Numerical Investigation of Hydrodynamic Responses of a Moored Liquefied Natural Gas Ship under Multimodal Waves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Setup
2.1. Wave Identification
2.2. Vessel Type and Mooring Configures Information
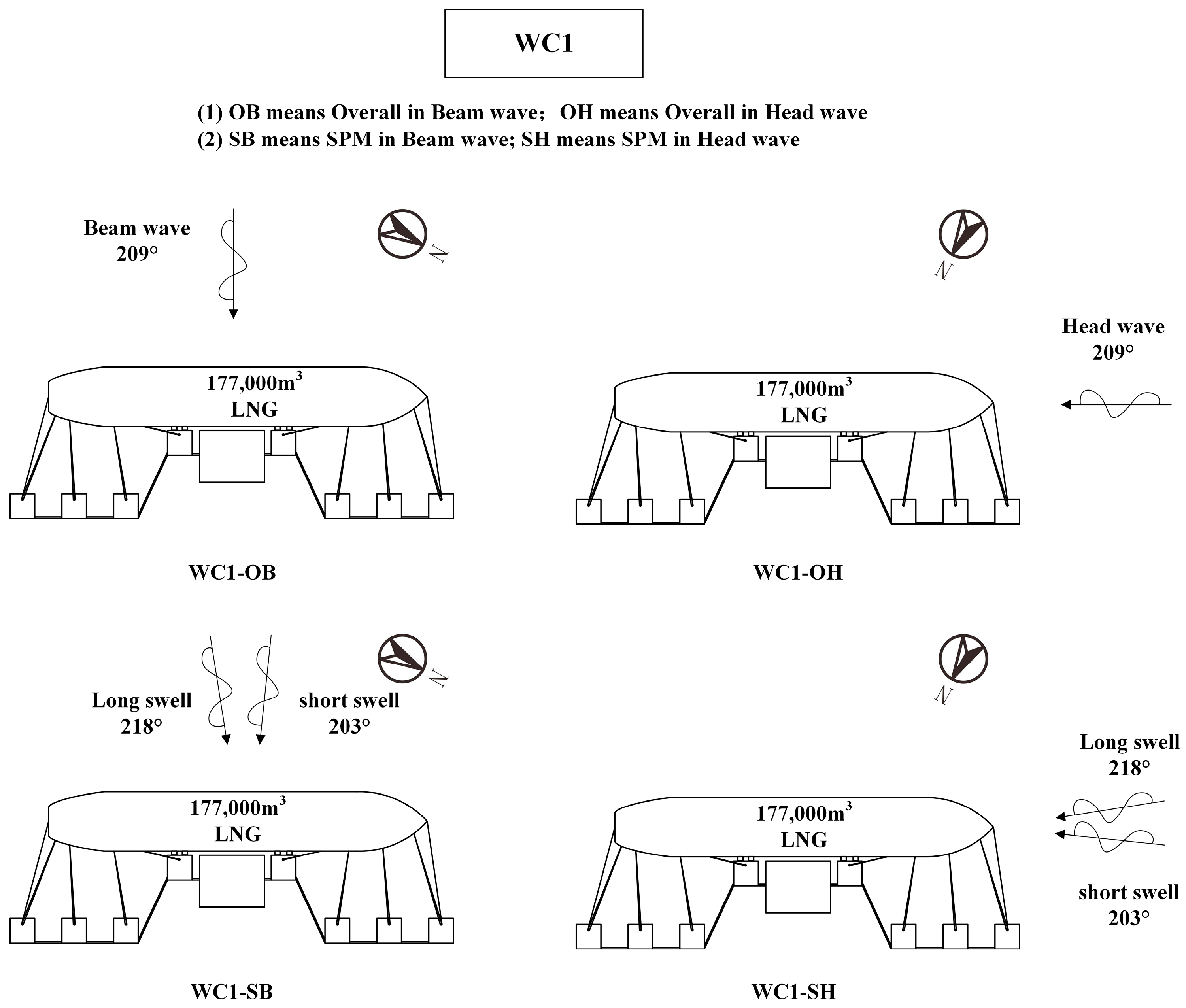
2.3. Computational Cases
3. Results and Discussion
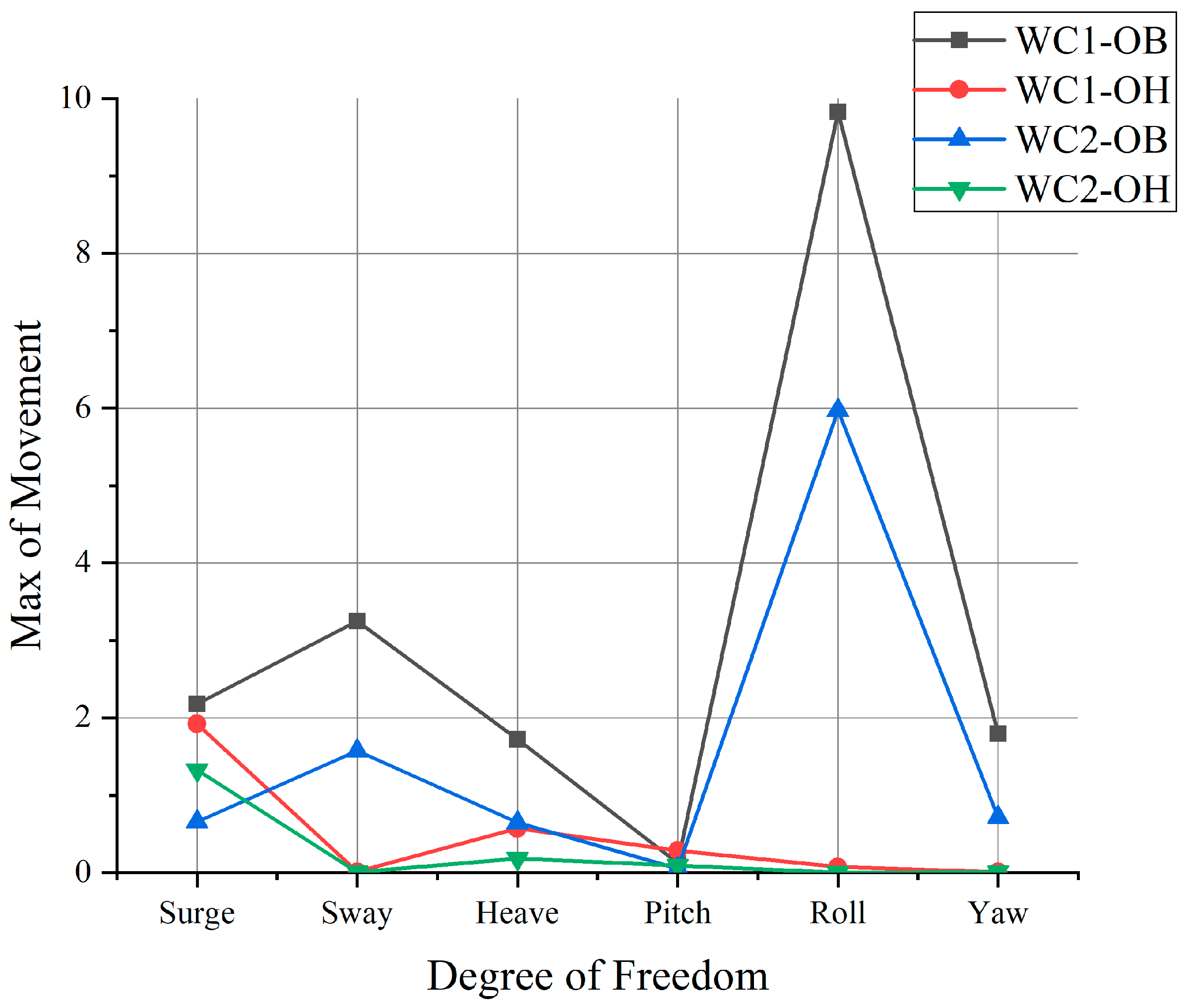
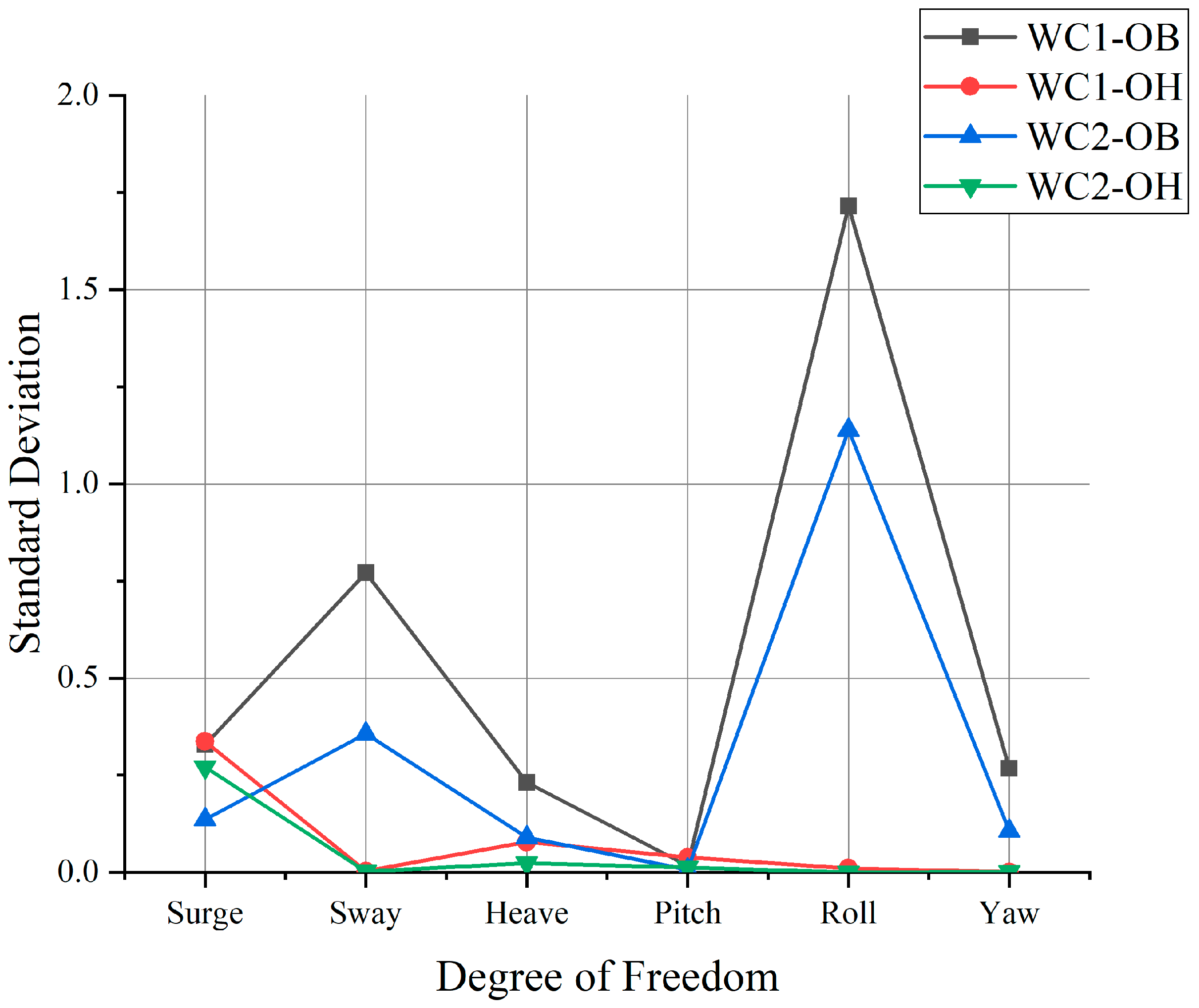
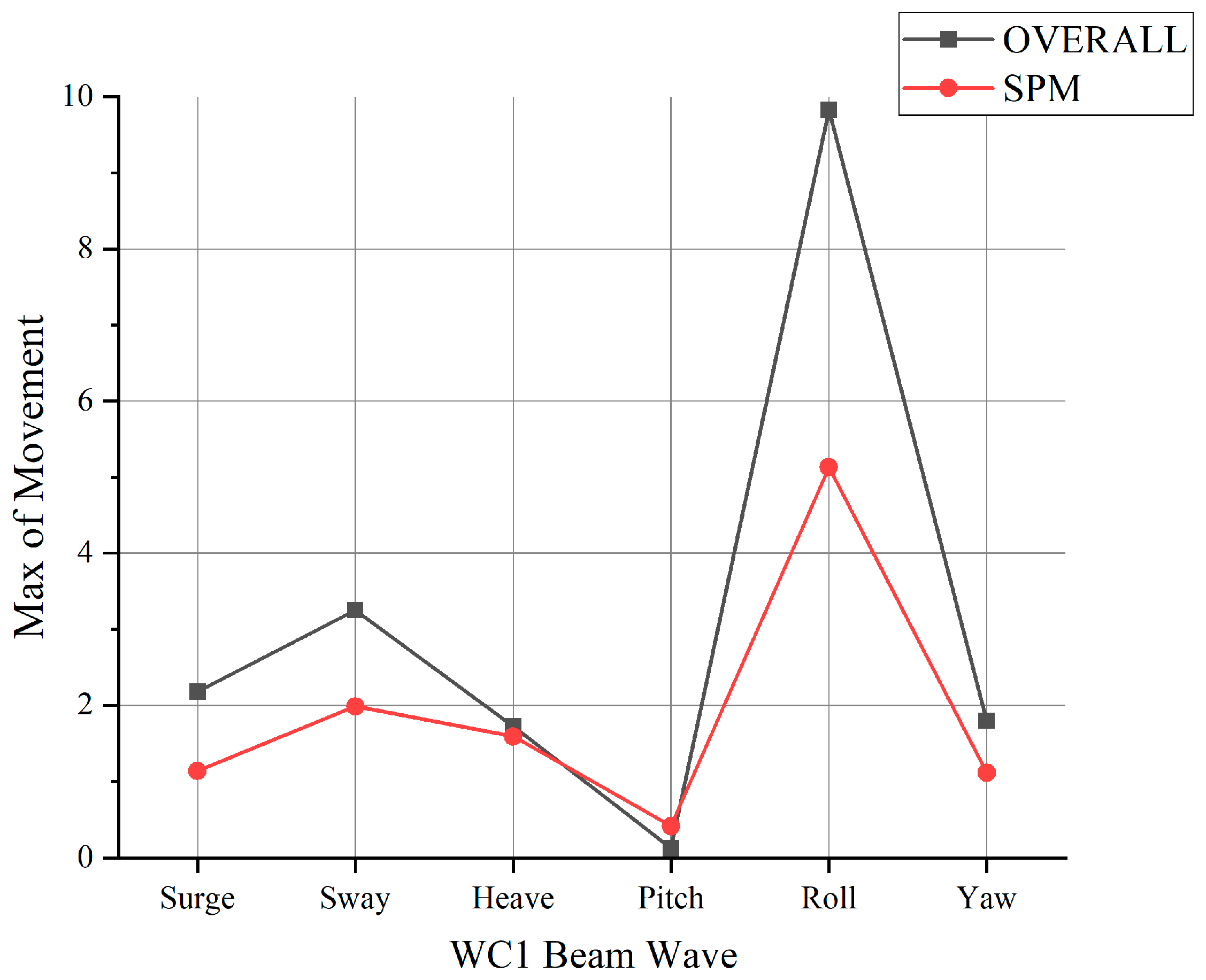
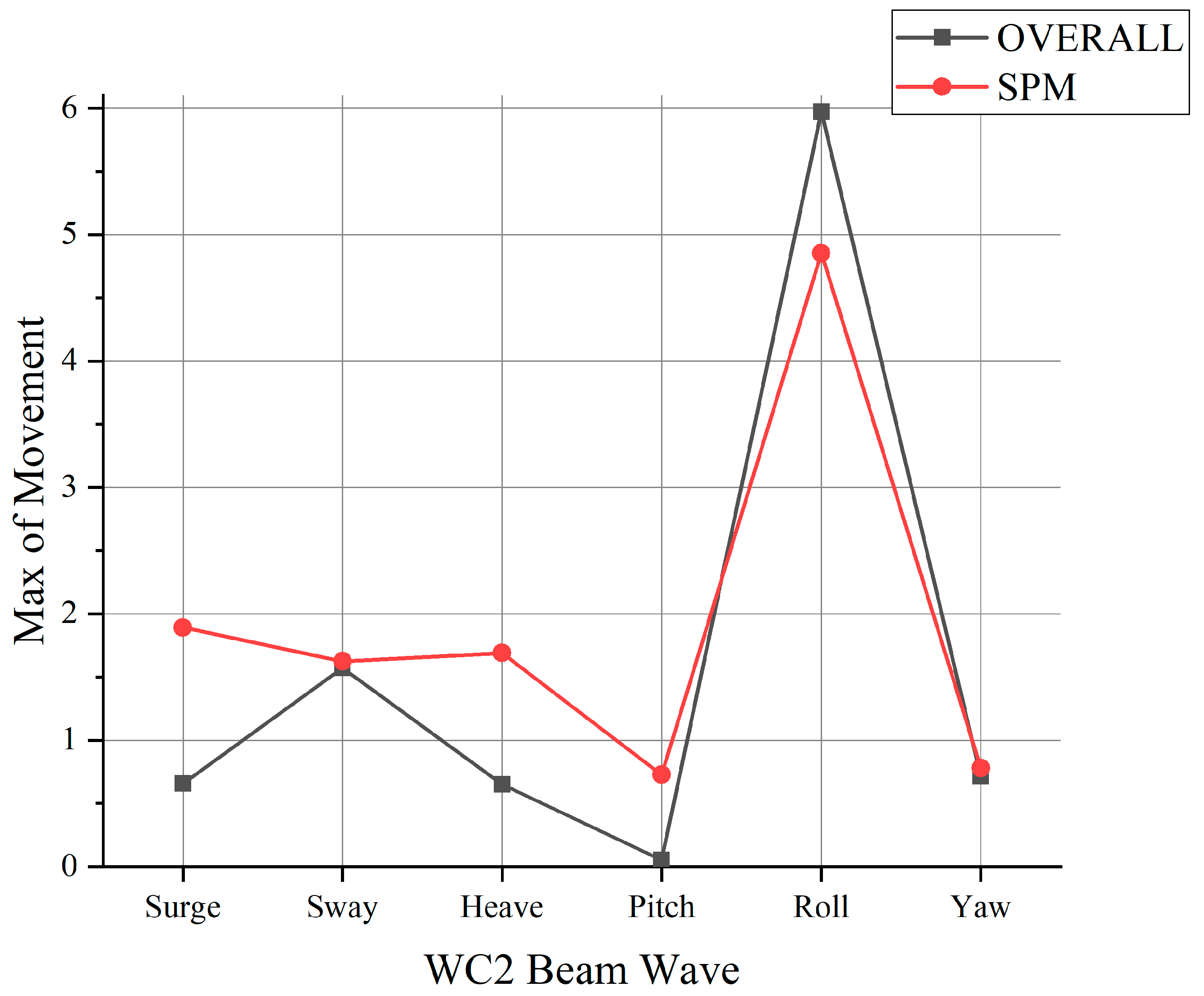
3.1. Discussion of the Results When OVERALL Is Used
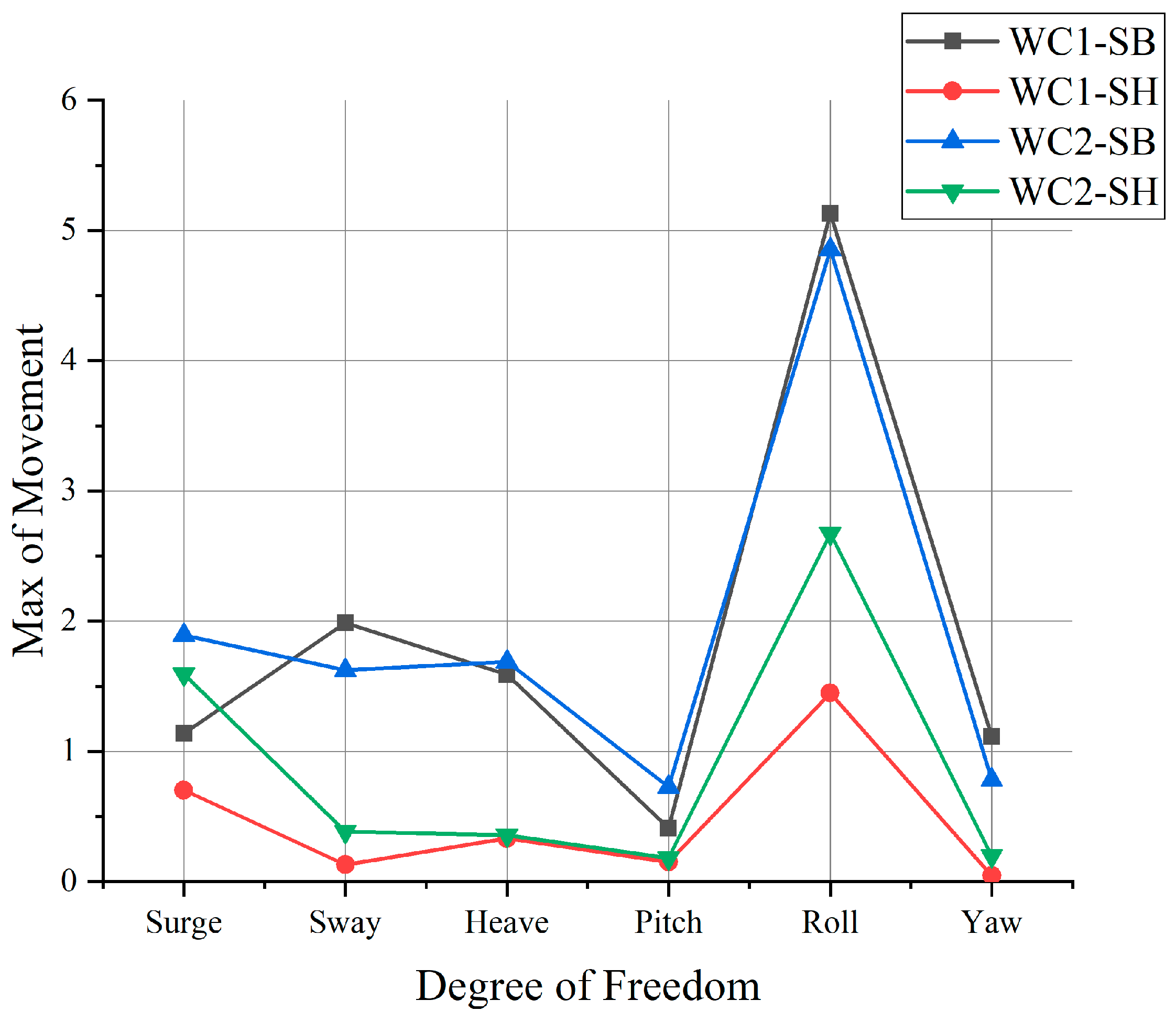
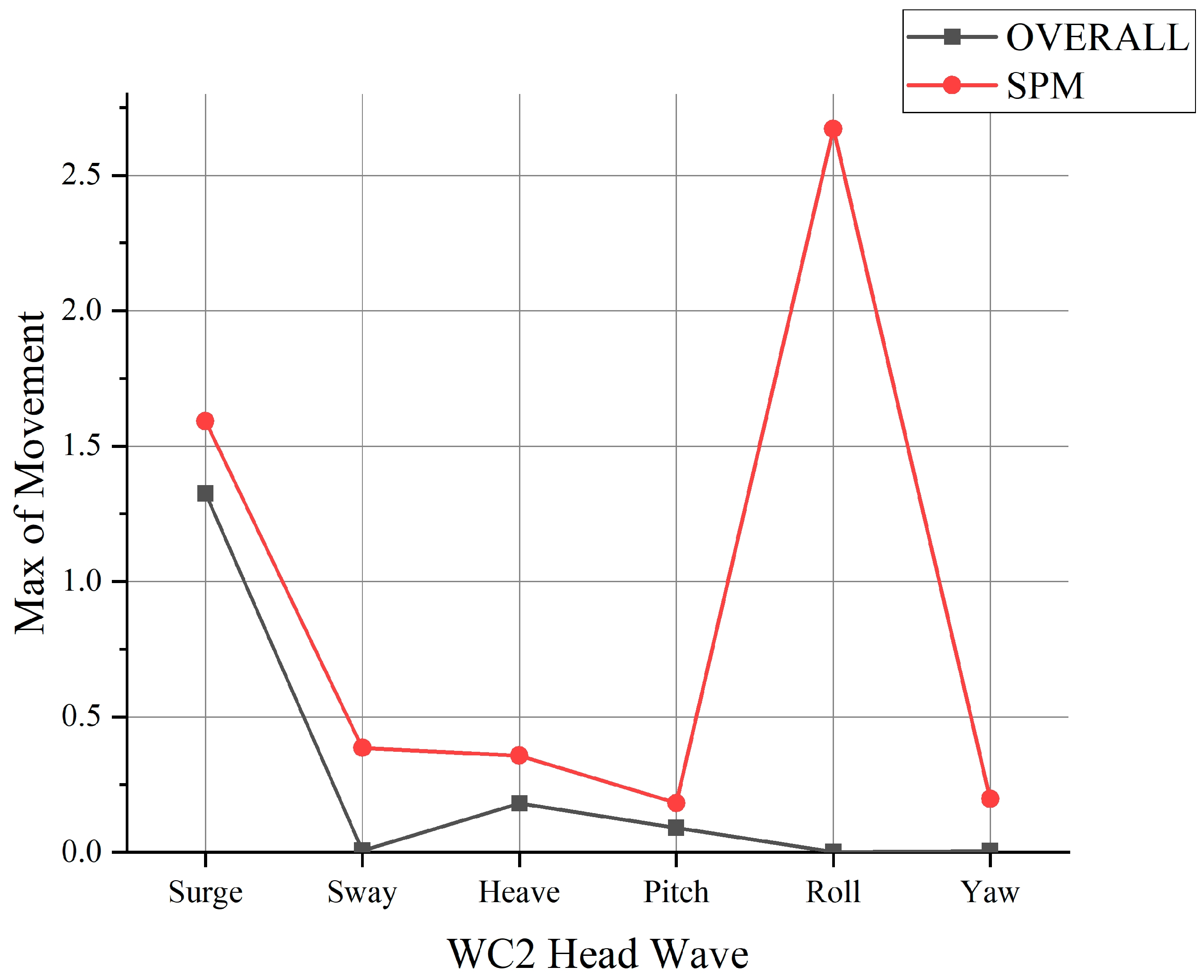
3.2. Discussion of the Results When SPM Is Used
3.3. Discussion of the Results Compared with OVERALL and SPM
4. Conclusions
- (1)
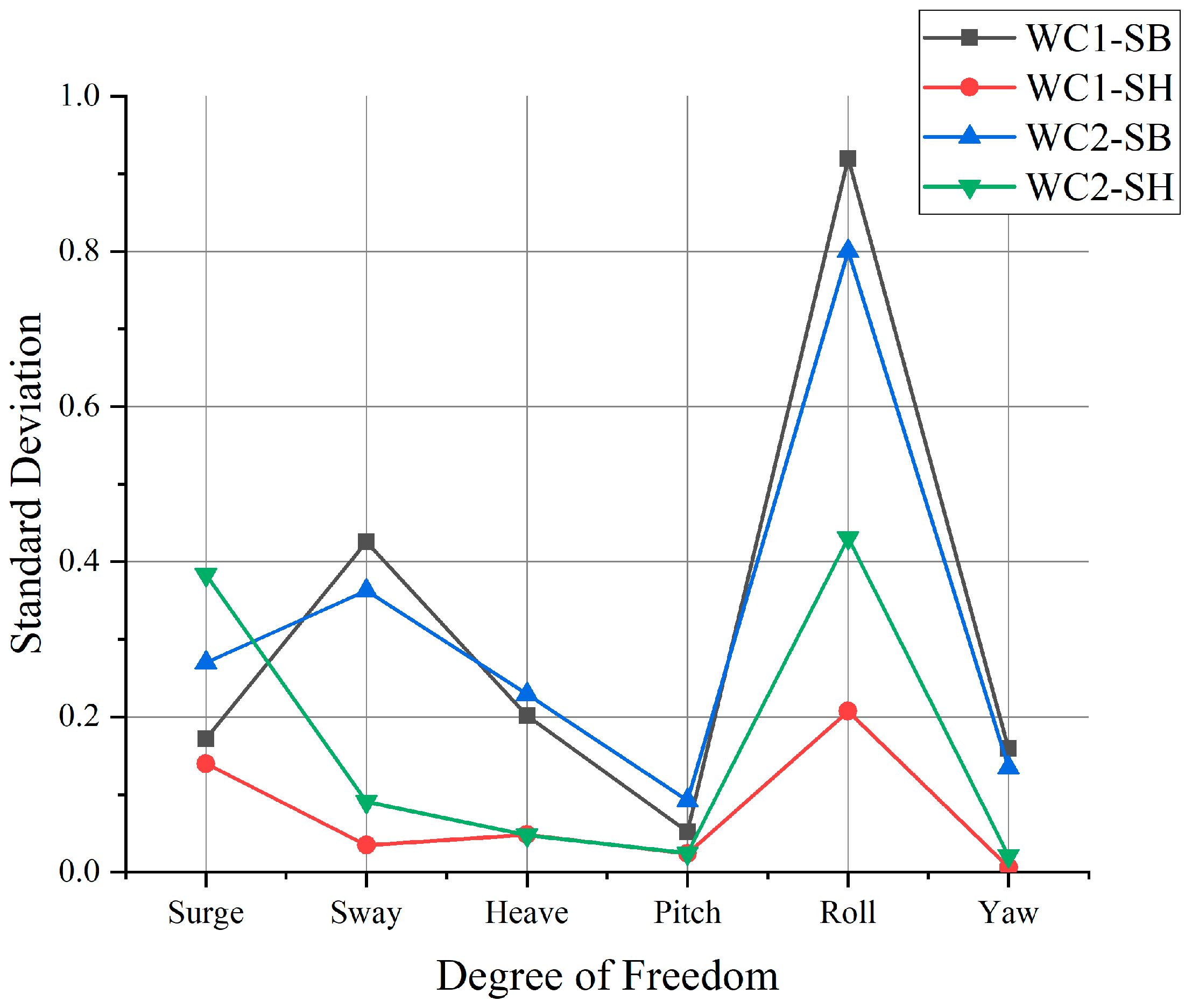
- Beam waves tend to induce more substantial vessel motion, particularly for roll motion. This heightened roll motion often exceeds regulatory limits. Conversely, head waves typically result in minimal vessel motion, with roll motion registering at approximately zero.
- (2)
- In the SPM method, even head waves would yield considerable roll motion.
- (3)
- Compared with the SPM method, OVERALL contributes to a higher magnitude of roll motion but underestimates the roll motion of head wave cases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pierson, W.J.; Neumann, G.; James, R.W. Practical Methods for Observing and Forecasting Ocean Waves by Means of Wave Spectra and Statistics; U.S. Naval Hydrographic Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselmann, S.; Bruning, C.; Hasselmann, K.; Heimbach, P. An improved algorithm for the retrieval of ocean wave spectra from synthetic aperture radar image spectra. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 16615–16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, J.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; Monbaliu, J. Spectral Partitioning and Identification of Wind Sea and Swell. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guachamin-Acero, W.; Portilla, J. Prediction of dynamic responses for execution of marine operations using partitioning of multimodal directional wave spectra and machine learning regression models. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 262, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobeto, H.; Menendez, M.; Losada, I.J.; Hemer, M. The effect of climate change on wind-wave directional spectra. Glob. Planet Chang. 2022, 213, 103820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhanovsky, A.V.; Soares, C.G. Modelling of multipeaked directional wave spectra. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2009, 31, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, C.; Rutllant, J.A.; Falvey, M. Wind waves climatology of the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4288–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbiriou, M.A.; Prevosto, M.; Maisondieu, C.; Clément, A.; Babarit, A. Influence of Sea-States Description on Wave Energy Production Assessment. In Proceedings of the European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Porto, Portugal, 11–13 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Portilla-Yandún, J.; Salazar, A.; Sosa, J.; Latandret, S.; Cavaleri, L. Modeling multiple wave systems in the eastern equatorial Pacific. Ocean. Dyn. 2020, 70, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Bowers, E.C. A mathematical model simulation of a ship moored against a quay in harbour. Hai Yang Gong Cheng 1995, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Sun, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yang, G.P.; Zhou, F. The effect of wave groupiness on a moored ship studied by numerical simulations. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2011, 23, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Veloso-Gomes, F. Experimental evaluation of the tension mooring effect on the response of moored ships. Coast. Eng. 2014, 85, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Yan, M.; Ma, Y.; Dong, G. Hydrodynamic response of moored ships to seismic-induced harbor oscillations. Coast. Eng. 2022, 176, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, A.v.L.B.; Campello, E.M.B.; Franzini, G.R.; Skaf, K.J. An assessment of mooring systems’ forces of ships berthed at dolphins. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 253, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L. Experimental Study on the LNG Berth Length Influence on Ship Mooring Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2014 Fifth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Engineering Applications, Zhangjiajie, China, 15–16 June 2014; pp. 461–463. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmin Zein, I.A.T.; Djatmiko, E.B. Mooring Tension Analysis of the Effect of Mooring Configuration Variations When LNG Carrier Moored to a Jetty. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 972, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chen, F.; Chen, J. Model Test on Influence of Berth Length on LNG Vessel Mooring under Wave-Current-Wind Loads. J. Coast. Res. Suppl. Spec. Issue 2018, 85, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lian, S.; Liu, C. Experimental research on LNG ship’s mooring. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Mechanical Design and Simulation (MDS 2022), Wuhan, China, 18–20 March 2022; p. 122615. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Hou, Q.; Huang, D.; Leng, J. A Hydrodynamical Study on Motions and Mooring Loads of the Small Scale LNG Carrier. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019—Marseille, Marseille, France, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.Q.; Wichers, J.E.W. The behaviour of LNG carrier moored to a jetty exposed to waves, swell, unsteady wind and current. China Ocean Eng. 1999, 13, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- van der Molen, W.; Ligteringen, H.; van der Lem, J.C.; de Waal, J.C.M. Behavior of a Moored LNG Ship in Swell Waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 129, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, N.C.; Chen, C.P.; Jiang, H.Z.; Cui, L. Experimental Study of Characteristics of Motions of a Large Mooring Ship in Long-Period Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Tech.-Taiw. 2014, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. A Comparative Study on the Motions of a Mooring LNG Ship in Bimodal Spectral Waves and Wind Waves; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 052047 (052048pp). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, G. Spectral Characteristics of Swell-Dominated Seas with In Situ Measurements in the Coastal Seas of Peru and Sri Lanka. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2022, 39, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Phillips, O.M. Automated analysis of ocean surface directional wave spectra. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTS. 165-2013; Design Code of GeneralLayout for Sea Ports. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Thoresen, C.A.J.L. Port Designer’s Handbook; ICE Publishing: Leeds, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
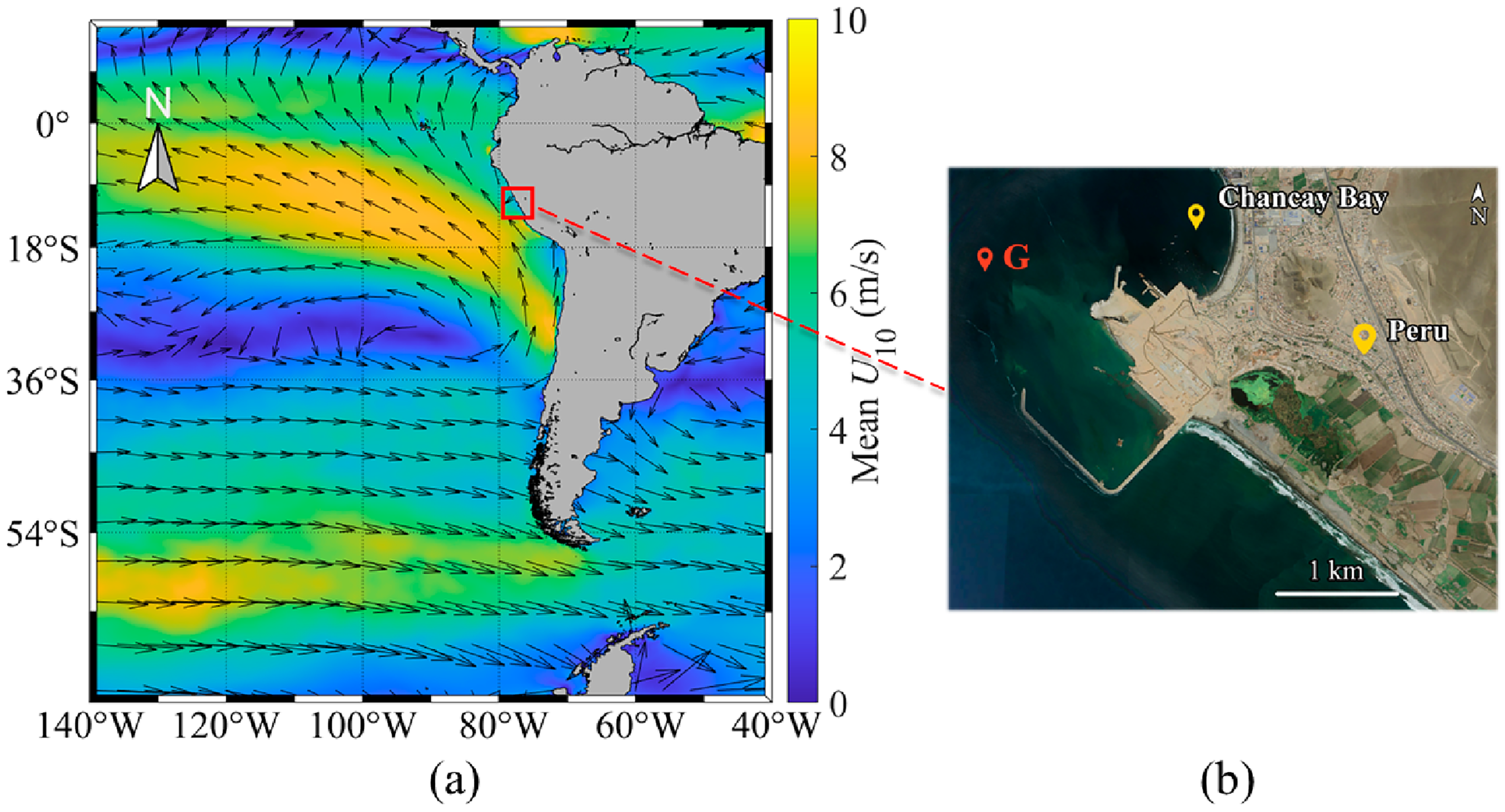
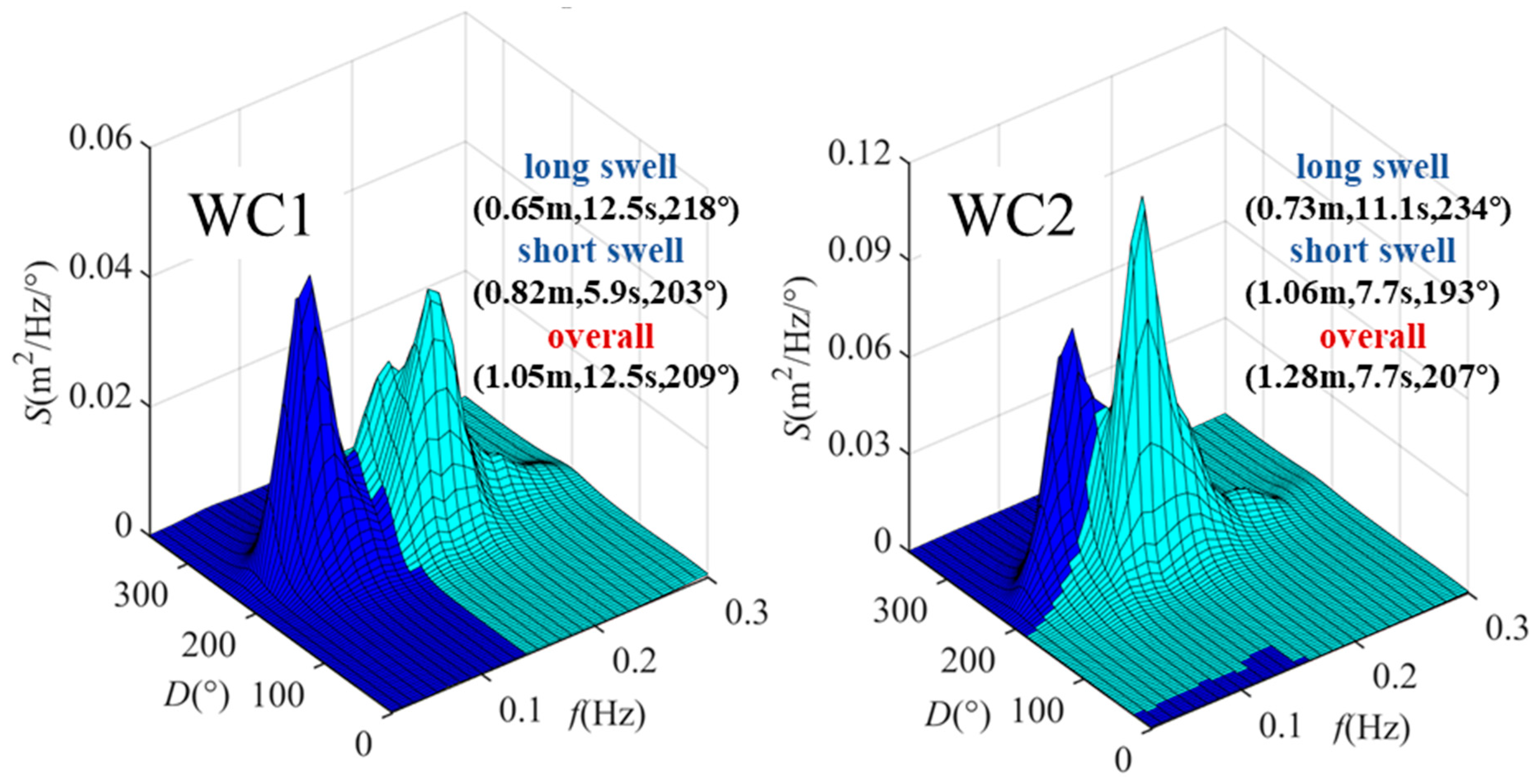

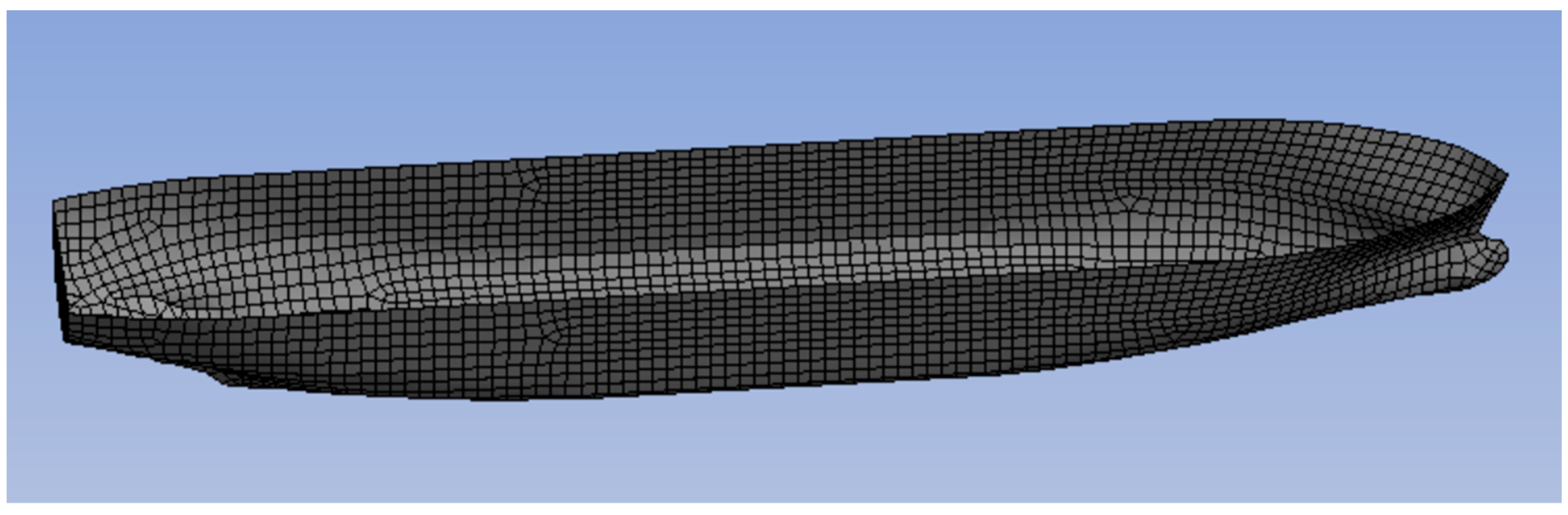
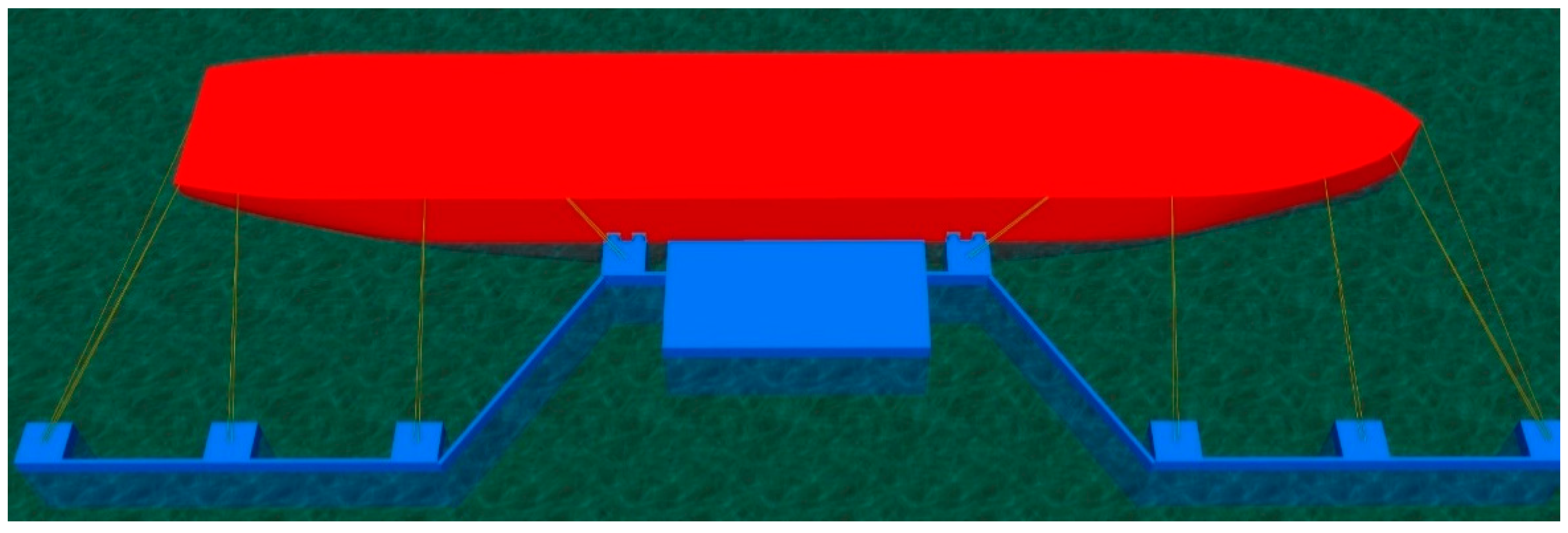
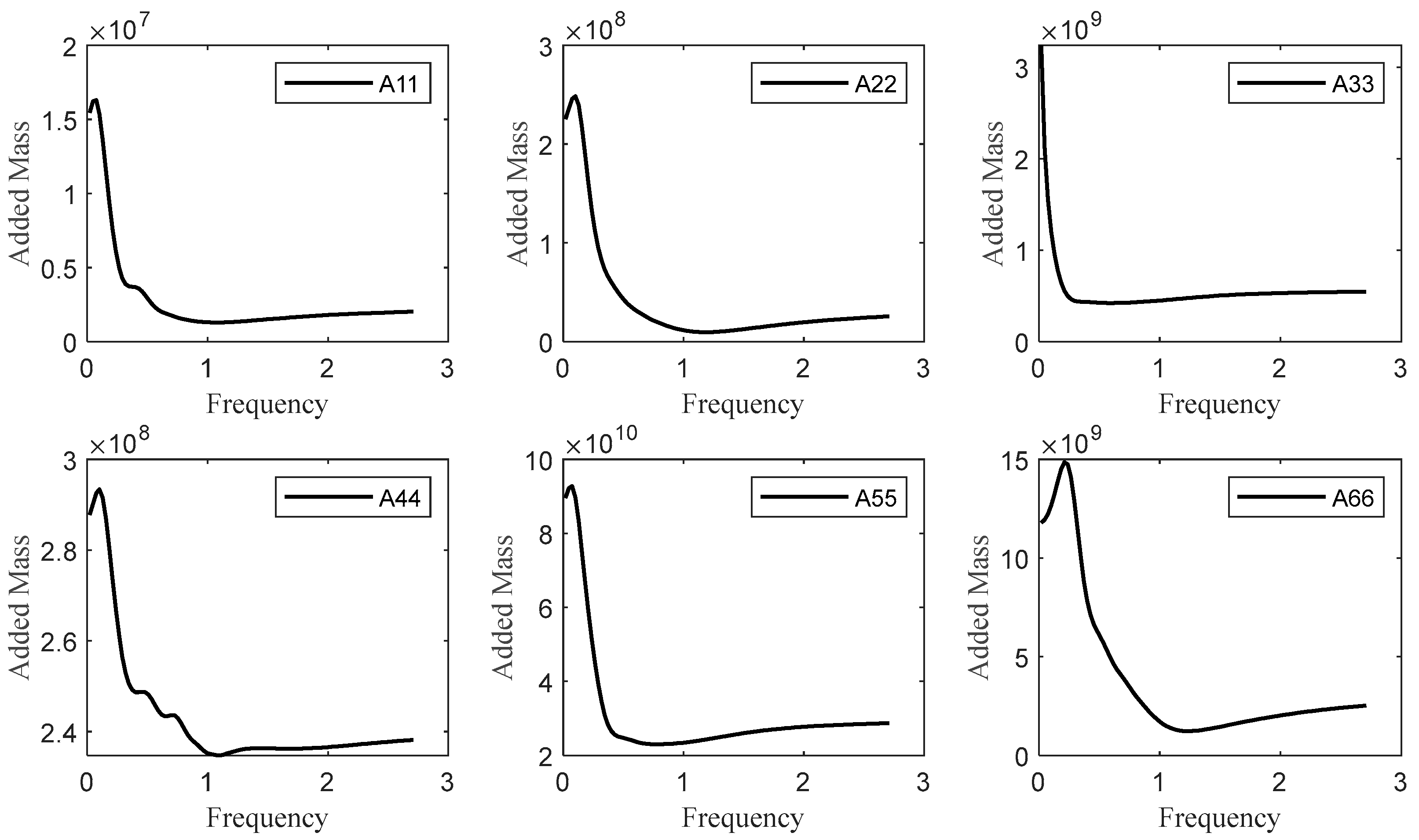
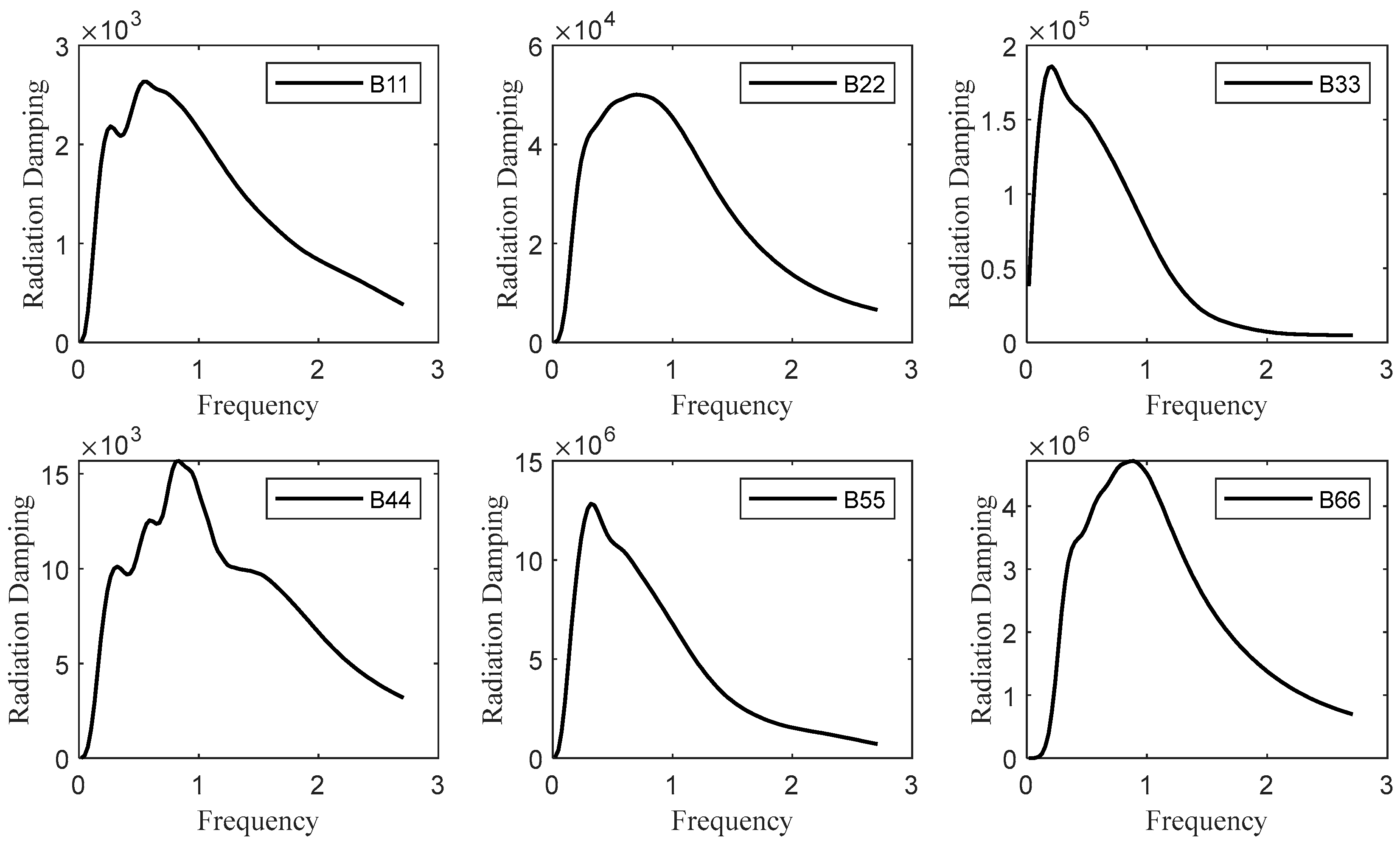
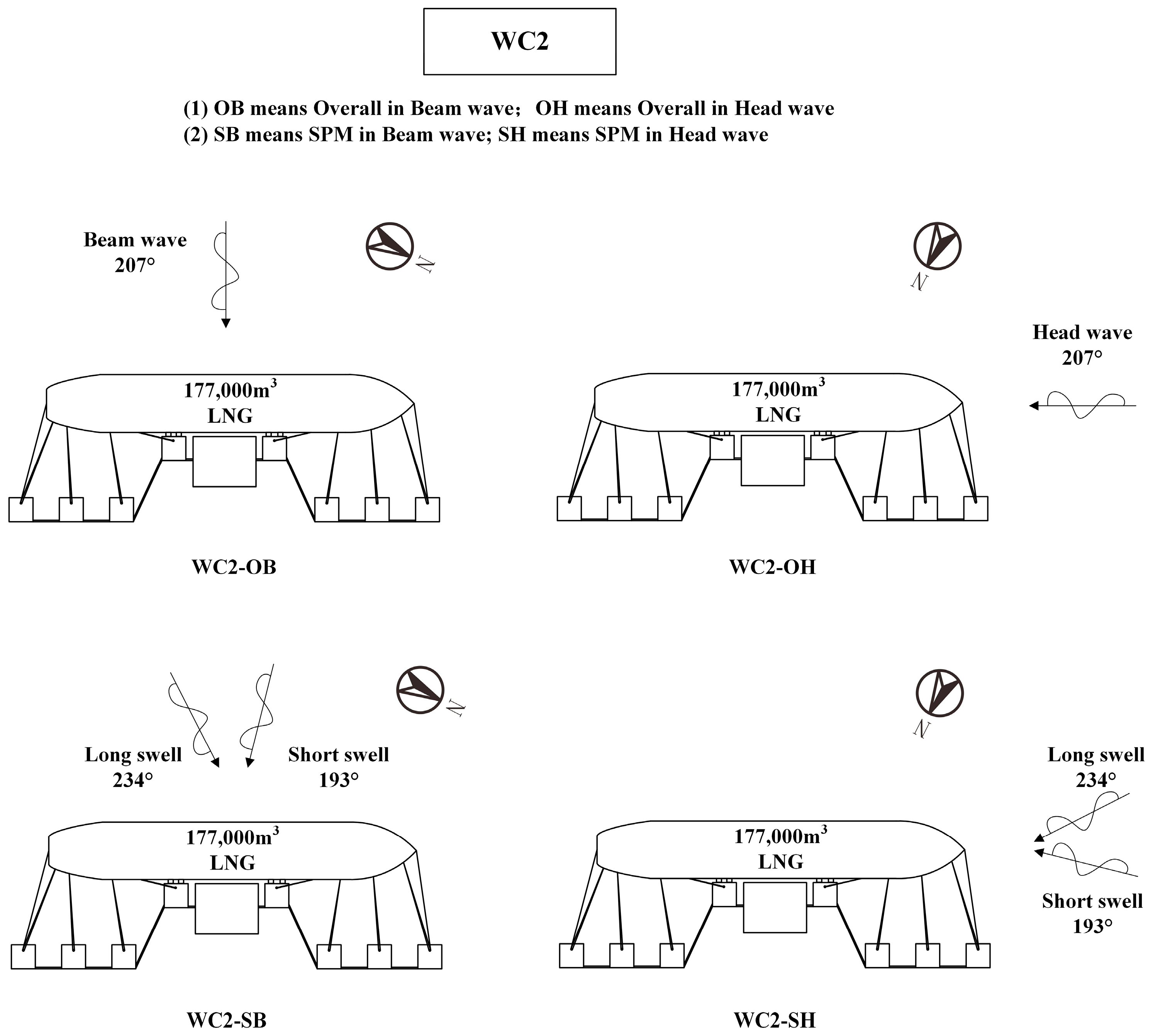

| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Displacement | tons | 115,257 |
| Draft | m | 11.8 |
| Overall length | m | 291.965 |
| Beam | m | 45.854 |
| Depth | m | 28 |
| Rxx | m | 11.6786 |
| Ryy | m | 72.9912 |
| Rzz | m | 72.9912 |
| Line | X (m) | Y (m) | Z (m) | Length (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −4.5 | 0 | 16.2 | 71.43 |
| 2 and 3 | −3.0 | −18.6 | 16.2 | 56.01 |
| 4 and 5 | 11 | −21.45 | 16.2 | 51.83 |
| 6 and 7 | 54 | −22.9 | 16.2 | 50.32 |
| 8 and 9 | 86.28 | −22.9 | 16.2 | 16.74 |
| 10 and 11 | 196.28 | −22.9 | 16.2 | 18.93 |
| 12 and 13 | 225 | −22.8 | 16.2 | 50.31 |
| 14 and 15 | 261 | −17.3 | 16.2 | 54.93 |
| 16 and 17 | 278 | −9.7 | 16.2 | 64.26 |
| 18 | 287.42 | 0 | 16.2 | 70.86 |
| Vessel Type | Limitation of Movement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNG | Surge (m) | Sway (m) | Heave (m) | Pitch (°) | Roll (°) | Yaw (°) |
| 2.0 | 2.0 | —— | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| Wave Cases | Wave Length (m) | Ship Length (m) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| WC1 | 145.34 | 291.965 | 0.50 |
| WC2 | 78.88 | 291.965 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, N.; Xu, T.; Xia, L.; Dong, G. Numerical Investigation of Hydrodynamic Responses of a Moored Liquefied Natural Gas Ship under Multimodal Waves. Water 2023, 15, 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213804
Lu N, Xu T, Xia L, Dong G. Numerical Investigation of Hydrodynamic Responses of a Moored Liquefied Natural Gas Ship under Multimodal Waves. Water. 2023; 15(21):3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213804
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Na, Tiaojian Xu, Lu Xia, and Guohai Dong. 2023. "Numerical Investigation of Hydrodynamic Responses of a Moored Liquefied Natural Gas Ship under Multimodal Waves" Water 15, no. 21: 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213804
APA StyleLu, N., Xu, T., Xia, L., & Dong, G. (2023). Numerical Investigation of Hydrodynamic Responses of a Moored Liquefied Natural Gas Ship under Multimodal Waves. Water, 15(21), 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213804





