Catalytic Performance of Fe-Rich Sludge in Pyrolysis of Waste Oil Scum as Volatiles and Magnetic Char
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
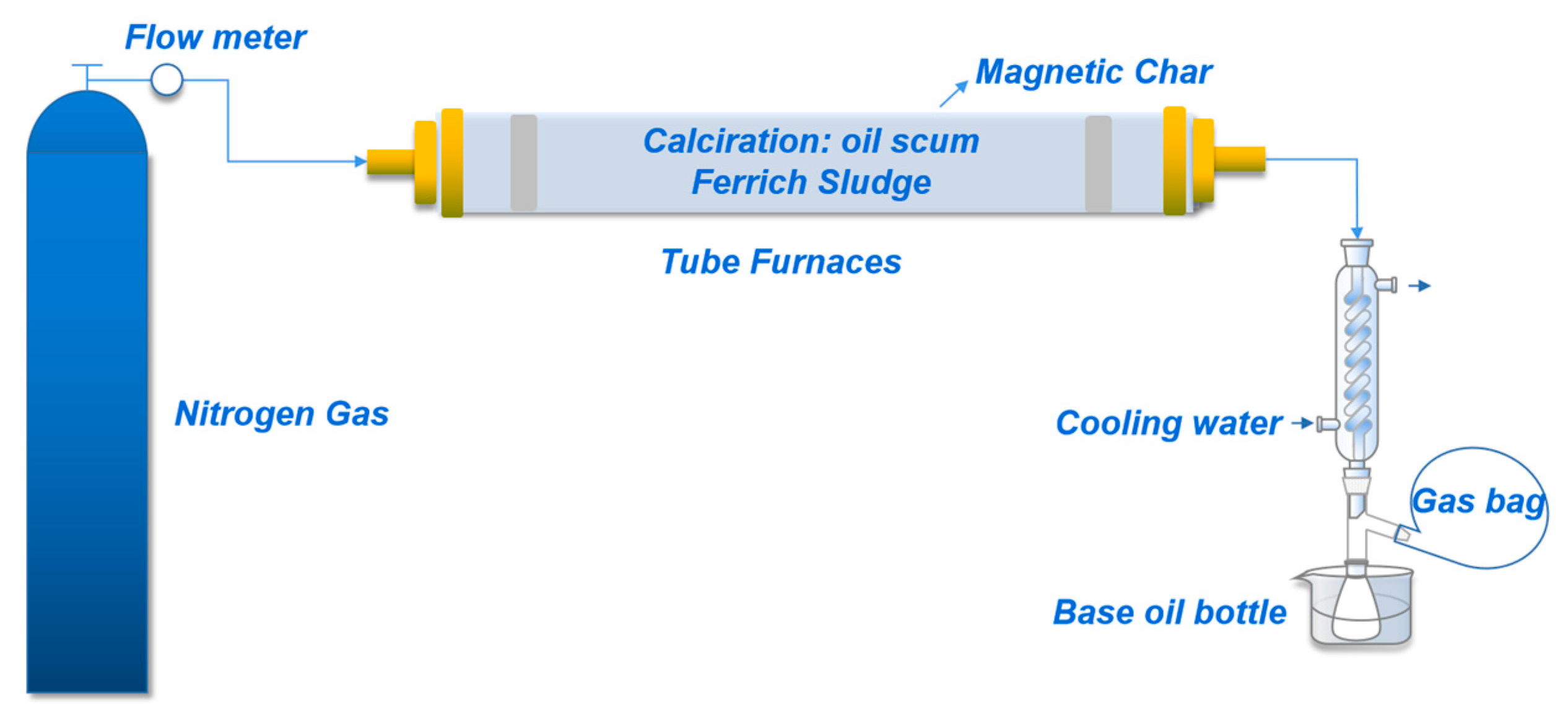
2.1. Oil Scum Pyrolysis
2.2. Chemical Reagent Experiment
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
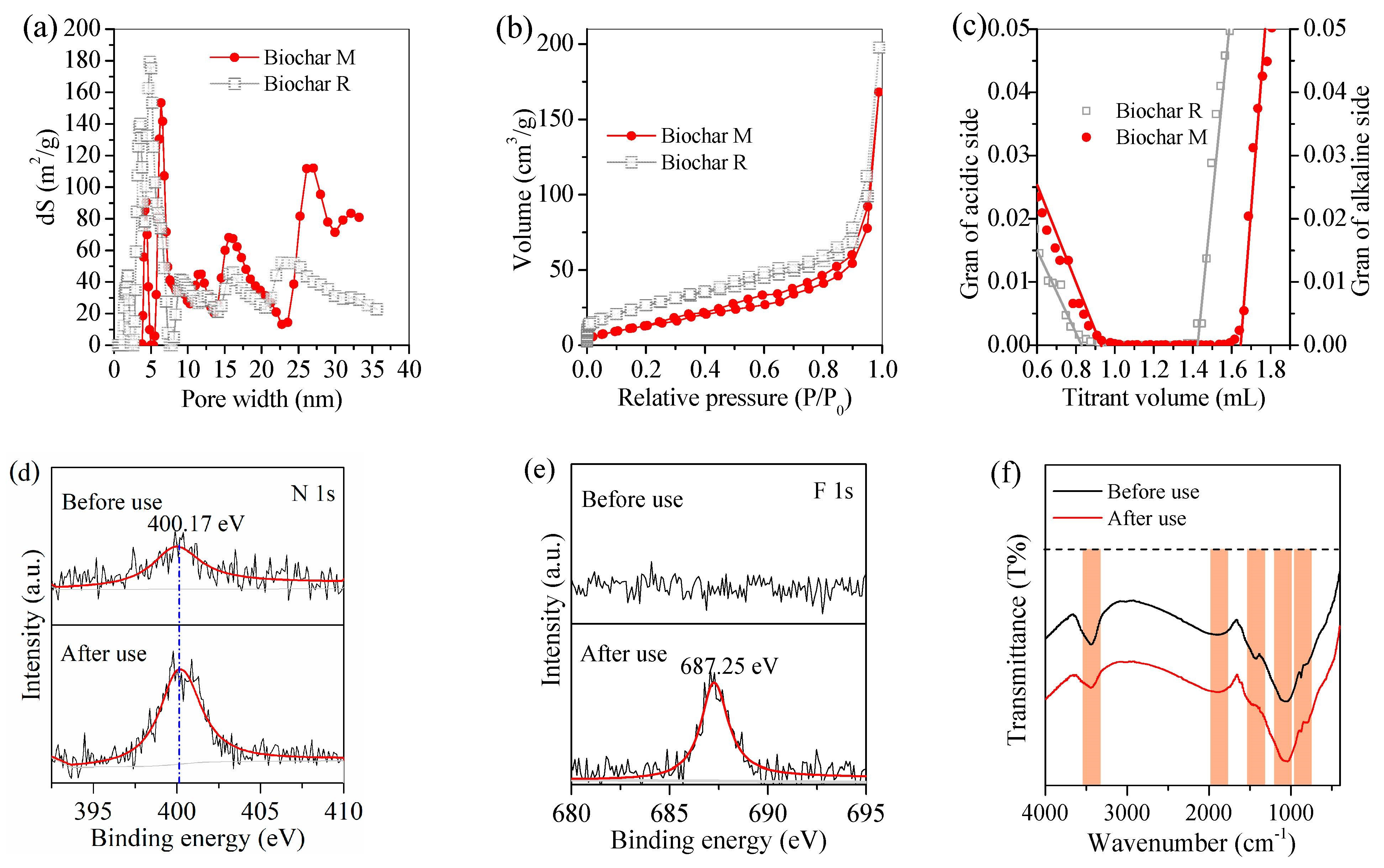
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
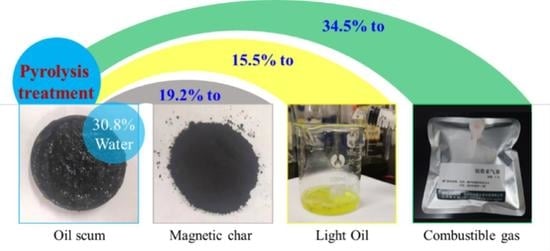
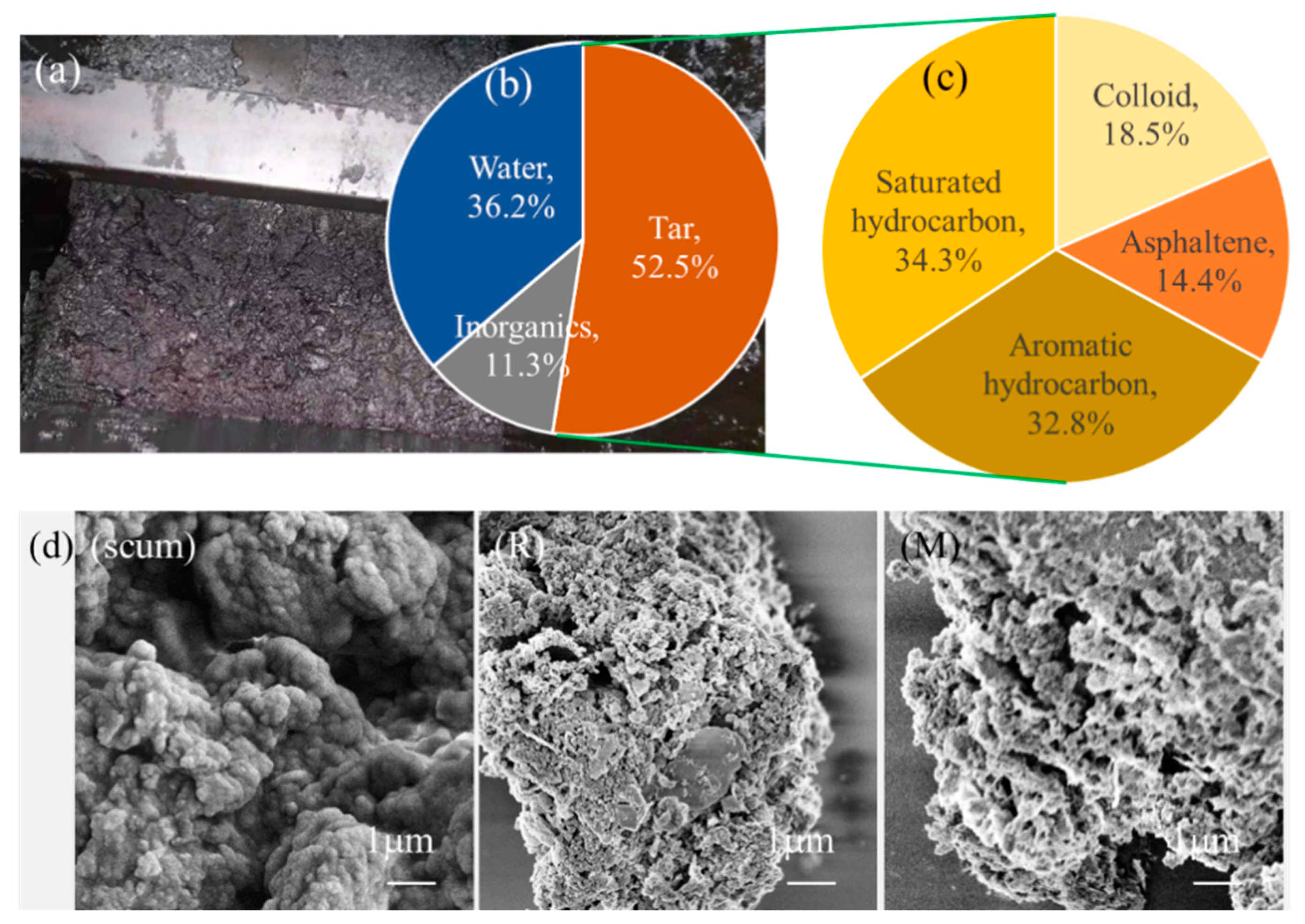
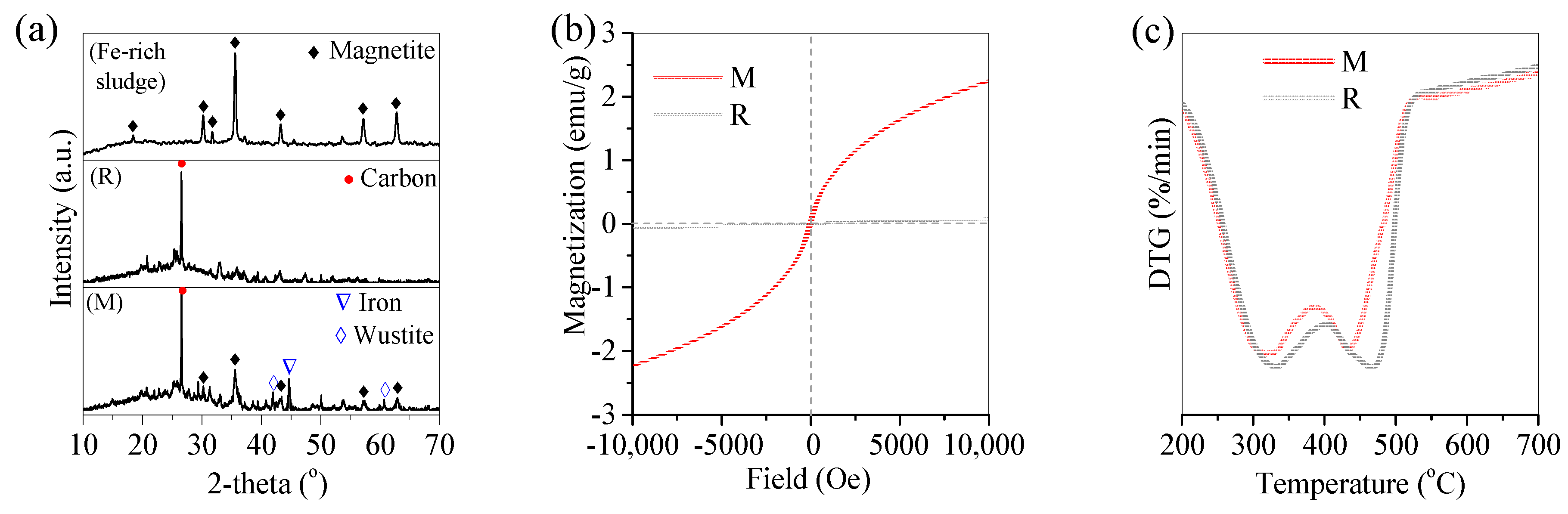
3.1. Pyrolysis of Oil Scum by Fe-Rich Sludge
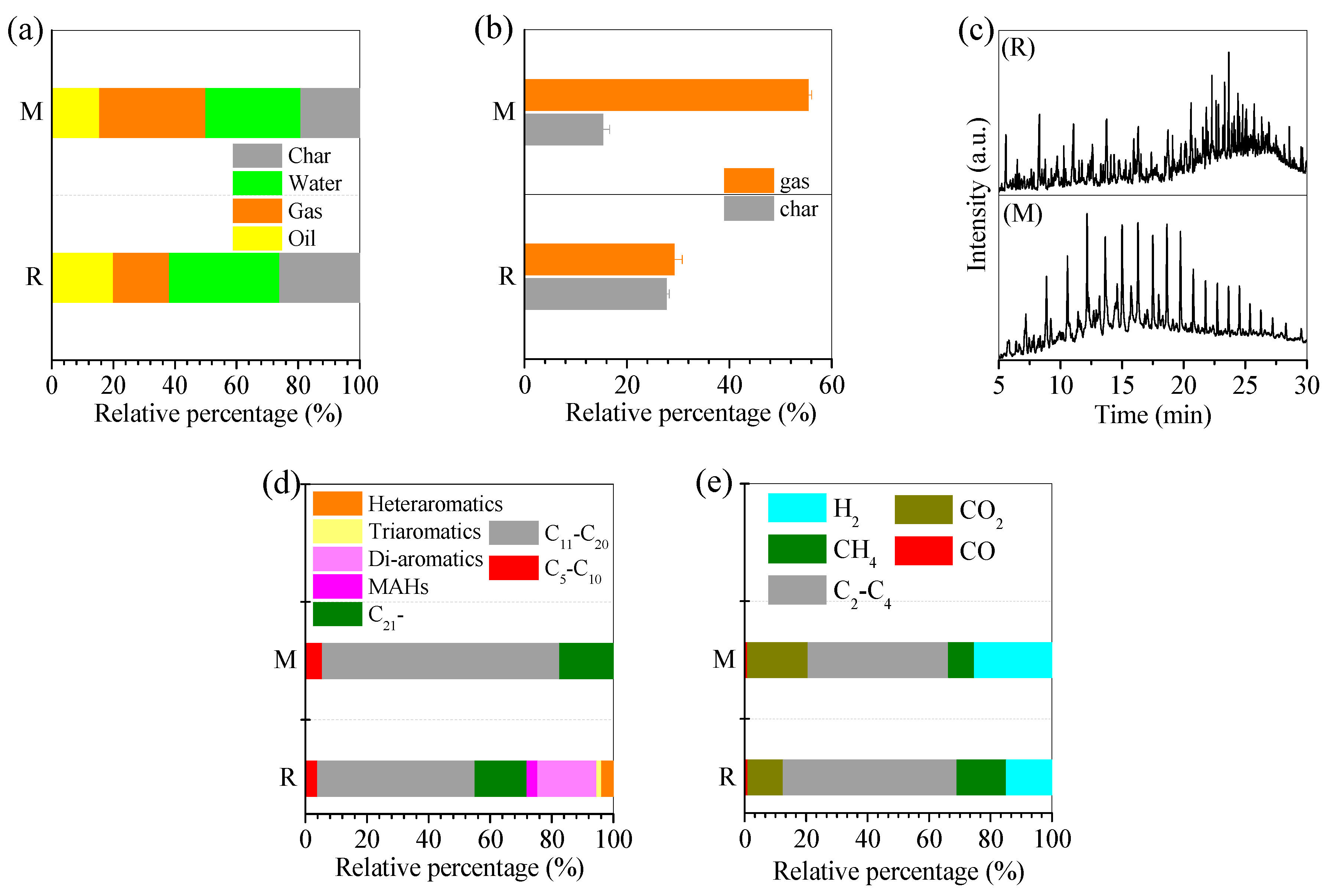
3.2. Pyrolysis Mechanism of Oil Scum
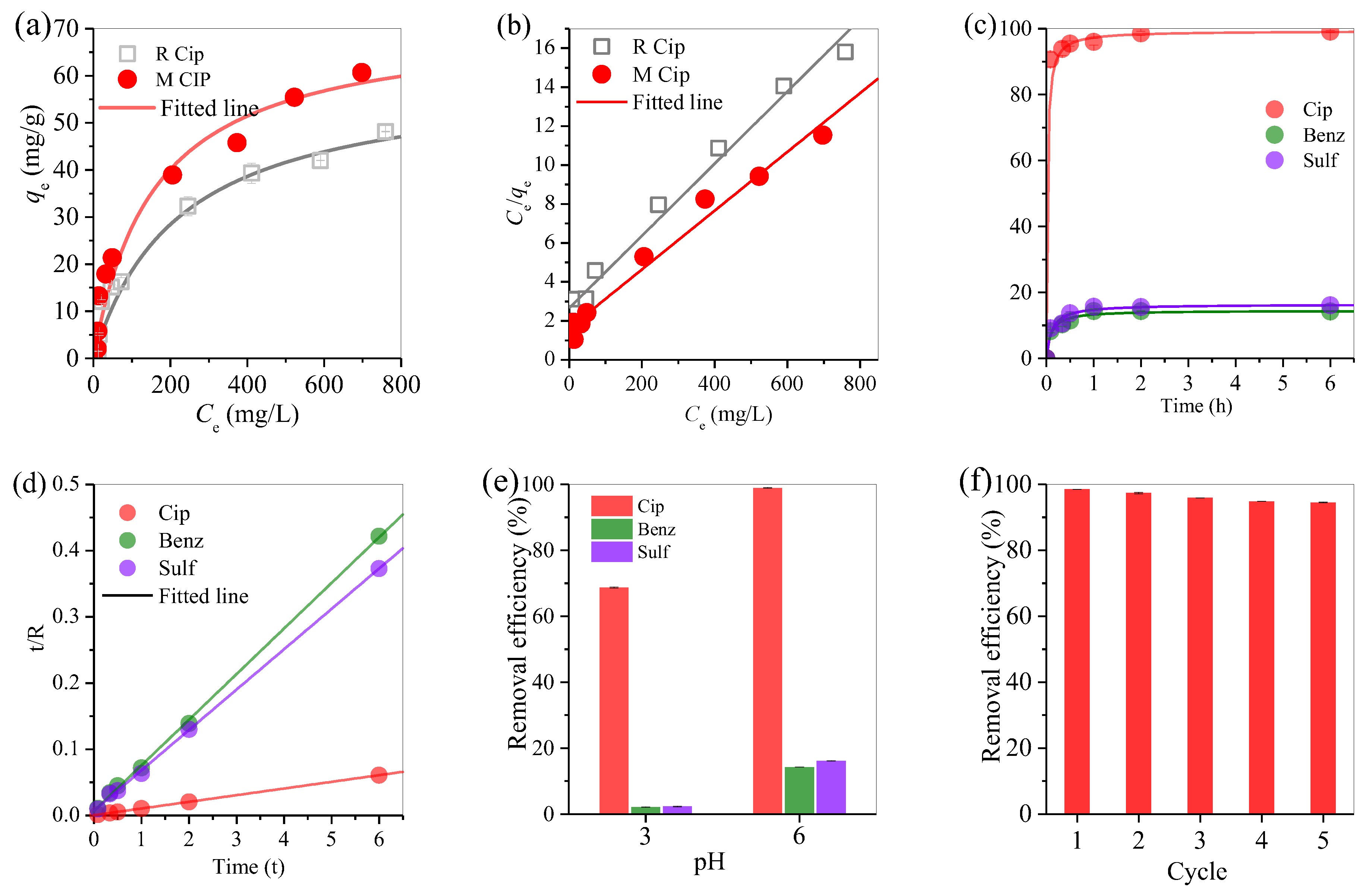
3.3. Adsorption Performance of Biochar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, N.K.; Suganya, K.; Sivapragsam, C.; Vanitha, S. Current Trends on Oil Sludge Characterization, Toxicity and Treatment Systems. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2020, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighat, M.; Majidian, N.; Hallajisani, A. Production of bio-oil from sewage sludge: A review on the thermal and catalytic conversion by pyrolysis. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 42, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Pandey, S.; Sumathy, K. Experimental investigation on waste heat recovery by refinery oil sludge incineration using fluidised-bed technique. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1998, 33, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiligiannis, A.; Tsiliyannis, C. Oil refinery sludge and renewable fuel blends as energy sources for the cement industry. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, J.; Zeng, G. Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Show, M.; Ong, S. Recovery of residual oil from the centrifuge sludge of a palm oil mill: Effect of enzyme digestion and surfactant treatment. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, H. Screening of inexpensive and efficient catalyst for microwave-assisted pyrolysis of ship oil sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Ali, M.; Chi, Y. Aromatic recovery from distillate oil of oily sludge through catalytic pyrolysis over Zn modified HZSM-5 zeolites. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 128, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Ates, F.; Yildirir, E.; Miskolczi, N. Investigation of thermal degradation kinetics and catalytic pyrolysis of industrial sludge produced from textile and leather industrial wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milato, J.V.; Frana, R.J.; Rocha, A.S.; Calderari, M. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of oil sludge with HDPE to obtain paraffinic products over HUSY zeolites prepared by dealumination and desilication. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 151, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, J.; Hou, H. A combination of solvent extraction and freeze thaw for oil recovery from petroleum refinery wastewater treatment pond sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelnasr, D.; Al Zubaidy, E.A. Treatment and Recovery of Oil-Based Sludge Using Solvent Extraction. In International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference; OnePetro: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Shu, Y.; Li, F.; Peng, G. Bimetallic catalysts as electrocatalytic cathode materials for the oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cell: A review. Green Energy Environ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Song, J.; Fan, W.; Yu, H.; Bian, D.; Huo, M. Synthesis and characterization of a magnetic adsorbent from negatively-valued iron mud for methylene blue adsorption. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.; Dong, G.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Huo, M.; Xu, K.; Liu, M. Recycling of groundwater treatment sludge to prepare nano-rod erdite particles for tetracycline adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, T.; Qu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Su, T.; Huo, Y. Effective recycling of Cu from electroplating wastewater effluent via the combined Fenton oxidation and hydrometallurgy route. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Su, T.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y. Simultaneous removal of sulfate and nitrate from real high-salt flue gas wastewater concentrate via a waste heat crystallization route. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Sun, T.; Liang, D.; Yu, H. Upcycling of Electroplating Sludge to Prepare Erdite-Bearing Nanorods for the Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater Effluent. Water 2020, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Tong, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. Non-free Fe dominated PMS activation for enhancing electro-Fenton efficiency in neutral wastewater. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 928, 117062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Dongxu, L.; Hongyu, C.; Suiyi, Z.; Xianze, W.; Jiakuan, Y.; Xinfeng, X.; Eskola, J.; Dejun, B. Review of resource utilization of Fe-rich sludges: Purification, upcycling, and application in wastewater treatment. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 460–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. The occurrence and fate of tetracyclines in two pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants of Northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.C.; Kolvenbach, B.A.; Nunes, O.C.; Corvini, P.F. Biodegradation of antibiotics: The new resistance determinants—Part I. New Biotechnol. 2020, 54, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Kan, Z.; Jia, Y. Catalytic ozonation mechanisms of Norfloxacin using Cu–CuFe2O4. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Janjani, H. Antibiotics adsorption from aqueous solutions using carbon nanotubes: A systematic review. Toxin Rev. 2018, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, S.; Ru, X.; Shu, X. Sulfur defect and Fe (III)(hydr) oxides on pyrite surface mediate tylosin adsorption in lake water: Effect of solution chemistry and dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 90248–90258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, A.; Adami, S. Adsorption and thermodynamic study of Cephalosporins antibiotics from aqueous solution onto MgO nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Dong, G.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Fan, W.; Zhou, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Hydrothermal synthesis of a magnetic adsorbent from wasted iron mud for effective removal of heavy metals from smelting wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22710–22724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrakhimov, V.; Abdrakhimova, E. Study of the distribution of iron oxides in intershale clay and oil sludge porous filler with Mossbauer spectroscopy. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2019, 53, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chi, Y. Preparation of Fe-char catalyst from tank cleaning oily sludge for the catalytic cracking of oily sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 139, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bendary, N.; El-Etriby, H.K.; Mahanna, H. Reuse of adsorption residuals for enhancing removal of ciprofloxacin from wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2021, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, G.; Pan, L.; Li, C.; You, F.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Shang, X. Study of ciprofloxacin removal by biochar obtained from used tea leaves. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Sorption of the Antimicrobial Ciprofloxacin to Aluminum and Iron Hydrous Oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Ji, M.; Qin, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, S. Catalytic Performance of Fe-Rich Sludge in Pyrolysis of Waste Oil Scum as Volatiles and Magnetic Char. Water 2023, 15, 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142637
Liu J, Ji M, Qin J, Zhu J, Zhu S. Catalytic Performance of Fe-Rich Sludge in Pyrolysis of Waste Oil Scum as Volatiles and Magnetic Char. Water. 2023; 15(14):2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142637
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiancong, Manhong Ji, Jiabao Qin, Jia Zhu, and Suiyi Zhu. 2023. "Catalytic Performance of Fe-Rich Sludge in Pyrolysis of Waste Oil Scum as Volatiles and Magnetic Char" Water 15, no. 14: 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142637
APA StyleLiu, J., Ji, M., Qin, J., Zhu, J., & Zhu, S. (2023). Catalytic Performance of Fe-Rich Sludge in Pyrolysis of Waste Oil Scum as Volatiles and Magnetic Char. Water, 15(14), 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142637