1. Introduction
Heavy metals (HMs) have become a serious problem over the past few decades due to their high toxicity [
1,
2], ability to accumulate within the food chain, and biomagnification characteristics [
3,
4]. It is important to note that many of these HMs are highly toxic, even at trace levels, resulting in widespread ecosystem damage [
5,
6,
7]. One such HM is lead (Pb(II)). In such a way, water pollution caused by Pb has attracted global attention. Although Pb(II) was usually released into the environment through natural processes in the past, today HMs pollution is mainly caused by anthropogenic activities [
8]. Studies have shown that damage to the kidneys, brain, nervous system, and liver is caused by the long-term use of Pb-contaminated water [
9]. HM ions can be removed from contaminated water by using various methods, including chemical precipitation, reverse osmosis, hydrolysis, ion exchange, surface adsorption, and electrochemical purification [
10,
11,
12].
In recent years, nanoscale zero-valent iron particles (nZVFe) with sizes ranging from 1 to 100 nm at least one dimension have shown good potential as an environmentally friendly strong reducing agent for removing various pollutant [
13], for instance, HMs such as nickel (Ni), cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)], cobalt (Co), arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb) from wastewater and polluted water [
14,
15,
16]. As a result of their high surface energy, direct interparticle interactions, and intrinsic magnetic interaction, bare iron nanoparticles (NPs) tend to agglomerate into micron or larger solid particles. Consequently, using bare nZVFe particles can have drawbacks, including aggregate formation, reducing specific surface area, producing a lower negative redox potential, and leading to poor mechanical and structural durability [
5]. Moreover, separating ZVFe NPs from contaminated soil or treated aqueous systems is very difficult [
17]. As a means of overcoming these disadvantages, the idea of immobilizing the ZVFe NPs into porous host materials was proposed and discussed in several research studies. Three main categories of porous host materials are available for the stabilization of iron NPs: (i) natural minerals, namely pillared clay [
18], pumice granular [
19,
20], acid activated sepiolites [
21,
22], montmorillonite [
23,
24], kaolin [
25], bentonite [
26,
27], zeolite [
28,
29,
30], biochar [
31,
32], and charcoal [
33]; (ii) biomaterials such as pine cone [
34], aquatic plant Azolla filiculoides [
35], cellulose nanofibrils [
36], walnut shell [
37], and macroporous alginate ([
38,
39]); and (iii) synthetic materials such as cationic resin [
40], anion exchange resin [
41], porous carbon sheet [
42], chelating resin [
43], titanate nanotube [
44], meso-porous silica carbon [
45], layered double hydroxide [
46,
47], activated carbon [
34,
48,
49], graphene oxide [
45,
50], chitosan [
51], carbon nanotube [
52], magnesium (hydr)oxide [
19,
53], and humic acid [
54].
In addition, it is possible to synthesize activated carbon by using various activating agents, and it is widely used in a variety of fields, including wastewater treatment [
55,
56,
57]. From previous studies, it was found that activated carbon materials are successful adsorbents for HMs. Because of their high pore volume, they have a significant potential to trap target HM ions [
58,
59]. As a result of its large specific surface area, stable microporous structure, wide availability, affordability, great adsorption capacity, and compatibility with the environment, biomass-derived activated carbon (BAC) can be an appropriate support material for nZVFe particles. Consequently, in addition to stabilizing iron NPs by providing more interaction between NPs and Pb ions, it will increase the absorption capacity of the resulting composite [
60,
61]. On the other hand, rice is the primary crop and staple food for more than half of the world’s population. According to the recent work [
62], rice is the world’s third most produced agricultural product, with 970 million tons produced globally in 2020. According to FAO statistics [
62], the area under rice cultivation in Iran was about 4200 km
2, and rice cultivation is a common occupation in Iran, especially in the north, where 2 million tons are produced annually. After harvesting this large amount of rice in the fields, many biowastes, such as rice husks and straw, remain, which can be considered valuable resources for a variety of purposes. In order to fully appreciate this fact, it is important to realize that the production of each kilogram of milled rice is accompanied by the production of approximately 1100 and 280 g of rice straw and rice husk, respectively [
63].
In this study, with the aim of win-win cooperation, BAC and ZVFe NPs were used together in order to verify the constructive interaction between the two counterparts and improve their remediation capability. The stabilization of nanosized iron particles on porous BAC support occurs through different mechanisms, including coordinating, adsorption, chelating, bridging processes, and immobilizing [
61]. As a result of the bidentate complexation, ferrous and ferric iron ions are complexed with -OH [
64], and stable bonds are also created through the reaction between the BAC surface functionalities and the iron oxide layer formed around the nZVFe core [
65]. As a result of the reduced intraparticle attraction, this phenomenon results in a reduction in ZVFe NPs’ agglomeration and enhances their dispersion on the surface of the BAC support [
61].
Therefore, the aims of this research were (i) the synthesis of RSAC and nZVFe–RSAC and investigation of the effects of Fe loading quantity on the properties of nanocomposite; (ii) the characterization of the novel nanocomposite with powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET-N2) technologies; (iii) to perform batch adsorption experiments under various operating conditions to determine the removal efficiency of Pb(II), investigating the effect of competing ions on the absorption of the target pollutant [Pb(II)], as well as examining nZVFe–RSAC’s recyclability; and (iv) to perform a detailed study of adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic functions of the adsorption process. In a broad way, this research focused on synthesizing and evaluating a novel super-porous, highly efficient adsorbent from agricultural wastes which are abundant and environmentally friendly, with a high potency of toxic Pb removal.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Analytical Techniques
All chemicals used in this research were purchased from Merck or Sigma-Aldrich at analytical grade, and all preparations were carried out by using distilled water (DI). Lead (II) stock solution was prepared by using appropriate amounts of
and using deionized water. The stock solution was diluted with deionized water in order to prepare solutions at different concentrations. The pH of the solutions was adjusted by using 0.1 M
and 0.1 M NaOH solutions and controlled by a pH meter (Metrohm, 827 pH Lab). Atomic absorption spectrophotometry was used to determine the concentration of Pb(II) solutions (Perkin-Elmer 3030). Additionally, rice straw (RS) elemental analyses were conducted by using a Costech ECS 4010 Elemental Analyzer, and the physical properties and compositions of RS and RSAC were determined based on the published literature [
63]. Using the standard test method, the total ash content of RS and RSAC was measured (ASTM D2866-2011). Moreover, the specific surface areas (SSAs) of the RS, RSAC, and nZVFe–RSAC samples were determined by means of a Belsorp mini II (BelJapan) instrument in accordance with the BET-N
2 method. A Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) and density functional theory (DFT) model were used to calculate the pore size and distribution of the pores, respectively [
66]. A Philips X’PERTMPD diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromatized (Cu-Kα radiation, λ = 1.54 Å) was employed in order to determine the XRD patterns of RS, RSAC, and nZVFe–RSAC samples. A scanning rate of 0.05 (
° s
−1) was used to record all samples between 10 and 70° (2θ). Finally, the morphology of RS, RSAC, and nZVFe–RSAC samples was examined by SEM (Hitachi S-4160, 20.0 kV). The pH
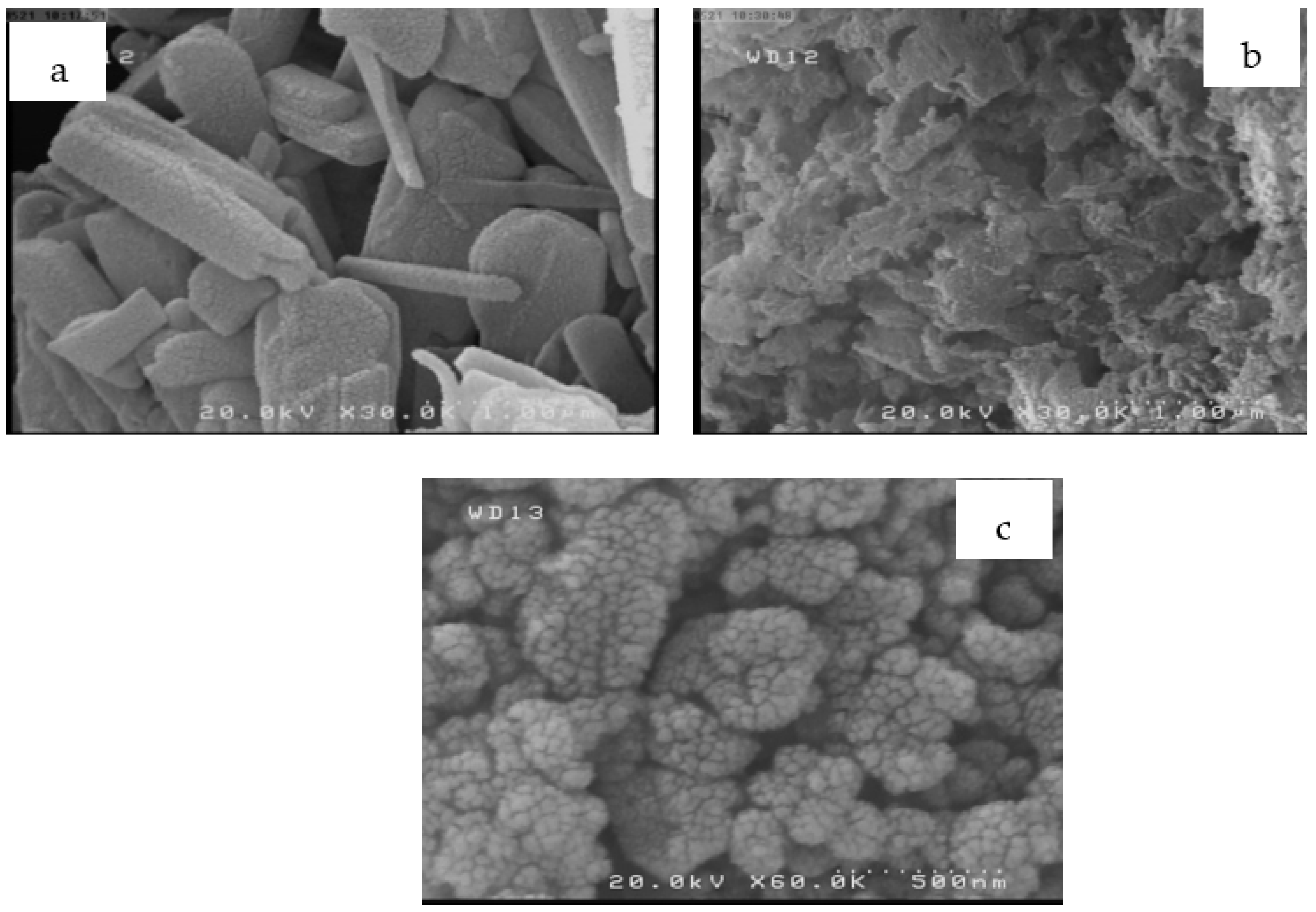
pzc (point of zero charge) was measured with a zeta-meter system 3.0+ (Meditop Co., Bangkok, Thailand).
2.2. Preparation of RSAC and nZVFe–RSAC
Rice straw (RS) was collected from the local farms of Guilan province, Iran; ground; and then sieved, using a 200-mesh sieve. Thereafter, to remove ash and water-soluble substances, the samples were soaked in a solution of NaOH (2 wt.%) for 48 h. A series of washes with DI water was conducted until neutrality was reached, and then the rice straws were dried at 80 °C for 24 h and stored for later use. From the treated RS, powdered activated carbon was prepared by using a thermochemical method. As a first step toward chemical activation, the dried RS samples were pre-oxidized at 200 °C in air atmosphere for 2 h. Then the prepared samples were impregnated with a 30 wt.%
solution, using an impregnation mass ratio of
. Two phases of thermal treatment were conducted on acid-impregnated samples in an electrical heating furnace, under an inert nitrogen atmosphere at a flow rate of 25 mL min
−1. During the first phase, a constant rate of 6 °C per minute was used to heat the reactor to 170 °C, and a 60-min period was spent maintaining samples at this temperature. It was followed by heating the reactor to 500 °C at a rate of 8 °C per minute and maintaining the samples at this temperature for 60 min. After carbonization, for the purpose of preventing reoxidation of the obtained solids, the furnace was gradually cooled in a stream of nitrogen gas during the night, until it reached room temperature [
67]. Following this, a solution of 1 mol L
−1 HCl was used for washing, and a vacuum flask was used for filtering. In the following stages, hot DI water was used for repeated washing of the final product until a pH value of 7 was reached in the rinsing water. As a final step, RSAC samples were dried at 105 °C in a vacuum for 24 h before being stored in a desiccator. In order to synthesize nZVFe–RSAC, ferrous iron solutions were reduced by using borohydride, and RSAC served as a porous support medium. First of all, to prepare the ferrous solution,
(iron/RSAC mass ratio 1:1) was dissolved in a mixture of absolute ethanol/DI water with a ratio of 1/4 (
v/
v). In the next step, the prepared solution was poured into an open flask with three necks, and the solution was stirred for four hours with 1 g of RSAC added to it. Then, on a magnetic stirrer, 55 mL of freshly prepared
aqueous solution (BH
4¯/Fe
2+ molar ratio of 3.0) was added to the mixture, drop by drop, leading to Fe
0 NPs formation and
evolution. Subsequently, by using
as a reduction agent and RSAC as a porous stabilizer, nZVFe–RSAC was synthesized in the solution by reducing Fe (II) to
. To prevent nZVFe–RSAC oxidization,
was used as an inert gas throughout the entire process described. After filtering the suspension and washing it with pure ethanol three times, the synthesized nanocomposite was extracted. Following vacuum drying at 75 °C overnight, the nanocomposite was stored in an
atmosphere for later use [
68].
2.3. Procedures for Adsorption Experiments
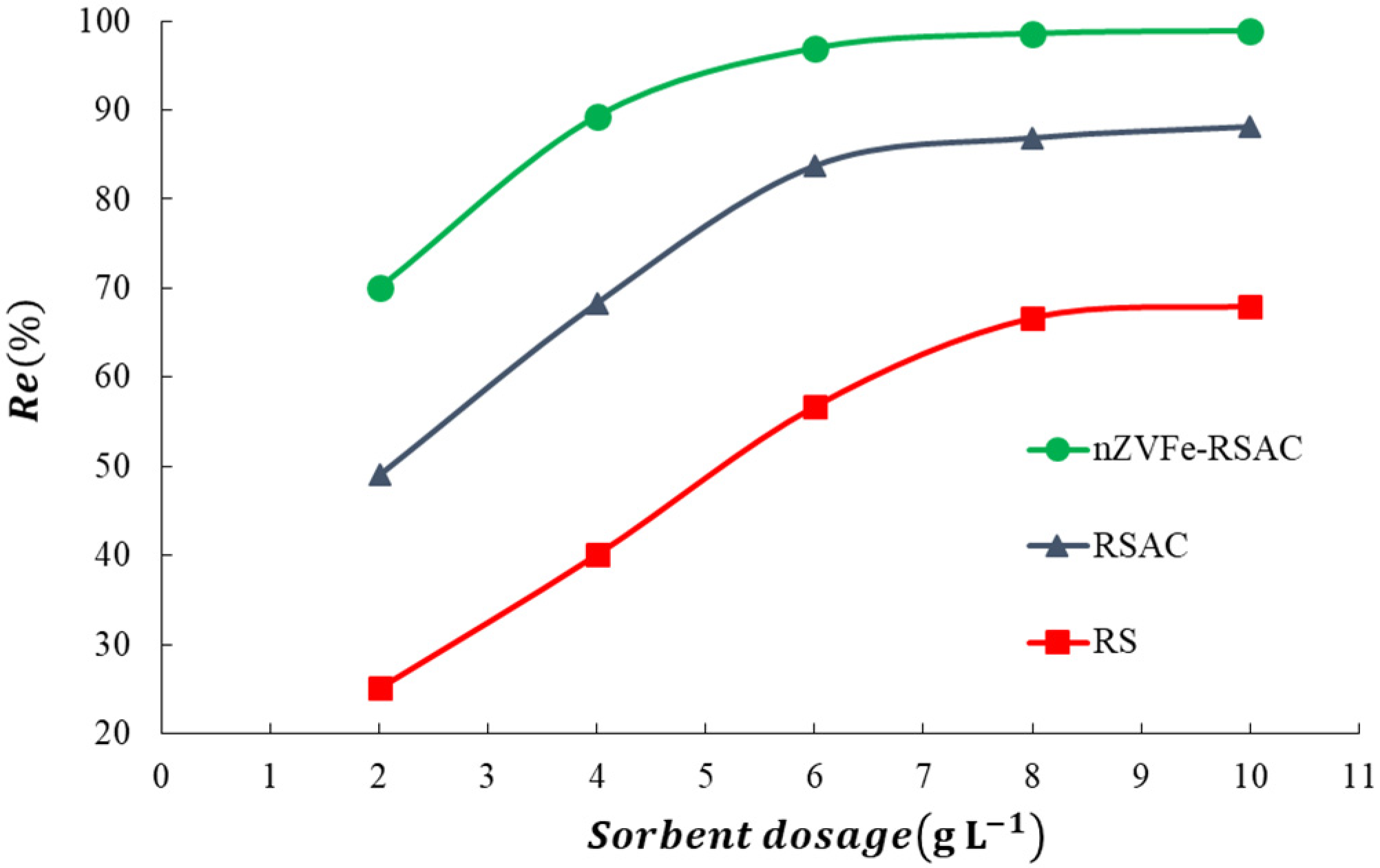
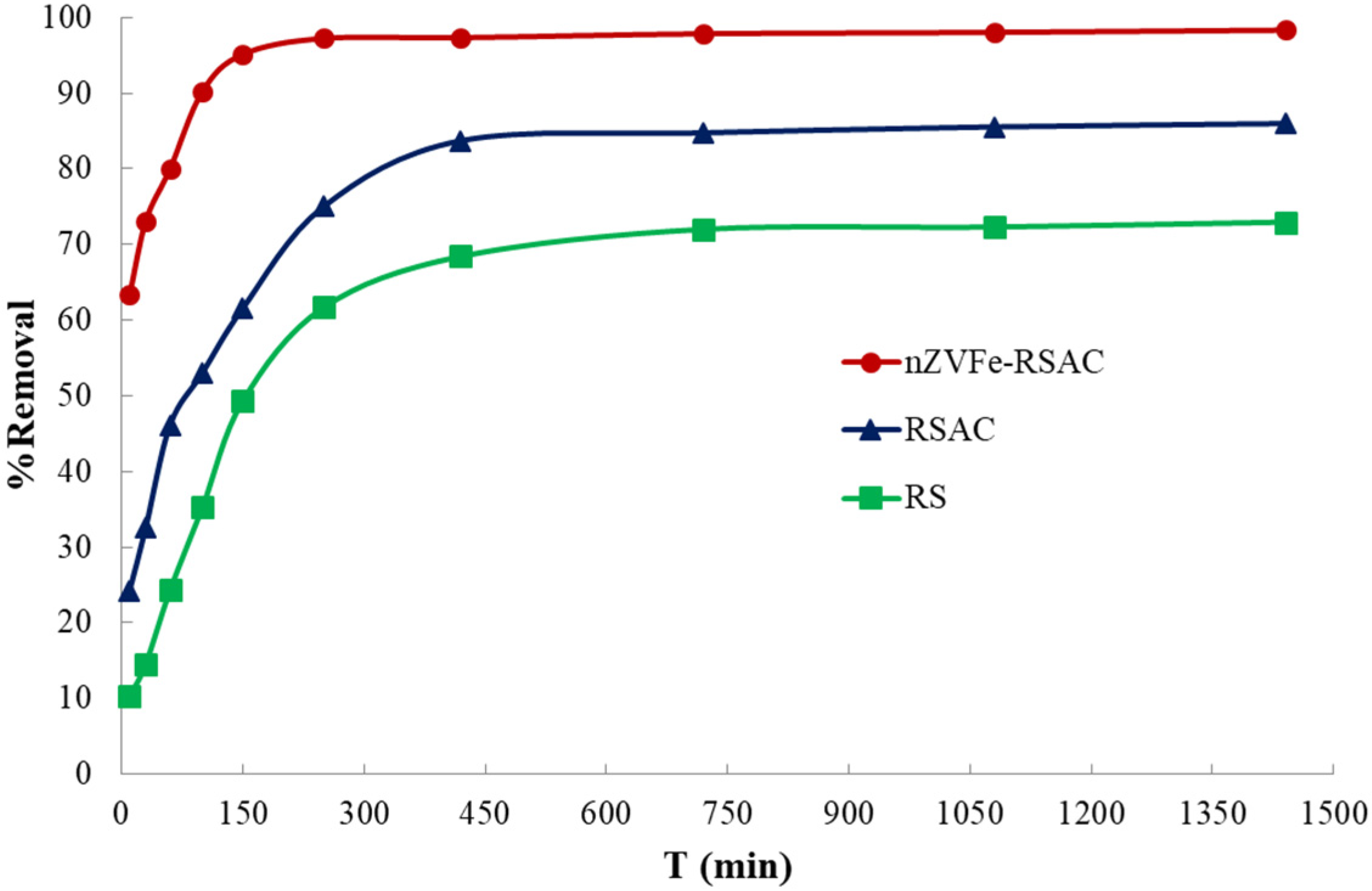
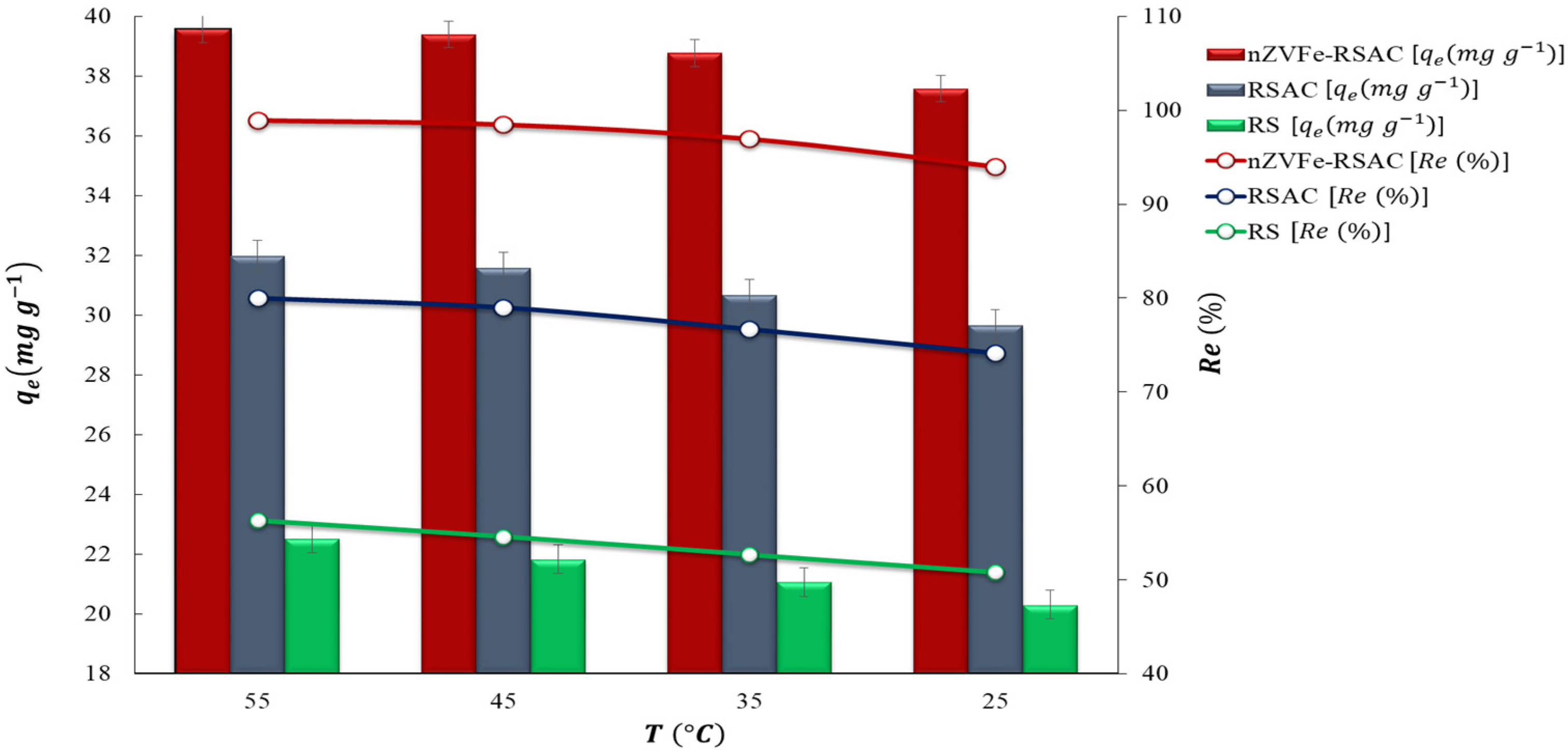
To obtain maximum performance, the factors that affect the adsorption process, including contact time, temperature, pH, amount of adsorbent, and initial concentration of target pollutant, need to be optimized. Using deionized distilled water, appropriate amounts of were dissolved in order to prepare aqueous solutions of Pb(II). Firstly, the pH was optimized in the range of pH 2–10. Afterward, the removal efficiency of Pb(II) ions was investigated for different adsorbent dosages between 2 and 10 (g L−1). The contact time has a substantial effect on the adsorption process. In order to determine the equilibrium time of the adsorption and the best-fitted kinetic model, kinetic studies were conducted. The contact time was optimized in the range of 2–1440 min for 100 (mg L−1) of target pollutant. Furthermore, to study the effect of the initial lead concentration on the adsorption efficiency, equilibrium isotherm experiments were conducted by using different initial lead concentrations ranging from 10 to 1000 (mg L−1). During these experiments, the initial pH of the solutions and the initial adsorption temperature were fixed at the (6 ± 0.1) and (25 ± 1 °C), respectively. Finally, the temperature effect on the Pb(II) removal efficiency was investigated in the range of 25–50 °C.
The batch experiments were conducted by using 0.1 g of sorbent and 10 mL of lead solution, at the desired pH and concentration, in polyethylene bottles (50 mL). Mixing was performed with a shaker at 200 rpm. In every batch adsorption experiment, three replicates of each type and concentration of water solution were produced to ensure representative results. A series of samples was collected throughout the adsorption experiments, filtered, and the target pollutant concentration was determined in the supernatant immediately after filtering. By using Equations (1) and (2), the adsorption capacity of sorbents (
(mg g
−1)) and the removal efficiency Pb(II) (Re %) were determined:
where
(mg L
−1) is the initial concentration of the target pollutant, and
(mg L
−1) represents the equilibrium concentration of the target pollutant. The V (L) and W (g) are the volume of adsorbate solution and the mass of adsorbent, respectively.
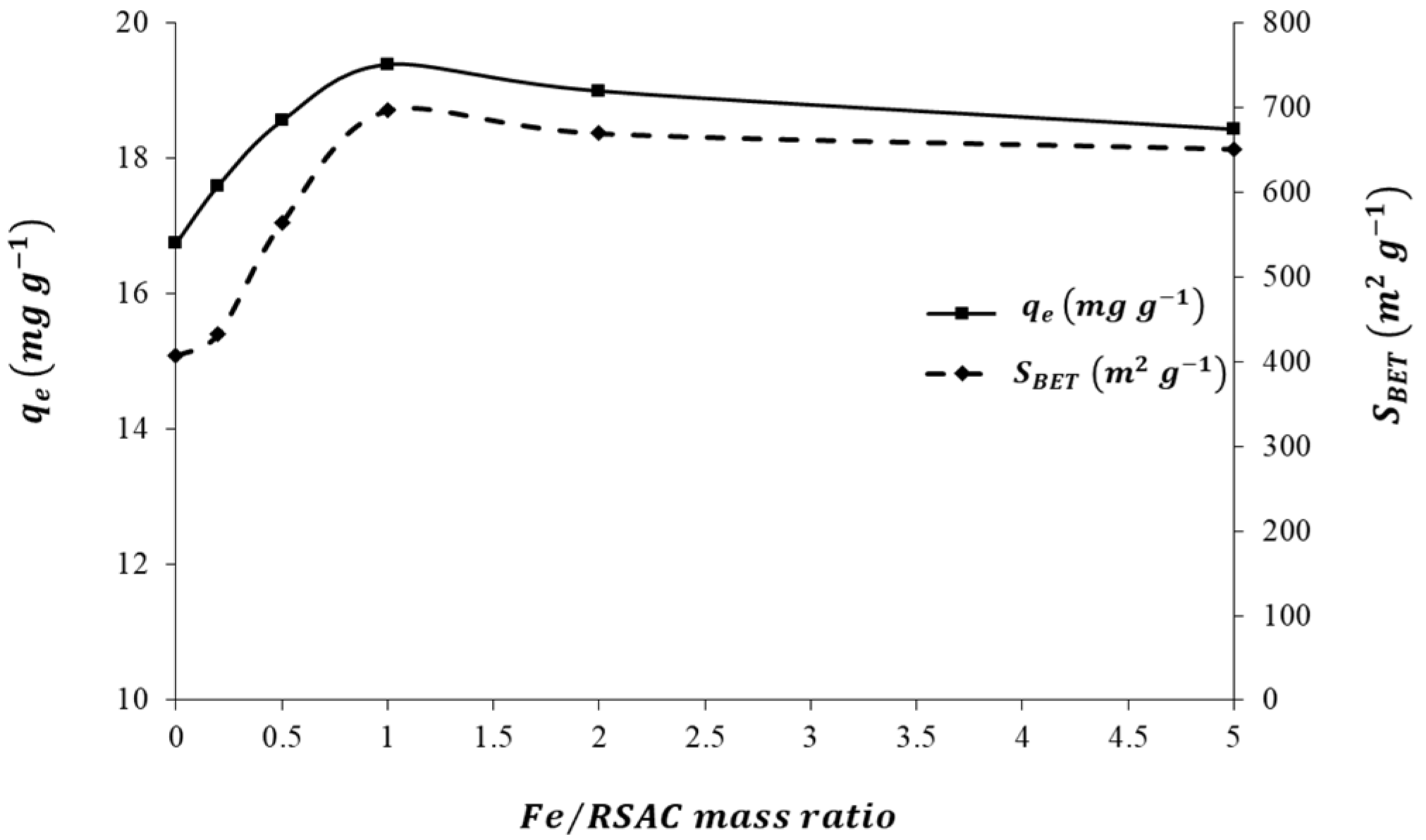
An evaluation of the effects of Fe loading quantities on the adsorption capacity of Pb(II) was conducted in order to optimize the preparation process for the nZVFe–RSAC nanocomposite. For this purpose, different nanocomposites were prepared with different mass ratios of Fe:RSAC, including 0:1, 0.2:1, 0.5:1, 1:1, 2:1, and 5:1. A similar mass of these adsorbents was then subjected to solutions containing 100 mg L−1 of Pb(II) in order to determine their adsorption capacities for Pb(II). The nanocomposite with the highest Pb(II) adsorption capacity was selected for further batch studies in regard to characterization, pH effect, adsorbents dosage, competing ions, and adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics.
To evaluate the effect of competing ions on the Pb(II)-removal efficiency, 0.5 g of adsorbent was added to solutions containing 30 mg L−1 Pb(II) and varying concentrations of background competitors (50–200 mg L−1), including Ni (II), Hg (II), Cu (II), and Cd (II), while maintaining the solution pH level at 6.0 ± 0.5. The solution of competing ions was prepared by using , , and salts.
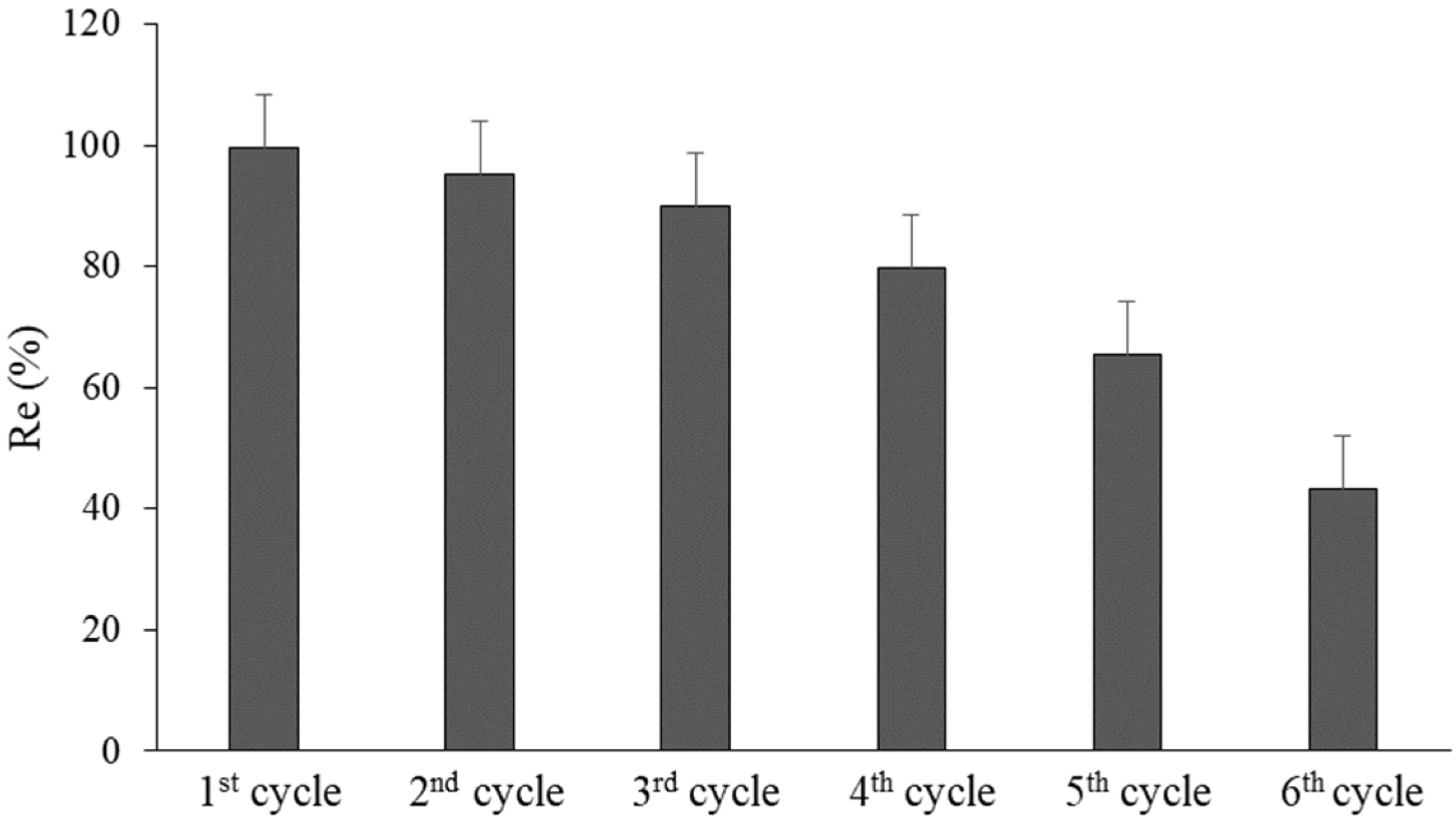
In addition, nZVFe–RSAC’s recyclability and reusability were evaluated through repeated cycles of Pb(II) adsorption and desorption at an initial concentration of 50 mg L
−1 for six consecutive cycles. Following the first cycle, the used nanocomposite was regenerated by washing it in HCl, (0.01 M) for removing the oxide layer and dissolving the precipitated. In the following step, the nanocomposite was washed with DI water, dried under vacuum overnight, and stored for the next treatment cycle [
17]. Three parallel measurements were used to determine the average value of Pb(II) removal efficiency, using Equation (2).
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics
In the present study, four widely used isotherm models, namely Redlich–Peterson (Equation (3)), Langmuir (Equation (4)), Langmuir–Freundlich (Equation (5)), and Freundlich (Equation (6)) [
69,
70] were employed to describe the isothermal behavior of adsorption. Modeling the experimental target pollutant (Pb(II)) isotherm data is required to understand the adsorption behavior and removability of adsorbents.
where the
refers to the amount of adsorbed ions per unit mass of adsorbent at equilibrium condition;
refers to the equilibrium concentration of ions in the solution;
represents the maximum sorption capacity of the used adsorbent for target pollutant; and
, n, a, b,
, and
are constants, and g in an exponent.
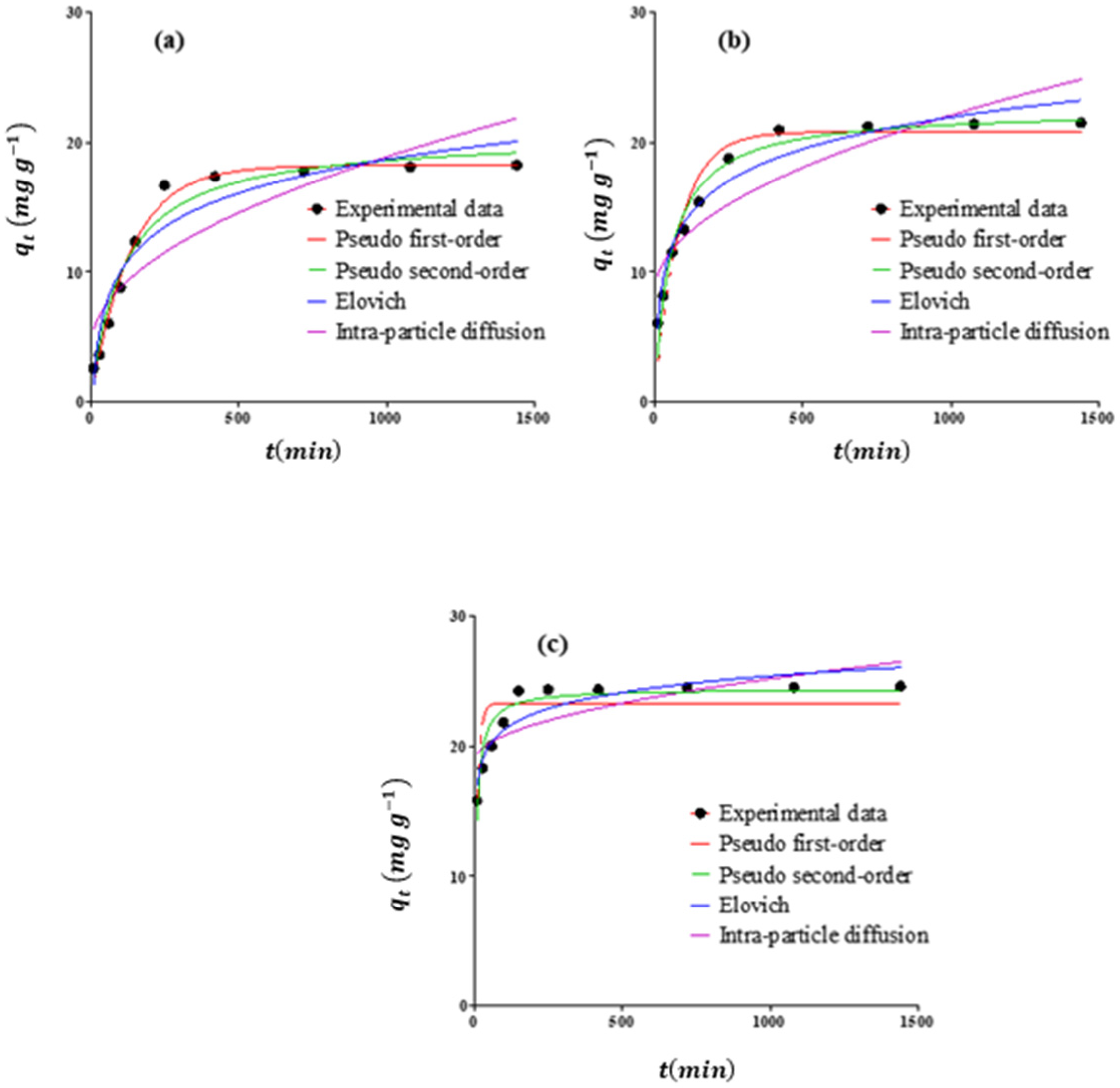
Furthermore, the kinetic models can help us understand the rate and order of the adsorption process and, therefore, to evaluate the performance of adsorbents. So, in this research, the experimental data were fitted to a number of kinetic models, such as pseudo second-order (Equation (7)), Elovich (Equation (8)), intraparticle diffusion (Equation (9)), and pseudo-first-order (Equation (10)) models [
71].
where
and
represent the quantity of the target pollutant sorbed by adsorbent at time t (min) and equilibrium condition, respectively;
and
are the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models’ rate constants, respectively;
demonstrates the rate constant of the intraparticle diffusion; and a constant
represents the thickness of the boundary layer of sorbent–sorbate system. Furthermore,
and
represent the adsorption rate at the start and the adsorption constant, respectively.
It is possible to calculate h
, the initial absorption rate, as follows:
The models’ parameters (Equations (3)–(10)) were evaluated and best utilized by nonlinear regression, which was performed by using the GraphPad Prism (V.7) tool. Among the applied models, the best fitted for the experimental data was evaluated based on the results of the determination coefficient (R2), in addition to Standard Error of Estimate (SEE). These two statistical parameters were calculated based on the comparison of the experimental and calculated values.
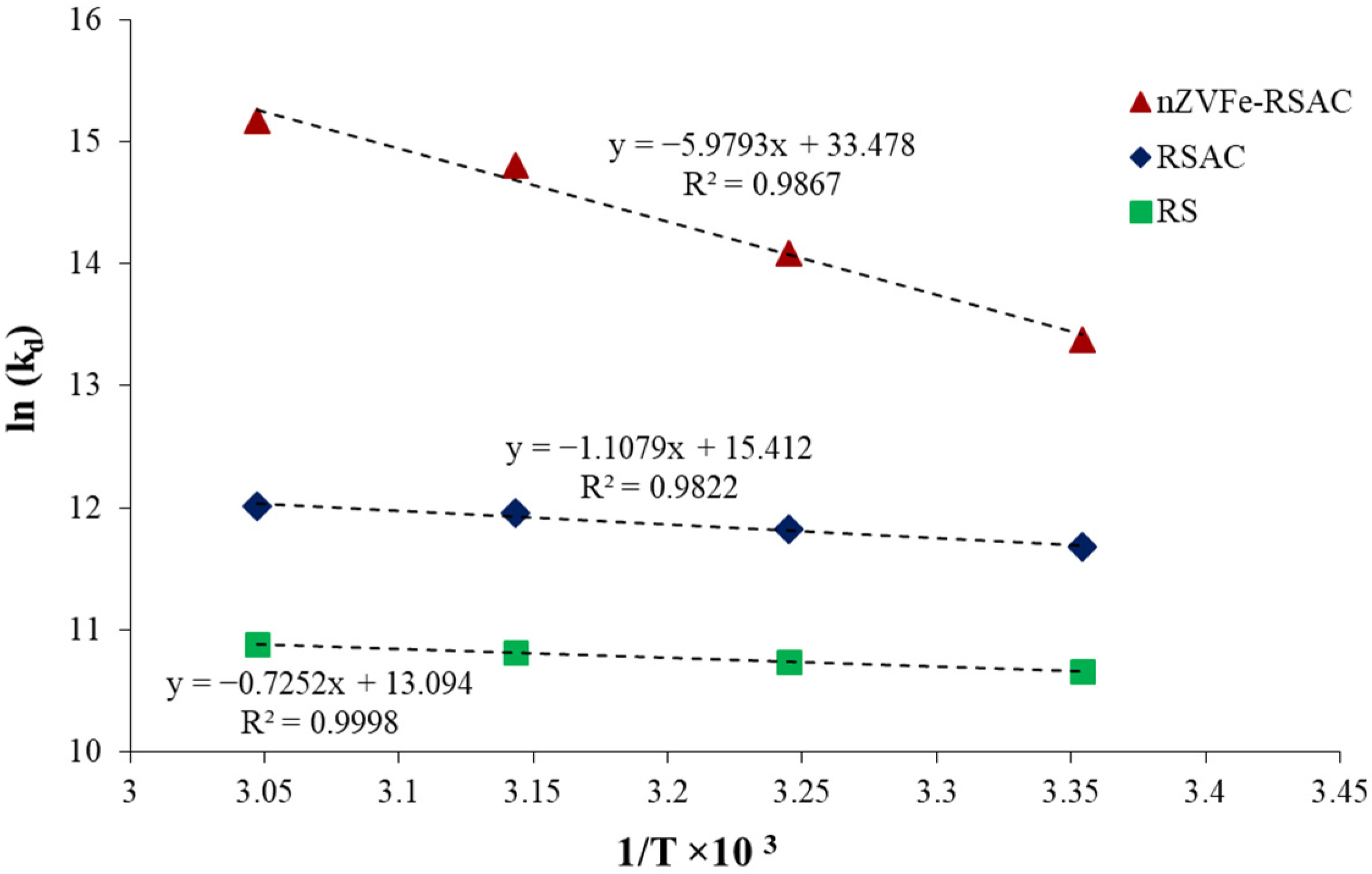
The adsorption behavior and spontaneity of adsorption processes are largely determined by thermodynamic studies. Further details are provided regarding the appropriate temperature range for the adsorption process, as well as the nature of the adsorbent and sorbate under equilibrium conditions. In order to accomplish this goal, using Equations ((12)–(14)), thermodynamic factors such as free energy
, enthalpy
, and entropy
were calculated [
72]:
where
,
, and
represent variations in Gibbs free energy, entropy, and enthalpy, respectively; R (8.314 J mol
−1 K
−1) and T (°K) are the gas constant and temperature, respectively;
is the thermodynamic equilibrium constant;
is the solid phase equilibrium concentration; and
represents the solution equilibrium concentration.
4. Conclusions
Wastewater treatment is a matter of concern, primarily because of the complexity, efficiency, and costs associated with this process [
96,
97,
98]. In this context, zero-valent iron NPs provide a possible solution to the problem of water treatment. However, a strong inclination to agglomerate has been reported as one of their significant drawbacks. To overcome this problem, the immobilization of nZVFe particles on porous host materials can be useful. In this study, with the aim of win-win cooperation, biomass-derived activated carbon and nZVFe particles were used to confirm the constructive interaction between the two counterparts and improve their respective remediation capabilities. In the first step, biomass-derived activated carbon was prepared from rice straw, using a thermal–chemical procedure (RSAC). Then the RSAC-supported nZVFe composite (nZVFe–RSAC) was synthesized by the sodium borohydride reduction method, and it was subsequently used to remove Pb(II) from the aqueous solution. Characterization by SEM and XRD techniques confirmed the high dispersion and activity of ZVFe nanoparticles with an average size of 46 nm after fixation on RSAC. Then this innovative nanocomposite was utilized to remove Pb(II) ions from the aqueous solution. In batch studies, the effects of various influencing factors on the process of Pb absorption, including contact time, amount of adsorbent, pH, temperature, and the initial concentration of the target pollutant, were investigated. The results showed that 6 (g L
−1) nZVFe–RSAC effectively removed about 97% of Pb(II) ions at pH = 6. Our investigation of the adsorption kinetics of Pb(II) ions on nZVFe–RSAC showed that this process follows a pseudo-second-order model. It strongly suggests that chemisorption, through the exchange or sharing of electrons between nanocomposite and Pb(II) ions, is the rate-limiting step in the adsorption process. Adsorption isotherm studies showed that the adsorption of Pb(II) onto nZVFe–RSAC fitted well with the Langmuir–Freundlich model
, and the maximum absorption capacity of the nanocomposite was 140.8
. Lastly, an investigation of the adsorption mechanism showed that nZVFe was involved in Pb(II) ions’ removal through two main processes: (I) Pb(II) adsorption on the surface of nZVFe particles and (II) participation in the redox reaction directly. Subsequently, all intermediates produced through the redox reaction between iron nanoparticles and Pb(II) were adsorbed on the nZVFe–RSAC surface and did not enter the solution. In summary, the nZVFe–RSAC nanocomposite had a bright application prospect of good efficiency in immobilizing ZVFe nanoparticles, as well as a practical removal effect on Pb(II). It is necessary to conduct further research in order to determine whether different methods of preparing biomass-derived activated carbon result in improved nZVFe–RSAC nanocomposite characteristics and the ability to remove Pb(II), and also to determine the adsorption isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics in order to facilitate comparisons with other adsorbents.