Abstract
Rainfall is an important factor that causes riverine flow and sediment transport, and extreme rainfall has a particularly significant effect on the fluctuations of riverine flow and sediment load. Based on the daily rainfall from 1990 to 2020, in the upper watershed of the Lianjiang River, which is one of the source tributaries of China’s largest freshwater lake (Poyang Lake), the 95th percentile method and minimum event interval time were employed to identify extreme rainfall events. Mann–Kendall test was used to check for abrupt changes in annual rainfall, riverine flow discharge, and riverine sediment loads, and to identify abrupt-change years; thus, different periods were divided via the abrupt change years. Multiple linear regression was applied to explore the lag effect of riverine flow-discharge and sediment-load response to antecedent rainfall, with different cumulative durations for each period. The results of the study indicated that (1) the expansion of garden land in 1995 caused a significant and abrupt change in sediment load. (2) Extreme rainfall events had a greater impact on riverine flow and sediment load as compared to ordinary rainfall. These events were found to explain more variations in riverine flow and sediment load, which led to longer lag times for both riverine flow and sediment transport. (3) The expansion of garden land under extreme rainfall conditions resulted in longer lag times for riverine flow and sediment transport, and reduced the need for antecedent rainfall with a longer pre-event time. Therefore, the analysis of antecedent rainfall and the lag response of riverine flow discharge and sediment load can help in understanding the response mechanism of riverine flow discharge and sediment load for the current era of increasing extreme rainfall. This analysis is crucial for improving the accuracy of simulating riverine flow and sediment under extreme rainfall conditions. Ultimately, it can contribute to effective watershed management during extreme rainfall events.
1. Introduction
The riverine flow–sediment relationship is an extremely complex hydrological process, and the impacts of climate change and human activities on riverine flow–sediment changes are hot topics that have been discussed [1,2]. Numerous studies have shown that climate change has altered riverine flow discharge and sediment loads, which has been exacerbated by intense human activities [3,4]. Riverine flow discharge and sediment loads depend on a series of flow and sediment generation and transportation related processions, which spatial and temporal variations are easily affected by the temporal and spatial distribution of rainfall, evaporation, infiltration, runoff generation, and soil erosion [3]. Clarifying the study period is the key to discussing flow–sediment changes [3,4,5,6,7]. There is a lag effect in the influence of rainfall events on runoff and sediment, and the antecedent rainfall also affects the lag effect [8]. Antecedent rainfall and rainfall events both play an important role in the variation of flow discharge and sediment loads. There have been limited investigations into the impact of rainfall on river flow and sediment loads, specifically exploring the periods of flow–sediment change, the duration of the antecedent rainfall, and differentiating between various types of rainfall.
In the red hilly area of China, the annual rainfall is high, ranging from 1.9 to 2.8 times the national average level, and is disproportionally distributed throughout the year [9,10]. This region is particularly vulnerable to extreme rainfall from April to September, making it one of China’s most affected areas by water erosion [10]. Riverine sediment load is primarily triggered by rainfall [11,12], and its fluctuation is particularly affected by extreme rainfall due to induced serious soil erosion [13]. Extreme rainfall events demonstrate more comprehensively the effects of rainfall on riverine flow discharge and sediment loads, providing valuable insights into this relationship. Previous studies have observed the impact of extreme rainfall (storms) on riverine flow and sediment loads, but event-based studies offer better insights into the nature of riverine flow and sediment loads.
Antecedent rainfall increases soil moisture and reduces soil infiltration, so the significance of antecedent rainfall in sediment-load processes cannot be understated. Studies have confirmed that the runoff coefficient can double when the soil is moistened by antecedent rainfall, due to the acceleration of runoff generation with moist soils [14,15]. Antecedent rainfall increases soil moisture, improves runoff conversion efficiency, accelerates riverine runoff discharge [13,16], enhances water erosion, and increases riverine sediment loads. The amount of riverine sediment load after rainfall is influenced by moist soil before the event [17]. Meanwhile, nearly 70% of the runoff was related to the antecedent soil water content [18]. Antecedent soil moisture correlates more strongly with riverine flow. Antecedent soil moisture and rainfall are the important factors influencing riverine flow discharge [14,19], and the combination of antecedent rainfall and intra-event rainfall is vital to generate riverine flow discharge and sediment loads [14,20]. Larger floods caused by extreme rainfall respond more strongly to antecedent rainfall [21,22]. Riverine sediment is also affected by antecedent rainfall that accumulates in the soil [23], which is an easily overlooked effect [24]. Rainfall intensity and antecedent rainfall are also important contributors to changes in riverine flow discharge and riverine sediment loads [2,25,26], and their specific roles can differ depending on the region [8,22,27,28]. Only sufficiently accumulated antecedent rainfall in the soil can trigger massive riverine sediment in response to extreme rainfall [29,30]. However, the response of riverine flow discharge and sediment loads to antecedent rainfall of different cumulative durations remains unknown. By simultaneously considering the impact of rainfall events and antecedent rainfall on riverine flow and sediment loads, we can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of how rainfall influences riverine flow and sediment loads.
In this study, the daily rainfall, and riverine flow discharge and sediment loads from 1990 to 2020 in the upper watershed of the Lianjiang River were analyzed. The main objectives of this study were to (1) clarify the change characteristics of rainfall, and riverine flow discharge and sediment load; (2) check the abrupt changes in annual rainfall, riverine flow discharge, and riverine sediment loads, and to identify the abrupt-change years; (3) identify the most significant days with antecedent rainfall affecting riverine flow discharge and sediment load, and the most significant lag effecting days of riverine flow discharge and sediment load. Thus, the lag effect of riverine flow-discharge and sediment-load response to antecedent rainfall were explored. The results of this study would help to understand the underlying mechanisms that govern the response of riverine flow and sediment to extreme rainfall conditions and in improving predictive models to accurately simulate these phenomena.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lianjiang River watershed (115°11′53″~115°11′53″ E, 25°02′52″~25°21′10″ N) with a total watershed area of 2339 km2, which is located in the southern red soil area in China. The Lianjiang River is a first-class tributary of the upper Ganjiang River. Ganjiang River is the largest inlet river of Poyang Lake (Figure 1), in China.
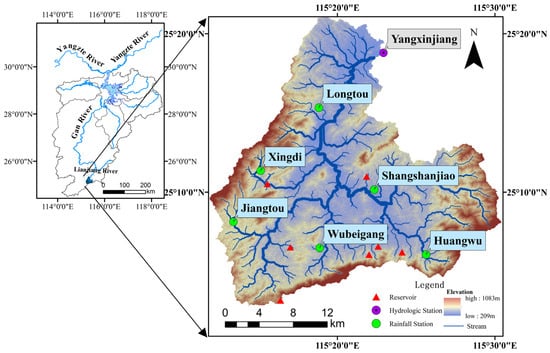
Figure 1.
Location of the study area in Poyang Lake watershed and the distributions of rainfall and hydrologic stations.
The average annual temperature is 18.7 °C; the annual runoff is 1.92 billion m3; and the annual suspended mass sediment transport is 259,000 t [9]. The upper watershed of the Lianjiang River, which was the focus of this study, is monitored by the hydrological station of Yangxinjiang. This station is responsible for managing a watershed area of 568 km2. The region is located in Anyuan County, where there was extensive promotion of citrus cultivation in the early 20th century due to policy initiatives. As a result, there have been significant changes in the land use in this area [9].
2.2. Data Collection
The hydrological data were obtained from the Jiangxi Provincial Hydrological Monitoring Center, which is the official hydrological monitoring institution, with the standard specifications for hydrological monitoring to acquire detailed and reliable hydrological data. This paper collected daily rainfall data from six rainfall stations (Huangya, Shangshanjiao, Wubeigang, Xingdi, Jiangtou, and Longtou) and one hydrological station (Yangxinjiang hydrological station), in the upper watershed of the Lianjiang River from 1990 to 2020, as well as daily runoff and sediment data from the Yangxinjiang hydrological station for the same period.
The land-use data were obtained from the geographic monitoring cloud platform (http://www.dsac.cn/, the accessed data was 12 August 2020) with a spatial resolution of 30 m during 1990–2020, with four periods of 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 [31], which are some of the most authoritative land-use data in China. Land-use types are classified into 6 main categories and 25 subcategories. The classification accuracy of crop land and urban-rural, industrial, mining, and residential land is consistently above 85%, while the accuracy of other land-use types is above 75% on average. This indicates a high level of accuracy in the classification process [31]. In these data, the other wooded land refers to young afforested land, traces, nurseries, and various types of gardens (orchards, mulberry gardens, tea gardens, hot crop gardens, etc.). Referring to the corresponding garden area of Anyuan County, in the statistical yearbook of Ganzhou City from 1992 to 2020 [32], the other wood land could be identified as garden land in the study area.
2.3. Definition of Extreme Rainfall Events
The rainfall data of the Lianjiang River watershed is based on rainfall data from seven stations. The average daily rainfall is calculated using the Thiessen polygon as the following formula.
where Ri is the amount of rainfall greater than 1 mm at each rainfall station (mm); si is the control area of each rainfall station (km2); S is the total area of the watershed (km2); n is the number of rainfall stations; and, here, n = 7 is taken. In this paper, the daily rainfall is selected to be greater than 1 mm, and the 95th percentile value was used as the threshold value [33]. The threshold for extreme rainfall in the upper reaches of the Lianjiang River watershed was calculated based on the average daily rainfall and is determined to be 41.71 mm.
2.4. Mann–Kendall Test
The Mann–Kendall method, or M–K Test, is a non-parametric diagnostic technique that can be applied to determine whether there is an abrupt change in time series data, and if so, when it occurs [34]. The M–K test does not require a normal distribution of the data series, which is very data-friendly [35]. In this study, the M–K test was applied to analyze the yearly rainfall, and riverine flow discharge and sediment load data to detect whether there was an abrupt change, and in which year the abrupt change happened.
2.5. Pre-Processing of Hydrological Data
In this study, a single rainfall event was defined as a continuous rainfall event where every daily rainfall was greater than 1 mm. Extreme rainfall events were defined as the rainfall events in which the daily rainfall exceeded the extreme rainfall threshold (41.71 mm) on any given day, while other rainfall events were considered as ordinary rainfall events. By analyzing the flood’s hydrological element extraction table of Yangxinjiang hydrological station from Jiangxi Provincial Hydrological Monitoring Center, it was found that the duration of flood events at Yangxinjiang hydrological station was almost no more than 5 days. In order to eliminate the interference of different flood events, this study only selected rainfall events with an interval of more than 7 days for analysis. During the period 1990–2020, 150 extreme rainfall events and 740 ordinary rainfall events were selected in this study.
2.6. Multiple Regression Analysis
Multiple linear regression models are an intuitive and efficient way to analyze complex problems [36]. In this study, we used the rainfall of the rainfall event as the fixed independent variable, and the riverine flow discharge or sediment load within the event as the dependent variable. We added antecedent rainfall at different accumulation times as an independent variable and riverine flow discharge or sediment load at different time durations as a dependent variable. The multiple linear regressions were fitted sequentially with the combination of every AP and RA or SA list in Table 1. The optimal model was selected based on the highest R2, which implied the highest degree of explanation.

Table 1.
Indicator labels and content.
3. Results
3.1. Change Characteristics of Rainfall, Riverine Flow Discharge, Sediment Load, and Garden Land
From 1990–2020, there were a total of 205 days with daily rainfall exceeding the given threshold and 3888 days with daily rainfall between 1 mm and the threshold. The yearly rainfall varied between 1080.9 and 2174 mm (Figure 2a); the yearly riverine flow discharge ranged from 172.39 to 1017.07 × 106 m3 (Figure 2c); and the yearly riverine sediment load ranged from 0.57 to 64.30 × 104 t (Figure 2e) from 1990 to 2020. The M–K test showed that rainfall (Figure 2b) and riverine flow discharge (Figure 2d) did not undergo a significant mutation (p > 0.05) from 1990 to 2020. Only riverine sediment load underwent a significant mutation, and the year of mutation was 1995 (p = 0.041) (Figure 2f). Therefore, the study period could be split into two periods with the abrupt year; thus, 1990–1995 is period 1 (P1) and 1996–2020 is period 2 (P2). Subsequently, the effects of rainfall events on riverine runoff discharge and sediment load were dissected under the above two different periods.
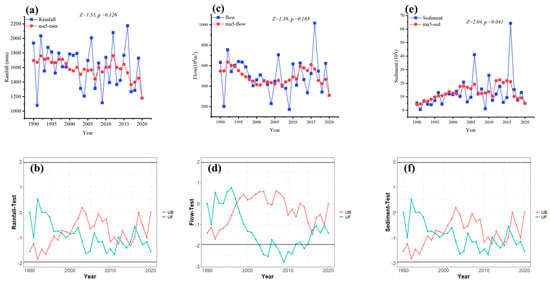
Figure 2.
Annual variations, and Mann–Kendall test of rainfall (a,b), flow discharge (c,d), and sediment load (e,f).
The garden area in Anyuan County generally increased from 1992 to 2020, reaching a peak of 192.59 km2 in 2014 (Figure 3). In terms of spatial expansion, newly developed orchards were relatively concentrated in distribution, and located mainly near the main stream and main tributaries of the Lianjiang River (Figure 3).
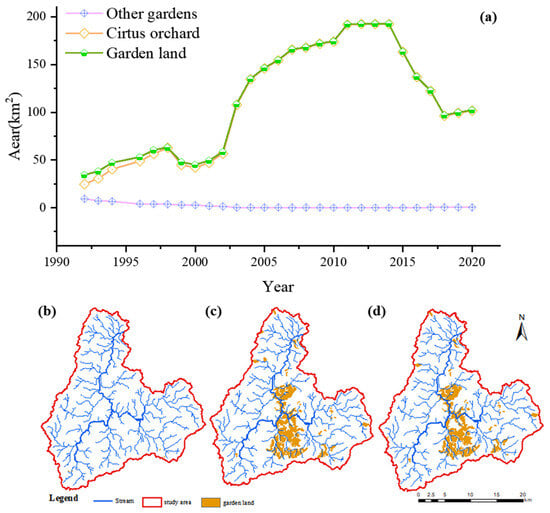
Figure 3.
The area of garden land in Anyuan country, from 1992 to 2020 (a), Spatial distribution of garden land in the upper Lianjiang River watershed ((b): 1990, (c): 2010, and (d): 2020).
3.2. Statistical Characteristics of Rainfall, Riverine Flow, and Riverine Sediment Loads in Different Periods
Compared with the P1 period, the rainfall decreased significantly in the P2 period. The mean extreme rainfall, mean ordinary rainfall, and total rainfall decreased from 328.10 mm, 796.55 mm and 1716.53 mm to 278.53 mm, 726.91 mm and 1584.54 mm, respectively (Figure 4). Similarly, the mean extreme rainfall, mean ordinary rainfall and total rainfall of river flow decreased from 241.01 × 106 m3 in P1, 146.36 × 106 m3, and 562.85 × 106 m3 to 222.17 × 106 m3, 125.02 × 106 m3, and 484.92 × 106 m3 in P2 (Figure 4). Interestingly, despite the decrease in rainfall and riverine flow, the riverine sediment loads increased significantly during P2 (Figure 4). The mean sediment loads of extreme, ordinary, and total rainfall increased from 0.60 × 104 t, 1.50 × 104 t, and 4.72 × 104 t in P1 to 2.89 × 104 t, 4.31 × 104 t, and 14.69 × 104 t, respectively, in P2 (Figure 4). The frequency of extreme and ordinary rainfall events was relatively stable at about 5 and 24 events, respectively (Figure 5). The proportion of ordinary and extreme rainfall events was also about the same in both periods, at over 45% and over 15%, respectively (Figure 5).
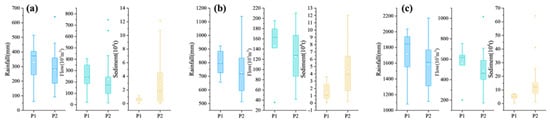
Figure 4.
Distribution characteristics of extreme rainfall (a), ordinary rainfall (b), total rainfall (c), and their corresponding riverine flow discharge and sediment load for different periods. Solid lines and square in this figure represent the median and mean, respectively. The box boundaries represent the 75% and 25% quartiles; the whisker caps represent the 90% and 10% quartiles; and the circles represent the 95% and 5% quartiles.
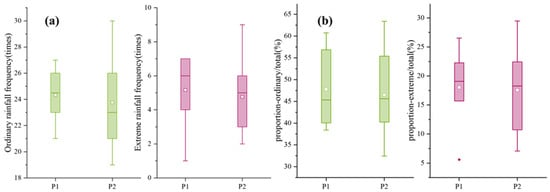
Figure 5.
The frequency (a) and proportion (b) distribution of ordinary and extreme rainfall in different periods. Solid lines and square in this figure represent the median and mean, respectively. The box boundaries represent the 75% and 25% quartiles; the whisker caps represent the 90% and 10% quartiles; and the circles represent the 95% and 5% quartiles.
It is noteworthy that the sediment-production capacity per unit of rainfall for extreme rainfall events in the P2 period was higher than that of ordinary rainfall; although, the frequency of occurrence was lower. Even small decreases in rainfall and a lower frequency of extreme events have the potential to cause an observed increase in sediment loads within river ecosystems.
3.3. Impact of Antecedent Rainfall on Runoff
From the period of P1 to P2, the optimal influence factor of the preceding rainfall on runoff in the extreme rainfall scenario changed from AP5 to AP7. The affected riverine flow discharge was extended from RA1 to RA7 (Table 2), and the degree of explanation in the period of P2 declined from 0.729 to 0.470. In contrast, the optimal influencing factor of riverine flow discharge by the antecedent rainfall changed from AP7 to AP2 in the ordinary rainfall scenario, and the affected riverine flow discharge was RA1 in both periods (Table 2).

Table 2.
Multiple regression modeling of antecedent rainfall and riverine flow discharge, under extreme and ordinary rainfall scenarios for different periods.
3.4. Impact of Antecedent Rainfall on Sediment
The regression model was statistically significant (p < 0.05) only in the extreme rainfall scenario (Table 3). During the P1 period, AP3 was the antecedent rainfall with the highest degree of explanation of riverine flow discharge, whereas the corresponding dependent variable was SA1. During the P2 period, AP7 and SA7 were the most highly explained independent and dependent variables, respectively. From P1 to P2, R2 decreased from 0.554 to 0.245 for the extreme rainfall scenario (Table 3).

Table 3.
Multiple regression modeling of antecedent rainfall and sediment under extreme and ordinary rainfall scenarios for different periods.
4. Discussion
Previous researchers have broadly attributed changes in riverine flow discharge and sediment load to both climate change and human activities [6,37,38]. Rainfall changes in the upper Lianjiang River watershed were not significant, so it was inferred that the dramatic increase in sediment could be due to human activities. The expansion of the garden land in the study area was drastic, and no large- or medium-sized reservoirs were built in the study area [9]. During the P2 period, extreme rainfall explained less of the riverine flow discharge (Table 2) and sediment load (Table 3), which may be related to the enhancement of human activities (orchard expansion). Conversion of orchards from forested land reduces surface vegetation cover and, consequently, runoff losses [39,40], which has a reduced scouring and transporting effect on soil particles.
Garden expansion increases riverine sediment loads in the red hilly area in China [5], and the same phenomenon is observed in the provinces of Granada and Málaga [41]. During the P2 period, the degree of explanation (R2) of rainfall events on riverine flow discharge decreased to 0.470 for the extreme rainfall scenario (Table 2). Rainfall and river flow decreased during P2, while river sediment loads increased significantly. Extreme and ordinary rainfall as a proportion of total rainfall did not change much between the two periods, while the corresponding average sediment loads increased by 4.8 and 2.8 times, respectively. The decrease in rainfall directly reduces river flow, while the increase in riverine sediment load is attributed to human activities [3,4]. Most of the new gardens were found near the main stem of the river (Figure 3). The conversion of land to orchards significantly impacts riverine flow discharge and sediment loads [41]. Newly reclaimed orchards often have severe soil erosion, and increased riverine sediment loads [1,11,15]. The presence of orchards near the main stem of the river reduces the distance over which runoff reaches the river, thereby increasing riverine flow discharge and sediment loads [37]. Orchard development or clean-cultivated orchards increased riverine sediment load [42,43,44,45]. In orchards, more than 80 percent of rainfall is lost through runoff, which can be reduced by 86 percent with optimal tillage practices [18]. Management practices in orchards are vital to riverine flow discharge and sediment loads [46]. The implementation of soil and water conservation measures in orchards is effective in reducing riverine sediment loads [43,45]. Extreme rainfall events and orchard-management practices are key factors influencing sediment yield in orchards [47].
The degree of explanation (R2) for the response of riverine sediment loads to antecedent rainfall was reduced to 0.245 (Table 3) during the P2 period. Soil and water conservation measures have played a crucial role in orchards [48]. With the fully functioning of soil and water conservation measures (e.g., horizontal terraces, anti-slope terraces, grass strip, etc.) after orchard maturity, water infiltration, and water retention capacity was effectively increased, and the time for runoff to reach the river was prolonged [46]. In addition, restored vegetation can effectively obstruct runoff from saturated soils [49] and reduce sediment loads [43,47]. Vegetation restoration also lengthens the time of runoff from the slope, to the flow, and into the river. Those all explain the insignificant response of riverine sediment loads to rainfall in the ordinary rainfall scenario during P2.
Extreme rainfall is a strong driver of riverine flow discharge and sediment load changes [2,9]. In other words, extreme rainfall is an important environmental factor for the lag time of antecedent rainfall on riverine flow discharge and sediment. Extreme rainfall produces fast-flowing runoff that is less consumptive. The lag time of riverine flow discharge depends on the soil-moisture conditions before the event [50]. Rainfall intensity severely affects flow-discharge lag time, and high-intensity and long-duration rainfall shortens the response time of river runoff [51]. Ordinary rainfall, on the other hand, requires the soil to reach the moist threshold for runoff to occur [14]. Rainfall and rainfall intensity are also important factors in the lag time of riverine flow discharge [52,53].
Lag time is a significant indicator of the lag effect, which varies during different periods of flow–sediment. During the P2 period, the lag time of the riverine flow discharge response to the rainfall was shortened from AP7 to AP2, in the ordinary rainfall scenario (Table 2). Garden-land reclamation removed vegetation from the surface. The consumption of runoff is reduced, and the demand for antecedent rainfall is reduced. Under the extreme rainfall scenario, the lag time for both riverine flow discharge and sediment during P2 is 7 days, and the duration of the antecedent rainfall corresponding to the riverine flow discharge and sediment is also 7 days (Table 2 and Table 3). Changes in riverine flow discharge are closely related to antecedent rainfall and land use [38]. The conversion process destroys the original ground cover [54], reducing evapotranspiration and moisture absorption from antecedent rainfall [55]. Soil-moist conditions can significantly increase riverine sediment concentration [56]. The lag effect is bound to change as more rainfall converges into the river. The lag time for riverine flow discharge is one day after the rainfall event for extreme rainfall in period P1 and for ordinary rainfall in both periods, while the lag time for riverine flow discharge is 7 days after the rainfall event for extreme rainfall in period P2. Haga et al. conducted a study and discovered that the antecedent soil-moisture conditions and the amount and intensity of rainfall played a crucial role in determining the lag time [29]. Davis conducted another study and demonstrated that implementing biological measures had a significant impact on both the peak flow and the delay in reaching the peak [57]. He et al. conducted a study and found that the lag effect in watershed was a consequence of the interaction among four factors: rainfall, watershed storage, human activities, and the lag period [52]. The increase in human activities, particularly garden development, in the Lianjiang River basin will undoubtedly alter the lag time of river runoff and sediment loading. Sultan et al. emphasized that implementing soil and water conservation measures in shrub forests and natural forests did not effectively reduce runoff [58]. However, the implementation of such measures in plantations could lead to a reduction in runoff of up to 34% [58]. On the one hand, ordinary rainfall events bring less moisture and even less runoff into the river, and the lag time of riverine flow discharge changes weakly. On the other hand, riverine flow discharge from extreme rainfall events is more responsive to orchard expansion, and a longer lag time for riverine flow discharge means more riverine flow discharge is generated. During the P1 period, there was a high amount of rainfall and frequency, and forest land remained untouched. This allowed for more interception of rainfall by the ground surface and less runoff into the river, resulting in lower sediment loads. In the P2 period, however, rainfall and frequency reduced, while garden land began to emerge, resulting in increased stripping of the ground surface and erosion. This led to more-successful conversion of rainfall to riverine flow, ultimately increasing its effect on the riverine sediment loads in the river.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we examined the rainfall, flow discharge, and sediment load data from the upper Lianjiang River watershed, located in the source area of Chinese largest freshwater lake (Poyang Lake), with humid climate, from 1990 to 2020. We defined extreme rainfall events, and then identified the mutation years in the annual flow-discharge and sediment-load data series, which divided the study period into different periods for further analysis. We also investigated the lag effect of riverine flow-discharge and sediment-load response to antecedent rainfall, with different cumulative durations for each period and rainfall event type. The results showed the following:
(1) During the period of 1990–2020, the sediment load in the upper Lianjiang River watershed experienced a significant abrupt change in 1995, while no such change occurred for rainfall and flow discharge. The increase in garden area, particularly near the main stem of the river, was identified as a potential factor contributing to the change in riverine sediment load.
(2) Extreme rainfall events had a greater impact on riverine flow discharge and sediment load, compared to regular rainfall events, leading to a more significant effect on the lag time of riverine flow discharge and sediment. Expanding garden land increased the lag times for riverine flow discharge and sediment load, and prolonged their response time to preceding rainfall. Garden growth and development reduced soil erosion by improving riverine flow and sediment loads through increased soil stability and better water infiltration.
The results could help to understand the response mechanism of riverine flow discharge and sediment load to antecedent rainfall, and improve the accuracy of simulating riverine flow and sediment under extreme rainfall conditions, which would contribute to effective watershed management during extreme rainfall events.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z., X.N., H.Z. and K.L.; supervision and funding acquisition, X.N., H.Z. and J.Z.; data analysis, L.Z. and X.N.; writing the manuscript, L.Z. and X.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42267058), Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology Major Science and Technology R&D Special “Unveiling” Project (20213AAG01012), Double Thousand Plan of Jiangxi Province (No. JXSQ2023102244),the Science Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Water Conservancy Department in China (202124ZDKT25, 202223YBKT18), and Science and Technology Plan Project of Zhejiang Provincial Water Conservancy Department (RB2023).
Data Availability Statement
Data for this work can be found within the article, and for further data, contact the first author or corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sriwongsitanon, N.; Taesombat, W. Effects of land cover on runoff coefficient. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadat, F.M.; Taimeh, A.Y. Effect of Rainfall Intensity, Slope, Land Use and Antecedent Soil Moisture on Soil Erosion in an Arid Environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Hou, X.L.; Qiao, J.X.; Zhang, W.C.; Fang, M.; Lin, M. Evaluation of soil erosion rates in the hilly-gully region of the Loess Plateau in China in the past 60 years using global fallout plutonium. Catena 2023, 220, 106666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.D.; Zhang, H.D.; Chen, J. Effect of rainfall variation and landscape change on runoff and sediment yield from a loess hilly catchment in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.L.; Yang, X.H.; Chen, S.X.; Cai, H.Y. An assessment of erosivity distribution and its influence on the effectiveness of land use conversion for reducing soil erosion in Jiangxi, China. Catena 2015, 125, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhai, J.Q.; Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M. Dynamics of Runoff and Suspended Sediment Transport in a Highly Erodible Catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.X.; Sang, Y.; Hu, J.W.; Wang, W.P.; Wang, H.X. Characteristics and attribution analysis of runoff and sediment evolution in the Wei River mainstream, China. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, 2432–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Nathan, R. Influence of changes in rainfall and soil moisture on trends in flooding. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.X.; Guo, Z.L.; Nie, X.F.; Liao, K.T.; Zheng, H.J. Effects of extreme rainfall events on runoff and sediment in the southern red soil area: A long series analysis based on the Upper Lianjiang River of Ganjiang River (1984–2020). J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, D.C.; Lu, X.X.; Yang, X.; Pan, X.Z.; Mu, H.; Shi, D.M.; Zhang, B. Soil Erosion Changes over the Past Five Decades in the Red Soil Region of Southern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2010, 7, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Tang, C.J.; Shi, Z.H. Role of groundcover management in controlling soil erosion under extreme rainfall in citrus orchards of southern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, W. Runoff velocity controls soil nitrogen leaching in subtropical restored forest in southern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 548, 121412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.; Leonard, M.; Deng, Y.; Westra, S. An empirical investigation into the effect of antecedent precipitation on flood volume. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Gao, L.; Huang, S.S.; Peng, X.H. Combined effects of rainfall types and antecedent soil moisture on runoff generation at a hillslope of red soil region. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Contreras, S.; Sole-Benet, A.; Canton, Y.; Domingo, F.; Lazaro, R.; Lin, H.; Van Wesemael, B.; Puigdefabregas, J. Controls of infiltration-runoff processes in Mediterranean karst rangelands in SE Spain. Catena 2011, 86, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhu, X.I.; Xiong, X.; Wu, T.; Zhou, S.Y.D.; Lie, Z.; Jiang, X.J.; Liu, J.X. Changes in soil infiltration and water flow paths: Insights from subtropical forest succession sequence. Catena 2023, 221, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.G.; Zeng, J.L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, H.J.; Xie, S.H. Effect of minimum inter-event time for rainfall event separation on rainfall properties and rainfall erosivity in a humid area of southern China. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrisqueta, J.M.; Plana, V.; Mounzer, O.H.; Mendez, J.; Ruiz-Sanchez, M.C. Effects of soil tillage on runoff generation in a Mediterranean apricot orchard. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 93, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Lamoureux, S.F.; Lafreniere, M.J.; Lewis, T. Hydrological and sediment yield response to summer rainfall in a small high Arctic watershed. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Rahardjo, H.; Nistor, M.M.; Satyanaga, A.; Leong, E.C.; Sham, A.W.L. Assessment of critical rainfall scenarios for slope stability analyses based on historical rainfall records in Singapore. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Nathan, R.; Stein, L.; O’Shea, D. Evidence of shorter more extreme rainfalls and increased flood variability under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, N.; Devineni, N. Scaling of Floods With Geomorphologic Characteristics and Precipitation Variability Across the Conterminous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR032815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defersha, M.B.; Quraishi, S.; Melesse, A. The effect of slope steepness and antecedent moisture content on interrill erosion, runoff and sediment size distribution in the highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.C. Effect of Antecedent Rainfall Patterns on Rainfall-Induced Slope Failure. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, F.L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.C.J.; Shi, H.Q. Interactive effects of rainfall intensity, kinetic energy and antecedent soil moisture regime on splash erosion in the Ultisol region of South China. Catena 2023, 222, 106863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, Y.L.; Luo, D.; Fan, B.H.; Chu, G.C. Storm runoff generation in headwater catchments on the Chinese Loess Plateau after long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.Y.; Ye, S. The relative importance of antecedent soil moisture and precipitation in flood generation in the middle and lower Yangtze River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4919–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cai, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, Z. Integrated erosion control measures and environmental effects in rocky mountainous areas in northern China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 25, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsutani, J.; Fujita, M.; Nishida, K.; Sakamoto, Y. Flow paths, rainfall properties, and antecedent soil moisture controlling lags to peak discharge in a granitic unchanneled catchment. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.Q.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.X.; Li, W.K.; Tian, Z.C.; Lin, L.R.; He, Y.B.; Chen, J.Z. Soil moisture dynamics near a gully head in relation to the trigger of collapse in granite red soil slope in southern China. Geomorphology 2023, 420, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzhou Municipal Bureau of Statistics, National Bureau of Statistics Ganzhou Survey Team. Ganzhou Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1993–1995, 1997–2021; pp. 0–376.
- Fang, N.F.; Shi, Z.H.; Yue, B.J.; Wang, L. The Characteristics of Extreme Erosion Events in a Small Mountainous Watershed. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Rahman, K.U. Identifying the Annual and Seasonal Trends of Hydrological and Climatic Variables in the Indus Basin Pakistan. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013-2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.G.; Yang, J.S.; Qi, D.L.; Sun, L.Y.; Cai, Q.G. Flow-sediment relationship as functions of spatial and temporal scales in hilly areas of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2012, 98, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Ma, Y.; Sivapalan, M. Multiscale temporal variability of flow-sediment relationships during the 1950s-2014 in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Borga, M.; Preciso, E.; Gaume, E. Characterisation of selected extreme flash floods in Europe and implications for flood risk management. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y. Aggregate-associated soil organic carbon fractions in subtropical soil undergoing vegetative restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4296–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Ruiz, J.A.; Raya, A.M.; Tarifa, D.F. Impact of erosion in the taluses of subtropical orchard terraces. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Terol, E.; Cerda, A. Effects of parent material on soil erosion within Mediterranean new vineyard plantations. Eng. Geol. 2018, 246, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Taguas, E.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Quantification of soil and water losses in an extensive olive orchard catchment in Southern Spain. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerd, A.; Terol, E.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Weed cover controls soil and water losses in rainfed olive groves in Sierra de Enguera, eastern Iberian Peninsula. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanis, I.K.; Seiradakis, K.D.; Sarchani, S.; Panagea, I.S.; Alexakis, D.D.; Koutroulis, A.G. The Impact of Soil-Improving Cropping Practices on Erosion Rates: A Stakeholder-Oriented Field Experiment Assessment. Land 2021, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tang, C.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Yang, J. Efficacy of orchard terrace measures to minimize water erosion caused by extreme rainfall in the hilly region of China: Long-term continuous in situ observations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, J.R.; Senciales, J.M.; Ramos, M.C.; Martinez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Lasanta, T.; Brevik, E.C.; Ries, J.B.; Sinoga, J.D.R. Understanding soil erosion processes in Mediterranean sloping vineyards (Montes de Malaga, Spain). Geoderma 2017, 296, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, F.; Monfared, A.B.; Jahansooz, M.R.; Esparza, E.T.; Keshavarzi, A.; Morera, A.G.; Fernandez, M.P.; Cerda, A. Analyzing long-term soil erosion in a ridge-shaped persimmon plantation in eastern Spain by means of ISUM measurements. Catena 2019, 183, 104176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Gomez, J.A.; Zema, D.A. Water Infiltration and Surface Runoff in Steep Clayey Soils of Olive Groves under Different Management Practices. Water 2019, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhang, F.B.; Wang, S.W.; Yang, M.Y. Combined influences of wheat-seedling cover and antecedent soil moisture on sheet erosion in small-flumes. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.Z.; Sun, T.Y.; Fei, K.; Zhang, L.P.; Fan, X.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Ni, L. Effects of erosion degree, rainfall intensity and slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield for the bare soils from the weathered granite slopes of SE China. Geomorphology 2020, 352, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Zhao, C.W.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, H.; Yang, Z.H. Temporal-spatial evolution of lagged response of runoff to rainfall in Karst drainage basin, Central Guizhou of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Emanuel, R.E.; McGlynn, B.L.; Miniat, C.F. Soil Moisture Responses to Rainfall: Implications for Runoff Generation. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, G.Q.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P. Experimental Study on Slope Runoff, Erosion and Sediment under Different Vegetation Types. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2415–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zou, L.; Xia, J.; Dou, M.; Li, H.W.; Song, Z.H. Untangling the effects of climate change and land use/cover change on spatiotemporal variation of evapotranspiration over China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, E.; Fusco, F.; Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W.; De Vita, P. Effect of antecedent-hydrological conditions on rainfall triggering of debris flows in ash-fall pyroclastic mantled slopes of Campania (southern Italy). Landslides 2016, 13, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P. Field performance of bioretention: Hydrology impacts. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, D.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Meshesha, D.T.; Masunaga, T.; Aklog, D.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K. Impact of Soil and Water Conservation Interventions on Watershed Runoff Response in a Tropical Humid Highland of Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 2018, 61, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).