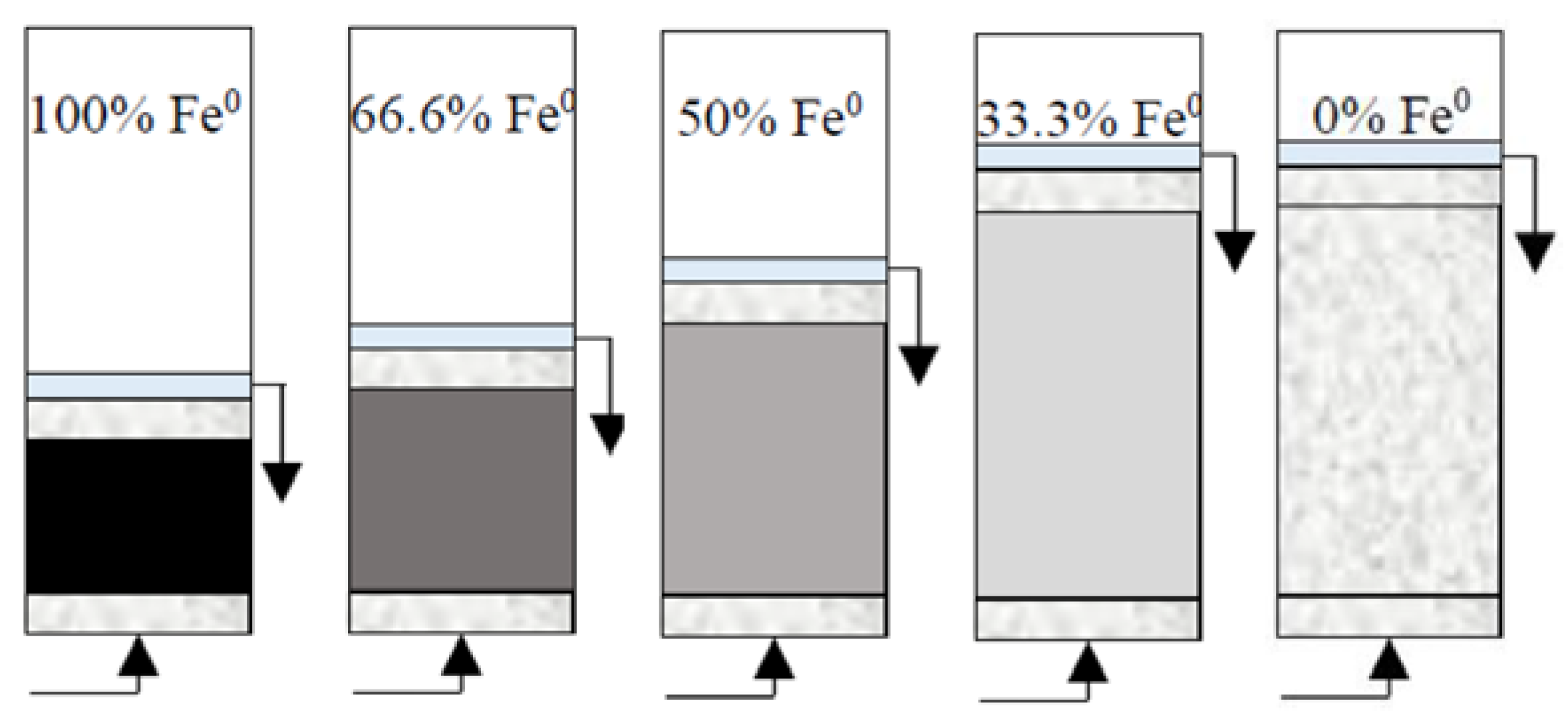
(1) Reactive zone with fixed Fe0 volume/mass (20 cm3/80 g) and variable total volume V2 (20, 30, 40 and 60 cm3) (Figure 2). These reactive zones corresponded to the following Fe0 volumetric percentages: (a) 100% (20 cm3 Fe0 only), (b) 66.6% (mixture of 20 cm3 Fe0 + 10 cm3 sand), (c) 50% (mixture of 20 cm3 Fe0 + 20 cm3 sand), and (d) 33.3% (mixture of 20 cm3 Fe0 + 40 cm3 sand). In addition, one control (0% Fe0) column experiment was carried out with reactive zone V2 containing only 60 cm3 sand. In order to investigate the influence of pH, an additional set of identical column experiments were conducted at pH 7.1.
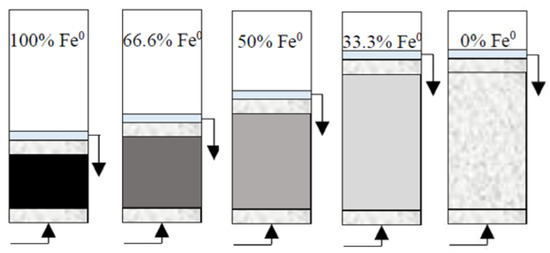
Figure 2.
Experimental setup for column tests with reactive zone having fixed Fe0 volume (20 cm3) and variable total volume V2 (20, 30, 40 and 60 cm3). The control (0% Fe0) column is also depicted.
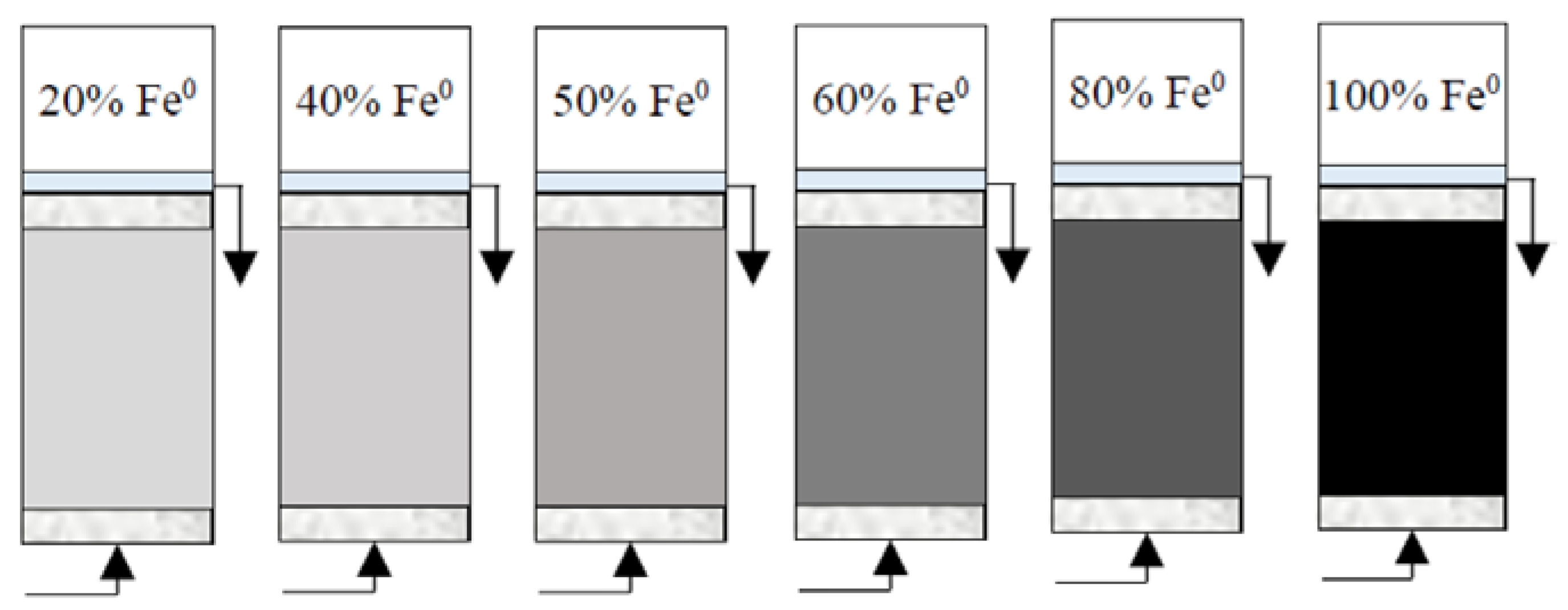
(2) Reactive zone with variable Fe0 volume/mass (10 cm3/40 g, 20/80 g, 25 cm3/100 g, 30 cm3/120 g, 40 cm3/160 g and 50 cm3/200 g) and fixed total volume V2 (50 cm3) (Figure 3). These reactive zones corresponded to the following Fe0 volumetric percentages: (a) 100% (50 cm3 Fe0 only), (b) 80% (mixture of 40 cm3 Fe0 + 10 cm3 sand), (c) 60% (mixture of 30 cm3 Fe0 + 20 cm3 sand), (d) 50% (mixture of 25 cm3 Fe0 + 25 cm3 sand), (e) 40% (mixture of 20 cm3 Fe0 + 30 cm3 sand) and (f) 20% (mixture of 10 cm3 Fe0 + 40 cm3 sand).
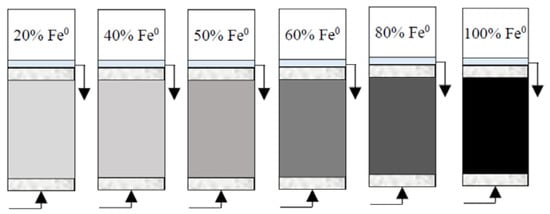
Figure 3.
Experimental setup for column tests with reactive zone having variable Fe0 volume (10, 20, 25, 30, 40 and 50 cm3) and fixed total volume V2 (50 cm3).
2.3. Analytical Procedure
Samples collected from batch and column tests were analyzed for CrVI, Crtotal, FeII and Fetotal via spectrophotometric methods using a Specord 200 PLUS spectrophotometer. CrVI concentration was determined by the 1,5-diphenylcarbazide method at 540 nm [50]; Crtotal was analyzed by oxidizing any CrIII with KMnO4, followed by analysis as CrVI. Then, CrIII, if any, was evaluated as the difference between Crtotal and CrVI. FeII concentrations in the effluent were analyzed by the 1,10-ortophenantroline method at 510 nm [51]. Fetotal was determined by reduction of any FeIII to FeII with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, followed by analysis as FeII; FeIII was determined from the difference between Fetotal and FeII. An Inolab 7320 pH-meter calibrated with three standards was used to measure the pH. All represented data are the mean values of two experimental replicates.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)—energy dispersive angle X-ray spectrometry (EDX) were employed to investigate the chemical composition and surface morphology of both fresh and exhausted Fe0 from batch experiments with high CrVI concentration. SEM-EDX analysis was performed on an Inspect S scanning electron microscope (FEI, Holland) coupled with a GENESIS XM 2i energy dispersive angle X-ray spectrometer to obtain the atom composition. XRD measurements were performed at 40 kV and 30 mA on an X’Pert PRO MPD Diffractometer (FEI, Holland) equipped with a Cu anode X-ray tube and PixCEL detector (Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54056 Å).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solid Phase Characterization
To ensure conciseness of this article, the results of SEM-EDX and XRD analysis are discussed only for the 20, 50 and 100% Fe0 system. Analysis of exhausted Fe0 SEM images (Figures S2–S4) reveals the occurrence of typical amorphous structures, attributable to secondary mineral phases (iron corrosion products), which did not exist on the fresh Fe0 surface (Figure S1). Furthermore, SEM micrographs also indicate that the highest amount of secondary mineral phases were formed at the surface of exhausted Fe0 from the 20% Fe0 system (Figure S4), while much lower quantities were observed at the surface of 50 and 100% Fe0 systems (Figures S2 and S3).
The EDX spectrum of exhausted Fe0 from all investigated systems (Figures S6–S8) showed the appearance of additional chromium peaks, which did not exist for fresh Fe0 (Figure S5), indicating the retaining of chromium on the Fe0; in addition, it was noticed that more intense chromium peaks were observed for the 20% Fe0 system, compared to the 50 and 100% Fe0 systems. Furthermore, EDX analysis also revealed a much greater oxygen content at the surface of exhausted Fe0 from the 20% Fe0 system, than at the surface of exhausted Fe0 from the 50 and 100% Fe0 systems. All this data strongly support the results of SEM analysis, indicating that the highest amount of iron corrosion products (Fe (hydr)oxides) existed at the surface of exhausted Fe0 from the 20% Fe0 system.
Analysis of the XRD diffractograms show that apart from the two peaks at 2θ values of 45° and 65° exhibited by fresh Fe0 [52] (Figure S9) no additional diffraction signals of other components were identified in the XRD pattern of exhausted Fe0 from the “Fe0 only” and the “Fe0 + sand” systems (Figures S10–S12); this could be attributed to the fact that secondary mineral phases occurred at the surface of exhausted Fe0 in minor amounts and/or in amorphous form. However, the intensity of the Fe0 peak at the 2θ value of 65° was significantly decreased for the exhausted Fe0 in comparison to fresh Fe0, attributable to the occurrence of iron corrosion products at the surface of exhausted Fe0; moreover, it was noticed that the higher the percentage of sand in the “Fe0 + sand” system, the lower the intensity of the 65° peak.
To sum up, the results of solid phase characterization clearly indicate that amending Fe0 with sand results in more intense corrosion processes affecting the Fe0 grains; the higher the volumetric ratio of sand in the “Fe0 + sand” system, the higher the amount of iron corrosion products generated.
3.2. Non-Disturbed Batch Tests
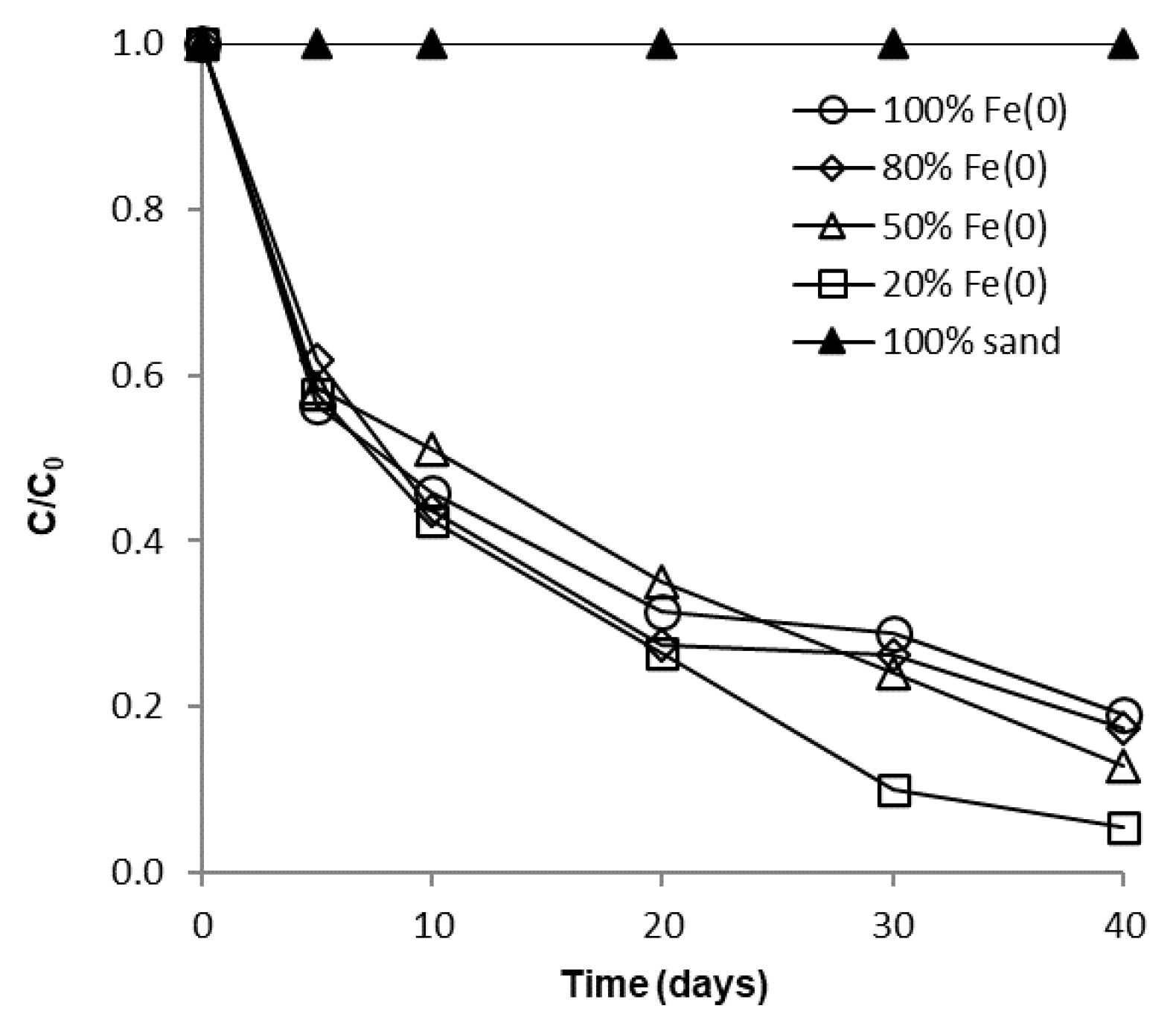
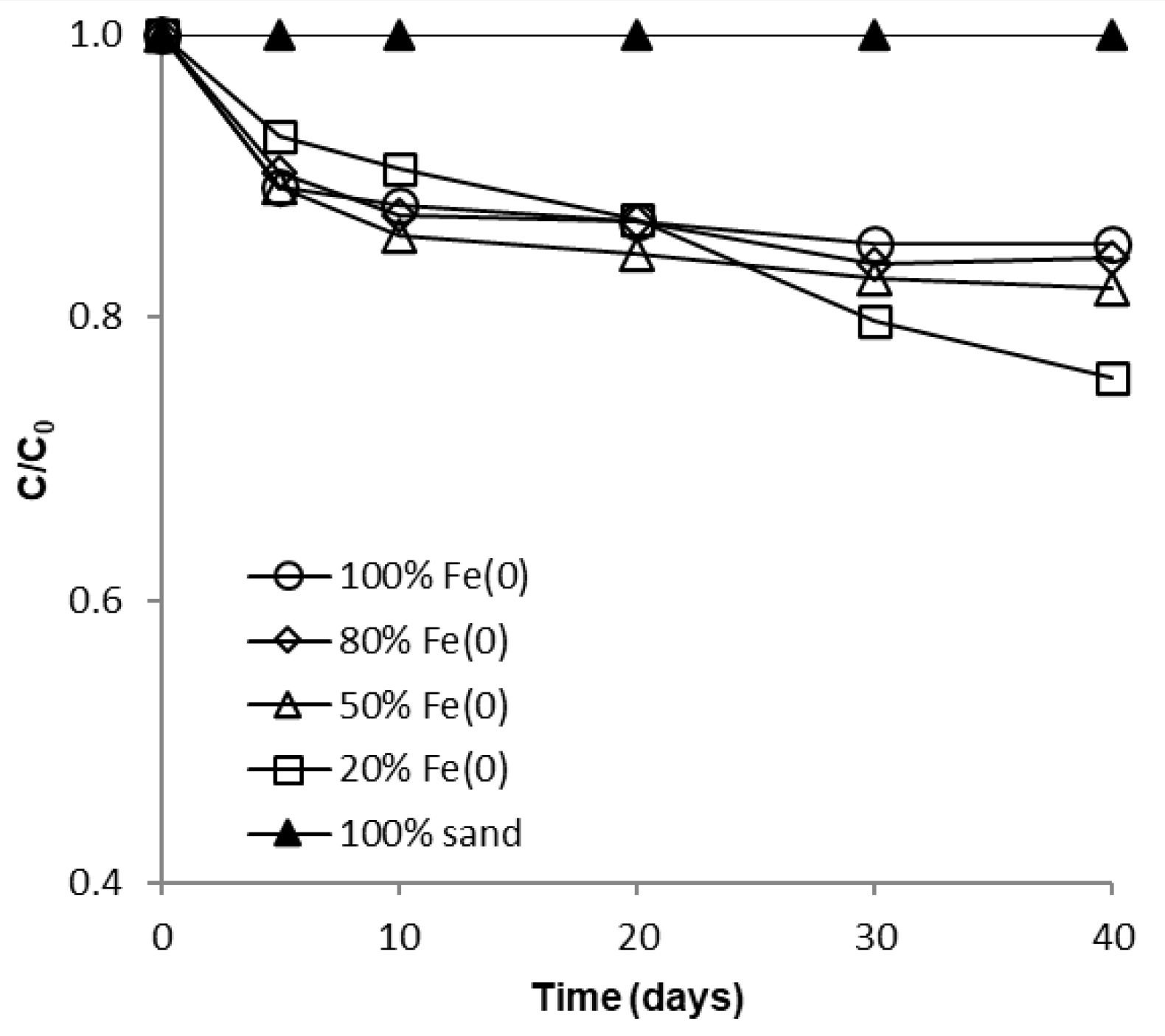
The influence of sand co-presence on CrVI removal with Fe0 in a non-disturbed batch system is depicted in Figure 4 and Figure 5. It is apparent from these figures that after 40 days no significant differences can be perceived between the 100% Fe0, the 80% Fe0 and the 50% Fe0 systems for both types of experiments. Instead, slightly better removal efficiencies of CrVI were noticed for the 20% Fe0 system than for systems with 50–100% Fe0. This is in agreement with results presented at Section 3.1, indicating that the most intense Cr EDX peaks were observed for the exhausted Fe0 from the 20% Fe0 system. It is important to note that the improvement of CrVI removal in the 20% Fe0 system was observed only after about 30 days of the experiment when important amounts iron corrosion products were already generated; this reveals the importance of iron corrosion products for the mechanism of CrVI removal.
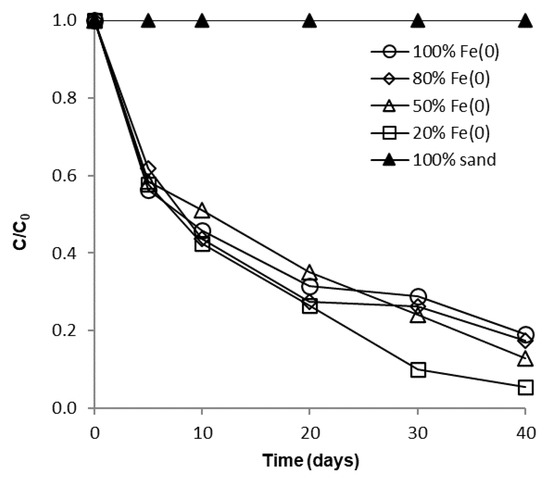
Figure 4.
Time profile of CrVI removal for batch experiments at low initial concentration.
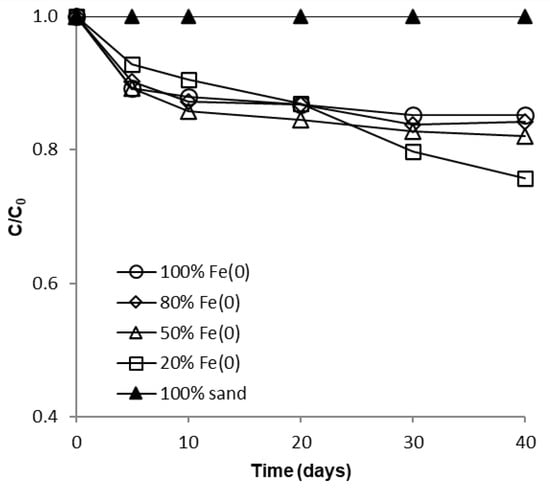
Figure 5.
Time profile of CrVI removal for batch experiments at high initial concentration.
Since the same CrVI: Fe0 mass ratio was applied in both types of tests (with low and high CrVI concentration), another important outcome that clearly results from analysis of Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure S13 is the fact that removal of CrVI with Fe0 was severely hindered by the increase of CrVI concentration, not only in the “Fe0 only”, but also in the “Fe0 + sand” system; this is in opposition to recent findings revealing that comparable removal efficacies were achieved both at low and high CrVI concentration in the “Fe0 + MnO2” system [47]. Therefore, it was revealed by the non-disturbed batch experiments that the ability of sand to improve the removal of CrVI with Fe0 is much lower than that of MnO2.
No CrVI removal was observed in the “sand only” system, in accord with earlier findings reporting that sand has no ability in adsorbing CrVI [46]. Dissolved FeII was not detected in the supernatant, regardless of type of experiment, which indicates that all FeII resulting from the Fe0 corrosion process was subsequently involved in: (1) indirect reduction of CrVI, (2) precipitation as a condensed phase of (oxy)hydroxides, and (3) oxidation to FeIII and subsequent precipitation as a condensed phase of (oxy)hydroxides. Dissolved FeIII and CrIII were also not identified in the supernatant, attributable to their (co-)precipitation as simple or/and mixed FeIII–CrIII (oxy)hydroxides, a process that occurs at pH > 4 [53].
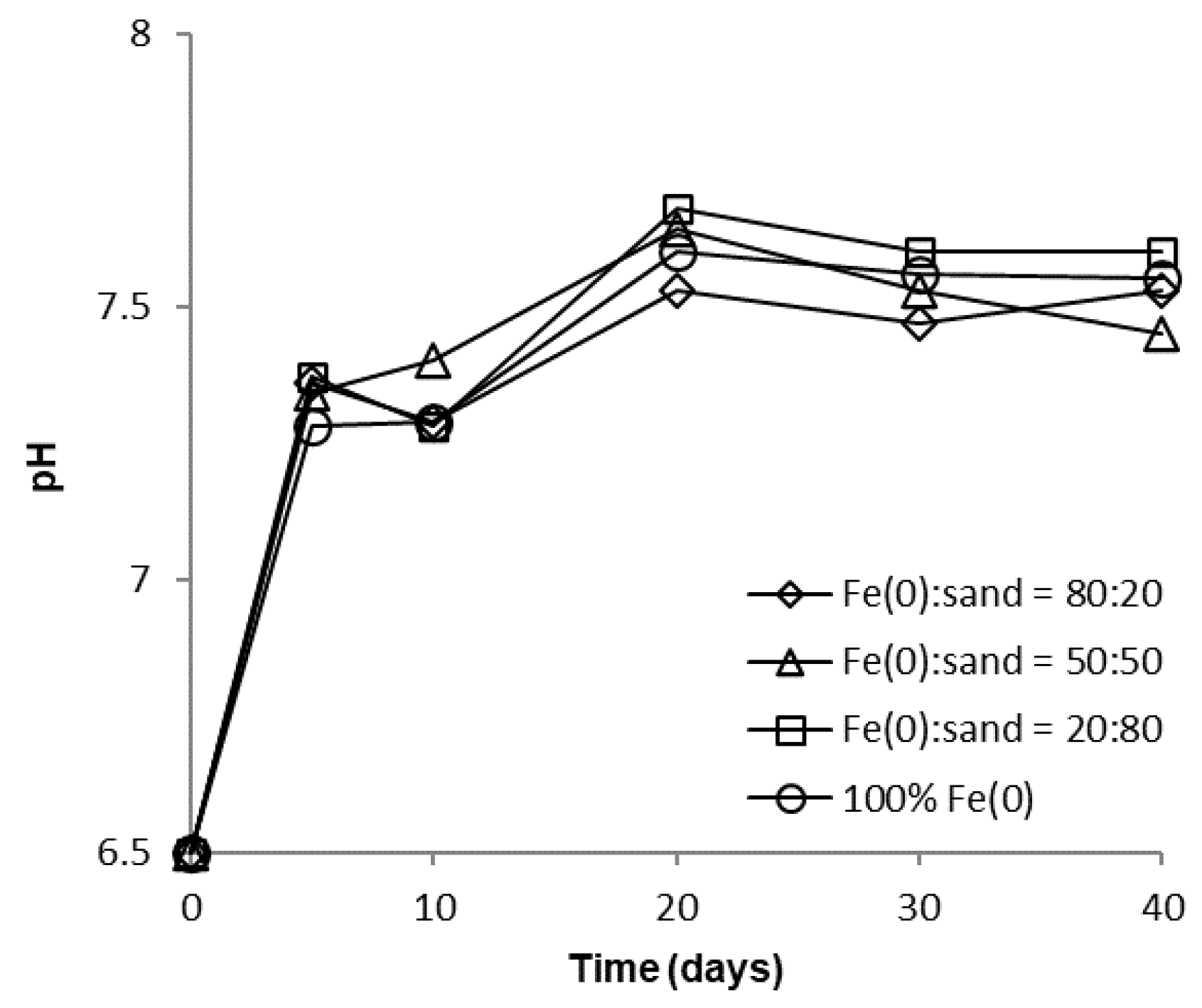
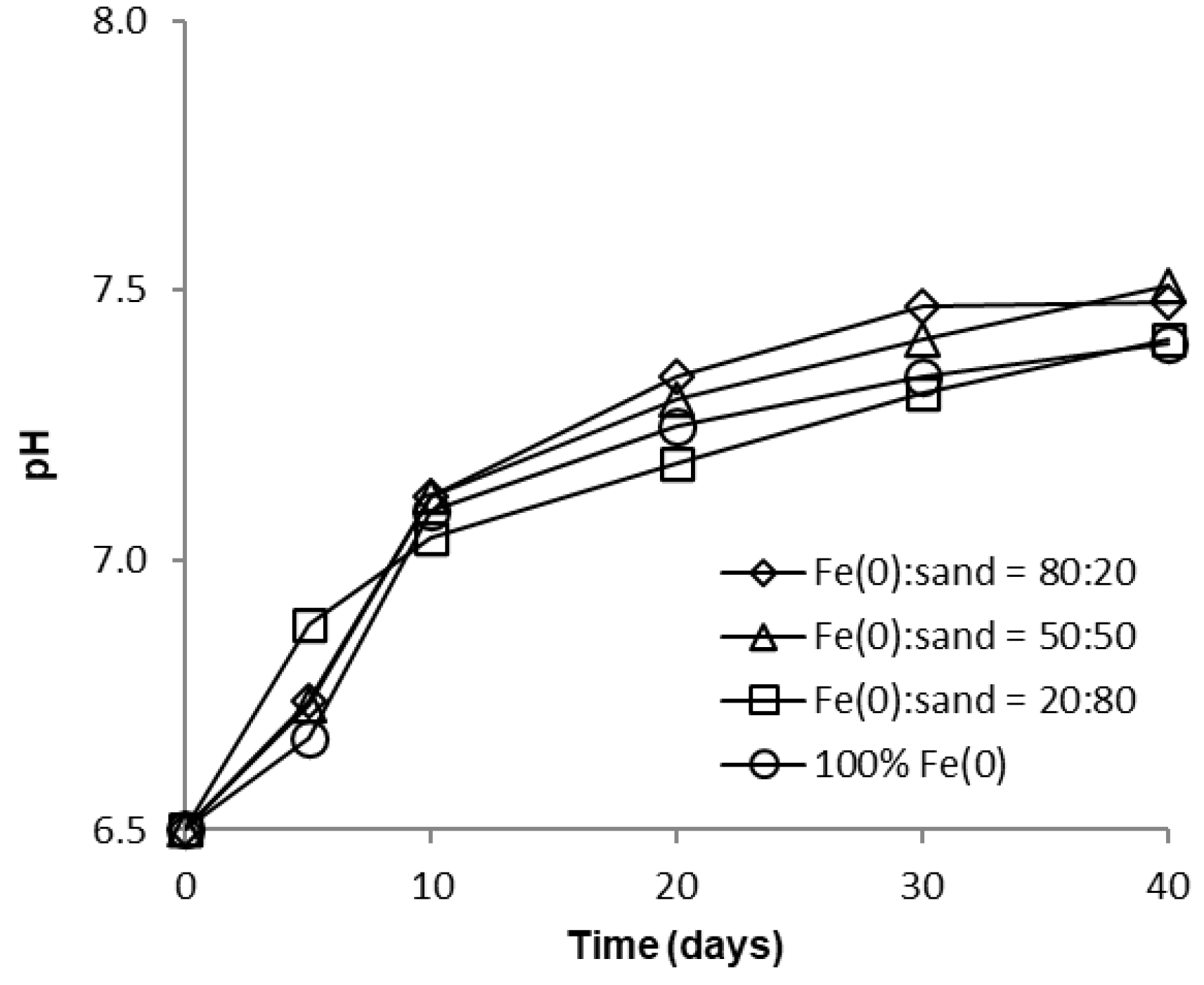
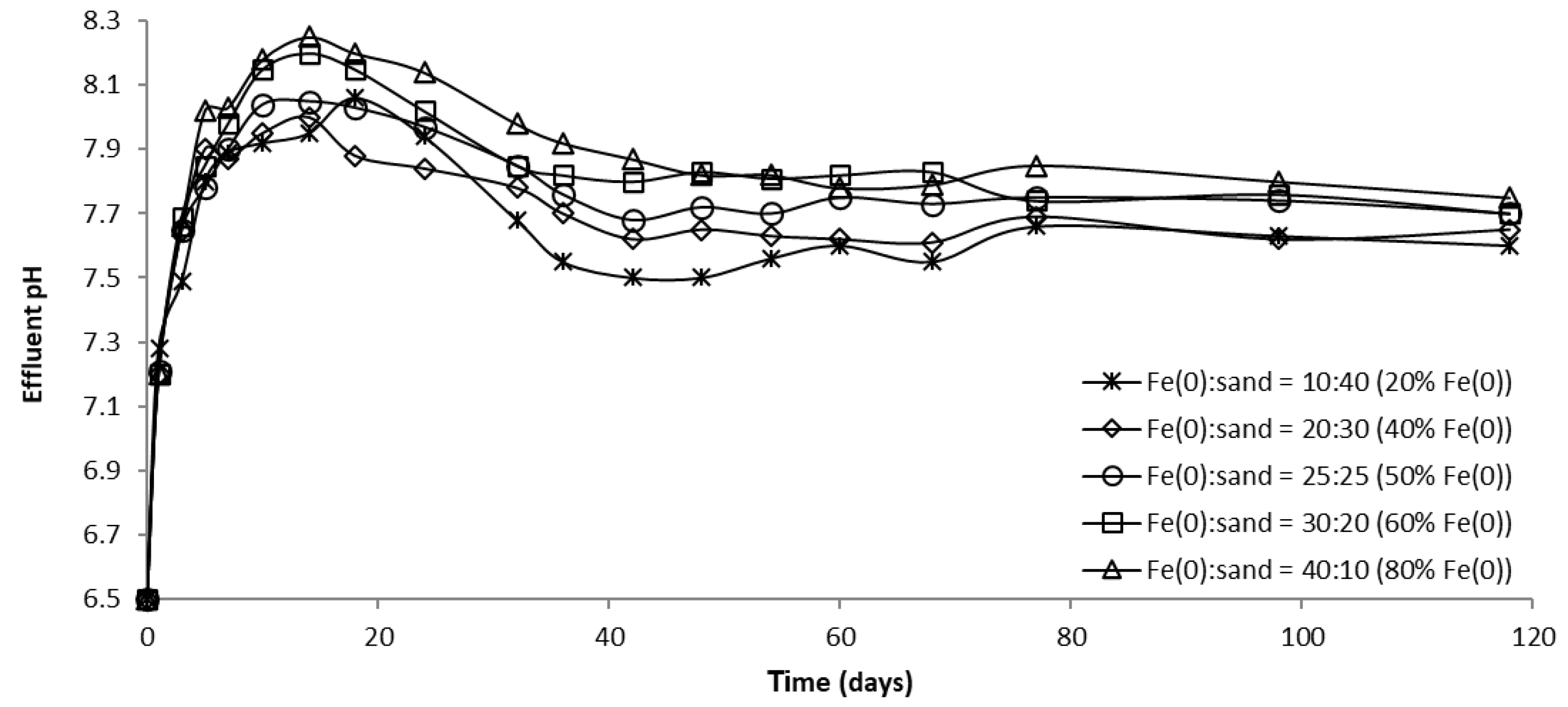
Over the course of batch experiments, pH increased from 6.5 to 7.5–7.7 and 7.4–7.5 for tests at low and high CrVI concentration, respectively (Figure 6 and Figure 7); the increase was more rapid for experiments at low CrVI concentration and rather sequential for tests at high CrVI concentration. No significant differences were observed between the final pH values (after 40 days) in the “Fe0 + sand” and the “Fe0 only” system. The pH increase was the result of: (1) HO-generation in Fe0 oxidative dissolution processes (Equations (1) and (2)), mainly due to oxidation with water, and (2) H+ consuming reactions (Equations (3)–(5)), mainly due to indirect reduction of CrVI with dissolved or solid FeII-based corrosion products [54].
Fe0 + 2H2O → Fe2+ + H2 + 2HO−
2Fe0 + O2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + 4HO−
3Fe0 + 2HCrO4− + 14H+ → 3Fe2+ + 2Cr3+ + 8H2O
HCrO4− + 3Fe2+ + 7H+ → 3Fe3+ + Cr3+ + 4H2O
3FeIIFeIII2O4 + HCrO4− + 14H2O + H+ → 4[Fe0.75Cr0.25](OH)3 + 6Fe(OH)3
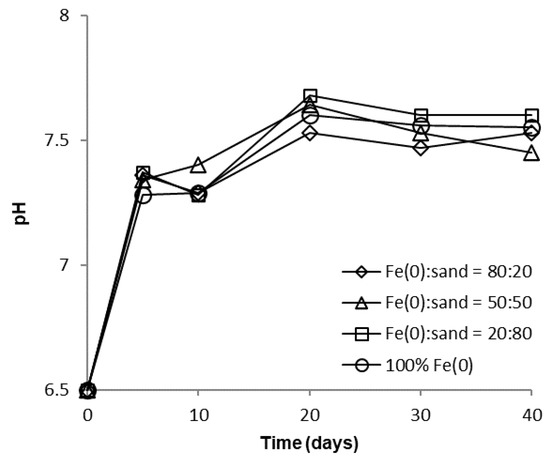
Figure 6.
Evolution of pH in batch experiments at low CrVI initial concentration.
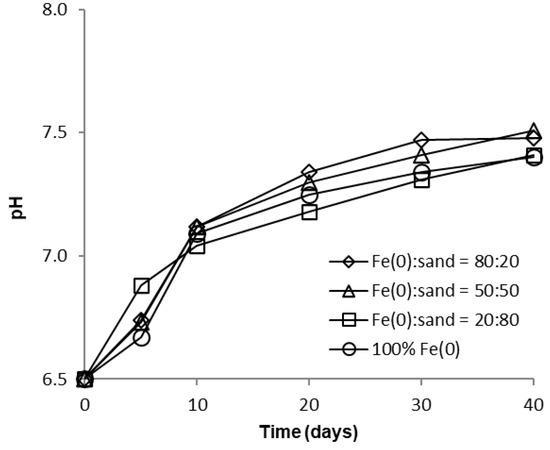
Figure 7.
Evolution of pH in batch experiments at high CrVI initial concentration.
However, passivation of the Fe0 surface with solid mineral phases (mainly Fe (oxy)hydroxides) will cause a decrease in Fe0 corrosion rates and, eventually, limit the pH increase, as can be seen from Figure 6 and Figure 7.
At this point, it should be recalled that mixing Fe0 with non-expansive materials (e.g., sand) was suggested as a tool to increase the long-term hydraulic conductivity of Fe0 beds [18,55]. So far, the present batch experiments suggest that a minor improvement of CrVI removal efficiency could also be achieved in an “Fe0+ sand” system, but only for the 20% Fe0 system. In order to further investigate the effect of sand co-presence on removal efficacy of CrVI, additional continuous-flow-through column experiments were carried out, and the results are discussed in the following sections.
3.3. CrVI Evolution in Column Tests
3.3.1. Column Tests with Reactive Zone Having a Fixed Fe0 Volume and Variable Total Volume V2
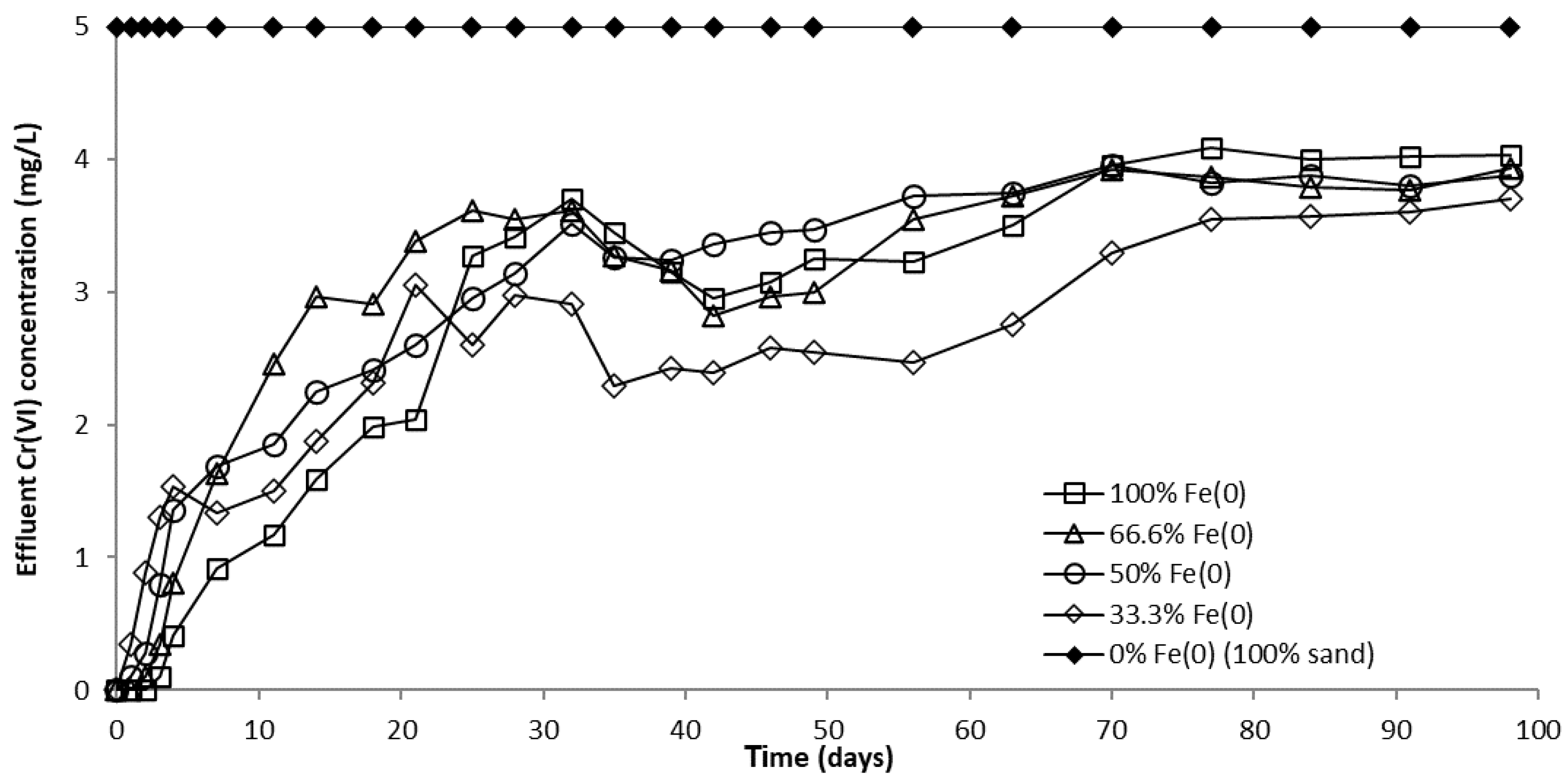
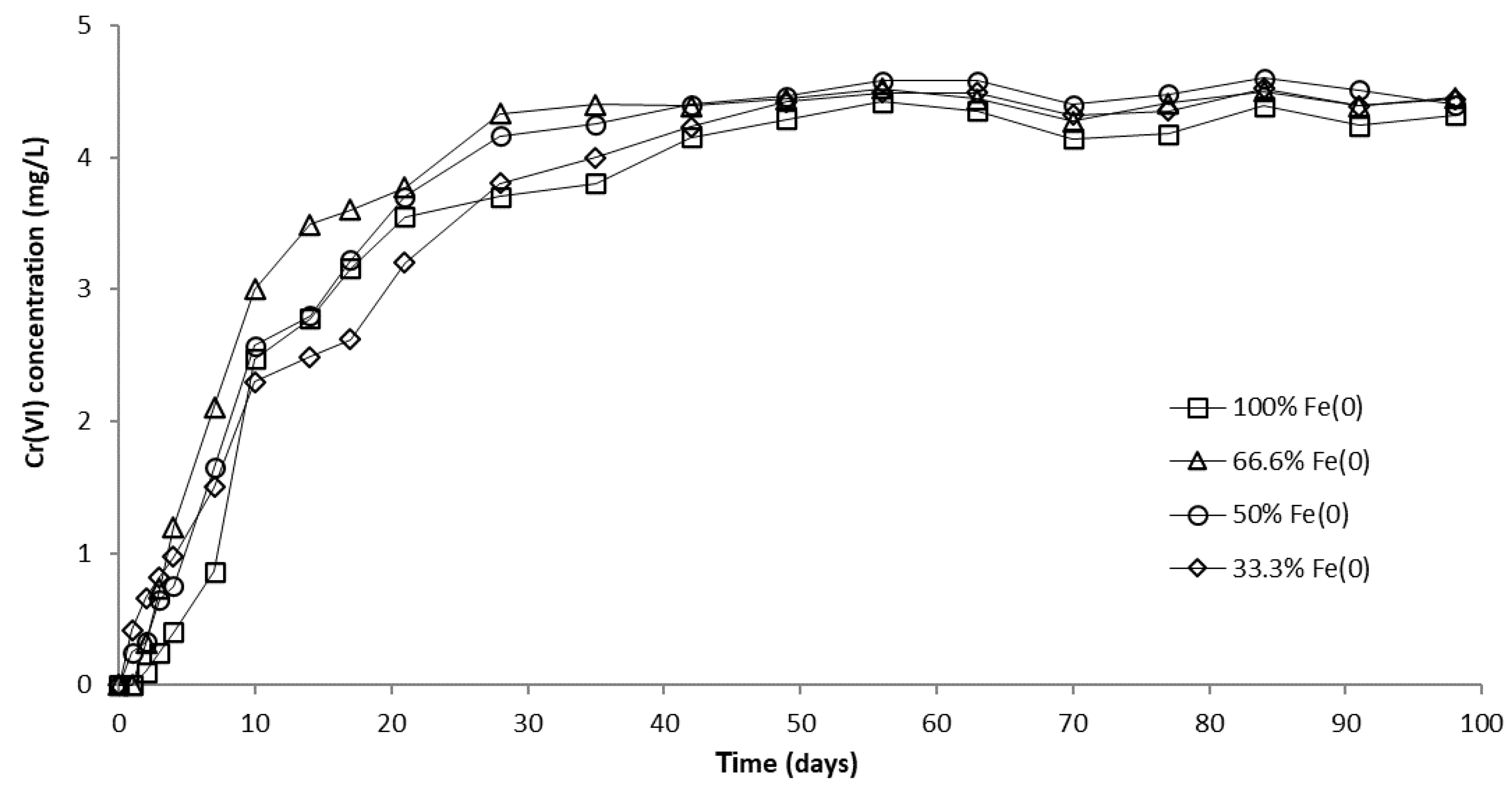
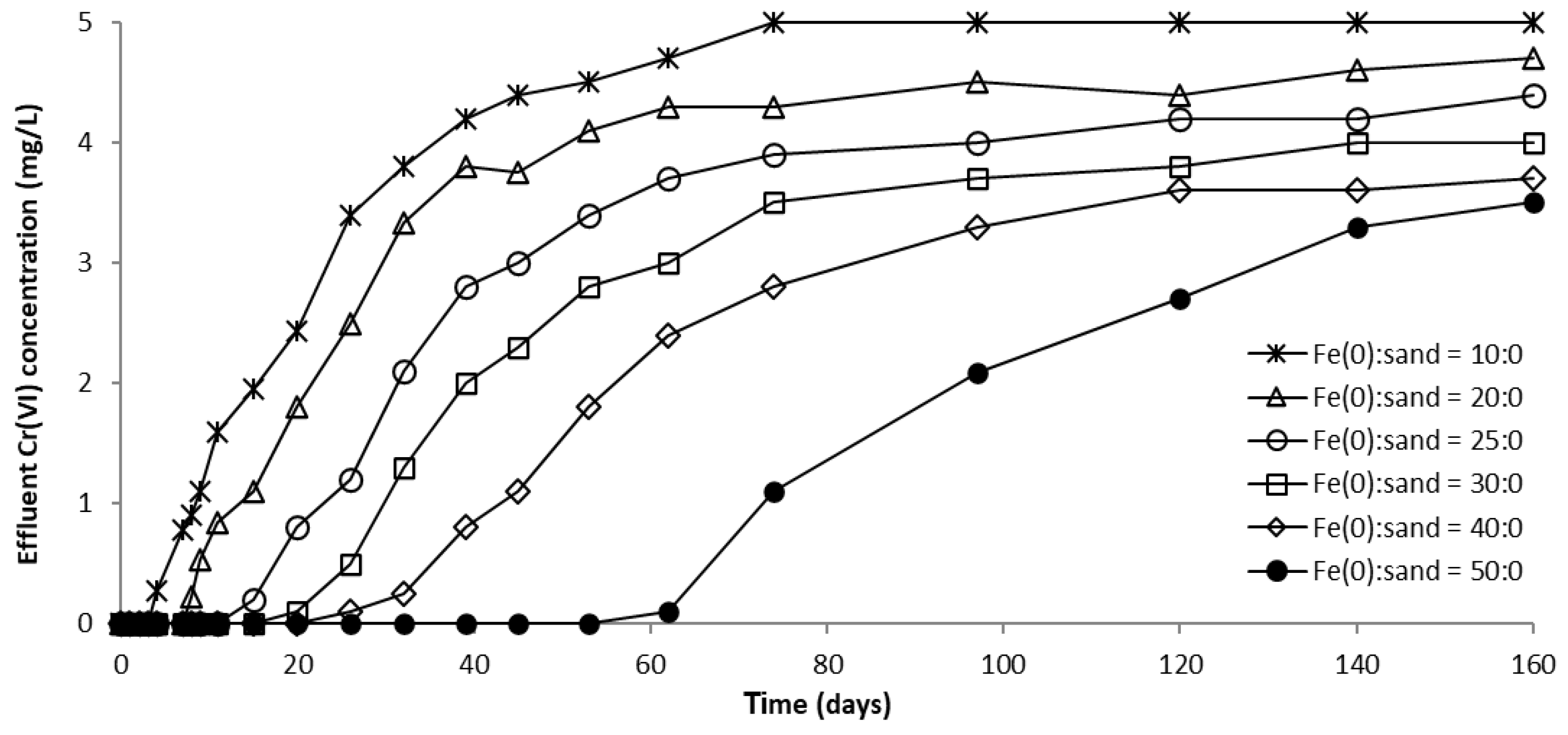
The evolution of CrVI removal in column experiments with a fixed Fe0 volume and variable total volume of the reactive zone is presented in Figure 8 and Figure S14. No CrVI removal was noticed in the “sand only” (0% Fe0) control system over the entire duration of the experiment, in concordance with results of non-disturbed batch experiments. In columns with an Fe0-based reactive zone, CrVI breakthrough occurred after 2 days in the 100% Fe0 system, 1 day in the 66.6% Fe0 system, and from the very first day of the experiment in the 50% and 33.3% Fe0 systems (Figure S14). Hence, it is obvious that mixing sand with Fe0 in the reactive zone has a negative effect on the breakthrough time. Therefore, so far, it could be presumed that the co-presence of sand inside the reactive zone may have a detrimental effect also on the efficiency of CrVI removal with Fe0. After the breakthrough, CrVI concentration continuously increased in all Fe0 based systems until reaching a quasi-steady-state concentration after about 70 days. The order of CrVI steady-state concentration value, which resulted from this study is: 100% Fe0 system > 50% Fe0 system ≈ 66.6% Fe0 system > 33.3% Fe0 system. Thus, there was no direct dependence between the value of CrVI steady-state concentration and the volumetric ratio of Fe0 in the reactive zone; while the lowest CrVI steady-state concentration was observed for the 33% Fe0 system, the highest CrVI steady-state concentration was noted for the 100% Fe0 system.
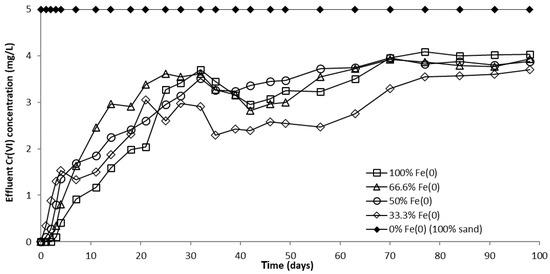
Figure 8.
CrVI concentration in column effluent vs. time for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2 at initial pH 6.5.
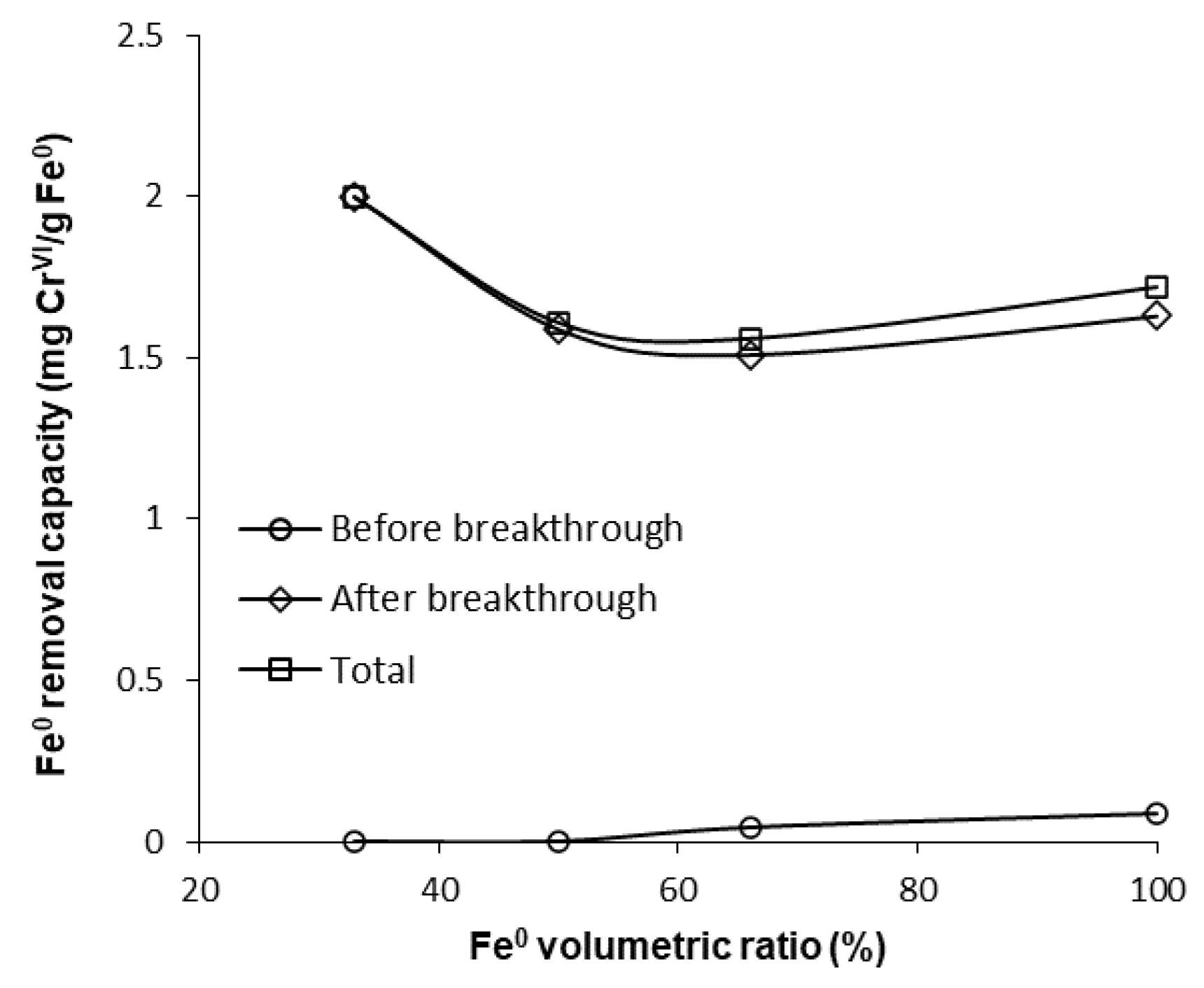
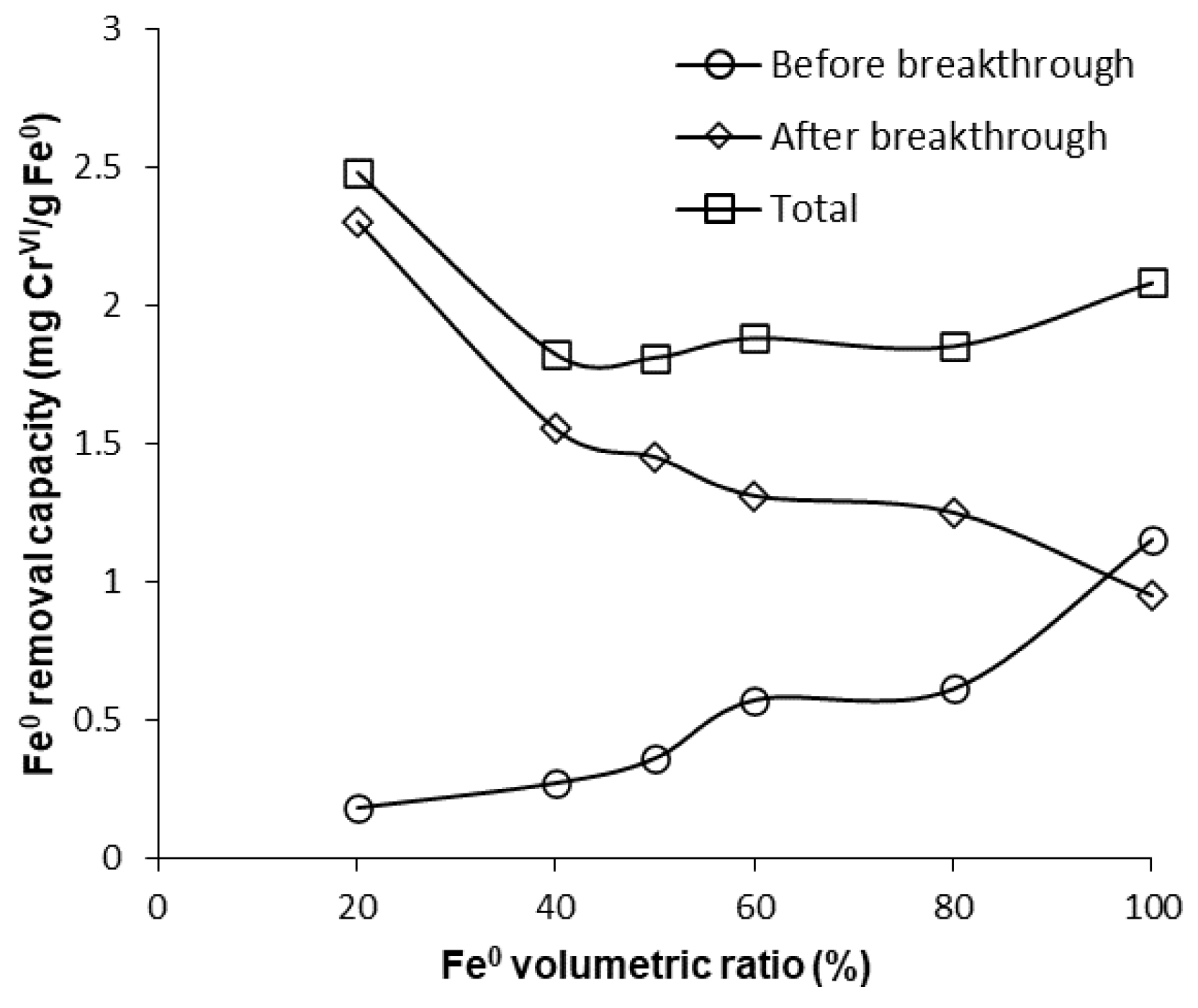
However, a comparison of the capacity of “Fe0 only” and “Fe0 + sand” systems to remove CrVI adds other important information, which counterbalances the aforementioned presumption. It can be seen from Figure 9 that the highest total CrVI removal capacity was observed for the 33% Fe0 system. The 100% Fe0 system exhibited the second best total CrVI removal capacity, higher than columns with 50% and 66.6% Fe0, but lower than the 33.3% Fe0 system. Therefore, it clearly results from these experiments that even though the 33.3% Fe0 system exhibited the fastest CrVI breakthrough, it displays the highest total CrVI removal capacity; this can be ascribed to the fact that the 33.3% Fe0 system showed the lowest value of CrVI in column effluent from day 25 till the end of the experiment. This behavior may be important, for instance, when treated water is blended in a certain proportion with clean water from a different source, and typical quality regulations are still achieved for the resulting mixed water in spite of CrVI breakthrough in the treated water.
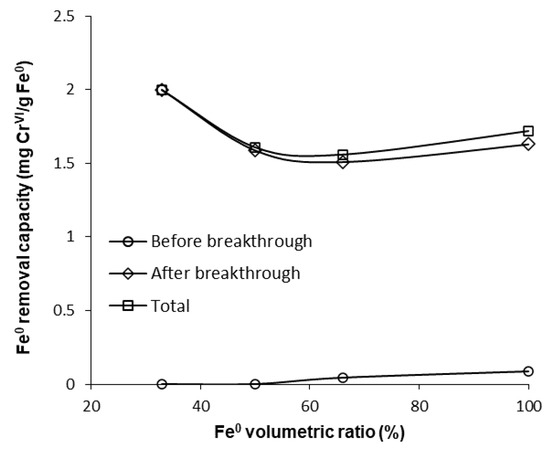
Figure 9.
CrVI removal capacity of Fe0 at pH 6.5 for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2.
Finding the 33.3% Fe0 column to be the most efficient Fe0-based system, in terms of mass of CrVI removed per mass unit of Fe0, is in correlation with results of previous studies indicating that to be sustainable an Fe0-based filter should contain less than 60% (vol) Fe0, ideally 25% [8,56,57,58].
In order to investigate the influence of pH, an identical column experiment was conducted using a CrVI solution with pH 7.1. The results presented in Figure 10 and Figure S15 reveal that the CrVI breakthrough occurred after 1 day in 100% and 66.6% Fe0 systems, while in 50% and 33.3% Fe0 systems, CrVI breakthrough was observed from the very first day of the experiment. After breakthrough, the concentration of CrVI in column effluents increased until a steady-state concentration was reached after about 40 days. The order of the CrVI steady-state concentration value was: 50% Fe0 system > 66.6% Fe0 system ≈ 33.3% Fe0 system > 100% Fe0 system. Therefore, the highest CrVI steady-state concentration at pH 7.1 was noted for the 50% Fe0 system, while the lowest was noted for the 100% Fe0 system, in contrast to experiments at pH 6.5, where highest and lowest CrVI steady-state concentration were observed for the 100% and 33.3% Fe0 system, respectively.
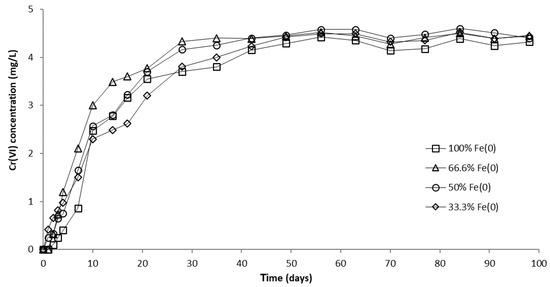
Figure 10.
CrVI concentration in column effluent vs. time for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2 at initial pH 7.1.
All these observations could suggest that the co-presence of sand inside the reactive zone could have a detrimental effect at pH 7.1. However, from the comparison of the capacity of the “Fe0 only” and the “Fe0 + sand” systems to remove CrVI (Figure 11), it can be seen that at pH 7.1 the 33.3% and 100% Fe0 systems exhibited similar total CrVI removal capacities. By gradually increasing the Fe0 ratio from 33% to 50% and to 66.6%, a decrease in total CrVI removal capacity was noted. Therefore, even though the 33.3% Fe0 system exhibited the fastest CrVI breakthrough, it displays a comparable CrVI total removal capacity to the 100% Fe0 system; this can be attributed mainly to the low rate of CrVI concentration increase observed for the 33.3% Fe0 system during the first 40 days following the breakthrough.
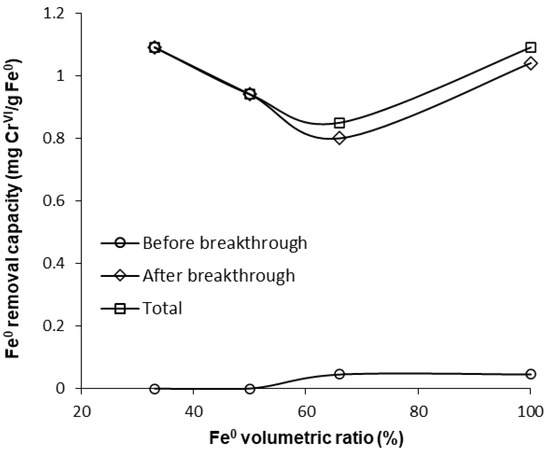
Figure 11.
CrVI removal capacity of Fe0 at pH 7.1 for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2.
CrVI breakthrough time in the 100% Fe0 system was lower at pH 7.1 (1 day) than at 6.5 (2 days), and CrVI breakthrough concentrations were higher at pH 7.1 than at 6.5 (Figures S14 and S15). In addition, faster rates of CrVI concentration increase after breakthrough, and higher values of steady-state CrVI concentration were noted at pH 7.1 than at 6.5 (Figure 8 and Figure 10). Furthermore, by comparing the values of CrVI removal capacities (Figure 9 and Figure 11), it can be seen that an increase in pH from 6.5 to 7.1 leads to a reduced CrVI removal efficiency in both the “Fe0 only” and the “Fe0 + sand” systems. While it is well-known that efficiency of CrVI removal with Fe0 decreases with increasing pH [54], the present experiments suggest that the magnitude of the positive effect of sand co-presence also decreases with increasing pH from 6.5 to 7.1.
The higher CrVI breakthrough concentrations, faster rates of CrVI concentration increase after breakthrough and higher values of steady-state CrVI concentration observed at pH 7.1 than at pH 6.5 can be ascribed to: (1) lower proton concentration at pH 7.1 than at 6.5, which from a thermodynamic standpoint hinders reduction of CrVI, (2) lower amounts of FeII generated as a result of lower rates of Fe0 corrosion at pH 7.1 than at 6.5, and (3) lower amounts of dissolved FeII existent in solution due to the scavenging of generated FeII by the surface of the sand and of Fe0 via adsorption, precipitation and oxidation to FeIII; this means that lower amounts of dissolved FeII are available for homogeneous indirect reduction of CrVI. Obviously, all mentioned FeII competitive processes occur both at pH 6.5 and 7.1. However, it must be recalled that efficiency of both FeII adsorption and precipitation processes increases with increasing solution pH. Moreover, it is well-known that the rate of FeII oxidation by dissolved O2 (existent in our tap water in a concentration of about 7 mg/L) also significantly increases with pH [59,60,61,62]. Therefore, the efficiency of all mentioned FeII competitive processes is higher at pH 7.1 than at pH 6.5.
3.3.2. Column Tests with Reactive Zone Having Variable Fe0 Volume and Fixed Total Volume V2
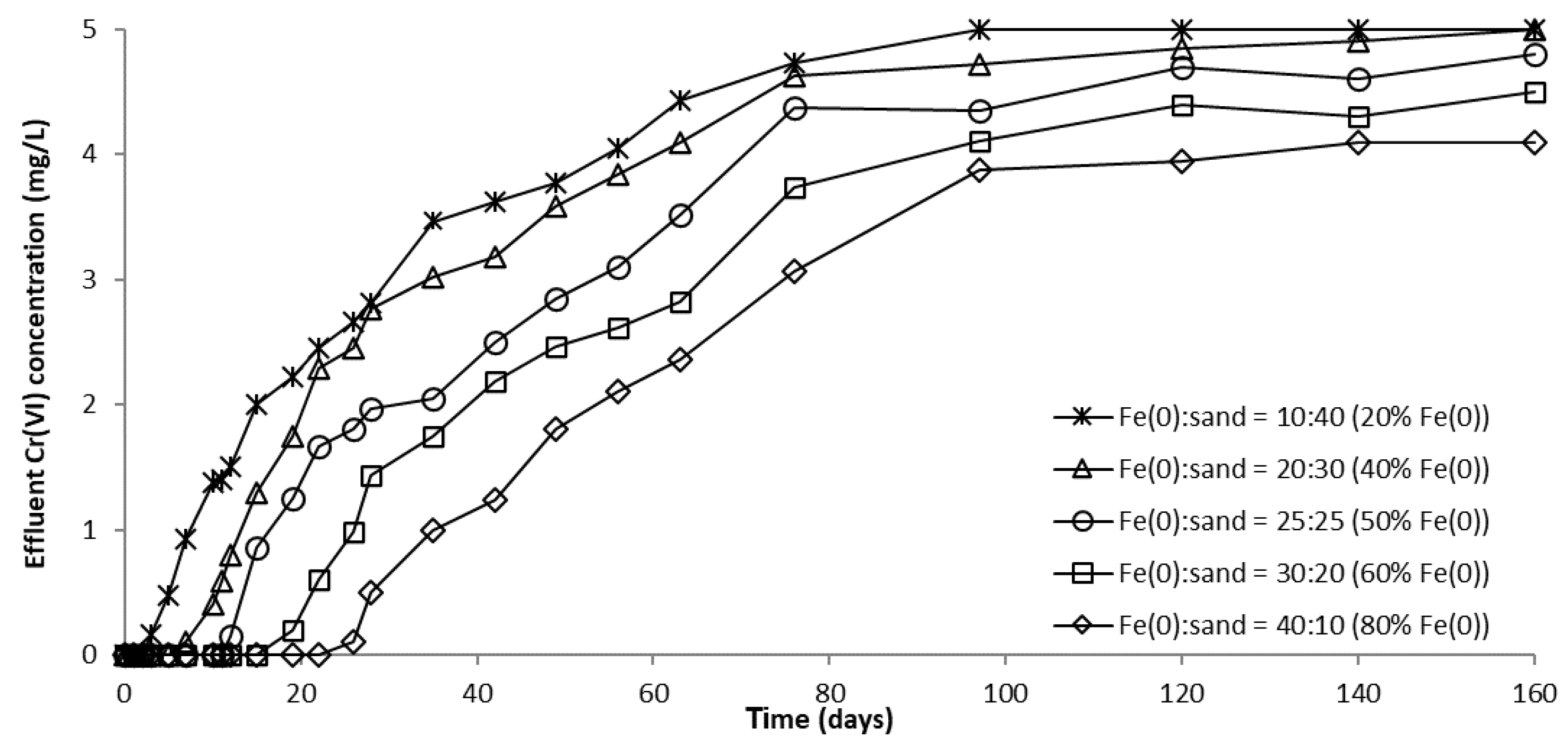
The evolution of CrVI removal in column experiments with variable Fe0 volume and fixed volume of total reactive zone is depicted in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure S16. It can be clearly seen from these images that the higher the volume (mass) of Fe0 within the reactive zone, the longer the breakthrough times and the higher the CrVI removal efficiencies. This is consistent with results of previous studies indicating that increasing the mass of Fe0 has a favorable effect on CrVI removal efficiency due to an increased Fe0 surface area and thus, a proportionally greater number of reactive sites available for removal of CrVI [54].
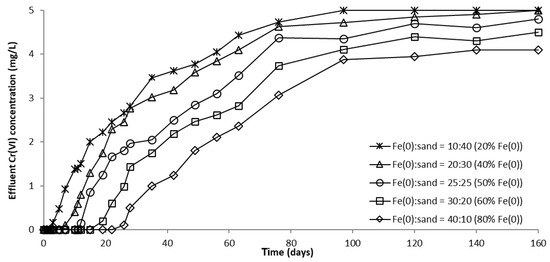
Figure 12.
CrVI concentration in column effluent vs. time for columns with “Fe0 + sand” reactive zone having variable Fe0 volume and fixed total volume V2.
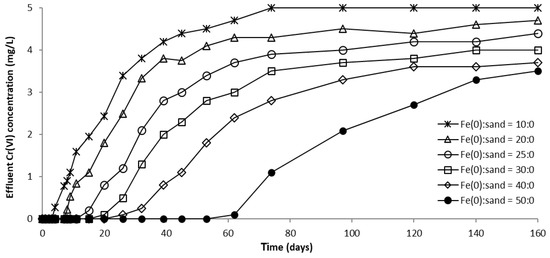
Figure 13.
CrVI concentration in column effluent vs. time for control columns packed with “Fe0 only” reactive zone.
For columns packed with a reactive zone containing 50–100% Fe0, CrVI concentration increased after breakthrough until a steady-state concentration was observed; the higher the volumetric percentage of Fe0 in the reactive zone, the lower the value of steady-state CrVI concentration. Instead, for columns packed with a reactive zone containing 20% and 40% Fe0, CrVI concentration continuously increased after breakthrough until the initial concentration of 5 mg/L was reached, and no steady-state concentration was observed; this behavior is attributable to the low amount of Fe0 in the reactive zone.
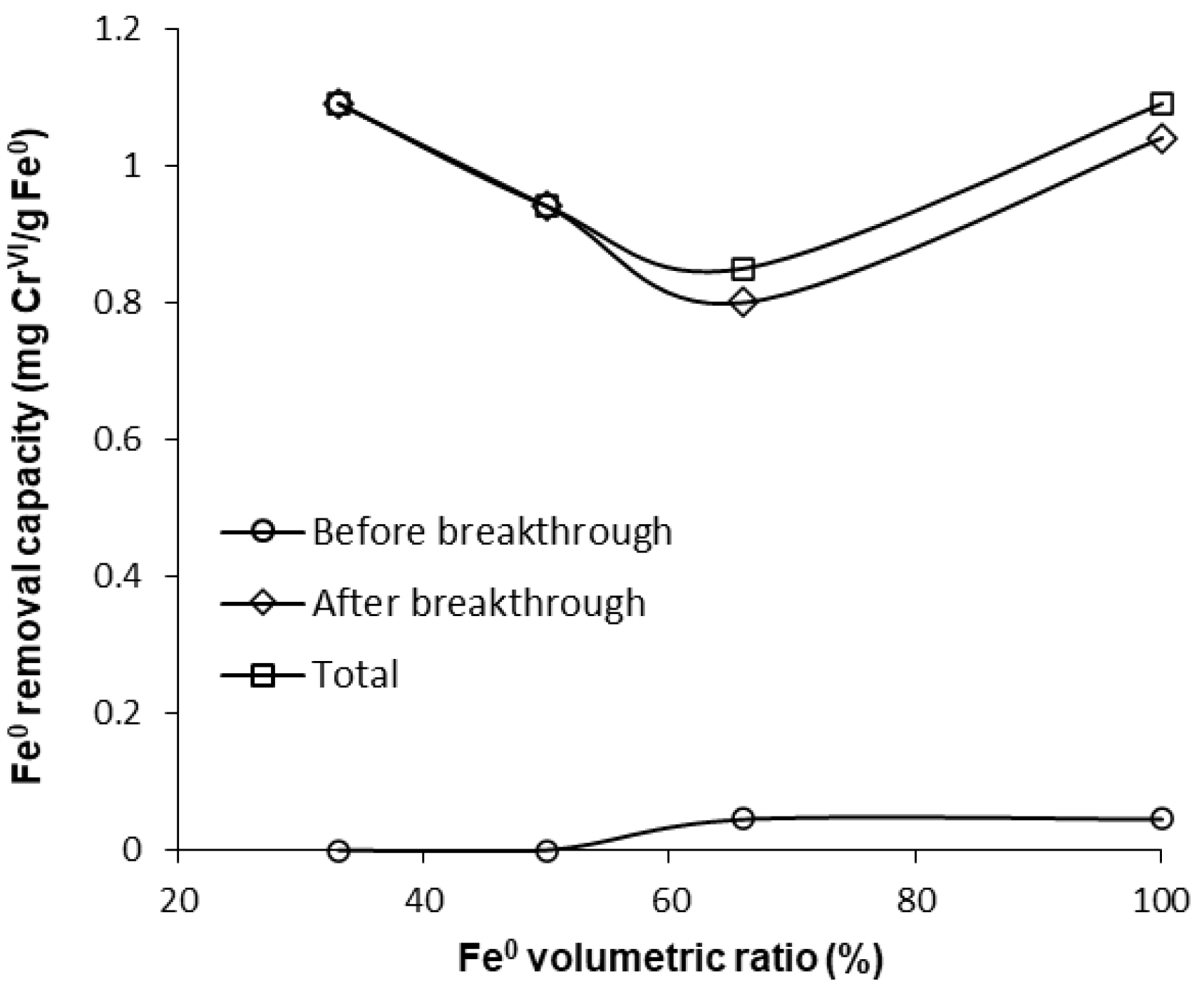
Furthermore, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure S16 also reveal that CrVI breakthrough occurred faster for the “Fe0 + sand” system than for the “Fe0 only” control system; the only exception was represented by column experiments with 40 cm3 Fe0, when CrVI breakthrough took place almost simultaneously for the “Fe0 + sand” and the “Fe0 only” systems. This confirms the results obtained in column tests with a reactive zone having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total volume V2 (Figure 8 and Figure 10), supporting the conclusion that the co-presence of sand inside the reactive zone shortens the duration of the period when the column operates with no CrVI detected in the effluent. However, a comparison of the total capacity of the “Fe0 only” and the “Fe0 + sand” system to remove CrVI (Figure 14) reveals that the highest total CrVI removal capacity was observed for the lowest Fe0 volumetric ratio in the reactive zone (i.e., 20% Fe0). Subsequently, by increasing the Fe0 volumetric ratio to 40%, an important decrease in total removal capacity was noted, which was also maintained quasi-constant when the Fe0 volumetric ratio was further increased up to 80%. Finally, an increase in total removal capacity was perceived for the column packed with 100% Fe0; however, total removal capacity of the 100% Fe0 system was lower than the 20% Fe0 system. This corroborates the results obtained in column tests with reactive zone having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total volume V2 (Section 3.3.1), revealing that a water treatment filter with 20–33% Fe0 volumetric ratio in the “Fe0 + sand” reactive zone could be more efficient for removal of CrVI than a 100% Fe0 system.
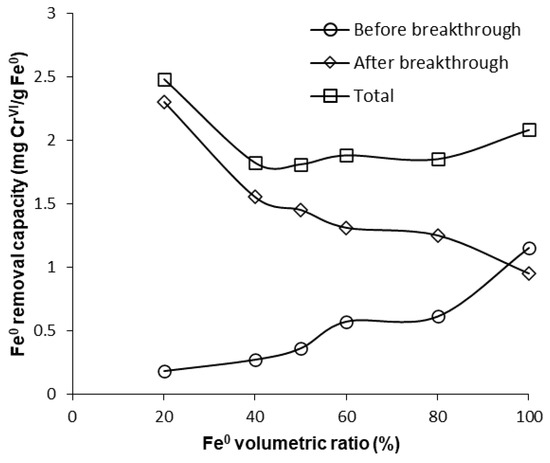
Figure 14.
CrVI removal capacity of Fe0 for columns having variable Fe0 volume and fixed total volume V2.
Column experiments carried out in this study confirmed the results of the non-disturbed batch test indicating that sand has no ability to retain CrVI; hence, the elevated removal efficiencies observed for the “Fe0 + sand” systems with the highest volumetric percentage of sand and the lowest of Fe0 cannot be attributed to CrVI adsorption on sand. There are, instead, several other effects of sand that may have caused this result: (1) sand can be regarded as a dispersant material, sustaining the system’s efficiency by avoiding/delaying the cementation/compaction of Fe(OH)n colloids, thus avoiding/delaying the porosity loss of the column reactive zone [41,63]; (2) sand helps expose more Fe0 surface to aqueous CrVI solution [64]; (3) for a fixed amount of Fe0, the volume of the reactive zone increases as a result of mixing Fe0 with sand; accordingly, higher hydraulic retention times will be recorded in “Fe0 + sand” than in “Fe0 only” system [10]; (4) sand offers a supplementary surface for precipitation of cations resulting from Fe0 corrosion, thus diminishing rates of Fe0 surface passivation [65]; (5) since FeII-bearing minerals precipitated on sand are not only good adsorbents for CrVI, but also stronger reductants than dissolved FeII [66], they are able to remove CrVI by a rapid adsorption–reduction mechanism [67]; and (6) FeII adsorbed on mineral surfaces (e.g., montmorillonite, kaolinite, α-FeOOH, γ-FeOOH, SiO2) has a higher tendency to reduce CrVI than dissolved FeII [68,69].
Effects (3), (4), (5) and (6) exerted by sand support the conclusion that the most important path of CrVI removal with Fe0 was the indirect reduction with FeII corrosion products (dissolved FeII and FeII-bearing secondary minerals) [47]. This agrees with previous reports [46] that ascribed the lack of dependency of the CrVI depletion rate constants on the Fe0 percentage in the column to the removal of CrVI via adsorption and reduction (with FeII) processes. Therefore, our results confirm the importance of adsorption and indirect reduction within the mechanism of CrVI removal with Fe0, in concordance with a recently postulated concept trying to revise the mechanism of contaminant removal in an Fe0-H2O system. As stated by this new concept, under environmental relevant pH values, Fe0 should be regarded mainly as the generator of removing agents (adsorbents/coagulants/reductants); accordingly, removal of contaminants with Fe0 occurs primarily due to adsorption/co-precipitation/size filtration processes, while contaminant reduction, when applicable, mostly results from indirect reducing agents and should be regarded as a parallel reaction of aqueous Fe0 corrosion [2,20,70,71].
3.4. pH Evolution in the Column Tests
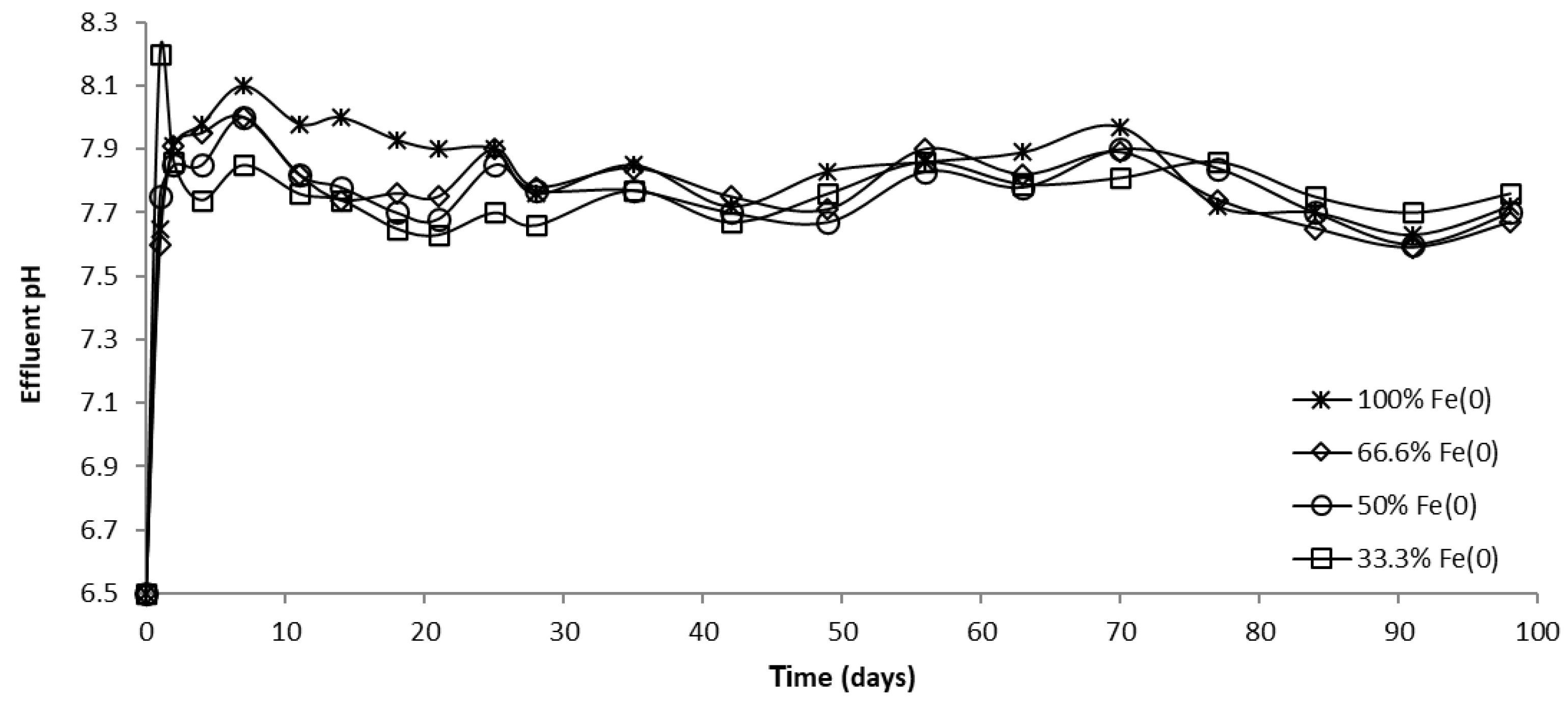
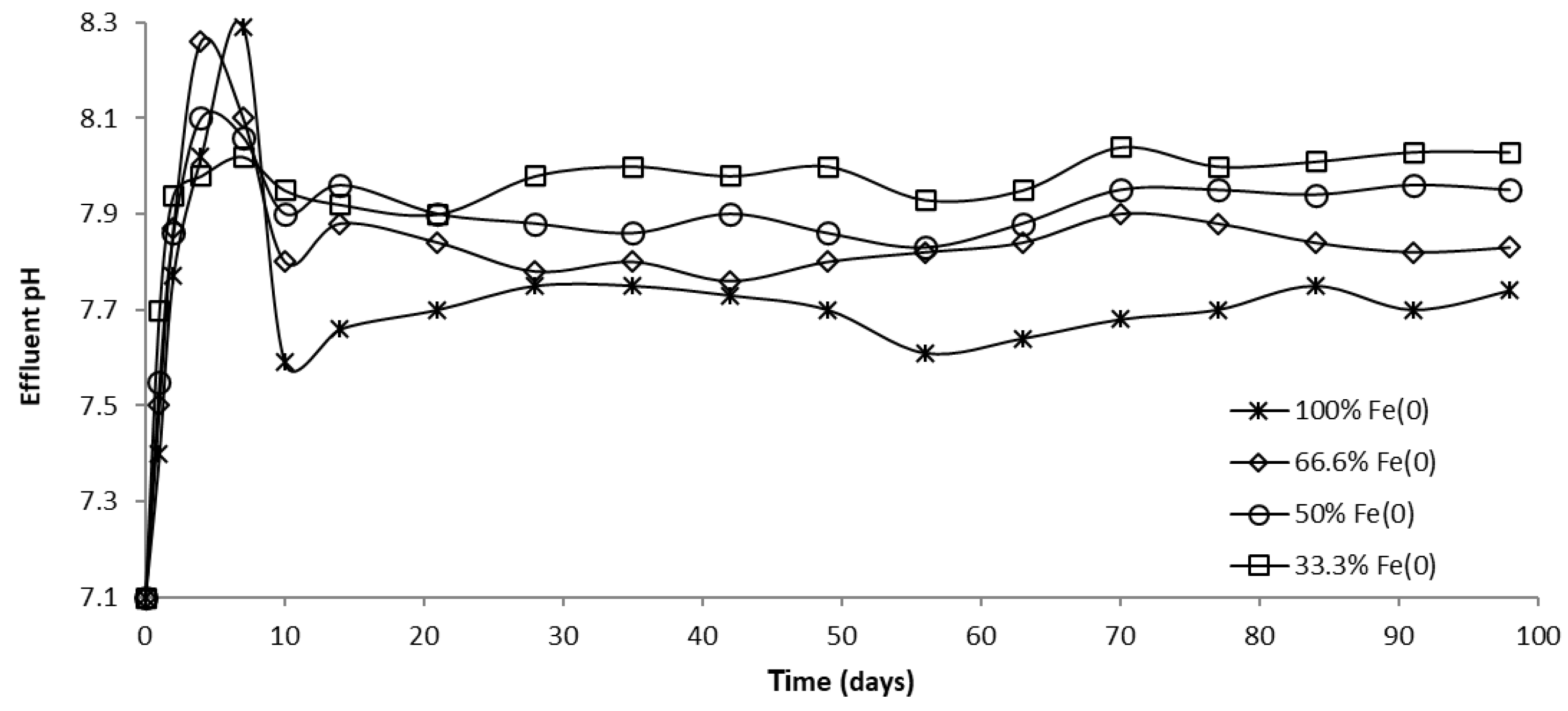
The evolution of pH in column effluents is presented in Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 17. It can be seen that at the beginning of the experiment, CrVI removal was accompanied by an increase in pH; Fe0 corrosion and CrVI reduction are responsible for this pH change, both processes involving the consumption of protons. Subsequently, the pH dropped until it reached a steady-state value, attributable to Fe0 surface passivation, which causes a decline in Fe0 corrosion.
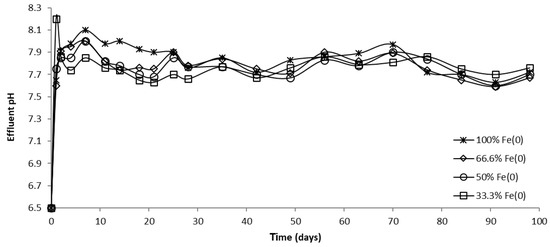
Figure 15.
The pH in column effluent vs. time for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2 at initial pH 6.5.
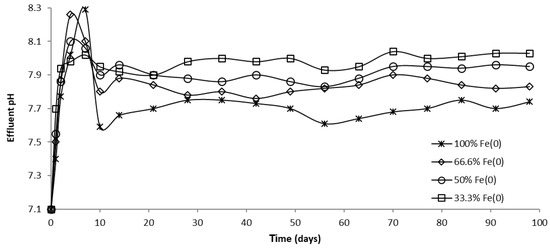
Figure 16.
The pH in column effluent vs. time for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2 at initial pH 7.1.
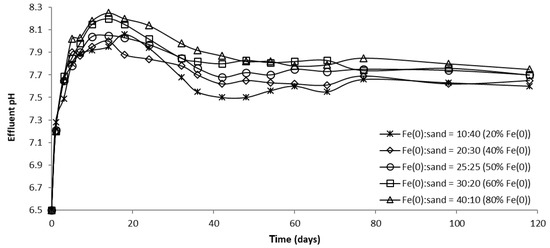
Figure 17.
The pH in column effluent vs. time for columns having variable Fe0 volume and fixed total reactive zone volume V2.
3.5. CrIII, FeIII and FeII Evolution in Column Tests
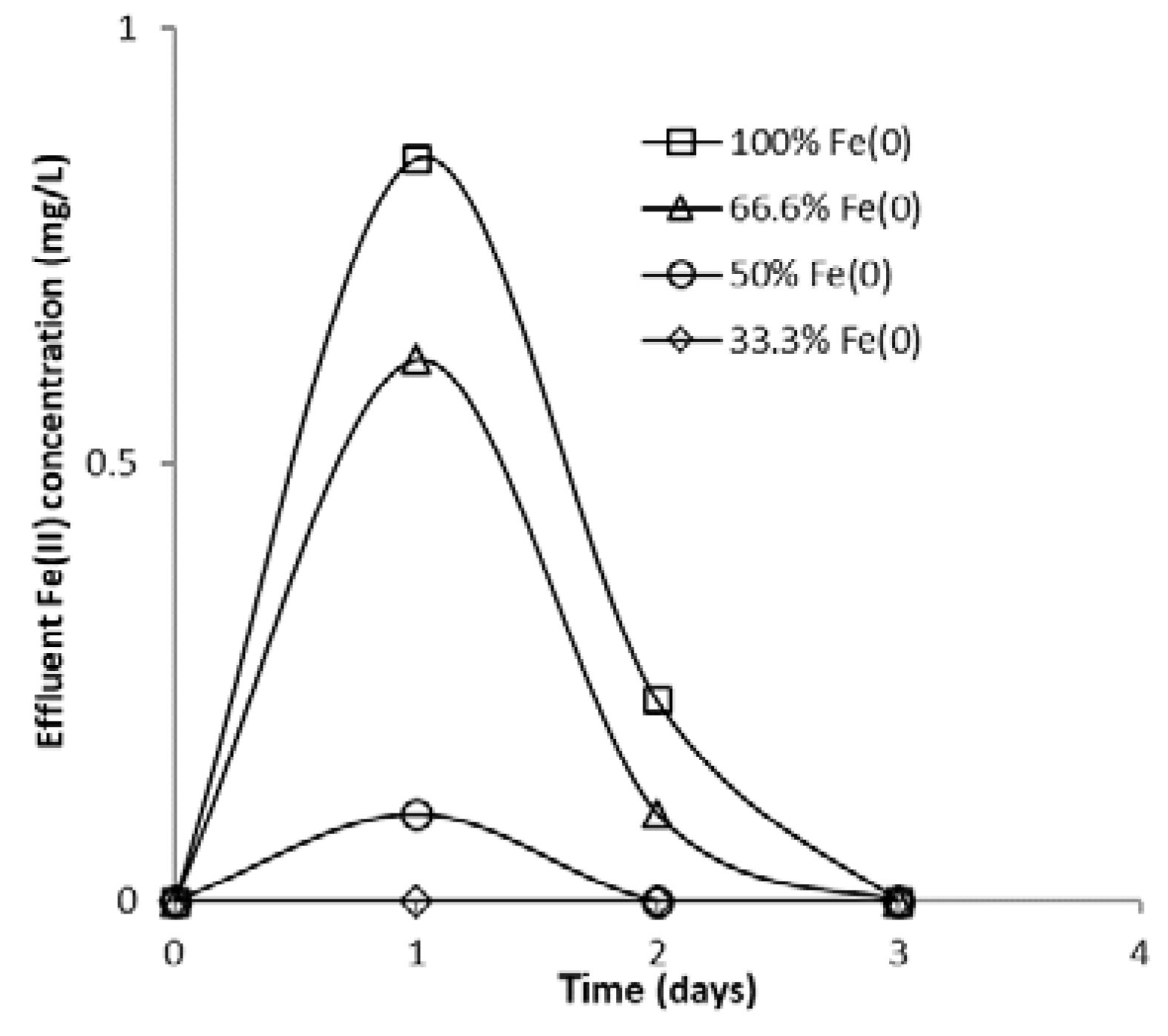
The presence of CrIII, FeIII and FeII in column effluent was investigated in column experiments having fixed Fe0 volume and a variable total reactive zone volume V2. No dissolved FeIII and CrIII was detected in column effluent, regardless of the type of experiment, which suggests that it was all retained inside the column via adsorption and (co-)precipitation. Small amounts of dissolved FeII were determined in column effluent at the beginning of the experiments conducted at pH 6.5; instead, at pH 7.1, no dissolved FeII was found, which suggests that all FeII was retained (precipitated/adsorbed/oxidized to FeIII and precipitated) inside the reactive zone.
The evolution of aqueous FeII concentration in column effluent as a function of elapsed time is presented in Figure 18. A rapid increase in iron concentration was noted during the first days of the experiment, followed by a rapid decrease in the following days. Since the main source of FeII species in column effluent is the Fe0 corrosion process (Equations (1) and (2)), the decrease in FeII concentration with increasing experimental time can be attributed to passivation of the Fe0 surface with solid iron (hydr)oxides, which lowers corrosion rates. Another important conclusion that can be drawn from Figure 18 is that higher FeII concentrations were observed in the effluent of the “Fe0 only” system than in the “Fe0 + sand” system, which is strong evidence of the ability of sand to retain Fe0 corrosion products.
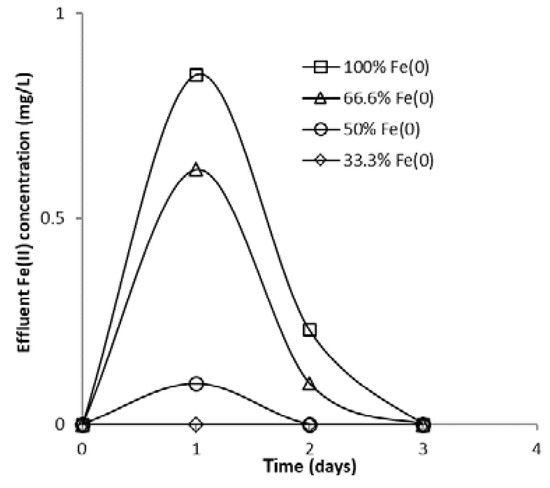
Figure 18.
FeII concentration in column effluent vs. time for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2 at initial pH 6.5.
The faster CrVI breakthrough observed at both pH 7.1 and 6.5 for the “Fe0 + sand” system compared to the “Fe0 only” system can be attributed to scavenging of FeII by sand via adsorption and precipitation processes followed by possible oxidation to FeIII. Section 3.3 shows that the solution pH inside the column was alkaline, which favors adsorption and/or precipitation of FeII at the surface of the sand and its subsequent oxidation to FeIII. This is in accord with results of previous studies reporting that adsorption of dissolved FeII on minerals (sand, iron oxide coated sand, calcite) is enhanced at higher pH, while subsequent oxidation of adsorbed FeII with dissolved O2 is catalyzed by the mineral surface and by the high pH [72,73,74,75]. Thus, it seems that dissolved FeII had the most important role in removal of CrVI (via homogeneous reduction to CrIII) at the beginning of the experiments, while solid FeII/FeIII-bearing secondary minerals were the major CrVI removal agents (via reduction and adsorption) during the second half of the experiments.
4. Conclusions
Non-disturbed batch and column experiments were carried out in this study with the aim of discerning the effect of sand co-presence on the efficiency of CrVI removal in Fe0-H2O system. Batch experiments showed a minor increase in the removal efficiency of CrVI for the “Fe0 + sand” system with the lowest Fe0 volumetric ratio (20%), compared to “Fe0 + sand” systems with higher Fe0 volumetric ratios (50, 80%) and “Fe0 alone” system (100% Fe0). Column experiments revealed that mixing sand with Fe0 in the reactive zone results in shortening the period during which the column operates with no CrVI detected in the effluent. In spite of this fact, column tests confirmed the findings of batch experiments showing that the “Fe0 + sand” system exerted the highest efficiency in the removal of CrVI when the lowest Fe0 volumetric ratio (20% and 33.3% Fe0) was applied. Moreover, column experiments further revealed that the “Fe0 + sand” system with the lowest Fe0 volumetric ratio displayed better CrVI removal efficiency than the “Fe0 alone” system (100% Fe0) at pH 6.5 and similar efficacy at pH 7.1. Thus, the co-presence of sand inside the column reactive zone exerts a positive effect on CrVI removal efficiency, which increases with decreasing pH below neutral. This behavior was ascribed to capacity of the “Fe0 + sand” system to sustain the corrosion process of Fe0 and to generate higher amounts of secondary adsorbents/reductants for CrVI removal. Based on the outcomes of the present study, we suggest that abatement of CrVI water pollution should be conducted using filters having a volumetric ratio Fe0:sand = 1:3. The present result corroborates those of Bilardi et al. [18] and Btatkeu et al. [8] who identified an Fe0 volumetric ratio of 25% as optimal for the removal of cationic pollutants (CuII, NiII, ZnII, methylene blue) in Fe0-H2O system amended with non-expansive additives (sand, pumice).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15040777/s1. Figure S1. SEM micrograph of fresh Fe0 at different magnifications; Figure S2. SEM micrograph of exhausted Fe0 from 100% Fe0 system at different magnifications; Figure S3. SEM micrograph of exhausted Fe0 from 50% Fe0 system at different magnifications; Figure S4. SEM micrograph of exhausted Fe0 from 20% Fe0 system at different magnifications; Figure S5. EDX pattern of fresh Fe0; Figure S6. EDX pattern of exhausted Fe0 from “Fe0 only” system; Figure S7. EDX pattern of exhausted Fe0 from “50% Fe0 + 50% sand” system; Figure S8. EDX pattern of exhausted Fe0 from “20% Fe0 + 80% sand” system; Figure S9. XRD pattern of fresh Fe0; Figure S10. XRD pattern of exhausted Fe0 from 100% Fe0 system; Figure S11. XRD pattern of exhausted Fe0 from 50% Fe0 system; Figure S12. XRD pattern of exhausted Fe0 from 20% Fe0 system; Figure S13. Profiles of CrVI removal efficiencies for non-disturbed batch experiments, after 40 experimental days.; Figure S14. Evolution of CrVI breakthrough at pH 6.5, for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2.; Figure S15. Evolution of CrVI breakthrough at pH 7.1, for columns having fixed Fe0 volume and variable total reactive zone volume V2.; Figure S16. Evolution of CrVI breakthrough, for columns having variable Fe0 volume and fixed total reactive zone volume V2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G. and I.B.; methodology, M.G. and I.B.; software, M.G.; validation, M.G. and I.B.; formal analysis, M.G. and I.B.; investigation, M.G. and I.B.; resources, M.G. and I.B.; data curation, M.G. and I.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.; writing—review and editing, M.G.; visualization, M.G. and I.B.; supervision, M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the four anonymous reviewers from Water, whose insightful comments and suggestions provided on earlier version of this manuscript helped improve and clarify this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mwakabona, H.T.; Nde-Tchoupe, A.I.; Njau, K.N.; Noubactep, C.; Wydra, K.D. Metallic iron for safe drinking water provision: Considering a lost knowledge. Water Res. 2017, 117, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubactep, C. Metallic iron for environmental remediation: A review of reviews. Water Res. 2015, 85, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Guan, X. The influences of iron characteristics, operating conditions and solution chemistry on contaminants removal by zero-valent iron: A review. Water Res. 2016, 100, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Cui, X.; Gwenzi, W.; Wu, S.; Noubactep, C. Fe0/H2O systems for environmental remediation: The scientific history and future research directions. Water 2018, 10, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 94–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E.; Harms, S.; Milburn, R.; Sprah, G.; Nadarajah, N. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride in the presence of iron and sulphur containing compounds. Chemosphere 1994, 29, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaf, K.V.K.; Ambika, S.; Nambi, I.M. Performance enhancement of zero valent iron based systems using depassivators: Optimization and kinetic mechanisms. Water Res. 2016, 102, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Btatkeu-K, B.D.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Tchatchueng, J.B.; Noubactep, C.; Caré, S. Determining the optimum Fe0 ratio for sustainable granular Fe0/sand water filters. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Lo, I.M.C.; He, D.; Dong, H. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 75, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaffari, M.G.; Bilardi, S.; Calabro, P.S.; Moraci, N. Nickel removal by zero valent iron/lapillus mixtures in column systems. Soils Found. 2017, 57, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C.; Care, S.; Togue-Kamga, F.; Schöner, A.; Woafo, P. Extending service life of household water filters by mixing metallic iron with sand. Clean Soil Air Water 2010, 38, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Care, S.; Crane, R.; Calabro, P.S.; Ghauch, A.; Temgoua, E.; Noubactep, C. Modeling the permeability loss of metallic iron water filtration systems. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Yang, H.; Cui, X.; Xiao, M.; Gatcha-Bandjun, N.; Kenmogne-Tchidjo, J.F.; Lufingo, M.; Amoah, B.K.; Tepong-Tsindé, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; et al. The suitability of hybrid Fe0/aggregate filtration systems for water treatment. Water 2022, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, K.; Noubactep, C. Effects of mixing granular iron with sand on the efficiency of methylene blue discoloration. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C. On the suitability of admixing sand to metallic iron for water treatment. Int. J. Environ. Poll. Solut. 2013, 1, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Makota, S.; Nassi, A.; Rui, H.; Noubactep, C. The suitability of pozzolan as admixing aggregate for Fe0-based filters. Water 2018, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hannesin, S.F.; Gillham, R.W. Long-term performance of an in situ “iron wall” for remediation of VOCs. Ground Water 1998, 36, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabro, P.S.; Care, S.; Moraci, N.; Noubactep, C. Improving the sustainability of granular iron/pumice systems for water treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 121, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebelle, T.C.; Makota, S.N.; Tepong-Tsinde, R.; Nassi, A.; Noubactep, C. Metallic iron and the dialogue of the deaf. Fres. Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 8331–8340. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Gwenzi, W.; Sipowo-Tala, V.R.; Noubactep, C. Water treatment using metallic iron: A tutorial review. Processes 2019, 7, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.J.; Kaplan, D.I.; Wietsma, T.W. Zero-valent iron for the in situ remediation of selected metals in groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 42, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jambor, J.L. In-situ remediation of chromate contaminated groundwater using permeable reactive walls: Laboratory Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melitas, N.; Chufe-Moscoso, O.; Farrell, J. Kinetics of soluble chromium removal from contaminated water by zerovalent iron media: Corrosion inhibition and passive oxide effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3948–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junyapoon, S.; Weerapong, S. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by scrap iron fillings. KMITL Sci. Technol. J. 2006, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gheju, M.; Iovi, A. Kinetics of hexavalent chromium reduction by scrap iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B135, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.E.; Kim, J.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoo, K.Y. Capacity of Cr(VI) reduction in an aqueous solution using different sources of zerovalent irons. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Kinetics of hexavalent chromium reduction by iron metal. Front. Environ. Sci. Engin. China 2008, 2, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wan, H.; Liu, T.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. The effect of different divalent cations on the reduction of hexavalent chromium by zerovalent iron. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Jin, Z.; Li, T.; Qi, X. Kinetics of hexavalent chromium removal from water by chitosan-Fe0 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.V.; Da Silva, L.M.; Jardim, W.F. Chemical reduction of hexavalent chromium and its immobilisation under batch conditions using a slurry reactor. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 203, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Mohammad, S.K.S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chaudhuri, B.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Dutta, B.K. Reduction of hexavalent chromium in aqueous medium with zerovalent iron. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, A.; Silva, A.; Carvalho, G.; de la Fuente, A.V.; Delerue-Matos, C. Heterogeneous kinetics of the reduction of chromium (VI) by elemental iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Cha, D.K.; Oh, Y.K.; Ko, K.B.; Jin, S.H. Wastewater screening method for evaluating applicability of zero-valent iron to industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidokht, L.; Khataee, A.R.; Reyhanitabar, A.; Oustan, S. Reductive removal of Cr(VI) by starch-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Desalination 2011, 270, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, J. Synthesis of agar-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles and removal study of hexavalent chromium. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, H.; Zhang, W.X.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, D.; Guan, X. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by zero-valent iron coupled with weak magnetic field: Role of magnetic gradient force. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mwamulima, T.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Song, S.; Peng, C. Removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using the fly ash-based adsorbent material-supported zero-valent iron. J. Molec. Liq. 2017, 243, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.X. Nanoencapsulation of hexavalent chromium with nanoscale zero-valent iron: High resolution chemical mapping of the passivation layer. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, C. The sequestration of Cr(VI) by zero valent iron under a non-uniform magnetic field: An interfacial dynamic reaction. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Korla fragrant pear peel extracts for the removal of aqueous Cr(VI). Ecol. Eng. 2020, 149, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, K.; Noubactep, C. Characterizing the impact of sand addition on the efficiency of granular iron for contaminant removal in batch systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Hu, R.; Nassi, A.; Noubactep, C.; Licha, T. Characterizing the reactivity of metallic iron for water defluoridation in batch studies. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerhoff, P.; James, J. Nitrate removal in zero-valent iron packed columns. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussam, A. Contending with a development disaster: SONO filters remove arsenic from well water in Bangladesh. Innovations 2009, 4, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.U.; Tinne, W.S.; Al-Amin, M.; Rahanaz, M. Social innovation and SONO filter for drinking water. Soc. Busin. Rev. 2018, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.I.; Gilmore, T.J. Zerovalent iron removal rates of aqueous Cr(VI) measured under flow conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 155, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheju, M.; Balcu, I. Sustaining the efficiency of the Fe(0)/H2O system for Cr(VI) removal by MnO2 amendment. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flury, B.; Eggenberger, U.; Mader, U. First results of operating and monitoring an innovative design of a permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of chromate contaminated groundwater. J. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Saitoh, O.; Numabe, A. Estimation of long-term changes in Cr(VI) concentration in public water after countermeasures against water pollution. J. Japan Soc. Water Environ. 2004, 27, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. 3500-Cr B; Colorimetric method. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Rice, E.W., Greenberg, A.E., Franson, M.A.H., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 3.67–3.68. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. 3500-Fe B; Phenantroline method. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Rice, E.W., Greenberg, A.E., Franson, M.A.H., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 3.77–3.78. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Hua, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zou, J.; Tian, G.; Fu, H. Carbothermal synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon-supported nano zero-valent iron with enhanced stability and activity for hexavalent chromium reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papassiopi, N.; Vaxevanidou, K.; Christou, C.; Karagianni, E.; Antipas, G.S.E. Synthesis, characterization and stability of Cr(III) and Fe(III)hydroxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheju, M. Decontamination of hexavalent chromium-polluted waters: Significance of metallic iron technology. In Enhancing Cleanup of Environmental Pollutants. Non Biological Approaches; Anjum, N., Gill, S., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 209–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabro, P.S.; Care, S.; Moraci, N.; Noubactep, C. Effect of pumice and sand on the sustainability of granular iron beds for the aqueous removal of CuII, NiII, and ZnII. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatcha-Bandjun, N.; Noubactep, C.; Loura, B.B. Mitigation of contamination in effluents by metallic iron: The role of iron corrosion products. Environ. Technol. Innovat. 2017, 8, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domga, R.; Togue-Kamga, F.; Noubactep, C.; Tchatchueng, J.B. Discussing porosity loss of Fe0 packed water filters at ground level. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C.; Care, S. Dimensioning metallic iron beds for efficient contaminant removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Hug, S.J. Kinetics and pH dependence of chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.E.; Li, G. Kinetics of chromate reduction by ferrous iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlautman, M.A.; Han, I. Effects of pH and dissolved oxygen on the reduction of hexavalent chromium by dissolved ferrous iron in poorly buffered aqueous systems. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eary, L.E.; Rai, D. Chromate removal from aqueous wastes by reduction with ferrous iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1988, 22, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu-Amoah, B.; Hu, R.; Nde-Tchoupe, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Metallic iron (Fe0)-based materials for aqueous phosphate removal: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdous, R.; Devlin, J.F. Visualizations and optimization of iron-sand mixtures for permeable reactive barriers. Ground Water Monit. Remed. 2015, 35, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Song, H.; Shin, W.S.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, Y.H. Effect of amorphous silica and silica sand on removal of chromium(VI) by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.F.; Paterson, M.L. Reduction of aqueous transition metal species on the surface of Fe(II)-containing oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1996, 60, 3799–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, E.J.; Lee, S.; Rudolph, J.; Xu, H.; Ginder-Vogel, M. The reactivity of Fe(II) associated with goethite formed during short redox cycles toward Cr(VI) reduction under oxic conditions. Chem. Geol. 2017, 464, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Hug, S.J. Influence of mineral surfaces on chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; Joe-Wong, C.; Maher, K. Cr(VI) reduction by Fe(II) sorbed to silica surfaces. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Gwenzi, W.; Pengou, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Noubactep, C. Fe0/H2O Filtration systems for decentralized safe drinking water: Where to from here? Water 2019, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hu, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Metallic iron for water remediation: Plenty of room for collaboration and convergence to advance the science. Water 2022, 14, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.W.; Huang, C.P.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, C.P.; Chen, H.T. Effect of pH on the oxidation of ferrous ion and immobilization technology of iron hydr(oxide) in fluidized bed reactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Greetham, M.R.; Schippers, J.C. Adsorption of iron(II) onto fillter media. J. Water SRT-Aqua. 1999, 48, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Buamah, R.; Petrusevski, B.; Schippers, J.C. Oxidation of adsorbed ferrous iron: Kinetics and influence of process conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, S.; Wolthers, M.; Charlet, L.; von Gunten, U. Sorption and catalytic oxidation of Fe(II) at the surface of calcite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).