Abstract
Waste oil scum is commonly discharged during the air flotation process at oil-bearing wastewater treatment plants and disposed as an additive in cement kilns and/or furnaces. Herein, it was mixed with a magnetite-rich waste sludge and then completely recycled as value-added gas/oil and magnetic char via a facile catalytic pyrolysis route. Results showed that the oil scum was a blackish gel and contained 36.2% water, 52.5% tar, and 11.3% inorganics. After direct pyrolysis, the conversion efficiencies of tar to gas, oil, and char were 30.2%, 41.2%, and 28.6%, respectively, and the generated gas/oil was rich in aromatics. By adding Fe-rich sludge, the efficiencies varied to 57.3%, 26.9%, and 15.8%, respectively, and the gas/oil mainly comprised a chain hydrocarbon. During oil scum pyrolysis, the redox reaction of tar to Fe-rich sludge enabled a cycle of Fe/magnetite to accelerate the cleavage of tar as volatiles and to steadily retard the polycondensation of tar as char. In addition, the added Fe-rich sludge not only activated the rest of the char and created more surface functional groups for contaminant adsorption but also endowed the char with a good magnetic response. Such magnetic char showed a maximum adsorption capacity of ciprofloxacin of 63.5 mg/g, higher than that without the Fe-sludge catalyst, and had ability to selectively adsorb ciprofloxacin from benzoic/sulfanilamide-bearing wastewater. In summary, a ‘waste to treat waste’ strategy was developed to recycle waste oil scum as combustible gas/oil and magnetic char with the addition of magnetite-rich sludge.
1. Introduction
Organic sludge is a gelatinous waste and generated at mass production from oil-bearing wastewater treatment plants. It is commonly comprised of 20–40% tar and 5–35% inorganics [1,2] and is disposed as hazardous waste by landfills. Only a part of it is mixed with fuel to be burned in furnaces and/or cement kilns [3,4]. Such routes are wasteful without the recycling of valuable hydrocarbon and char and also cause serious pollution [1,5] without proper disposal.
Considering that organic components are abundant in the sludge, it is separated as value-added products, e.g., high grade fuel [3], lipids [6], aromatic distillates, and char. Such separation methods included pyrolysis [2,7,8,9,10], freeze thawing [11], hot emulsion, enzyme digestion [6], solvent washing [11,12], and so on. Among such methods, pyrolysis has merit to crack aromatics as volatiles [7]. This enables a practical route to massively produce high-grade fuel and char materials. It is reported that the cleavage of aromatics was enhanced with the presence of solid substances, e.g., chemical halite [7], metal oxides [9,13], and zeolites [8,9,10]. This enabled a route to treat the oil sludge with the generation of an abundance of valuable fuel. However, the added substances are of value and cannot be recycled after pyrolysis. Thus, a “waste to treat waste” strategy should be developed to catalytically pyrolyze organic sludge by other solid waste.
Fe-rich sludge is a waste generated from water treatment plants in surface processing, steel making, and water purification industries [14,15]. Such sludge commonly contains various Fe-bearing substances [16,17], including ferric/ferrous oxyhydroxides, hematite, and magnetite. Such Fe-bearing substances have shown merits to directly adsorb and/or to catalytically decompose organics [18]. Especially in catalytic decomposition, the surface Fe was involved in the redox reaction and showed a cycling of Fe2+/Fe3+ to activate catalyst [19,20], resulting in the acceleration of organics decomposition. Considering that the redox reaction of the Fe-bearing substance also took placed at a high-temperature, the Fe-rich sludge has shown potential applications in the co-pyrolysis of oil sludge, but such co-pyrolysis is rarely reported.
In recent decades, antibiotics have been abused and, accordingly, detected nearby the discharge outlets of pharmacies [21], hospitals and, aquaculture wastewater plants [22]. Accordingly, such antibiotics form residues and are frequently identified in soil/surface water nearby. Given that antibiotics show high affinity to coordinate metals, they show biotoxicity to microbes and are refractory to biodegradation [23,24]. Thus, many natural and synthesized materials, including carbon [25], pyrite [26], and man-made materials [27], have been used to remove such antibiotics. Given that the char material has been massively generated in the pyrolysis of organic sludge and poses a promising prospect in environmental pollution control [28], it can be used as a final barrier to remove such antibiotics in water treatment plants. Such performance also valorized the pyrolyzed char.
Herein, an organic scum was collected from an oil-bearing wastewater treatment plant and then pyrolyzed as three products, e.g., combustible volatiles, base oil, and biochar, with the addition of Fe-rich sludge from a pickling wastewater treatment plant. The pyrolysis products were analyzed and then the generated biochar was used for the selective removal of ciprofloxacin.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oil Scum Pyrolysis
The oil scum was collected from the sludge thickener in the oil-bearing wastewater treatment plant (Jilin, China). Fe-rich sludge was acquired from a precipitation vessel in a cold-rolling wastewater treatment plant (Jilin, China). The pyrolysis experiments were performed as follows. First, 5 g of Fe-rich sludge and 40 mL oil scum were mixed in a crucible and then heated at a rate of 10 °C/min to 700 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere and then kept for 10 min. Second, the pyrolysis gas was cooled down to separate the condensational oil and gas with a beaker and a series of bags, respectively, whilst the rest of the char was placed into a tube and named M. This process is shown in Figure 1. A control experiment was also carried out without the addition of the Fe-rich waste, and the generated char was named R. The collected gas and oil were characterized by GC-MS.

Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the pyrolysis process.
2.2. Chemical Reagent Experiment
To identify the catalytic performance of the Fe-rich sludge, a supplementary experiment was performed as follows: 5 g of iron powder was directly heated to 700 °C according to the abovementioned steps in Section 2.1, and then the generated product was collected and characterized. In parallel, the same weight of iron powder was mixed with 40 mL nitrobenzene and then treated at 700 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere, and the obtained solid product was also analyzed.
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
Two chars (e.g., M and R) were generated in Section 2.1, and their adsorption performance was analyzed as follows. First, 0.1 g of char M was dispersed into a 100 mL solution containing 50 mg/L ciprofloxacin (short for Cip) to form a suspension. Second, the suspension was agitated at 100 rpm for 6 h and then centrifuged at 5500 rpm for 5 min to separate the char and solution. The separated solution was analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (Shimazu LC-20A, Kyoto, Japan). A control experiment was also performed by replacing Cip with benzoic and sulfanilamide). The used char was regenerated with calcination at 700 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere for 10 min and then reused for the removal of Cip according to the above-mentioned steps. The abovementioned experiments were replicated three times, and the average data were reported.
2.4. Characterization
The water, tar, and inorganic contents in the oil scum were determined by using the Dean–Stark device (ZNHW-II, Yuming-Shanghai, China) as follows. First, weighted oil scum was placed into a filter cartridge and then transferred into a 500 mL round-bottom flask containing 200 mL of methylbenzene. Second, the flask was connected to a water distributor and condensing pipe and then heated to evaporate the methylbenzene/water to flush the oil scum. Third, the tar phase was collected at the flask bottom, and the water phase was kept in the water distributor. The rest was dredged in a filter cartridge and was directly dried at 105 °C and then weighted. The experiment was repeated three times, and the average date were reported.
The relative content of aromatic hydrocarbon, saturated hydrocarbon, colloid, and asphaltene in the tar phase was determined as follows. The collected tar phase was evaporated and then redissolved in a 30 mL n-hexane, followed by placing it on a table for 12 h to precipitate asphaltene. After filtration, the rest of the solution was concentrated to less than 5 mL and then transferred into a column filled with silica gel and aluminum oxide spheres. The column was washed with a 5 mL n-hexane 6 times and then with 5 mL of a mixture of dichloromethane and n-hexane at the volume ratio of 2:1 for 4 times and, finally, with 10 mL of absolute ethyl alcohol and 10 mL chloroform in turn. Such eluent was evaporated at <40 °C and then weighted.
The char’s magnetization was measured at room temperature by using a magnetometer (Quantum Design, San Diego, CA, USA) with a SQUID-VSM system. The corresponding X-ray diffraction patterns were determined with a diffractometer (Rigaku, Takatsuki, Japan) using Cu-Kα radiation. The valence states of F and N on the char surface were determined through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (VG-ADES, Waltham, UK) with an Mg-Kα X-ray source at a residual gas pressure lower than 10−8 Pa. Their surface morphology was observed with a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM; FEI Co., Hillsboro, OR, USA) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. Their specific surface areas were determined through nitrogen adsorption–desorption measurements (TriStar 3000, Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA)). Their calcination performance was analyzed using thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC, STA449C, NETZSCH, Selb, Germany). The Fourier transform infrared spectra were determined using a spectrometer (Nicolet 6700, Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) using K-Br wafer. The total surface site concentrations of chars R and M were determined using the in situ Gran plot method according to the description by Zhu et al. [26].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pyrolysis of Oil Scum by Fe-Rich Sludge
The oil scum was a blackish gel (Figure 2a) and collected in steel buckets. It was comprised of 36.2% water, 52.5% tar, and 11.3% inorganic substances (Figure 2b). In the tar, aromatic hydrocarbon and saturated hydrocarbon occupied 32.8% and 34.3%, separately, whilst colloid and asphaltene occupied only 18.5% and 14.4% (Figure 2c), indicating that the value-added hydrocarbon was abundant and can be separated.

Figure 2.
(a) Picture of raw oil scum: major composition of (b) oil scum, (c) tar, and (d) SEM image of scum and its pyrolyzed product.
The oil scum was watery, but, after drying, it showed a smooth surface (Figure 2d scum). When the oil scum was directly pyrolyzed, it was converted to 19.9% oil, 18.2% gas, and 26.1% char, with the release of 35.8% water (Figure 3a). The mass calculation result showed that nearly 30.2% of the tar was converted to gas, whilst 28.6% of the tar was involved in the char formation (Figure 3b). The generated oil contained various organics (Figure 3c(R)) that was predominated by 19.2% di-aromatics, 51.2% C11-20, and 17% C21- hydrocarbons (Figure 3d(R)), whilst the generated gas was predominated by 56.5% short chain hydrocarbon with 2–4 carbons (Figure 3e(R)). After pyrolysis, the rest of the char showed a porous surface (Figure 2d(R)) and had potential application in the adsorption of contaminants from wastewater. This demonstrated the generation of combustible gas, base oil, and char from the oil scum pyrolysis.
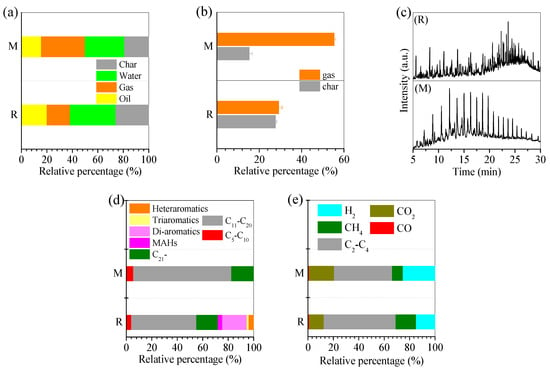
Figure 3.
(a) Relative percentage of generated product, (b) conversion efficiency of tar to gas and char, (c,d) oil spectra and composition, and (e) gas composition.
When the Fe-rich sludge was mixed with the oil scum, the corresponding products included 15.5% oil, 34.5% gas, 30.8% water, and 19.2% biochar (Figure 3a(M)). It was noted that the conversion efficiency of tar to gas/oil and biochar varied by 57.3% and 15.8% (Figure 3b(M)). This confirmed that the Fe-rich waste was effective for increasing the gas yield and steadily inhibiting the conversion of tar to char. Even though the oil yield was only 15.5%, it showed at a high quality that the aromatics were at a low level, and the chain hydrocarbon with C11-20 and C21- occupied 94.6% (Figure 3c,d(M)). Moreover, in the generated gas, the relative percentage of C2-4 to H2 apparently varied from 56.5% to 14.9% (Figure 3e(R)), and from 45.7% to 25.3% (Figure 3e(M)), respectively. The rest of the char also showed a porous, coarse surface (Figure 2d(M)). This confirmed that the Fe-rich waste was effective in the catalytic pyrolysis of organic sludge.
3.2. Pyrolysis Mechanism of Oil Scum
The oil scum was rich in tar. At a high temperature, the polycondensation of the tar as char occurred, especially on the surface of the rest of the inorganics. Such char had a porous surface and showed the typical XRD peak of carbon (Figure 4a(R)). However, its saturation monetization was only 0.04 emu/g, demonstrating that its weakly magnetized (Figure 4b(R)). However, the Fe-rich sludge was abundant in magnetite (Figure 4a, Fe-rich sludge). When it was mixed with the oil scum, the catalytic pyrolysis occurred. Accordingly, the corresponding char also showed the typical peaks of carbon, iron, and wustite (Figure 4a(M)) and showed the saturation magnetization of 2.2 emu/g (Figure 4b(M)). This revealed that the redox reaction of magnetite to tar occurred, with the generation of metal iron and wustite byproducts.
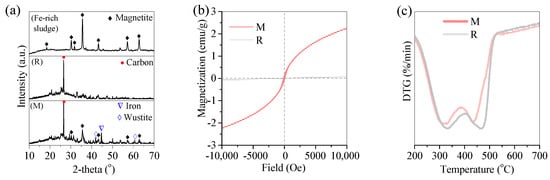
Figure 4.
(a) XRD pattern, (b) saturation magnetization of Fe-rich sludge and the generated char, and (c) TG curves of oil scum without/with Fe-rich sludge.
The oil scum was comprised of organic tar, inorganics, and an abundance of water and was pyrolyzed with the following steps. First, the water and a few light tars were evaporated rapidly with the temperature increased to 100 °C from the room temperature. Second, as the temperature increased from 100 °C to 200 °C, the rearrangement reaction of the inner tar started alongside the continued releasing of volatiles. Third, in the temperature range of 200–450 °C, the release of the light tar completed, but the rearrangement reaction continued. Fourth, when the temperature was increased to above 450 °C, the cleavage reaction of the tar occurred, which produced and released an abundance of volatiles (Figure 4c). In parallel, the polymerization of the tar as a macromer also took place, followed by the polycondensation of the macromer as char via a semicoke reaction [29]. In the presence of the Fe-rich waste, it served as hot spot to heat the adjacent organic sludge and to accelerate the evaporation of the water and light tar. However, at a high temperature, the redox reaction of magnetite to tar took place and accelerated the dehydrogenation of hydrocarbon and the cleavage of macromer organics, with the formation of Fe and wustite (Figure 5a). Subsequently, the Fe showed a high reduction potential to accelerate the decarbonylation and decarboxylation of the tar [30], resulting in the reoxidation of Fe to Fe oxides. However, the reduction of magnetite to Fe and wustite was observed in the corresponding XRD pattern, but the reoxidation of Fe to Fe oxides was not found.
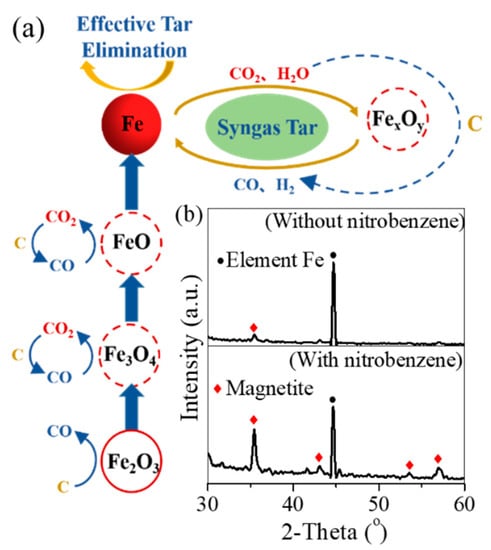
Figure 5.
(a) Illustration graph of Fe/Fe oxides in the pyrolysis of oil sludge and (b) XRD patters of Fe powder calcination in nitrogen atmosphere condition without/with nitrobenzene.
To identify the potential oxidation reaction of Fe in the pyrolysis of oil scum and Fe-rich sludge, the pure chemical experiment was carried out. The pure iron powder was directly heated to 700 °C under nitrogen gas conditions, and the corresponding product also exhibited the sharp peaks of Fe (Figure 5b). The small peak of magnetite was related to the oxidation of the iron powder in air before it was added to the pyrolysis system. However, when the iron powder was mixed with nitrobenzene, the generated product showed the sharp peaks of Fe and magnetite. This confirmed the mass production of magnetite in the presence of nitrobenzene. Therefore, the re-oxidation of Fe to Fe oxides occurred in the co-pyrolysis of the oil scum and Fe-rich sludge.
In summary, a cycle of Fe oxides/ Fe was formed in the catalytic pyrolysis of tar, which not only accelerated the conversion of tar to volatiles but also retarded the polycondensation of macromer organics as char. A portion of the magnetite was also covered and allowed to rest in the generated biochar, which enabled the biochar to have a good magnetic response, which can lead to easy separation with the magnetic field after use.
3.3. Adsorption Performance of Biochar
Two chars were generated from the oil scum pyrolysis and then used for the adsorption of typical antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Char R was effective in the adsorption of ciprofloxacin (Figure 6a). The classical Langmuir isotherm model was used to test the experimental data and the equations are expressed as follows.
where, KL and aL are the Langmuir isotherm constants and Ce is the ciprofloxacin concentration in the sampled solution. The corresponding linear graph showed that the adsorption data fit well with the Langmuir isotherm model (Figure 6b), whilst the maximum adsorption capacity of the ciprofloxacin on char R was 50.2 mg/g. Compared with char R, char M had a good magnetic response (Figure 4b) and showed the maximum adsorption capacity of 63.5 mg/g ciprofloxacin, which was higher than that of char R. Thus, the adsorption performance of char M was also analyzed with the adsorption kinetics, as shown in Figure 6c. The adsorption capacity increased rapidly at the initial 30 min and slowly in the following 30 min and then kept constant within the subsequent 5 h. Such adsorption was studied as a function of adsorption time at room temperature and then analyzed with the typical pseudo-second order kinetic model.
where t represents time, qe and qt are the equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg/L) and the adsorption capacity (mg/L) at t min, respectively, and k1 is the pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constant.
Ce/qe = 1/KL + Ce × aL/KL
T/qt = 1/(k1 × qe2) + t/qe
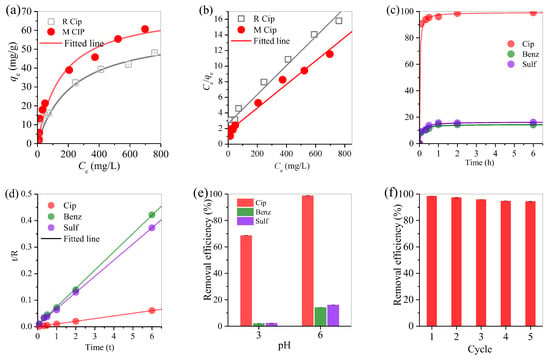
Figure 6.
Adsorption performance of char: (a) adsorption capacity of Cip, (b) fitted plot of Cip adsorption, (c) removal efficiency, (d) fitted line of Cip removal, (e) pH effect, and (f) reuse performance.
The linear fitting curves demonstrated that the adsorption of ciprofloxacin, benzoic, and sulfanilamide on char M were fitted well with the pseudo-second-order model. This demonstrated that the chemical adsorption predominated in the removal of ciprofloxacin, benzoic, and sulfanilamide. However, char M also showed selective adsorption of ciprofloxacin. For instance, when char M was added into the wastewater containing ciprofloxacin, benzoic, and sulfanilamide, the adsorption equilibrium was achieved in 1 h. However, the removal efficiency of ciprofloxacin was 98.9%, but that of benzoic and sulfanilamide were only 14.2% and 16.1%, respectively (Figure 6c). It was also found that, when the initial pH was adjusted to pH 3, the removal efficiencies were steadily decreased to 68.7% for ciprofloxacin, 2.1% for benzoic, and 2.2% for sulfanilamide (Figure 6e). This revealed that char M had high selective adsorption of ciprofloxacin. When biochar M was reused for 5 times, the removal efficiency of ciprofloxacin slightly dropped to 94.5% (Figure 6f). This confirmed the good reuse performance of biochar M.
The surface characterization of the chars was also analyzed. Char M exhibited well-developed pores with the average pore size of 19.2 nm, slightly larger than that of 12.7 nm of char R (Figure 7a). However, its BET surface area was only 96.3 m2/g, smaller than that (123.6 m2/g) of char R (Figure 7b). It was noted that Fe-rich waste was involved in char M preparation. Such Fe-bearing substances showed large density and weight compared with char materials. Therefore, the BET data was not accurate enough to describe the effective adsorption sites. Char M showed a higher adsorption capacity of ciprofloxacin compared to char R. The effective adsorption sites on the surfaces of chars R/M are an important factor in determining the effectiveness of an adsorbent, which can be measured with the in situ Gran plot method (Figure 7c). It was found that the concentration of surface adsorption sites was 1.47 mmol/g for char M and 1.18 mmol/g for char R. This suggested that char M employed more functional sites for ciprofloxacin adsorption in comparison with char R.
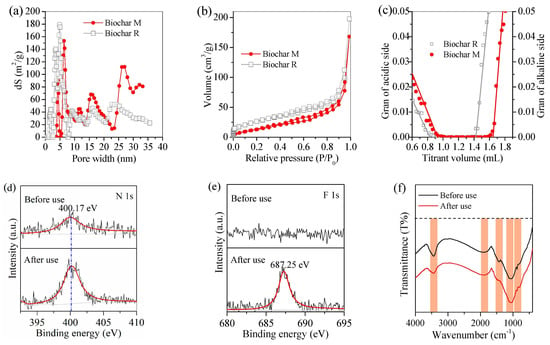
Figure 7.
Characterization of biochar: (a) pore size distribution, (b) BET surface area, (c) Gran plot, (d) N1s, (e) F 1s XPS spectra, and (f) FTIR spectra of magnetic char before and after use.
After adsorption, the used magnetic char showed similar morphology and XRD patterns to that without use. The corresponding Fe 2p and O1s XPS spectra did not change, apparently, before and after use. However, after use, the sharp peaks of N1s and F1s at the binding energies of 400.17 eV and 687.25 eV were observed (Figure 7d,e), agreeing with the functional groups of fluorine and piperazine on ciprofloxacin. This steadily showed the adsorption of ciprofloxacin on magnetic char. The corresponding FTIR spectra showed that five sharp peaks were observed and the peak strengths of the used one are significantly different (Figure 7f). Such findings suggest that the hydroxyl groups are abundant on the magnetic char and play key roles in the adsorption of ciprofloxacin.
Tar was abundant in the organic sludge and was involved in the polycondensation of char. Such tar contained hydroxyl, carboxyl, sulfhydryl [31], and other functional groups [32]. Accordingly, the formed char carried such groups and exhibited desirable adsorption sites for contaminant removal, as described in Figure 5. Ciprofloxacin was a typical antibiotic and was cationic at a pH of <6.1 but converted to anionic form at a pH of >8.7, whilst it was in the zwitterionic form at a pH range of 6.1 to 8.7 [33]. Thus, at a pH of <6.1, the cationic ciprofloxacin was easily attached onto the adsorption sites of the biochar, compared with anionic and zwitterionic forms. When the initial pH was decreased to 3, more H+ was accumulated in the water and was then attached to the sites, in comparison with the cationic ciprofloxacin, which led to a decrease in ciprofloxacin removal efficiency. Similar performance also took place for the adsorption of benzoic and sulfanilamide. It is noted that benzoic and sulfanilamide are anionic organics and used as chemical intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. More than 14% of benzoic and sulfanilamide was adsorbed by biochar M. Considering that the polycyclic aromatic was rich in tar and involved in the biochar formation, a portion of the aromatic raised the π-π interactions [32] and then played a negative role in the adsorption process.
With the addition of Fe-rich waste in the pyrolysis of organic sludge, the catalytic decomposition and decarbonylation/decarboxylation of tar occurred on the Fe-bearing particles, which led to the release of volatiles. Such volatiles escaped from inside to outside and then created abundant channels on the char surface. Therefore, the surface site concentration of char M was steadily increased. In summary, the Fe-rich waste exhibited three merits in organic sludge pyrolysis. First, it enabled a cycle of Fe/magnetite to accelerate the catalytical cleavage of tar and, subsequently, to reduce the char yield. Second, it showed a high efficiency to split the aromatics into a massive chain hydrocarbon to improve the volatiles (oil/gas) quality. Third, it was effective at activating char to produce more functional surface sites for contaminant adsorption.
The catalytic pyrolysis of the waste oil scum as value-added volatiles and magnetic char by the waste Fe-rich sludge was highlighted in this study, but some experimental conditions should be optimized in the future. First, the pyrolysis conditions should be optimized to increase the conversion efficiency of tar to volatiles and to lower the yield of magnetic char. With such optimized conditions, the catalytic pyrolysis mechanism of the waste oil scum by the Fe-rich sludge can be further interpreted. Second, special equipment should be developed to collect the combustible gas prior to carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases. Third, the magnetic char showed high removal efficiency of ciprofloxacin but was ineffective in the removal of benzoic and sulfanilamide. This demonstrated its low efficiency in the organic wastewater treatment.
4. Conclusions
The waste oil scum was effectively recycled as combustible gas/oil and magnetic char via a facile catalytic pyrolysis route with the addition of Fe-rich sludge. In the oil scum, the tar occupied 52.5% and effectively converted to volatiles and biochar. The added Fe-rich sludge showed superior efficiency in the catalytic cleavage of tar as a chain hydrocarbon, which apparently increased the conversion efficiency of tar to volatiles from 71.4% to 84.2% and effectively reduced the content of aromatics in the volatiles. It also enhanced the magnetic response of the rest of the char and activated the rest of the char to provide abundant surface sites for ciprofloxacin adsorption. This provided an alternative strategy to recycle the waste oil scum with the Fe-rich sludge. This method also proposed the possibility for the synchronous reutilization of other Fe-rich waste, e.g., red mud and groundwater treatment sludge, and the other oil-rich waste which is massively generated in wastewater treatment and oil-refining industries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and M.J.; methodology, J.L.; software, M.J.; validation, J.Q.; formal analysis, J.L. and M.J.; investigation, M.J.; resources, J.L.; data curation, J.L. and S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L. and M.J.; writing—review and editing, J.Z. and S.Z.; visualization, J.L. and M.J.; supervision, J.Z. and S.Z.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (52100054, 51908375, 52070038), the Innovative Research Team Program of Jilin Province (No. 20210509043RQ), the Shenzhen Polytechnic Project (6020320003K), and the Department of Education of Guangdong Province (2019GGCZX007).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sharma, N.K.; Suganya, K.; Sivapragsam, C.; Vanitha, S. Current Trends on Oil Sludge Characterization, Toxicity and Treatment Systems. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2020, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighat, M.; Majidian, N.; Hallajisani, A. Production of bio-oil from sewage sludge: A review on the thermal and catalytic conversion by pyrolysis. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 42, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Pandey, S.; Sumathy, K. Experimental investigation on waste heat recovery by refinery oil sludge incineration using fluidised-bed technique. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1998, 33, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiligiannis, A.; Tsiliyannis, C. Oil refinery sludge and renewable fuel blends as energy sources for the cement industry. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, J.; Zeng, G. Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Show, M.; Ong, S. Recovery of residual oil from the centrifuge sludge of a palm oil mill: Effect of enzyme digestion and surfactant treatment. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, H. Screening of inexpensive and efficient catalyst for microwave-assisted pyrolysis of ship oil sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Ali, M.; Chi, Y. Aromatic recovery from distillate oil of oily sludge through catalytic pyrolysis over Zn modified HZSM-5 zeolites. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 128, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Ates, F.; Yildirir, E.; Miskolczi, N. Investigation of thermal degradation kinetics and catalytic pyrolysis of industrial sludge produced from textile and leather industrial wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milato, J.V.; Frana, R.J.; Rocha, A.S.; Calderari, M. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of oil sludge with HDPE to obtain paraffinic products over HUSY zeolites prepared by dealumination and desilication. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 151, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, J.; Hou, H. A combination of solvent extraction and freeze thaw for oil recovery from petroleum refinery wastewater treatment pond sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelnasr, D.; Al Zubaidy, E.A. Treatment and Recovery of Oil-Based Sludge Using Solvent Extraction. In International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference; OnePetro: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Shu, Y.; Li, F.; Peng, G. Bimetallic catalysts as electrocatalytic cathode materials for the oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cell: A review. Green Energy Environ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Song, J.; Fan, W.; Yu, H.; Bian, D.; Huo, M. Synthesis and characterization of a magnetic adsorbent from negatively-valued iron mud for methylene blue adsorption. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Dong, G.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Huo, M.; Xu, K.; Liu, M. Recycling of groundwater treatment sludge to prepare nano-rod erdite particles for tetracycline adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, T.; Qu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Su, T.; Huo, Y. Effective recycling of Cu from electroplating wastewater effluent via the combined Fenton oxidation and hydrometallurgy route. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Su, T.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y. Simultaneous removal of sulfate and nitrate from real high-salt flue gas wastewater concentrate via a waste heat crystallization route. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Sun, T.; Liang, D.; Yu, H. Upcycling of Electroplating Sludge to Prepare Erdite-Bearing Nanorods for the Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater Effluent. Water 2020, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Tong, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. Non-free Fe dominated PMS activation for enhancing electro-Fenton efficiency in neutral wastewater. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 928, 117062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Dongxu, L.; Hongyu, C.; Suiyi, Z.; Xianze, W.; Jiakuan, Y.; Xinfeng, X.; Eskola, J.; Dejun, B. Review of resource utilization of Fe-rich sludges: Purification, upcycling, and application in wastewater treatment. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 460–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. The occurrence and fate of tetracyclines in two pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants of Northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.C.; Kolvenbach, B.A.; Nunes, O.C.; Corvini, P.F. Biodegradation of antibiotics: The new resistance determinants—Part I. New Biotechnol. 2020, 54, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Kan, Z.; Jia, Y. Catalytic ozonation mechanisms of Norfloxacin using Cu–CuFe2O4. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Janjani, H. Antibiotics adsorption from aqueous solutions using carbon nanotubes: A systematic review. Toxin Rev. 2018, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, S.; Ru, X.; Shu, X. Sulfur defect and Fe (III)(hydr) oxides on pyrite surface mediate tylosin adsorption in lake water: Effect of solution chemistry and dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 90248–90258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, A.; Adami, S. Adsorption and thermodynamic study of Cephalosporins antibiotics from aqueous solution onto MgO nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Dong, G.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Fan, W.; Zhou, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Hydrothermal synthesis of a magnetic adsorbent from wasted iron mud for effective removal of heavy metals from smelting wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22710–22724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrakhimov, V.; Abdrakhimova, E. Study of the distribution of iron oxides in intershale clay and oil sludge porous filler with Mossbauer spectroscopy. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2019, 53, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chi, Y. Preparation of Fe-char catalyst from tank cleaning oily sludge for the catalytic cracking of oily sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 139, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bendary, N.; El-Etriby, H.K.; Mahanna, H. Reuse of adsorption residuals for enhancing removal of ciprofloxacin from wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2021, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, G.; Pan, L.; Li, C.; You, F.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Shang, X. Study of ciprofloxacin removal by biochar obtained from used tea leaves. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Sorption of the Antimicrobial Ciprofloxacin to Aluminum and Iron Hydrous Oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).