Spatio-Temporal Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality with Water Level Fluctuation in a Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Site Description
2.2. Study Methods
2.2.1. Water Quality Monitoring
- w is the weighting factor ranging between 0 and 1;
- q means the rating number assigned to a parameter ranging from 0 to 100.
2.2.2. Algal Abundance Monitoring
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
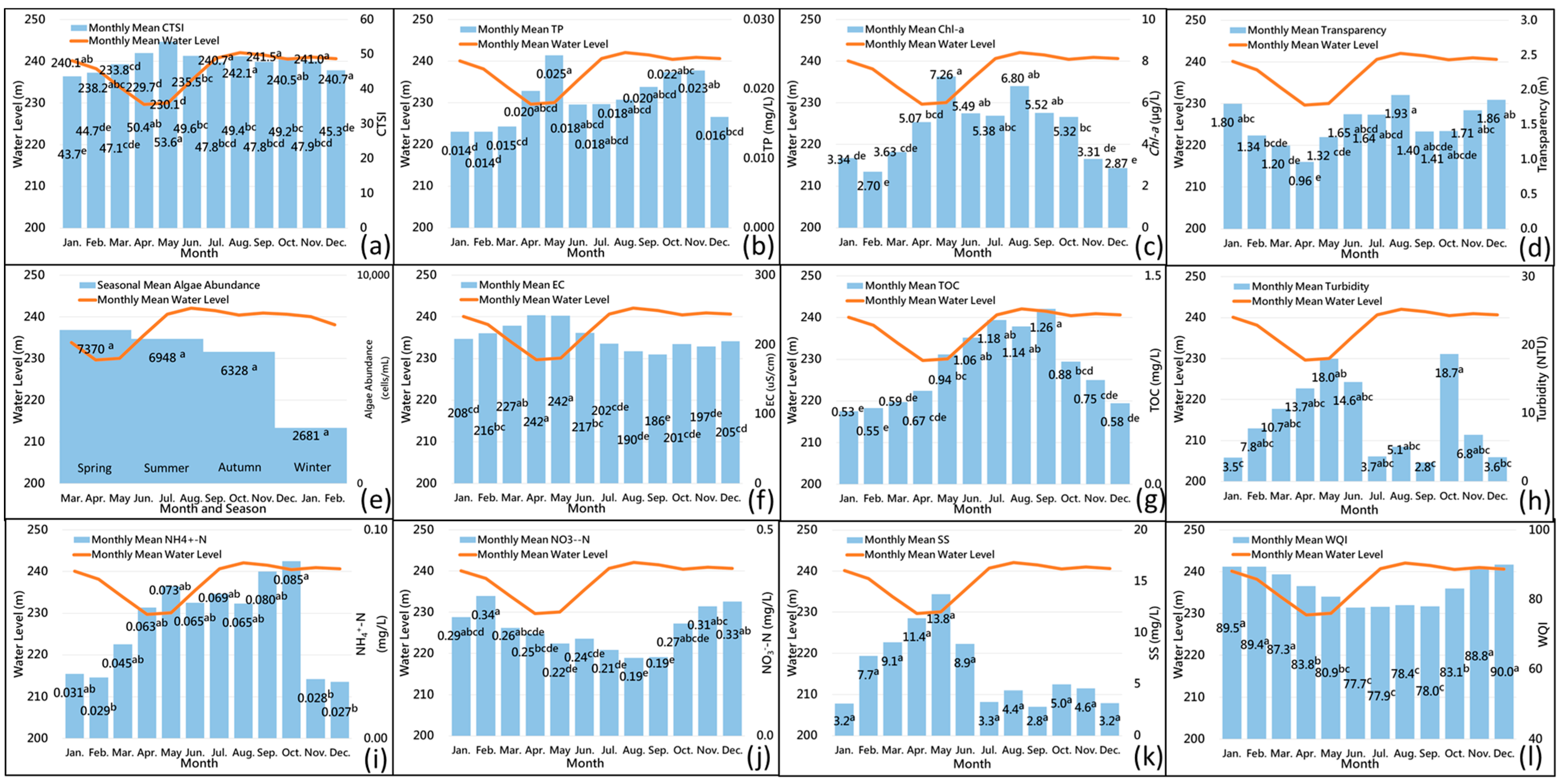
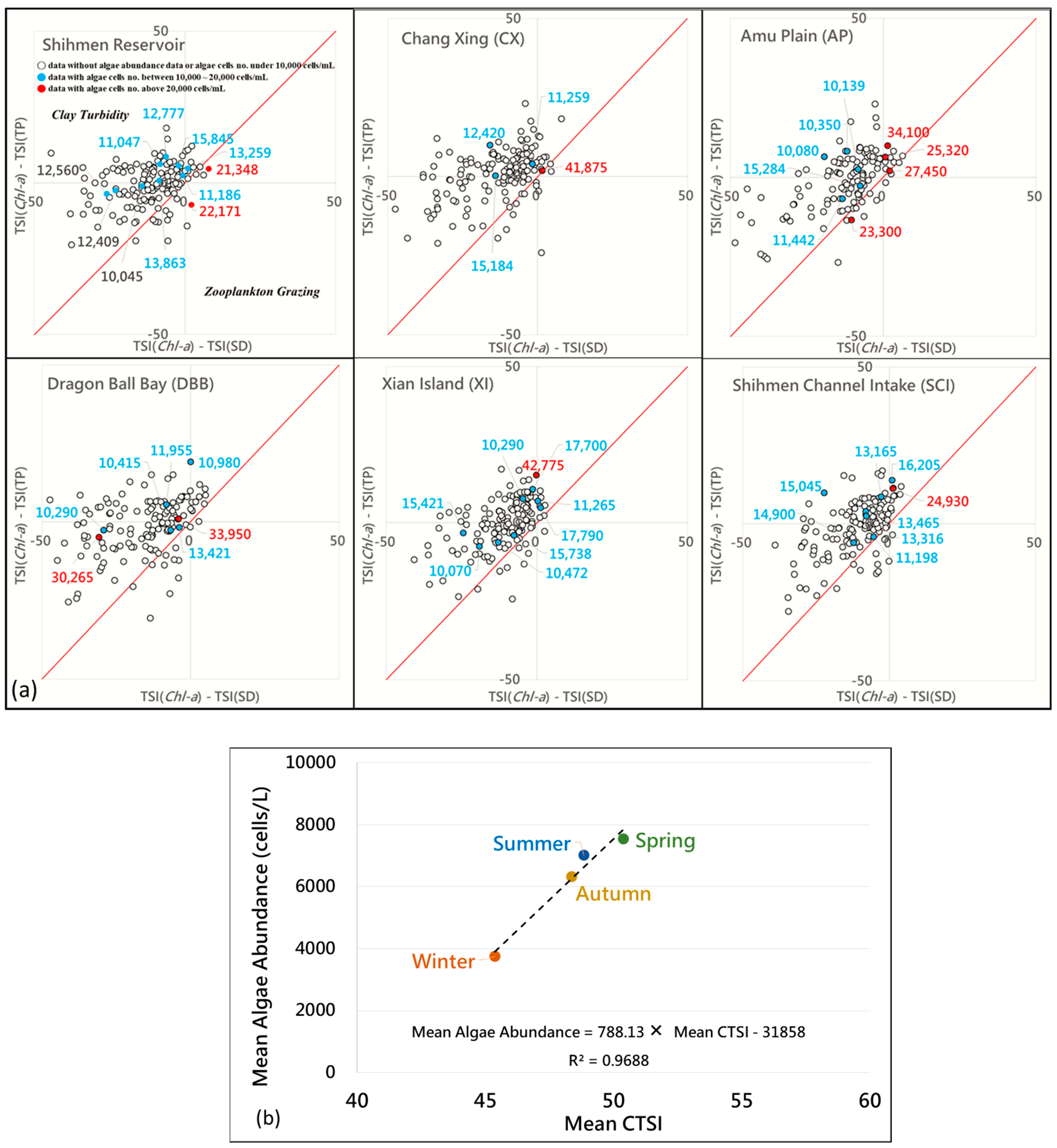
3.1. Temporal Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality in Reservoir
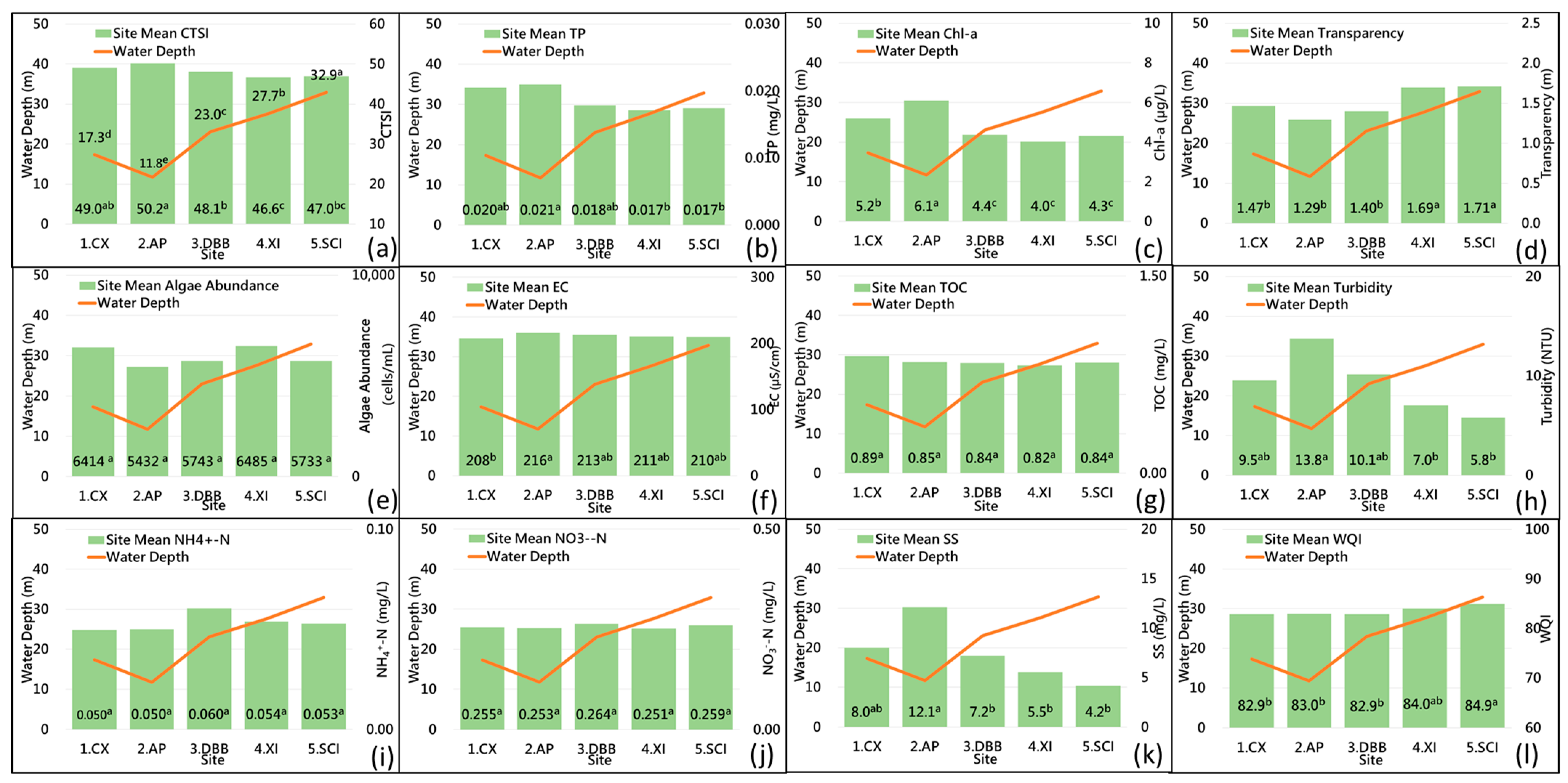
3.2. Spatial Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality of the Reservoir
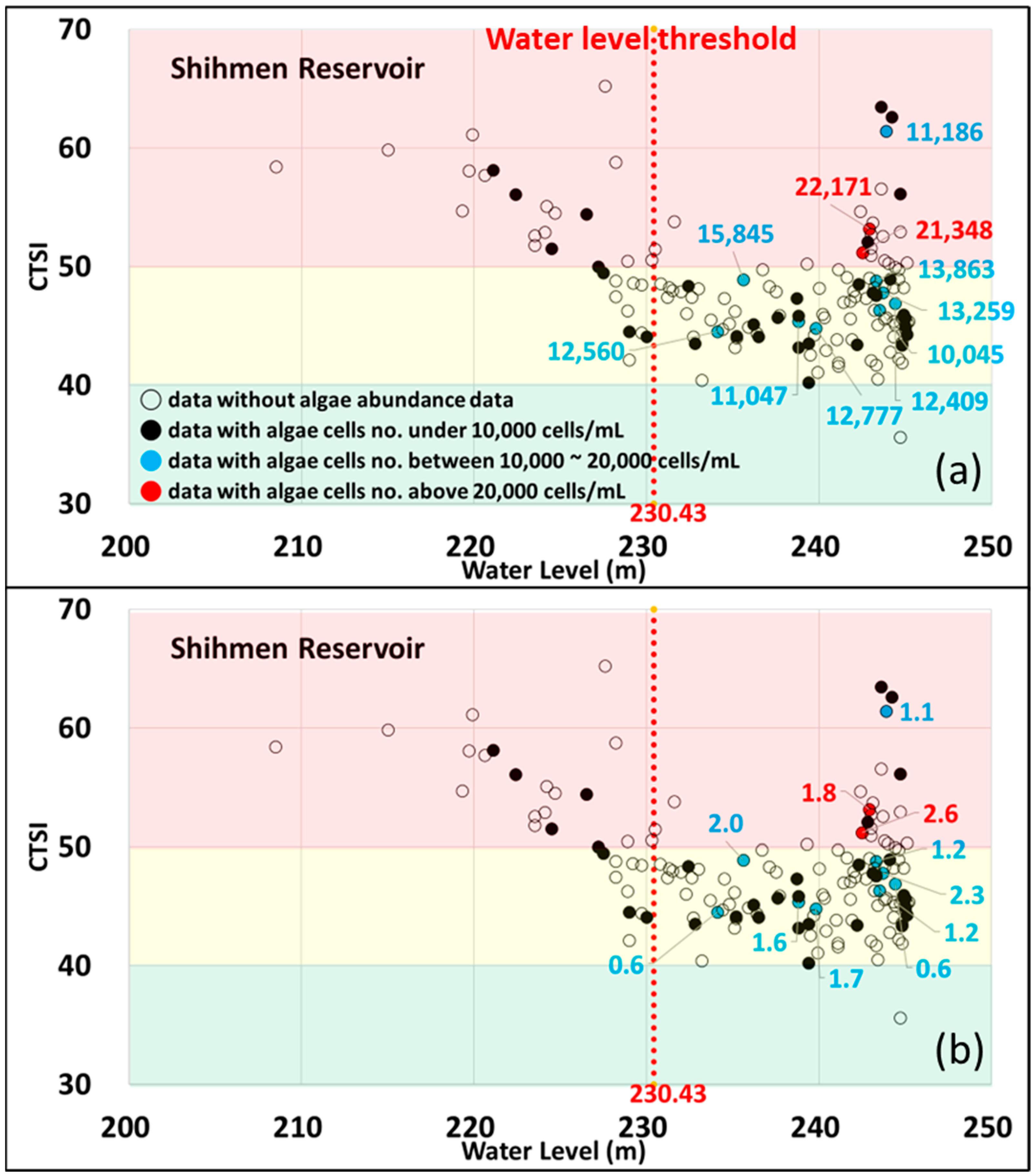
3.3. Water Quality Difference with Water Level of Reservoir
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leira, M.; Cantonati, M. Effects of water-level fluctuations on lakes: An annotated bibliography. In Ecological Effects of Water-Level Fluctuations in Lakes; Wantzen, K.M., Rothhaupt, K.O., Mörtl, M., Cantonati, M., Tóth, L.G., Fischer, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2008; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinka, M.; Ágoston-Szabó, E.; Berczik, Á.; Kutrucz, G. Influence of water level fluctuation on the spatial dynamic of the water chemistry at Lake Ferto/Neusiedler See. Limnologica. 2008, 34, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsten, S.; Marttunen, M.; Palomaeki, R.; Riihimaeki, J.; Alasaarela, E. Towards an ecologically based regulation practice in Finnish hydroelectric lakes. Regul River. 1996, 12, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.T.; Brock, M.A. How do depth, duration and frequency of flooding influence the establishment of wetland plant communities? Plant Ecol. 2000, 147, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Valk, A.G. Water-level fluctuations in North American prairie wetlands. Hydrobiologia 2005, 539, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Papastergiadou, E. Effects of a long term water level reduction on the ecology and water quality in an eastern Mediterranean lake. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ec. 2013, 411, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, I.; Smith, R. The effect of localised nutrient enrichment on the shallow, epilithic periphyton of oligotrophic Lake Taupo, New Zealand. New Zeal. J. Mar. Fresh. 1993, 27, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punning, J.M.; Puusepp, L. Diatom assemblages in sediments of Lake Juusa, Southern Estonia with an assessment of their habitat. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, M.; Hosper, S.H. Water-level management as a tool for the restoration of shallow lakes in the Netherlands. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2002, 18, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Hilt, S. Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: Options for management. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mageed, A.A.A.; Heikal, M.T. Factors affecting seasonal patterns in epilimnion zooplankton community in one of the largest man-made lake in Africa (Lake Nasser, Egypt). Limnologica 2006, 36, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Olden, J.D.; Xia, W.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Hughes, R.M.; Chen, Y. Hydrology and water quality shape macroinvertebrate patterns and facilitate non-native species dispersals in an inter-basin water transfer system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, T.; Sukenik, A.; Nishri, A. Lake Kinneret: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. In Lake Kinneret: Ecology and Management; Zohary, T., Sukenik, A., Berman, T., Nishri, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Nederland, 2014; pp. 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Song, J.H.; Jun, S.M.; Kang, M.S. Impact assessment of water-level management on water quality in an estuary reservoir using a watershed-reservoir linkage model. Agr. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Teubner, K.; Chen, Y. Water quality characteristics of Poyang Lake, China, in response to changes in the water level. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, S.L.; Wiley, K.B. Great Lakes toxic sediments and climate change: Implications for environmental remediation. Global Environ. Chang. 1993, 3, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Qi, X.; Zhou, S.; Niu, H.; Zhang, T. Spatiotemporal distribution of phosphorus fractions and the potential release risks in sediments in a Yangtze River connected lake: New insights into the influence of water-level fluctuation. J. Soils Sediments. 2023, 23, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, B.; Yu, J.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, E.; Li, Q.; Yin, H. Water-level fluctuations regulate the availability and diffusion kinetics process of phosphorus at lake water–sediment interface. Water Resour. 2021, 200, 117258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parparov, A.; Gal, G.; Hamilton, D.; Kasprzak, P.; Ostapenia, A. Water quality assessment, trophic classification and water resources management. J. Water Res. Prot. 2010, 2, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, W.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.; Fujii, M. Assessing the agricultural drainage water with water quality indices in the El-Salam Canal Mega Project, Egypt. Water 2019, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iticescu, C.; Georgescu, L.P.; Murariu, G.; Topa, C.; Timofti, M.; Pintilie, V.; Arseni, M. Lower Danube water quality quantified through WQI and multivariate analysis. Water 2019, 11, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, M.S.A.; Lin, J.; Chiang Hsieh, L.; Zafirah, Y.; Andhikaputra, G.; Wang, Y. Influencing factors analysis of Taiwan eutrophicated reservoirs. Water 2020, 12, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parparov, A.; Hambright, K.D.; Hakanson, L.; Ostapenia, A.P. Water quality quantification: Basics and implementation. Hydrobiologia 2006, 560, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serehy, H.A.; Abdallah, H.S.; Al-Misned, F.A.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A. Assessing water quality and classifying trophic status for scientifically based managing the water resources of the Lake Timsah, the lake with salinity stratification along the Suez Canal. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, B. Temporal and spatial variation in water quality in the Three Gorges Reservoir from 1998 to 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 768, 144866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitran, G.E.; Vuta, L.I.; Popa, B.; Popa, F. Hydrological variability impact on eutrophication in a large Romanian Border Reservoir, Stanca–Costesti. Water 2020, 12, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, F.I.B.; Lima, P. deF.; Leitão, R.C.; Paulino, W.D.; Santaella, S.T. Influence of rainfall on the trophic status of a Brazilian semiarid reservoir. Acta Sci. 2013, 35, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, A.M.; Boavida, M. Seasonal water level fluctuations: Implications for reservoir limnology and management. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 10, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E.; Havens, K.E. Simple graphical methods for the interpretation of relationships between trophic state variables. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Atique, U.; An, K. Assessment of water quality based on trophic status and nutrients-chlorophyll empirical models of different elevation reservoirs. Water 2021, 13, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R.; Hubbart, J.A. Empirical estimation of non-chlorophyll light attenuation in Missouri reservoirs using deviation from the maximum observed value in the Secchi-Chlorophyll relationship. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.F.; de Sousa Brandão, I.L.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; de Oliveira, A.A.F.; Saraiva, A.C.F.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Ishihara, H., Jr. Using hydrodynamic and water quality variables to assess eutrophication in a tropical hydroelectric reservoir. J. Env. Manag. 2020, 256, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. Expanding the trophic state concept to identify non-nutrient limited lakes and reservoirs. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Enhancing the States’ Lake Management Programs, Chicago, IL, USA, 17–18 May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; van Leeuwen, C.H.A.; van de Waal, D.B.; Bakker, E.S. Impacts of sediment resuspension on phytoplankton biomass production and trophic transfer: Implications for shallow lake restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 808, 152156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H. Effect of nutrients and non-algal turbidity on blue-green algal biomass in four North Carolina reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1990, 6, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C. Effect of turbidity on algal growth. Circular 1974, 121, 1–12. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/158322708.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Naselli-Flores, L.; Barone, R. Water-level fluctuations in Mediterranean reservoirs: Setting a dewatering threshold as a management tool to improve water quality. Hydrobiologia 2005, 548, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Water Quality | WQI | TSI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Descriptor | Rank | Descriptor | |
| Excellent | 91–100 | Eminently usable for all purposes | <40 | Oligotrophic |
| Good | 71–90 | Suitable for all uses | 40–50 | Mesotrophic |
| Intermediate | 51–70 | Main use and/or some uses may be jeopardized | 50–60 | Eutrophic |
| Bad | 25–50 | Unsuitable for main and/or several uses | 60–80 | Eutrophic |
| Very Bad | 0–25 | Totally unsuitable for main and/or many uses | >80 | Eutrophic |
| Monitoring Station | Station Characteristic Description |
|---|---|
| Chang Xin (CX) 24°48′18″ N; 121°18′48″ E | The main entrance of the reservoir storage area (the middle of the river section) |
| Amu Plain (AP) 24°48′53″ N; 121°18′36″ E | The entrance of Sanmin Creek, a tributary of the reservoir. The upstream is agricultural and recreational areas (right bank of the reservoir storage area) |
| Dragon Ball Bay (DBB) 24°49′06″ N; 121°17′09″ E | The entrance of Nanzigou Creek, a tributary of the reservoir. The upstream is an agricultural and recreational area (right bank of the reservoir storage area) |
| Xian Island (XI) 24°48′20″ N; 121°15′07″ E | Small village area (left bank of the reservoir storage area) |
| Shihmen Channel Intake (SCI) 24°48′35″ N; 121°14′28″ E | Public water supply intake |
| Water Level (m) | Water Depth (m) | CTSI | WQI | Water Temp. (°C) | EC (μS/cm) | DO (mg/L) | pH | SS (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Water Level (>230.43 m) n = 121 | Mean | 240.5 | 24.7 | 47.1 | 83.7 | 23.6 | 203 | 9.1 | 8.57 | 4.3 |
| SD | 4.4 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 20 | 0.8 | 0.45 | 10.3 | |
| Low Water Level (<230.43 m) n = 30 | Mean | 225.0 | 14.7 | 52.6 | 83.8 | 22.5 | 252 | 8.0 | 8.17 | 19.9 |
| SD | 5.0 | 3.1 | 5.7 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 19 | 1.2 | 0.35 | 17.6 | |
| Significance (p-value) | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.969 | 0.203 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | |
| TP (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) | Trans-parency (m) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | NO3−-N (mg/L) | Chl-a (μg/L) | TOC (mg/L) | E. Coli. (CFU/100 mL) | Algae no. (cells) | ||
| High Water Level (>230.43 m) n = 121 | Mean | 0.018 | 5.5 | 1.7 | 0.050 | 0.258 | 4.68 | 0.885 | 245 | 6587 |
| SD | 0.009 | 15.0 | 0.6 | 0.061 | 0.125 | 2.62 | 0.486 | 664 | 5810 | |
| Low Water Level (<230.43 m) n = 30 | Mean | 0.022 | 25.2 | 0.8 | 0.078 | 0.258 | 4.99 | 0.643 | 262 | 2966 |
| SD | 0.013 | 23.6 | 0.5 | 0.093 | 0.097 | 3.30 | 0.176 | 303 | 2560 | |
| Significance (p-value) | 0.079 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.118 | 0.982 | 0.587 | 0.000 * | 0.890 | 0.011 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, W.; Chen, H.; Peng, M.; Chang, T. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality with Water Level Fluctuation in a Reservoir. Water 2023, 15, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173154
Liao W, Chen H, Peng M, Chang T. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality with Water Level Fluctuation in a Reservoir. Water. 2023; 15(17):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173154
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Wenwen, Hsinan Chen, Meijeng Peng, and Tawei Chang. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Variation of Trophic Status and Water Quality with Water Level Fluctuation in a Reservoir" Water 15, no. 17: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173154






