Impact of Naproxen on Wastewater Biological Treatment: Focus on Reactor Performance and Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Influence of NPX on Nutrient Removal in Wastewater
2.3. Analytical Methods
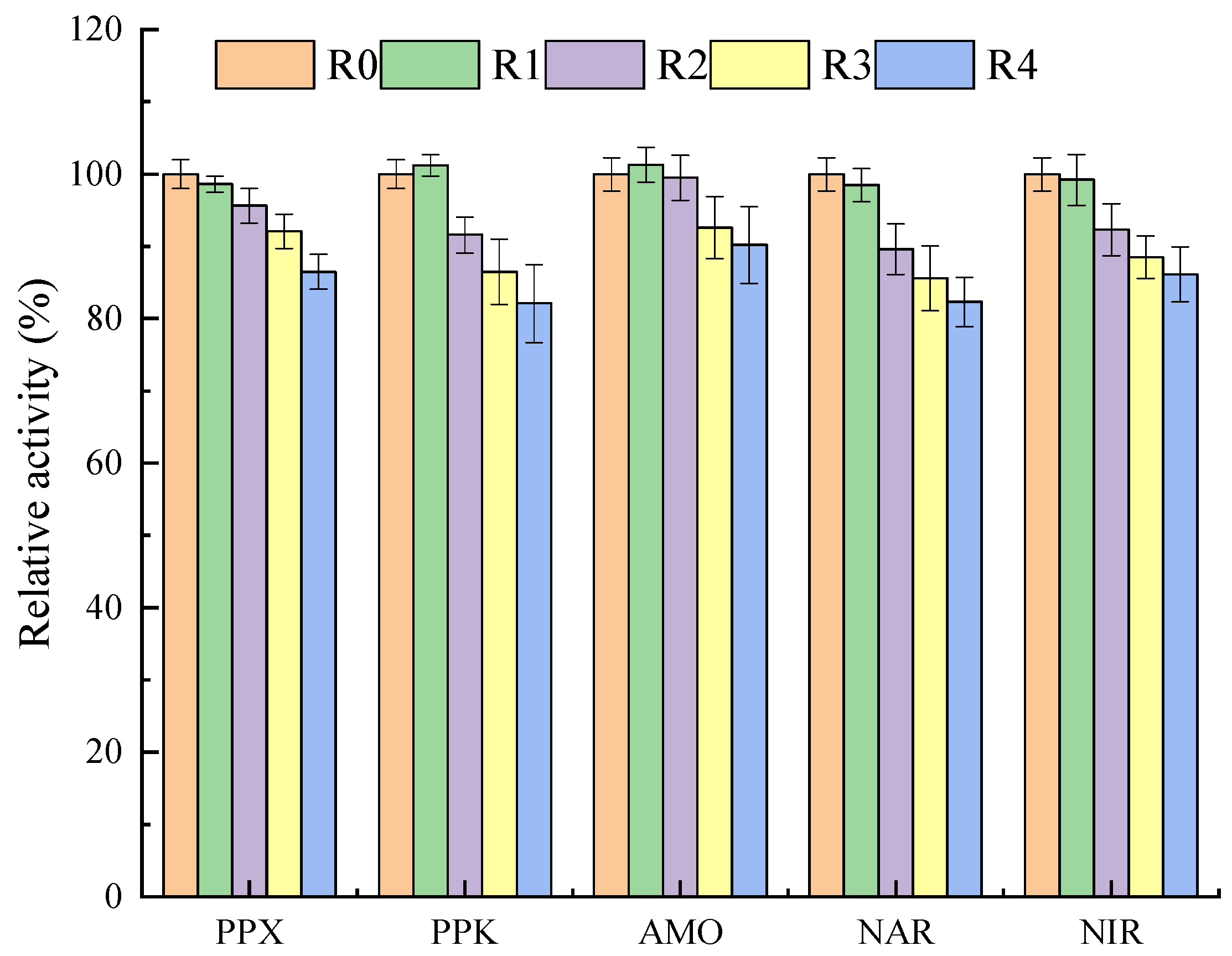
3. Results and Discussion
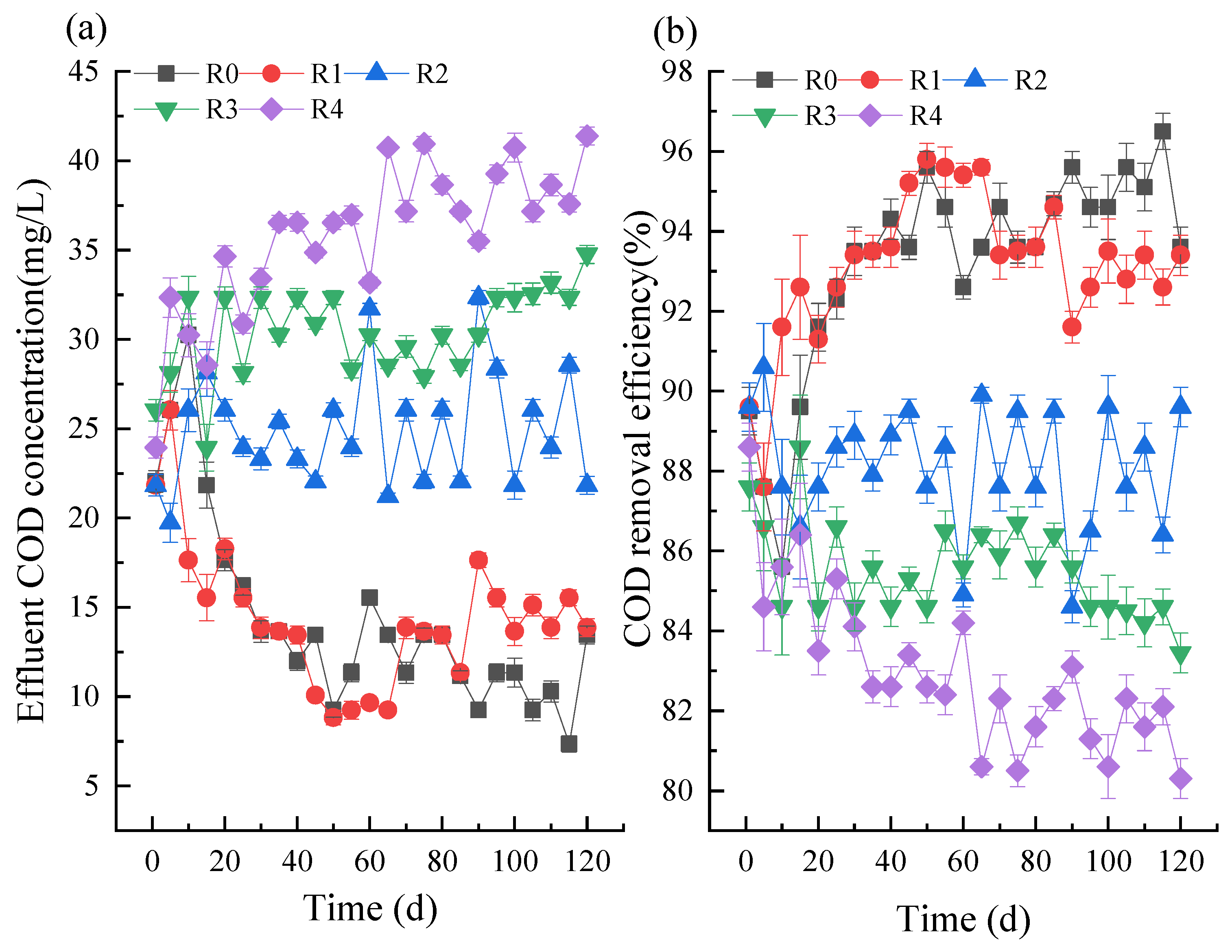
3.1. Effects of NPX on COD and Nutrient Removal
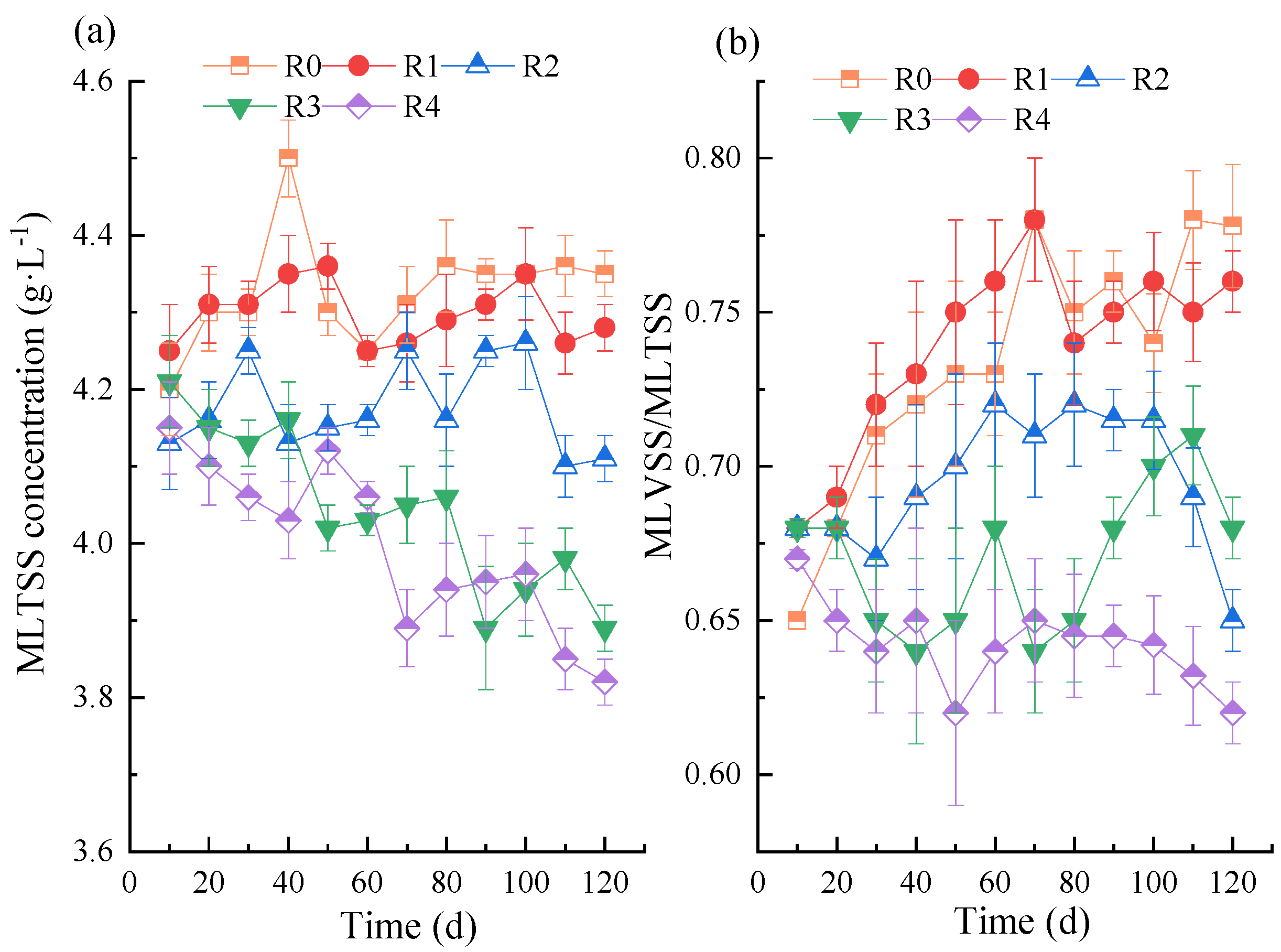
3.2. Effect of NPX on Activated Sludge Concentration
3.3. Effect of NPX on EPS Content in Activated Sludge
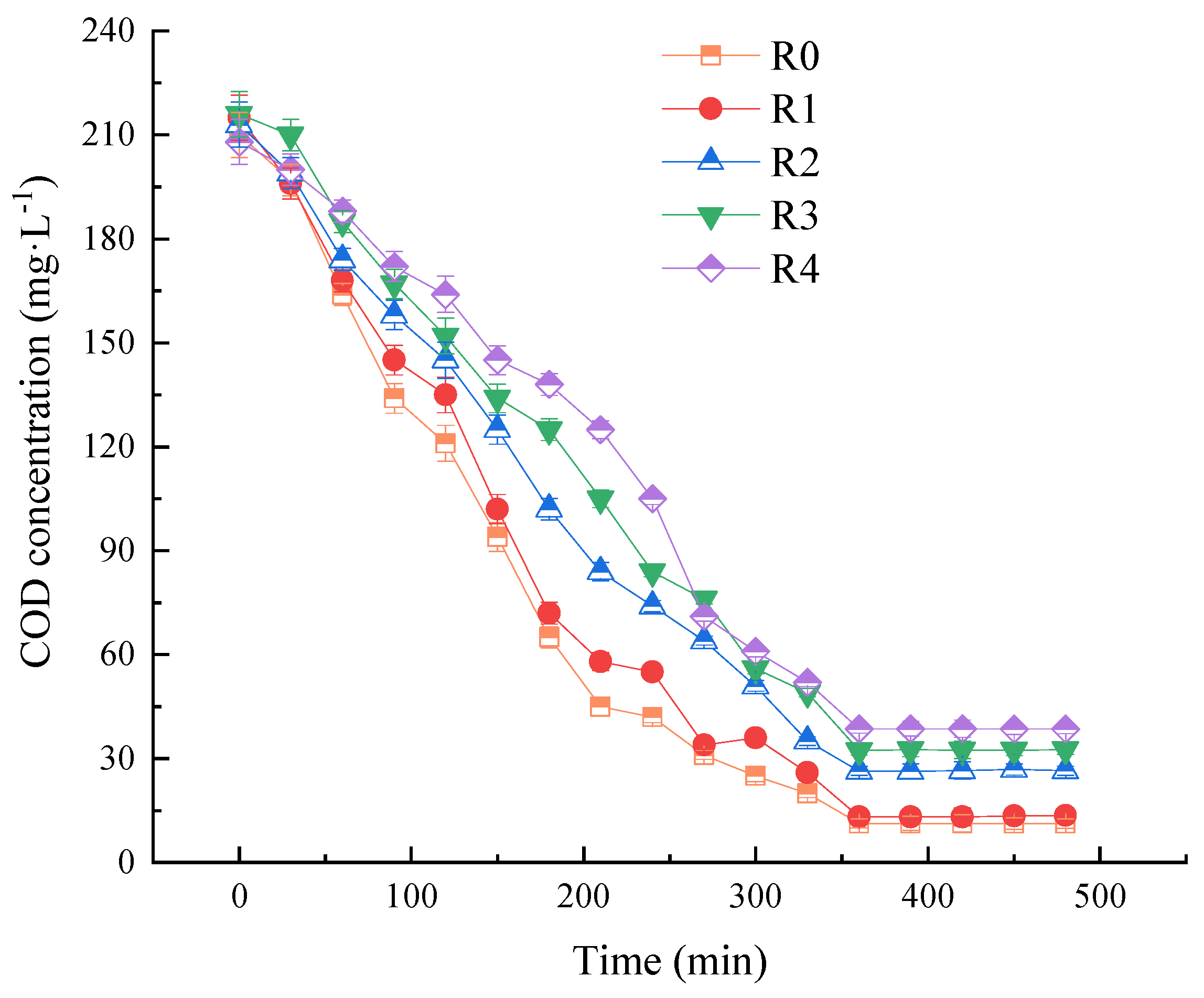
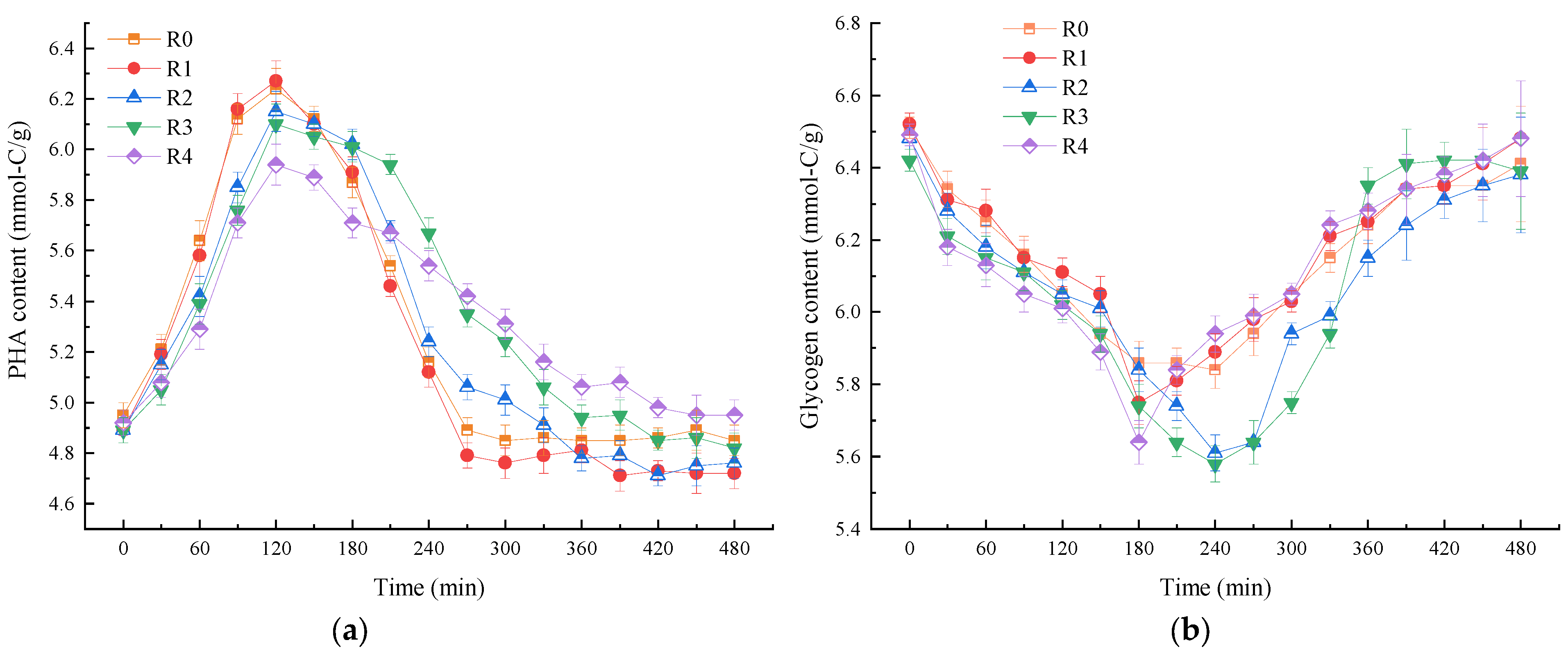
3.4. Effect of NPX on the Nutrient and Intracellular Polymer Content during a Typical Cycle
3.5. Impact of NPX on the Activity of Nutrient Removal-Related Enzymes
3.6. Implementation Significance and Research Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.; Qiu, G.; Wei, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Song, Y. Activated carbon enhanced traditional activated sludge process for chemical explosion accident wastewater treatment. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qin, C.; Sui, M.; Luo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Understanding the mechanism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers reducing the anaerobic co-digestion efficiency of excess sludge and kitchen waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41357–41367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, O.; Yerushalmi, L.; Haghighat, F. Wastewater treatment in the pulp-and-paper industry: A review of treatment processes and the associated greenhouse gas emission. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lian, Q.; Yin, H.; Peng, J.; Sheng, M.; Wang, Y. Enhancing real-time prediction of effluent water quality of wastewater treatment plant based on improved feedforward neural network coupled with optimization algorithm. Water 2022, 14, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, V.K. Detection and remediation of chiral pharmaceuticals from wastewater: A review. Chirality 2022, 34, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Álvarez, J.C.; Prado, B.; González, D.; Sánchez, Y.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B. Environmental fate of naproxen, carbamazepine and triclosan in wastewater, surface water and wastewater irrigated soil—Results of laboratory scale experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozinski, J.M.; Lahti, M.; Meierjohann, A.; Oikari, A.; Kronberg, L. The anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, naproxen and ibuprofen are found in the bile of wild fish caught downstream of a wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.J.; Wang, L.; Hashim, N.H.; Mcdonald, J.A. Distinct enantiomeric signals of ibuprofen and naproxen in treated wastewater and sewer overflow. Chirality 2014, 26, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Multi-residue enantiomeric analysis of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in environmental samples by chiral liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 9085–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Qu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, F.; Yu, Y.; Yu, G. Simultaneous enantiomeric analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environment by chiral LC-MS/MS: A pilot study in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliman, F.A.; Gavrilescu, M. Pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocrine disrupting agents in the environment—A review. Clean-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancová, V.; Ziková, A.; Svobodová, Z.; Kloas, W. Effects of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) naproxen on gene expression of antioxidant enzymes in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, J.; Zhao, J. Insights into the mechanism of naproxen inhibiting biohydrogen production from sludge dark fermentation. Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 167, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.R.; Zhang, S.; Grimm, D.A. Naproxen removal from water by chlorination and biofilm processes. Water Res. 2005, 39, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancheros, J.C.; Madera-Parra, C.A.; Caselles-Osorio, A.; Torres-López, W.A.; Vargas-Ramírez, X.M. Ibuprofen and Naproxen removal from domestic wastewater using a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland coupled to ozonation. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 135, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszyńska, D.; Guzik, U. Naproxen in the environment: Its occurrence, toxicity to nontarget organisms and biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ríos, A.L.M.; Gutierrez-Suarez, K.; Carmona, Z.; Ramos, C.G.; Oliveira, L.F.S. Pharmaceuticals as emerging pollutants: Case naproxen an overview. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qurie, M.; Khamis, M.; Malek, F.; Nir, S.; Bufo, S.A.; Abbadi, J.; Scrano, L.; Karaman, R. Stability and removal of naproxen and its metabolite by advanced membrane wastewater treatment plant and micelle–C lay complex. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qin, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J. Impact of emerging pollutant florfenicol on enhanced biological phosphorus removal process: Focus on reactor performance and related mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Bian, R. Effect of fluoxetine on enhanced biological phosphorus removal using a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xin, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X. Diclofenac inhibited the biological phosphorus removal: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Guan, D.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H. New insights into mechanism of emerging pollutant polybrominated diphenyl ether inhibiting sludge dark fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 368, 128358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M. Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen towards freshwater invertebrates: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, W.C.; Welch, A.M.; Ramirez, J.N.; Rein, L.C. Naproxen and Its phototransformation products: Persistence and ecotoxicity to toad tadpoles (Anaxyrus terrestris), individually and in mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Sheng, G.P.; Fang, W.; Wang, Y.P.; Fang, C.Y.; Shao, L.M.; Yu, H.Q. Calcium effect on the metabolic pathway of phosphorus accumulating organisms in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Water Res. 2015, 84, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Zhang, H.L.; Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Roles of extracellular polymeric substances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal process. Water Res. 2015, 86, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Fang, W.; Wang, Y.P.; Sheng, G.P.; Zeng, R.J.; Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q. Phosphorus removal in an enhanced biological phosphorus removal process: Roles of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11482–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, T.; Zeng, G. Improved biological phosphorus removal performance driven by the aerobic/extended-idle regime with propionate as the sole carbon source. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3868–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, D.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D. Calcium hypochlorite-coupled aged refuse promotes hydrogen production from sludge anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Welles, L.; Zhang, X.; Pronk, M.; de Graaff, D.; van Loosdrecht, M. Stress-induced assays for polyphosphate quantification by uncoupling acetic acid uptake and anaerobic phosphorus release. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, C.R.; Randall, A.A. A biochemical hypothesis explaining the response of enhanced biological phosphorus removal biomass to organic substrates. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresi, E.; Tang, K.; Deng, J.; Sund, C.; Smets, B.F.; Christensson, M.; Andersen, H.R. Removal of micropollutants during biological phosphorus removal: Impact of redox conditions in MBBR. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Parrella, A.; Previtera, L.; Rubino, M. Ecotoxicity of naproxen and its phototransformation products. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 348, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górny, D.; Guzik, U.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Wojcieszyńska, D. Naproxen ecotoxicity and biodegradation by Bacillus thuringiensis B1 (2015b) strain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmen, A.; Lemos, P.C.; Carvalho, G.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J.; Blackall, L.L.; Reis, M.A. Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: From micro to macro scale. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2271–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; An, H.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, G. Effect of ciprofloxacin on biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Zhang, W. Impact of Naproxen on Wastewater Biological Treatment: Focus on Reactor Performance and Mechanisms. Water 2023, 15, 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142615
Wei L, Zhang W. Impact of Naproxen on Wastewater Biological Treatment: Focus on Reactor Performance and Mechanisms. Water. 2023; 15(14):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142615
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lidan, and Wenbin Zhang. 2023. "Impact of Naproxen on Wastewater Biological Treatment: Focus on Reactor Performance and Mechanisms" Water 15, no. 14: 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142615
APA StyleWei, L., & Zhang, W. (2023). Impact of Naproxen on Wastewater Biological Treatment: Focus on Reactor Performance and Mechanisms. Water, 15(14), 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142615




