Effects of Decomposition of Submerged Aquatic Plants on CO2 and CH4 Release in River Sediment–Water Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Decay and Composition Change of Plant Decayed Matter
2.3.2. DO and pH in Sediment–Water Interface
2.3.3. Determination of Organic Matter in Sediment
2.3.4. Gas Collection and Analysis
2.3.5. Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes of Organic Matter in Sediment–Water Environment
3.1.1. Decay of Plant Decayed Matter
3.1.2. Effects of Decomposition of Aquatic Plants on Organic Matter in Sediments
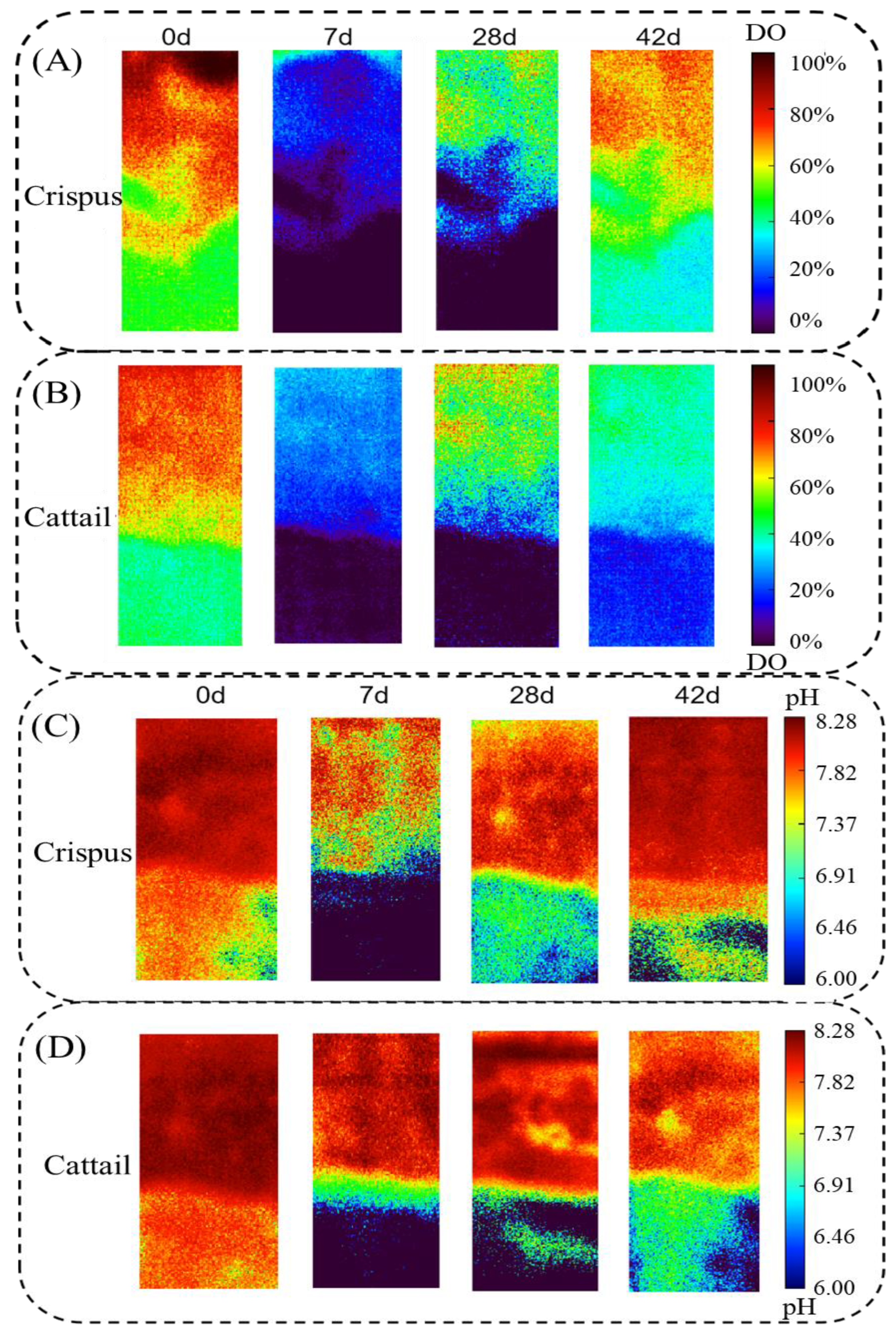
3.2. DO and pH in the Sediment–Water Interface
3.3. Changes of CO2 and CH4 Flux
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongaarts, J. Intergovernmental panel on climate change special report on global warming of 1.5 °C Switzerland: IPCC. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2019, 45, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.Q.; Xia, X.H.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.B.; Wang, J.F.; Xi, N.N.; Zhang, Q.R. Intense methane ebullition from urban inland waters and its significant contribution to greenhouse gas emissions. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschke, S.; Bousquet, P.; Ciais, P.; Saunois, M.; Canadell, J.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Bergamaschi, P.; Bergmann, D.; Blake, D.R.; Bruhwiler, L. Three decades of global methane sources and sinks. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunois, M.; Bousquet, P.; Poulter, B.; Peregon, A.; Ciais, P.; Canadell, J.; Dlugokencky, E.; Etiope, G.; Bastviken, D.; Houweling, S. The global methane budget 2000–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 697–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marano, A.V.; Pires-Zottarelli, C.L.A.; Barrera, M.D.; Steciow, M.M.; Gleason, F.H. Diversity, role in decomposition, and succession of zoosporic fungi and straminipiles on submerged decaying leaves in a woodland stream. Hydrobiologia 2011, 659, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, A.; Richards, J.H.; Scinto, L.J. Plant decomposition in wetlands: Effects of hydrologic variation in a re-created everglades. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Tong, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, M.; Xu, J.; Xiao, R.; Wu, J. Nutrients release and greenhouse gas emission during decomposition of Myriophyllum aquaticum in a sediment-water system. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, M.; Kosten, S.; Aben, R.; Kazanjian, G.; Hilt, S.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Van Donk, E.; Bakker, E.S. Warming enhances sedimentation and decomposition of organic carbon in shallow macrophyte-dominated systems with zero net effect on carbon burial. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5231–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartosiewicz, M.; Maranger, R.; Przytulska, A.; Laurion, I. Effects of phytoplankton blooms on fluxes and emissions of greenhouse gases in a eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2021, 196, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hao, T.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Li, Z. Effects of sediment-borne nutrient and litter quality on macrophyte decomposition and nutrient release. Hydrobiologia 2017, 787, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, B.; Yang, Q.; Lan, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Z. Effects of plant species on macrophyte decomposition under three nutrient conditions in a eutrophic shallow lake, North China. Ecol. Model. 2013, 252, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.S.; Fonseca, M.N.; Esteves, B.S.; Chagas, G.G. Decomposition of Egeria densa Planchon (Hydrocharitaceae) in a well oxygenated tropical aquatic ecosystem. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.F.; Tao, Y.; Liu, W.; Xing, W.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Ma, L. C, N, and P stoichiometry and their interaction with different plant communities and soils in subtropical riparian wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.L.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, Y.S.; Xie, Z.H.; Wang, G.H.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, J.D.; Jin, J. Plant phosphorus acquisition links to phosphorus transformation in the rhizospheres of soybean and rice grown under CO2 and temperature co-elevation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yu, J.; Tesso, T.; Dowell, F.; Wang, D. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared techniques: A mini-review. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glud, R.N.; Ramsing, N.B.; Gundersen, J.K.; Klimant, I. Planar optrodes: A new tool for fine scale measurements of two-dimensional O2 distribution in benthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 140, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, H.H.; Campbell, C.A.; Brandt, S.A.; Lafond, G.P.; Townley-Smith, L. Light-fraction organic matter in soils from long-term crop rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.J.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P. Effects of Long-term Fertilization on Maize Yield, Active Organic Matter and pH Value of Black Soil. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Strobel, B.W.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Andersen, M.K.; Raulund-Rasmussen, K. Composition and reactivity of DOC in forest floor soil solutions in relation to tree species and soil type. Biogeochemistry 2001, 56, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D.M. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—A review. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Q.; Chen, Q.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Yi, Q.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Ma, H.H.; Hu, L.M. Nitrous oxide emissions from cascade hydropower reservoirs in the upper Mekong River. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Yeager, K.M.; Wan, G.J.; Li, J.; Tao, F.X.; Lue, Y.C.; Liu, F.; Fan, C.X. The spatial distribution and emission of nitrous oxide (N2O) in a large eutrophic lake in eastern China: Anthropogenic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3330–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trfmbly, A.; Varflvy, L.; Roehm, C.; Garneau, M. Green House Gas Emisions—Fluxes and Proceses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, L.K.; Frost, P.C. Biomass loss and nutrient release from decomposing aquatic macrophytes: Effects of detrital mixing. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.J.; Deng, H.G.; Wang, D.Q.; Ye, M.W.; Tan, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Xu, S.Y. Nitrous oxide emissions in the Shanghai river network: Implications for the effects of urban sewage and IPCC methodology. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, D.; Bartoli, M.; Viaroli, P. Decomposition of four macrophytes in wetland sediments: Organic matter and nutrient decay and associated benthic processes. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Wang, B.; Ye, C.; Ba, Y.X. The release of nitrogen and phosphorus during the decomposition process of submerged macrophyte (Hydrilla verticillata Royle) with different biomass levels. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, C.; Liang, R.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Y. Phosphorus release during decomposition of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton crispus. Limnology 2018, 19, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, M.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Hirata, S.; Kato, T.; Mo, W.; Cao, G.; Mariko, S. Carbon dioxide dynamics and controls in a deep-water wetland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalena, J.K.; Bottomley, P.J.; Myrold, D.D. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization from light- and heavyfraction additions to soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L. Microbes participated in macrophyte leaf litters decomposition in freshwater habitat. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, G. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling by extracellular organic matters (EOM) of Microcystis aeruginosa in stationary phase: Influences of interfacial characteristics of foulants and fouling mechanisms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; Spencer, R.G.M. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornut, J.; Clivot, H.; Chauvet, E.; Elger, A.; Pagnout, C.; Guerold, F. Effect of acidification on leaf litter decomposition in benthic and hyporheic zones of woodland streams. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6430–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrier-Uijl, A.P.; Veraart, A.J.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Berendse, F.; Veenendaal, E. Release of CO2 and CH4 from lakes and drainage ditches in temperate wetlands. Biogeochemistry 2011, 102, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Pu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Lee, X. Methane flux dynamics in a submerged aquatic vegetation zone in a subtropical lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Tao, Y.; Mao, Z.D.; Gu, Q.J.; Han, Y.X.; Hu, B.L.; Wang, H.W.; Lai, A.X.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L.L. Iron oxides act as an alternative electron acceptor for aerobic methanotrophs in anoxic lake sediments. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| TOC | AOM | LFOM | HFOM | CH4 | CO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | −0.335 * | 0.136 | 0.363 ** | −0.191 | 1 | 0.825 ** |
| CO2 | −0.133 | 0.035 | 0.286 * | −0.013 | 0.825 ** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, T.; Tian, L.; Zhang, C.; Chao, J.; Han, T. Effects of Decomposition of Submerged Aquatic Plants on CO2 and CH4 Release in River Sediment–Water Environment. Water 2023, 15, 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162863
Xie J, Gao Y, Xu X, Chen T, Tian L, Zhang C, Chao J, Han T. Effects of Decomposition of Submerged Aquatic Plants on CO2 and CH4 Release in River Sediment–Water Environment. Water. 2023; 15(16):2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162863
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Jizheng, Yuexiang Gao, Xueting Xu, Ting Chen, Lingyun Tian, Chenxi Zhang, Jianying Chao, and Tianlun Han. 2023. "Effects of Decomposition of Submerged Aquatic Plants on CO2 and CH4 Release in River Sediment–Water Environment" Water 15, no. 16: 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162863




