Harnessing Evanescent Waves in UV-Irradiated TiO2-Coated Quartz Optical Fibers Improves Pollutant Degradation in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Experimental Materials
2.2. Modeling the Light Propagation in TiO2-QOFs as a Function of Coating Structures
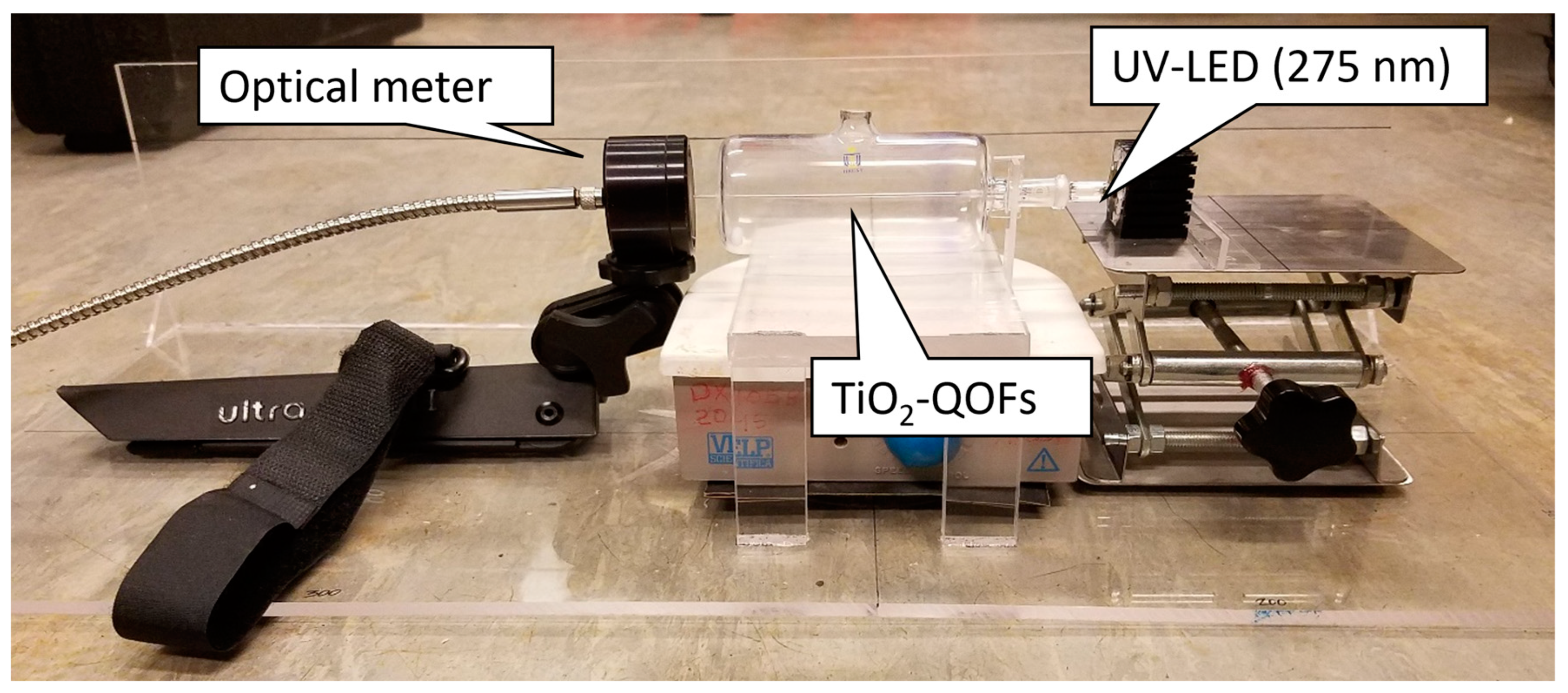
2.3. Experimental Setup and Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coating TiO2 on Quartz Optical Fibers
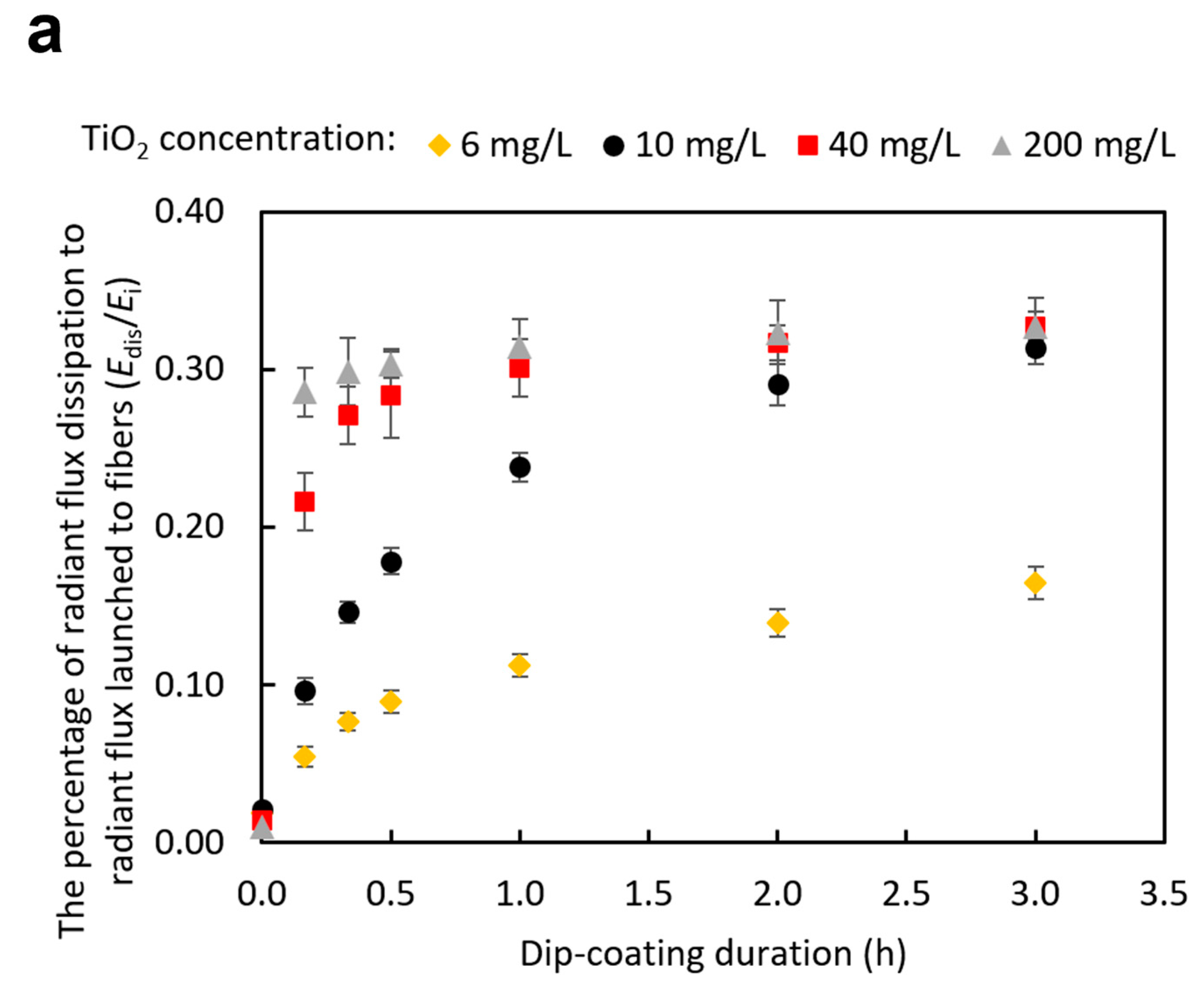
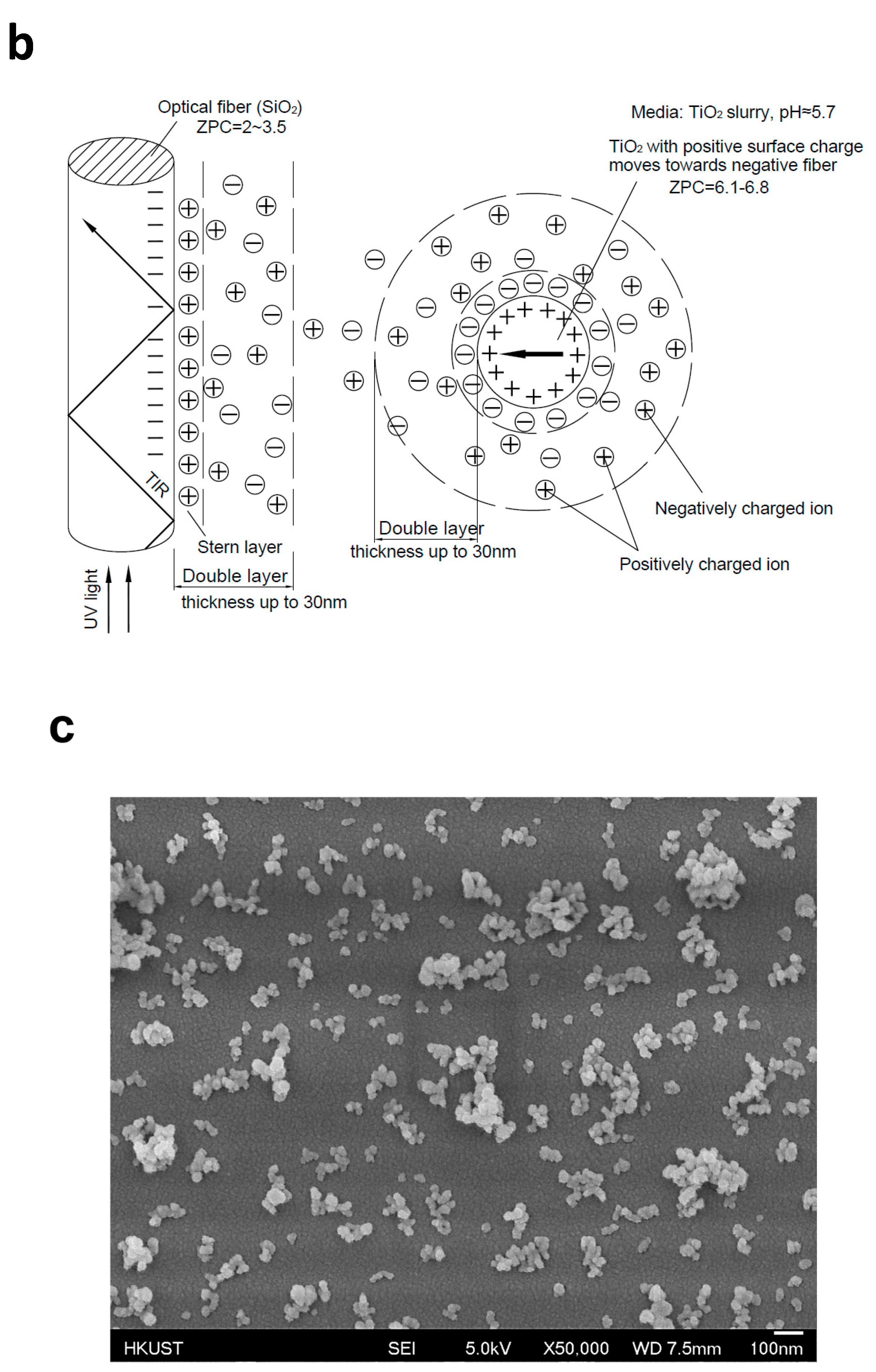
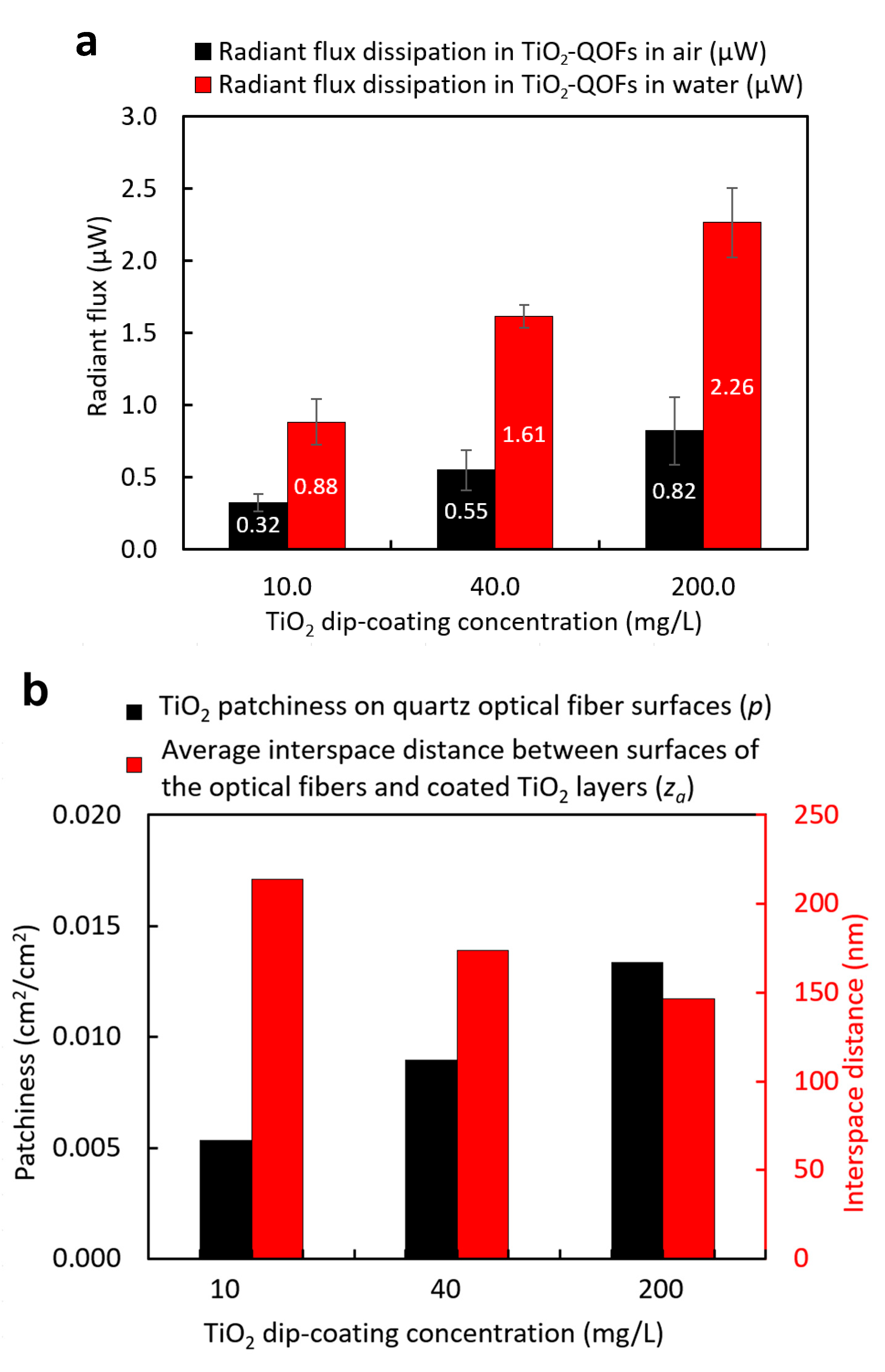
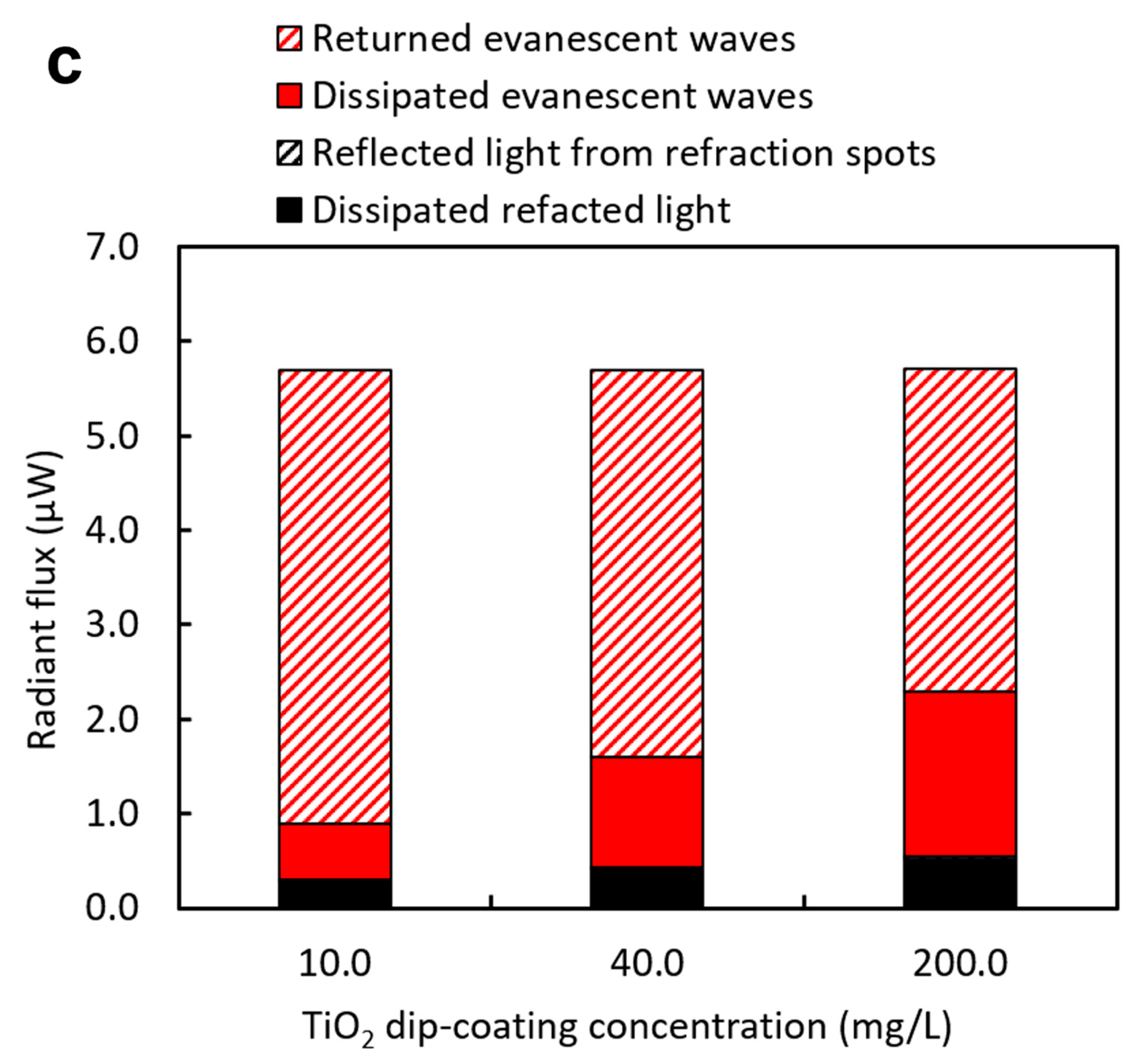
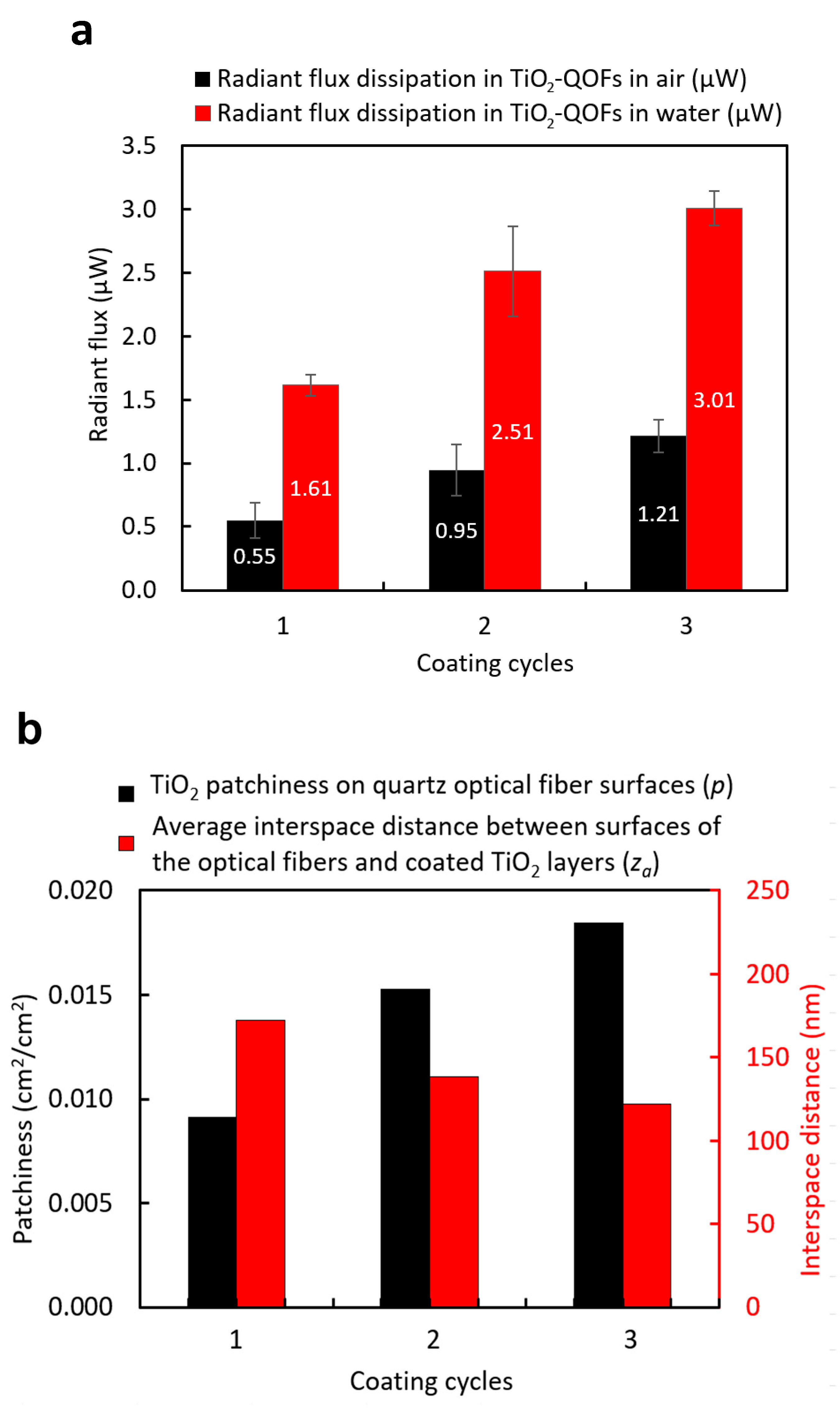
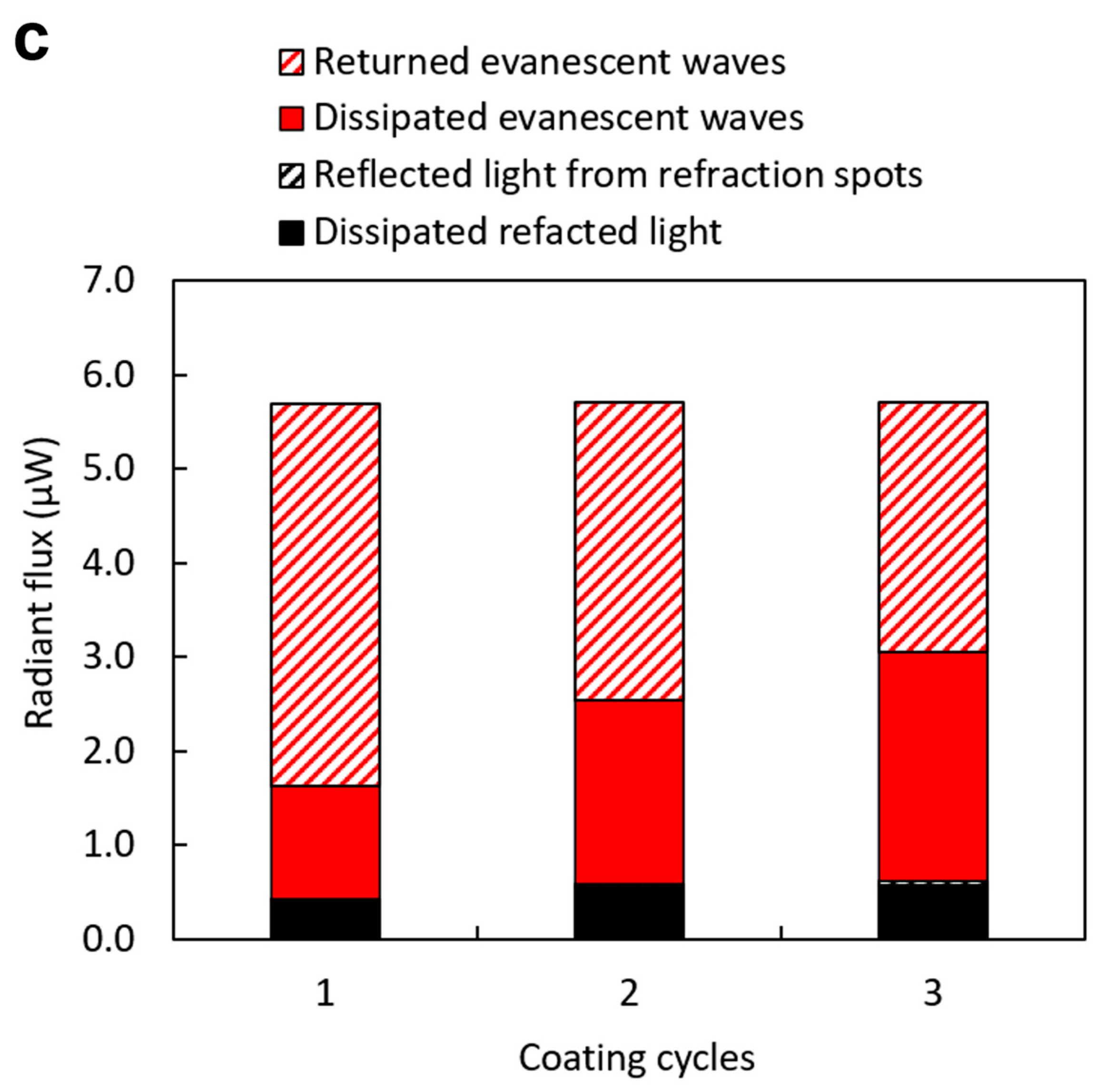
3.2. Effects of Dip-Coating Conditions on Coating Structures and the Resulting Evanescent Waves
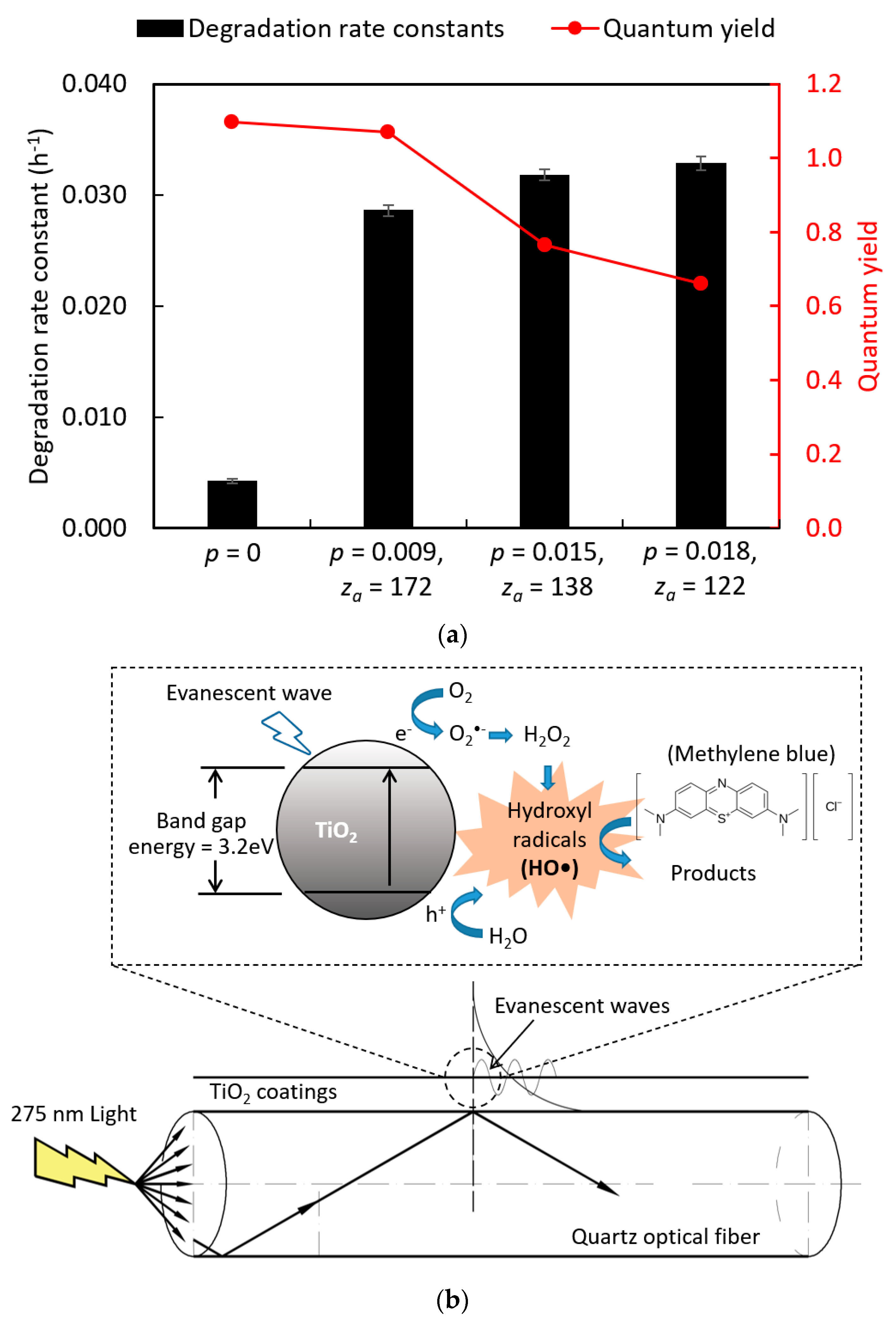
3.3. Enhanced Pollutant Degradation Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The Challenge of Micropollutants in Aquatic Systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Shang, C. Removal of micropollutants in drinking water using UV-LED/chlorine advanced oxidation process followed by activated carbon adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esplugas, S.; Giménez, J.; Contreras, S.; Pascual, E.; Rodríguez, M. Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for phenol degradation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, M.; Yin, R.; Zhang, S. Applicability of light sources and the inner filter effect in UV/acetylacetone and UV/H2O2 processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 335, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cassol, G.; Zhao, J.; Sato, Y.; Jing, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, C.; Yang, X.; Ao, Z.; Chen, G.; et al. Superfast degradation of micropollutants in water by reactive species generated from the reaction between chlorine dioxide and sulfite. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Peng, J.; Yin, R.; Fan, M.; Yang, X.; Shang, C. Multi-angle comparison of UV/chlorine, UV/monochloramine, and UV/chlorine dioxide processes for water treatment and reuse. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yin, R.; Yang, X.; Shang, C. A novel UVA/ClO2 advanced oxidation process for the degradation of micropollutants in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.M. Heterogeneous photocatalysis: Fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonaro, S.; Sugihara, M.N.; Strathmann, T.J. Continuous-flow photocatalytic treatment of pharmaceutical micropollutants: Activity, inhibition, and deactivation of TiO2 photocatalysts in wastewater effluent. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Ling, L.; Lu, S.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Shang, C. Degradation of aliphatic halogenated contaminants in water by UVA/Cu–TiO2 and UVA/TiO2 photocatalytic processes: Structure-activity relationship and role of reactive species. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, T.E.; Frimmel, F.H. Photocatalytic degradation of carbamazepine, clofibric acid and iomeprol with P25 and Hombikat UV100 in the presence of natural organic matter (NOM) and other organic water constituents. Water Res. 2005, 39, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: A review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satuf, M.L.; Brandi, R.J.; Cassano, A.E.; Alfano, O.M. Quantum efficiencies of 4-chlorophenol photocatalytic degradation and mineralization in a well-mixed slurry reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcó, D.; Giménez, J.; Addardak, A.; Cervera-March, S.; Esplugas, S. Effects of radiation absorption and catalyst concentration on the photocatalytic degradation of pollutants. Catal. Today 2002, 76, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, R.E.; Ollis, D.F. Photoassisted heterogeneous catalysis with optical fibers: I. Isolated single fiber. AIChE J. 1977, 23, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, R.E.; Ollis, D.F. Photo-assisted heterogeneous catalysis with optical fibers II. Nonisothermal single fiber and fiber bundle. AIChE J. 1980, 26, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstadler, K.; Bauer, R.; Novallc, S.; Heisler, G. New reactor design for photocatalytic wastewater treatment with TiO2 immobilized on fused-silica glass fibers: Photomineralization of 4-chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Design of H3PW12O40/TiO2 and Ag/H3PW12O40/TiO2 film-coated optical fiber photoreactor for the degradation of aqueous rhodamine B and 4-nitrophenol under simulated sunlight irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ao, Y.; Fu, D.; Lin, Y.; Shen, X.; Yuan, C.; Yin, Z. Photocatalytic activity on TiO2-coated side-glowing optical fiber reactor under solar light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 199, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peill, N.J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Development and optimization of a TiO2-coated fiber-optic cable reactor: Photocatalytic degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danion, A.; Disdier, J.; Guillard, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Malic acid photocatalytic degradation using a TiO2-coated optical fiber reactor. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 190, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Tugaoen, H.; Brame, J.; Sinha, S.; Li, C.; Schoepf, J.; Hristovski, K.; Kim, J.-H.; Shang, C.; Westerhoff, P. Coupling light emitting diodes with photocatalyst-coated optical fibers improves quantum yield of pollutant oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13319–13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugaoen, H.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Hristovski, K.; Westerhoff, P. Compact light-emitting diode optical fiber immobilized TiO2 reactor for photocatalytic water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Ko, J.Y.; Park, H.; Chung, J.S. Investigation on TiO2-coated optical fibers for gas-phase photocatalytic oxidation of acetone. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 31, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peill, N.J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Chemical and physical characterization of a TiO2-coated fiber optic cable reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peill, N.J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Mathematical model of a photocatalytic fiber-optic cable reactor for heterogeneous photocatalysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ling, L.; Westerhoff, P.; Shang, C. Evanescent waves modulate energy efficiency of photocatalysis within TiO2 coated optical fibers illuminated using LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lanzarini-Lopes, M.; Westerhoff, E.; Long, X.; Rho, H.; Bi, Y.; Ling, L.; Westerhoff, P. Evanescent wave interactions with nanoparticles on optical fiber modulate side emission of germicidal ultraviolet light. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, T.-H.; Dong, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, W. Study on the propagation mechanism of evanescent waves in one-dimensional periodic photonic crystal. Phys. Lett. A 2015, 379, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; O’Sullivan, M. Fiber Optic Measurement Techniques; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Peatross, J.; Michael, W. Physics of Light and Optics; Brigham Young Univ. Press: Provo, UT, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, H. Anti-reflection surface with particle coating deposited by electrostatic attraction. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarioua, A.; Zerdaoui, M. Photocatalytic activities of TiO2 layers immobilized on glass substrates by dip-coating technique toward the decolorization of methyl orange as a model organic pollutant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, R.; Ukrainczyk, L. Surface chemistry of SiO2 and TiO2-SiO2 glasses as determined by titration of soot particles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 277, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hutter, J.; Sprik, M. Coupling of Surface Chemistry and Electric Double Layer at TiO2 Electrochemical Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 3871–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Jin, Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.K.; Park, D. Photocatalytic TiO2 deposition by chemical vapor deposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 73, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrabose, G.; Dey, A.; Gaur, S.S.; Pitchaimuthu, S.; Jagadeesan, H.; Braithwaite, N.S.-J.; Selvaraj, V.; Kumar, V.; Krishnamurthy, S. Removal and degradation of mixed dye pollutants by integrated adsorption-photocatalysis technique using 2-D MoS2/TiO2 nanocomposite. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Ling, T.; Chin, L. Photocatalytic Activity of Modified TiO2 for Methyl Orange Removal. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukcongar, S.; Alwindawi, A.G.J.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Ozaytekin, I. Reactive Dye Removal by Photocatalysis and Sonophotocatalysis Processes Using Ag/TiO2/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, B.; Sarker, A.; Shareque, A.M.; Dey, S.C.; Islam, M.T.; Das, A.K.; Shamsuddin, S.M.; Molla, M.A.I.; Sarker, M. Preparation of Activated Carbon/TiO2 Nanohybrids for Photodegradation of Reactive Red-35 Dye Using Sunlight. Photochem 2021, 1, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, M.H.; Meenakshi, S. Synergistic Effect of Chitosan and Titanium Dioxide on the Removal of Toxic Dyes by the Photodegradation Technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohilla, S.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumari, S.; Petru, M.; Amor, N.; Noman, M.T.; Dalal, J. Excellent UV-Light Triggered Photocatalytic Performance of ZnO.SiO2 Nanocomposite for Water Pollutant Compound Methyl Orange Dye. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarathna, L.; Bandara, A.; Ng, W.; Weerasooriya, R. Fluoride adsorption on γ − Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dye | TiO2 Composites | Radiation | Degradation Rate Constants (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylene blue (MB) | 2.5 wt% MoS2/TiO2 at 0.5 g/L | 350–1100 nm at 300 W | 0.005 | [40] |
| Methyl Orange (MO) | Ag/TiO2 at 2 g/L | UVA at 11 W | 0.011 | [41] |
| Reactive Red 195 (RR195) | Ag/ Fe3O4/TiO2 at 0.1 g/L | UVA at 27 W | 0.077 | [42] |
| Reactive Red 35 (RR35) | 20 wt% Activated carbon/TiO2 at 0.1 g/L | Solar light | 0.087 | [43] |
| Methylene blue (MB) | Chitosan/TiO2 | 365 nm at 64 W | 0.081 | [44] |
| Rhodamine B (RB) | Chitosan/TiO2 | 365 nm at 64 W | 0.058 | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Shang, C.; Ling, L. Harnessing Evanescent Waves in UV-Irradiated TiO2-Coated Quartz Optical Fibers Improves Pollutant Degradation in Water. Water 2023, 15, 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122226
Song Y, Shang C, Ling L. Harnessing Evanescent Waves in UV-Irradiated TiO2-Coated Quartz Optical Fibers Improves Pollutant Degradation in Water. Water. 2023; 15(12):2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122226
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yinghao, Chii Shang, and Li Ling. 2023. "Harnessing Evanescent Waves in UV-Irradiated TiO2-Coated Quartz Optical Fibers Improves Pollutant Degradation in Water" Water 15, no. 12: 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122226
APA StyleSong, Y., Shang, C., & Ling, L. (2023). Harnessing Evanescent Waves in UV-Irradiated TiO2-Coated Quartz Optical Fibers Improves Pollutant Degradation in Water. Water, 15(12), 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122226








