Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Watershed Characterization
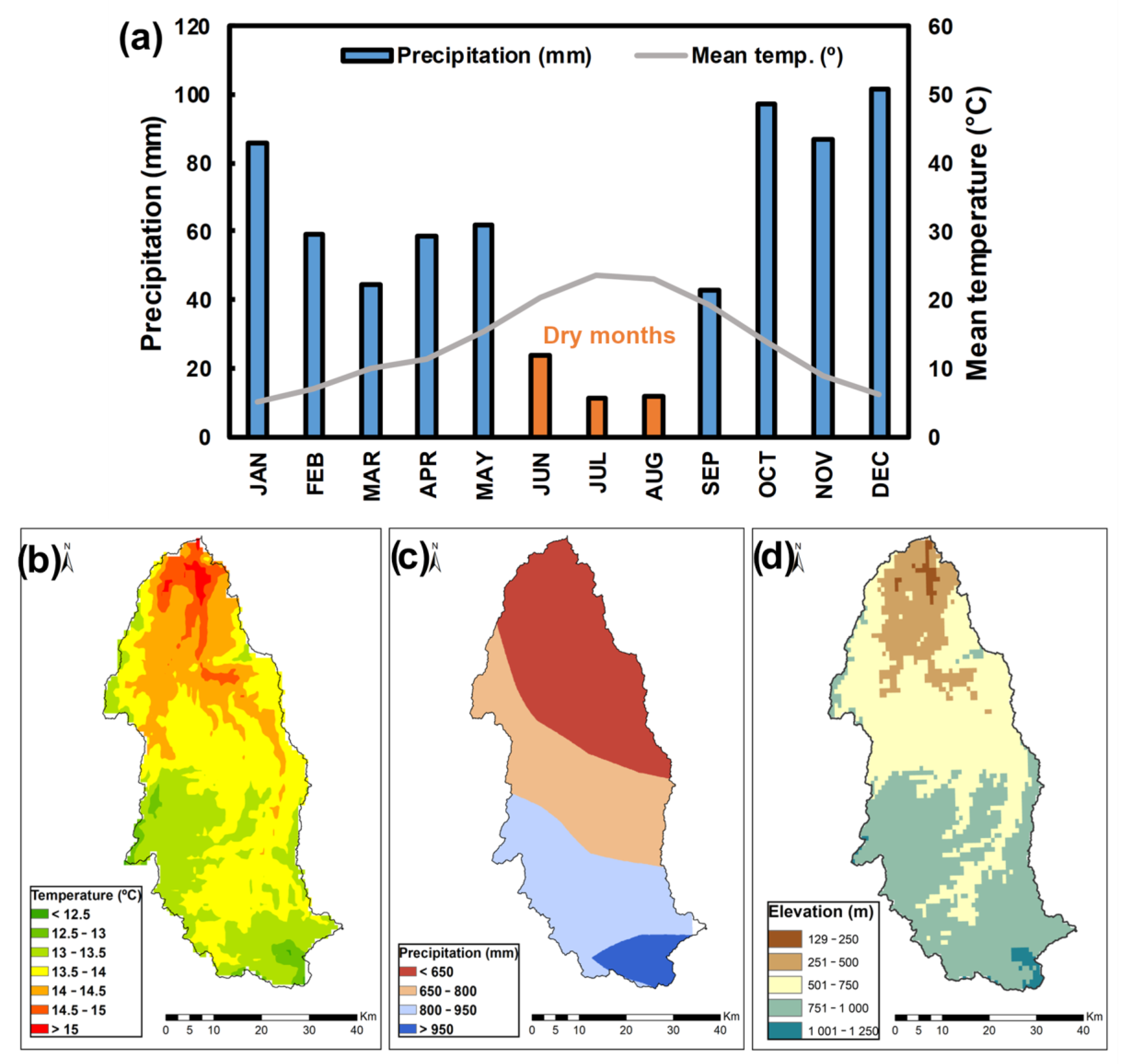
2.2. Climatic Characterization of the Basin
2.3. Hydrological Model Characterization
2.4. Recent-Past and Future Climate Data
2.5. Côa Watershed Delineation and Segmentation
2.6. Hydrometric Model Evaluation
2.7. Future Uncertainties Irrigation Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Hydrological Model Evaluation: Historical Period
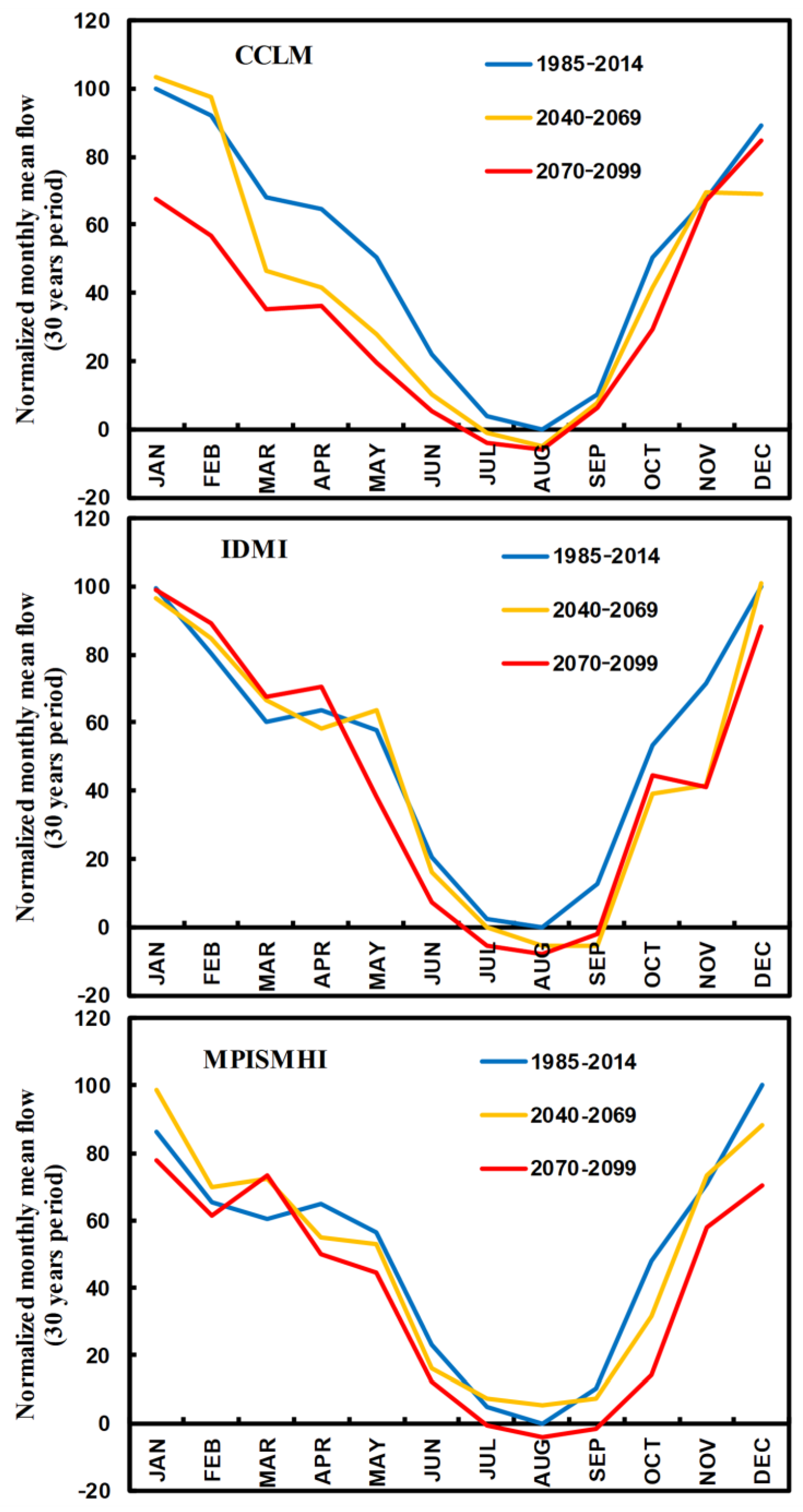
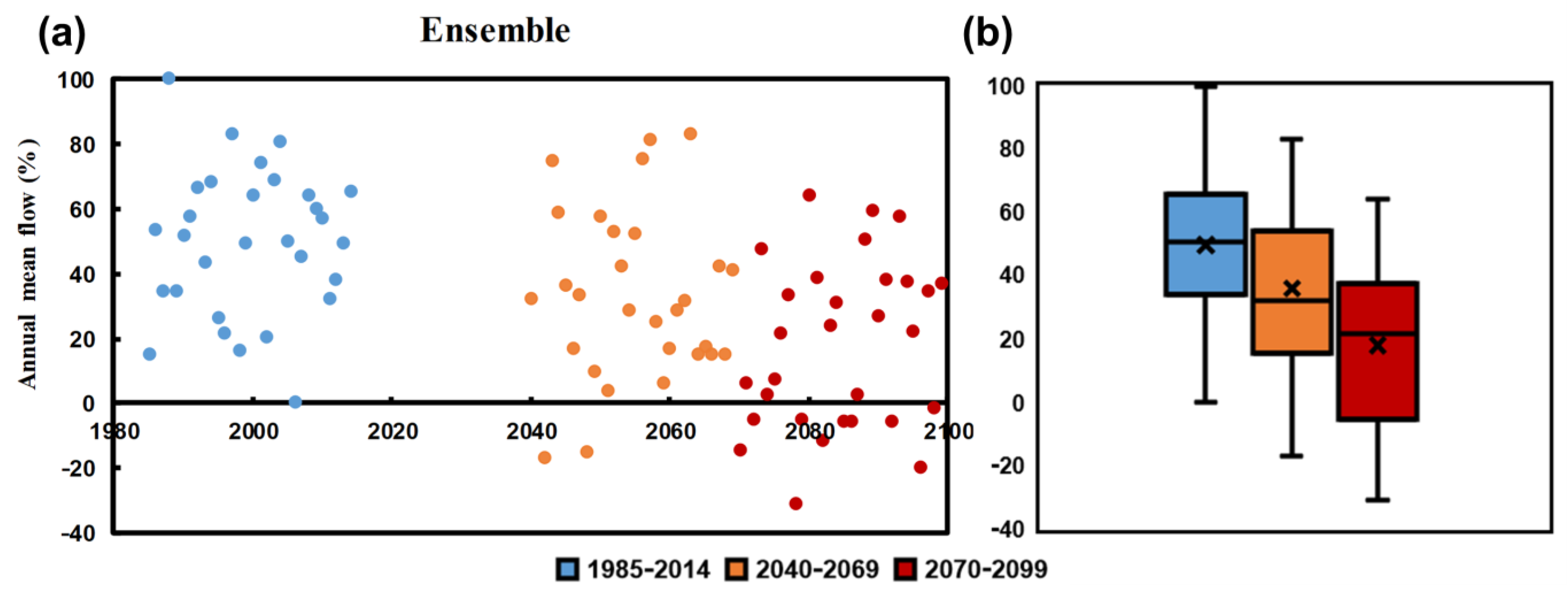
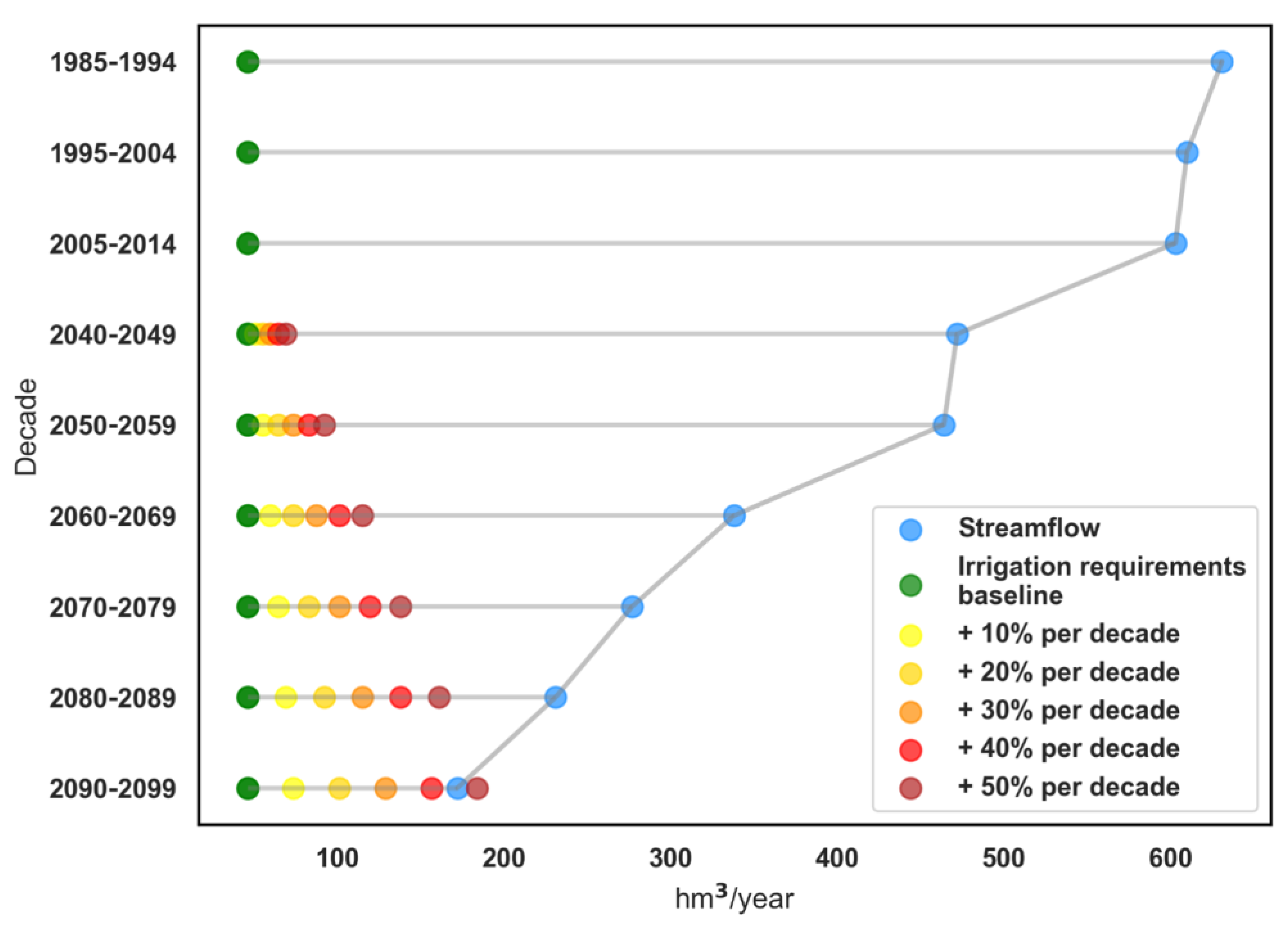
3.2. Future Streamflow in the Côa River
3.3. Future Irrigation Scenarios
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- APA. Plano de Gestão Hidrográfica do Douro 2016–2021—Parte 2—Caracterização e Diagnostico; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Amadora, Portugal, 2019; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- SNIG Carta de Uso e Ocupação do Solo. Available online: https://snig.dgterritorio.gov.pt/rndg/srv/por/catalog.search#/home (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Fraga, H.; Santos, J.A. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Chilling and Forcing for the Main Fresh Fruit Regions in Portugal. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 689121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Shu, L.; Xiao, T.; Shui, T. Landscape Configuration Effects on Outdoor Thermal Comfort across Campus—A Case Study. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.M.; Guimarães, R.C.; Moreira, M. Apontamentos Para as Aulas de Hidrologia; Departamento de Engenharia Rural: Evora, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- CPPE—Companhia Portuguesa de Produção de Electricidade, S.A. Avaliação Comparada dos Aproveitamentos do Baixo Sabor e do Alto Côa; CPPE—Companhia Portuguesa de Produção de Electricidade, S.A: Setúbal, Portugal, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bednar-Friedl, B.; Biesbroek, R.; Schmidt, D.N.; Alexander, P.; Børsheim, K.Y.; Carnicer, J.; Georgopoulou, E.; Haasnoot, M.; Cozannet, G.L.; Lionello, P.; et al. Europe. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1817–1927. ISBN 978-1-00-932584-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, H.; Guimarães, N.; Freitas, T.R.; Malheiro, A.C.; Santos, J.A. Future Scenarios for Olive Tree and Grapevine Potential Yields in the World Heritage Côa Region, Portugal. Agronomy 2022, 12, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.R.; Santos, J.A.; Silva, A.P.; Martins, J.; Fraga, H. Climate Change Projections for Bioclimatic Distribution of Castanea Sativa in Portugal. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Menz, C.; De Abreu Jaffe, M.S.; Costafreda-Aumedes, S.; Moriondo, M.; Leolini, L.; Torres-Matallana, A.; Molitor, D.; Junk, J.; Fraga, H.; et al. Projections of Climate Change Impacts on Flowering-Veraison Water Deficits for Riesling and Müller-Thurgau in Germany. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.; Burke, M.; Tebaldi, C.; Mastrandrea, M.; Falcon, W.; Naylor, R. Prioritizing Climate Change Adaptation Needs for Food Security in 2030. Science 2008, 319, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Williams, J.; Perry, C.J.; Molle, F.; Ringler, C.; Steduto, P.; Udall, B.; Wheeler, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Garrick, D.; et al. The Paradox of Irrigation Efficiency. Science 2018, 361, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Flores, F.; Moneo, M. Challenges to Manage the Risk of Water Scarcity and Climate Change in the Mediterranean. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pordata. Superfície Agrícola Utilizada: Irrigável e Regada (%); Pordata: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, S.N.; Arnell, N.W. A Global Assessment of the Impact of Climate Change on Water Scarcity. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisser, D.; Frolking, S.; Douglas, E.M.; Fekete, B.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Schumann, A.H. Global Irrigation Water Demand: Variability and Uncertainties Arising from Agricultural and Climate Data Sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorguner, M.; Kavvas, M.L. Modeling Impacts of Future Climate Change on Reservoir Storages and Irrigation Water Demands in a Mediterranean Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Honrado, J.P.; Cerejeira, J.; Sousa, R.; Fernandes, P.M.; Vaz, A.S.; Alves, M.; Araújo, M.; Carvalho-Santos, C.; Fonseca, A.; et al. On the Development of a Regional Climate Change Adaptation Plan: Integrating Model-Assisted Projections and Stakeholders’ Perceptions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.; Western, A.; Vertessy, R. A Critical Review of Paired Catchment Studies with Reference to Seasonal Flows and Climatic Variability; Murray Darling Basin Commission: Canberra, Australia, 2003.
- Yang, X.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, X.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S.; Yong, B. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Evapotranspiration and Runoff at Shalamulun River Watershed, China. Hydrol. Res. 2012, 43, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondermann, M.N.; de Oliveira, R.P. Climate Adaptation Needs to Reduce Water Scarcity Vulnerability in the Tagus River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gómez, A.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; Leduc, S.; Sastre-Merlín, A.; Molina-Navarro, E. Streamflow Components and Climate Change: Lessons Learnt and Energy Implications after Hydrological Modeling Experiences in Catchments with a Mediterranean Climate. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajarmizad, M.; Harun, S.; Salarpour, M. A Review on Theoretical Consideration and Types of Models in Hydrology. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, M.; Ramos, C. Análise Morfométrica do Estádio Evolutivo de Sub-bacias da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Côa. In Atas do V Congresso Nacional de Geomorfologia; Associação Portuguesa de Geomorfólogos: Porto, Portugal, 2010; pp. 475–480. ISBN 978-989-96462-2-3. [Google Scholar]
- van Emmerik, T.; Mulder, G.; Eilander, D.; Piet, M.; Savenije, H. Predicting the Ungauged Basin: Model Validation and Realism Assessment. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinerson, R.S.; Kittle, J.L.; Duda, P.B. BASINS: Better Assessment Science Integrating Point and Nonpoint Sources. In Decision Support Systems for Risk-Based Management of Contaminated Sites; Marcomini, A., Suter, G.W., II, Critto, A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-0-387-09721-3. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, D.; Raftery, A.E. Inference for Deterministic Simulation Models: The Bayesian Melding Approach. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2000, 95, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.R.; Imhoff, J.C.; Kittle, J.L., Jr.; Donigian, A.S., Jr.; Johanson, R.C. Hydrological Simulation Program—FORTRAN User’s Manual for Version 11. In Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA/600/R-97/080; US Environmental Protection Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Herrera, S.; Cardoso, R.M.; Soares, P.M.M.; Espírito-Santo, F.; Viterbo, P. Iberia01: Daily Gridded (0.1° Resolution) Dataset of Precipitation and Temperatures over the Iberian Peninsula. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service. CORDEX Regional Climate Model Data on Single Levels; Copernicus Climate Change Service: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pitman, A.J.; Arneth, A.; Ganzeveld, L. Regionalizing Global Climate Models: Regionalizing Global Climate Models. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Stott, P.A.; Mitchell, J.F.B.; Schnur, R.; Delworth, T.L. Quantifying the Uncertainty in Forecasts of Anthropogenic Climate Change. Nature 2000, 407, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The Representative Concentration Pathways: An Overview. Climatic Chang. 2011, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE. O Uso da Água na Agricultura: 2011; Instituto Nacional de Estatística: Madrid, Portugal, 2011; p. 95.
- Esteve, P.; Varela-Ortega, C.; Blanco-Gutiérrez, I.; Downing, T.E. A Hydro-Economic Model for the Assessment of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation in Irrigated Agriculture. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanasaki, N.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T. A Reservoir Operation Scheme for Global River Routing Models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, L.; Iglesias, A.; Granados, A.; Mediero, L.; Martin-Carrasco, F. Quantitative Assessment of Climate Change Vulnerability of Irrigation Demands in Mediterranean Europe. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. Agricultural Irrigation Demand under Present and Future Climate Scenarios in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 306–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Sun, W.; Teng, J.; Song, H.; Yao, X. Effect of Length of the Observed Dataset on the Calibration of a Distributed Hydrological Model. Proc. IAHS 2015, 368, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Im, S.; Brannan, K.M.; Cho, J.H.; Mostaghimi, S. A Comparison of SWAT and HSPF Models for Simulating Hydrologic and Water Quality Responses from an Urbanizing Watershed. In Proceedings of the 2003 ASAE Annual International Meeting Sponsored by ASAE Riviera Hotel and Convention Center, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Knapp, H.V.; Arnold, J.G.; Demissie, M. Hydrological Modeling of the Iroquois River Watershed Using HSPF and SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeb Yazdi, M.; Ketabchy, M.; Sample, D.J.; Scott, D.; Liao, H. An Evaluation of HSPF and SWMM for Simulating Streamflow Regimes in an Urban Watershed. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 118, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siam, M.S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Climate Change Enhances Interannual Variability of the Nile River Flow. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Fuoco, D.; Maiolo, M.; Mendicino, G.; Smiatek, G.; Kunstmann, H. Evaluating the Uncertainty of Climate Model Structure and Bias Correction on the Hydrological Impact of Projected Climate Change in a Mediterranean Catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiel, K.; Wanders, N.; Selten, F.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Added Value of Large Ensemble Simulations for Assessing Extreme River Discharge in a 2 °C Warmer World. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; van der Sluijs, J.P.; Højberg, A.L.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Uncertainty in the Environmental Modelling Process—A Framework and Guidance. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlman, J.D. Uncertainties in Projections of Human-Caused Climate Warming. Science 1997, 278, 1416–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious Surface Coverage: The Emergence of a Key Environmental Indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The Natural Flow Regime. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A Review of Paired Catchment Studies for Determining Changes in Water Yield Resulting from Alterations in Vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Hydrologic Modeling: Progress and Future Directions. Geosci. Lett. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, D.; Jovanovic, T.; Mejía, A.; Hathaway, J.; Daly, E. Technical Note: Long-Term Memory Loss of Urban Streams as a Metric for Catchment Classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3551–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas Cuenca, J.; del Campo García, A. Euro-Mediterranean Information System on Know How in the Water Sector—Study on Irrigation Water Management in the Mediterranean Region; Euro-Mediterranean Water Information System: Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Droogers, P.; Aerts, J. Adaptation Strategies to Climate Change and Climate Variability: A Comparative Study between Seven Contrasting River Basins. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2005, 30, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, D.M.; Grantham, T.E.; Eng, K.; Wolock, D.M. Biological Relevance of Streamflow Metrics: Regional and National Perspectives. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, F.N.; Costa, S.C.; Pinheiro, P.J.; Alvarez, T.; Reis, F.M. Metodologia Integrada para Determinação de Regimes de Caudais Ecológicos Aplicada em Rios Ibéricos—Aqualogus-Eflow. RH 2014, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, V.; Huang, Y.F.; Koo, C.H.; Ahmed, A.N.; El-Shafie, A. A Review of Reservoir Operation Optimisations: From Traditional Models to Metaheuristic Algorithms. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3435–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.; Jha, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gassman, P.; Wolter, C. Impact of Land Use and Land Cover Change on the Water Balance of a Large Agricultural Watershed: Historical Effects and Future Directions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00A09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, N.; Pádua, L.; Sousa, J.J.; Bento, A.; Couto, P. Almond Cultivar Identification Using Machine Learning Classifiers Applied to UAV-Based Multispectral Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 1533–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Sangiorgio, M.; Beltran-Peña, A.A.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P.; Fung, I. Potential for Sustainable Irrigation Expansion in a 3 °C Warmer Climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29526–29534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Chu, Z.; Xia, T.; Zheng, B. Application of Ecological Restoration Technologies for the Improvement of Biodiversity and Ecosystem in the River. Water 2022, 14, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Rulli, M.C.; Dell’Angelo, J.; D’Odorico, P. Global Agricultural Economic Water Scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Ford, J.; Ley, D.; Bazaz, A.; Revi, A. Assessing the Feasibility of Adaptation Options: Methodological Advancements and Directions for Climate Adaptation Research and Practice. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Santos, J.A. Vineyard Mulching as a Climate Change Adaptation Measure: Future Simulations for Alentejo, Portugal. Agric. Syst. 2018, 164, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, M.B.; Payne, J.T.; Kristensen, M.; Madsen, H. An Evaluation of the Impact of Model Structure on Hydrological Modelling Uncertainty for Streamflow Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2004, 298, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozbahani, R.; Schreider, S.; Abbasi, B. Optimal Water Allocation through a Multi-Objective Compromise between Environmental, Social, and Economic Preferences. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 64, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
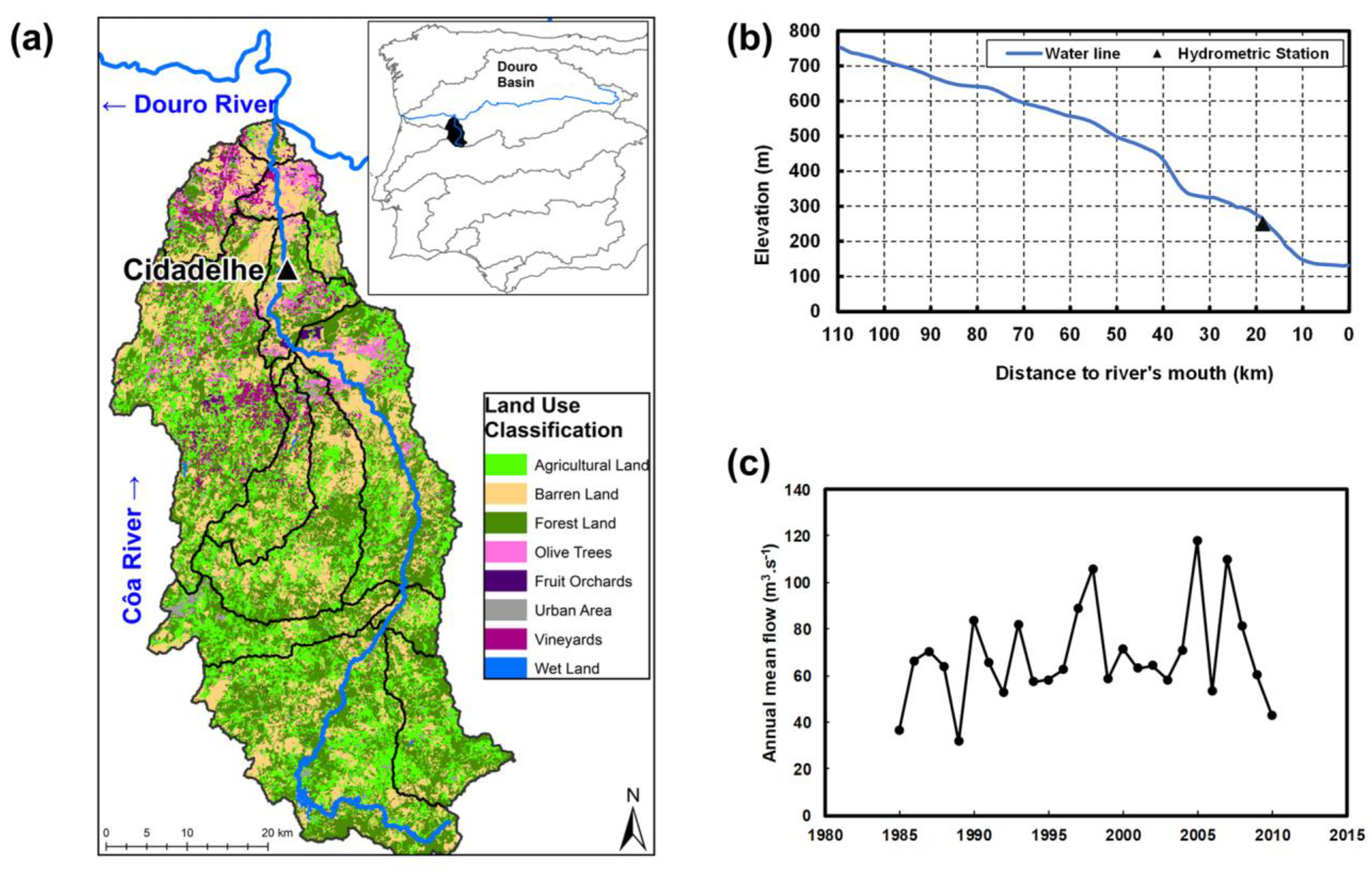

| Land Use Type | Area (ha) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Forest Land | 89,981 | 35.7 |
| Barren Land | 73,280 | 29.1 |
| Agricultural Land (annual crops, pastures) | 60,155 | 23.9 |
| Vineyard | 11,484 | 4.6 |
| Olive | 9151 | 3.6 |
| Urban Land | 5021 | 2.0 |
| Orchards (nut trees) | 1644 | 0.7 |
| Wetland | 1213 | 0.5 |
| Total | 251,929 | 100 |
| Global Climate Model (GCM) | Regional Climate Model (RCM) | ABREV |
|---|---|---|
| CNRM-CERFACS-CNRM-CM5 | CLMcom-CCLM4-8-17 | CCLM |
| MPI-M-MPI-ESM-L | SMHI-RCA4 | MPISMHI |
| IHCEC-EC-EARTH | DMI-HIRHAM5 | IDMI |
| Land Use Type | Area (ha) | Irrigated Area (Country Ref. 15.9%) | Annual Irrigation Requirements (m3·ha−1·yr−1) | Annual Irrigation Requirements per Hectare (hm3·yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural land | 60,155 | 9565 | 4000 | 38 |
| Vineyards | 11,484 | 1826 | 2000 | 4 |
| Olive | 9151 | 1455 | 2000 | 3 |
| Orchards (mostly nut trees) | 1644 | 261 | 2000 | 1 |
| Total | 82,434 | 13,107 | 10,000 | 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, D.; Fonseca, A.; Stolarski, O.; Freitas, T.R.; Guimarães, N.; Santos, J.A.; Fraga, H. Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation. Water 2023, 15, 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152739
Rodrigues D, Fonseca A, Stolarski O, Freitas TR, Guimarães N, Santos JA, Fraga H. Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation. Water. 2023; 15(15):2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152739
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Diogo, André Fonseca, Oiliam Stolarski, Teresa R. Freitas, Nathalie Guimarães, João A. Santos, and Helder Fraga. 2023. "Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation" Water 15, no. 15: 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152739
APA StyleRodrigues, D., Fonseca, A., Stolarski, O., Freitas, T. R., Guimarães, N., Santos, J. A., & Fraga, H. (2023). Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation. Water, 15(15), 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152739










