Evaluation of Biofloc-Based Probiotic Isolates on Growth Performance and Physiological Responses in Litopenaeus vannamei
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biofloc Production and Isolation of Probiotic Bacteria
2.2. Molecular Confirmation of Identified Probiotic Bacterial Isolates
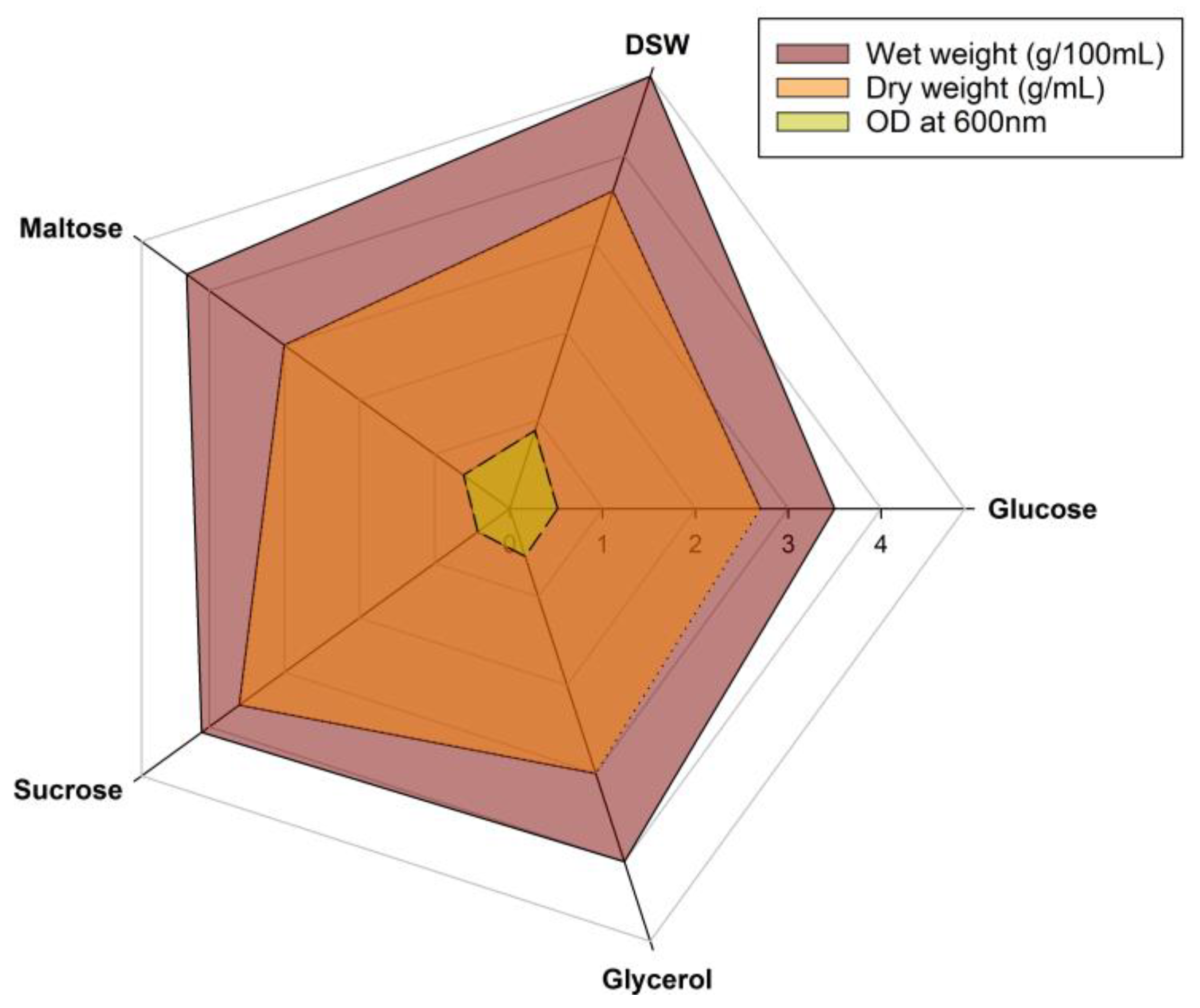
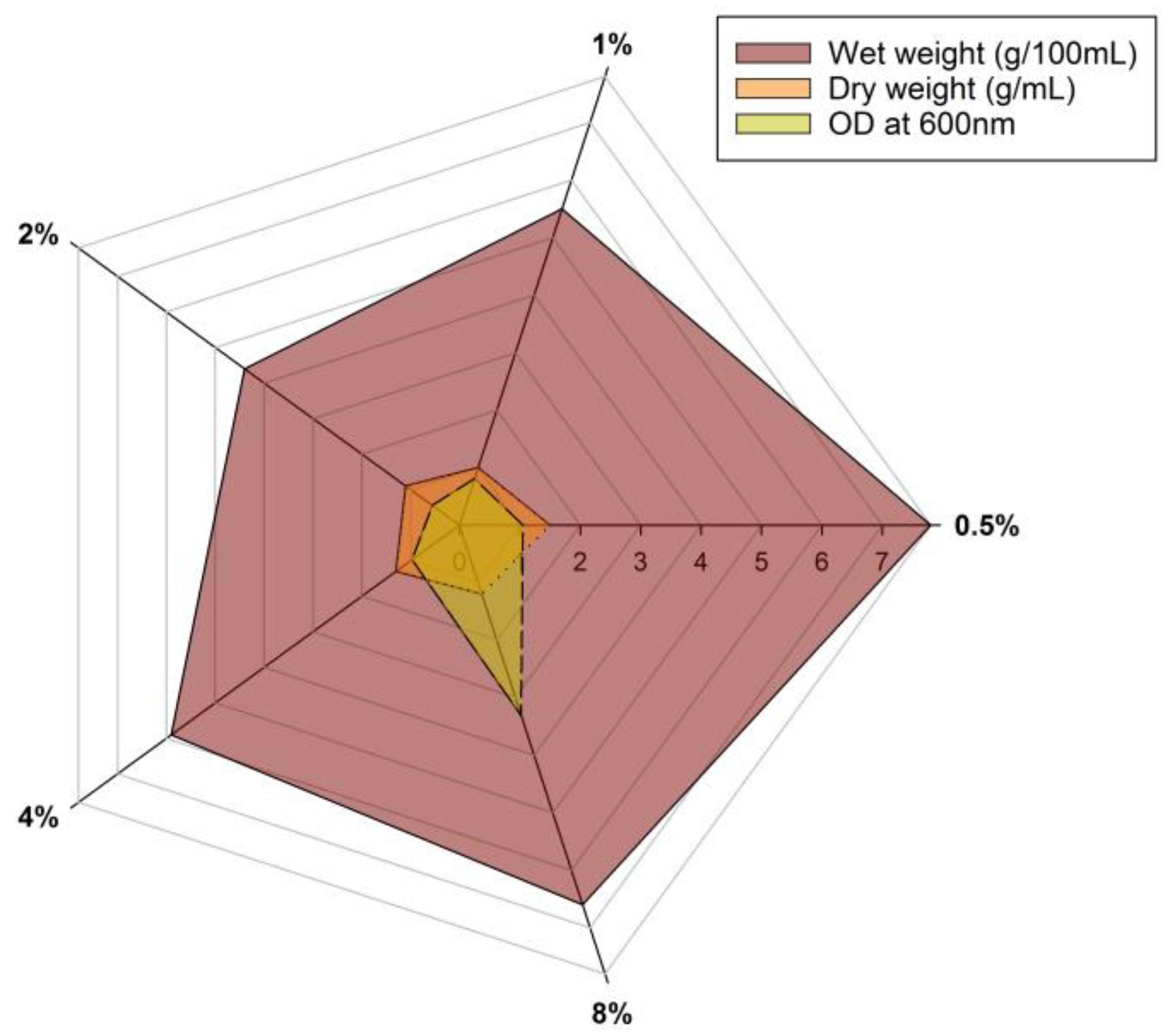
2.3. Medium Optimization
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Water Quality Parameters
2.6. Growth Parameters
2.6.1. Total Vibrio Count
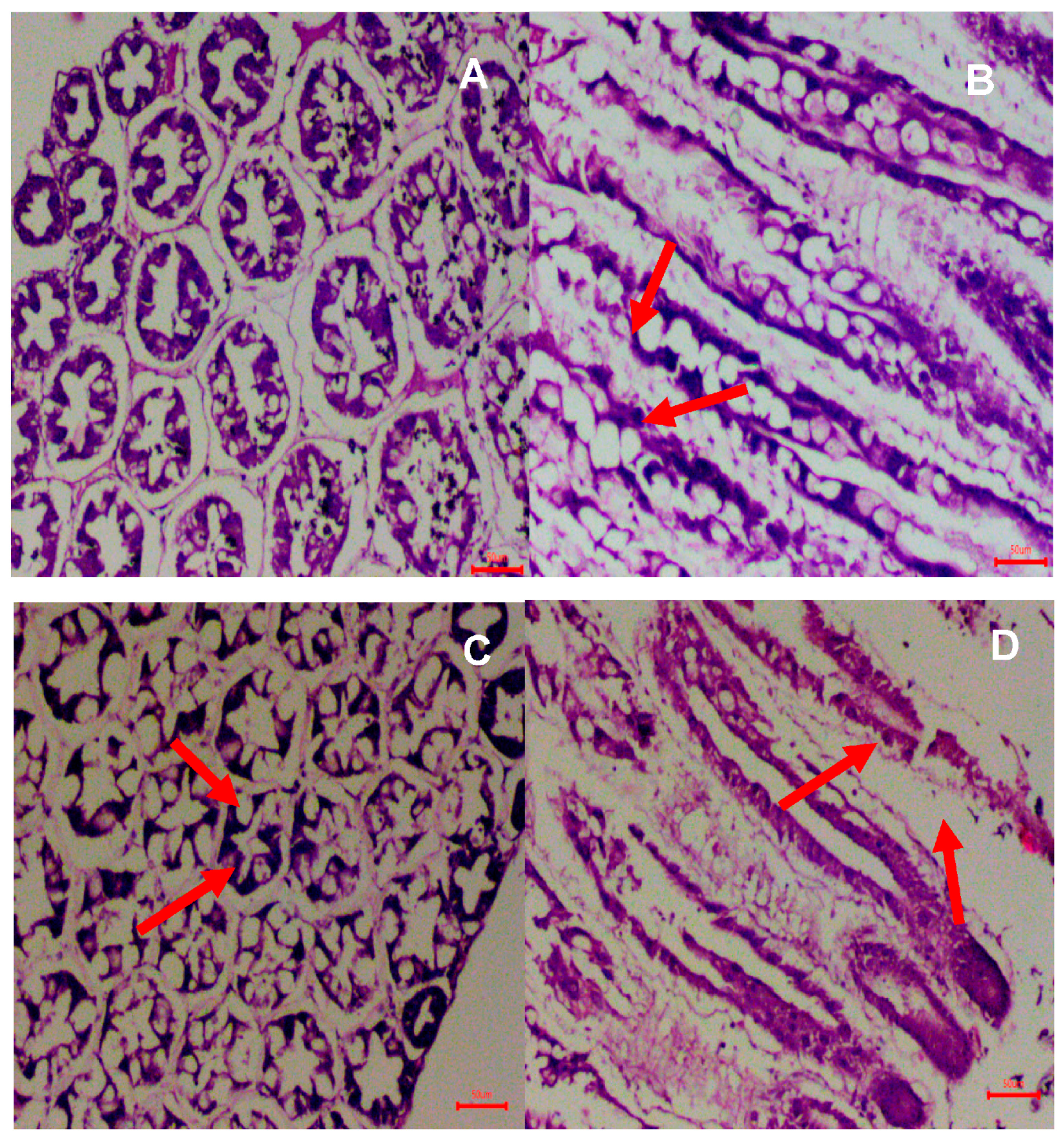
2.6.2. Histological Analysis
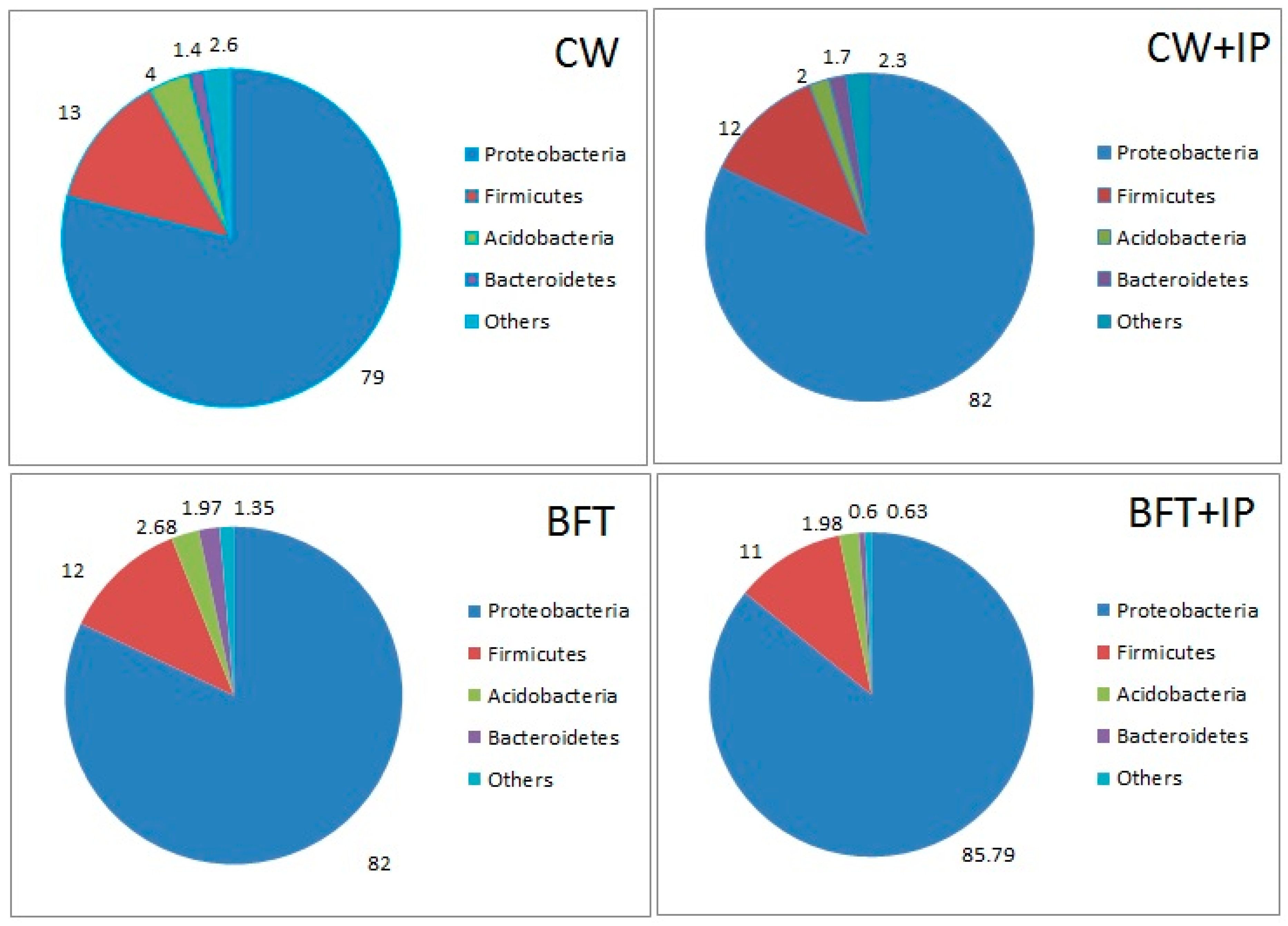
2.6.3. Shrimp Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.6.4. Statistical Analysis of Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Confirmation
3.2. Medium Optimization
3.3. Water Quality Parameters
3.3.1. Parameters of Water
3.3.2. Growth Parameters
3.3.3. Total Vibrio Count
3.4. Histological Analysis
3.5. Microbiome Content of Shrimp Gut
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, I.C.; Chien, Y.H. The pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in Asia: The world’s most widely cultured alien crustacean. In In the Wrong Place-Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 489–519. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guide Book; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lezama-Cervantes, C.; Paniagua-Michel, J. Effects of constructed microbial mats on water quality and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei post-larvae. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Boardman, G.D.; Lawrence, A.L.; Marsh, L.; Flick, G.J., Jr. Microbial floc meal as a replacement ingredient for fish meal and soybean protein in shrimp feed. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hai, N.; Fotedar, R. A review of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture. J. Appl. Aquac. 2010, 22, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Halet, D.; Vervaeren, H.; Boon, N.; Van de Wiele, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. The bacterial storage compound poly-β-hydroxybutyrate protects Artemia franciscana from pathogenic Vibrio campbellii. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatesoupe, F.J. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, D.J.W. Probiotics and bioremediation in aquaculture. Asian Shrimp News 1996, 26, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Utiswannakul, P.; Sangchai, S.; Rengpipat, S. Enhanced growth of black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon by dietary supplementation with Bacillus (BP11) as a probiotic. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zokaeifar, H.; Babaei, N.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Balcazar, J.L. Administration of Bacillus subtilis strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, growth performance, immune response, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K.; Xin, F.; Wang, B. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and the corresponding supernatant on the survival, growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interaminense, J.A.; Vogeley, J.L.; Gouveia, C.K.; Portela, R.W.; Oliveira, J.P.; Andrade, H.A.; Peixoto, S.M.; Soares, R.B.; Buarque, D.S.; Bezerra, R.S. In vitro and in vivo potential probiotic activity of Bacillus subtilis and Shewanella algae for use in Litopenaeus vannamei rearing. Aquaculture 2018, 488, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yuan, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Li, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Y. In vitro screening of putative probiotics and their dual beneficial effects: To white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae and to the rearing water. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepaamorndech, S.; Chantarasakha, K.; Kingcha, Y.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Phromson, M.; Sriariyanun, M.; Kirschke, C.P.; Huang, L.; Visessanguan, W. Effects of Bacillus aryabhattai TBRC8450 on vibriosis resistance and immune enhancement in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, M.S.; Butler, R.N.; Howarth, G.S. Inflammatory bowel disease: Current insights into pathogenesis and new therapeutic options; probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, O.N.; Nilmini, S.L.I.; Stolic, P.; Vasiljevic, T.; Shah, N.P. Survival and activity of selected probiotic organisms in set-type yoghurt during cold storage. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninawe, A.S.; Selvin, J. Probiotics in shrimp aquaculture: Avenues and challenges. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauville, M.R.; Zambonino-Infante, J.L.; Gordon Bell, J.; Migaud, H.; Main, K.L. Effects of a mix of Bacillus sp. as a potential probiotic for Florida pompano, common snook and red drum larvae performances and digestive enzyme activities. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decamp, O.; Moriarty, D.J.; Lavens, P. Probiotics for shrimp larviculture: Review of field data from Asia and Latin America. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taw, N. Intensive Shrimp Farming Systems in Asia: Commercial Implementation of Biosecure and Biofloc Production Systems to Help Control Shrimp Farming Diseases; SPS Publishers: Hyderabad, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, R.; Chen, W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, K. Effects of feeding level and C/N ratio on water quality, growth performance, immune and antioxidant status of Litopenaeus vannamei in zero–water exchange bioflocs-based outdoor soil culture ponds. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 101, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, R.H.; Buchanan, R.E.; Gibbons, N.E. Genus II aeromonas. In Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 8th ed.; Buchanan, R.E., Gibbons, N.E., Eds.; Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1974; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Kesselring, J.C.; Gruber, C.; Standen, B.; Wein, S. Continuous and pulse-feeding application of multispecies probiotic bacteria in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Bae, J.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of Potential Probiotics Bacillus subtilis WB60, Pediococcus pentosaceus, and Lactococcus lactis on Growth Performance, Immune Response, Gut Histology and Immune-Related Genes in Whiteleg Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, U.; Rogall, T.; Blöcker, H.; Emde, M.; Böttger, E.C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 7, 7843–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, H.; Moh, J.H.Z.; Kasan, N.A.; Suratman, S.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Identification of biofloc microscopic composition as the natural bioremediation in zero water exchange of Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, culture in closed hatchery system. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fuentes, J.A.; Pérez-Rostro, C.I.; Hernández-Vergara, M.P.; Monroy-Dosta, M.D.C. Variation of the bacterial composition of biofloc and the intestine of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus, cultivated using biofloc technology, supplied different feed rations. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Cruz, P.; Ibáñez, A.L.; Monroy Hermosillo, O.A.; Ramírez Saad, H.C. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. Int. Sch. Res. Netw. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 916845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Esakkiraj, P.; Jayashree, S.; Saranya, C.; Das, R.R.; Sundaram, M. Colonization of enzymatic bacterial flora in biofloc grown shrimp Penaeus vannamei and evaluation of their beneficial effect. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Suresh, P.V. Biodegradation of shrimp biowaste by marine Exiguobacterium sp. CFR26M and concomitant production of extracellular protease and antioxidant materials: Production and process optimization by response surface methodology. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Saranya, C.; Sundaram, M.; Kannan, S.V.; Das, R.R.; Kumar, R.S.; Rajesh, P.; Otta, S.K. Carbon: Nitrogen (C: N) ratio level variation influences microbial community of the system and growth as well as immunity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in biofloc based culture system. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 81, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniasari, D.; Ekasari, J. Nursery culture performance of Litopenaeus vannamei with probiotics addition and different C/N Ratio under laboratory condition. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2010, 17, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Krummenauer, D.; Peixoto, S.; Cavalli, R.O.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Superintensive culture of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in a biofloc technology system in southern Brazil at different stocking densities. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Welsh, C.F.; Rishel, K.L. Performance evaluation of the Hydrotech belt filter using coagulation/flocculation aids (alum/polymers) for the removal of suspended solids and phosphorus from intensive recirculating aquaculture microscreen backwash effluent. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 35, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Practical aspects of chemistry in pond aquaculture. Progress. Fish-Cult. 1997, 59, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Rivera, D.; Prieto-Davó, A.; Escalante, K.; Chávez, C.; Cuzon, G.; Gaxiola, G. Probiotic effect of FLOC on Vibrios in the pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2014, 424, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, M.; Panigrahi, A.; Ganesh, J.; Rekha, P.N.; Sivagnanam, S.; Rajamanickam, S.; Gopal, C. Evaluation of Different Probiotic Strains for Growth Performance and Immunomodulation in Pacific White Shrimp Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931. Indian J. Fish. 2017, 64, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.H.; Song, X.L.; Yang, C.H.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, G.C. The application of bioflocs technology in high-intensive, zero exchange farming systems of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture 2012, 354, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, M.R.; Goncalves, A.N.; Vieira, F.N.; Seifert, W.Q.; Bachère, E.; Rosa, R.D.; Perazzolo, L.M. Exploring the impact of the biofloc rearing system and an oral WSSV challenge on the intestinal bacteriome of Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Jiang, K.; Qi, C.; Wang, L. Bacterial population in intestines of Litopenaeus vannamei fed different probiotics or probiotic supernatant. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Albores, F.; Porchas-Cornejo, M.A.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Villalpando-Canchola, E.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R. Bacterial biota of shrimp intestine is significantly modified by the use of a probiotic mixture: A high throughput sequencing approach. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liao, S.A.; Wang, A.L. The effect of different carbon sources on the nutritional composition, microbial community and structure of bioflocs. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöbken, D. Diversity and Ecology of Marine Planctomycetes. Doctoral Dissertation, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tzuc, J.T.; Escalante, D.R.; Herrera, R.R.; Cortés, G.G.; Ortiz, M.L.A. Microbiota from Litopenaeus vannamei: Digestive tract microbial community of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | CW | CW + IP | BFT | BFT + IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.41 ± 0.93 a (6.85–8.34) | 7.76 ± 0.76 b (7.00–8.52) | 7.82 ± 0.69 c (6.46–8.51) | 7.50 ± 1.25 d (6.72–8.75) |
| Temperature (°C) | 30 ± 0.5 (29.9–30.3) | 30 ± 0.5 (29.9–30.5) | 30 ± 0.5 (29.9–30.1) | 30 ± 0.5 (29.9–30.3) |
| Alkalinity(mg/L) | 110 ± 5 a (80–118) | 143 ± 7 b (80–152) | 135 ± 9 c (84–176) | 105 ± 13 d (76–110) |
| Nitrite (NO2-N) (mg/L) | 0.052 ± 0.017 (0.011–0.069) | 0.02 ± 0.015 a (0.001–0.037) | 0.028 ± 0.005 (0.002–0.045) | 0.042 ± 0.015 b (0.004–0.062) |
| Ammonia (NH3-N) (mg/L) | 0.047 ± 0.017 (0.011–0.069) | 0.052 ± 0.005 (0.001–0.065) | 0.049 ± 0.005 (0.002–0.055) | 0.050 ± 0.01 (0.004–0.062) |
| DO (mg/L) | 4.91 ± 0.51 (4.10–5.64) | 4.77 ± 0.27 a (4.32–5.43) | 4.87 ± 0.83 b (4.56–5.32) | 4.7 ± 0.8 c (4.33–5.21) |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 360 ± 4 a (220–420) | 196 ± 13 b (156–252) | 190 ± 11 c (140–264) | 181 ± 20 d (140–236) |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 40 ± 23 a (21.6–62.4) | 48 ± 14 b (24–67.8) | 38.7 ± 11 c (21.6–60) | 35.2 ± 11 d (24–55.2) |
| Treatment | Final Weight (g) | Weight Gain (g) | SGR * | FCR ** | PER *** | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | 1.03 ± 0.005 a | 0.98 ± 0.004 a | 5.21 ± 0.015 a | 2.55 ± 0.05 a | 1.3 ± 0.05 | 92 a |
| CW + IP | 1.7 ± 0.007 a | 1.65 ± 0.002 | 6.05 ± 0.012 | 1.51 ± 0.015 | 2.2 ± 0.02 a | 95 b |
| BFT | 2.25 ± 0.015 b | 2.20 ± 0.006 b | 6.52 ± 0.012 b | 1.13 ± 0.01 b | 2.9 ± 0.01 b | 95 |
| BFT + IP | 2.47 ± 0.003 c | 2.43 ± 0.005 c | 6.67 ± 0.004 c | 1.02 ± 0.012 c | 3.24 ± 0.02 c | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menaga, M.; Rajasulochana, P.; Felix, S.; Sudarshan, S.; Kapoor, A.; Gandla, K.; Saleh, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.E.; El Deeb, S. Evaluation of Biofloc-Based Probiotic Isolates on Growth Performance and Physiological Responses in Litopenaeus vannamei. Water 2023, 15, 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163010
Menaga M, Rajasulochana P, Felix S, Sudarshan S, Kapoor A, Gandla K, Saleh MM, Ibrahim AE, El Deeb S. Evaluation of Biofloc-Based Probiotic Isolates on Growth Performance and Physiological Responses in Litopenaeus vannamei. Water. 2023; 15(16):3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenaga, Meenakshisundaram, Perepi Rajasulochana, Sugantham Felix, Shanmugam Sudarshan, Ashish Kapoor, Kumaraswamy Gandla, Moustafa M. Saleh, Adel Ehab Ibrahim, and Sami El Deeb. 2023. "Evaluation of Biofloc-Based Probiotic Isolates on Growth Performance and Physiological Responses in Litopenaeus vannamei" Water 15, no. 16: 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163010






