Impact of the Hydroelectric Dam on Aquifer Recharge Processes in the Krško Field and the Vrbina Area: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
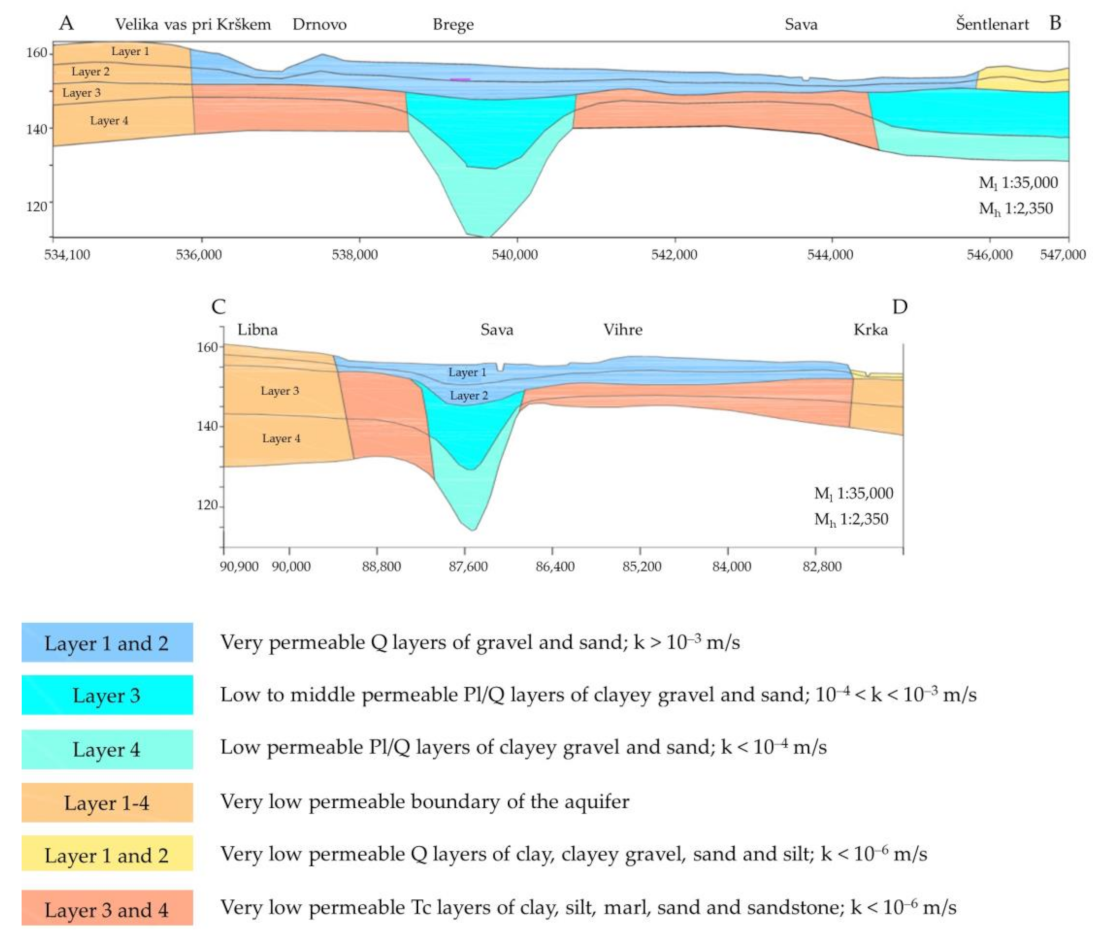
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
- δ18O—weighted average of the oxygen isotopic composition of precipitation/sampled water;
- Pi—precipitation amount/water volume of the sample (i);
- δi18O—oxygen isotopic composition of the sample (i).
3. Results
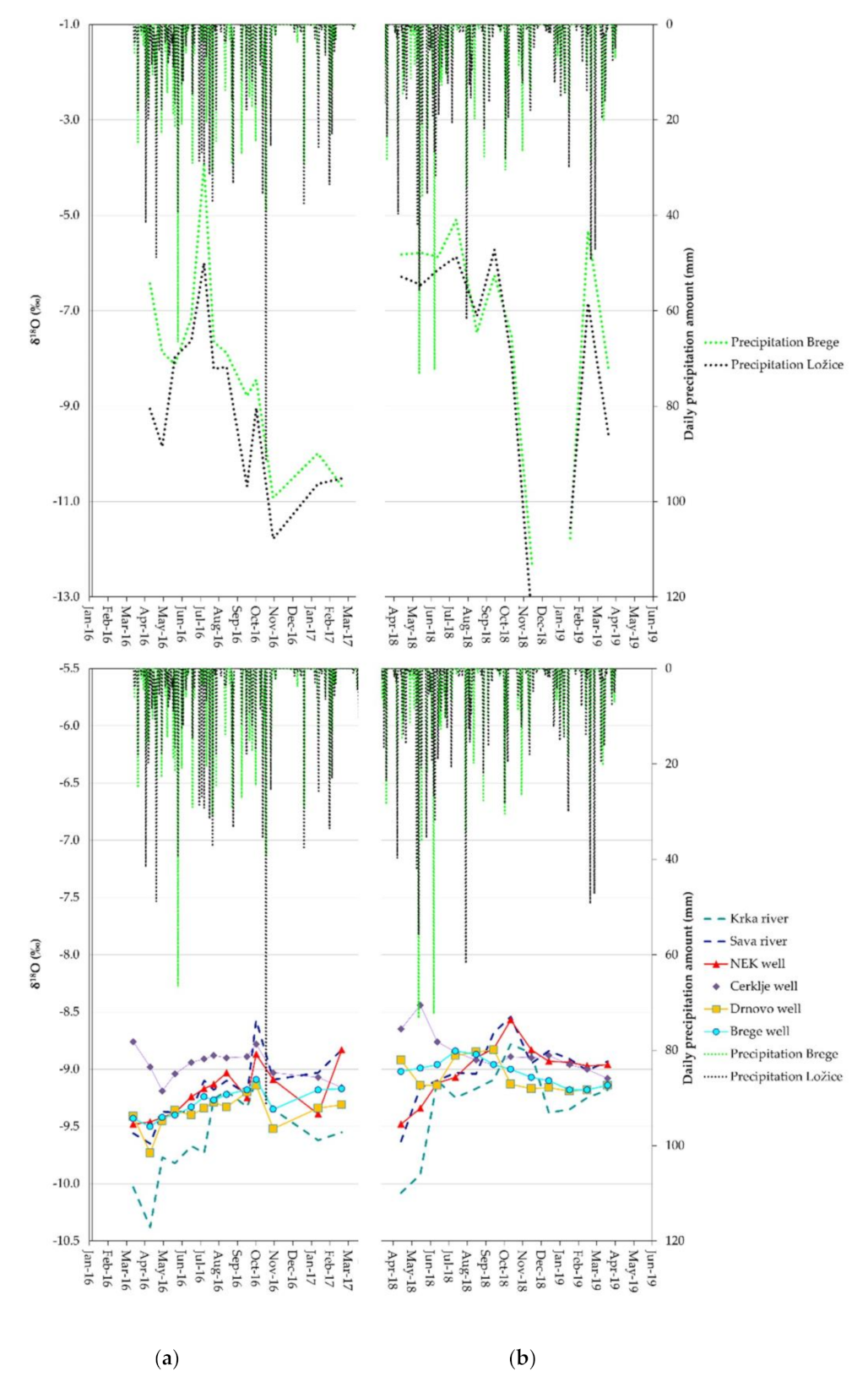
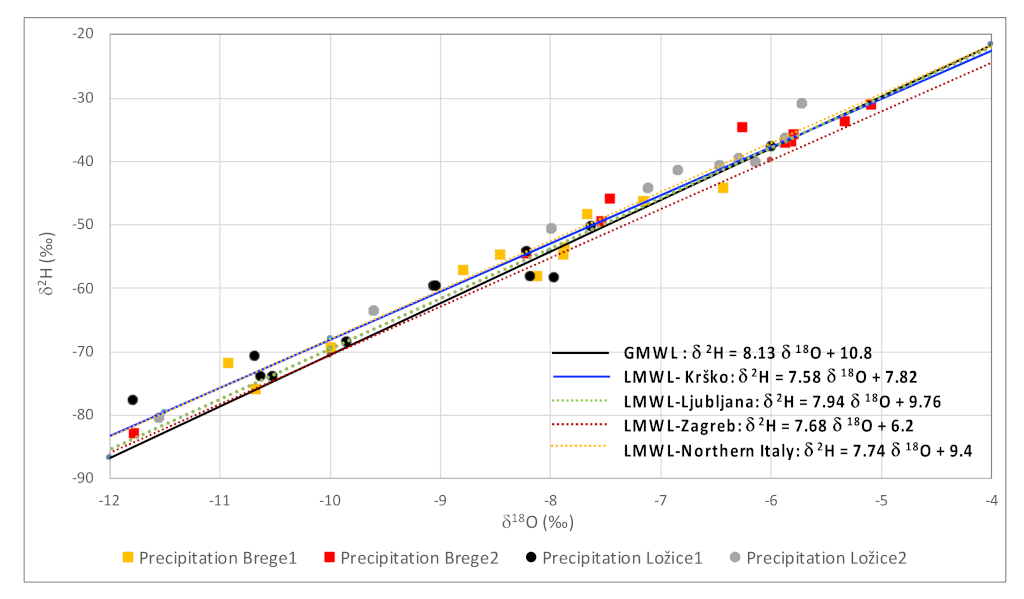
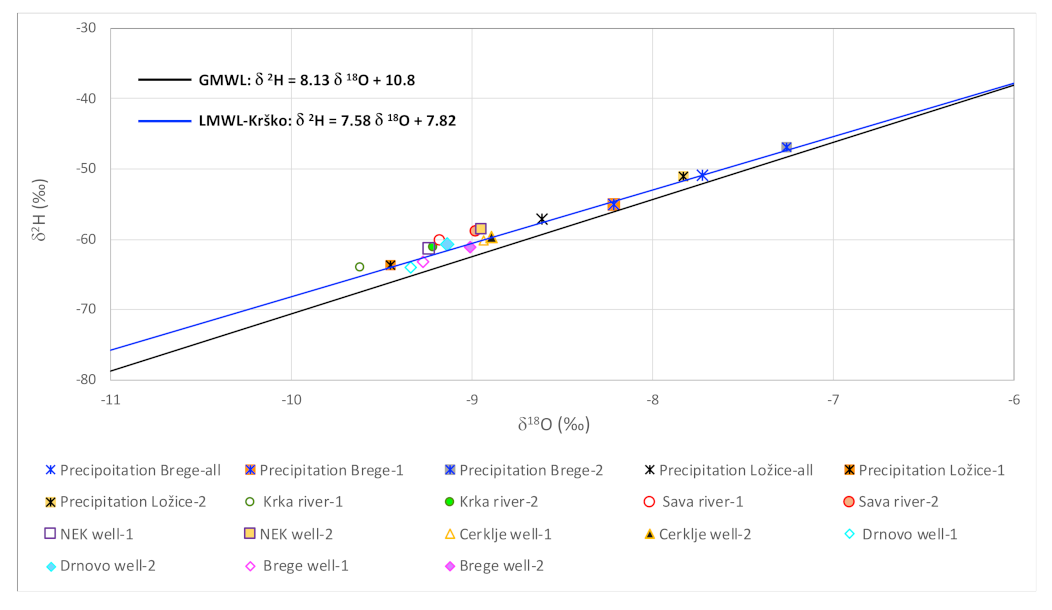
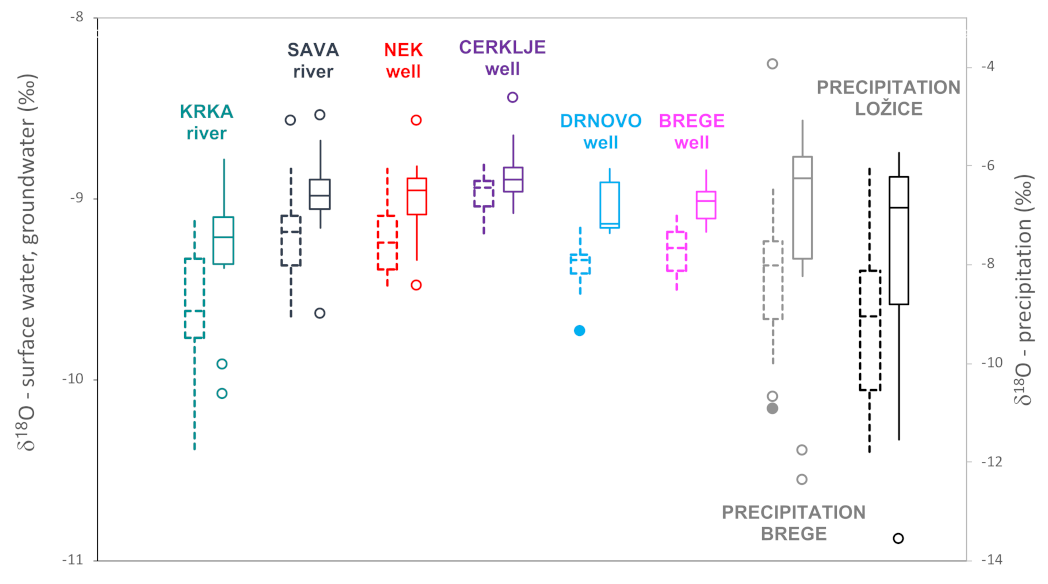
3.1. Isotopic Composition of 18O and 2H
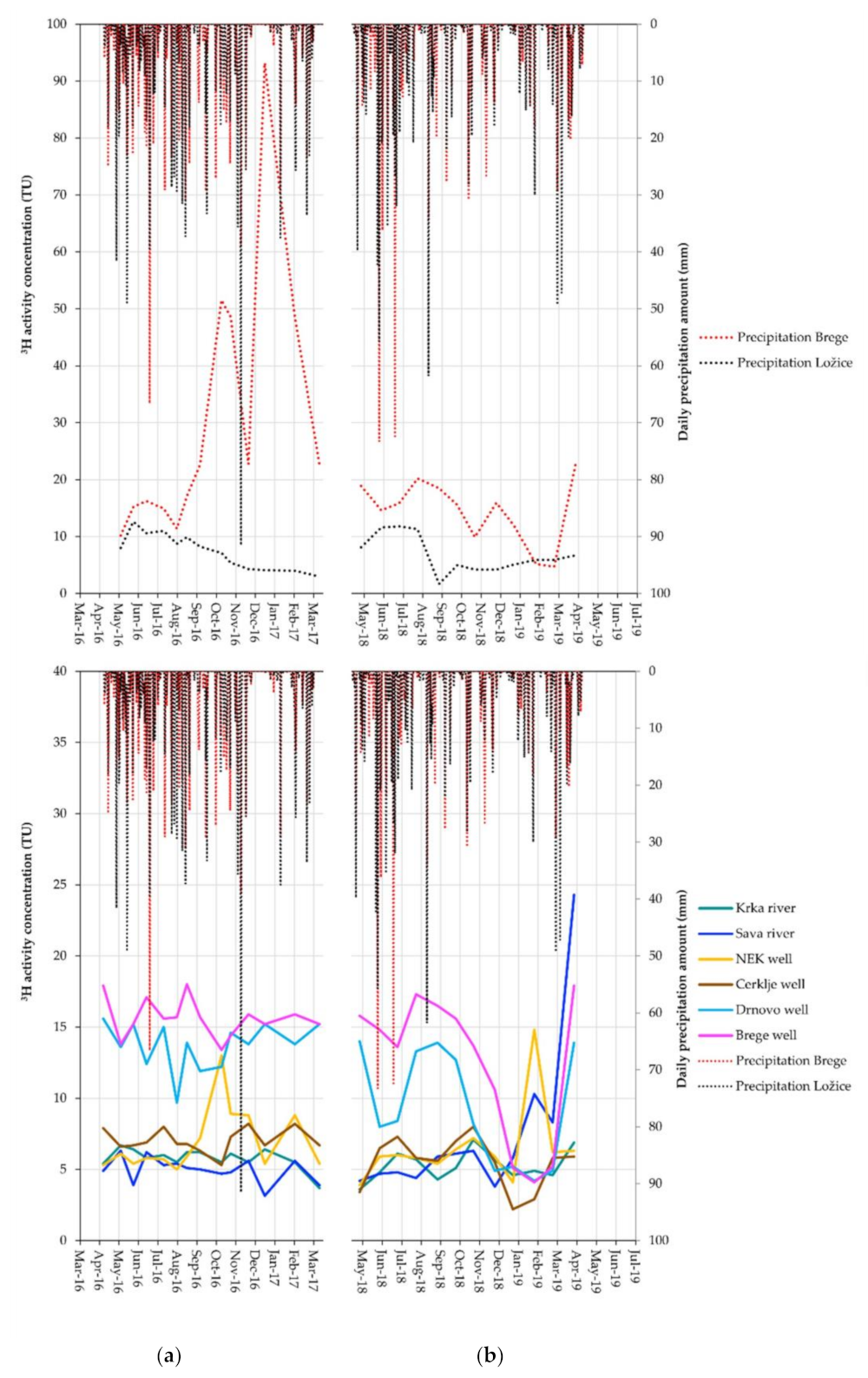
3.2. Tritium Activity Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petauer, D.; Hiti, T.; Juren, A. Simulacije Vpliva Izgradnje HE Brežice na Podzemno Vodo Vodonosnikov Krškega Polja in Vrbine; GEORAZ & GeoSi: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Petauer, D.; Hiti, T.; Juren, A.; Kvaternik, K.; Brenčič, M. Novelacija Matematičnega Modela HE Brežice s Podatki Novo Izvedenih Vrtin na Območju Spodnji Stari Grad s Simulacijo Vplivov Zajezbe HE Brežice na Gladino Podzemne Vode z Noveliranim Modelom Umerjenim na Srednji in Visoki Nivo Podzemne Vode; GEORAZ, GeoSi & IBE: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petauer, D.; Hiti, T.; Juren, A.; Kvaternik, K.; Brenčič, M. Simulacije Vplivov HE Brežice na Podzemne Vode pred Izgradnjo HE Mokrice; GEORAZ, GeoSi & IBE: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bronić, I.K.; Barešić, J. Application of Stable Isotopes and Tritium in Hydrology. Water 2021, 13, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreča, P.; Kern, Z. Use of Water Isotopes in Hydrological Processes. Water 2020, 12, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stichler, W.; Mao-Szewski, P.; Moser, H. Modelling of River Water Infiltration Using Oxygen-18 Data. J. Hydrol. 1986, 83, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloszewski, P.; Rauert, W.; Trimborn, P.; Herrmann, A.; Rau, R. Isotope Hydrological Study of Mean Transit Times in an Alpine Basin (Wimbachtal, Germany). J. Hydrol. 1992, 140, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publisher: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; ISBN 044450155X. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Sang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Guo, H. Impact of Landscape Dams on River Water Cycle in Urban and Peri-Urban Areas in the Shiyang River Basin: Evidence Obtained from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Cumulative Effects of Cascade Dams on River Water Cycle: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, S.; Lian, E.; Li, C.; Yang, C.; Wei, H. Three Gorges Dam Alters the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Water Cycle in the Dry Seasons: Evidence from H-O Isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, S.; Lian, E.; Yang, C.; Deng, K.; Liu, Z. Damming Effect on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) River Water Cycle Based on Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Records. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xia, Y. River Damming and Drought Affect Water Cycle Dynamics in an Ephemeral River Based on Stable Isotopes: The Dagu River of North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.L.; Do, T.N.; Trinh, A.D. Application of Water Stable Isotopes for Hydrological Characterization of the Red River (Asia). Water 2021, 13, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Pang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, G. Constraining the Water Cycle Model of an Important Karstic Catchment in Southeast Tibetan Plateau Using Isotopic Tracers (2 h,18 o,3 h,222 Rn). Water 2020, 12, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Kocman, D.; Miljevi, N.; Vre, P.; Vrzel, J.; Povinec, P. Distribution of H and O Stable Isotopes in the Surface Waters of the Sava River, the Major Tributary of the Danube River. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlov, J.; Kovač, Z.; Nakić, Z.; Barešić, J. Using Water Stable Isotopes for Identifying Groundwater Recharge Sources of the Unconfined Alluvial Zagreb Aquifer (Croatia). Water 2019, 11, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brkić, Ž.; Kuhta, M.; Hunjak, T.; Larva, O. Regional Isotopic Signatures of Groundwater in Croatia. Water 2020, 12, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako, D.; Gibrilla, A.; Maloszewski, P.; Ganyaglo, S.Y.; Rai, S.P. Tracing Stable Isotopes (Δ2H and Δ18O) from Meteoric Water to Groundwater in the Densu River Basin of Ghana. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, T.; Karlović, I.; Tadić, M.P.; Larva, O. Application of Stable Water Isotopes to Improve Conceptual Model of Alluvial Aquifer in the Varaždin Area. Water 2020, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagode, K.; Kanduč, T.; Lojen, S.; Železnik, B.B.; Jamnik, B.; Vreča, P. Synthesis of Past Isotope Hydrology Investigations in the Area of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Geologija 2020, 63, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzel, J.; Solomon, D.K.; Blažeka, Ž.; Ogrinc, N. The Study of the Interactions between Groundwater and Sava River Water in the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer System (Slovenia). J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezga, K.; Urbanc, J.; Cerar, S. The Isotope Altitude Effect Reflected in Groundwater: A Case Study from Slovenia. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Trinidad, J.; Pacheco-Guerrero, A.; Júnez-Ferreira, H.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Hernández-Antonio, A. Identifying Groundwater Recharge Sites through Environmental Stable Isotopes in an Alluvial Aquifer. Water 2017, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.J.; Bonell, M.; Stewart, M.K.; Pearce, A.J. Deuterium Variations in Storm Rainfall: Implications for Stream Hydrograph Separation. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 4th ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Isotope Hydrology: A Study of the Water Cycle; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Duliński, M.; Różański, K.; Pierchała, A.; Gorczyca, Z.; Marzec, M. Isotopic Composition of Precipitation in Poland: A 44-Year Record. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronić, I.K.; Barešić, J.; Borković, D.; Sironić, A.; Mikelić, I.L.; Vreča, P. Long-Term Isotope Records of Precipitation in Zagreb, Croatia. Water 2020, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Criss, R.E.; Davisson, M.L.; Surbeck, H.; Winston, E.E. Isotopic Techniques. In Methods in Karst Hydrogeology, International Contribution to Hydrogeology 26; Goldscheider, N., Drew, D., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2007; pp. 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, S. Utilization of Decadal Tritium Variation for Assessing the Residence Time of Base Flow. Ground Water 2007, 45, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.L.; Unterweger, M.P. Comprehensive Review and Critical Evaluation of the Half-Life of Tritium. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2000, 105, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, G.A.; Lehr, J.H.; Perrochet, P. Groundwater Age; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, B.D.; Osenbrück, K.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Solomon, D.K.; Cook, P.; Rózanski, K.; Kipfer, R. Dating of “Young” Groundwaters Using Environmental Trasers: Advantages, Applications, and Research Needs. Isot. Environ. Heal. Stud. 2010, 46, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, D. Technogenic Tritium in Central European Precipitations. Isot. Isot. Environ. Heal. Stud. 1990, 26, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavič-Cindro, D.; Zorko, B. Ovrednotenje Izpustov iz NEK in Primerjava z Meritvami v Okolju—Stanje pred Polnitvijo Akumulacijskega Jeza za HE Brežice; IJS: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Glavič-Cindro, D.; Zorko, B. Nadzor Radioaktivnosti v Okolici Nuklearne Elektrarne Krško, Poročilo za Leto 2018. IJS: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Slovenian Environment Agency, Climate. Available online: https://Meteo.Arso.Gov.Si/Met/Sl/Climate/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- IAEA/GNIP Precipitation Sampling Guide. Available online: http://www-Naweb.Iaea.Org/Napc/Ih/Documents/Other/Gnip_manual_v2.02_en_hq.Pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- IAEA. Statistical Treatment of Environmental Isotopes in Precipitation; Technical Report Series 331; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, S.; Mayeda, T. Variation of O18 Content of Waters from Natural Sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Ueda, A.; Mizukami, K.; Takatori, I. Automatic ΔD and Δ18O Analyses of Multi-Water Samples Using H2- and CO2-Water Equilibration Methods with a Common Equilibration Set-Up. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrument. Part A. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1989, 40, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.; Brockwell, T.; Merren, T.; Fourel, F.; Phillips, A.M. On-Line High-Precision Stable Hydrogen Isotopic Analyses on Nanoliter Water Samples. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3570–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopes in the Hydrologic Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier-Augenstein, W.; Schimmelmann, A. A Guide for Proper Utilisation of Stable Isotope Reference Materials(). Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2019, 55, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical Methods in Water Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguds-Araguds, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic Patterns in Modern Global Precipitation. In Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records–Geophysical Monograph 78; Swart, P.K., Lohman, K.C., McKenzie, J., Savin, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mook, W.G. Environmental Isotopes in the Hydrological Cycle, Principles and Applications, Volumes I, IV and V. In Technical Documents in Hydrology No. 39; IAEA-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vreča, P.; Krajcar Bronić, I.; Leis, A.; Demšar, M. Isotopic Composition of Precipitation at the Station Ljubljana (Reaktor), Slovenia—Period 2007–2010. Geologija 2014, 57, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longinelli, A.; Selmlo, E. Isotopic Composition of Precipitation in Italy: A First Overall Map. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfahl, S.; Sodemann, H. What Controls Deuterium Excess in Global Precipitation? Clim. Past 2014, 10, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gat, J.R.; Carmi, I. Evolution of the Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Waters in the Mediterranean Sea Area. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R.; Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotope Survey of the Fresh Water Occurrences in Israel and the Northern Jordan Rift Valley. J. Hydrol. 1972, 16, 177–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreča, P.; Bronić, I.K.; Horvatinčić, N.; Barešić, J. Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation in Slovenia and Croatia: Comparison of Continental and Maritime Stations. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, Z.; Hatvani, I.G.; Czuppon, G.; Fórizs, I.; Erdélyi, D.; Kanduč, T.; Palcsu, L.; Vreča, P. Isotopic ‘Altitude’ and ‘Continental’ Effects in Modern Precipitation across the Adriatic–Pannonian Region. Water 2020, 12, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poage, M.A.; Chamberlain, C.P. Empirical Relationships Between Elevation and the Stable Isotope Composition of Precipitation and Surface Waters: Considerations for Studies of Paleoelevation Change. Am. J. Sci. 2001, 301, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petauer, D.; Hiti, T.; Supovec, I. Hidrogeološka Obdelava Podatkov Monitoringa Podzemne Vode na Vplivnem Območju HE Brežice, Avgust 2017—Avgust 2018—Fazno Poročilo: Nivoji Podzemne Vode I Leto po Dvigu Zajezbe v AB HE Brežice na Nazivno Koto 153 m.n.v.; GEORAZ & HGEM: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Petauer, D.; Supovec, I. Hidrogeološka Obdelava Podatkov Monitoringa Podzemne Vode na Vplivnem Območju HE Brežice, Avgust 2017—September 2019—Fazno Poročilo: Nivoji Podzemne Vode 2 Leti po Dvigu Zajezbe v AB HE Brežice na Nazivno Koto 153 m.n.v.; GEORAZ & HGEM: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]



| Name of Sampling Location | Well Depth (m) | Water Type | Coordinates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | |||
| Sava river | Surface water | 538,269.50 | 90,003.31 | |
| Krka river | 540,615.96 | 82,077.78 | ||
| NEK well | 10.0 | Groundwater | 540,489.49 | 88,349.86 |
| Cerklje well | 8.8 | 540,938.88 | 83,055.74 | |
| Brege well | 13.1 | 539,329.55 | 86,882.22 | |
| Drnovo well | 18.8 | 537,823.41 | 86,333.60 | |
| Precipitation Brege | Precipitation | 539,316.85 | 86,901.27 | |
| Precipitation Puste Ložice | 534,128.64 | 100,937.54 | ||
| Sample Name | Median before/after Filling | Minimum before/after Filling | Maximum before/after Filling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ18O (‰) | Krka river | −9.62/−9.22 | −10.38/−10.08 | −9.09/−8.78 |
| Sava river | −9.18/−8.98 | −9.65/−9.63 | −8.83/−8.54 | |
| NEK well | −9.24/−8.95 | −9.48/−9.48 | −8.83/−8.57 | |
| Cerklje well | −8.94/−8.90 | −9.19/−9.08 | −8.78/−8.44 | |
| Drnovo well | −9.34/−9.14 | −9.52/−9.19 | −9.14/−8.83 | |
| Brege well | −9.27/−9.01 | −9.50/−9.18 | −9.09/−8.84 | |
| Precipitation Brege | −8.00/−6.26 | −9.99/−12.35 | −6.43/−5.09 | |
| Precipitation Ložice | −9.05/−6.84 | −11.78/−13.56 | −6.00/−5.72 | |
| δ2H (‰) | Krka river | −63.9/−61.1 | −70.6/−68.2 | −60.4/−56.4 |
| Sava river | −60.1/−58.9 | −64.2/−64.6 | −56.3/−54.3 | |
| NEK well | −61.2/−58.6 | −63.1/−64.0 | −59.4/−54.8 | |
| Cerklje well | −60.1/−59.7 | −62.7/−61.0 | 61.00/−58.0 | |
| Drnovo well | −63.9/−60.7 | −66.2/−61.2 | −62.2/−59.8 | |
| Brege well | −63.1/−61.1 | −65.2/−61.6 | −62.3/−59.7 | |
| Precipitation Brege | −54.8/−37.2 | −75.9/−84.9 | −24.2/−31.1 | |
| Precipitation Ložice | −59.6/−41.5 | −77.6/−96.0 | −37.6/−31.0 | |
| d-excess (‰) | Krka river | 12.5/12.8 | 12.0/11.6 | 13.9/13.8 |
| Sava river | 13.0/13.0 | 10.5/11.9 | 13.9/14.0 | |
| NEK well | 12.7/13.0 | 10.9/11.9 | 13.7/13.7 | |
| Cerklje well | 11.5/11.4 | 9.2/9.5 | 12.6/11.9 | |
| Drnovo well | 11.0/13.2 | 9.9/10.9 | 11.7/15.1 | |
| Brege well | 10.8/11.3 | 9.2/10.3 | 12.5/12.0 | |
| Precipitation Brege | 9.9/10.7 | 6.8/8.9 | 15.5/15.4 | |
| Precipitation Ložice | 11.0/12.4 | 5.4/9.1 | 16.6/14.7 | |
| 3H activity concentration (TU) | Krka river | 5.9/5.0 | 5.4/3.6 | 6.7/7.1 |
| Sava river | 5.1/5.9 | 3.9/3.8 | 6.3/24.3 | |
| NEK well | 5.9/6.0 | 5.0/3.9 | 8.9/14.8 | |
| Cerklje well | 6.8/5.8 | 5.3/2.2 | 8.2/8.0 | |
| Drnovo well | 13.8/8.3 | 9.7/4.2 | 15.6/14.0 | |
| Brege well | 15.7/14.3 | 13.4/4.1 | 18.0/17.9 | |
| Precipitation Brege | 16.7/15.7 | 10.2/4.7 | 22.7/22.7 | |
| Precipitation Ložice | 8.1/5.9 | 4.3/1.7 | 12.6/11.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trček, B.; Mesarec, B. Impact of the Hydroelectric Dam on Aquifer Recharge Processes in the Krško Field and the Vrbina Area: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. Water 2023, 15, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030412
Trček B, Mesarec B. Impact of the Hydroelectric Dam on Aquifer Recharge Processes in the Krško Field and the Vrbina Area: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. Water. 2023; 15(3):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030412
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrček, Branka, and Beno Mesarec. 2023. "Impact of the Hydroelectric Dam on Aquifer Recharge Processes in the Krško Field and the Vrbina Area: Evidence from Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes" Water 15, no. 3: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030412





