Analysis of Water Chemistry Characteristics and Main Ion Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Nagqu Area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in Summer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Sample Collection, Testing, and Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Sample Testing
2.2.3. Classification of Lake Water Chemistry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lake Water Chemistry Characteristics
3.1.1. Physicochemical Analysis of Lakes
3.1.2. Nutrient Levels of Lake Water
3.2. Lake Water Chemical Types
3.3. Lake Water Chemistry Characteristics and Types
3.3.1. Gibbs Diagram
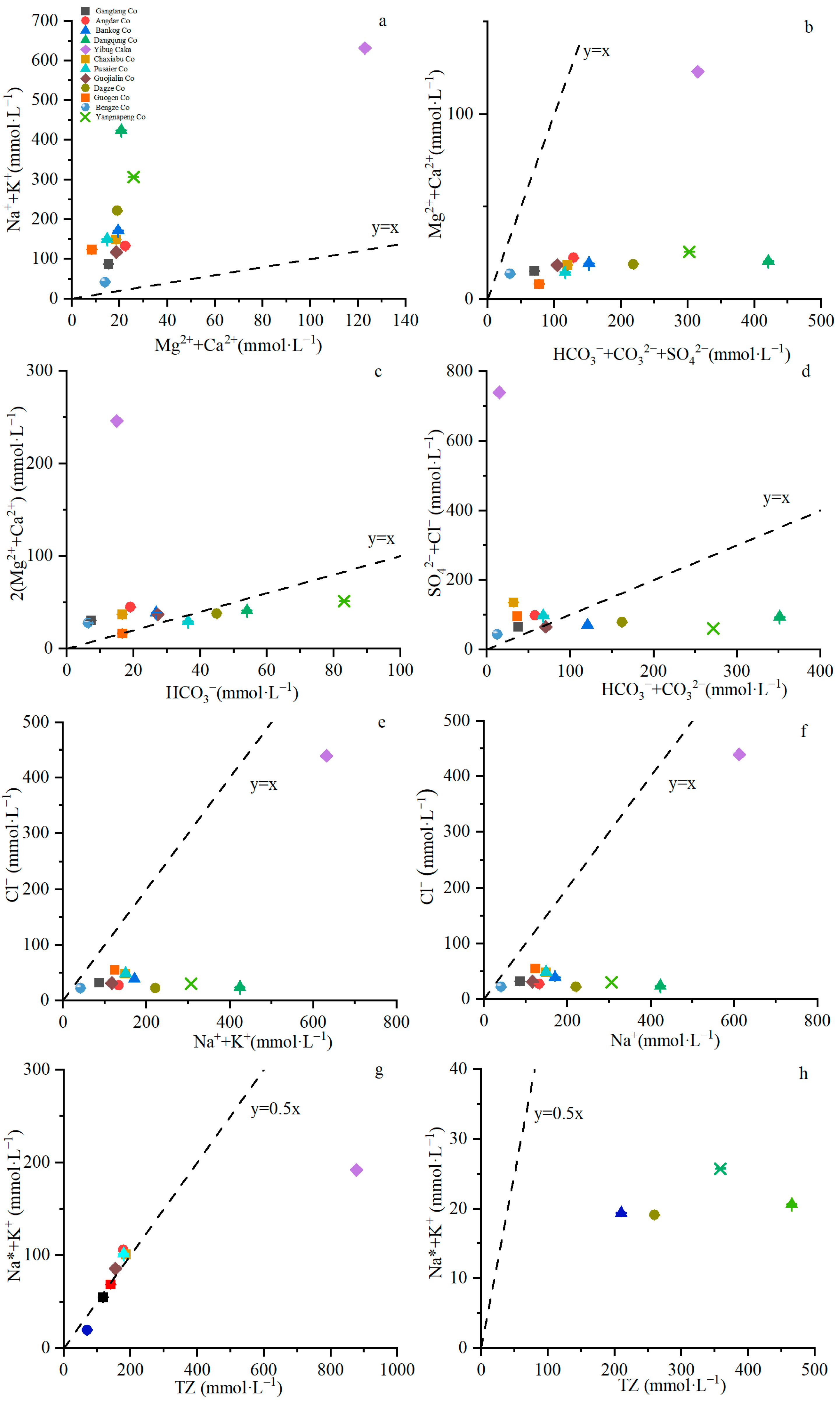
3.3.2. Correlation Analysis Studies
3.3.3. Main Sources of Ions in the Lakes
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The pH values of all 12 lakes were above 8.00, indicating they were alkaline environments. The lakes had high levels of hardness, alkalinity, and mineralization, and most were salt lakes. According to the surface water environmental quality standards, all 12 lakes had class V water.
- (2)
- The cations in the 12 lakes were mainly Na+, and the anions were mainly HCO3− + CO32−. Gangtang Co, Angdar Co, Yibug Caka, Pusaier Co, Bengze Co, Chaxibu Co, and Guogen Co were in the later stages of lake succession, while Bankog Co, Dangqung Co, Guojialin Co, Dagze Co, and Yangnapeng Co were in the initial stage of lake succession.
- (3)
- The hydrochemical composition of the 12 lakes was controlled by evaporation–crystallization. The ions in the lakes may have similar sources, with most coming from the erosion of evaporite and carbonate rocks.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.-Q.; Pan, B.-Z.; Han, X.; Li, G.; Wang, T.-Y. Water Environmental Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Lakes in Tibetan Plateau. In Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022; Volume 43, pp. 5073–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Niu, Z. Characteristics of changes in lake temperature in China and their response to climate change. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zheng, M.; Wei, L. Change of the lakes in Tibetan Plateau and its response to climate in the past forty years. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 310–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Yu, L.; Cai, G.; An, M.; Xia, P. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Water Quality in Caohai Lake. J. Hydroecol. 2016, 37, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X. Lake environmental changes in response to acid deposition in Southwest China over the last century: Evidence from sedimentary diatoms in Lake Longtan of the Simian Mountains. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Zou, W.; Guo, C.; Ji, P.; Da, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Changing characteristics and driving factors of trophic state of lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River in the past 30 years. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Shi, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, R.; Qian, X.; Jiang, Y. Organic pollutants and ambient severity for the drinking water source of western Taihu Lake. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, J.-L.; Cheng, F.; Deng, H.; Zhang, E.-W.; Li, Y.-X. Monitoring and evaluation of eco-environmental quality of lake basin regions in Central Yunnan Province, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.-C.; Qu, J.-J.; Liao, K.-T.; Niu, Q.-H.; Han, Q.-J. Damage by wind-blown sand and its control along Qinghai-Tibet Railway in China. Aeolian Res. 2010, 1, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zeng, Y.; Lubczynski, M.W.; Roy, J.; Yu, L.; Qian, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Han, L.; Zheng, H.; et al. A first investigation of hydrogeology and hydrogeophysics of the Maqu catchment in the Yellow River source region. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4727–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kang, S.; Liu, Y.; Hou, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, Q. Distribution of major ions in waters and their response to regional climatic change in Tibetan lakes. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 743–754. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, S. Passive microwave remote sensing of lake freeze-thawing over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L. The Influence of Climate Change on Lake Variations of the Tibet Plateau in the Period of 1973–2017. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 493–503. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Zhu, P.; De, J.; Guo, X. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Zheng, M. Bio-ecological resources of saline lakes in Tibet and their economic prospect. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J.; Lai, X.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Lake hydrology in China: Advances and prospects. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1360–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Duan, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S. Influences of climate change on area variation of Qinghai Lake on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since 1980s. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, W.; Zhao, L.; Xie, H.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hong, Y. Lake Surface Water Temperature Change Over the Tibetan Plateau From 2001 to 2015: A Sensitive Indicator of the Warming Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11177–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: Trends, patterns, and mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Bird, B.W.; Zhang, G.; Tian, L. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.J.; Zheng, M.P. Influence of climate change on saline lakes of the Tibet Plateau, 1973–2010. Geomorphology 2015, 246, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, C.; Wang, G.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F. Chemical characteristics and impact factors of the Drem-tso Lake and supplying runoff in the Southern Tibet. Arid. Land Geogr. 2017, 40, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.-M.; Kang, S.-C.; Zhang, Q.-G.; Huang, J.; Wang, K. Temporal and spatial variations of major ions in Nam Co Lake water, Tibetan Plateau. In Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing kexue; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012; Volume 33, pp. 2295–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Jiang, L. Spatial-temporal patterns of major ion chemistry and its controlling factors in the Manasarovar Basin, Tibet. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.M.; Yuan, X.Y.; Ge, M.; Li, J.; Sun, H. Water chemistry characteristics and controlling factors in the northern rivers in the Taihu Basin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Yang, H.; Guo, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Major Ion Sources of Lake Caohai in Guizhou Province. Earth Environ. 2021, 49, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Shi, X.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wu, Y. Hydrochemical properties and controlling factors of the Dali Lake and its inflow river water in Inner Mongolia. Environ. Chem. 2016, 35, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, C.; Zha, X.; Gao, X.; Yu, M. Hydrochemical characteristics and factors controlling of natural water in the western, southern, and northeastern border areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 975–991. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Sun, M.; Yao, X.; Gong, N.; Li, X.; Qi, M. Lake water in the Tibet Plateau: Quality change and current status evaluation. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 900–910. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Yu, F.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Shang, F.; Xie, M. The research of climate change of past 2000 years based on isotopes of sediment ostracods shells in serlin co, Tibet. Quat. Sci. 2023, 43, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of hillslope runoff generation and its controlling factors on an alpine grassland in the Silin Co basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 2388–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W. Exploring the water storage changes in the largest lake (Selin Co) over the Tibetan Plateau during 2003–2012 from a basin-wide hydrological modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8060–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Qiu, R.; Li, J. Analysis of the water color transitional change in Qinghai Lake during the past 35 years observed from Landsat and MODIS. J. Hydrol. -Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Characteristics Analysis of Temperature and Precipitation in Qinghai Lake Basin. J. China Hydrol. 2022, 42, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Xiong, X.; Ao, H.; Hu, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ma, R.; Wu, C. Differences in water environment characteristics between the newly lakeshore zone and the main lake area of qinghai lake. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Niu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Yan, D.; Xiao, S. Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of the upper Yarlung Zangbo River in summer. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 815–825. [Google Scholar]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Y. Climate change over the yarlung zangbo river basin during 1961–2005. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dou, H. China Lakes Record; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 431, 457, 467. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Li, B. China Salt Lake Chronicle; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 47–51, 53, 69–71, 75–76, 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bianduo; Bianbaciren; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Zhaxiyangzong. The response of lake change to climate fluctuation in north Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in last 30 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T. Changes in Glacial Lakes in Naqu from 1990 to 2020. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 58, 936–944. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y. Experiments in the Chemistry of Aquaculture Water Environments; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 2–4, 9–11, 15–25, 70–72, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, R.; Zhu, L. Lake Water in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin in South Tibetan Region: Quality and Evaluation. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2012, 34, 950–958. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Du, Q.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. The impact of well drawdowns on the mixing process of river water and groundwater and water quality in a riverside well field, Northeast China. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Lin, T.; Ma, J. Major Ion Chemistry and Influencing Factors of Three Typical Lakes in Inner Mongolia Plateau. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Bai, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Chadwick, D.; Strokal, M.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Challenges and strategies for agricultural green development in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2021, 18, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; She, D.; Ge, J.; Shan, J.; Pan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hong, Y. Impact on denitrification potential and threshold of ditches sediment with exogenous carbon and nitrogen addition: A case of ditches in Ningxia Yellow River Irrigation area. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 5856–5863. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. GHZB-2002. 2002. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgth/200910/W020090724340379457140.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2002).
- Zhou, N.; Xu, X.; Yuan, Z. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations Trends and the Effects of Human Activities in China’s 14 Typical Lakes During 2010 and 2018. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Study on Eutrophication and Change of Nutrients in the Daya Bay. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2002, 21, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Lu, J. Distribution characteristic of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Poyang during high water period. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Neurochem. Int. 1984, 6, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A.C.; Soler, J.M.; Ganor, J.; Burch, T.E.; Nagy, K.L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2361–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yao, X.; Gao, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhang, C. Hydrochemistry characteristics of major ions in Lake Qinghai during the freeze-up period and controlling factors. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Major ion chemistry of water and its controlling factors in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 600–608. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.F. Global Environment: Water, Air, and Geochemical Cycles; Berner, E.K., Berner, R.A., Eds.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; 376p, ISBN 0-13-301169-0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Miao, W.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Tang, Q.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Zhao, X. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Salt-Formation Elements Sources of Li-Rich Brines in Kushui Lake, West Kunlun. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 4161–4174. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao-hua, H.O.U.; Hai, X.U.; Zhi-sheng, A.N. Major Ion Chemistry of Waters in Lake Qinghai Catchment and the Possible Controls. Earth Environ. 2009, 37, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.B.; Zhu, L.P.; Ju, J.T.; Wang, Y. Water Chemistry of Eastern Nam Lake Area and Inflowing Rivers in Tibet. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2009, 29, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.-M.; An, Y.-L.; Wu, Q.-X.; Luo, J.; Jiang, H. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Sources of Qingshuijiang River Basin at Wet Season in Guizhou Province. In Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 36, pp. 1565–1572. [Google Scholar]
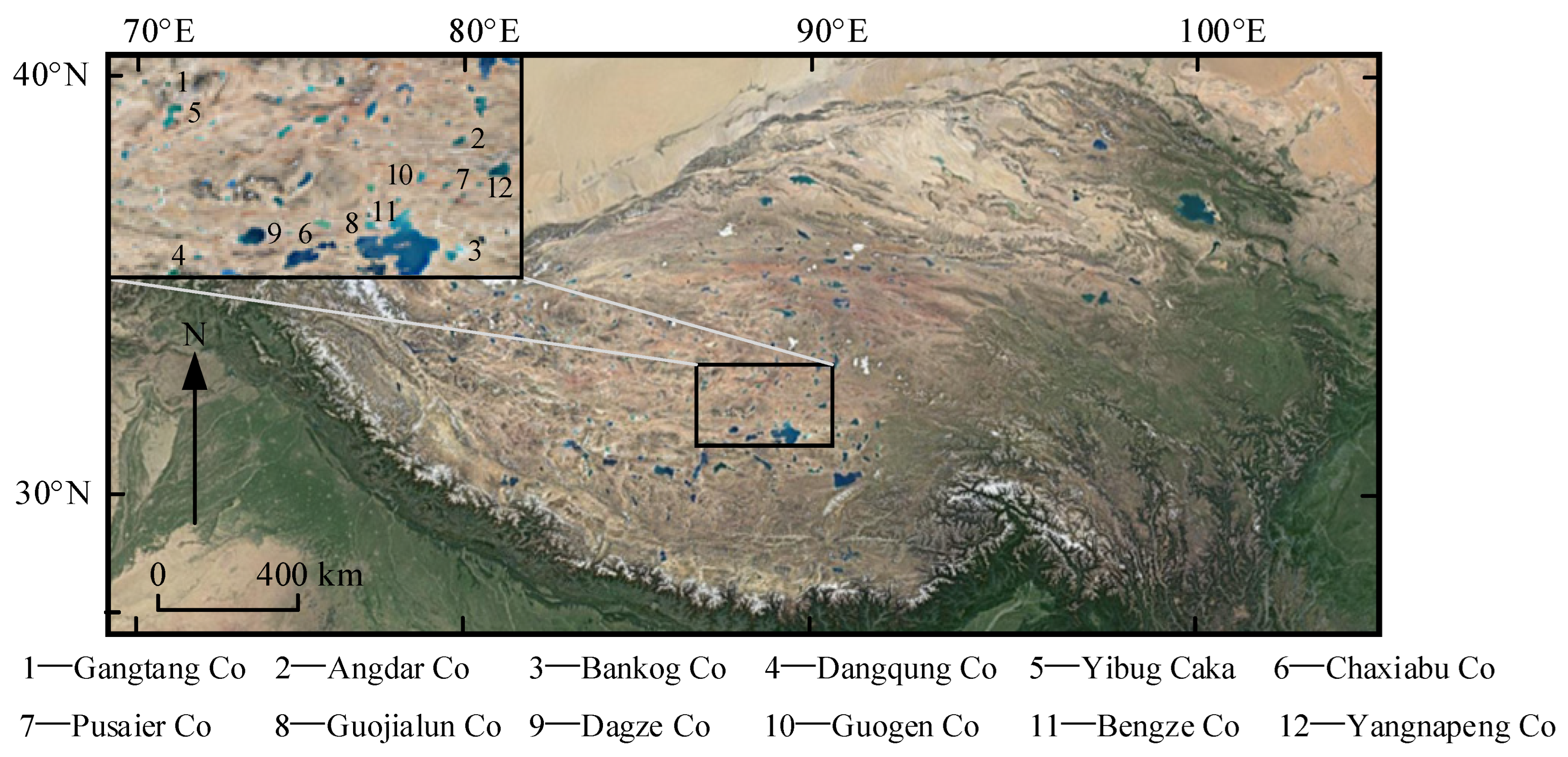
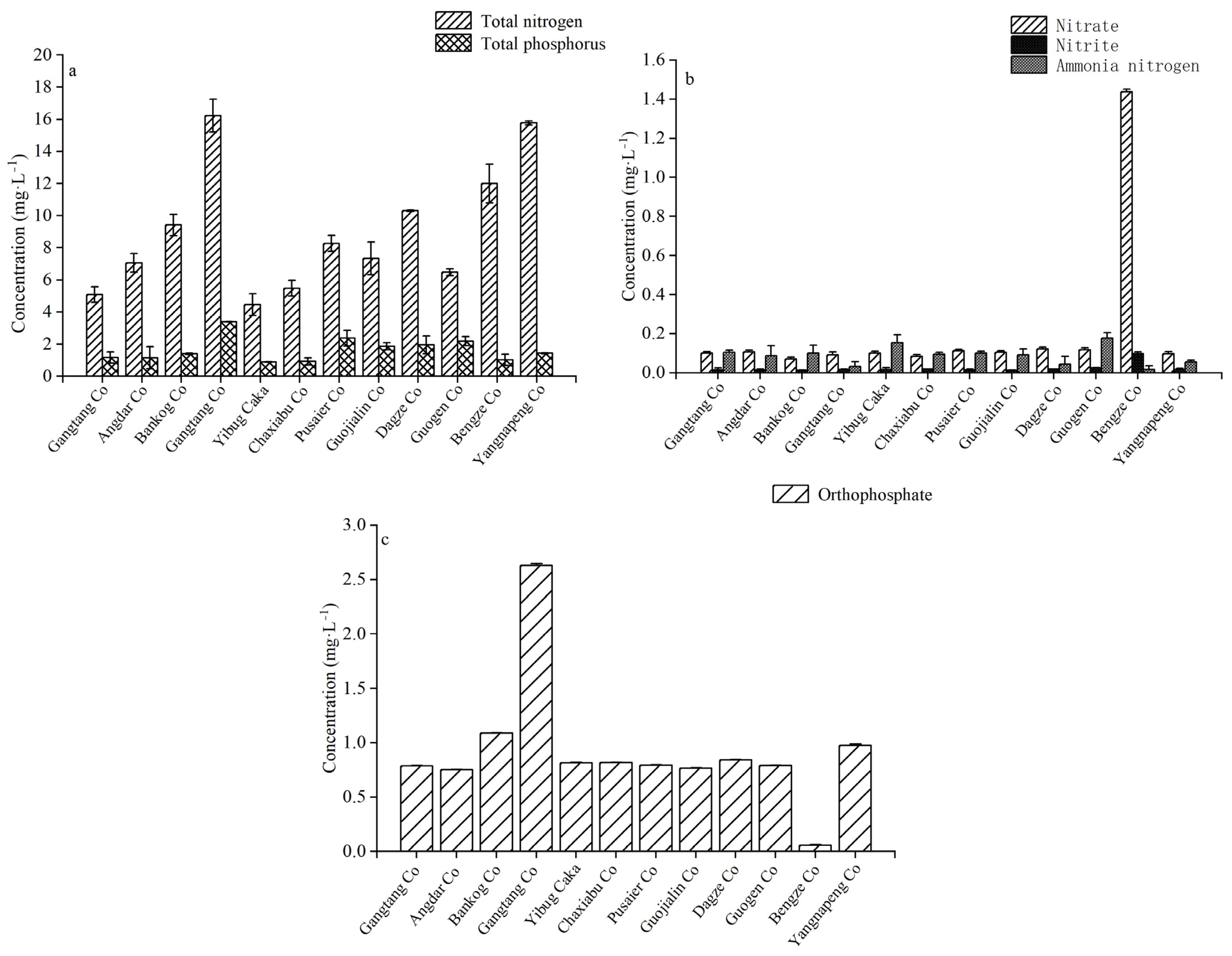
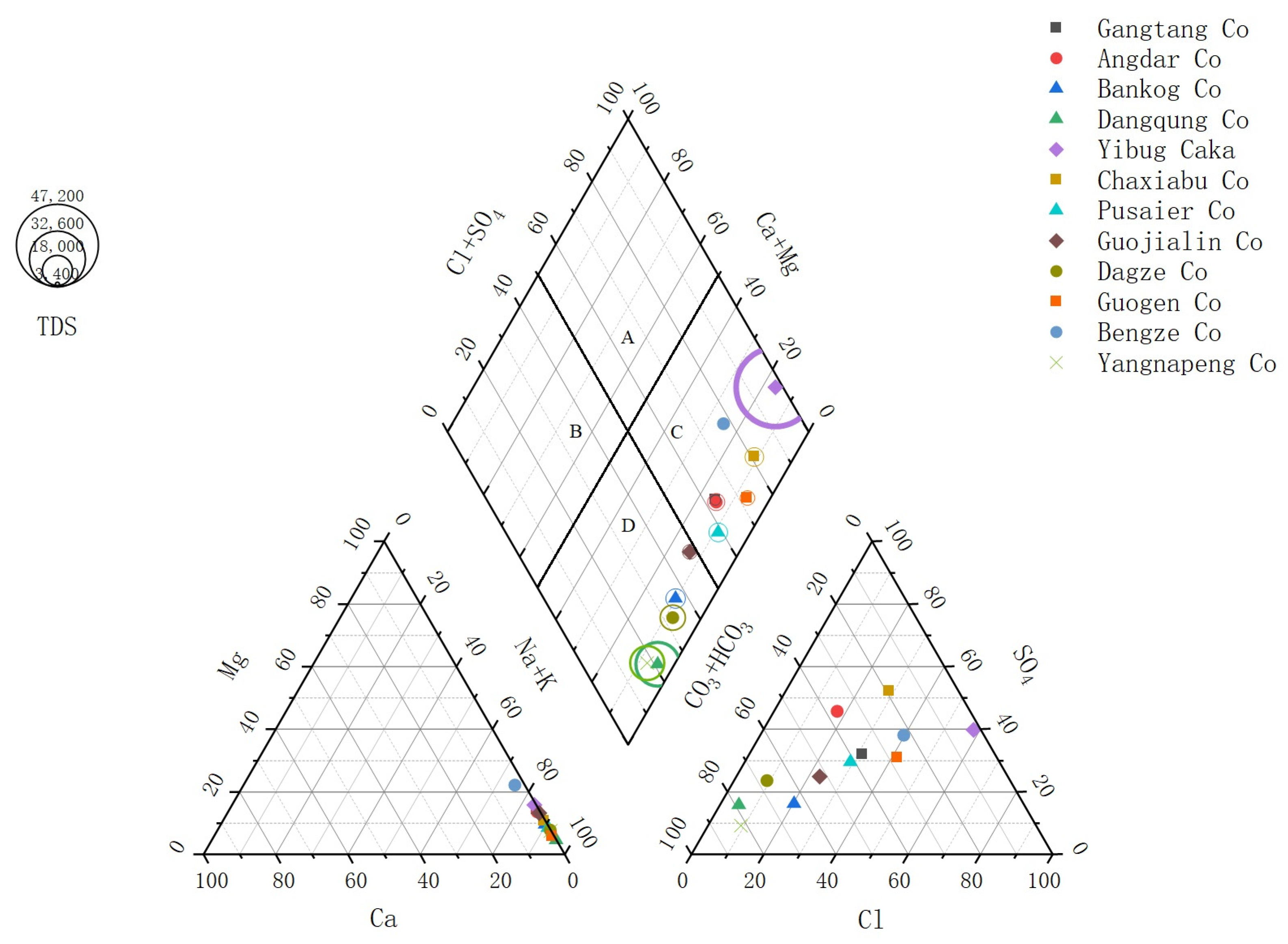
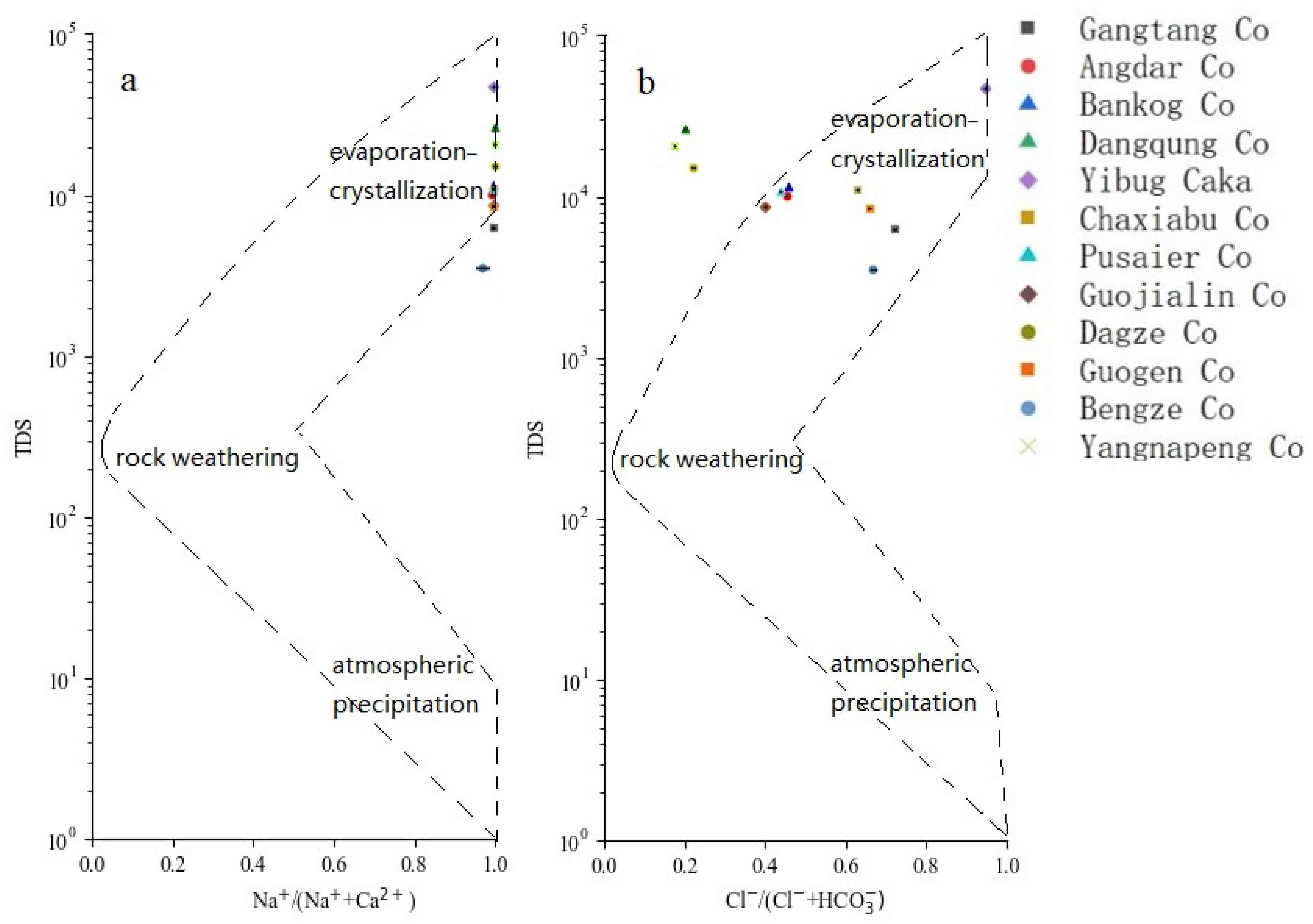
| Lake | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Altitude (m) | Date | Weather |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bengze Co | 32°04′57.88″ | 88°38′42.50″ | 4536 | 31 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Chaxiabu Co | 31°55′45.66″ | 87°52′21.06″ | 4680 | 31 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Guogen Co | 32°21′23.87″ | 89°10′30.44″ | 4659 | 31 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Pusaier Co | 32°22′29.93″ | 89°29′58.92″ | 4586 | 31 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Guojialin Co | 32°01′40.35″ | 88°31′18.15″ | 4524 | 31 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Dagze Co | 31°49′40.52″ | 87°23′02.71″ | 4459 | 31 July 2020 | Cloudy |
| Yangnapeng Co | 32°19′46.64″ | 89°47′49″ | 4620 | 30 July 2020 | Rainy |
| Angdar Co | 32°40′00″ | 89°31′36″ | 4900 | 30 July 2020 | Cloudy |
| Bankog Co | 31°44′21.86″ | 89°25′49.61″ | 4515 | 26 July 2020 | Sunny |
| Gangtang Co | 33°10′17.90″ | 86°39′51.08″ | 4866 | 1 August 2020 | Sunny |
| Yibug Caka | 32°59′31.10″ | 86°40′06.09″ | 4557 | 1 August 2020 | Rainy |
| Dangqung Co | 31°35′26.16″ | 86°47′30.24″ | 4475 | 2 August 2020 | Sunny |
| Lake | Physicochemical Analysis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Conductivity (mS·m−1) | pH | DO (mg·L−1) | Salinity (‰) | Oxidation/Reduction (mV) | Alkalinity (mmol·L−1) | Hardness (mmol·L−1) | TDS (g·L−1) | |
| Bengze Co | 20.60 | 1.27 | 8.90 | 6.81 | 0.64 | −52.60 | 12.38 ± 0.76 | 13.71 ± 0.03 | 3.53 ± 0.02 |
| Chaxiabu Co | 19.18 | 5.34 | 8.96 | 6.42 | 2.89 | −100.30 | 31.96 ± 0.41 | 18.27 ± 0.12 | 11.06 ± 0.02 |
| Guogen Co | 12.74 | 8.36 | 8.98 | 7.26 | 4.67 | −85.10 | 36.41 ± 0.35 | 8.2 ± 0.19 | 8.49 ± 0.03 |
| Pusaier Co | 13.53 | 8.29 | 9.00 | 6.62 | 4.70 | −105.70 | 67.75 ± 0.9 | 14.49 ± 0.14 | 10.85 ± 0.03 |
| Guojialin Co | 16.14 | 17.20 | 8.94 | 5.38 | 10.20 | −105.50 | 70.7 ± 0.57 | 18.35 ± 0.03 | 8.63 ± 0.02 |
| Dagze Co | 18.86 | 19.75 | 8.19 | 6.62 | 11.82 | −113.50 | 162.12 ± 1.15 | 18.84 ± 0.08 | 15.11 ± 0.03 |
| Yangnapeng Co | 18.55 | 49.32 | 9.03 | 3.58 | 32.31 | −94.00 | 271.67 ± 0.78 | 25.42 ± 0.14 | 20.68 ± 0.02 |
| Angdar Co | 13.28 | 51.55 | 8.87 | 5.33 | 33.88 | −79.20 | 57.42 ± 0.33 | 22.17 ± 0.8 | 10.06 ± 0.02 |
| Bankog Co | 14.40 | 65.39 | 9.24 | 7.20 | 44.25 | −65.10 | 125.84 ± 0.29 | 19.13 ± 0.56 | 11.52 ± 0.03 |
| Gangtang Co | 13.78 | 67.01 | 8.85 | 3.73 | 45.52 | −90.90 | 37.64 ± 0.23 | 15.15 ± 0.07 | 6.27 ± 0.02 |
| Yibug Caka | 16.32 | 72.47 | 8.76 | 5.36 | 49.85 | −93.00 | 15 ± 0.4 | 121.35 ± 0.07 | 47.27 ± 0.02 |
| Dangqung Co | 15.78 | 138.20 | 8.80 | 12.82 | 106.90 | −61.40 | 351.04 ± 0.21 | 20.36 ± 0.2 | 26.43 ± 0.02 |
| Hydration Index | Classification Standards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| TP (mg·L−1) | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| TN (mg·L−1) | 0.20 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.00 |
| Lake | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | CO32− | HCO3− | Cl− | SO42− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bengze Co | 937 ± 9.38 | 43 ± 0.36 | 31 ± 0.80 | 148 ± 1.09 | 179 ± 3.38 | 391 ± 4.80 | 785 ± 1.73 | 1019 ± 1.72 |
| Chaxiabu Co | 3406 ± 6.91 | 42 ± 0.15 | 16 ± 0.40 | 213 ± 4.01 | 461 ± 2.94 | 1013 ± 3.13 | 1707 ± 1.72 | 4206 ± 3.68 |
| Guogen Co | 2824 ± 7.76 | 42 ± 0.31 | 11 ± 0.20 | 93 ± 5.23 | 592 ± 0.84 | 1017 ± 4.37 | 1956 ± 0.5 | 1953 ± 7.79 |
| Pusaier Co | 3424 ± 9.14 | 40 ± 0.24 | 13 ± 0.22 | 168 ± 5.23 | 943 ± 5.48 | 2216 ± 5.74 | 1714 ± 0.56 | 2331 ± 2.05 |
| Guojialin Co | 2670 ± 9.27 | 39 ± 0.29 | 15 ± 1.6 | 214 ± 0.61 | 1303 ± 2.28 | 1663 ± 6.12 | 1110 ± 1.55 | 1617 ± 1.82 |
| Dagze Co | 5073 ± 9.49 | 43 ± 0.12 | 7 ± 2.20 | 225 ± 2.68 | 3515 ± 4.08 | 2742 ± 6.93 | 777 ± 1.19 | 2726 ± 2.29 |
| Yangnapeng Co | 7040 ± 2.87 | 39 ± 0.15 | 14 ± 2.14 | 301 ± 5.47 | 5656 ± 5.64 | 5070 ± 1.04 | 1078 ± 0.79 | 1480 ± 3.16 |
| Angdar Co | 3049 ± 2.24 | 34 ± 1.03 | 26 ± 1.80 | 254 ± 5.84 | 1151 ± 3.9 | 1164 ± 2.43 | 967 ± 0.81 | 3419 ± 3.77 |
| Bankog Co | 3920 ± 6.02 | 34 ± 0.43 | 22 ± 2.20 | 219 ± 4.5 | 2824 ± 4.56 | 1637 ± 1.59 | 1375 ± 3.69 | 1488 ± 3.31 |
| Gangtang Co | 1978 ± 4.19 | 43 ± 0.43 | 12 ± 1.60 | 177 ± 2.31 | 911 ± 2.28 | 444 ± 1.13 | 1141 ± 2.34 | 1568 ± 2.78 |
| Yibug Caka | 14072 ± 4.07 | 41 ± 0.34 | 82 ± 2.61 | 1426 ± 1.95 | - | 913 ± 4.69 | 834 ± 2.32 | 1741 ± 1.96 |
| Dangqung Co | 9731 ± 4.02 | 38 ± 0.50 | 12 ± 1.60 | 241 ± 5.11 | 8912 ± 2.10 | 3292 ± 2.08 | 836 ± 3.12 | 3364 ± 3.93 |
| CO32− | HCO3− | Cl− | SO42− | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | NO3− | TDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO32− | 1 | |||||||||
| HCO3− | 0.844 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| Cl− | −0.304 | −0.073 | 1 | |||||||
| SO42− | 0.229 | 0.299 | 0.132 | 1 | ||||||
| Na+ | 0.906 ** | 0.899 ** | −0.042 | 0.514 | 1 | |||||
| K+ | −0.401 | −0.308 | 0.021 | −0.111 | −0.312 | 1 | ||||
| Ca2+ | −0.438 | −0.421 | −0.115 | −0.293 | −0.506 | −0.488 | 1 | |||
| Mg2+ | 0.695 * | 0.637 * | −0.44 | 0.258 | 0.627 * | −0.476 | 0.062 | 1 | ||
| NO3− | −0.051 | 0.099 | −0.061 | 0.142 | −0.026 | 0.452 | −0.54 | −0.247 | 1 | |
| TDS | 0.896 ** | 0.909 ** | −0.062 | 0.533 | 0.998 ** | −0.315 | −0.478 | 0.659 * | −0.025 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. Analysis of Water Chemistry Characteristics and Main Ion Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Nagqu Area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in Summer. Water 2023, 15, 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162900
Jin Y, Zhu B, Wang F, Sun S, Wang P, Liu X. Analysis of Water Chemistry Characteristics and Main Ion Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Nagqu Area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in Summer. Water. 2023; 15(16):2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162900
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yifan, Boshan Zhu, Fang Wang, Shichun Sun, Pengfei Wang, and Xiaoshou Liu. 2023. "Analysis of Water Chemistry Characteristics and Main Ion Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Nagqu Area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in Summer" Water 15, no. 16: 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162900
APA StyleJin, Y., Zhu, B., Wang, F., Sun, S., Wang, P., & Liu, X. (2023). Analysis of Water Chemistry Characteristics and Main Ion Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Nagqu Area of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in Summer. Water, 15(16), 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162900







