Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in a Semi-Arid Basin of the Brazilian Savanna under Different Land Use, Climate Change, and Conservation Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Mean Annual Sediment Yield in the Basin
2.3. InVEST Sediment Delivery Ratio Model
2.4. Data Sources and Processing
2.4.1. Cover-Management (C) and Support Practice (P) Factors
2.4.2. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
2.4.3. Rainfall Erosivity (R)
2.4.4. Soil Erodibility (K)
2.5. Model Calibration
2.6. Erosion, Sedimentation, and On- and Off-Site Soil Loss Tolerance
2.7. Simulation Scenarios
- Land use Scenarios:
- Conservation Scenarios
- Climate change scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Rating Curve (SRC)
3.2. Model Calibration
3.3. Model Simulation Scenarios
3.3.1. Soil Loss
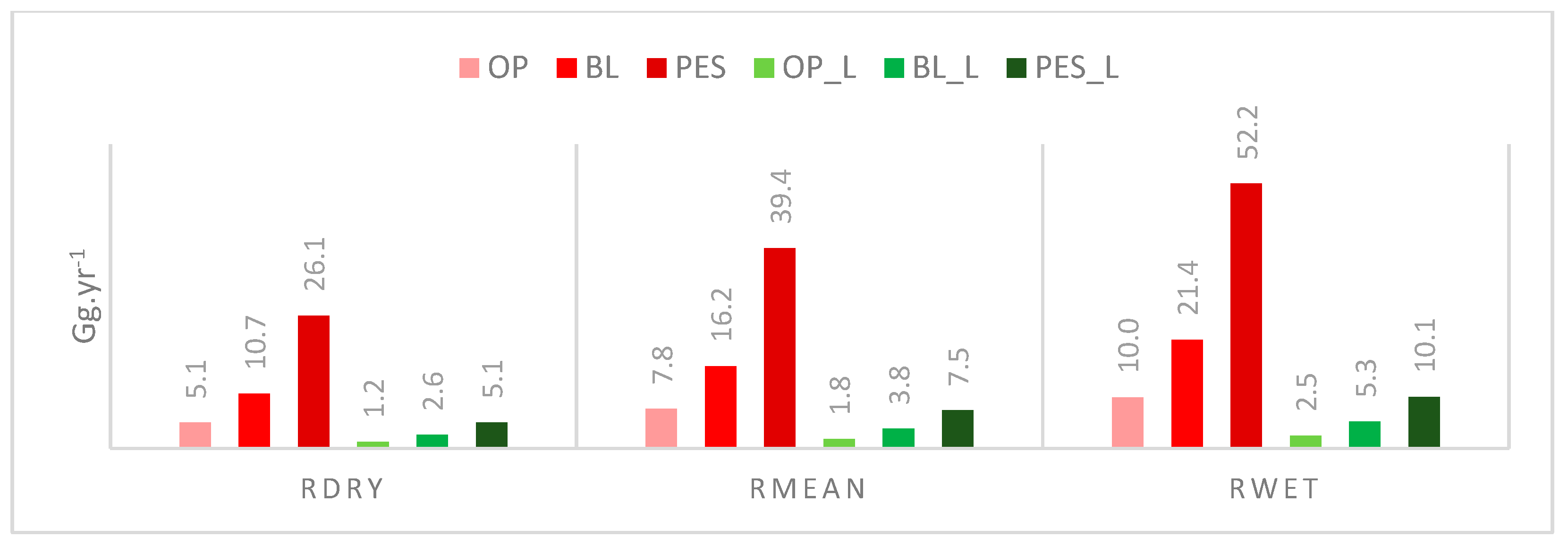
3.3.2. Basin Sediment Yield and Exported Sediment
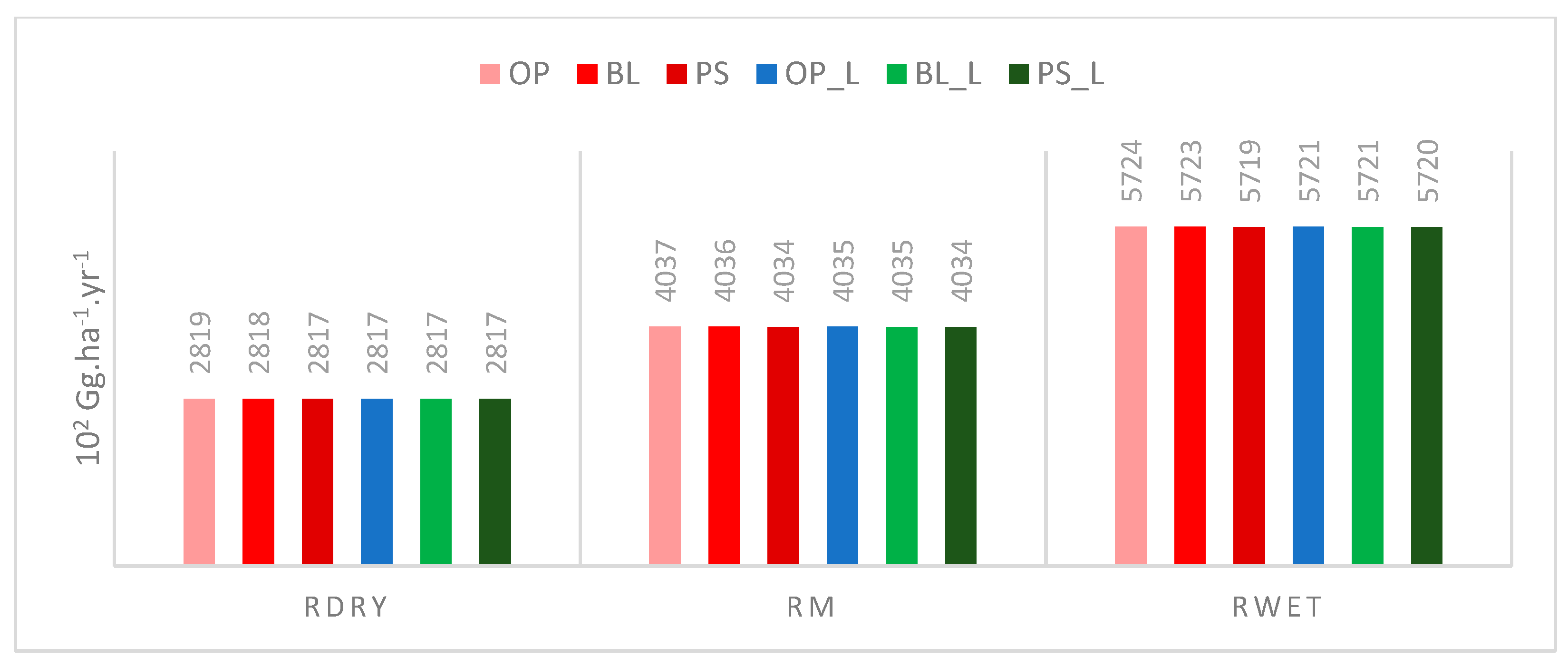
3.3.3. Sediment Retention
3.3.4. Conservation Practices
4. Discussion
4.1. Sediment Rating Curve (SRC)
4.2. Calibration Model
4.3. Soil Loss
4.4. Exported Sediment
4.5. Sediment Retention
4.6. Land Conservation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Healthy Soils Are the Basis for Healthy Food Production; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Montanarella, L. Agricultural Policy: Govern Our Soils. Nature 2015, 528, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, D.P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Global Soil Erosion by Water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmus, M.; Renner, I.; Ullrich, S. Integração de Serviços Ecossistêmicos Ao Planejamento Do Desenvolvimento; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Bonn, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, Challenges and Limitations of Soil Erosion Modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anache, J.A.A.; Wendland, E.C.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Flanagan, D.C.; Nearing, M.A. Runoff and Soil Erosion Plot-Scale Studies under Natural Rainfall: A Meta-Analysis of the Brazilian Experience. Catena 2017, 152, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Simões, S.; Dalla Nora, E.; de Sousa-Neto, E.; Forti, M.; Ometto, J. Agricultural Expansion in the Brazilian Cerrado: Increased Soil and Nutrient Losses and Decreased Agricultural Productivity. Land 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.R.S.; Uagoda, R.; Chaves, H.M.L. Rates, Factors, and Tolerances of Water Erosion in the Cerrado Biome (Brazil): A Meta-analysis of Runoff Plot Data. Earth Surf. Process Land. 2022, 47, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, F.A.; Zolin, C.A.; Paulino, J.; de Souza, A.P.; da Matos, E.S.; de Souza Magalhães, C.A.; de Farias Neto, A.L. Water Erosion on an Oxisol under Integrated Crop-Forest Systems in a Transitional Area between the Amazon and Cerrado Biomes. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perović, V.; Kadović, R.; Djurdjević, V.; Braunović, S.; Čakmak, D.; Mitrović, M.; Pavlović, P. Effects of Changes in Climate and Land Use on Soil Erosion: A Case Study of the Vranjska Valley, Serbia. Reg. Environ. Change 2019, 19, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Cunha, A.P.; Alves, L.M. Variabilidade e Mudanças Climáticas No Semiárido Brasileiro; Instituto Nacional do Semiárido: Campina Grande, Brazil, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Anache, J.A.A.; Flanagan, D.C.; Srivastava, A.; Wendland, E.C. Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Runoff and Soil Erosion at the Hillslope Scale in the Brazilian Cerrado. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Ferreira, V. Unidades de Paisagem Da Bacia Do Rio Jequitinhonha, Em Minas Gerais: Subsídios Para a Gestão de Recursos Hídricos. Caminhos Geogr. 2011, 12, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Sousa, A.A.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Pinto-Correia, T.; Aguilera, P.A.; Barandica, J.M.; Rescia, A.J. A Comparative Analysis of Soil Loss Tolerance and Productivity of the Olive Groves in the Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) Areas Norte Alentejano (Portugal) and Estepa (Andalusia, Spain). Agronomy 2021, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schertz, D.L. The Basis for Soil Loss Tolerances. J. Soil Water Conserv. Jan. 1983, 38, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoni, J.; Neto, F.L. Conservação Do Solo, 9th ed.; Ícone: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, G.A.; Sheshukov, A.; Cruse, R.; Kolar, R.L.; Guertault, L.; Gesch, K.R.; Dutnell, R.C. Reservoir Sedimentation and Upstream Sediment Sources: Perspectives and Future Research Needs on Streambank and Gully Erosion. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.S. Soil Erosion and Conservation, 3rd ed.; National Soil Resources Institute, Cranfield University: Bedford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J. Tolerable versus Actual Soil Erosion Rates in Europe. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 94, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldenhauer, W.C.; Onstad, C.A. Achieving Specified Soil Loss Levels. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1975, 30, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, H.M.L.; Piau, L.P. Efeito Da Variabilidade Da Precipitação Pluvial e Do Uso e Manejo Do Solo Sobre o Escoamento Superficial e o Aporte de Sedimento de Uma Bacia Hidrográfica Do Distrito Federal. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2008, 32, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.R.; Chaves, H.M.L.; Camelo, A.P. Calibração e Validação Da Equação Universal de Perda de Solos Modificada (MUSLE) Utilizando Dados Hidrossedimentológicos Locais. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2011, 35, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrado, M.; Acuña, V.; Ennaanay, D.; Tallis, H.; Sabater, S. Impact of Climate Extremes on Hydrological Ecosystem Services in a Heavily Humanized Mediterranean Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L.; Tye, A.; Obst, C.G. Soil Natural Capital in Europe; a Framework for State and Change Assessment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croke, J.; Nethery, M. Modelling Runoff and Soil Erosion in Logged Forests: Scope and Application of Some Existing Models. Catena 2006, 67, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, H.M.L.; Nearing, M.A. Uncertainty Analysis of the WEPP Soil Erosin Model. Trans. ASAE 1991, 34, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Douglass, J.; Wolny, S.; Arkema, K.; Bernhardt, J.; Bierbower, W.; Chaumont, N.; Denu, D.; Fisher, D.; Glowinski, K.; et al. InVEST 3.11.0. User’s Guide; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Da Cunha, E.R.; Santos, C.A.G.; da Silva, R.M.; Panachuki, E.; de Oliveira, P.T.S.; de Oliveira, N.S.; dos Falcão, K.S. Assessment of Current and Future Land Use/Cover Changes in Soil Erosion in the Rio Da Prata Basin (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Anjinho, P.S.; Barbosa, M.A.G.A.; Mauad, F.F. Evaluation of InVEST’s Water Ecosystem Service Models in a Brazilian Subtropical Basin. Water 2022, 14, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A New Approach to Modeling the Sediment Retention Service (InVEST 3.0): Case Study of the Cape Fear Catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, B.F.; Ribeiro, T.C.L.; Gonçalves, D.A.; de Sousa Júnior, W.C.; Giarolla, A.; Arraut, E.M. Payments for Ecosystem Services to Water Resources Protection in Paraíba Do Sul Environmental Protection Area. Ambiente Soc. 2020, 23, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.I.; Mota da Silva, J.; Ponette-González, A.G.; Silva, M.L.N.; da Rocha, H.R. Modeling the On-Site and off-Site Benefits of Atlantic Forest Conservation in a Brazilian Watershed. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 48, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.I.; Mota da Silva, J.; Silva, M.L.N.; Guimarães, J.L.B.; Sousa Júnior, W.C.; de Figueiredo, R.O.; da Rocha, H.R. Analyzing Ecological Restoration Strategies for Water and Soil Conservation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Valencia, J.; Schmitt, R.; Shrestha, M.; Piman, T.; Sharp, R.P.; Francesconi, W.; Guswa, A.J. Modeling Seasonal Water Yield for Landscape Management: Applications in Peru and Myanmar. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 270, 110792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse, L.M.; Nearing, M.A.; Laflen, J.M.; Nicks, A.D. Error Assessment in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. IBGE Cidades. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- de Carvalho, O.C. Hidrossendimentologia Prática, 2nd ed.; CPRM: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE. IBGE—Informações Ambientais. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/cartas-e-mapas/informacoes-ambientais/15842-biomas.html?edicao=16060&t=acesso-ao-produto (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- IBGE. Semiárido Brasileiro. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/cartas-e-mapas/mapas-regionais/15974-semiarido-brasileiro.html (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Souza, C.M.; Shimbo, J.Z.; Rosa, M.R.; Parente, L.L.; Alencar, A.A.; Rudorff, B.F.T.; Hasenack, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Ferreira, L.G.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; et al. Reconstructing Three Decades of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Brazilian Biomes with Landsat Archive and Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA—Agência Nacional de Águas. Hidroweb: Sistemas de Informações Hidrológicas; ANA—Agência Nacional de Águas: Brasilia, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.E.F.W.; Lopes, W.T.A.; de Carvalho, N.O.; da Silva, E.M.; Vieira, M.R. Fluxo de Sedimentos Em Suspensão No Exutório de Grandes Bacias Hidrográficas Em Território Brasileiro. In Proceedings of the VII Encontro Nacional de Engenharia de Sedimentos, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 20–24 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIs Procedure for Automatically Calculating the USLE LS Factor on Topographically Complex Landscape Units. J. Soil 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Vigiak, O.; Borselli, L.; Newham, L.T.H.; McInnes, J.; Roberts, A.M. Comparison of Conceptual Landscape Metrics to Define Hillslope-Scale Sediment Delivery Ratio. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, L.; Cassi, P.; Torri, D. Prolegomena to Sediment and Flow Connectivity in the Landscape: A GIS and Field Numerical Assessment. Catena 2008, 75, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetto, A.M. Hidrologia e Recursos Hídricos; EESC-USP: São Paulo, Brazil, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, S.G.; Silva, M.L.N.; Avanzi, J.C.; Curi, N.; Fonseca, S. Fator Cobertura e Manejo Do Solo e Perdas de Solo e Água Em Cultivo de Eucalipdo e Em Mata Atlântica Nos Tabuleiros Costeiros Do Estado Do Espírito Santo. Sci. For. 2010, 38, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, J.C.N.; de Andrade, E.M.; Medeiros, P.H.A.; de Araújo Neto, J.R.; de Palácio, H.A.Q.; do Rodrigues, R.N. Determination of the Cover Factor and the MUSLE Coefficients in Watersheds in the Brazilian Semiarid Region. Rev. Bras. De Eng. Agric. E Ambient. 2014, 18, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochnow, D.; Dechen, S.C.F.; de Maria, I.C.; de Castro, O.M.; Vieira, S.R. Razão de Perdas de Terra e Fator C Da Cultura Do Cafeeiro Em Cinco Espaçamentos, Em Pindorama (SP). Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2005, 29, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGAM. Plano Diretor de Recursos Hídricos Dos Afluentes Mineiros Do Rio Pardo_PA1; IGAM: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, A.G.; de Carvalho, O.A., Jr.; Guimarães, R.F.; Bias, E.d.S.; Corrêa, D.C.; Gomes, R.A.T. Vertical Accuracy Assessment of the Processed Srtm Data for the Brazilian Territory. Bol. Ciências Geodésicas 2019, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.G.; dos Teixeira, A.S.; de Andrade, E.M.; de Lucena, A.M.P.; de Castro, M.A.H. Análise Da Influência Vegetacional Na Altimetria Dos Dados SRTM Em Bacias Hidrográficas No Semiárido. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2010, 41, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D. Handbook of Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE. Bases Cartográficas Contínuas. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/cartas-e-mapas/bases-cartograficas-continuas/15759-brasil.html?=&t=acesso-ao-produto (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Da Silva, A.M. Rainfall Erosivity Map for Brazil. Catena 2004, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, K.; Sparks, A.H.; Ashmall, W.; van Etten, J.; Solberg, S.Ø. Chirps: API Client for the CHIRPS Precipitation Data in R. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.B.; Haugen, J.E.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical Note: Downscaling RCM Precipitation to the Station Scale Using Statistical Transformations—A Comparison of Methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, L. Análise de Incertezas e Avaliação Dos Fatores Influentes No Desempenho de Modelos de Simulação de Bacias Hidrográficas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, H.M.L. Incertezas Na Predição Da Erosão Com a USLE: Impactos e Mitigação. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2010, 34, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL SNUC—Sistema Nacional de Unidades de Conservação Da Natureza. Lei No 9.985; BRASIL SNUC: Brasilia, Brazil , 2000. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL Código Florestal. Lei No 12.651; BRASIL Código Florestal: Brasilia, Brazil , 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Wendland, E. Orders of Magnitude Increase in Soil Erosion Associated with Land Use Change from Native to Cultivated Vegetation in a Brazilian Savannah Environment. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2015, 40, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anache, J.A.A. Alterações No Ciclo Hidrológico e Na Perda de Solo Devido Aos Diferentes Usos Do Solo e Variações Climáticas Em Área de Cerrado. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cândido, B.M.; Silva, M.L.N.; Curi, N.; Batista, P.V.G. Erosão Hídrica Pós-Plantio Em Florestas de Eucalipto Na Bacia Do Rio Paraná, No Leste Do Mato Grosso Do Sul. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2014, 38, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Silva, M.L.N.; Avanzi, J.C.; Curi, N.; Souza, F.S. de Erosão Hídrica Em Latossolo Vermelho Sob Diversos Sistemas de Manejo Do Cafeeiro No Sul de Minas Gerais. Ciência Agrotecnologia 2007, 31, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.S.; Silva, M.L.N.; Curi, N.; Leite, F.P.; Brito, L.d.F. Erosão Hídrica Pós-Plantio Em Florestas de Eucalipto Na Região Centro-Leste de Minas Gerais. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2006, 41, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, S.M.; de Almeida, S.P.; Ribeiro, J.F. Cerrado: Ecologia e Flora; Embrapa Cerrados: Brasilia, Brazil, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, P.C.G.; de Moura, M.S.B.; Kiill, L.H.P.; de Brito, L.T.L.; Pereira, L.A.; Sá, I.B.; Correia, R.C.; de Teixeira, A.H.C.; Cunha, T.J.F.; Guimarães Filho, C. Caracterização Do Semiárido Brasileiro: Fatores Naturais e Humanos. In Semiárido Brasileiro: Pesquisa, Desenvolvimento e Inovação; Embrapa Semiárido; Embrapa Semiárido: Petrolina, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.E.F.W.; Silva, M.d.S. Estimativa Da Contribuição Hídrica Do Cerrado Para As Grandes Bacias Hidrográficas Brasileiras. In Proceedings of the XVII Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos, Associação Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos. São Paulo, Brazil, 25–29 November 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.E.F.W. Modelagem Numérica Do Fluxo Da Água No Solo e Do Escoamento de Base Em Uma Bacia Experimental Em Área Agrícola No Cerrado (Distrito Federal). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasilia, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gmach, M.-R.; Dias, B.O.; Silva, C.A.; Nóbrega, J.C.A.; Lustosa-Filho, J.F.; Siqueira-Neto, M. Soil Organic Matter Dynamics and Land-Use Change on Oxisols in the Cerrado, Brazil. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 14, e00178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, A.A.; Belmont, P.; Hawkins, C.P.; Wilcock, P. Near-Channel Versus Watershed Controls on Sediment Rating Curves. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1901–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Deng, J.; Lin, Y.; Belete, M.; Wang, K.; Comber, A.; Huang, L.; Gan, M. Identifying the Effects of Land Use Change on Sediment Export: Integrating Sediment Source and Sediment Delivery in the Qiantang River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, R.; Dragovich, D.; Webb, A.A. Distributed Empirical Algorithms to Estimate Catchment Scale Sediment Connectivity and Yield in a Subtropical Region. Hydrol. Process 2014, 28, 2671–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.A. Use and Misuse of the USLE. J. Soiland Water Conserv. 1976, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Durigan, G.; Munhoz, C.B.; Zakia, M.J.B.; Oliveira, R.S.; Pilon, N.A.L.; do Valle, R.S.T.; Walter, B.M.T.; Honda, E.A.; Pott, A. Cerrado Wetlands: Multiple Ecosystems Deserving Legal Protection as a Unique and Irreplaceable Treasure. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 20, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellmann, K. Simulating the Impact of Land Use Change and Climate Change on the Supply of Ecosystem Services in a Rubber-Dominated Watershed in Southwestern China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Honenheim, Stuttgart-Hohenheim, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gashaw, T.; Bantider, A.; Zeleke, G.; Alamirew, T.; Jemberu, W.; Worqlul, A.W.; Dile, Y.T.; Bewket, W.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adem, A.A.; et al. Evaluating InVEST Model for Estimating Soil Loss and Sediment Export in Data Scarce Regions of the Abbay (Upper Blue Nile) Basin: Implications for Land Managers. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Zaied, M.; Jomaa, S.; Ouessar, M. Soil Erosion Estimates in Arid Region: A Case Study of the Koutine Catchment, Southeastern Tunisia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
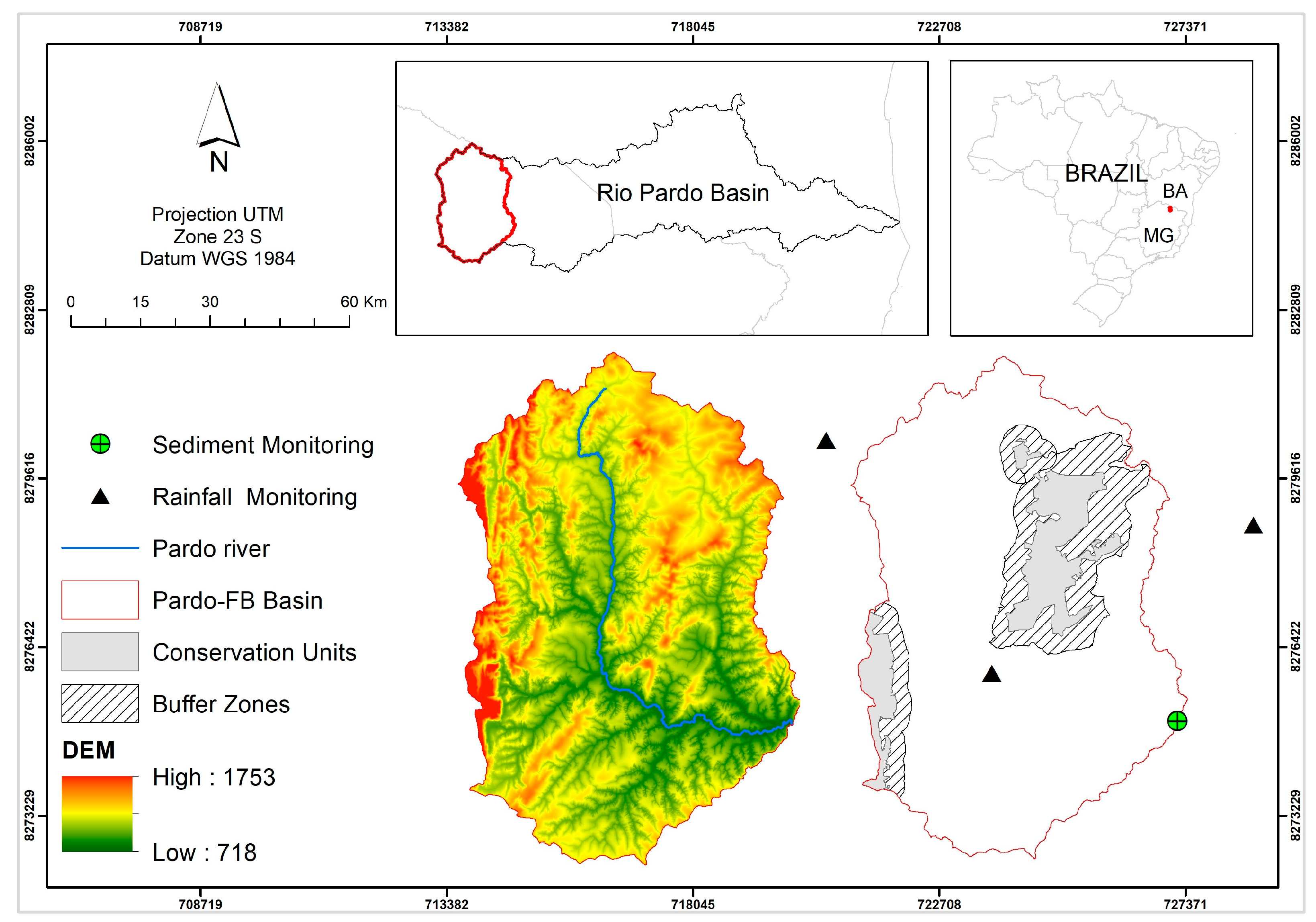

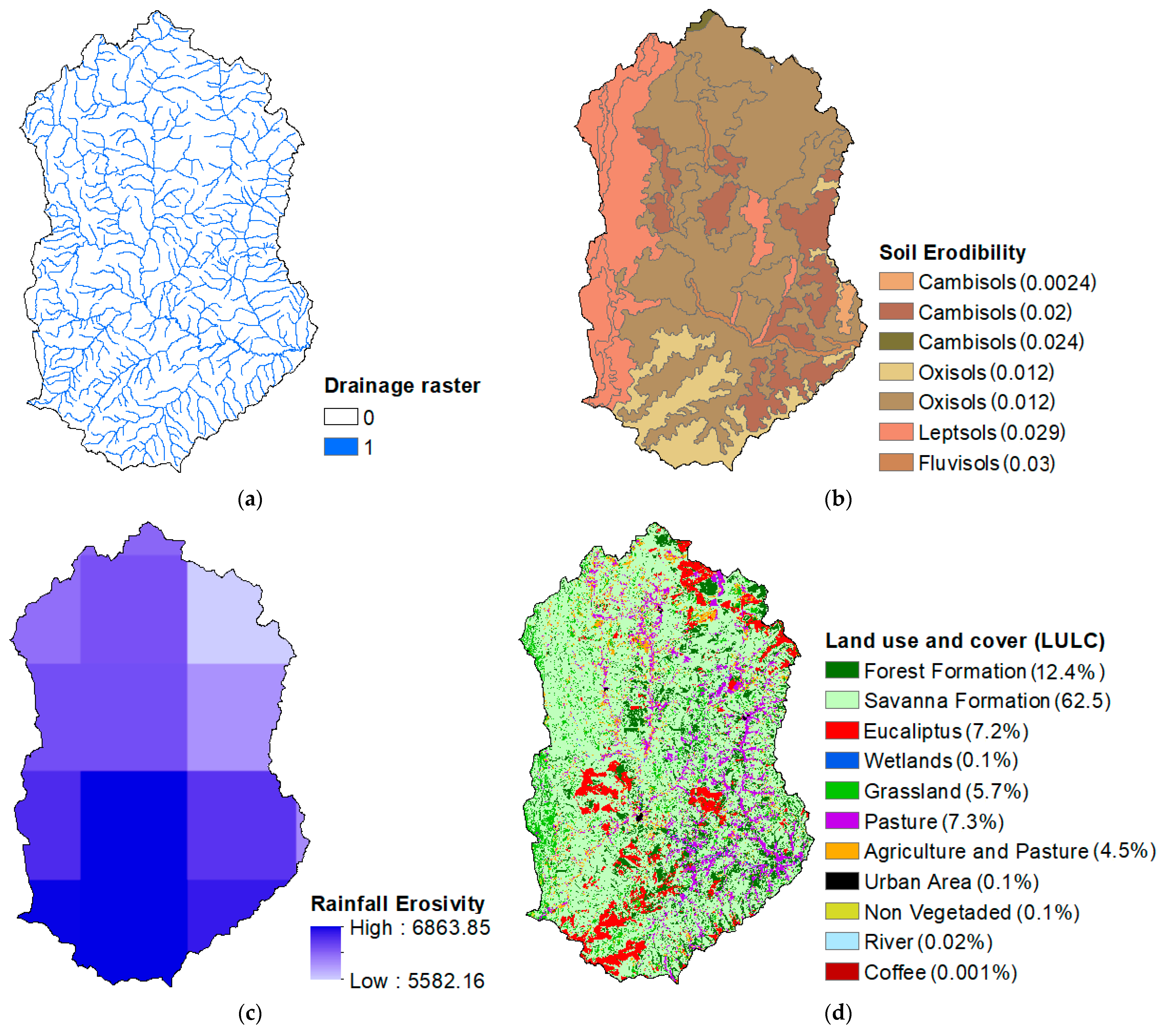



| LULC | Factor C | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Native vegetation | ||
| Forests Formation | 0.004 | [43,48] |
| Savanna Formation | 0.012 | [43,48] |
| Grassland | 0.013 | [43,48] |
| Wetlands | 0 | [43] |
| Anthropic areas | ||
| Eucalyptus plantation | 0.3 | [49] |
| Pasture | 0.035 | [50] |
| Mosaic of Agriculture and Pasture | 0.15 | [50] |
| Coffee | 0.11 | [51] |
| Non vegetated * | 1 | [43] |
| Urban Area | 0.03 | [52] |
| Other | ||
| Rocky Outcrop | 0 | [43] |
| River | 0 | [43] |
| Scenarios | Rdry | Rm | Rwet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤T | >T | ≤T | >T | ≤T | >T | |
| OP | 77.3 | 22.7 | 68.6 | 31.4 | 61.2 | 38.8 |
| BL | 71.8 | 28.2 | 62.7 | 37.3 | 55.2 | 44.8 |
| PE | 66.1 | 33.9 | 56.9 | 43.1 | 49.7 | 50.3 |
| OP_L | 80.0 | 20.0 | 72.0 | 28.0 | 64.8 | 35.2 |
| BL_L | 75.6 | 24.4 | 67.1 | 32.9 | 59.9 | 40.1 |
| PE_L | 71.1 | 28.9 | 62.5 | 37.5 | 55.4 | 44.6 |
| Scenarios | Rdry | Rm | Rwet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤T | >T | ≤T | >T | ≤T | >T | |
| OP | 99.99 | 0.01 | 99.94 | 0.06 | 99.93 | 0.07 |
| BL | 100.0 | 0.0 | 99.84 | 0.16 | 99.78 | 0.22 |
| PE | 100.0 | 0.0 | 99.42 | 0.58 | 99.16 | 0.84 |
| OP_L | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 |
| BL_L | 100.0 | 0.0 | 99.99 | 0.01 | 99.98 | 0.02 |
| PE_L | 100.0 | 0.0 | 99.95 | 0.05 | 99.91 | 0.09 |
| Variable & Scenario | Scenario Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP -> OP_L | BL -> BL_L | PE -> PE_L | ||
| Soil Loss | Rdry | 19.6 | 22.8 | 24.3 |
| Rm | 20.5 | 23.5 | 24.8 | |
| Rwet | 19.4 | 22.8 | 24.5 | |
| Sediment export | Rdry | 75.8 | 75.4 | 80.5 |
| Rm | 77.0 | 76.3 | 81.0 | |
| Rwet | 75.3 | 75.4 | 80.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bendito, B.P.C.; Chaves, H.M.L.; Scariot, A. Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in a Semi-Arid Basin of the Brazilian Savanna under Different Land Use, Climate Change, and Conservation Scenarios. Water 2023, 15, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030563
Bendito BPC, Chaves HML, Scariot A. Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in a Semi-Arid Basin of the Brazilian Savanna under Different Land Use, Climate Change, and Conservation Scenarios. Water. 2023; 15(3):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030563
Chicago/Turabian StyleBendito, Bianca Pietsch Cunha, Henrique Marinho Leite Chaves, and Aldicir Scariot. 2023. "Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in a Semi-Arid Basin of the Brazilian Savanna under Different Land Use, Climate Change, and Conservation Scenarios" Water 15, no. 3: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030563
APA StyleBendito, B. P. C., Chaves, H. M. L., & Scariot, A. (2023). Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in a Semi-Arid Basin of the Brazilian Savanna under Different Land Use, Climate Change, and Conservation Scenarios. Water, 15(3), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030563







