Numerical Modelling and Performance Evaluation of Vacuum Membrane Distillation for Energy-Efficient Seawater Desalination: Towards Energy-Efficient Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
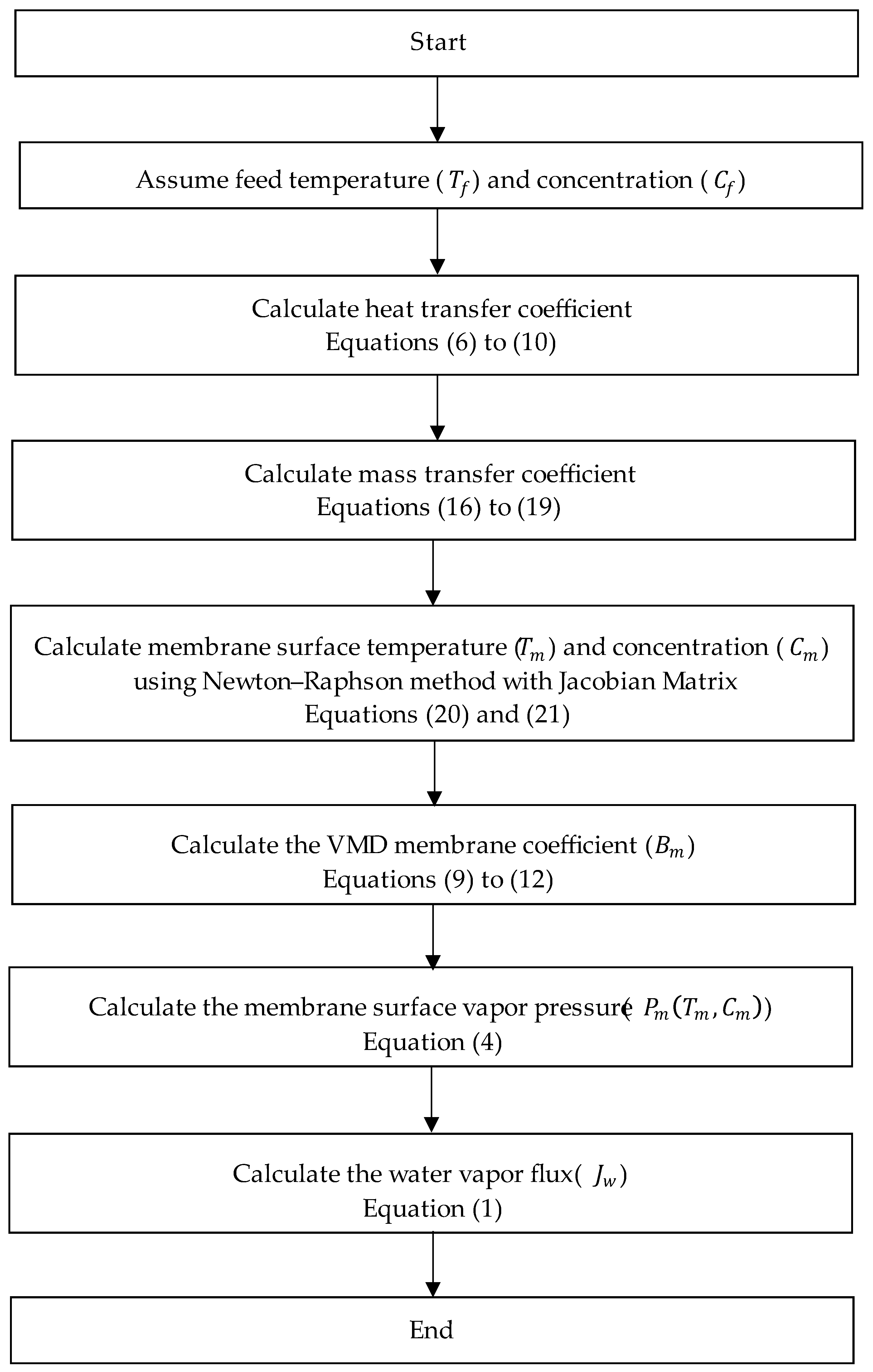
2.1. VMD Modeling
2.1.1. Single-Stage VMD
- The process is considered to be in a steady state.
- The transfer of momentum within the vacuum domain is considered to be insignificant.
- A negligible heat transfer is assumed in the permeate domain, as well as through the membrane by means of conduction.
- The transfer of mass within the permeate is not considered, and it is assumed that the mass fraction of water vapor is equal to one.
- It is presumed that the distillate does not contain any salt.
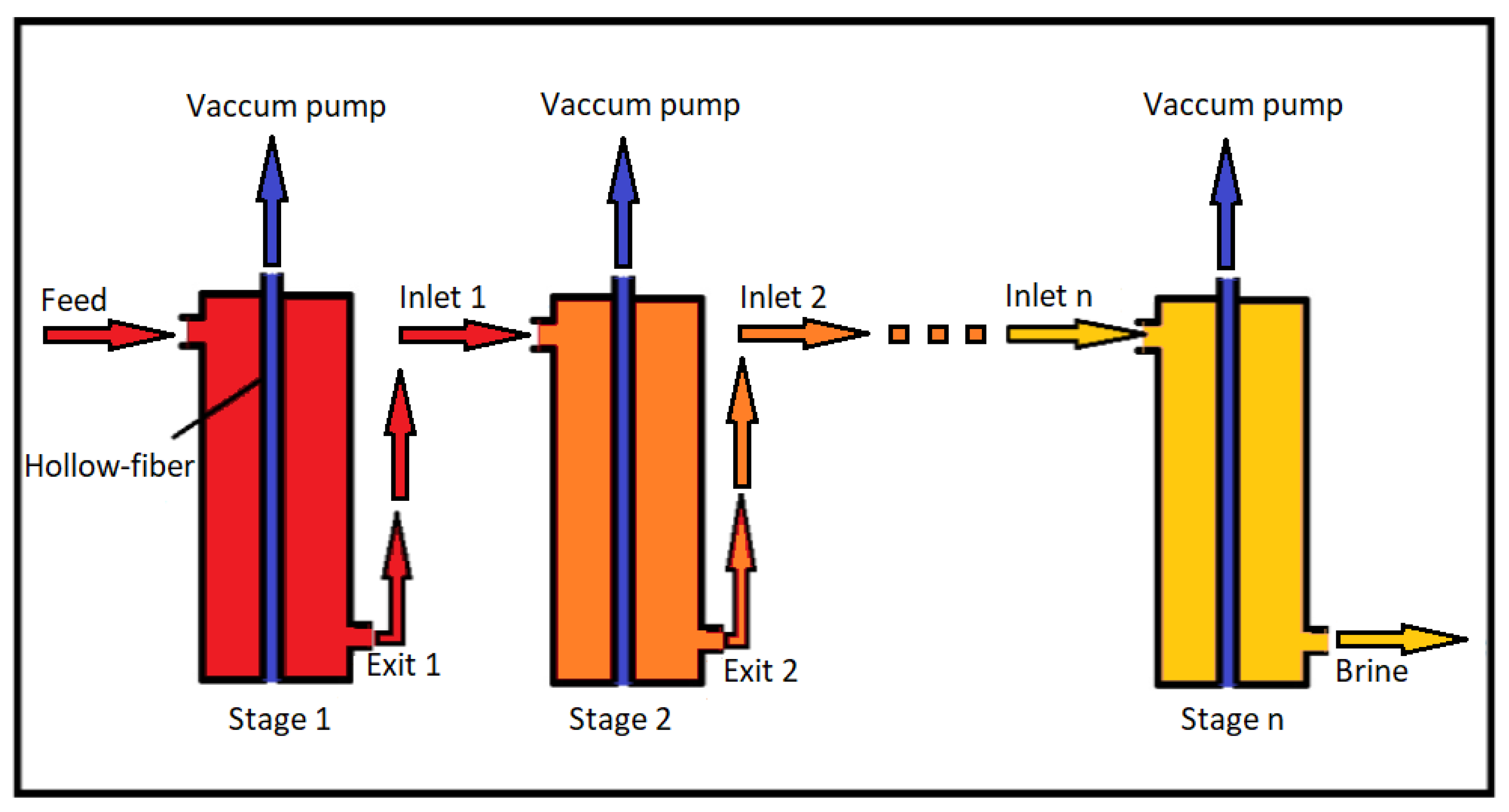
2.1.2. Multi-Staging in VMD
3. Results
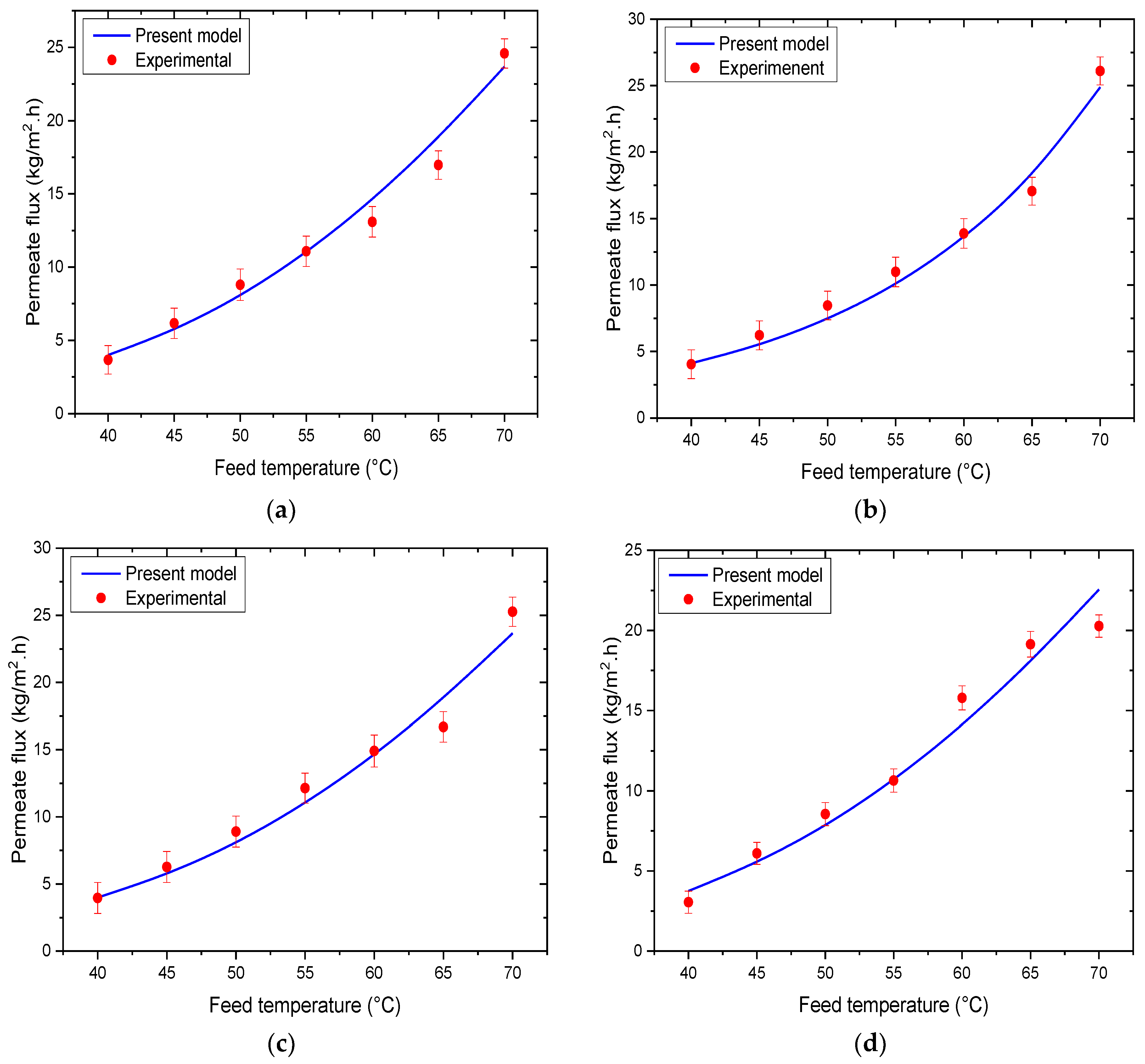
3.1. Model Validation
3.2. Impact of Operating Conditions
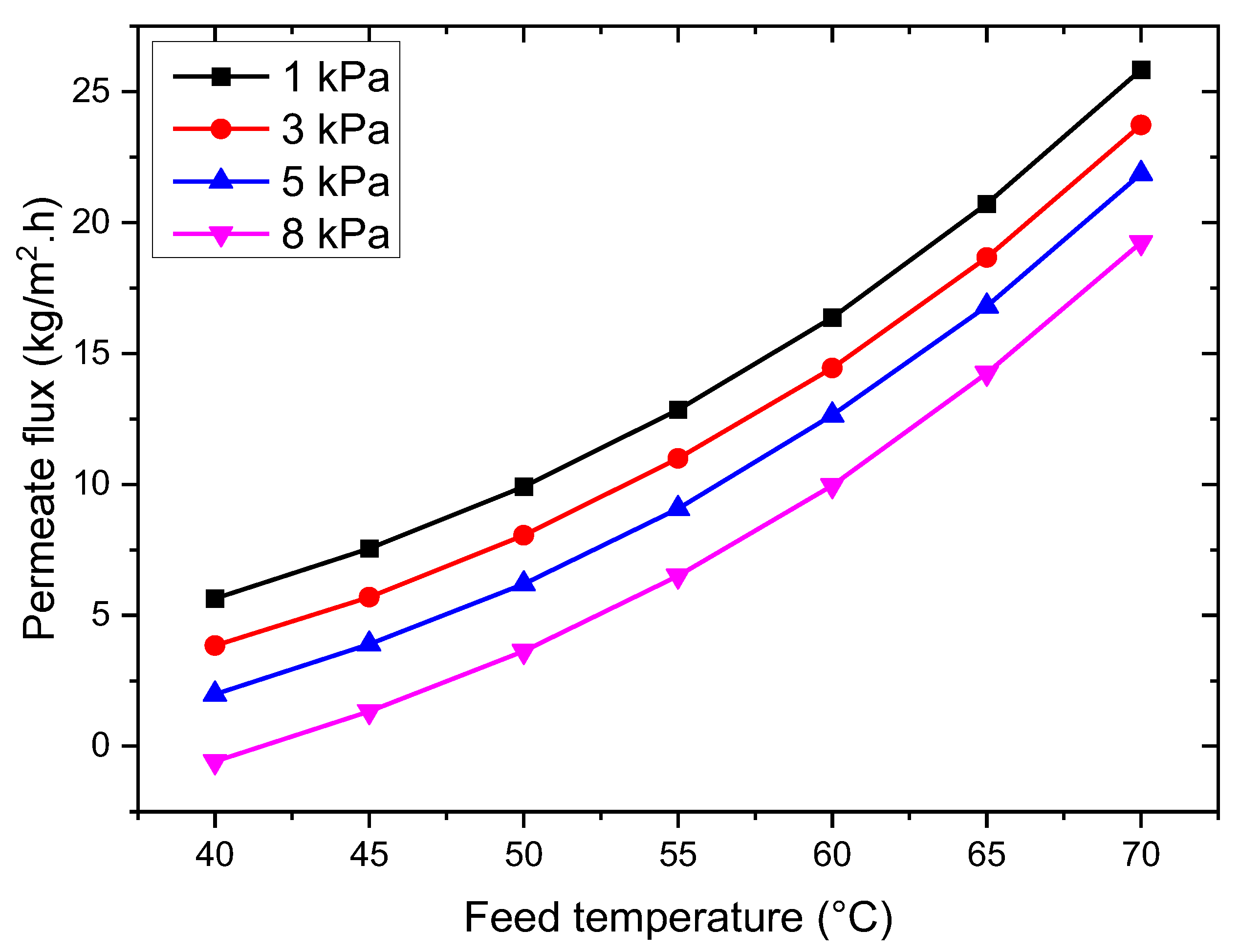
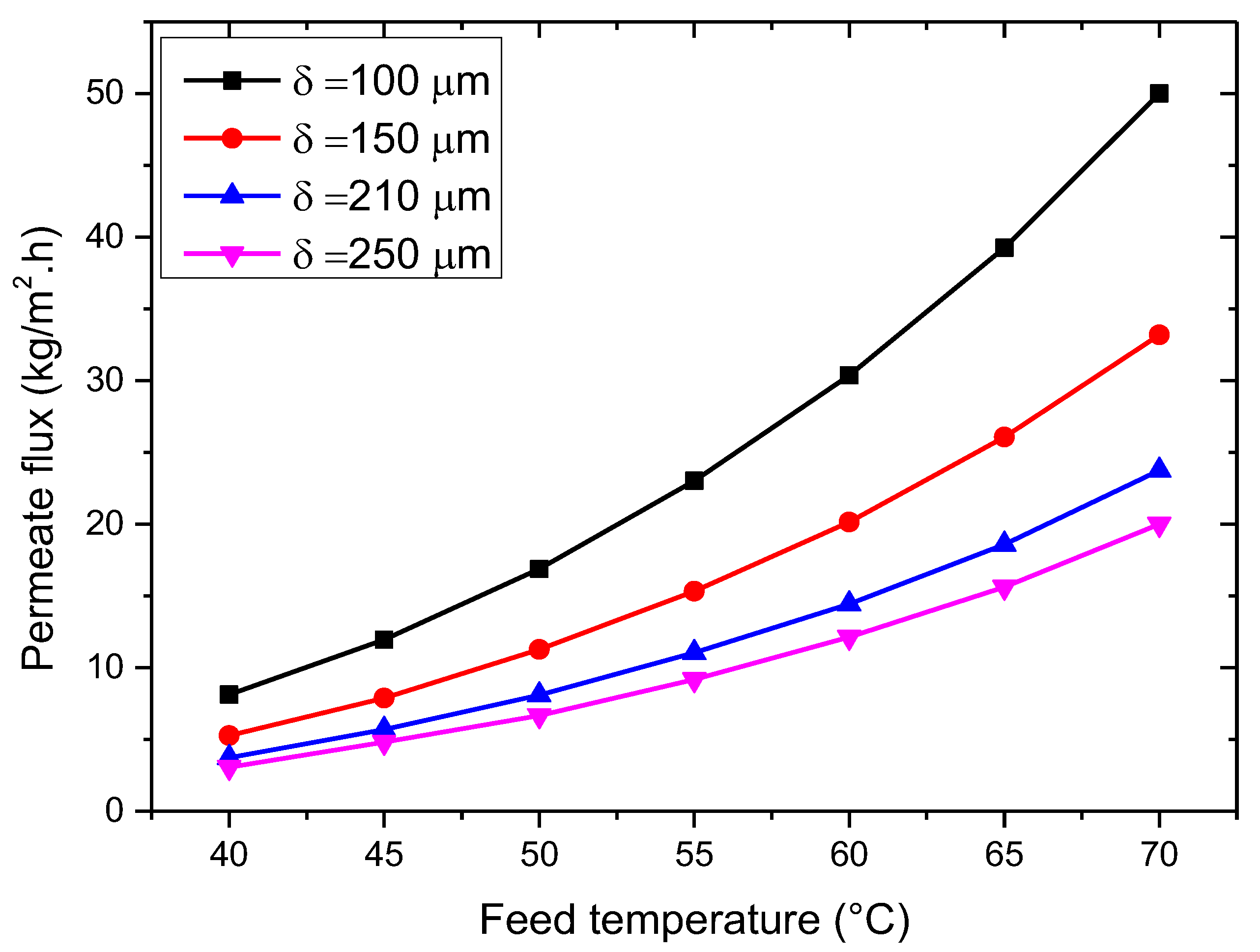
3.2.1. Influence of Feed Temperature
3.2.2. Effect of Vacuum Pressure
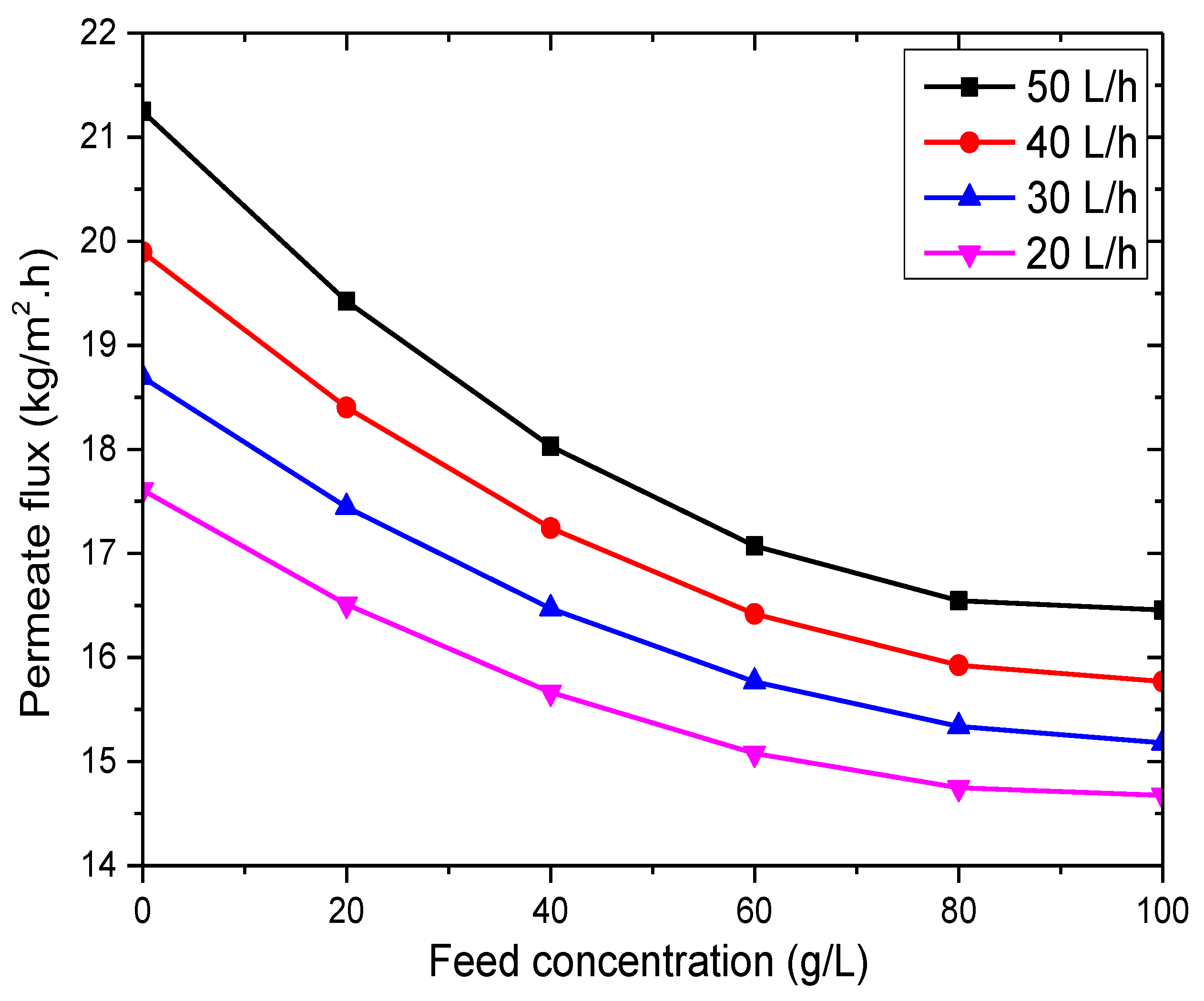
3.2.3. Effect of Feed Concentration
3.2.4. Effect of Feed Flow Rate
3.2.5. Effect of Membrane Characteristics
3.3. Polarization Effect
3.3.1. Temperature Polarization
3.3.2. Concentration Polarization
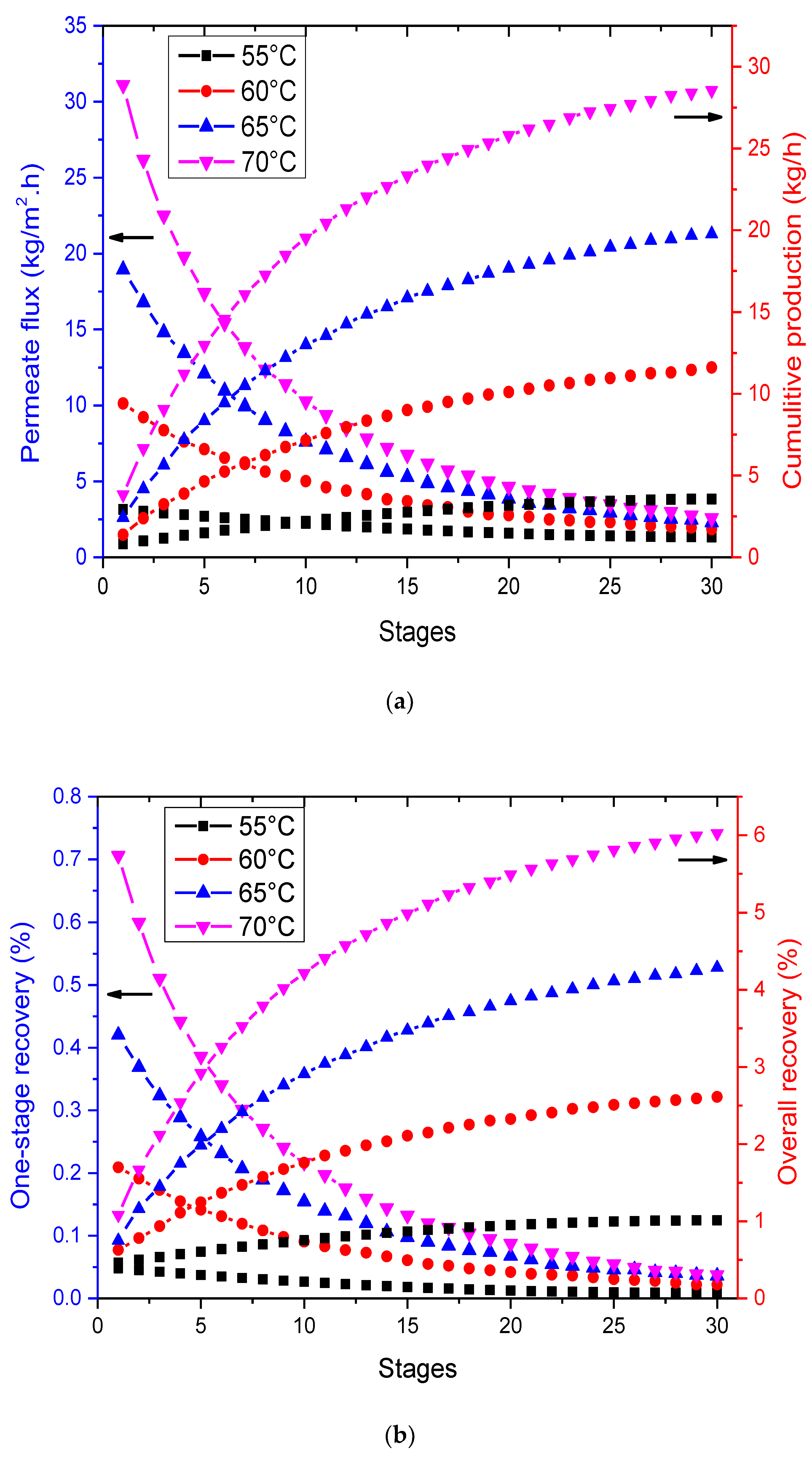
3.4. Effect of Multi-Staging in VMD
4. Conclusions
- The proposed numerical model provides a better fit with experimental data by introducing the polarization concentration phenomenon. As a result, the numerical model developed in this study could be used with confidence to simulate and design a VMD system for specific operating conditions.
- The VMD permeation flux increases with rising feed temperature and flow rate but decreases with increased feed salt concentration and vacuum pressure. At 35 g/L feed concentration, 65 °C feed temperature, 50 L/h feed flow rate, and 3 kPa vacuum pressure, the permeation flux reached 18.42 kg/m2·h.
- The VMD process has minimal sensitivity to feed concentration, making it highly advantageous for water desalination.
- The permeate flux increases with membrane porosity and decreases with membrane thickness.
- The most influential factor in determining the permeation flux is feed temperature, followed by membrane thickness, vacuum pressure, membrane porosity, feed concentration, and feed flow rate.
- Temperature polarization has a more significant effect on the permeate flux than concentration polarization.
- Multi-staging is a promising approach to enhance the performance of VMD and has the potential to make this process more efficient. However, it is important to optimize the operating conditions for each stage to ensure that the maximum separation efficiency is achieved while minimizing the energy consumption.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| effective membrane area | [m2] | |
| permeate coefficient of the membrane | [kg·m2·s−1·Pa−1] | |
| solute concentration | [g/kg] | |
| solute concentration on the membrane surface | [g/kg] | |
| concentration of the feed solution | [g/kg] | |
| concentration of the permeate. | [g/kg] | |
| water heat capacity | [J·kg−1·K] | |
| diffusion coefficient of solute | [m2·s−1] | |
| hydraulic diameter | [m] | |
| heat transfer coefficient | [W·m−2·s−1] | |
| latent heat of vaporization | [J·kg−1] | |
| water vapor flux | [kg·m−2·s−1] | |
| mass transfer coefficient | [m·s−1] | |
| effective length of fiber | [m] | |
| molecular mass of water | [kg·mol−1] | |
| Nusselt number | ||
| pressure | [Pa] | |
| Prandtl number | ||
| pressure in the vacuum side | [Pa] | |
| Q | flow rate | [L/h] |
| flow rate of steam | ||
| permeate flow rate. | ||
| volumetric flow rate of the feed solution | ||
| volumetric flow rate of the permeate | ||
| gas constant water recovery | [J mol−1·K−1] [%] | |
| membrane pore radius | [m] | |
| Reynolds numbers | ||
| water recovery | ||
| , | water recovery | |
| Schmidt number | ||
| Sherwood number | ||
| temperature | [K] | |
| bulk feed outlet temperature | [K] | |
| membrane surface feed | [K] | |
| permeate side temperature | [K] | |
| Greek symbols | ||
| membrane thickness | [m] | |
| membrane porosity | [-] | |
| membrane thermal efficiency | [%] | |
| membrane pore tortuosity | [-] | |
| ρ | water density | [kg·m−1] |
| thermal conductivity of the water | [W·m−1·K−1] | |
| dynamic viscosity | [Pa·s−1] | |
| Subscripts | ||
| b,i | brine, inlet | |
| b,o | brine, outlet | |
| f | feed | |
| i,n | stage number | |
| M | membrane surface | |
| v | vacuum | |
| t | total | |
References
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zuo, J.; Liu, D.; Cui, F.; Wang, W. Three-dimensional porous photo-thermal fiber felt with salt-resistant property for high efficient solar distillation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Hou, Y.; Bi, S.; Wang, M.; Hou, X. Ternary hierarchical structure based solar-driven evaporator for long-lasting concentrated brine treatment. EcoMat 2023, 5, e12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, L.; He, T.; Chen, S.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L. Seawater desalination technology and engineering in China: A review. Desalination 2021, 498, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xing, W.; Yan, J.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, L.; Gao, J. Stretchable and Superhydrophilic Polyaniline/Halloysite Decorated Nanofiber Composite Evaporator for High Efficiency Seawater Desalination. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, Z.; Bouaziz, M.N.; Boumaza, M. Techno-economic analysis of an integrated solar vacuum membrane distillation system for the treatment of reverse osmosis desalination brine. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 83, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.N.; Guen, F.Z.; Ahmed, S.A.; Saleem, H.; Khalil, M.J.; Zaidi, S.J. Energy consumption and environmental impact assessment of desalination plants and brine disposal strategies. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M. Membranes and theoretical modeling of membrane distillation: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 56–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, J.; Chung, H.W.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, J.H. Energy efficiency of membrane distillation up to high salinity: Evaluating critical system size and optimal membrane thickness. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, Y.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of hollow fiber membrane properties and operating conditions on pre-venting scale precipitation in seawater desalination with vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2022, 527, 115578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Deka, B.J.; Kim, K.-J.; An, A.K. Regeneration of superhydrophobic TiO2 electrospun membranes in seawater desalination by water flushing in membrane distillation. Desalination 2019, 468, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, F.; Al-Rub, F.A.; Bani-Melhem, K. Desalination by vacuum membrane distillation: Sensitivity analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Tan, X.; Li, K.; Teo, W.K. Removal of 1,1,1-trichloroethane from water using a Poly(Vinylidene fluoride) hollow fiber membrane module: Vacuum membrane distillation operation. Sep. Purf. Tech. 2006, 52, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger-Jørgensen, R.; Meyer, A.S.; Varming, C.; Jonsson, G. Recovery of volatile aroma compounds from black currant juice by vacuum membrane distillation. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericq, J.P.; Laborie, S.; Cabassud, C. Vacuum membrane distillation of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5260–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabassud, C.; Wirth, D. Membrane distillation for water desalination: How to choose an appropriate membrane? Desalination 2003, 157, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Han, J.; Sohn, J.; Lee, S.; Hwang, T.-M. Experimental comparison of direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD) with vacuum membrane distillation (VMD). Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6299–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Hao, C.; Ni, L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, R.; Meng, J.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, C. Experimental and theoretical research on N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone concentration by vacuum membrane distillation using polypropylene hollow fiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashoor, B.; Mansour, S.; Giwa, A.; Dufour, V.; Hasan, S. Principles and applications of direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD): A comprehensive review. Desalination 2016, 398, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, K.; Li, B. Mass transfer in hollow fiber vacuum membrane distillation process based on membrane structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 532, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Lu, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. Experimental study of the optimal vacuum pressure in vacuum assisted air gap membrane distillation process. Desalination 2017, 414, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumée, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.-D.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in Membrane Distillation for Water Desalination and Purification Applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.E. Water and air gap membrane distillation for water desalination—An experimental comparative study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, R.D.; Murphy, J.R.; Achilli, A. A stepwise model of direct contact membrane distillation for application to large-scale systems: Experimental results and model predictions. Desalination 2016, 378, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Lior, N. Critical review of membrane distillation performance criteria. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 20093–20140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, S.O.; Camacho, L.M. Heat and Mass Transport in Modeling Membrane Distillation Configurations: A Review. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbur, B.B.; Wu, C.; Duan, F. Multi-criteria thermoeconomic and thermodynamic assessments of the desalination-integrated two-phase liquid-immersion data center cooling system. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 10453–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termpiyakul, P.; Jiraratananon, R.; Srisurichan, S. Heat and mass transfer characteristics of a direct contact membrane distil-lation process for desalination. Desalination 2005, 177, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Tay, M.; Field, R.W. Novel method for the design and assessment of direct contact membrane distillation modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericq, J.-P.; Laborie, S.; Cabassud, C. Vacuum membrane distillation for an integrated seawater desalination process. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 9, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.A.; Malinauskas, A.P. Gas Transport in Porous Media: The Dusty Gas Model; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R. Transport in Porous Catalysts; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, K.W.; Lloyd, D.R. Review: Membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 124, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Abildskov, J.; Jonsson, G.; Gani, R. Modeling and analysis of vacuum membrane distillation for the recovery of volatile aroma compounds from black currant juice. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, S.; Singh, K.; Chaurasia, S.P.; Agarwal, M.; Dohare, R.K. Parametric Sensitivity Analysis of Vacuum Membrane Distillation for Desalination Process. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemical, Ecology and Environmental Sciences, ICCEES, Pattaya, Thailand, 17–18 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-G.; Kim, W.-S. Numerical modeling of the vacuum membrane distillation process. Desalination 2013, 331, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Novel design of liquid distributors for VMD performance improvement based on cross-flow membrane module. Desalination 2014, 336, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, H.; Bakhtiari, O.; Mohammadi, T. Analysis of heat and mass transfer in vacuum membrane distillation for water de-salination using computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Desalination Water. Treat. 2015, 55, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, Y.B.; Woo, S.Y. Detailed modeling and simulation of an out-in configuration vacuum membrane distillation process. Water Res. 2018, 132, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, L.; Li, B. Simulation of heat and mass transfer with cross-flow hollow fiber vacuum membrane distillation: The influence of fiber arrangement. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, M.; Lovineh, S.G.; Raji, M. Numerical simulation and theoretical study on effects of operating parameters in Persian Gulf desalination using vacuum membrane distillation. J. Model. Eng. 2018, 16, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dragoi, E.-N.; Vasseghian, Y. Modeling of mass transfer in vacuum membrane distillation process for radioactive wastewater treatment using artificial neural networks. Toxin Rev. 2020, 40, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F. How far can membrane characteristic parameters bestow at the vacuum membrane distillation (VMD) performance: Modeling and simulation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1211–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbatly, R.; Chiam, C.-K. Evaluation of geothermal energy in desalination by vacuum membrane distillation. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Heinzl, W.; Wenzel, M.; Büttner, S.; Bollen, F.; Lange, G.; Heinzl, S.; Sarda, N. Experimental study of the memsys vac-uum-multi-effect-membrane-distillation (VMEMD) module. Desalination 2013, 323, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-G.; Kim, W.-S. Numerical study on multi-stage vacuum membrane distillation with economic evaluation. Desalination 2014, 339, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Boutikos, P.; Mathioulakis, E.; Belessiotis, V. Experimental evaluation of the performance and energy efficiency of a Vacuum Multi-Effect Membrane Distillation system. Desalination 2017, 408, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ji, S.; Qi, J.; Wang, S. Numerical modeling and economic evaluation of two multi-effect vacuum membrane distillation (ME-VMD) processes. Desalination 2017, 419, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zeid, M.A.E.R.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.L.; Hou, L. A comprehensive review of vacuum membrane dis-tillation technique. Desalination 2015, 356, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.; Fane, A.; Fell, C. Heat and mass transfer in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 33, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Voinea, O.C.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Vacuum membrane distillation of the main pear aroma compound: Experimental study and mass transfer modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Peng, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, J.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, P.; Wang, X.-K. Vacuum membrane distillation simulation of desalination using polypropylene hydrophobic microporous membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharqawy, M.H.; Lienhard, V.J.H.; Zubair, S.M. Thermophysical properties of seawater: A review of existing correlations and data. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 16, 354–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, S.; Gostoli, C.; Sarti, G. Separation efficiency in vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.C. Heat Transfer, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Laganà, F.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E. Direct contact membrane distillation: Modelling and concentration experiments. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 166, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherayan, M. Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McCutcheon, R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengual, J.; Khayet, M.; Godino, M. Heat and mass transfer in vacuum membrane distillation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, C.-K.; Sarbatly, R. Vacuum membrane distillation processes for aqueous solution treatment—A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2013, 74, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Nam, S.-H.; Hwang, T.-M.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y. Effect of operating parameters on temperature and concentration po-larization in vacuum membrane distillation process. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Peng, Y. Application of PVDF membranes in desalination and comparison of the VMD and DCMD processes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 79, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, S.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Carnevale, M.C.; Rosselli, A.; Drioli, E. Preparation of hollow fiber membrane from PVDF/PVP blends and their application in VMD. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangarkar, B.L.; Sane, M.G.; Parjane, S.B.; Abhang, R.M.; Guddad, M. The heat and mass transfer phenomena in vacuum membrane distillation for desalination. Int. J. Chem. Biol. Eng. 2010, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, M.; Ramezanianpour, M.; O’halloran, G. Mine Water Treatment Using a Vacuum Membrane Distillation System. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Preparation and properties of PTFE hollow fiber membranes for desalination through vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Ray, P.; Singh, K.; Singh, P.S. Preparation and characterization of highly micro-porous PVDF membranes for desali-nation of saline water through vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2014, 346, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.; Moustafa, A.F.; Al Anezi, A.A.; El-Sayed, H.E.M. Performance of a newly developed titanium oxide nano-tubes/polyether sulfone blend membrane for water desalination using vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2014, 346, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Feasibility research of potable water production via solar-heated hollow fiber membrane distillation system. Desalination 2009, 247, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Ali, A.; Simone, S.; Macedonio, F.; Al-Jlil, S.; Al Shabonah, F.; Al-Romaih, H.; Al-Harbi, O.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A. Novel PVDF hollow fiber membranes for vacuum and direct contact membrane distillation applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkar, K.; Qin, Y. Novel Membrane and Device for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Based Desalination Process, Report; New Jersey Institute of Technology: Newark, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, D.; Cabassud, C. Water desalination using membrane distillation: Comparison between inside/out and outside/in per-meation. Desalination 2022, 147, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wei, H.; Lu, X. Study on the Reverse Osmosis Rejected Water Treatment Process Based on Vacuum Membrane Distillation. J. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 1, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.L.; Xiao, C.F.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, X.F. Study on the effects and properties of hydrophobic poly(tetrafluoroethylene) mem-brane. Desalination 2011, 277, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.-D.; Duke, M.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z.; Groth, A.; Tun, C.; Gray, S. Influence of module design and membrane com-pressibility on VMD performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Wang, J.; Hou, D.; Yin, Z.; Luan, Z. Effect of microwave irradiation on vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.-D.; Duke, M.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z.; Groth, A.; Tun, C.; Gray, S. Modelling of vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Cojocaru, C. Air gap membrane distillation: Desalination, modeling and optimization. Desalination 2011, 287, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Khaleel, S.R. Performance of vacuum poly(propylene) membrane distillation (VMD) for saline water desalination. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2017, 120, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Membrane Type | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|
| Thickness (μm) | 210 |
| Porosity (%) | 60 |
| Tortuosity (−) | 1.4 |
| Average pore size (μm) | 0.3–0.7 |
| Effective length of fiber (mm) | 100–250 |
| Effective membrane area (mm2) | 28 × 102 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Feed inlet temperature | 40–70 °C |
| Vacuum pressure on the permeate side | 1–8 kPa |
| Feed concentration | 0–100 g/L |
| Feed flow rate | 30–90 L/h |
| Number of VMD stages | 1–30 |
| Feed Temperature (°C) | Permeate Flux (kg/m2·h) | Mean Absolute Percentage Error (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Flux | Present Model | Tang et al. [51] | Present Model | Tang et al. [51] | |
| 40 | 4.048 | 4.111 | 4.112 | 3.76 | 6.57 |
| 45 | 6.217 | 5.764 | 5.550 | ||
| 50 | 8.458 | 8.100 | 7.492 | ||
| 55 | 10.988 | 10.611 | 10.113 | ||
| 60 | 13.879 | 13.543 | 13.651 | ||
| 65 | 17.060 | 17.901 | 18.427 | ||
| 70 | 26.096 | 25.449 | 24.874 | ||
| Ref. | Membrane Type | Membrane Characteristics | Operating Conditions | Jw (kg/m2·h) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ (μm) | L (mm) | A (mm2) | ε (%) | r (μm) | Cf (g/L) | Tf (°C) | Qf (L/min) | Pv (kPa) | |||
| [63] | PVDF | 0.17 | - | - | 80.62 | 0.16 | 23.27 | 50 | 0.53 | 2 | 17.9 |
| [64] | PTFE-FS | 175 | - | 3.6 × 102 | 70 | 0.22 | 30 | 60 | 0.9 | 3 | 12 |
| [65] | PTFE-HF | - | - | 0.8 × 106 | - | 0.2 | 0 | 65 | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| [66] | PTFE-HF | 75 | 390 | 4 × 104 | 63.4 | 0.46 | 30 | 80 | 0.6 | 1 | 17.2 |
| [67] | PVDF-FS | - | - | - | - | 1 | 30 | 75 | - | - | 12.1 |
| [68] | TNTs-PES-FS | - | - | 17.34 × 102 | - | - | 7 | 65 | 0.66 | 30 | 15.2 |
| [69] | PTFE-FS | 175 | - | 3.6 × 102 | 70 | 0.22 | 7 | 60 | 0.916 | 1.5 | 28.34 |
| [70] | PVDF-HF | 0.23 | 200 | - | 83.39 | 0.318 | DW | 50 | 0.1 | 4 | 41.78 |
| [71] | PVDF-HF | 170 | - | - | 80.62 | 0.16 | DW | 50 | 0.51 | 2 | 17.9 |
| [72] | PVDF-HF | - | - | 8 × 104 | - | 0.2 | 15 | 25 | - | 1 | 0.54 |
| [72] | PE-HF | - | - | 0.2 × 106 | - | 0.1 | 15 | 25 | - | 1 | 0.216 |
| [73] | PVDF-HF | 150 | 90 | 2 × 104 | 85 | 0.16 | 1 CaO | 75 | - | 5.3 | 17 |
| [74] | PVDF-FS | 121.4 | - | 23.5 × 102 | 76.5 | 0.2 | GW | 60 | 0.5 | 30 | 6.56 |
| [75] | PTFE-FS | 45.2 | - | - | 38.6 | - | DW | 70 | 0.533 | 2 | 9.45 |
| [75] | PVDF-FS | 0.082 | - | 26.4 × 102 | 78 | 0.49 | 35 | 73 | 0.9 | 31.5 | 22.4 |
| [76] | PP-HF | - | 250 | - | - | - | - | 70 | 0.8 | 2 | 38 |
| [77] | PVDF-HF | 0.011 | 200 | 104 | 79 | 0.25 | - | 68 | 0.14 | 5.3 | 22 |
| [78] | PP-HF | 0.7 | 250 | - | 85 | 0.3 | - | 72 | - | 3 | 37 |
| [79] | PP-HF | 450 | 180 | 10.18 × 102 | 70 | 0.2 | 35 | 65 | 0.6 | 12.7 | 65.8 |
| Present study | PP-HF | 210 | 250 | 28 × 102 | 60 | 0.3 | 35 | 65 | 0.833 | 3 | 18.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Triki, Z.; Fergani, Z.; Lekmine, S.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Zamouche, M.; Kebir, M.; Assadi, A.A.; Khezami, L.; Zhang, J. Numerical Modelling and Performance Evaluation of Vacuum Membrane Distillation for Energy-Efficient Seawater Desalination: Towards Energy-Efficient Solutions. Water 2023, 15, 3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203612
Triki Z, Fergani Z, Lekmine S, Tahraoui H, Amrane A, Zamouche M, Kebir M, Assadi AA, Khezami L, Zhang J. Numerical Modelling and Performance Evaluation of Vacuum Membrane Distillation for Energy-Efficient Seawater Desalination: Towards Energy-Efficient Solutions. Water. 2023; 15(20):3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203612
Chicago/Turabian StyleTriki, Zakaria, Zineb Fergani, Sabrina Lekmine, Hichem Tahraoui, Abdeltif Amrane, Meriem Zamouche, Mohammed Kebir, Amin Aymen Assadi, Lotfi Khezami, and Jie Zhang. 2023. "Numerical Modelling and Performance Evaluation of Vacuum Membrane Distillation for Energy-Efficient Seawater Desalination: Towards Energy-Efficient Solutions" Water 15, no. 20: 3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203612










