Removal of Disperse Yellow-42 Dye by Catalytic Ozonation Using Iron and Manganese-Loaded Zeolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sampling of Real Textile Dye Wastewater
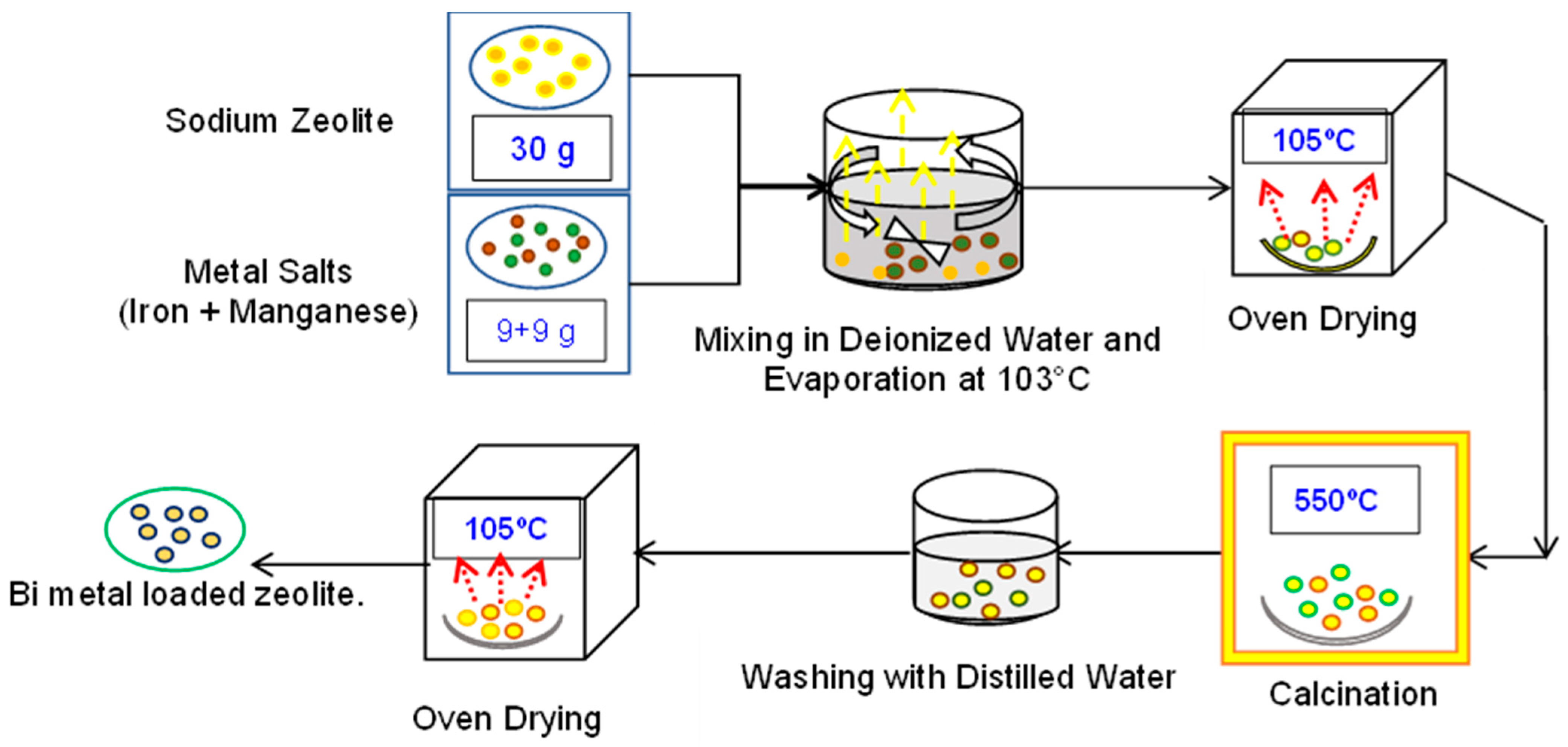
2.3. Preparation of Fe and Mn-Loaded Sodium Zeolite Catalyst
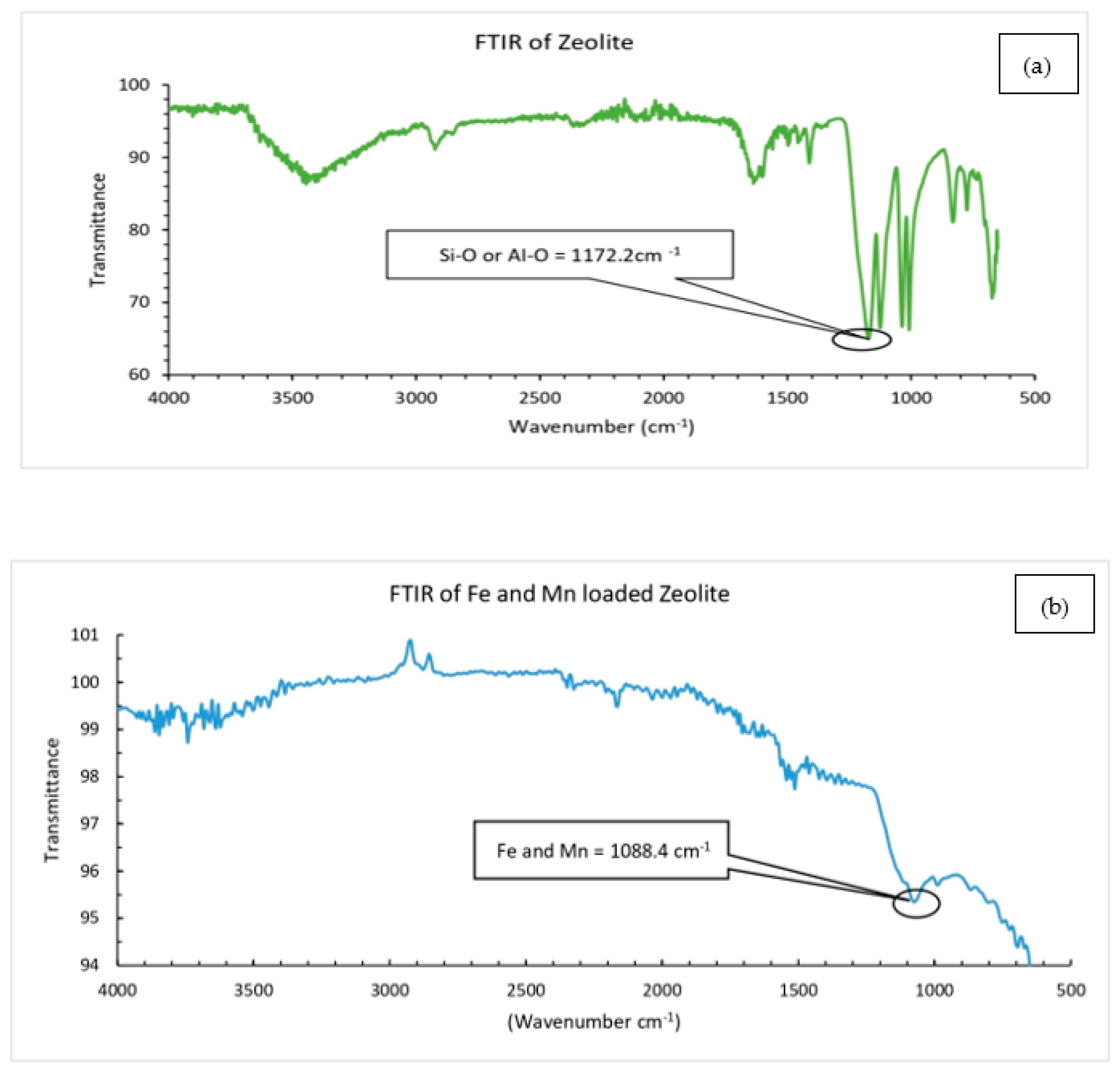
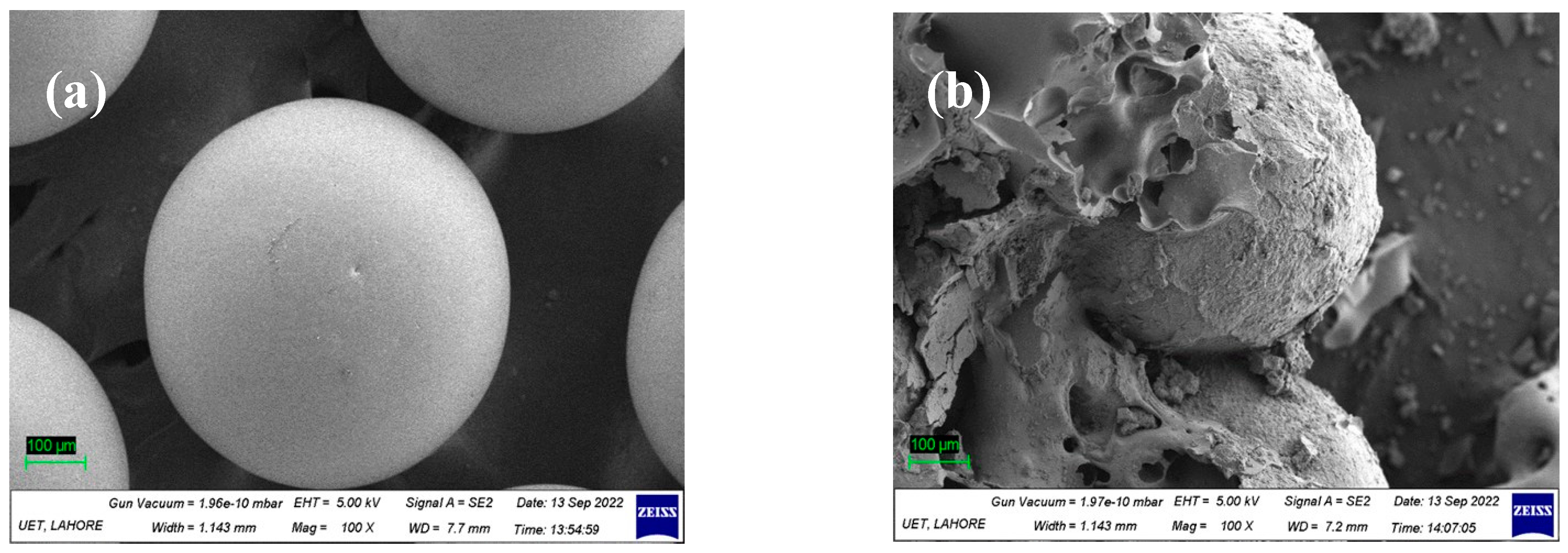
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Preparation of the Disperse Yellow 42 Dye Solution
2.6. Experimental Setup
2.7. Experimental Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Catalysts
3.2. Optimization of the Factors Affecting the Removal Efficiency
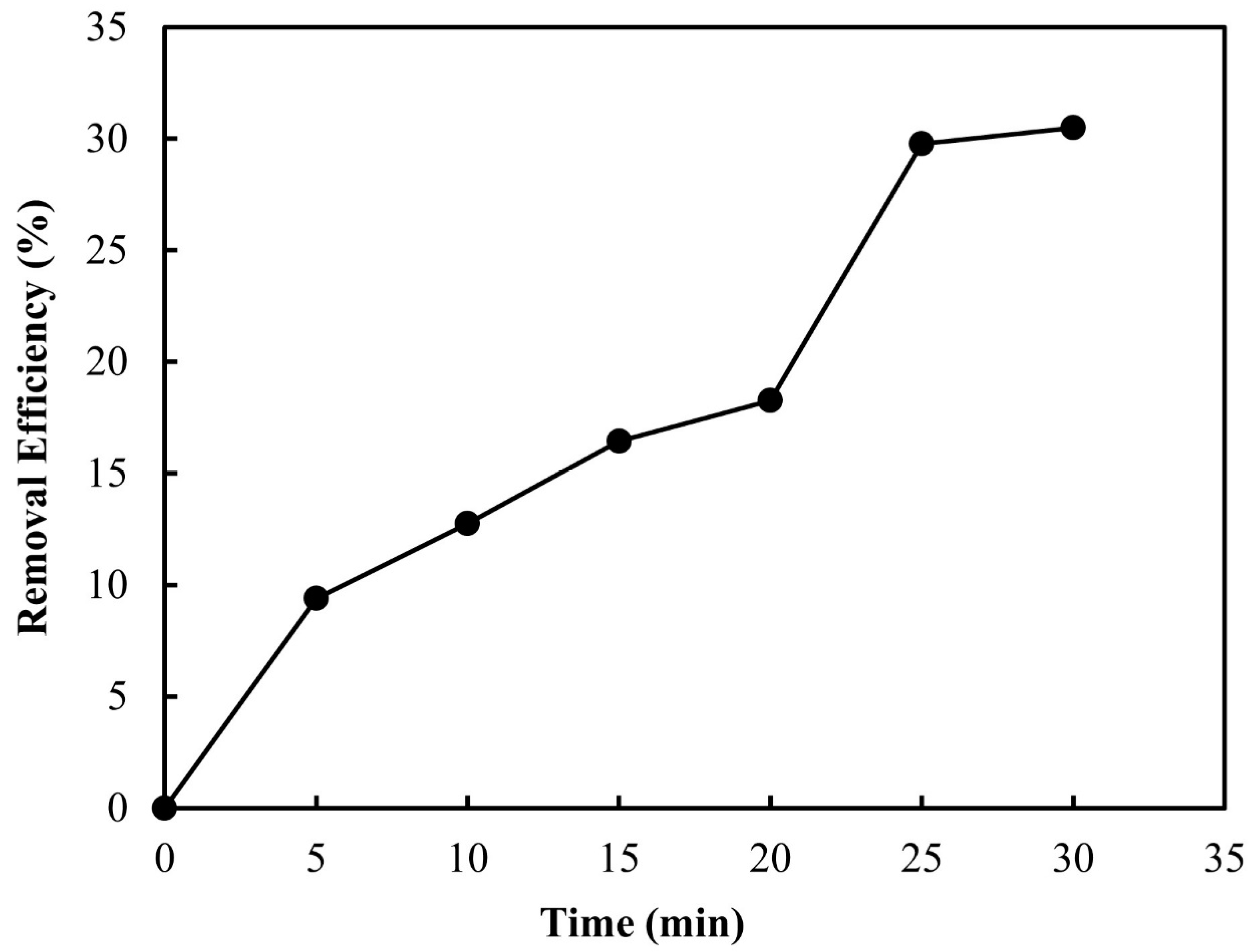
3.2.1. Ozone Contact Time
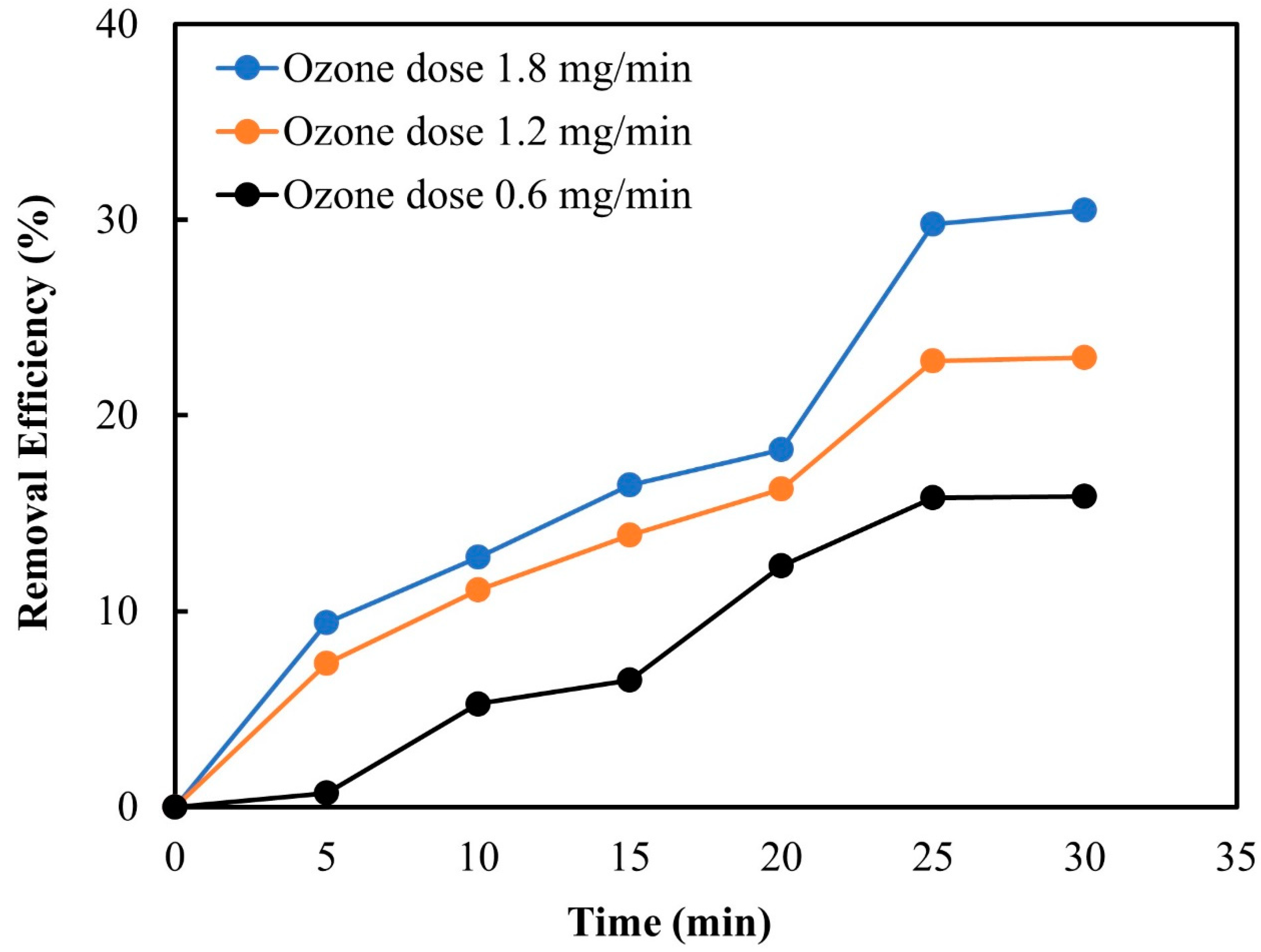
3.2.2. Ozone Dose
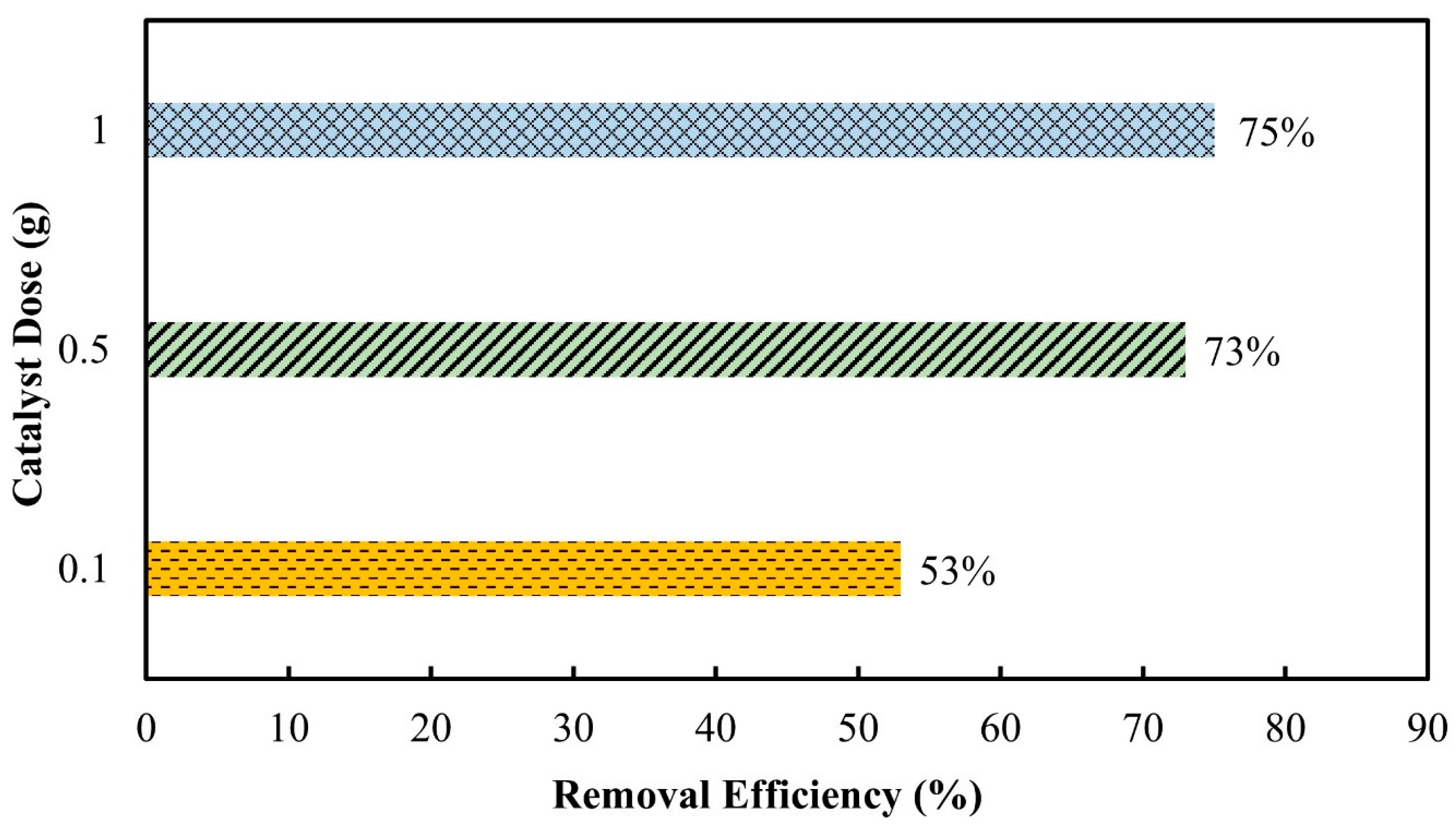
3.2.3. Catalyst Dose
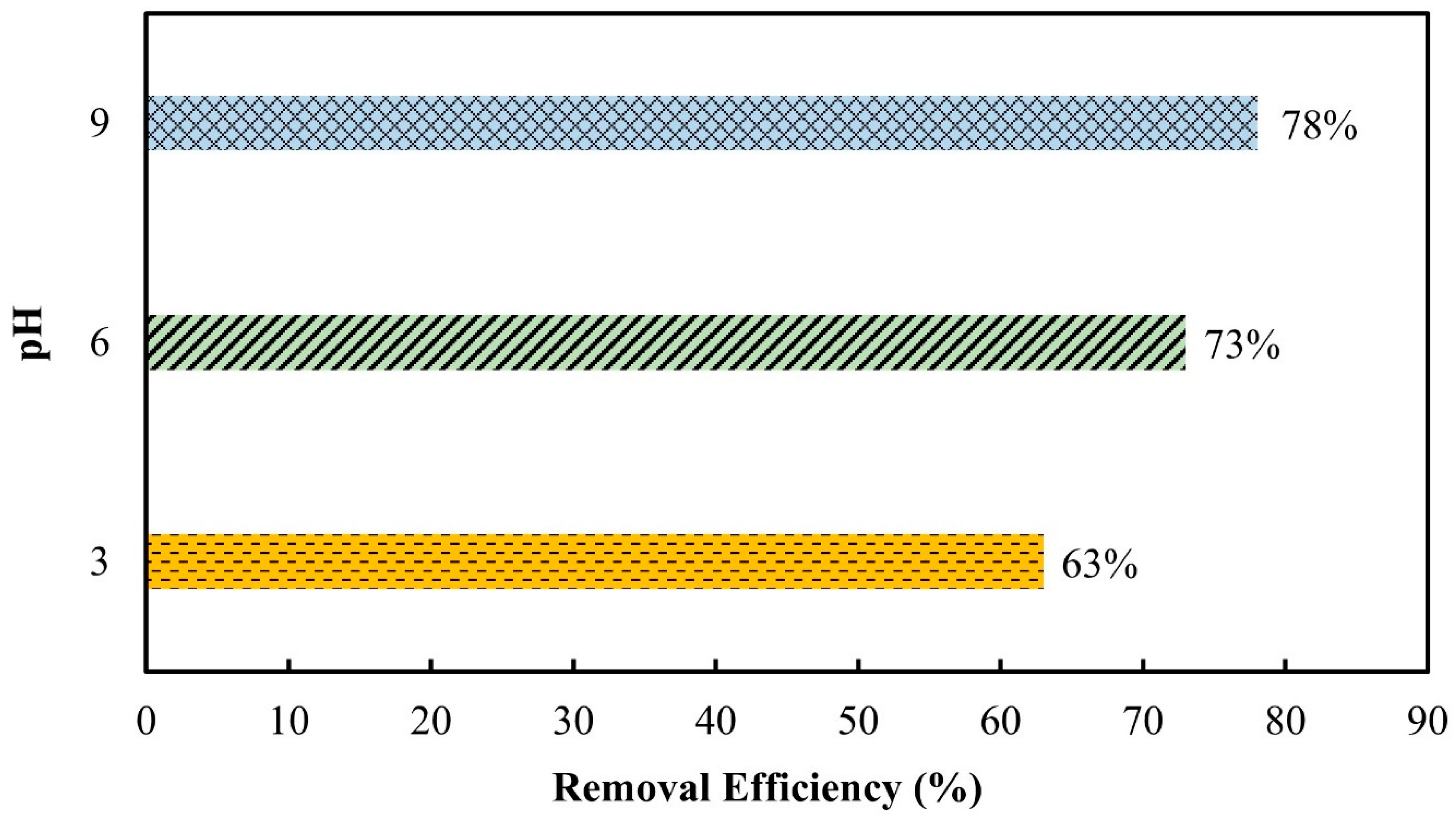
3.2.4. pH Effect
3.2.5. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenger Effect
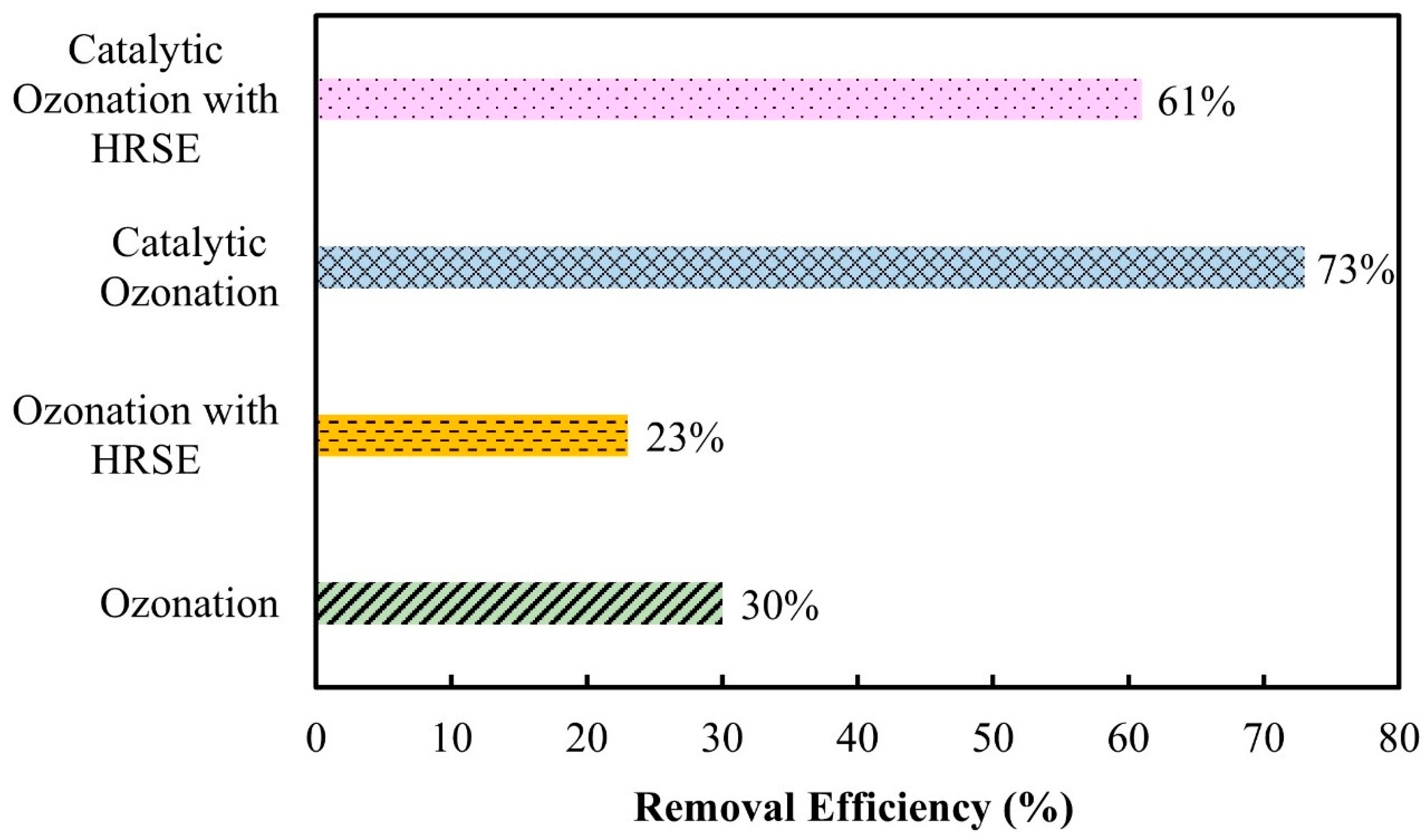
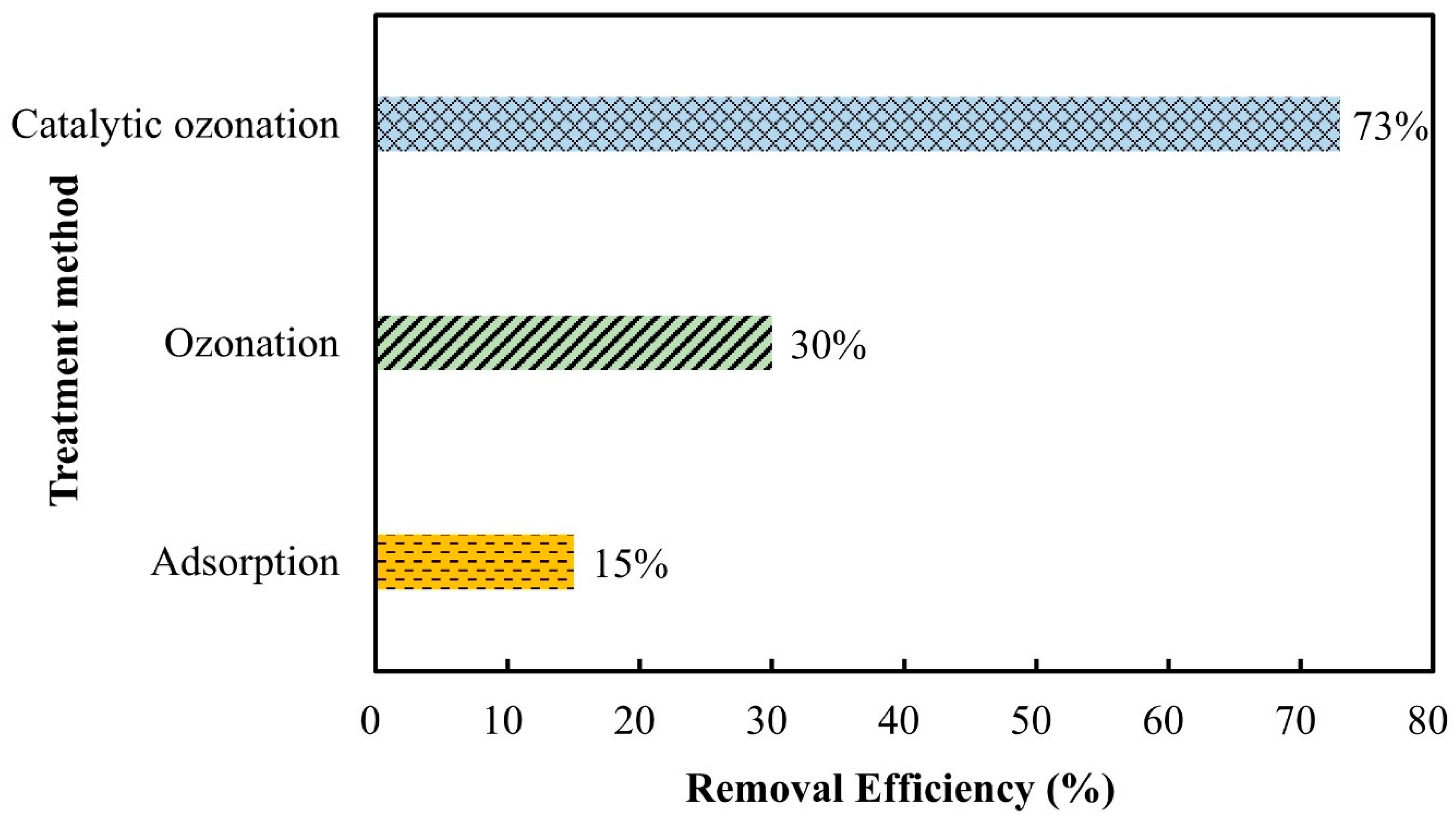
3.3. Comparison of Various Treatment Processes
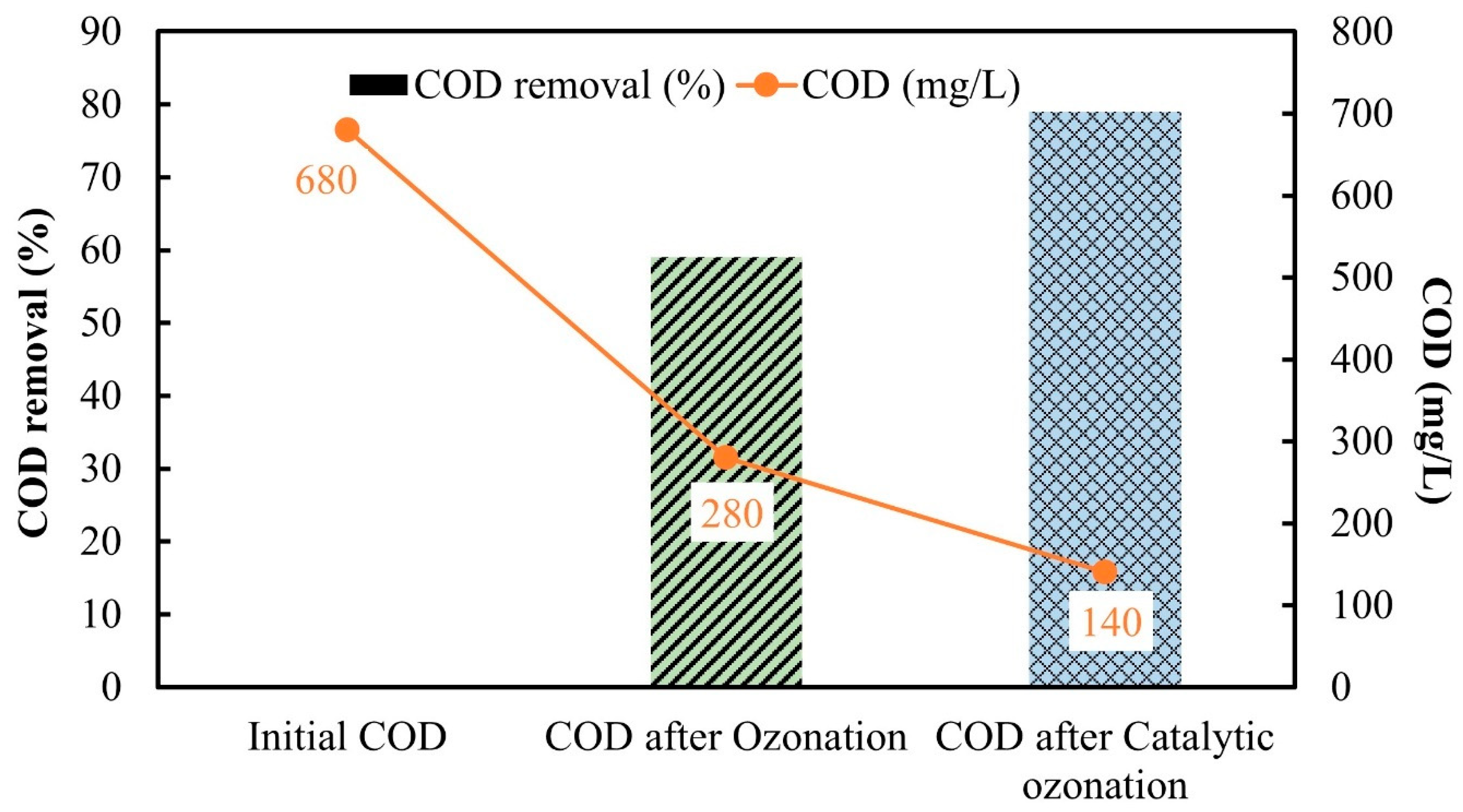
3.4. COD Removal of Real Textile Dye Wastewater
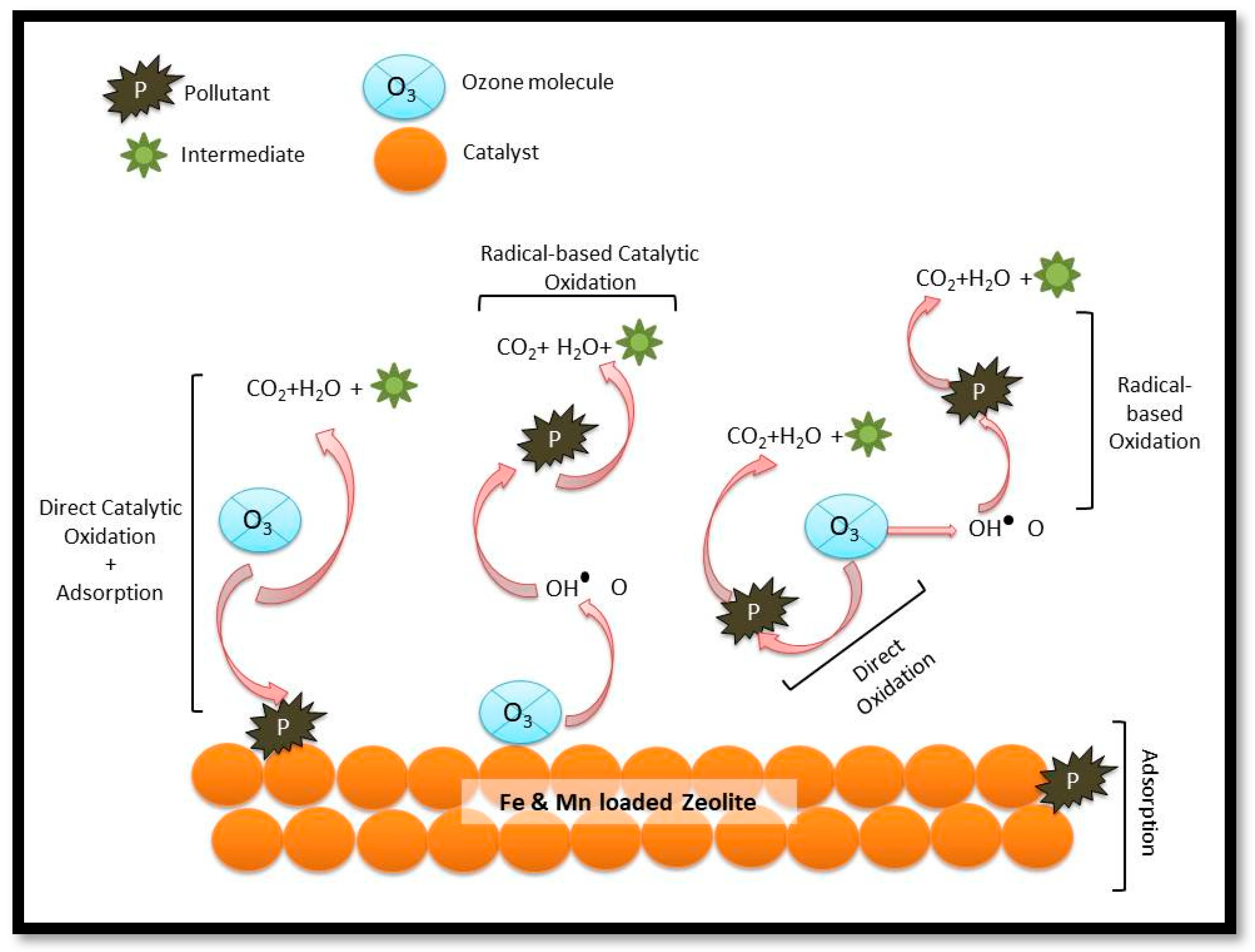
3.5. Proposed Mechanism
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayat, N.; Hussain, A.; Lohano, H.D. Eco-labeling and sustainability: A case of textile industry in Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlie, B.; Teshome, B.; Jemberie, M. Textile effluent treatment methods and eco-friendly resolution of textile wastewater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100230. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, O.S.; Ikhlaq, A.; Ashar, U.U.; Qazi, U.Y.; Akram, A.; Kalim, I.; Alazmi, A.; Shamsah, S.M.I.; Al-Sodani, K.A.A.; Javaid, R. Application of poly aluminum chloride and alum as catalyst in catalytic ozonation process after coagulation for the treatment of textile wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 115977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaideen, K.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Olabi, A.G. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldivar-Díaz, J.M.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Castillo-Suárez, L.A.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Solache Ríos, M.J.; Alcántara-Valladolid, A.E. Synergistic electrocoagulation–precipitation process using magnesium electrodes for denim wastewater treatment: Bifunctional support electrolyte effect. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berradi, M.; Hsissou, R.; Khudhair, M.; Assouag, M.; Cherkaoui, O.; El Bachiri, A.; El Harfi, A. Textile finishing dyes and their impact on aquatic environs. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, R.A.; Saleh, H.M.; Al-Hilifi, J.A.; Ahmed, L.M. Influence the addition of Fe2+ and H2O2 on removal and decolorization of textile dye (dispersive yellow 42 dye). Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Yaqub Qazi, U.; Ichiro Kawasaki, S. Highly efficient decomposition of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using tubular reactor coated with thin layer of PdO. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendaoui, K.; Trabelsi-Ayadi, M.; Ayari, F. Optimization and mechanisms analysis of indigo dye removal using continuous electrocoagulation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 29, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisuzzaman, S.M.; Joseph, C.G.; Pang, C.K.; Affandi, N.A.; Maruja, S.N.; Vijayan, V. Current Trends in the Utilization of Photolysis and Photocatalysis Treatment Processes for the Remediation of Dye Wastewater: A Short Review. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Krishnan, S.; Scaria, J.; Eghbali, P.; Nidheesh, P. Z-scheme photocatalysts for visible-light-driven pollutants degradation: A review on recent advancements. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 25, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; El Nemr, A. Advanced oxidation processes for textile wastewater treatment. Int. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Millbern, Z.; Trettin, A.; Wu, R.; Demmler, M.; Vinueza, N.R. Synthetic dyes: A mass spectrometry approach and applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Eghbali, P.; Metin, Ö. Sonocatalytic removal of methylene blue from water solution by cobalt ferrite/mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (CoFe2O4/mpg-C3N4) nanocomposites: Response surface methodology approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32140–32155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modirshahla, N.; Behnajady, M.A.; Rahbarfam, R.; Hassani, A. Effects of operational parameters on decolorization of CI Acid Red 88 by UV/H2O2 process: Evaluation of electrical energy consumption. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, P.; Şahin, E.; Masteri-Farahani, M. Immobilization of a molybdenum-glycine Schiff base complex within the nanocages of zeolite Y with flexible ligand method. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, L.F.; da Silva, G.R.; Peres, A.E.C. Zeolite application in wastewater treatment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4544104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, H.M.S.; Feroze, N.; Ramzan, N.; Sagir, M.; Babar, M.; Tahir, M.S.; Shamshad, J.; Mubashir, M.; Khoo, K.S. Fe-zeolite catalyst for ozonation of pulp and paper wastewater for sustainable water resources. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, Z. Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, A.; Hu, C.; Nie, Y.; Qu, J. Catalytic ozonation of toxic pollutants over magnetic cobalt-doped Fe3O4 suspensions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 117–118, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wu, Y. Catalytic ozonation of sulfosalicylic acid over manganese oxide supported on mesoporous ceria. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Zafar, M.; Javed, F.; Yasar, A.; Akram, A.; Shabbir, S.; Qi, F. Catalytic ozonation for the removal of reactive black 5 (RB-5) dye using zeolites modified with CuMn2O4/gC3N4 in a synergic electro flocculation-catalytic ozonation process. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Fiaz, U.; Rizvi, O.S.; Akram, A.; Qazi, U.Y.; Masood, Z.; Irfan, M.; Al-Sodani, K.A.A.; Kanwal, M.; Shamsah, S.M.I. Catalytic Ozonation Combined with Conventional Treatment Technologies for the Recycling of Automobile Service Station Wastewater. Water 2022, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Use of Cu(II)-incorporated zeolite Y for decolourization of dyes in water: A case study with aqueous methylene blue and Congo red. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zou, L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization and properties of iron oxide-coated zeolite as adsorbent for removal of copper(II) from solution in fixed bed column. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Abassi, M.; Ranjbar, M. A new nano-ZnO/perlite as an efficient catalyst for catalytic ozonation of azo dye. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 24, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, K.E.; Maris, T. Enhanced degradation of an azo dye by catalytic ozonation over Ni-containing layered double hydroxide nanocatalysts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.M.; Cardoso, I.M.; da Silva, L.P.; Esteves da Silva, J.C. Copper (II)-Doped Carbon Dots as Catalyst for Ozone Degradation of Textile Dyes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Demeestere, K.; Hulle, S.V. Comparison and performance assessment of ozone-based AOPs in view of trace organic contaminants abatement in water and wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Hussain, A.; Gilani, S.R.; Qazi, U.Y.; Akram, A.; Al-Sodani, K.A.A.; Javaid, R. Synergistically ozone and Fe-zeolite based catalytic purification of milk from heavy metals and pathogens. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W. The influence of some heavy metals cations on the FTIR spectra of zeolites. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 555, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Javed, F.; Akram, A.; Rehman, A.; Qi, F.; Javed, M.; Mehdi, M.J.; Waheed, F.; Naveed, S.; Aziz, H.A. Synergic catalytic ozonation and electroflocculation process for the treatment of veterinary pharmaceutical wastewater in a hybrid reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Munir, H.M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Ramzan, N.; Azhar, U.; Sagir, M.; Tahir, M.S.; Ikhlaq, A.; Mubashir, M.; Khoo, K.S. Comparative study of ozonation and ozonation catalyzed by Fe-loaded biochar as catalyst to remove methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dye | Disperse Yellow 42 |
|---|---|
| Molecular structure | 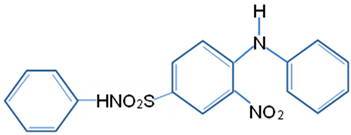 |
| Chemical formula | C18H15N3O4S |
| Chemical name | 4-anilino-3-nitro-N-phenyl benzene sulfonamide |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 369.40 |
| λmax (nm) | 488 |
| Material | Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cc/g) | Fe (%) | Mn (%) | PHpzc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium zeolite | 9.4 | 5.45 | 7.19 | - | - | 6.2 ± 0.2 |
| Multi-metal-loaded sodium zeolite | 39.6 | 5.96 | 12.45 | 0.66 | 0.45 | 6.1 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, Z.; Ikhlaq, A.; Qazi, U.Y.; Akram, A.; Ul-Hasan, I.; Alazmi, A.; Qi, F.; Javaid, R. Removal of Disperse Yellow-42 Dye by Catalytic Ozonation Using Iron and Manganese-Loaded Zeolites. Water 2023, 15, 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173097
Ali Z, Ikhlaq A, Qazi UY, Akram A, Ul-Hasan I, Alazmi A, Qi F, Javaid R. Removal of Disperse Yellow-42 Dye by Catalytic Ozonation Using Iron and Manganese-Loaded Zeolites. Water. 2023; 15(17):3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Zarafshan, Amir Ikhlaq, Umair Yaqub Qazi, Asia Akram, Iftikhar Ul-Hasan, Amira Alazmi, Fei Qi, and Rahat Javaid. 2023. "Removal of Disperse Yellow-42 Dye by Catalytic Ozonation Using Iron and Manganese-Loaded Zeolites" Water 15, no. 17: 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173097





