Water Quality Index (WQI) Analysis as an Indicator of Ecosystem Health in an Urban River Basin on Borneo Island
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Data
2.3. Water Quality Index Calculation
0.16 × SISS + 0.12 × SIpH
| WQI Parameter | Thresholds Value | Best Fitted Sub-Index Equation | (2) |
| DO (in % saturation) | for x ≤ 8 for 8 < x < 92 for x ≥ 92 | SIDO = 0 SIDO = −0.395 + 0.030x2 − 0.00020x2 SIDO = 100 | |
| BOD | for x ≤ 5 for x > 5 | SIBOD = 100.4 − 4.23x SIBOD = 108 × exp(−0.055x) − 0.1x | |
| COD | for x ≤ 20 for x > 20 | SICOD = −1.33x + 99.1 SICOD = 103 × exp(−0.0157x) − 0.04x | |
| NH3-N | for x ≤ 0.3 for 0.3 < x < 4 for x ≥ 4 | SIAN = 1005 − 105x SIAN = 94 × exp(−0.573x) − 5 × |x − 2| SIAN = 0 | |
| SS | for x ≤ 100 for 100 < x < 1000 for x ≥ 1000 | SISS = 97.5 × exp(−0.00676x) + 0.05x SISS = 71 × exp(−0.0016x) − 0.015x SISS = 0 | |
| pH | for x < 5.5 for 5.5 ≤ x < 7 for 7 ≤ x < 8.75 for x ≥ 8.75 | SIpH = 17.2 − 17.2x + 5.02x2 SIpH = −242 + 95.5x − 6.67x2 SIpH = −181 + 82.4x − 6.05x2 SIpH = 536 − 77.0x + 2.76x2 |
2.4. Analysis
3. Results
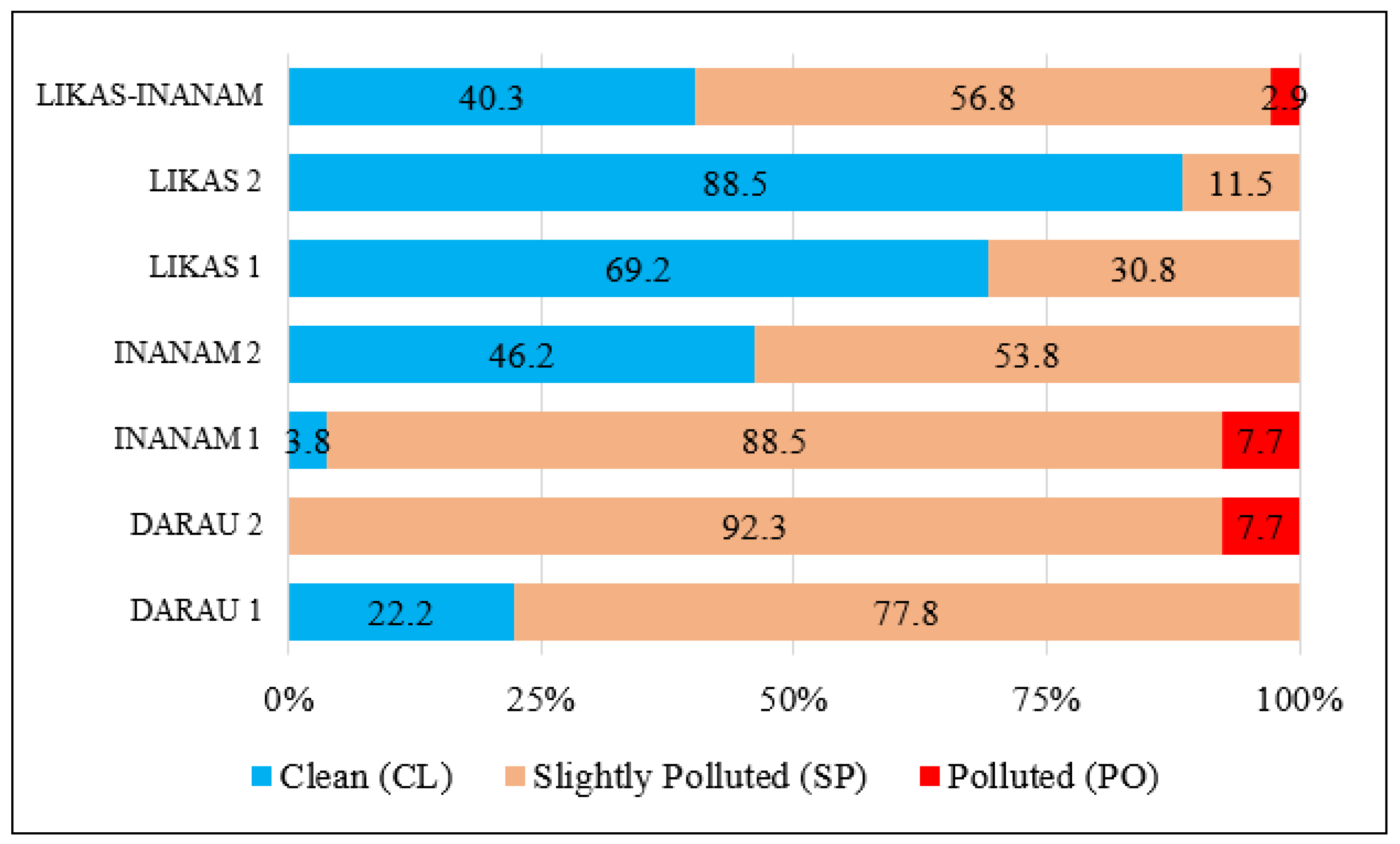
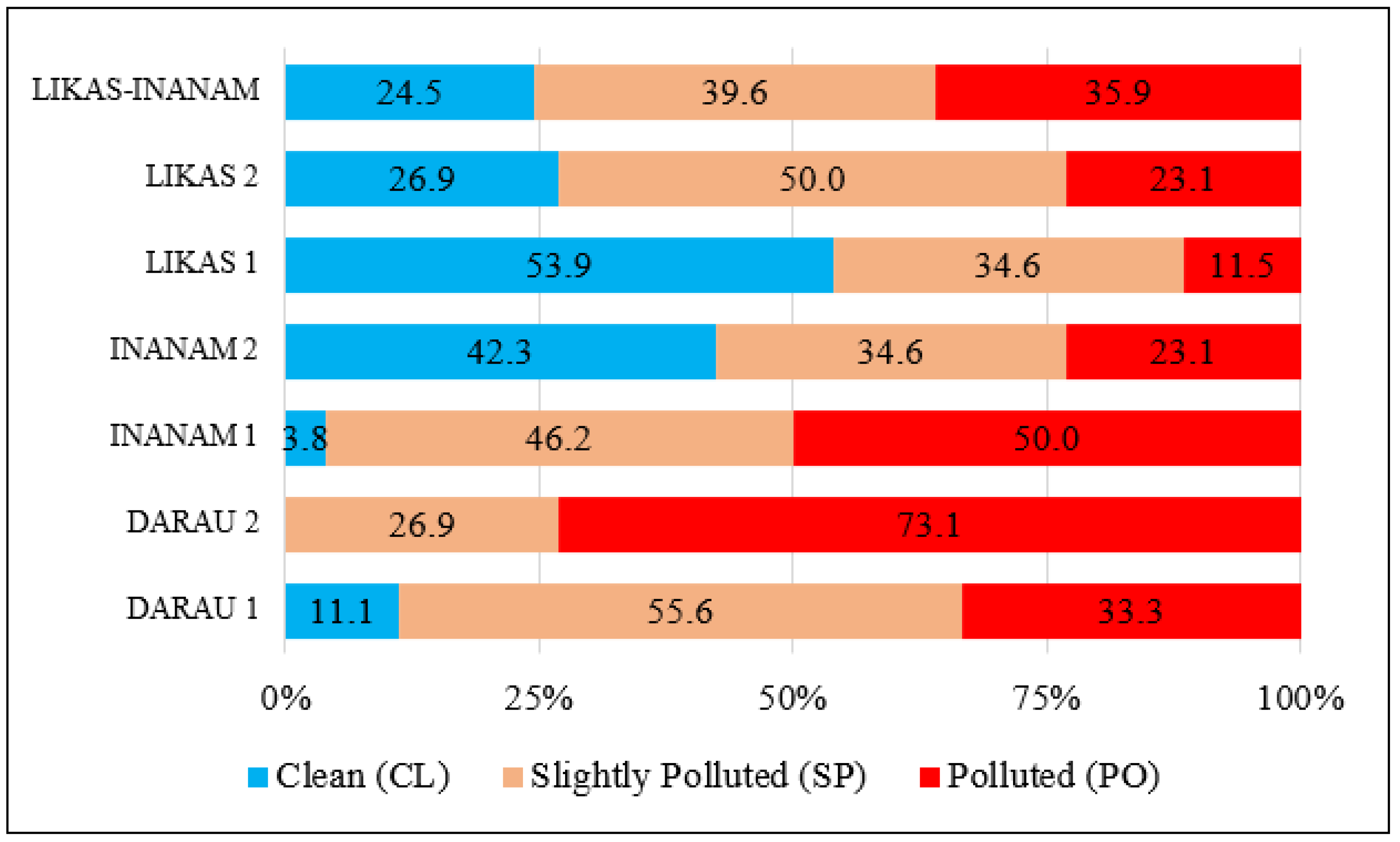
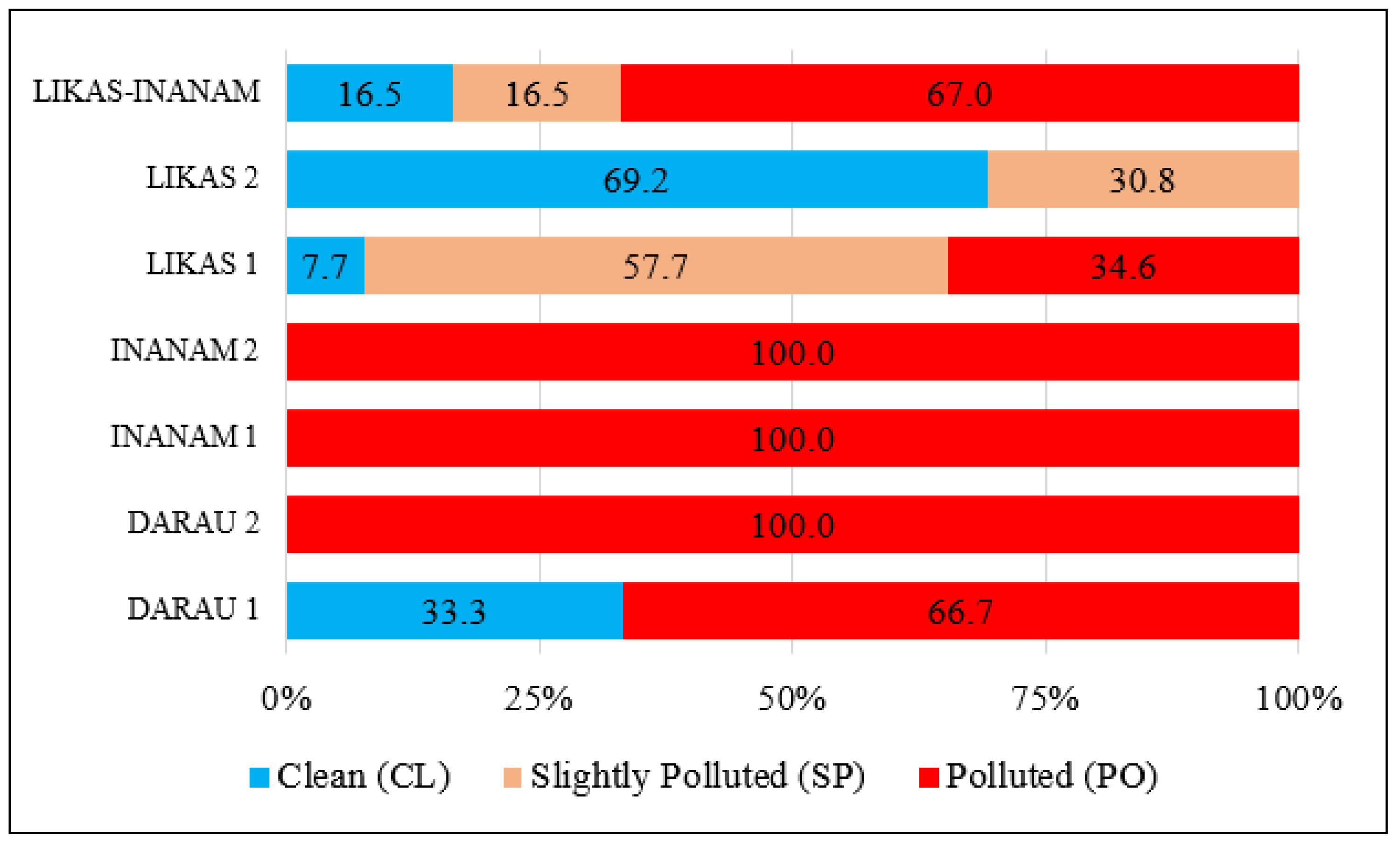
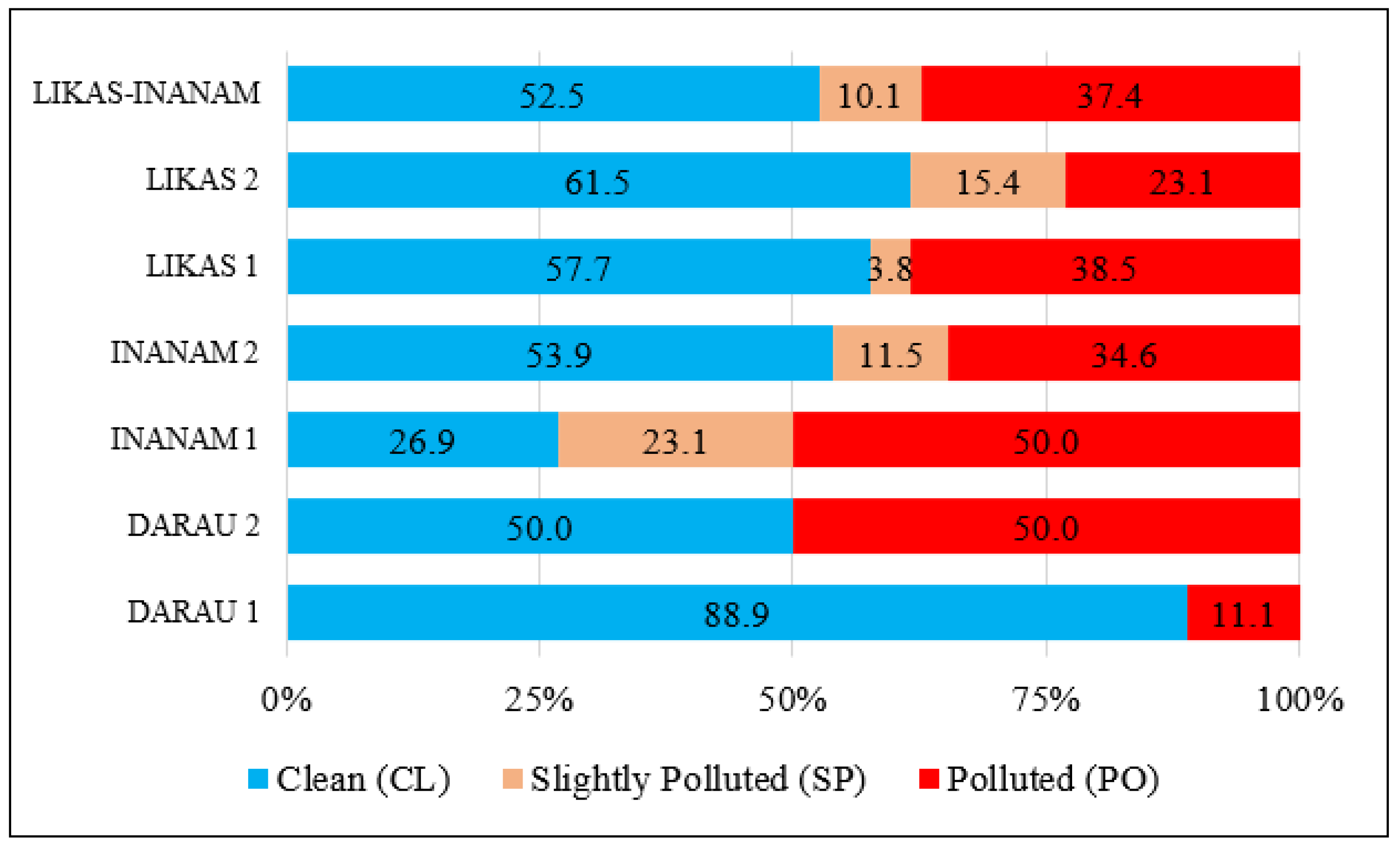
3.1. Pattern of the DoE-WQI
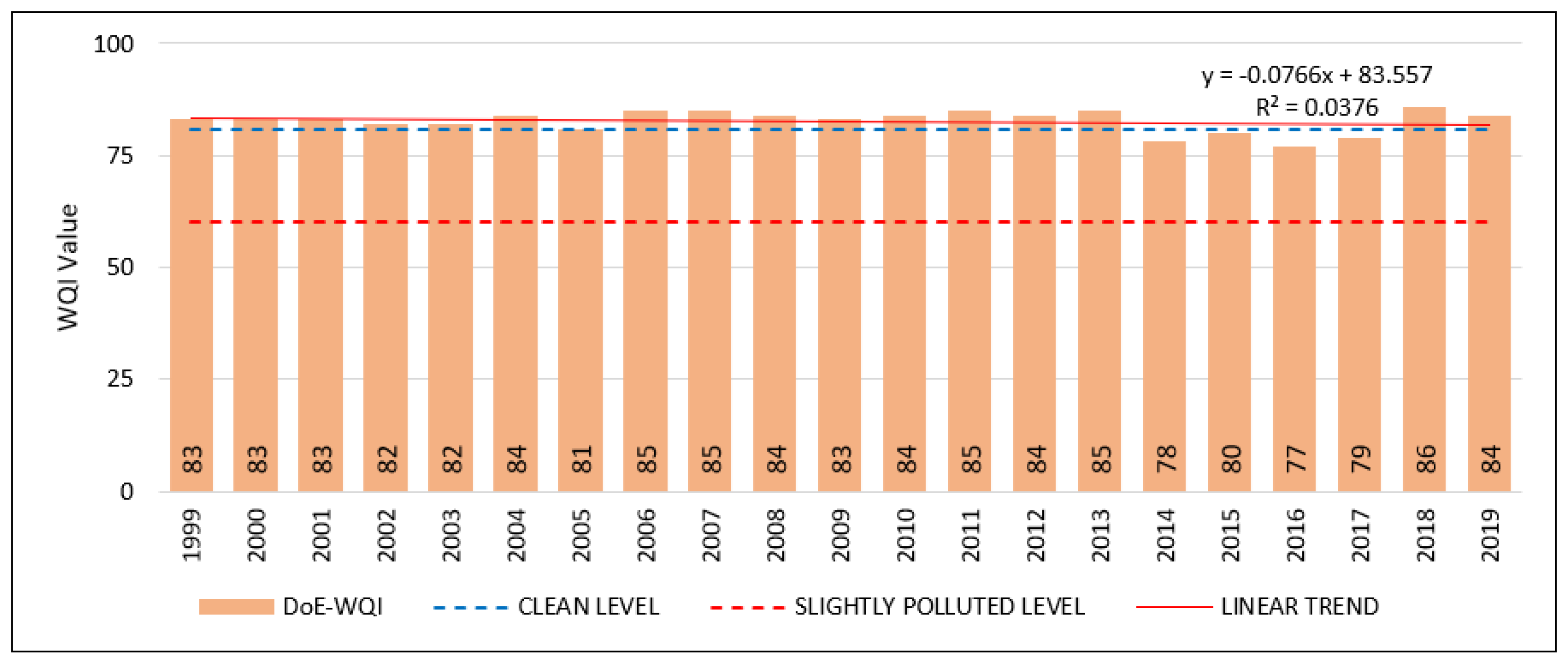
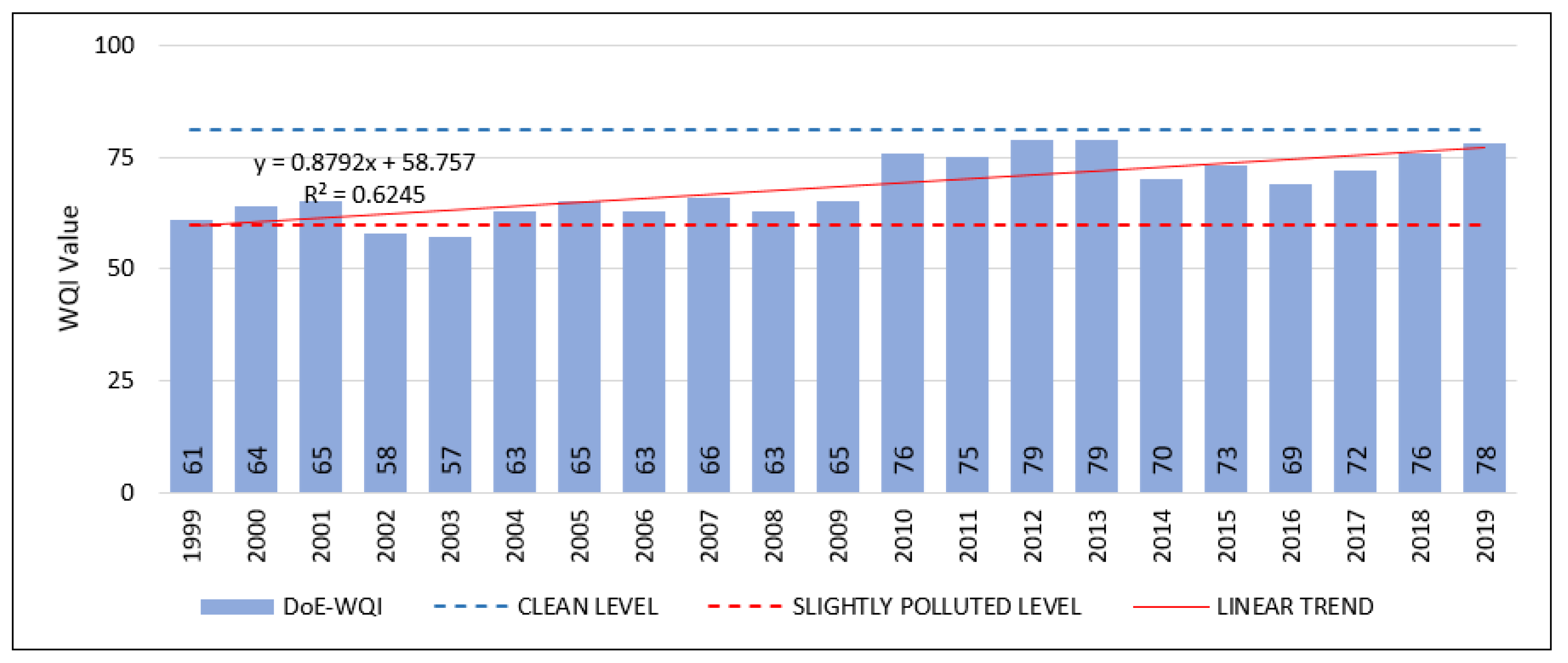
3.2. Trend of DoE-WQI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Postel, S.; Richter, B. Rivers for Life; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Paul, M.J.; Taulbee, W.K. Stream ecosystem function in urbanizing landscapes. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis. In ZooKeys; Island Press: Singapore, 2005; p. 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.V. Nutrient Budget of the River Maine, Co. Antrim. Agric. Water Qual. Tech. Bull. Lond. 1976, 32, 315–339. [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran, E.; Nellemann, C.; Baker, E.; Bos, R.; Osborn, D.; Savelli, H. Sick Water? The Central Role of Wastewater Management in Sustainable Development. A Rapid Response Assessment; UNEP Publication: Nairobi, Kenya, 2010; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/9156 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Rashleigh, B.; Lagutov, V.; Salathe, T. Ecosystem Services of Rivers: The Don River (Russian Federation) and Roanoke River (USA). In Environmental Security in Watersheds: The Sea of Azov; Lagutov, V., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Twort, A.C.; Law, F.M.; Crowley, F.W. Bekalan Air; Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1994.
- Hongyu, D.; Xuejun, S.; Hong, J.; Zenghui, K.; Zhibao, W.; Yongli, C. Research on the cooling island effects of water body: A case study of Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Niemczynowicz, J. Urban hydrology and water management–present and future challenges. Urban Water 1999, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habersack, H.; Hein, T.; Stanica, A.; Liska, I.; Mair, R.; Jäger, E.; Hauer, C.; Bradley, C. Challenges of river basin management: Current status of, and prospects for, the River Danube from a river engineering perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 828–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- N-Water. In Tackling a Global Crisis: International Year of Sanitation 2008; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Available online: http://esa.un.org/iys/docs/IYS_flagship_web_small.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- UNESCO. The Global Water Quality Challenge & SDGs. 2021. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/waterquality-iiwq/wq-challenge (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- USDA. What Is a Watershed? Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/pa/water/watersheds/?cid=nrcs142p2_018202 (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Gurnell, A.; Lee, M.; Souch, C. Urban rivers: Hydrology, geomorphology, ecology and opportunities for change. Geogr. Compass 2007, 1, 1118–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Mohmadisa, H.; Mohd Hairy, I.; Mohamad Suhaily Yusri, C.N. Land Use Change and River Water Quality Level in Ipoh City, Perak. Malays. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 10, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Spatial and temporal variation in water quality of the Huangpu River in Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2015, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Kimirei, I.A.; Yu, C.; Shen, Q.; Gao, Q. Assessment of urban river water pollution with urbanization in East Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 40812–40825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafar, A.; Dollah, R.; Sakke, N.; Mapa, M.T.; Joko, E.P.; Radzi, M.M.; Imang, U.; Ahmad, S.A.; Wahab, A.A.; Sipatau, J.A. Tourism and natural hazards: River landform changes due to geohazards and its influence on ecotourism economy development in Sabah, Malaysia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, A.; Sakke, N.; Mapa, M.T.; Dollah, R.; George, F. The Adaptive Capacity in Flood Hazards and Enhancement of Local Knowledge among Floodplain Community in Beaufort District, Sabah, Malaysia. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Impacts Responses 2022, 14, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, A.; Sakke, N.; Mapa, M.T.; Dollah, R.; Joko, E.P. Assessing flood risks and the coping strategy: A community adaptation in floodplain areas at Beaufort district in east Malaysia. Disaster Adv. 2022, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Peng, S. Assessing the effects of landscape pattern on river water quality at multiple scales: A case study of the Dongjiang River watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, J.; Dujardin, J.; Reggers, R.; Bashir, I.; Canters, F.; Batelaan, O. Mapping impervious surface change from remote sensing for hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.P.; Khu, S.T.; Yu, X.Y. Spatial variations of storm runoff pollution and their correlation with land-use in a rapidly urbanizing catchment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.I.; Lundin, J.I.; Mitchell, C.J.; Davis, J.W.; Young, G.; Scholz, N.L.; McIntyre, J.K. An urban stormwater runoff mortality syndrome in juvenile coho salmon. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 214, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Asawa, T.; Murakami, A.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, H.S. Influence of urban form on the cooling effect of a small urban river. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 183, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Osterlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC (National Research Council). Urban Stormwater Management in the United States; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Sanchez, E.; Colmenarejo, M.E.; Vicente, J.; Rubio, A.; Garcia., M.G.; Travieso., L.; Borja., R. Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2007, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesiri, B.; Liu, A.; Goonetilleke, A. Impact of global warming on urban stormwater quality: From the perspective of an alternative water resource. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Shang, R.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2018, 144, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaafar, A.A.; Ali, S.I.; El-Shawadfy, M.A.; Salama, Z.A.; Sękara, A.; Ulrichs, C.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Ascorbic Acid Induces the Increase of Secondary Metabolites, Antioxidant Activity, Growth, and Productivity of the Common Bean under Water Stress Conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, M.; Jamil, N.R.; Abdullah, A.F.B. Impact of land uses on water quality in Malaysia: A review. Ecol. Process. 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavaty, S.; Sharma, T.R.; Sureshkumar, P. Water quality index of river Cauvery in Tiruchirappalli district, Tamilnadu. Arch. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Haddis, A.; Getahun, T.; Mengistie, E.; Jemal, A.; Smets, I.; van der Bruggen, B. Challenges to surface water quality in mid-sized African cities: Conclusions from Awetu-Kito Rivers in Jimma, south-west Ethiopia. Water Environ. J. 2014, 28, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesilind, P.A.; Peirce, J.J.; Weiner, R. Kejuruteraan Alam Sekitar, 2nd ed.; UTM Publisher: Skudai, Malaysia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Bao, J.; Goddard III, W.A.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. High-performance bifunctional porous non-noble metal phosphide catalyst for overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bega, J.M.M.; Albertin, L.L.; de Oliveira, J.N. Development of water quality index as a tool for urban water resources management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18588–18600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhapi, I.; Tirivarombo, S. Sewage discharges and nutrient levels in Marimba River, Zimbabwe. Water SA 2004, 30, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capps, K.A.; Bentsen, C.N.; Ramírez, A. Poverty, urbanization, and environmental degradation: Urban streams in the developing world. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonam, T.; Tanushree, B.; Sukalyan, C. Water quality indices-important tools for water quality assessment: A review. Int. J. Adv. Chem. 2013, 1, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Belt, K.T. The urban watershed continuum: Evolving spatial and temporal dimensions. Urban Ecosyst. 2012, 15, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Feng, P.; Dong, L. The effects of surface pollution on urban river water quality under rainfall events in Wuqing district, Tianjin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, S. Perbandaran, Iklim Bandar & Pencemaran Udara; Dewan Bahasa & Pustaka: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1982.
- Jahi, J.M. Impak Pembangunan Terhadap Alam Sekitar; UKM Publisher: Bangi, Malaysia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- JPS Selangor. Pengurusan Sungai. 2019. Available online: http://water.selangor.gov.my/index.php/ms/maklumat-jabatan/fungsi-jabatan/pengurusan-sungai (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- JPS. Kompendium Data Dan Maklumat Asas JPS. 2018. Available online: https://www.water.gov.my/jps/resources/Compendium/kompendium2018.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Ng, K.C. Sources and spatial distribution of heavy metal pollution in the Langat River Basin, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7457–7469. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, M.P.; Takada, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ohno, K.; Yamada, J.; Kouno, E.; Kumata, H. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azyana, Y.; Na, N.N. Land use and catchment size/scale on the water quality deterioration of Kinta River, Perak, Malaysia. Malays. J. Sci. 2012, 31, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahady, T.D. Degradation and Improvement of Urban River Water Quality. In Water Quality-Factors and Impacts; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.; Townsend, K.; Hale, R.; Sharley, D.; Pettigrove, V. How is ecosystem health defined and measured? A critical review of freshwater and estuarine studies. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliki Abdullah, M.S.; Hapani, M.; Muhamad Salleh, N.F.; Wan Alias, W.M.S. Ecosystem health assessment of sungai Pengkalan Chepa basin: Water quality and heavy metal analysis. Sains Malays. 2020, 49, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, M. Ecosystem health indicators. In Encyclopaedia of Ecology, 2nd ed.; Issue April; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, A.; Abdul Maulud, K.N.; Pratiwi, D.; Phelia, A.; Rossi, F.; Zuhairi, N.Z. Trend of Water Quality Status in Kelantan River Downstream, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Rekayasa Sipil 2020, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ithnin, I.; Sakke, N. Influence of land use on water quality: A study on the Linggi River Basin, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Indones. J. Geogr. 2004, 36, 39–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ma’arof, N.; Hua, A.K. Kualiti air Sungai UTM: Satu penilaian awal berpandukan enam parameter Indeks Kualiti Air. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2015, 1, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, A.; Idris, A.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Muiby, S.A. A Revised Water Quality Index Proposed for the assessment of surface water quality in Malaysia. Pollut. Res. 2003, 26, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Dollah, R.; Jafar, R.; Joko, E.P.; Sakke, N.; Mapa, M.T.; Atang, C.; Hung, C.V.; George, F. Perception of youth in East Malaysia (Sabah) towards the Malaysia National COVID-19 Immunisation Programme (PICK). J. Public Health Dev. 2022, 20, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Mohamad, S. Kelangsungan dominasi Barisan Nasional di Sabah dalam Pilihan Raya Umum ke-13. Kaji. Malays. 2014, 32, 171–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hafizy, A.M. The Sources of Pollution in the Likas and Inanam River Basin in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia. Sosiohumanika 2009, 2, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Google Earth Pro 7.3. Inanam-Likas Basin Landuse 5°58′54.59″ N, 116°9′13.24″ E, Elevation 0M. Eye Alt 21.34 km. 2013. Available online: http://www.google.com/earth/index.html (accessed on 4 July 2023).
- JUPEM. Malaysia: Kota Kinabalu (Peta Topografi); No Siri 5/116/1; Pengarah Pemetaan: Negara, Malaysia, 1984.
- JUPEM. Malaysia: Telipok (Peta Topografi); No Siri 6/116/13; Pengarah Pemetaan: Negara, Malaysia, 1982.
- DOE (Department of Environment Malaysia). Environmental Quality Report 2018; Department of Environment Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2019.
- Herman, U.L.; Zamali, T.; Ajimi, J. Fuzzy Assessment for Water Quality in Inanam Likas River Basin, Sabah, East of Malaysia. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2016, 6, 8013–8019. [Google Scholar]
- JAS. Data Kualiti Air Lembangan Likas 2014–2018; Department of Environment: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2019.
- JAS. Environmental Quality Report 2019; Department of Environment: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2019.
- DOE (Department of Environment Malaysia). Development of Water Quality Criteria and Standards for Malaysia; Department of Environment: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1985.
- Anhar, S. Kualiti dan Pencemaran Air di Malaysia. In Alam Sekitar dan Pengurusannya di Malaysia; Sham, S., Samad, H.A., Jamaluddin, M.J., Eds.; Working Group on Urban Ecosystems Malaysian National MAB Committee—UNESCO: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1993; pp. 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Advanced Studies. Water Quality Criteria and Standards for Malaysia; Consultant Group on Water Quality, Institute of Advance Study, Universiti Malaya: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1986; Volume 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naubi, I.; Zardari, N.H.; Shirazi, S.M.; Ibrahim, N.F.B.; Baloo, L. Effectiveness of water quality index for monitoring Malaysian river water quality. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, T.; Määttä, A.; Anttila, P.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Amnell, T. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann-Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimates—The Excel Template Application Makesens; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002.
- Hashim, M.; Nayan, N.; Setyowati, D.L.; Said, Z.M.; Mahat, H.; Saleh, Y. Analysis of Water Quality Trends Using the Mann-Kendall Test and Sen’s Estimator of Slope in a Tropical River Basin. Pollution 2021, 7, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakke, N.; Mapa, M.T.; Saudi, A. Analysis of several hydrological-drought duration parameters in Mengalong River Basin, Sipitang, Sabah. Malays. J. Geosci. 2018, 2, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Ahmadi, K.; Ramavandi, B. Trend analysis of long-term water quality for Zohre River water, Iran. Pollut. Res. 2015, 34, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha, A. Detecting surface water quality trends using Mann-Kendall tests and Sen’s slope estimates. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2013, 1, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tabari, H.; Marofi, S.; Ahmadi, M. Long-term variations of water quality parameters in the Maroon River, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lento, J.; Dillon, P.J.; Somers, K.M. Evaluating long-term trends in littoral benthicmacroinvertebrate communities of lakes recovering from acid deposition. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 7175–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.N.; Malik, M.F. Factors affecting water pollution: A review. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2017, 7, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, H.; Jin, W.; Li, H.; He, Z. Urban river pollution control in developing countries Nat. Sustainability 2019, 2, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Haryati, S.; Nurasyikin, M.; Azlina, M.Y.; Sharifah Meryam, S.M. Status kualiti air sungai di beberapa kawasan luar bandar, di negeri Johor dan kesannya kepada kehidupan. Asian J. Environ. Hist. Herit. 2018, 2, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Shao, Q.; Ding, X. The impact of socioeconomic system on the river system in a heavily disturbed basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, J.T.; Reddy, V.R. Impact of irrigation water quality on human health: A case study in India. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2800–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J. The urban environment and health in a world of increasing globalization: Issues for developing countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nyenje, P.M.; Havik, J.C.N.; Foppen, J.W.; Muwanga, A.; Kulabako, R. Understanding the fate of sanitation-related nutrients in a shallow sandy aquifer below an urban slum area. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 164, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phiri, O.; Mumba, P.; Moyo, B.H.Z.; Kadewa, W. Assessment of the impact of industrial effluents on water quality of receiving rivers in urban areas of Malawi. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 2, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deaton, M.L.; Winebrake, J.J. Dynamic Modeling of Environmental Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada. Water Quality Source Book—A Guide to Water Quality Parameter; Inland Waters Directorate Water Quality Branch Ottawa: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1979.
- Hur, J.; Cho, J. Prediction of BOD, COD, and total nitrogen concentrations in a typical urban river using a fluorescence excitation-emission matrix with PARAFAC and UV absorption indices. Sensors 2012, 12, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, I. Sediment: A major river management issue. In Rivers: Towards Sustainable Development; Chan, N.W., Ed.; USM Publisher: Penang, Malaysia, 2000; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Goher, M.E.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Monien, I.A.; Fahmy, A.H.; El-Sayed, S.M. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality and Heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan Ruslan, I. Hakisan tanih dan kemerosotan tanah: Beberapa kes di Malaysia. In Alam Sekitar dan Kesejahteraan Masyarakat Malaysia; Jamaluddin, M.J., Ed.; Pusat Pengajian Siswazah UKM: Bangi, Malaysia, 2004; pp. 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, C.; Makeschin, M.; Weiß, H.; Lorz, C. Sediments in urban river basins: Identification of sediment sources within the Lago Paranoá catchment, Brasilia DF, Brazil–using the fingerprint approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, O.H.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Needelman, B.A.; Gellis, A.C. Suspended-sediment source in an urban watershed, Northeast Banch Anacostia River, Maryland. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramaningsih, V.; Suprayogi, S.; Suprayogi, S. Pollution load capacity analysis of BOD, COD, and TSS in Karang Mumus River, Samarinda. Indones. J. Chem. 2020, 20, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
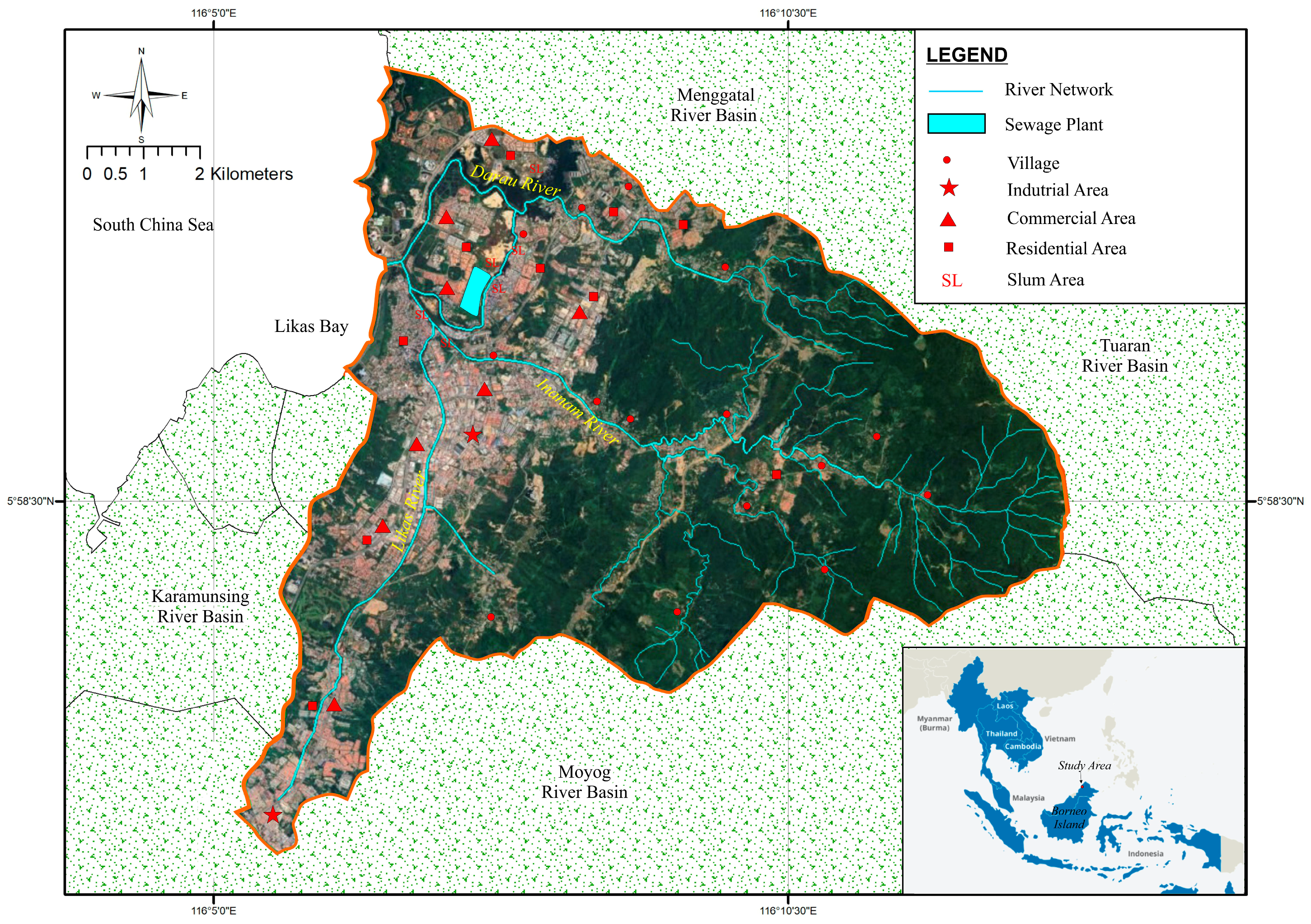

| Station | Geographical Coordinates | Frequency of Sampling/Year | Number of Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1—DARAU 1 | 116°8′38.46″ E 6°1′10.57″ N | 2017 (3) and 2018 (6) | 9 |
| D2—DARAU 2 | 116°7′4.97″ E 6°1′10.17″ N | 2014–2017 (5) and 2018 (6) | 26 |
| I1—INANAM 1 | 116°8′18.94″ E 5°59′43.18″ N | 2014–2017 (5) and 2018 (6) | 26 |
| I2—INANAM 2 | 116°11′48.53″ E 5°58′32.64″ N | 2014–2017 (5) and 2018 (6) | 26 |
| L1—LIKAS 1 | 116°7′8.82″ E 5°59′2.45″ N | 2014–2017 (5) and 2018 (6) | 26 |
| L2—LIKAS 2 | 116°7′8.66″ E 5°59′36.70″ N | 2014–2017 (5) and 2018 (6) | 26 |
| Sub-Index and Water Quality Index | Index Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Slightly Polluted | Polluted | |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) | 91–100 | 80–90 | 0–79 |
| Ammoniacal Nitrogen (NH3-N) | 92–100 | 71–91 | 0–70 |
| Suspended Solids (SS) | 76–100 | 70–75 | 0–69 |
| Water Quality Index (DoE-WQI) | 81–100 | 60–80 | 0–59 |
| Station | Min | Max | Mean (Median) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARAU 1 | 60.4 | 93.6 | 73.9 (72.8) | 11.8 |
| DARAU 2 | 57.2 | 78 | 69.2 (69.1) | 5.8 |
| INANAM 1 | 52.3 | 82.5 | 71.9 (73.7) | 7 |
| INANAM 2 | 69.5 | 86.8 | 79.1 (80.1) | 5.7 |
| LIKAS 1 | 73.7 | 92.2 | 83.6 (84.8) | 5.7 |
| LIKAS 2 | 59.8 | 94.5 | 87.0 (89.4) | 8.5 |
| LIKAS-INANAM | 52.3 | 94.5 | 77.9 (77.3) | 9.6 |
| Station | Min | Max | Mean (Median) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARAU 1 | 43.2 | 91.9 | 74.4 (79.3) | 14.6 |
| DARAU 2 | 38.3 | 83.5 | 66.9 (68.8) | 13.6 |
| INANAM 1 | 34.0 | 91.9 | 70.7 (78.1) | 16.0 |
| INANAM 2 | 48.6 | 96.2 | 82.3 (96.5) | 13.9 |
| LIKAS 1 | 51.5 | 96.6 | 85.5 (91.9) | 14.0 |
| LIKAS 2 | 36.1 | 96.6 | 80.5 (83.5) | 17.5 |
| LIKAS-INANAM | 34.0 | 96.6 | 77.0 (79.3) | 16.3 |
| Station | Min | Max | Mean (Median) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARAU 1 | 6.4 | 99.6 | 38.8 (10.7) | 45.6 |
| DARAU 2 | 12.5 | 32.4 | 22.6 (20.2) | 6.7 |
| INANAM 1 | 32.7 | 48.0 | 39.1 (38.6) | 5.4 |
| INANAM 2 | 48.8 | 66.4 | 57.7 (57.7) | 4.8 |
| LIKAS 1 | 67.1 | 83.7 | 73.9 (72.2) | 5.5 |
| LIKAS 2 | 84.8 | 99.5 | 93.7 (93.2) | 4.0 |
| LIKAS-INANAM | 6.4 | 99.6 | 56.2 (56.8) | 27.5 |
| Station | Min | Max | Mean (Median) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARAU 1 | 66.5 | 92.2 | 80.3 (79.7) | 7.1 |
| DARAU 2 | 50 | 96.9 | 72.4 (71.7) | 15.5 |
| INANAM 1 | 10.9 | 90.5 | 69.7 (69.6) | 15.3 |
| INANAM 2 | 8 | 93.9 | 69.9 (77.1) | 21.7 |
| LIKAS 1 | 25.6 | 96.9 | 73.5 (80.6) | 19.1 |
| LIKAS 2 | 16.5 | 96.9 | 79.7 (87.2) | 19.6 |
| LIKAS-INANAM | 8 | 96.9 | 73.5 (77.3) | 18.1 |
| Inanam | Likas | |
|---|---|---|
| Kendall’s tau | 0.03 | 0.58 |
| S | 5 | 120 |
| Var(S) | 1061.67 | 1087.33 |
| p-value | 0.902 | 0.0003 |
| alpha | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Sen’s Slope (Q) | −0.235 | 0.556 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakke, N.; Jafar, A.; Dollah, R.; Asis, A.H.B.; Mapa, M.T.; Abas, A. Water Quality Index (WQI) Analysis as an Indicator of Ecosystem Health in an Urban River Basin on Borneo Island. Water 2023, 15, 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152717
Sakke N, Jafar A, Dollah R, Asis AHB, Mapa MT, Abas A. Water Quality Index (WQI) Analysis as an Indicator of Ecosystem Health in an Urban River Basin on Borneo Island. Water. 2023; 15(15):2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152717
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakke, Nordin, Adi Jafar, Ramli Dollah, Abdul Hair Beddu Asis, Mohammad Tahir Mapa, and Azlan Abas. 2023. "Water Quality Index (WQI) Analysis as an Indicator of Ecosystem Health in an Urban River Basin on Borneo Island" Water 15, no. 15: 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152717
APA StyleSakke, N., Jafar, A., Dollah, R., Asis, A. H. B., Mapa, M. T., & Abas, A. (2023). Water Quality Index (WQI) Analysis as an Indicator of Ecosystem Health in an Urban River Basin on Borneo Island. Water, 15(15), 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152717








