Interlinkages of Water-Related SDG Indicators Globally and in Low-Income Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
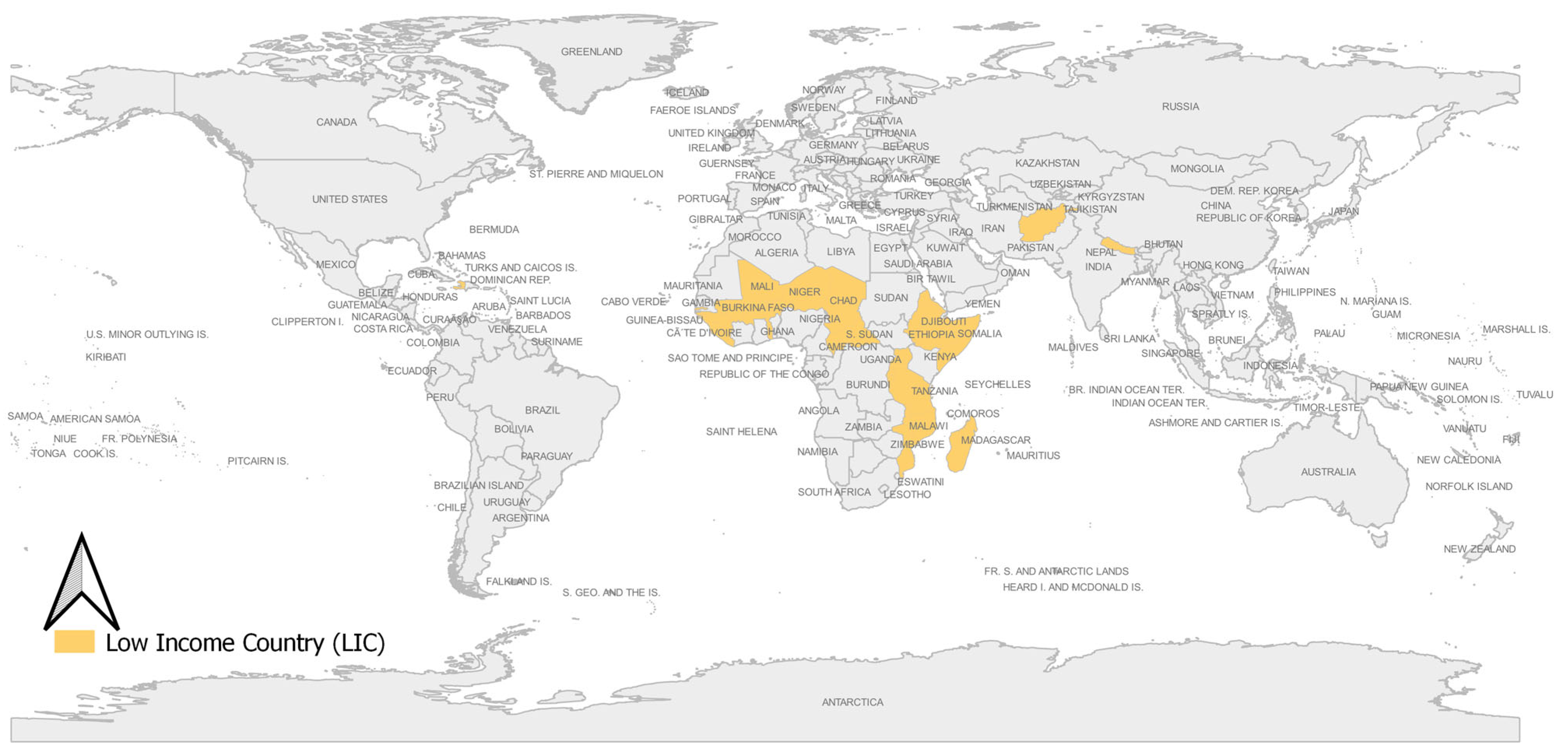
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Extracting Synergies and Trade-Offs through Statistical Logic: Spearman’s Rank Correlation (ρ)
2.3.2. Identifying Influential Variables: Magnitude of the Standardized Coefficient (Beta) in the Multiple Linear Regression
3. Results
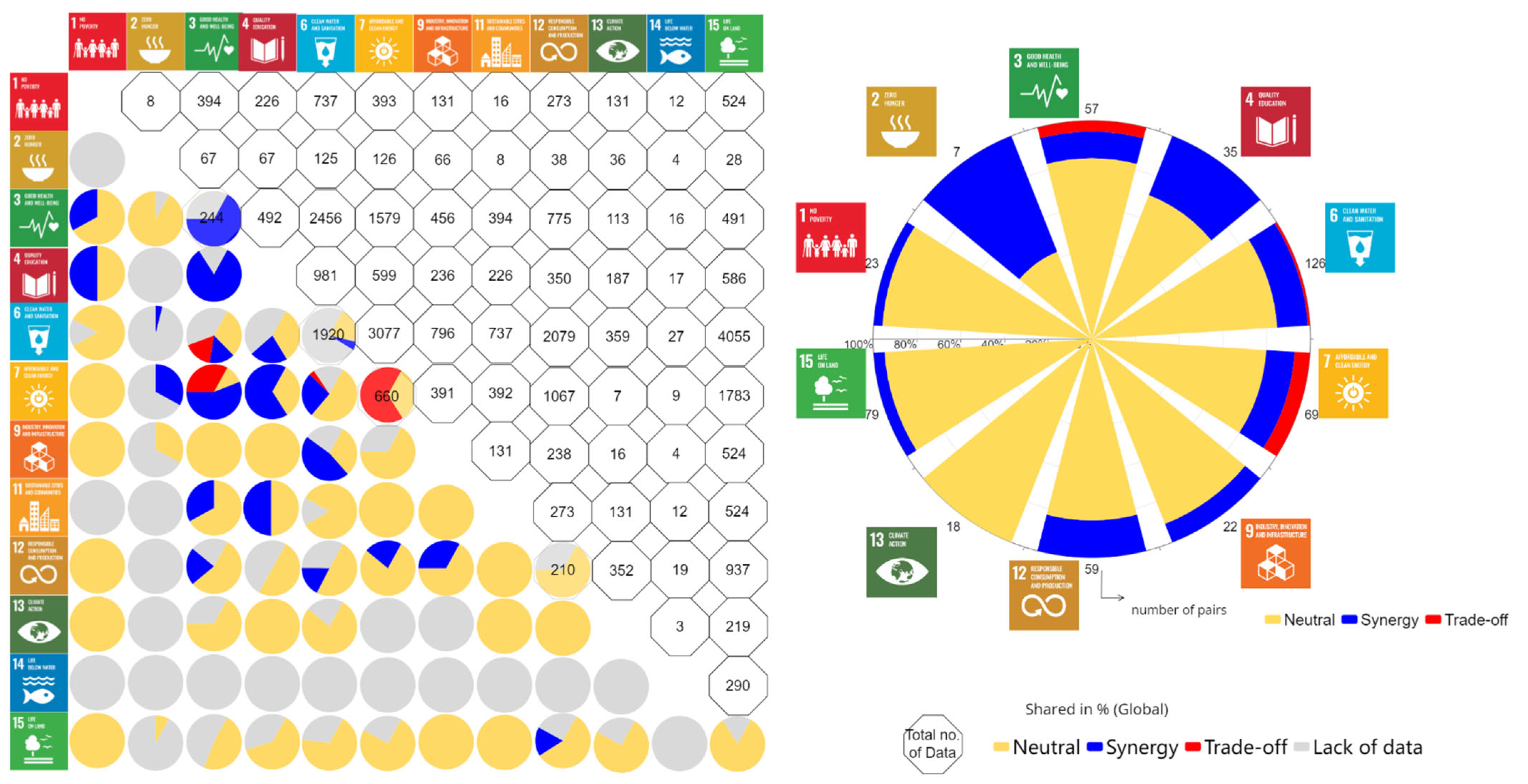
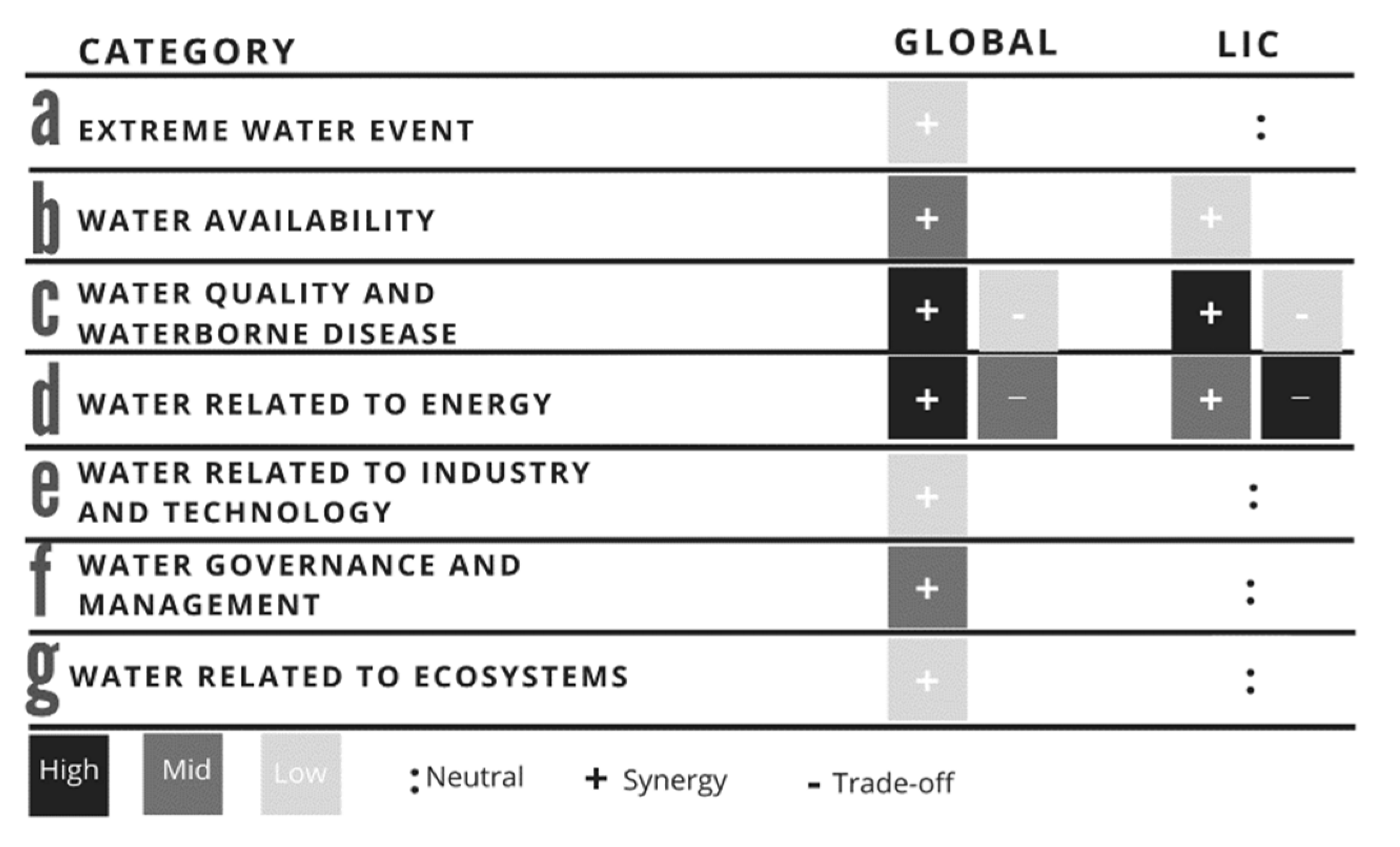
3.1. Interlinkages between Water-Related SDG Indicators in Global
3.1.1. Water Facilities in Schools
3.1.2. Health and Water
3.1.3. Energy- and Water-Related SDG Nexus
3.1.4. Research Development and Waste Treatment
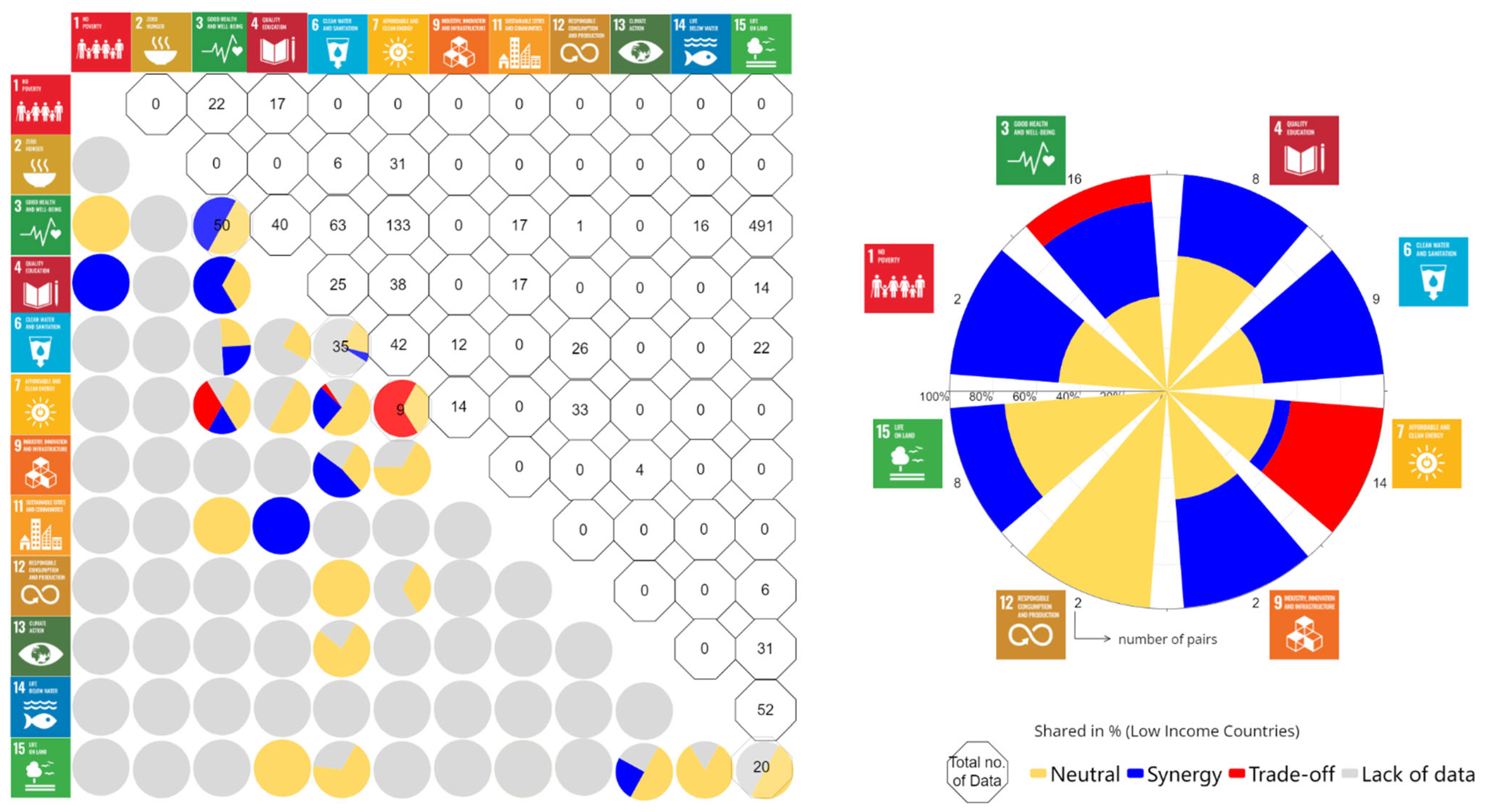
3.2. Interlinkages between Water-Related SDG Indicators in Low-Income Countries (LIC)
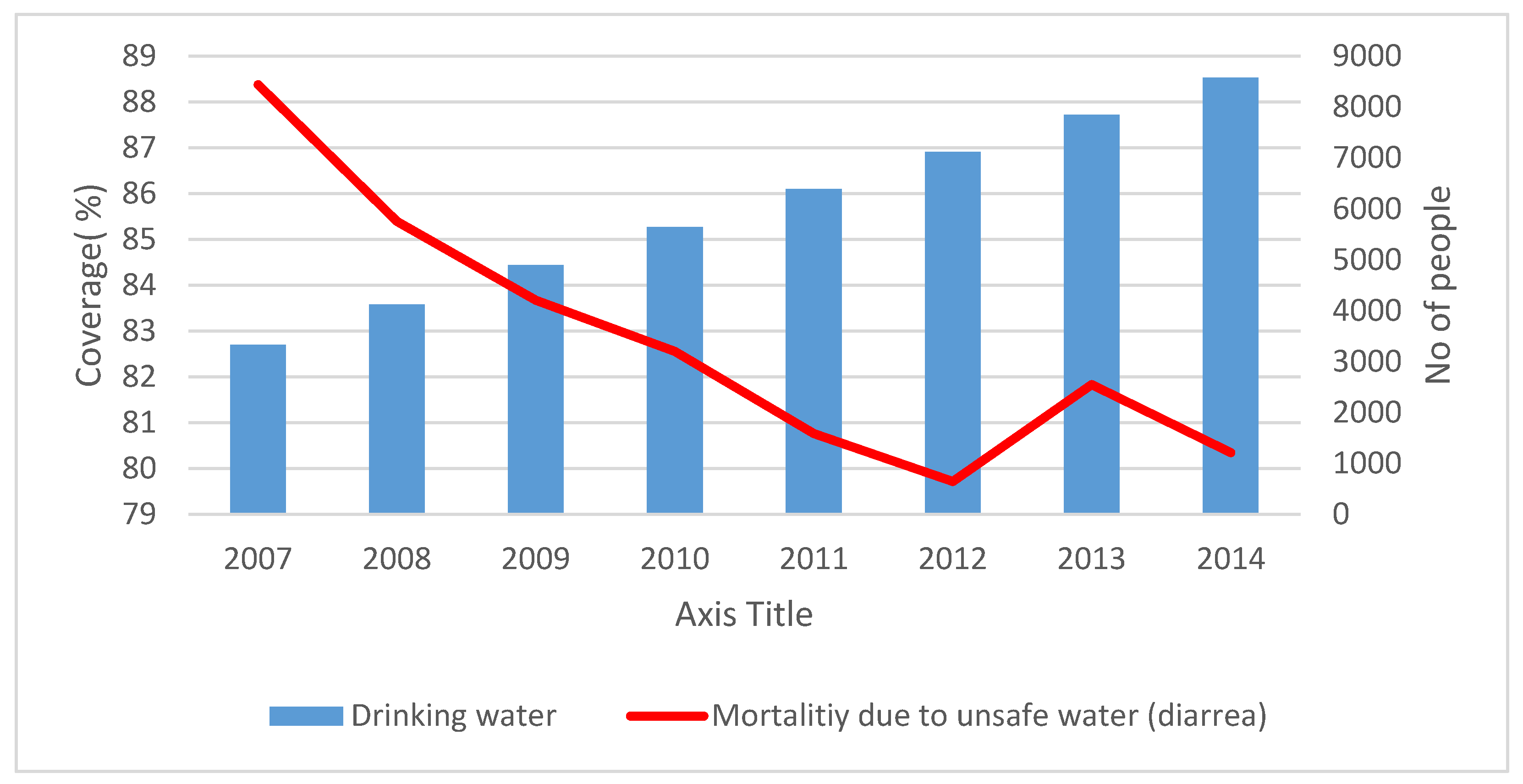
3.3. Mortality Due to Unsafe Water and Sanitation in Low-Income Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Priority Keys in Water-Related SDGs
4.2. Future Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO; UNICEF. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017. 2017, pp. 1–6. Available online: https://washdata.org/sites/default/files/documents/reports/2018-01/JMP-2017-report-final-highlights.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Cronk, R.; Guo, A.; Fleming, L.; Bartram, J. Factors associated with water quality, sanitation, and hygiene in rural schools in 14 low- and middle-income countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, H. Clean Water and Sanitation. Our World Data. 2021. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/clean-water-sanitation (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Nilsson, M.; Griggs, D.; Visbeck, M. Policy: Map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 2016, 534, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J.P. A Systematic Study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth’s Futur. 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali Swain, R.; Ranganathan, S. Modeling interlinkages between sustainable development goals using network analysis. World Dev. 2021, 138, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippidis, G.; Shutes, L.; M’Barek, R.; Ronzon, T.; Tabeau, A.; van Meijl, H. Snakes and ladders: World development pathways’ synergies and trade-offs through the lens of the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimba, A. Global investigation of synergy and trade-off between water-related SDG indicators. In Proceedings of the Hydrological and Water Resources Society/Japan Hydrological Science Society, Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 September 2021; Volume 34, p. 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flörke, M.; Bärlund, I.; van Vliet, M.T.; Bouwman, A.F.; Wada, Y. Analysing trade-offs between SDGs related to water quality using salinity as a marker. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P.; Kropp, J.P. Variations in sustainable development goal interactions: Population, regional, and income disaggregation. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, G.; Chapagain, S.K.; Fukushi, K.; Papong, S.; Sudarma, I.M.; Rimba, A.B.; Osawa, T. An extended Input-Output framework for evaluating industrial sectors and provincial-level water consumption in Indonesia. Water Resour. Ind. 2021, 25, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, S.K.; Mohan, G.; Rimba, A.B.; Payus, C.; Sudarma, I.M.; Fukushi, K. Analyzing the relationship between water pollution and economic activity for a more effective pollution control policy in Bali Province, Indonesia. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2022, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, E.L.F.; Revi, B.L.A.; Preston, E.R.; Carr, S.H.; Eriksen, L.R.; Fernandez-Carril, B.; Glavovic, N.J.M.; Hilmi, D.; Ley, R.; Mukerji, M.S.; et al. Climate Resilient Development Pathways. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; H.-O. Pörtner, D.C., Roberts, M., Tignor, E.S., Poloczanska, K., Mintenbeck, A., Alegría, M., Craig, S., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, V., Möller, A., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2655–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WorldBank. The World by Income and Regionitle. The World Bank. 2020. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/the-world-by-income-and-region.html (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Baah-Kumi, B.; Ward, F.A. Poverty mitigation through optimized water development and use: Insights from the Volta Basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanya, S.; Stifel, D. Viewpoint: Water, agriculture & poverty in an era of climate change: Why do we know so little? Food Policy 2020, 93, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonj, C.; Githinji, S.; Kistemann, T. The impact of water on health and ill-health in a sub-Saharan African wetland: Exploring both sides of the coin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.T.; Oduor, C.; Nyothach, E.; Laserson, K.F.; Amek, N.; Eleveld, A.; Mason, L.; Rheingans, R.; Beynon, C.; Mohammed, A.; et al. Water, sanitation and hygiene conditions in kenyan rural schools: Are schools meeting the needs of menstruating girls? Water 2014, 6, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, A.; Anadon, L.D. The water-energy nexus in Middle East and North Africa. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4529–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, P.; Adapa, L.M.; Buisman, C. How can innovation theories be applied to water technology innovation? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, I.B.; Beleño de Oliveira, A.K.; Marques, L.S.; Quintanilha Barbosa, A.A.; Veról, A.P.; Magalhães, P.C.; Miguez, M.G. A framework to support flood prevention and mitigation in the landscape and urban planning process regarding water dynamics. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 122983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, Q.; Khan, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Urban water resource management for sustainable environment planning using artificial intelligence techniques. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalkhali, M.; Dilkina, B.; Mo, W. The role of climate change and decentralization in urban water services: A dynamic energy-water nexus analysis. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, A.B.; Mohan, G.; Chapagain, S.K.; Arumansawang, A.; Payus, C.; Fukushi, K.; Osawa, T.; Avtar, R. Impact of population growth and land use and land cover (LULC) changes on water quality in tourism-dependent economies using a geographically weighted regression approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25920–25938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Perera, D.; Glickman, T.; Taing, L. Water-related disasters and their health impacts: A global review. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 8, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Tanoue, M.; Sasaki, O.; Zhou, X.; Yamazaki, D. Global exposure to flooding from the new CMIP6 climate model projections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Lei, Y.; Yao, H.; Ge, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, L. Estimation and influencing factors of agricultural water efficiency in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noordwijk, M.; Duguma, L.A.; Dewi, S.; Leimona, B.; Catacutan, D.C.; Lusiana, B.; Öborn, I.; Hairiah, K.; Minang, P.A. SDG synergy between agriculture and forestry in the food, energy, water and income nexus: Reinventing agroforestry? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 34, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P. Achieving sustainable development goals in agricultural energy-water-food nexus system: An integrated inexact multi-objective optimization approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonj, C.; Githinji, S.; Höser, C.; Stein, A.; Blanford, J.; Grossi, V. Kenyan school book knowledge for water, sanitation, hygiene and health education interventions: Disconnect, integration or opportunities? Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 235, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayo, F.K.; Nakamura, K.; Al-Sobaihi, S.; Seino, K. Is the source of domestic water associated with the risk of malaria infection? Spatial variability and a mixed-effects multilevel analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagidede, P.; Alagidede, A.N. The public health effects of water and sanitation in selected West African countries. Public Health 2016, 130, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwire, G.; Sack, D.A.; Kagirita, A.; Obala, T.; Debes, A.K.; Ram, M.; Komakech, H.; George, C.M.; Orach, C.G. The quality of drinking and domestic water from the surface water sources (lakes, rivers, irrigation canals and ponds) and springs in cholera prone communities of Uganda: An analysis of vital physicochemical parameters. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.; Bowling, M.; Bartram, J.; Lyn Kayser, G. Water, sanitation, and hygiene in schools: Status and implications of low coverage in Ethiopia, Kenya, Mozambique, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zambia. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.C.; Graziele, I.; Marques, R.C.; Gonçalves, J. Investment in drinking water and sanitation infrastructure and its impact on waterborne diseases dissemination: The Brazilian case. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, D.M.; Martín Martín, J.M.; Guaita Martínez, J.M.; Morales Pachón, A. Analyzing the real size of the tourism industry on the basis of an assessment of water consumption patterns. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremillion, P.; Avellán, T. Wastewater As a Resource: The Water-Waste-Energy Nexus in Sub-Saharan Africa; Institute for Integrated Management of Material Fluxes and of Resources, UNU-FLORES: Dresden, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–4. Available online: http://collections.unu.edu/eserv/UNU:5768/PolicyBrief2016_No1.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Aboelnga, H.T.; El-Naser, H.; Ribbe, L.; Frechen, F.B. Assessing water security in water-scarce cities: Applying the integrated urban water security index (IUWSI) in Madaba, Jordan. Water 2020, 12, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarda-Mallorquí, A.; Garcia, X.; Ribas, A. Mass tourism and water efficiency in the hotel industry: A case study. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 61, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanham, D.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Wada, Y.; Bouraoui, F.; de Roo, A.; Mekonnen, M.M.; van de Bund, W.J.; Batelaan, O.; Pavelic, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; et al. Physical water scarcity metrics for monitoring progress towards SDG target 6.4: An evaluation of indicator 6.4.2 “Level of water stress”. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Dong, J.; Menarguez, M.A.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Hooker, K.V.; David Hambright, K. Continued decrease of open surface water body area in Oklahoma during 1984–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, D.M.G.; Martín, J.M.M.; Martínez, J.M.G.; Sáez-Fernández, F.J. An analysis of the cost of water supply linked to the tourism industry. An application to the case of the Island of Ibiza in Spain. Water 2020, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgegren, I.; McConville, J.; Landaeta, G.; Rauch, S. A multiple regime analysis of the water and sanitation sectors in the Kanata metropolitan region, Bolivia. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, A.; Scandurra, G.; Thomas, A. Factors affecting official development assistance distribution. A panel investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 126970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, C.K.; Locke, M.; Fraga, J.P.R.; Beleño de Oliveira, A.K.; Veról, A.P.; Canedo de Magalhães, P.; Miguez, M.G. Integrated water resouce management as a development driver—Prospecting a sanitation improvement cycle for the greater Rio de Janeiro using the city blueprint approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzabosco, A.; Kenway, S.J.; Conrad, S.A.; Lant, P.A. Renewable electricity generation in the Australian water industry: Lessons learned and challenges for the future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkar, G.A.; Mahalingam, A.; Deep, A.; Thillairajan, A. Impact of Private Sector Participation on access and quality in provision of electricity, telecom and water services in developing countries: A systematic review. Util. Policy 2013, 27, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, I.; Smith, K.R. Towards safe drinking water and clean cooking for all. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e361–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, U.; Sadiqa, A.; Gulagi, A.; Breyer, C. Irrigation efficiency and renewable energy powered desalination as key components of Pakistan’s water management strategy. Smart Energy 2021, 4, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Beane, G.; Garriga, R.G.; Avello, P.; Ellis, L.; Fisher, S.; Leten, J.; Ruiz-Apilánez, I.; Shouler, M.; Ward, R.; et al. City Water Resilience Framework: A governance based planning tool to enhance urban water resilience. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 77, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Malik, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Ali, N.; Malik, S.; Bilal, M. Environmental impacts of hazardous waste, and management strategies to reconcile circular economy and eco-sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.; Lu, C.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; Zhou, B. Characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in water and sediment surrounding two e-waste dismantling regions in Taizhou, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, H.S.; Turley, C. Chapter 13—Ocean acidification and climate change. In Climate Change, 3rd ed.; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherland, 2021; pp. 251–279. [Google Scholar]
- Piaggio, M.; Siikamäki, J. The value of forest water purification ecosystem services in Costa Rica. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo, E.; Acosta-González, G.; Ortega-Camacho, D.; Ventura-Sanchez, K. Water quality in natural protected areas in Cancun, Mexico: A historic perspective for decision makers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 48, 102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haaren, B.; Andreoli, R.; Dumas, P.; Lille, D.; Géraux, H. Characterizing forest ecosystem services degradation within water catchments. An application to a South West Pacific tropical and semi-arid island (New Caledonia). Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Complementary effects of surface water and groundwater on soil moisture dynamics in a degraded coastal floodplain forest. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Iwata, T. Effects of forest growth in different vegetation communities on forest catchment water balance. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 809, 151159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breman, J.G.; Egan, A.; Keusch, G.T. Introduction and summary: The intolerable burden of malaria: A new look at the numbers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 64, iv–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, A.F. Chapter 12—Multiple Regression: Predicting One Variable From Several Others, 7th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, Netherland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, E.L.; Daly, J.G.; Lee, R.M.; Mozaffarian, R.S.; Walsh, K.; Carter, J.; Gortmaker, S.L. Providing students with adequate school drinking water access in an era of aging infrastructure: A mixed methods investigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Smedley, P.L. Groundwater geochemistry and health: An overview. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1996, 113, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosec, K. The child health implications of privatizing africa’s urban water supply. J. Health Econ. 2014, 35, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, E.; Oberholster, P.J. Using heavy metal pollution indices to assess water quality of surface and groundwater on catchment levels in South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 182, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Abel, N.; Taylor, M.B. The use of quantitative microbial risk assessment to estimate the health risk from viral water exposures in sub-Saharan Africa: A review. Microb. Risk Anal. 2018, 8, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A.; Nahar, A.; Hosenuzzaman, M. Global renewable energy-based electricity generation and smart grid system for energy security. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 197136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Economic and social council. Int. Organ. 2020, 16, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neto, G.C.; de Jesus Cardoso Correia, A.; Schroeder, A.M. Economic and environmental assessment of recycling and reuse of electronic waste: Multiple case studies in Brazil and Switzerland. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management. Washington, DC, USA. 2012. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/302341468126264791/pdf/68135-REVISED-What-a-Waste-2012-Final-updated.pdf%0Ahttp://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1458457 (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- PACE. A New Circular Vision for Electronics Time for a Global Reboot. Geneva. 2019. Available online: www.weforum.org (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Monteiro, R.J.R.; Lopes, C.B.; Rocha, L.S.; Coelho, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Sustainable approach for recycling seafood wastes for the removal of priority hazardous substances (Hg and Cd) from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payus, C.M.; Refdin, M.A.; Zahari, N.Z.; Rimba, A.B.; Geetha, M.; Saroj, C.; Gasparatos, A.; Fukushi, K.; Alvin Oliver, P. Durian husk wastes as low-cost adsorbent for physical pollutants removal: Groundwater supply. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 42, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.T.; Adhitya, A.; Srinivasan, R. Sustainability trends in the process industries: A text mining-based analysis. Comput. Ind. 2014, 65, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Biggs, R.; Norström, A.V.; Reyers, B.; Rockström, J. Social-ecological resilience and biosphere-based sustainability science. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L. Sustainable Development in the Netherlands-Building blocls for Environmental Policy for 2030; The Hague: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntouda, J.; Sikodf, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Abba, I. Access to drinking water and health of populations in Sub-Saharan Africa. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2013, 336, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Wolf, J.; Bartram, J.; Clasen, T.; Cumming, O.; Freeman, M.C.; Gordon, B.; Hunter, P.R.; Medlicott, K.; Johnston, R. Burden of disease from inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene for selected adverse health outcomes: An updated analysis with a focus on low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbo, A.; Castro Delgado, R.; Arcos González, P. Water sanitation and hygiene in Sub-Saharan Africa: Coverage, risks of diarrheal diseases, and urbanization. J. Biosaf. Biosecurity 2021, 3, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Miller-Petrie, M.K.; Lindstedt, P.A.; Baumann, M.M.; Johnson, K.B.; Blacker, B.F.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Mapping geographical inequalities in access to drinking water and sanitation facilities in low-income and middle-income countries, 2000–2017. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1162–e1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayemba, D. A Look at Africa’s Largest Dams. 2021. Available online: https://constructionreviewonline.com/biggest-projects/africas-largest-dams/ (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Keiser, J.; De Castro, M.C.; Maltese, M.F.; Bos, R.; Tanner, M.; Singer, B.H.; Utzinger, J. Effect of irrigation and large dams on the burden of malaria on a global and regional scale. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharoy, S.S.; Pittluck, R.; Clasen, T. Review of drivers and barriers of water and sanitation policies for urban informal settlements in low-income and middle-income countries. Util. Policy 2019, 60, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.C.; Denich, M.; Warchold, A.; Kropp, J.P.; Pradhan, P. A systems model of SDG target influence on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 17, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, C.; Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Are we successful in turning trade-offs into synergies? Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Shrestha, S.; Yokomichi, H.; Nishida, K. Relationship between diarrhoea risk and the combinations of drinking water sources in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Int. Health 2021, 14, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, M. Mental and physical health impacts of water/sanitation infrastructure in First Nations communities in Canada: An analysis of the Regional Health Survey. World Dev. 2021, 145, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelberger, L.; Dev, S.; Howe, T.; Barnes, D.L.; Bortz, E.; Briggs, B.R.; Cochran, P.; Dotson, A.D.; Drown, D.M.; Hahn, M.B.; et al. Implications of inadequate water and sanitation infrastructure for community spread of COVID-19 in remote Alaskan communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, S.B.; Morssink, C.; Campos, P.A. Safe access to safe water in low income countries: Water fetching in current times. Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 72, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rimba, A.B.; Atmaja, T.; Mohan, G.; Chapagain, S.K.; Andi, A.; Payus, C.; Fukushi, K. Identifying Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Change from 2000 to 2025 driven by tourism growth: A study case in Bali. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, A.B.; Chapagain, S.K.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K.; Mohan, G. Investigating Water Sustainability and Land Use/Land Cover Change (LULC) As the Impact Of Tourism Activity In Bali, Indonesia. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 6531–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, A.B.; Setiawati, M.; Sambah, A.; Miura, F. Physical Flood Vulnerability Mapping Applying Geospatial Techniques in Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. Urban Sci. 2017, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, A.B.; Miura, F. Evaluating the Extraction Approaches of Flood Extended Area by Using ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 Images as a Rapid Response to Flood Disaster. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 05, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayu, T.; Kim, H.; Oki, T. Water Governance Contribution to Water and Sanitation Access Equality in Developing Countries. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global flood risk under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoue, M.; Taguchi, R.; Alifu, H.; Hirabayashi, Y. Residual flood damage under intensive adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Forests and Water Book: Forests and Water Valuation and Payments for Forest Ecosystem Services; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Z.; Hanasaki, N.; Heck, V.; Hasegawa, T.; Fujimori, S. Global bioenergy with carbon capture and storage potential is largely constrained by sustainable irrigation. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Indicator | Description | Category | References | UN Data Trend (P = Positive/N = Negative) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5.1 | Number of deaths and missing persons | A | [25,26] | N |
| 2 | 2.3.1 | Production per labor unit by classes of farming/pastoral/forestry sectors farming/pastoral/forestry enterprise | B | [27] | P |
| 3 | 2.3.2 | Average income of small-scale food producers | B | [28] | N |
| 4 | 2.4.1 | Agricultural area under productive and sustainable agriculture | B | [29] | No data |
| 5 | 3.3.3 | Malaria | C | [30,31] | N |
| 6 | 3.3.5 | Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases | C | [32] | N |
| 7 | 3.9.2 | Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene | C | [33] | N |
| 8 | 4.a.1a | Schools with drinking water | B, C | [2] | P |
| 9 | 4.a.1b | Schools with basic handwashing | B, C | [34] | P |
| 10 | 6.1.1 | Population with safe drinking water | C | [35,36] | P |
| 11 | 6.3.1 | Proportion of wastewater safely treated | C, G | [37] | P |
| 12 | 6.3.2 | Proportion of water bodies with good ambient water quality | C | [38] | P |
| 13 | 6.4.1 | Change in water-use efficiency over time | B, F | [36,39] | P |
| 14 | 6.4.2 | Water stress level: proportion of water withdrawal and freshwater | B, F | [40] | P |
| 15 | 6.6.1a | Nationally derived extent of open water bodies | B, F | [41,42] | N |
| 16 | 6.6.1b | Water body extent | B, F | [41] | N |
| 17 | 6.a.1 | Amount of water- and sanitation-related official development assistance | C, F | [43,44] | P |
| 18 | 6.b.1 | Communities with water and sanitation management supported by government | F | [45] | P |
| 19 | 7.1.1 | Proportion of population with access to electricity | D | [46,47] | P |
| 20 | 7.1.2 | Proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology | D | [48] | P |
| 21 | 7.2.1 | Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption | D | [49] | N |
| 22 | 9.5.1 | Research and development | E | [20] | P |
| 23 | 11.3.2 | Cities with a direct participation structure of civil society in urban planning | F | [50] | No data |
| 24 | 11.5.1 | Number of deaths and missing persons | A | [25,26] | N |
| 25 | 12.2.2 | Domestic material consumption | B, E | [11] | P |
| 26 | 12.4.2a | Hazardous waste treated or disposed (%) | C, G | [51] | P |
| 27 | 12.4.2b | Electronic waste recycling (%) | C, G | [52] | P |
| 28 | 13.1.2 | Number of deaths and missing persons | A | [25,26] | N |
| 29 | 14.3.1 | Average marine acidity (pH) (agreed suite of representative sampling stations) | G | [53] | P |
| 30 | 15.1.1 | Forest area as a proportion of total land area | G | [54] | N |
| 31 | 15.1.2 | Terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity in protected areas | G | [55] | P |
| 32 | 15.3.1 | Degraded land over total land area | G | [56,57] | P |
| 33 | 15.5.1 | Red List index | G | [58] | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rimba, A.B.; Hirabayashi, Y. Interlinkages of Water-Related SDG Indicators Globally and in Low-Income Countries. Water 2023, 15, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040613
Rimba AB, Hirabayashi Y. Interlinkages of Water-Related SDG Indicators Globally and in Low-Income Countries. Water. 2023; 15(4):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040613
Chicago/Turabian StyleRimba, Andi Besse, and Yukiko Hirabayashi. 2023. "Interlinkages of Water-Related SDG Indicators Globally and in Low-Income Countries" Water 15, no. 4: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040613






