Abstract
Piggery wastewater contains high amounts of feces, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other contaminants, introducing serious pollution into water, soil, and the atmosphere. Biological treatment technology is widely used in large-scale pig farms because of its high efficiency and economical advantages. In this study, two typical biological treatment systems—a distributed-inflow biological reactor (DBR) and a two-stage anoxic/aerobic (A/O/A/O)—were adopted to treat piggery wastewater to compare the treatment performance, the dissolved organic matter (DOM) composition, and the microbial distribution characteristics. The results show that the A/O/A/O system had better removal performance in terms of chemical oxygen demand (COD) compared to the DBR system, and similarly effective at removing and ammonia nitrogen (NH-N) and total nitrogen (TN). Using parallel factor analysis of the fluorescence excitation–emission matrix, four DOM components—namely fulvic acid-like/humic-like substances (C1), tyrosine-like substances (C2), humic-like substances (C3), and tryptophan-like substances (C4)—were tracked in piggery wastewater. Protein-like substances were significantly degraded, while humic-like substances were difficult for microorganisms to utilize. The endogenous input and humus characteristics of effluents were enhanced. Bacteroidetes (43.9% and 37.5% ) and Proteobacteria (43.1% and 56.7%) are the dominant bacteria in DBR and A/O/A/O systems. The microbial metabolites in DBR and A/O/A/O systems are mainly composed of amino acids, sugars, alcohols, and other small molecules, while those in the municipal sewage treatment plant system is mainly composed of ketones, amines, acids, lipids, and other small molecules. The results of microbial communities and metabolites can help to trace the process of biological systems treating piggery wastewater.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the global population is increasing concurrent with the rapid development of modern industry and economy, and the demand for meat products is also increasing. China is the biggest producer of pork products in the world. According to the Statistical Bulletin of the National Economic and Social Development 2021, China’s pork production increased by 28.8% to 52.96 million tons in 2021, and the stock of pigs at the end of the year increased by 10.5% compared to the previous year, reaching a total of 449.22 million pigs. Previous studies have shown that each small-scale pig farm in China produces about 1300 tons of piggery wastewater annually, including feces, urine, and washing wastewater [1]. In 2018, the total amount of wastewater produced via pig farming in China was approximately 160 million tons [2]. As a kind of complex wastewater with high concentration, piggery wastewater not only contains high concentrations of suspended solids, organic matter, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, but also toxic compounds such as antibiotics and heavy metals. If discharged without proper disposal, it causes water eutrophication, soil heavy metal pollution, and air pollution, posing a significant threat to the environment and human health [3,4].
In order to control environmental pollution from piggery wastewater, appropriate treatment is required. In recent years, researchers have employed a variety of treatment techniques, including microbial fuel cells (MFC) [5], countercurrent solid reactor (USR) [6], bioelectrochemical systems, and membrane technology [7,8], in order to improve the removal rate of chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia nitrogen (NH-N), phosphate, and antibiotics in piggery wastewater [9]. However, for high-strength piggery wastewater treatment, these treatment technologies mentioned above require high operation and maintenance costs, and complex pumping systems. As a low-cost, strong impact resistance, and mature technology, biological treatment technology is widely used in a variety of sewage treatment, including piggery wastewater [10]. The two-stage anoxic/aerobic (A/O/A/O) process can not only remove high concentration of COD, but also remove ammonia nitrogen. It is is one of the most common methods used for treating piggery wastewater [11]. The distributed-inflow biological reactor (DBR) is a new biological treatment device for piggery wastewater developed in our previous work [12]. DBR adopts continuous feeding and step-feed mode to optimize the distribution and rational utilization of carbon sources in wastewater and improve the efficiency of denitrification and nitrogen removal. The two biological treatment systems have their own advantages. It is crucial to determine the differences in their processing performance to develop new systems combining their advantages in the future.
In this study, DBR and A/O/A/O processes were used to treat the actual piggery wastewater from a pig farm in Wuhan, China. The removal performances of COD, NH-N, and total nitrogen (TN) of the two systems were compared. Dissolved organic matter (DOM), a kind of organic mixture with complex composition, structure, and environmental behavior, exists in a range of natural and engineered water bodies [13]. The composition of and changes in DOM in the influent and effluent of the two systems were analyzed, the characteristics of piggery wastewater before and after treatment were discussed, and the differences in bacterial communities and microbial metabolome in the sludge of the two systems were determined. Revealing DOM composition changes and microbial community structure can help us achieve better control and a deeper understanding of the microbial treatment process of piggery wastewater and provide new insights for further treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setups
As shown in Figure 1a, the DBR system consisted of a feed tank, DBR-1 with a volume of 31.25 L, and DBR-2 with a volume of 30.625 L. DBR-1 comprised a biological reaction zone and a precipitation separation zone. In the biological reaction zone, aeration was achieved using an air pump, and agitation was achieved using a mechanical mixer. The air pump and mixer were operated alternately under the control of an automatic timer to achieve aerobic and anoxic environments. DBR-1 effluent entered DBR-2 directly, and DBR-2 had the same structure as DBR-1. The influent flow rates of DBR-1 and DBR-2 were 7 mL/min and 3 mL/min, respectively [12]. The total hydraulic retention time was 103 h and the sludge retention time was 20–30 d.

Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the DBR system (a) and the A/O/A/O system (b).
As shown in Figure 1b, the A/O/A/O system consisted of a feed tank, A/O-1, and A/O-2. The effective volume of both A1 and A2 is 8 L, the hydraulic retention time is 20 h, and a mechanical mixer is set to achieve an anoxic environment. Next, O1 and O2 were set with aeration pipes with effective volumes of 16 L and a hydraulic retention time of 40 h. The influent flow rates of A1 and A2 were 7 mL/min and 3 mL/min, respectively. The reflux ratio of A/O-1 (R1) digestive fluid was 100%. The reflux ratio of the A/O-2 (R2) digestion solution was 100%. The sludge reflux ratio (R3) was set to 100%, and the retention time of sludge was 20–30 d.
The airflow rate of the DBR system was 2–4 L/min, and that of the aerobic zone of the A/O/A/O system was 1–2 L/min. Both biological systems are made of plexiglass. The experimental influent of piggery wastewater was collected from a commercial pig farm in Wuhan, China. The piggery wastewater was filtered through a screen with a diameter of 0.8 mm, which was used as the test influent after standing precipitation was carried out to remove large particles. Influent COD was 1652∼6210 mg/L, TN was 405∼2076 mg/L, NH-N was 372∼1612 mg/L, SS was 2247∼3136 mg/L, and pH was 7.0∼9.1 mg/L. The seed sludge in this study was collected from the Longwangzui wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) (Wuhan, China).
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.2.1. Water Sampling and Measurement
During the stable operation, water samples were collected daily from the feed tank and the effluent tanks of DBR and A/O/A/O systems. The concentrations of COD, NH-N, and TN were analyzed according to the standard methods [14]. The dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration was determined using a DO meter (3410, WTW Company, Munich, Germany).
2.2.2. Excitation Emission Analysis
To understand the composition and changes in the DOM of piggery wastewater, water samples were collected from the feed tank and the reaction tanks of the two biological systems every day for 25 consecutive days. Pre-treatments were conducted before fluorescence testing. The influent water was diluted 100 times, and the effluent from each reaction tank of the DBR system and the A/O/A/O biological system was diluted 10 times, and filtered by a 0.45 μm membrane. Each reactor had 25 samples. A fluorescence spectrometer (Hitachi, F-4600) was used to test the water samples. Fluorescence intensities were normalized to Raman scattering units, and ultra-pure water was used for the blank removal of Raman scattering. The excitation wavelength was 220–500 nm, and the emission wavelength was 220–550 nm. The scanning step was 5 nm, the excitation slit width was 5 nm, and the emission slit width was 10 nm.
2.2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
In order to comprehensively reveal the bacterial communities present in the biological system, five activated sludge samples were collected from WWTP, DBR-1, DBR-2, O1, and O2. Each sample was extracted using a PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (MOBIO, USA) and the DNA concentration was determined by TinyGene Biotechnology, Shanghai, China. Primers 515F (GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA) and 926R (CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT) were used to independently amplify the V4-V5 region of the bacterial 16S-rRNA gene. Subsequently, sequencing was performed on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Sample reads were allocated by barcode. The paired reads were spliced into a sequence. The optimized sequence was obtained through quality control and filtering. Mother (Version 1.33.2) was used for statistical and visual analysis of community structure and phylogeny.
2.2.4. Microbial Metabolome Analysis
The quenching reagent prepared and 60% methanol–water were pre-cooled in a dry ice environment for reserve. Then, 15 mL of quenching agent were mixed with 15 mL of the microbial sample, and the mixture was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 4 min. The GC-TOF-MS Pegasus HT (LECO USA) test platform was used to test and analyze the low-abundance microbial metabolites.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal Performance of the DBR and the A/O/A/O Systems
The effluent concentrations of COD, NH-N, and TN were detected to evaluate the performance of the DBR and the A/O/A/O processes under continuous operation. As shown in Figure 2a, with the same influent conditions, the average effluent COD of the DBR and A/O/A/O systems were 454 mg/L and 389 mg/L, resulting in removal rates of 87.9% and 90.2%, respectively. Although the removal rate difference between the two systems is only 2.3% (the corresponding COD difference is 165 mg/L), the removal rate curve of the A/O/A/O system is basically above the DBR system. This indicates that the COD removal performance of the A/O/A/O system is better than that of the DBR system. The setting of internal reflux and continuous aeration in the A/O/A/O system is conducive to the growth of microorganisms, denitrification, and the removal of COD. As shown in Figure 2b, the average effluent NH-N concentration of the DBR and the A/O/A/O systems was 29 mg/L and 26 mg/L, resulting in removal rates of 96% and 96.7%, respectively. This indicates that the nitrification performance of the two systems was similar, which can also be seen from the removal rate curves. As shown in Figure 2c, the average effluent TN of the DBR system was 166 mg/L, and the removal rate was 80.4%, which is higher than that of the A/O/A/O system (195 mg/L and 78.1%). However, from the removal rate curves, the two curves fluctuate across each other (i.e., large standard deviations), and no one has an absolute advantage. This indicates that the TN removal performance of the two systems is almost the same.
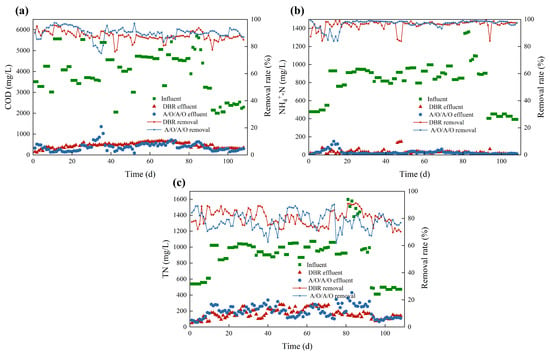
Figure 2.
Concentration and removal rate of COD (a), NH-N (b) and TN (c) in the DBR and the A/O/A/O systems.
3.2. Composition Characteristics of DOM
The fluorescence excitation–emission matrix combined parallel factor (EEM-PARAFAC) analysis method can efficiently and accurately measure the DOM composition and relative content in water samples and has been widely used in marine, river, and engineering water bodies [15,16]. EEM-PARAFC analysis can be used to decompose the fluorescence spectrum into independent fluorescence components [17]. Figure 3 shows the four DOM components of piggery wastewater. Component 1 had two fluorescence peaks at Ex/Em 240/410 nm and 320/410 nm and was identified as a fulvic-like and humic-like substance (C1) [16]. Component 2 had a fluorescence peak at Ex/Em 225/340 nm. A component with a fluorescence peak at Ex = 235∼240 nm/Em = 340∼355 nm in the PARAFAC analysis was identified as a tyrosine-like substance (C2) [18]. Component 3 had two fluorescence peaks at Ex/Em 260/485 nm and 365/485 nm and was considered to be a humic-like substance (C3) [17]. There was a fluorescence peak at Ex/Em 280/340 nm of component 4, which could be considered a tryptophan-like substance (C4) [19].
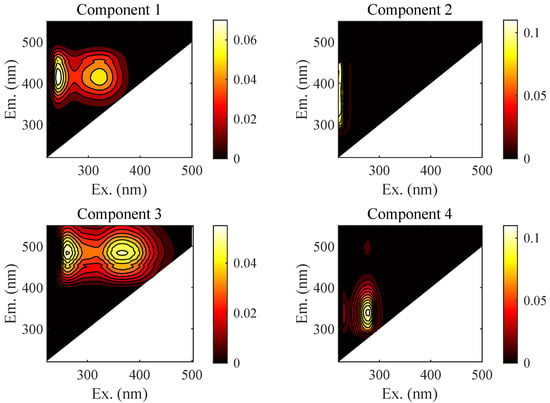
Figure 3.
EEM plots of four DOM components. Component 1, component 2, component 3, and component 4 are written as C1, C2, C3, and C4.
As shown in Figure 4a, C1 had the lowest score in the influent tank, and a very similar score in the DBR and the A/O/A/O systems. C2 had the highest score in the influent tank, and its score reduced significantly in both DBR and A/O/A/O systems. In particular, the A/O/A/O system was very successful at degrading C2. The score of C3 in the influent tank was very low, but it increased significantly in the DBR and A/O/A/O systems. This phenomenon indicates that C3 belongs to microbial metabolism products. C4 had the highest score in the influent tank, which was consistent with C2. This phenomenon indicates that amino-acid-like protein substances are easily utilized and degraded by microorganisms. Figure 4b shows the average total fluorescence intensity (TFI) of the influent, the DBR reactor, and the A/O/A/O reactor. The average TFI of the influent of piggery wastewater was 2.2. The average TFI of the DBR and A/O/A/O reactors was about 1.3 and 1.0, respectively. This phenomenon indicates that the organic matter degradation of piggery wastewater was obvious after biological treatment; in other words, a lot of organic matter was removed by microorganisms. The average TFI of the A/O/A/O system was slightly lower than that of the DBR system. This phenomenon indicates that the degradation ability of organic matter in the A/O/A/O system is stronger than that in the DBR system, which is consistent with the better removal performance of chemical pollutants in the A/O/A/O system. According to the statistical distribution of total fluorescence intensity of 25 samples, the standard deviation of each reactor in the A/O/A/O system is lower than that in the DBR system, indicating that the A/O/A/O system has better stability.
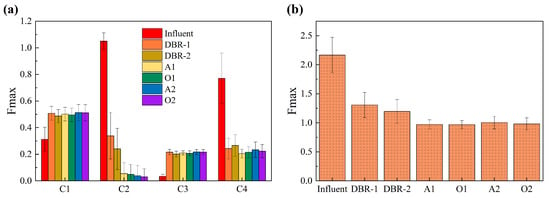
Figure 4.
Average maximum fluorescence intensity (Fmax) of (a) each organic component and (b) all four organic components in different reactors of 25 samples.
3.3. Characteristics of Fluorescence Spectral Indexes
Figure 5 shows the variation diagram of fluorescence spectral indexes that can reflect the chemical characteristics of DOM in piggery wastewater [20]. The fluorescence index (FI), humus index (HIX), and biological index (BIX) were used as supplementary evaluation indexes. As shown in Figure 5a, the average FI of the influent was 1.88. The average FI of the DBR and A/O/A/O systems was higher than 1.9. This phenomenon indicates that the endogenous characteristics of discharge water increased after biological treatment. Microbial endogenous metabolites are the metabolites of activated sludge flora, and they are difficult for microorganisms to degrade [21]. The average value of the effluent FI of each reaction tank in the DBR system was slightly higher than that in the A/O/A/O system, indicating that the DBR system had stronger endogenous characteristics. HIX can reflect the degree of humification of DOM. As shown in Figure 5b, the average HIX of the influent was about one. The effluent HIX of each reaction tank of the DBR system was around five, and that of the A/O/A/O system was between five and six. Thus, the humification characteristics of piggery wastewater after biological treatment were enhanced, and the enhancement performance of the A/O/A/O system was greater than that of the DBR system. BIX represents the biological activity of DOM in water. As shown in Figure 5c, the influent BIX was about 0.6, the BIX of the DBR system was nearly 0.8, the BIX of the A1 and O1 tanks was about 0.8, and the BIX of A2 and O2 tanks was about 0.75. This phenomenon indicates that the influent bioactivity was very weak, and a new soluble organic matter was produced after biological treatment [22].
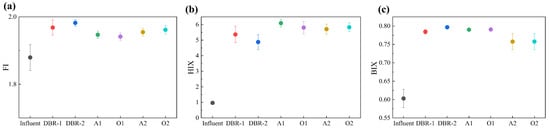
Figure 5.
Variation diagram of fluorescence spectral indexes: (a) FI; (b) HIX; and (c) BIX.
3.4. Characteristics of the Microbial Community
As shown in Figure 6a, at the phylum level, the abundances of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes in the WWTP system were 64% and 23%, respectively, accounting for a total of 87% abundance. They were the main dominant bacteria phyla in the biological treatment system of urban sewage [23,24]. In DBR-1 and DBR-2, the abundances of Proteobacteria were 41% and 45%, respectively, and that of Bacteroidetes reached 49% and 39%, respectively. Compared with the WWTP system, Proteobacteria was significantly reduced, while the opposite was true for Bacteroidetes. Bacteroidetes adapted to the piggery wastewater containing a high concentration of pollutants. In O1 and O2, the total abundances of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes reached 94.4% and 94%, respectively, which was higher than that of WWTP and DBR systems. In addition, Proteobacteria and Bacteroides are responsible for the stable removal of NH-N from piggery wastewater [25,26], which also explains why the A/O/A/O system had better NH-N removal performance.
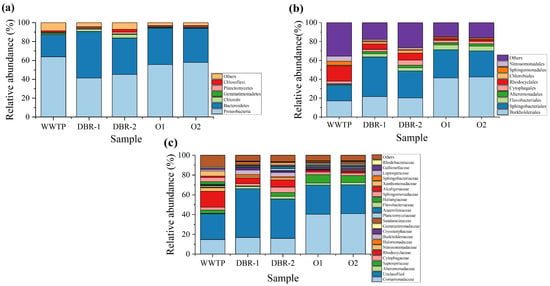
Figure 6.
The taxonomic analysis of the bacterial community. Relative abundances of the bacterial taxonomic groups at phylum level (a), order level (b), and family level (c) in DBR and A/O/A/O.
Figure 6b shows the composition and structure of microflora in WWTP, DBR, and A/O/A/O systems at the order level. The main dominant bacteria of WWTP were Burkholderiales (17%), Sphingobacteriales (16.9%), and Rhodocyclales (16.1%), respectively. The DBR system had the main dominant bacteria of Sphingobacteriales (35.2%), Burkholderiales (21%), and Rhodocyclales (6.6%), while the A/O/A/O system mainly consisted of Burkholderiales (42%), Sphingobacteriales (28.6%), and Flavobacteriales (5.1%). Compared with the WWTP system, Burkholderiales and Sphingobacteriales occupied a higher proportion in DBR and A/O/A/O systems, while Rhodocyclales have a lower proportion. Burkholderiales belonged to the Bataproteobacteria class of the phylum proteobacteria and were located in ecological environments, such as water and soil [27]. Yang et al. analyzed activated sludge from four A2/O process wastewater treatment plants in the Tianjin and Shandong Provinces, China, and obtained similar results [28].
Figure 6c shows the composition and structure of microflora in WWTP, DBR, and A/O/A/O systems at the family level. The main dominant bacteria of WWTP were Rhodocyclaceae (16.1%), Comamonadaceae (14.7%), Xanthomonadaceae (5.1%), Sphingomonadaceae (4.2%), and Nitrosomonadaceae (3.5%). The main dominant bacteria in the DBR system included Comamonadaceae (16.3%), Rhodocyclaceae (6.6%), Burkholderiaceae (4.3%), and Cytophagaceae (2.4%), while those in the A/O/A/O system included Comamonadaceae (40.7%), Saprospiraceae (7.7%), and Cytophagaceae (2.6%). Compared with WWTP and DBR systems, Comamonadaceae occupied a higher proportion in the A/O/A/O system, with a relative abundance of up to 40%. The relative abundance of Rhodocyclaceae was 16.1% in WWTP, 6∼7% in the DBR system, and 1.7% in the A/O/A/O system. The relative abundance of Saprospiraceae was 7∼8.5% in A/O/A/O systems, but this decreased significantly in WWTP and DBR systems.
3.5. Characteristics of Metabolite
Figure 7 shows the taxonomic analysis of the metabolite characteristics. Among the large number of metabolites produced by microorganisms in the WWTP system, the following have high relative abundance: 2-Hydroxy-2-Phenylacetophenone (15.9%), putrescine (8.7%), Ethanolamine (4.4%), ribose (3.6%), glutamine (1.9%), and 2Deoxyerythritol (1.8%). In the DBR system, the metabolites with high relative abundance are 5-Oxoproline (11.1%), D-Arabitol (8.7%), L-Alanine (4.3%), Methyl Phosphate (3.2%), Heptadecanoic Acid (3%), Trehalose (2.7%), and Ethanolamine (2.3 %). In the A/O/A/O system, the metabolites with high relative abundance are 5-Oxoproline (9.7%), galactose (6.7%), D-Arabitol (6.0%), L-Alanine (5.3%), glycerol (3.1%), palmitic acid (2.7%), Fructose 2, and 6-Biphosphate degr prod (2.6%). The metabolites of microorganisms in the WWTP system were mainly composed of small molecules such as ketones, amines, acids, and lipids, while the metabolites in DBR and A/O/A/O systems comprised small molecules such as amino acids, sugars, and alcohols [29,30].
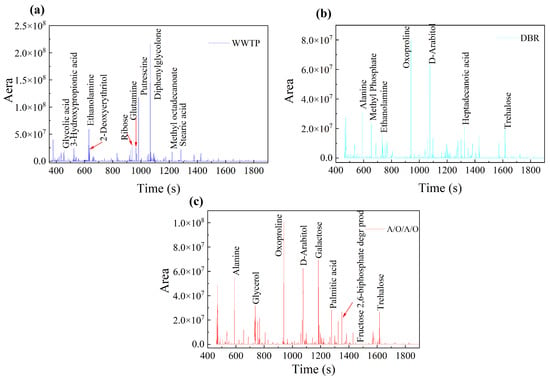
Figure 7.
Metabolite analysis in WWTP (a); DBR (b); and A/O/A/O (c) systems.
4. Conclusions
In summation, the performance, DOM composition, and microbial communities between DBR and A/O/A/O systems for piggery wastewater treatment have been compared in this study. The removal rate of NH-N and COD in the A/O/A/O system was better than that in the DBR system, while the removal rate of TN in the DBR system was better than that in the A/O/A/O system. Offering advantages such as low energy consumption and occupying a small amount of land, the DBR system is more suitable for large-scale treatment of piggery wastewater than the A/O/A/O system. Using the EEM-PARAFC analysis method, we identified four DOM components in piggery wastewater, which were fulvic acid-like/humic-like substances (C1), tyrosine-like substances (C2), humic-like substances (C3), and tryptophan-like substances (C4), respectively. Protein organic compounds C2 and C4 were degraded significantly, while humus organic compounds C1 were difficult for microorganisms to utilize. The C3 concentration in influent was very low but increased significantly in DBR and A/O/A/O systems, indicating that C3 might be a microbial metabolite. According to fluorescence spectral indexes, the endogenous characteristics and humus characteristics of piggery wastewater were enhanced after biological treatment. At the phylum level, Bacteroidetes (43.9% and 37.5%) and Proteobacteria (43.1% and 56.7%) dominated in DBR and A/O/A/O systems. In the A/O/A/O system, the total abundances of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes reached 94.2%, which was higher than that of the DBR (87%) system. Proteobacteria and Bacteroides are responsible for the stable removal of NH-N from piggery wastewater. At the order and family level, Sphingobacteriales (35.2%), Burkholderiales (21%), Comamonadaceae (16.3%), and Rhodocyclaceae (6.6%) were primarily involved in the removal of organic matter and nitrogen in the DBR system. The predominant bacteria of the A/O/A/O system were Burkholderiales (42%), Sphingobacterales (28.6%), Comamonadaceae (40.7%), and Saprospiraceae (7.7%). The microbial metabolites in the WWTP system were mainly composed of small molecules such as ketones, amines, acids, and lipids, while those in the DBR and A/O/A/O systems were mainly composed of amino acids, sugars, and alcohols.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L., J.G., Z.Z. and Y.C.; Data curation, J.L. and Z.Z.; Funding acquisition, J.G. and B.Z.; Investigation, J.L., Z.Z. and Y.C.; Methodology, J.L. and Z.Z.; Resources, B.Z.; Software, Y.C.; Supervision, Z.Z. and Y.C.; Validation, Z.Z.; Visualization, J.L.; Writing—original draft, J.L.; Writing—review and editing, J.G., Z.Z., Y.C., and B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2012AA06A304).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. Impacts of small-scale industrialized swine farming on local soil, water and crop qualities in a hilly red soil region of subtropical China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Hu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R.; Zheng, H. Coupling of biochar-mediated absorption and algal-bacterial system to enhance nutrients recovery from swine wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.; Nguyen, D.; Kumar, S. Microalgae biomass from swine wastewater and its conversion to bioenergy. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Riddicka, B.A.; Li, R.; Able, J.R.; Boakye-Boaten, N.A.; Shahbazi, A. Sustainable production of algal biomass and biofuels using swine wastewater in North Carolina, US. Sustainability 2016, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Kim, J.; Oh, S.; Regan, J.M.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, F. Comparison of three biomass-retaining reactors of the ASBR, the UBF and the USR treating swine wastewater for biogas production. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.; Arola, K.; Brewster, E.T.; Mehta, C.M.; Batstone, D.J. Nutrient recovery from wastewater through pilot scale electrodialysis. Water Res. 2018, 135, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Removal of antibiotics by sequencing-batch membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Narindri, B.; Chu, H.; Whang, L.M. Recent advancement on biological technologies and strategies for resource recovery from swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Visvanathan, C.; Abeynayaka, A. Effect of organic loading rate on VFA production, organic matter removal and microbial activity of a two-stage thermophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5353–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, T. Effect of Different Influent Flow Distribution Ratios on Multistage A/O Process for Removal of Carbon and Nitrogen. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, B. Efficient and microbial communities for pollutant removal in a distributed-inflow biological reactor (DBR) for treating piggery wastewater. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95987–95998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ghulam, A.; Trumbo, A.L.; Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Jing, Y. Evaluation and estimation of surface water quality in an arid region based on EEM-PARAFAC and 3D fluorescence spectral index: A case study of the Ebinur Lake Watershed, China. Catena 2017, 155, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S. Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. Am. Public Health Assoc. 1998, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Ly, Q.V.; Asif, M.B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Seasonal occurrence of N-nitrosamines and their association with dissolved organic matter in full-scale drinking water systems: Determination by LC-MS and EEM-PARAFAC. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. EEM–PARAFAC characterization of dissolved organic matter and its relationship with disinfection by-products formation potential in drinking water sources of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Hambly, A.; Singh, S.; Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Stuetz, R.; Khan, S.J. Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: Toward a unified PARAFAC model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2909–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tang, S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a submerged membrane bioreactor by using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, L.D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.Q.; Tao, X.M.; Tian, G.M. The evolution of bacterial community structure and function in microalgal-bacterial consortia with inorganic nitrogen fluctuations in piggery digestate. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Wei, L.; He, S.; Wu, H. Tracing dissolved organic matter in inflowing rivers of Nansi Lake as a storage reservoir: Implications for water-quality control. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Sheng, G.P.; Liu, X.W.; Yu, H.Q. Characterizing the extracellular and intracellular fluorescent products of activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Wen, X.; Xia, Y. Microbial community structures in different wastewater treatment plants as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 117, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Shao, M.F.; Ye, L. 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Song, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Luo, A.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Ye, Y. Deciphering dissolved organic matter from freshwater aquaculture ponds in Eastern China based on optical and molecular signatures. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, L.D.; Lin, D.X.; Qiu, D.S.; Chen, J.P.; Tao, X.M.; Tian, G.M. Characteristics and performances of microalgal-bacterial consortia in a mixture of raw piggery digestate and anoxic aerated effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.; Jing, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, R.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Huo, L.; et al. Discovery of recombinases enables genome mining of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters in Burkholderiales species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4255–E4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, R.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Song, C.; Qiao, C.; Mulchandani, A. Phylogenetic diversity and metabolic potential of activated sludge microbial communities in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7408–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauffret, A.; Baran, N.; Joulian, C. Effect of pesticides and metabolites on groundwater bacterial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Fang, Z. Microbial structures, functions, and metabolic pathways in wastewater treatment bioreactors revealed using high-throughput sequencing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13244–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).