Evaluation of Ground and Surface Water Hydrochemistry for Irrigation Suitability in Borneo: Insights from Brunei Darussalam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geographic Location and Climate
2.1.2. Regional Geological and Hydrological Settings
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Water Classification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Characteristics of Water Quality
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
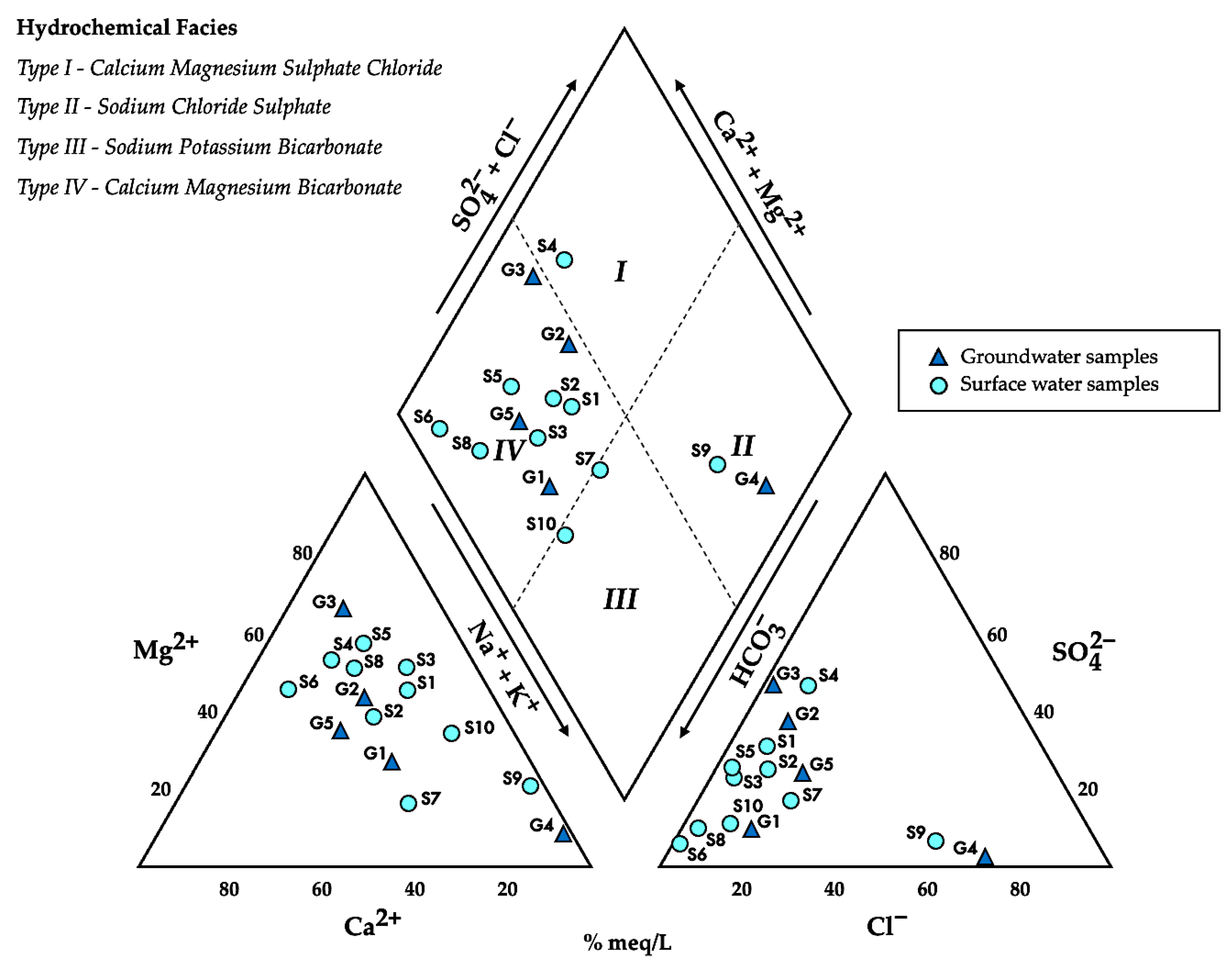
3.1.2. Hydrochemical Facies
3.1.3. Heavy Metals Assessment
3.2. Classification for Irrigation Suitability
3.2.1. Salinity Hazard
| Indices | Range | Classification | Reference | Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater | Surface Water | ||||
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) | <750 | No problem | [16,50] | G1–G3, G5 | S1–S10 |
| 750–3000 | Slight to Moderate | G4 | - | ||
| >3000 | Severe | - | - | ||
| Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) | <10 | Excellent | [16,50] | G1–G3, G5 | S1–S10 |
| 10–18 | Good | G4 | - | ||
| 18–26 | Doubtful | - | - | ||
| >26 | Unsuitable | - | - | ||
| Sodium Percentage (Na%) | <20 | Excellent | [64] | G3 | S4, S6 |
| 20–40 | Good | G2, G5 | S1–S3, S5, S8 | ||
| 40–60 | Permissible | G1 | S7, S10 | ||
| 60–80 | Doubtful | - | S9 | ||
| >80 | Unsafe | G4 | - | ||
| Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC) | <1.25 | Good | [52] | G1–G3, G5 | S1–S10 |
| 1.25–2.5 | Doubtful | - | - | ||
| >2.5 | Unsuitable | G4 | - | ||
| Magnesium Adsorption Ratio (MAR) | <50% | Suitable | [53] | G1, G5 | S6, S7 |
| >50% | Unsuitable | G2–G4 | S1–S5, S8–S10 | ||
| Kelley’s Ratio (KR) | <1 | Suitable | [54] | G1, G3, G5 | S1–S8, S10 |
| >1 | Unsuitable | G2, G4 | S9 | ||
| Total Hardness (TH) | <75 | Soft | [46] | G1–G5 | S1–S10 |
| 75–150 | Moderately hard | - | - | ||
| 150–300 | Hard | - | - | ||
| >300 | Very hard | - | - | ||
| Potential Salinity (PS) | <3 | Excellent | [51] | G1–G3, G5 | S1–S10 |
| 3–5 | Good | - | - | ||
| >5 | Unsuitable | G4 | - | ||
| Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) | 0–25 | Excellent | [56] | G1–G3, G5 | S1–S10 |
| 26–50 | Good | - | - | ||
| 51–75 | Poor | - | - | ||
| 76–100 | Very Poor | G4 | - | ||
| >100 | Unsuitable | - | - | ||
3.2.2. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
3.2.3. Sodium Percentage (Na%)
3.2.4. Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
3.2.5. Magnesium Adsorption Ratio (MAR)
3.2.6. Kelley’s Ratio (KR)
3.2.7. Total Hardness (TH)
3.2.8. Potential Salinity (PS)
3.2.9. Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
3.3. The Impact of Water Quality on Agricultural Development
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanjra, M.A.; Qureshi, M.A. Global water crisis and future food security in an era of climate change. Food Policy 2010, 35, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, J. The rising pressure of global water shortages. Nature 2015, 517, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gude, V.G. Desalination and water reuse to address global water scarcity. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essink, G. Improving fresh groundwater supply—Problems and solutions. Contribution of working group II to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Ocean Coast Manag. 2001, 44, 429–449. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, L.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, A.; Tunio, I.A.; Sassanelli, C. Water Quality Assessment and Monitoring in Pakistan: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, T.; Benkhard, B.; Vasvári, P.; Csorba, P.; Kiss, E.; Balla, D.; Fazekas, I.; Csépes, E.; Berkat, A.; Szabó, G. Hydrochemical assessment of the Kisköre Reservoir (Lake Tisza) and the impacts of water quality on tourism development. Water 2023, 15, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Mirza, M.A.; Choudhary, M.A.; Kim, K.H.; Raza, W.; Raza, N. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in crops in wastewater irrigated zone and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; Qi, X. Treated Wastewater Irrigation—A Review. Water 2021, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, S.S.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Joardar, M.; Ghosh, B.; Roychowdhury, T. Quality and health risk evaluation for groundwater in Nadia district, West Bengal: An approach on its suitability for drinking and domestic purpose. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Yousefi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Radfard, M.; Yousefi, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Hum. Ecol. 2018, 25, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.J.; Finlayson, C.M.; Filkenmark, M. Managing water in agriculture for food production and other ecosystem services. Agri. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Sarwar, G.; Shah, S.H.; Muhammad, S. Soil Salinity Research in 21st Century in Pakistan: Its Impact on Availability of Plant Nutrients, Growth and Yield of Crops. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 52, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ryan, M.C.; Sun, B. The influence of irrigation and Wuliangsuhai Lake on groundwater quality in eastern Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qian, H.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y. Alterations of groundwater chemistry due to modern water transfer for irrigation over decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachi, N.; Kachi, S.; Bousnoubra, H. Effects of irrigated agriculture on water and soil quality (case perimeter Guelma, Algeria). Soil Water Res. 2016, 1, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture: Irrigation and Drainage; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Bhatta, D. Environmental studies on river water quality with reference to suitability for agricultural purposes: Mahandi river estuarine system, India—A case study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 155, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salifu, M.; Aidoo, F.; Hayford, M.S.; Adomako, D.; Asare, E. Evaluating the suitability of groundwater for irrigational purposes in some selected districts of the Upper West region of Ghana. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 3, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, G.; Aberra, D.; Fufa, F. Evaluation of the suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes in Jimma zone of Oromia, Ethiopia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabeygi, M.; Yousefi, N.; Abbasnia, A.; Youzi, H.; Alikhani, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of scaling potential and corrosiveness of water supply networks, Iran. J. Water Supply. 2017, 66, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Tewari, G.; Kumar, S. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Suitability of Irrigation Purposes: A Case Study in the Udham Singh Nagar. Uttarakhand. J. Chem. 2020, 15, 6924026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouiti, S.; Azaza, F.H.; Melki, F.E.; Hamdi, M.; Celico, F.; Zammouri, M. Groundwater quality assessment for different uses using various water quality indices in semi-arid region of central Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46669–46691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; He, K.; Sulaiman, N.M.N. Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in Selangor River basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 644, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidiac, S.; Najjar, P.E.; Ouaini, N.; Rayess, Y.E.; Azzi, D.E. A comprehensive review of water quality indices (WQIs): History, models, attempts and perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 349–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. AQUASTAT Country Profile—Brunei Darussalam; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Aziz, H.M.M. Baseline Study of the Chemical Composition of Brunei Darussalam Rivers. PhD Thesis, Brunel University, Uxbridge, UK, 2005; 218p. [Google Scholar]
- Hj Kamis, M.; Zaini, A.F.; Yahya, M.A.Y.; Abas, M.A.N.; Hassan, M.A.S. Causes and Impacts of Water Crisis and Achieving Water Security: Application to Brunei. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356419567_Causes_and_Impacts_of_Water_Crisis_and_Achieving_Water_Security_Application_to_Brunei_17b8525_Mubarak_bin_Haji_Kamis_17b8526_Akhimullah_Farhan_bin_Zaini_17B8532_Muhammad_Aizuddin_Yaqin_bin_Haji_Yahaya?channel=doi&linkId=6199ceecd7d1af224b11eff6&showFulltext=true (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Khalid, M. Plans to Prevent the Degradation of Water Quality in Brunei. The Borgen Project. Available online: https://borgenproject.org/water-quality-brunei/ (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Gödeke, S.H.; Malik, O.A.; Lai, D.T.C.; Bretzler, A.; Schirmer, M.; Mansor, N.H. Water quality investigation in Brunei Darussalam: Investigation of the influence of climate change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grealish, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, R.W. Acid sulphate soil characterisation in Negara Brunei Darussalam: A case study to inform management decisions. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, A.S.; Abdul Latiff, A.H.; Lim, L.H.; Gödeke, S.H. Groundwater investigation of a coastal aquifer in Brunei Darussalam using seismic refraction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Napiah, M.N. Status and Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) in Brunei Darussalam. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiuddin, K.B.M. Supplementary irrigation to rain-fed paddy: A case study of Kg Bebuloh paddy scheme. In Proceedings of the 12th International Water Technology Conference (IWTC), Alexandria, Egypt, 27–30 March 2008; Volume 12, pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiuddin, K.B.M. Rain harvesting and stream storage for supplementary irrigation to rain-fed paddy schemes: A case study of Selapon Paddy Scheme. Sustain. Irrig. Drain. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 185, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Azffri, S.L.; Azaman, A.; Sukri, R.S.; Jaafar, S.M.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Schirmer, M.; Gödeke, S.H. Soil and groundwater investigation for sustainable agricultural development: A case study from Brunei Darussalam. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azffri, S.L.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Gödeke, S.H. Electrical resistivity tomography and induced polarization study for groundwater exploration in the agricultural development areas of Brunei Darussalam. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azffri, S.L.; Ali Ahmad, A.S.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Khalid, A.A.; Murphy, J.J.; Gödeke, S.H. Groundwater exploration through 2D electrical resistivity tomography in Labi agricultural site, Belait District, Brunei Darussalam. Thai Geos. J. 2022, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandal, S.T. The Geology and Hydrocarbon Resources of Negara Brunei Darussalam; Brunei Shell Petroleum Company: Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1996; 243p. [Google Scholar]
- Brunei Darussalam Meteorological Department. Climate. Available online: www.bruneiweather.com.bn (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Hasan, D.; Ratnayake, U.; Shams, S. Evaluation of rainfall and temperature trends in Brunei Darussalam. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference, Bali, Indonesia, 29 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.S. Geology of North-West Borneo: Sarawak, Brunei and Sabah; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; 421p. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, C.; Back, S.; Van Rensbergen, P.; Cravello, P.; Lambiase, J. Characteristics of repeated, detached Miocene-Pliocene tectonic inversion events in a large delta province on an active margin, Brunei Darussalam, Borneo. J. Struct. Geol. 2003, 25, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, G.K. Hydrological Characteristics and Water Resources. Singapore. J. Trop. Geog. 1992, 13, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Moeck, C.; Grech-Cumbo, N.; Podgorski, J.; Bretzler, A.; Gurdak, J.J.; Berg, M.; Schirmer, M. A global-scale dataset of direct natural groundwater recharge rates: A review of variables, processes, and relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.J.; Carter, I.C.; Davison, I.; Bridle, R.C. The Staged Construction of Imang Dam. Ensuring Reservoir Safety into the Future. 2008. Available online: https://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/10.1680/ersitf.35225.0030 (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3: A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, Inverse Geochemical Calculations. In Modeling Techniques; Techniques and Methods, 6-A43; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P. Groundwater quality in Western China: Challenges and paths forward for groundwater quality research in Western China. Expos. Health 2016, 8, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.J. A survey of charge balance errors on published analyses of potable ground and surface waters. Groundwater 1994, 32, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agricultural handbook 60; USDA and IBH Pub. Coy Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1954; pp. 98–99.
- Doneen, L.D. The influence of crop and soil on percolating water. In Proceedings of the Biennial Conference on Groundwater Recharge, Davis, CA, USA, 28 June 1961; pp. 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonate irrigation water. Soils Sci. 1950, 69, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, I.I.M. Groundwater, 2nd ed.; Wiley Eastern Limited: New Delhi, India, 1987; pp. 344–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proc. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1940, 66, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.K. An index-number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. 1965, 37, 292–315. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index-do we dare. Water Sew Work 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. EoS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Salinity Laboratory. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. In United States Development Agency Handbook 60; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; p. 147. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Water; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; 969p.
- Pascale, S.D.; Orsini, F.; Pardossi, A. Irrigation water quality for greenhouse horticulture. In Good Agricultural Practices for Greenhouse Vegetable Crops. Principles for Mediterranean Climate Areas; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 169–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremeskel, G.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Kifle, M.; Meresa, E.; Gebremedhin, T.; Girmay, A. Salinization pattern and its spatial distribution in the irrigated agriculture of Northern Ethiopia: An integrated approach of quantitative and spatial analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawla, K.; Mohamed, H. Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality in greenhouse-intensive agricultural areas in the coastal zone of Tunisia: Case of Taboulba region. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 10–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fipps, G. Irrigation water quality standards and salinity management strategies. Agrilife Ext. 2003, 1667, 18. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/87829 (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Srivastava, A.K.; Parimal, P.S. Source rock weathering and groundwater suitability for irrigation in Purna alluvial basin, Maharashtra, central India. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 129, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteieb, S.; Cherif, S.; Tarhouni, J. Hydrochemical assessment of water quality for irrigation: A case study of the Medjerda River in Tunisia. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.M.; Kang, S.; Tripathee, L.; Paudyal, R.; Sillanpaa, M. Major ions and irrigation water quality assessment of the Nepalese Himalayan rivers. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 2668–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Quality of water for irrigation. Soil Sci. 1972, 113, 227–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; Kotb, W.K.; Bonanomi, G.; Fakhry, H.; Marraiki, N.A.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Xie, C.; Liang, J.; Ma, H. Risk assessment of groundwater hydrochemistry for irrigation suitability in Ordos Basin, China. Nat. Hazards 2020, 101, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamvroula, D.E.; Alexakis, D.E. Evaluating the Performance of Water Quality Indices: Application in Surface Water of Lake Union, Washington State-USA. Hydrology 2022, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, A.; Andrade, E.M.; Chaves, L.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisostomo, L.A. A new proposal of the classification of irrigation water. Cienc. Agron. 2010, 413, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, S.; Karakuş, C.B. Estimation of irrigation water quality index with development of an optimum model: A case study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4771–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gödeke, S.H.; Jamil, H.; Schirmer, M.; Anja Bretzler, A.; Shamsuddin, N.; Mansor, N.H. Iron and manganese mobilisation due to dam height increase for a tropical reservoir in Southeast Asia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Maneechot, L.; Bharambe, K.P.; Fong, C.S.; Sulaiman, N.M.N. Applications of artificial intelligence methods for monsoonal river classification in Selangor River basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 194, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.L.; Chia, M.Y.; Koo, C.H.; Huang, Y.F. Integration of advanced optimization algorithms into least square support vector machine (LSSVM) for water quality index prediction. Water Supply 2022, 22, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on the surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhip, M.A.A.B.H.; Gödeke, S.H.; Cobb, A.R.; Sukri, R.S. Seismic refraction study, single well test and physical core analysis of anthropogenic degraded Peat at the Badas Peat Dome, Brunei Darussalam. Eng. Geol. 2020, 273, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, H.; Mumtaz, S.; Qamar, A.M. Water quality monitoring: From conventional to emerging technologies. Water Supply 2021, 20, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
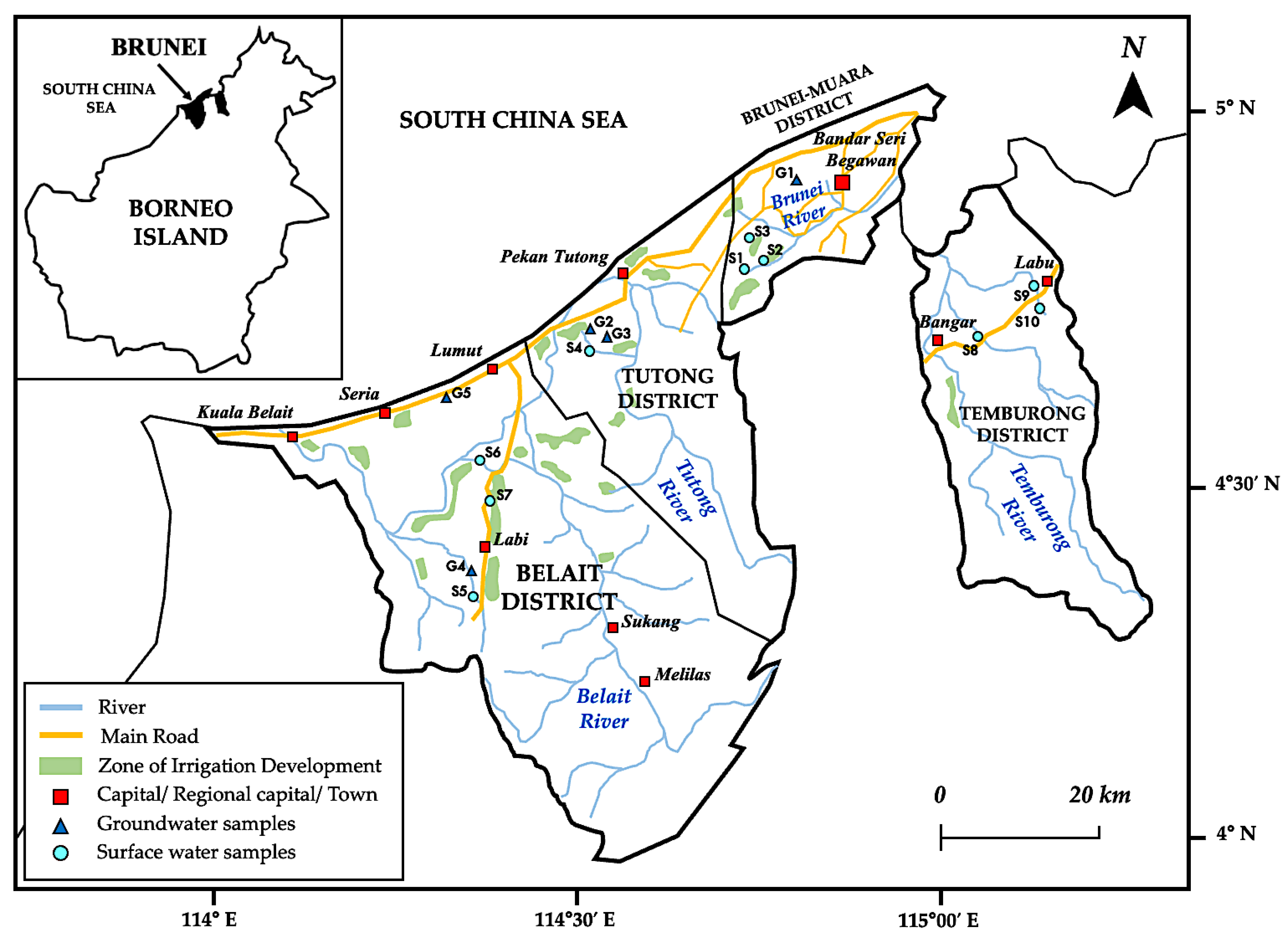




| District | Sample ID | Coordinates | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | |||
| Brunei-Muara | G1 | 4°56′06.8″ N | 114°52′49.4″ E | Flowing artesian; irrigation use. Water flow rate of 0.5 m3/h; well depth of 50 m bgl. |
| Tutong | G2 | 4°42′00.6″ N | 114°38′18.6″ E | Flowing artesian; potable water. Water flow rate of 1–2 m3/h; well depth of 20 m bgl. |
| G3 | 4°41′59.5″ N | 114°38′20.1″ E | Flowing artesian; potable water. Water flow rate of 1–2 m3/h; well depth of 25 m bgl. | |
| Belait | G4 | 4°23′07.4″ N | 114°27′11.6″ E | Irrigation use; water flow rate of 5–12 m3/h [37]. Well depth of 80 m bgl; submersible pump depth of 60 m bgl. |
| G5 | 4°39′07.4″ N | 114°25′32.4″ E | Flowing artesian; potable water. Water flow rate of 28.8 m3/h; well depth of 200 m bgl. | |
| District | Sample ID | Coordinates | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | |||
| Brunei-Muara | S1 | 4°47′19.9″ N | 114°48′58.7″ E | Wasan river; drainage and source for paddy field irrigation. |
| S2 | 4°47′38.5″ N | 114°49′17.4″ E | Panchor river; drainage and source for paddy field irrigation. | |
| S3 | 4°48′05.9″ N | 114°48′06.2″ E | Imang reservoir; main source for irrigation in Brunei-Muara. Reservoir capacity of 8 million cubic metres [46]. | |
| Tutong | S4 | 4°41′57.6″ N | 114°38′19.3″ E | Penapar river; located near construction site of new dam. |
| Belait | S5 | 4°22′04.3″ N | 114°27′23.6″ E | Rampayoh river; drainage and source for paddy field irrigation. |
| S6 | 4°32′20.5″ N | 114°28′04.7″ E | Belait river; located near residential area. | |
| S7 | 4°30′56.1″ N | 114°28′28.9″ E | Luagan lake; located near recreational area. | |
| Temburong | S8 | 4°43′02.7″ N | 115°06′33.0″ E | Lamaling river; located near residential and commercial areas. |
| S9 | 4°45′50.2″ N | 115°11′10.8″ E | Labu river; located near recreational area and paddy field. | |
| S10 | 4°45′04.0″ N | 115°12′07.7″ E | Senukoh river; located near recreational area and paddy field. | |
| Sampling Event | Parameters | Method | Reference | Detection Limits * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January-2022 | Sodium, magnesium, calcium, potassium | Ion chromatography | EN ISO 14911 | 0.5, 1.5 |
| Chloride, sulphate | Ion chromatography | EN ISO 10304-1 | 0.5, 0.1 | |
| Bicarbonate, carbonate | Titration | EN ISO 9963-1 | 1 | |
| September-2022 | Sodium, magnesium, calcium, potassium | Ion chromatography | APHA 3120-N | 0.1 |
| Chloride | Titration | APHA 4500-Cl-E | 1 | |
| Sulphate | Turbidimetric | APHA 4500-SO-E | 1 | |
| Bicarbonate, carbonate | Titration | APHA 2320B | 1 | |
| Iron, zinc, lead, copper, chromium, cadmium, arsenic | Ion chromatography | APHA 3125B | 0.001, 0.0005 |
| Sample | Sample ID | pH | EC μS/cm | Na+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | K+ | SO42− | Cl− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | ||||||||||
| Groundwater | G1 | 4.8 | 28.5 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 15.5 |
| G2 | 4.6 | 50.0 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 10.0 | |
| G3 | 5.2 | 68.5 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 17.5 | 1.2 | 28.0 | |
| G4 | 6.3 | 1127 | 190 | 7.4 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 306 | 198 | |
| G5 | 6.5 | 85.0 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 4.3 | 1.3 | 9.0 | 1.0 | 36.0 | |
| Surface Water | S1 | 6.1 | 90.5 | 5.3 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 17.5 | 4.0 | 44.0 |
| S2 | 6.6 | 133 | 6.7 | 4.3 | 5.5 | 2.4 | 15.5 | 5.9 | 53.5 | |
| S3 | 6.9 | 51.0 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 19.5 | |
| S4 | 4.6 | 51.5 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 9.0 | 1.2 | 11.0 | |
| S5 | 5.4 | 38.0 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 8.0 | 0.9 | 28.0 | |
| S6 | 4.9 | 30.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 3.0 | 0.5 | 73.0 | |
| S7 | 4.8 | 39.0 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | |
| S8 | 6.8 | 32.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 36.5 | |
| S9 | 6.3 | 202 | 27.0 | 3.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 5.5 | 46.1 | 47.0 | |
| S10 | 6.8 | 51.5 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 3.7 | 2.8 | 34.5 | |
| Worldwide Standard Limits | ||||||||||
| FAO * | 6.5–8.4 | <750 | <920 | <60 | <400 | <30 | <960 | <1050 | <150 | |
| Sample | Sample ID | Fe | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cr | Cd | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | ||||||||
| Groundwater | G1 | 0.78 | 0.007 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0005 | <0.001 |
| G2 | 0.19 | 0.029 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0005 | <0.001 | |
| G3 | 1.53 | 0.016 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0005 | 0.002 | |
| G4 | 2.92 | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0005 | <0.001 | |
| G5 | 1.17 | 0.008 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0005 | <0.001 | |
| Surface Water | S1 | 0.94 | 0.018 | 0.0005 | 0.0065 | 0.0016 | <0.0001 | 0.0028 |
| S2 | 0.73 | 0.012 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0011 | <0.0001 | 0.0012 | |
| S3 | 0.10 | 0.009 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.0012 | |
| S4 | 0.39 | 0.037 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| S5 | 0.10 | 0.041 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | |
| S7 | 0.64 | 0.051 | 0.0004 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.0009 | |
| S8 | 0.10 | 0.014 | <0.0001 | 0.0016 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | |
| S9 | 0.60 | 0.012 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | |
| S10 | 0.09 | 0.017 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | |
| Worldwide Standard Limits | ||||||||
| FAO * | <5.0 | <2.0 | <5.0 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <0.01 | <0.1 | |
| Sample | Sample ID | SAR | Na% | RSC | MAR | KR | TH | PS | IWQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater | G1 | 0.2 | 42.6 | 0.22 | 45.2 | 0.64 | 1.5 | 0.07 | 3.1 |
| G2 | 0.1 | 28.2 | 0.14 | 59.1 | 1.31 | 4.5 | 0.09 | 2.9 | |
| G3 | 0.1 | 13.0 | 0.36 | 74.8 | 0.32 | 14.7 | 0.22 | 5.8 | |
| G4 | 11.1 | 90.4 | 3.15 | 85.3 | 78.8 | 35.7 | 8.64 | 80 | |
| G5 | 0.3 | 27.8 | 0.31 | 46.9 | 0.43 | 20.2 | 0.12 | 7.7 | |
| Surface Water | S1 | 0.4 | 36.1 | 0.42 | 69.2 | 0.61 | 20.2 | 0.29 | 9.1 |
| S2 | 0.4 | 32.0 | 0.17 | 56.3 | 0.33 | 31.3 | 0.33 | 11.6 | |
| S3 | 0.3 | 34.7 | −0.40 | 75.9 | 0.14 | 11.2 | 0.07 | 4.5 | |
| S4 | 0.1 | 16.5 | −0.22 | 62.3 | 0.05 | 7.3 | 0.13 | 3.1 | |
| S5 | 0.1 | 21.3 | 0.07 | 72.8 | 0.06 | 7.1 | 0.11 | 5 | |
| S6 | 0.02 | 10.9 | 0.78 | 49.7 | 0.01 | 2.5 | 0.05 | 11 | |
| S7 | 0.2 | 52.9 | −0.55 | 32.0 | 0.04 | 2.6 | 0.04 | 2 | |
| S8 | 0.2 | 23.6 | −0.02 | 65.8 | 0.08 | 8.6 | 0.06 | 6.1 | |
| S9 | 2.4 | 76.4 | 0.56 | 85.0 | 4.41 | 14.8 | 1.36 | 16 | |
| S10 | 0.5 | 52.4 | 0.33 | 71.2 | 0.60 | 6.6 | 0.12 | 6.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azffri, S.L.; Thong, C.S.; Lim, L.H.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Schirmer, M.; Gödeke, S.H. Evaluation of Ground and Surface Water Hydrochemistry for Irrigation Suitability in Borneo: Insights from Brunei Darussalam. Water 2023, 15, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122154
Azffri SL, Thong CS, Lim LH, Ibrahim MF, Schirmer M, Gödeke SH. Evaluation of Ground and Surface Water Hydrochemistry for Irrigation Suitability in Borneo: Insights from Brunei Darussalam. Water. 2023; 15(12):2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122154
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzffri, Siti Lieyana, Chua Siaw Thong, Lee Hoon Lim, Md Faizan Ibrahim, Mario Schirmer, and Stefan Herwig Gödeke. 2023. "Evaluation of Ground and Surface Water Hydrochemistry for Irrigation Suitability in Borneo: Insights from Brunei Darussalam" Water 15, no. 12: 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122154
APA StyleAzffri, S. L., Thong, C. S., Lim, L. H., Ibrahim, M. F., Schirmer, M., & Gödeke, S. H. (2023). Evaluation of Ground and Surface Water Hydrochemistry for Irrigation Suitability in Borneo: Insights from Brunei Darussalam. Water, 15(12), 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122154







