Flood Simulations Using a Sensor Network and Support Vector Machine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
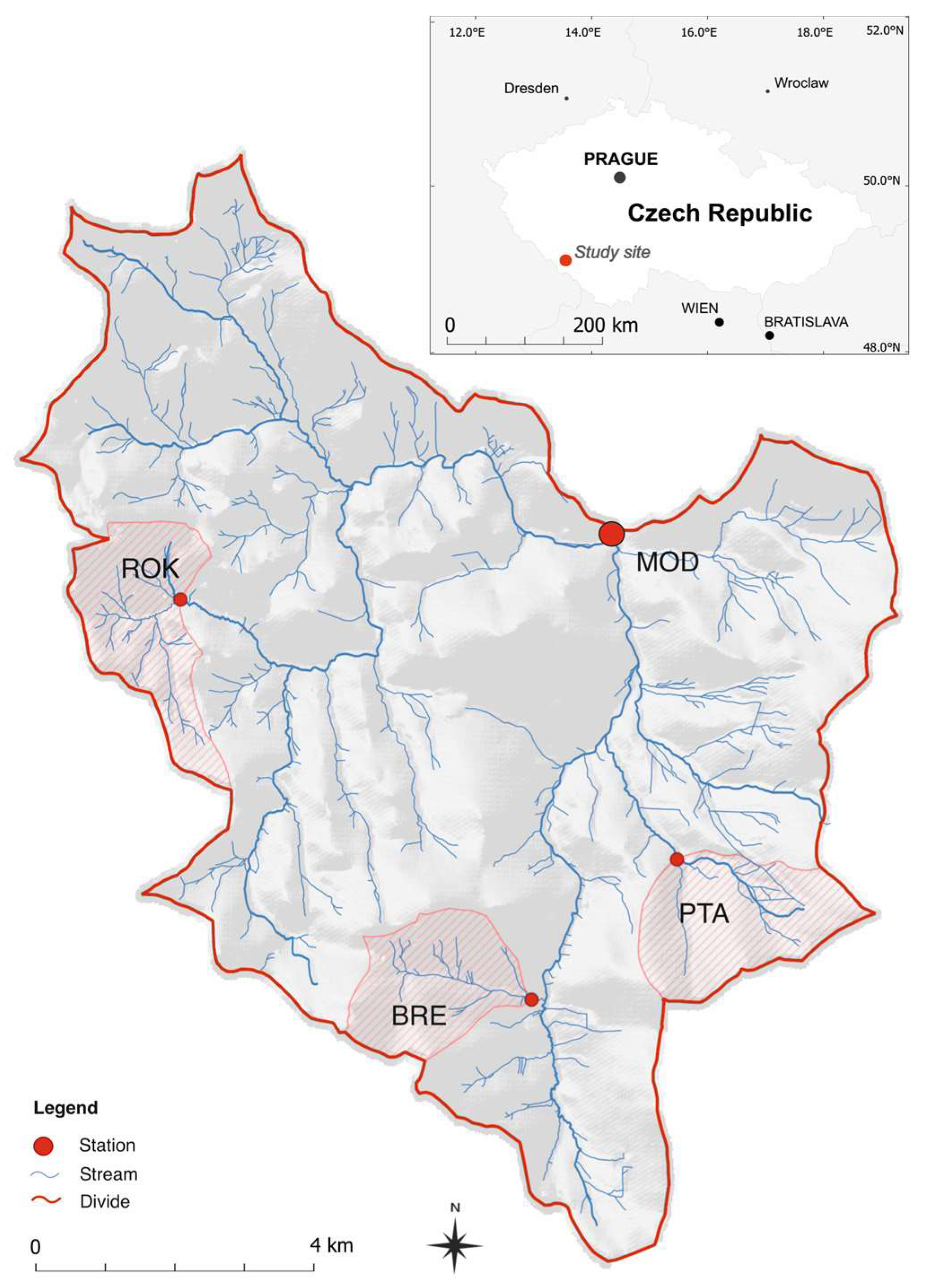
2.1. Study Area
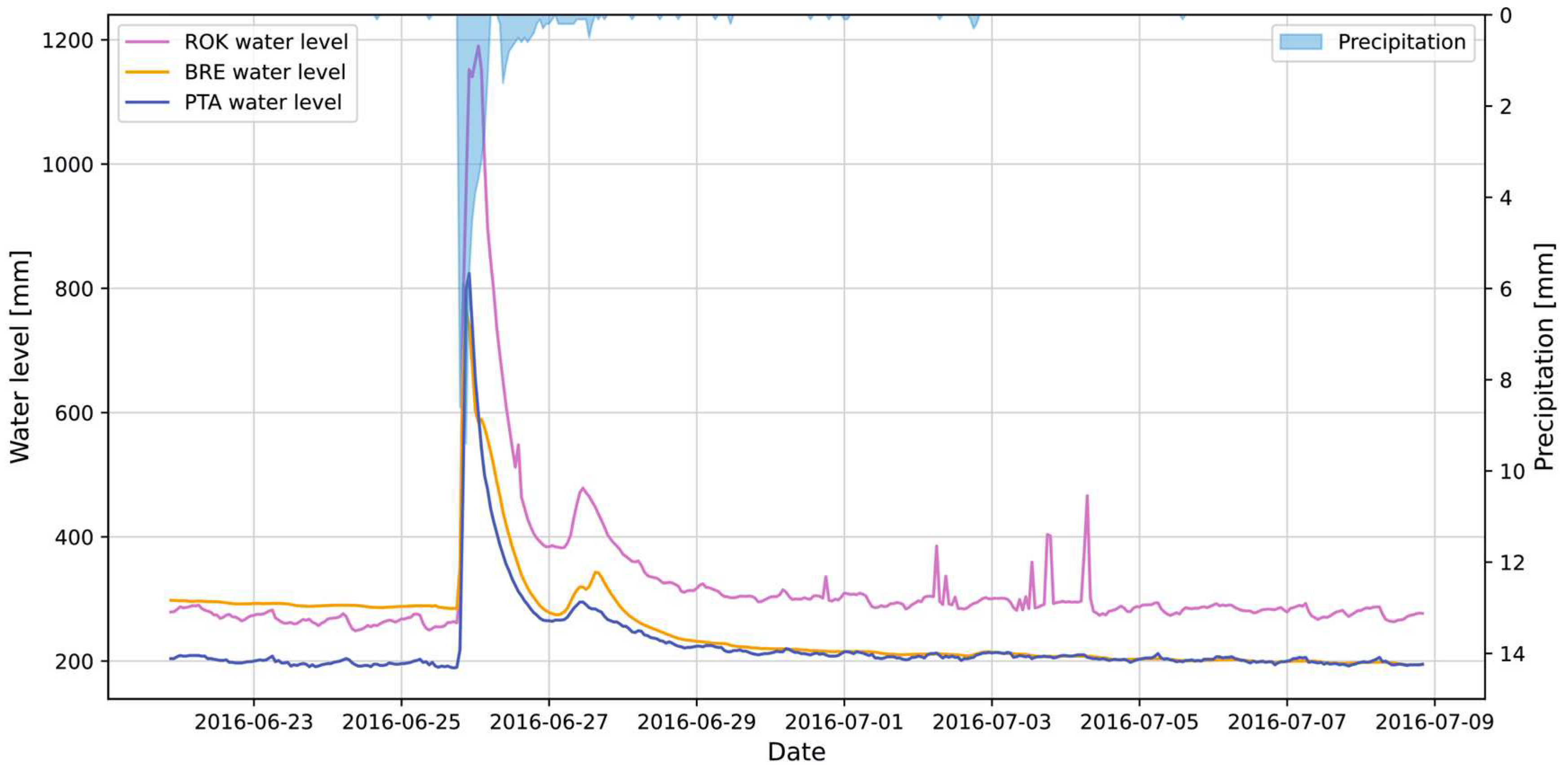
2.2. Sensor Network
2.3. Input Data
2.4. Model Setup
2.5. Model Training, Validation, and Simulation Scenarios
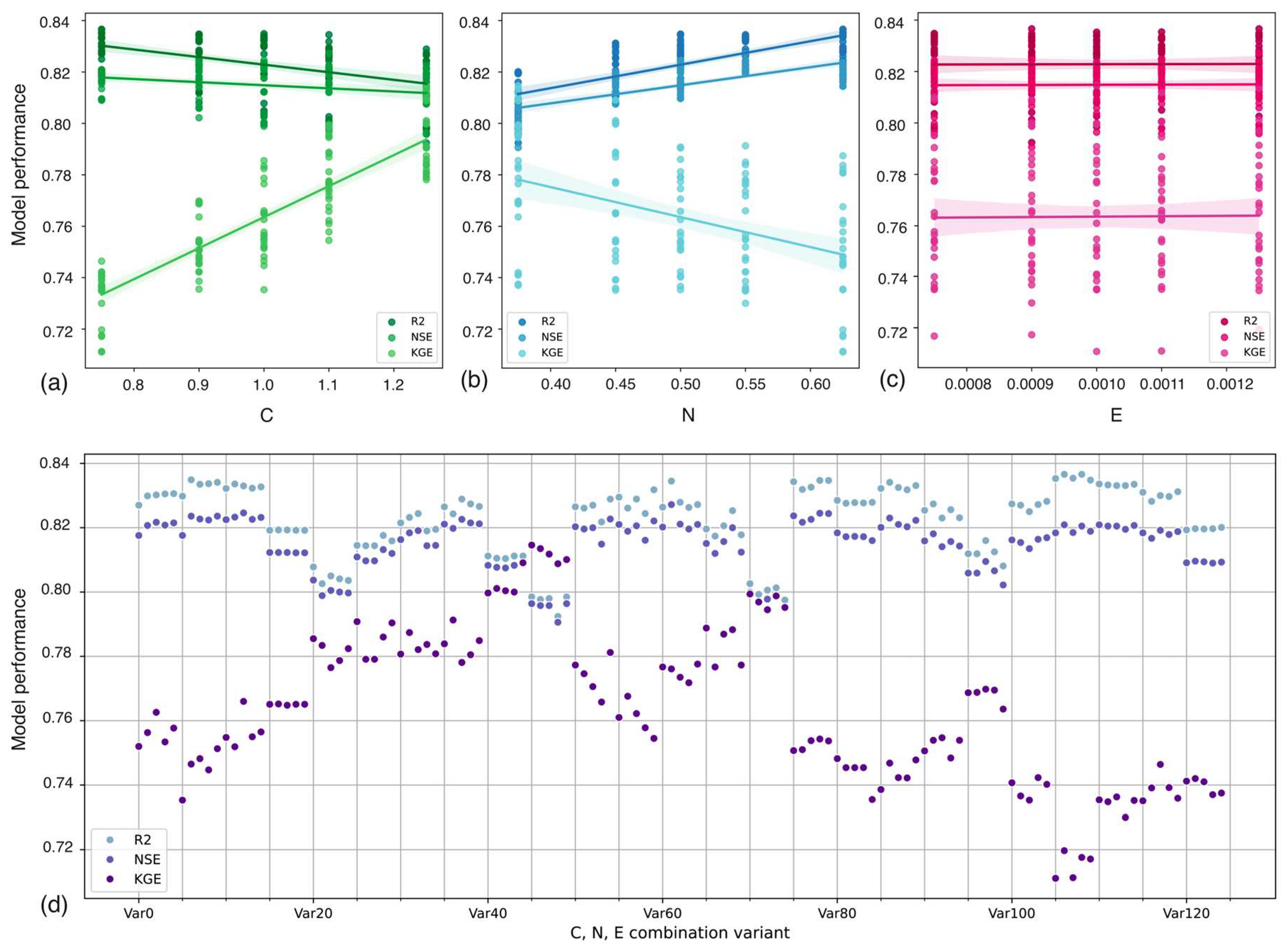
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis and Model Parametrization
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity Analysis and Model Validation
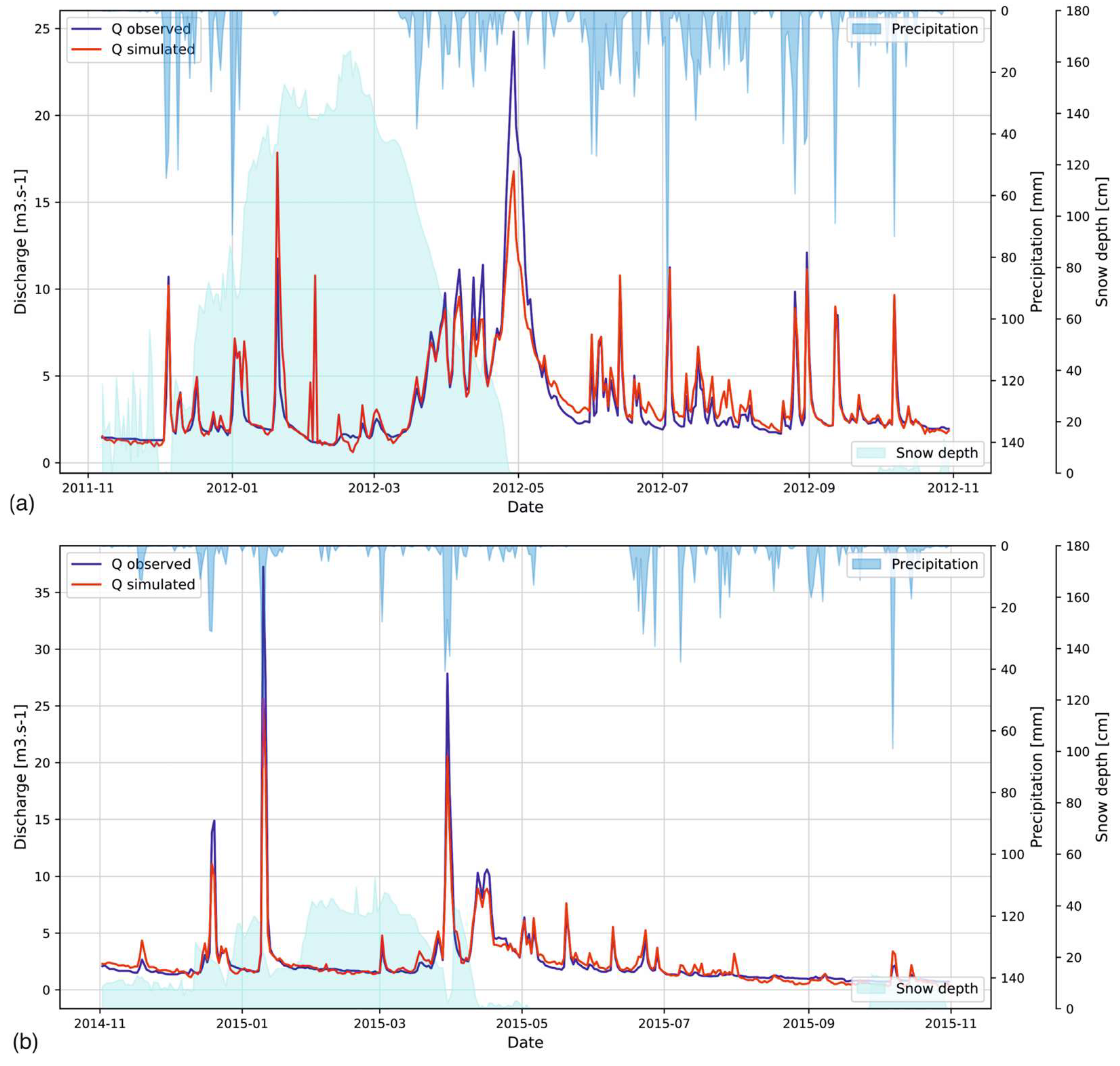
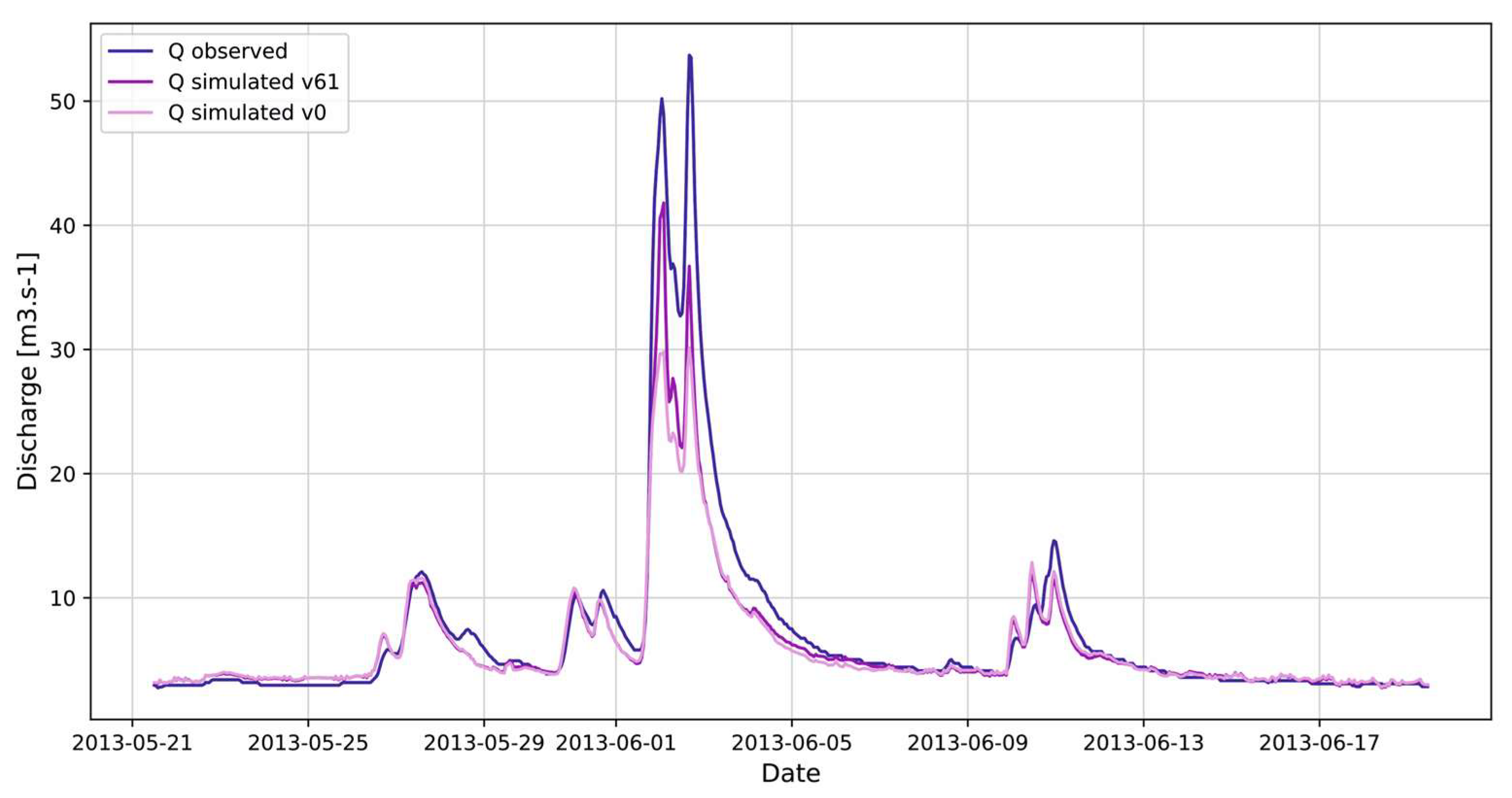
3.2. Floods from Frontal Precipitation
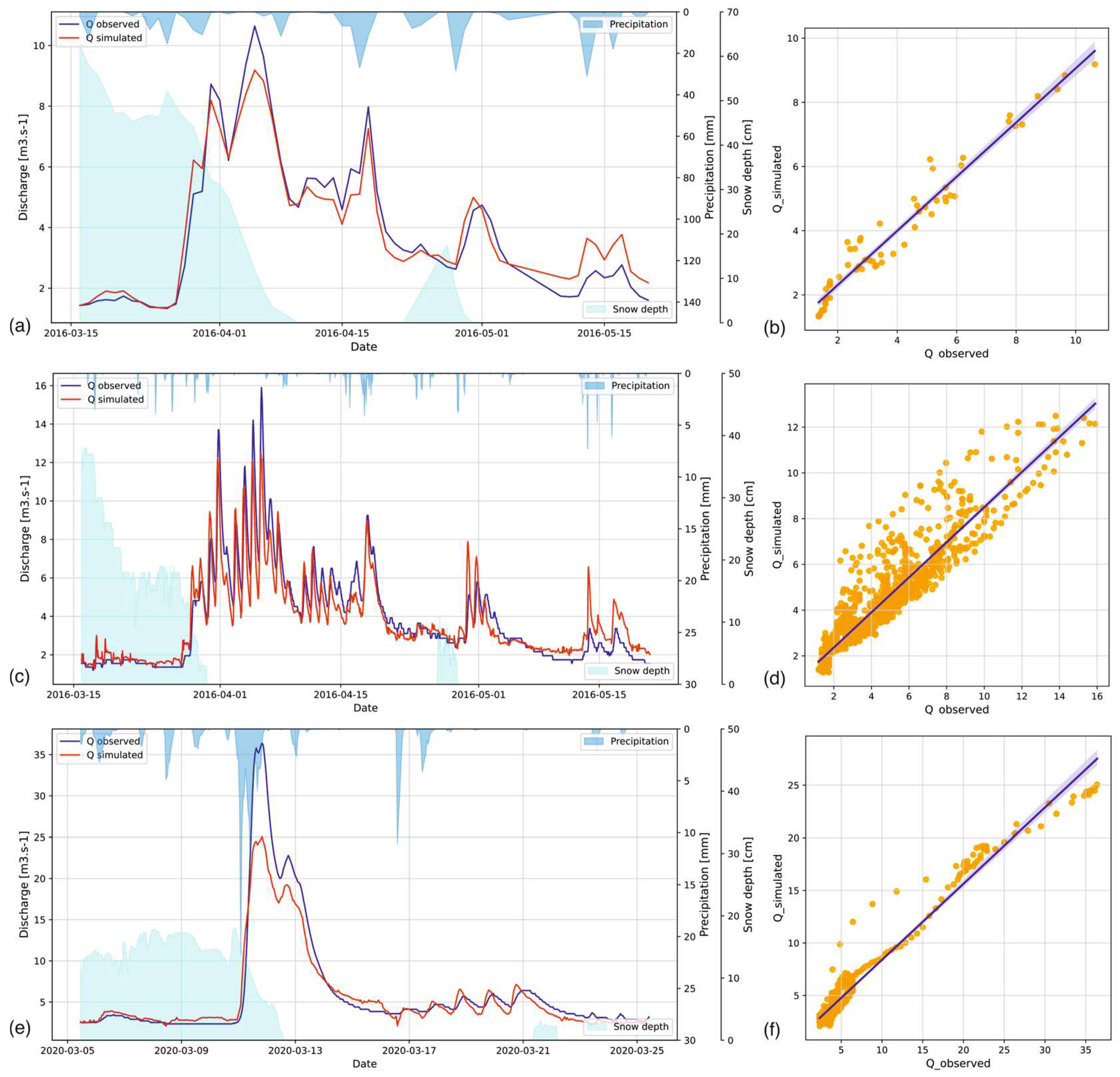
3.3. Convective Storms
3.4. Snowmelt Floods
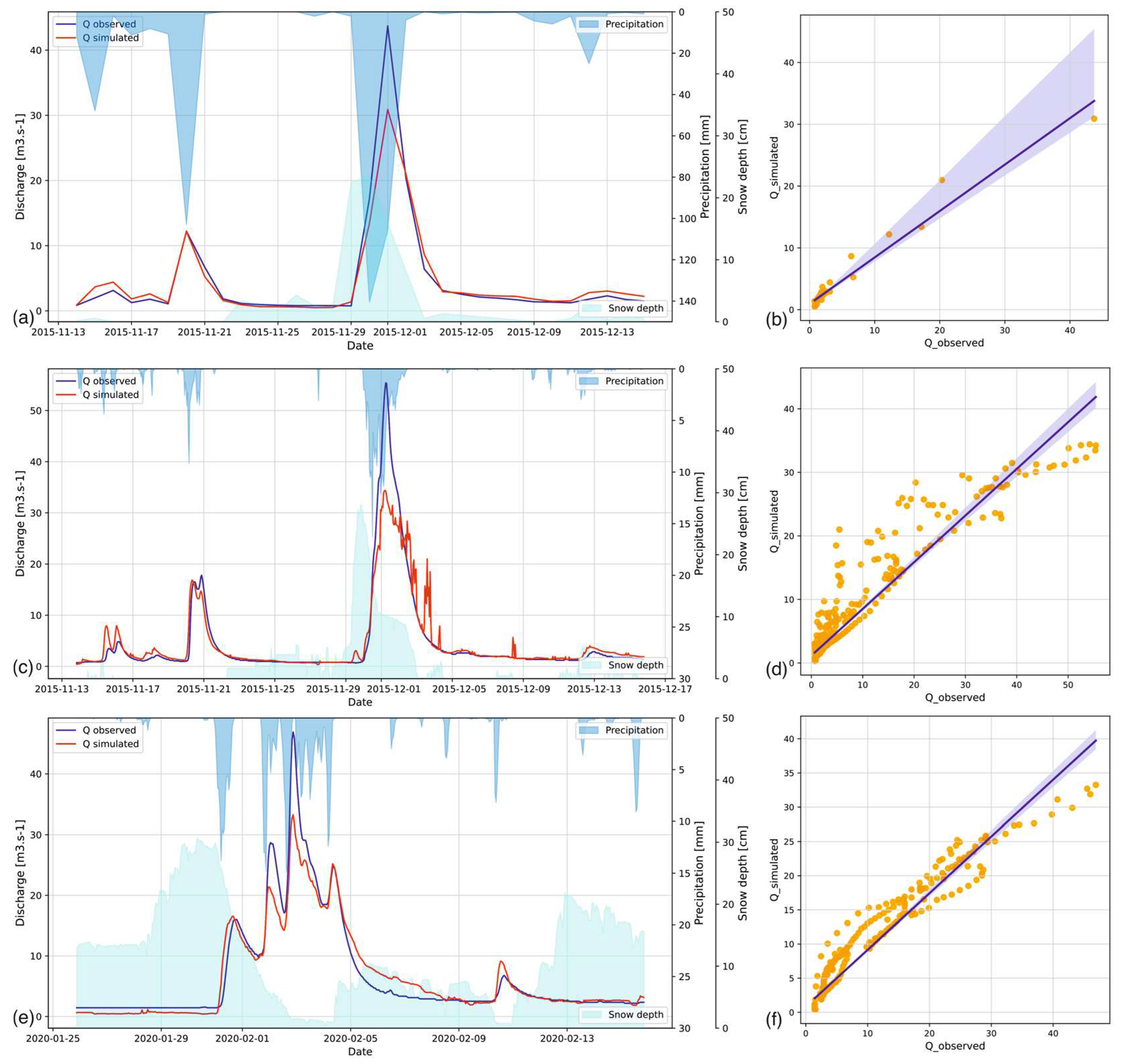
3.5. Rain-On-Snow Floods
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainties Due to the Physiography
4.2. Limitations of Sensor Network Monitoring
4.3. Effect of Timestep Aggregation
4.4. Impact of Sensitivity Analysis on Model Performance
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| SVR Parameter Values | Performance Metrics Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | C | N | E | R2 | NSE | KGE | RMSE |
| Var0 | 1.00 | 0.500 | 0.00100 | 0.827 | 0.818 | 0.752 | 1.624 |
| Var1 | 1.00 | 0.500 | 0.00125 | 0.830 | 0.821 | 0.756 | 1.610 |
| Var2 | 1.00 | 0.500 | 0.00110 | 0.830 | 0.822 | 0.763 | 1.605 |
| Var3 | 1.00 | 0.500 | 0.00090 | 0.831 | 0.821 | 0.753 | 1.609 |
| Var4 | 1.00 | 0.500 | 0.00075 | 0.831 | 0.822 | 0.758 | 1.606 |
| Var5 | 1.00 | 0.625 | 0.00100 | 0.830 | 0.818 | 0.735 | 1.624 |
| Var6 | 1.00 | 0.625 | 0.00125 | 0.835 | 0.824 | 0.747 | 1.597 |
| Var7 | 1.00 | 0.625 | 0.00110 | 0.834 | 0.823 | 0.748 | 1.601 |
| Var8 | 1.00 | 0.625 | 0.00090 | 0.834 | 0.822 | 0.745 | 1.602 |
| Var9 | 1.00 | 0.625 | 0.00075 | 0.834 | 0.824 | 0.751 | 1.596 |
| Var10 | 1.00 | 0.550 | 0.00100 | 0.832 | 0.823 | 0.755 | 1.602 |
| Var11 | 1.00 | 0.550 | 0.00125 | 0.834 | 0.823 | 0.752 | 1.598 |
| Var12 | 1.00 | 0.550 | 0.00110 | 0.833 | 0.825 | 0.766 | 1.592 |
| Var13 | 1.00 | 0.550 | 0.00090 | 0.832 | 0.823 | 0.755 | 1.601 |
| Var14 | 1.00 | 0.550 | 0.00075 | 0.833 | 0.823 | 0.757 | 1.599 |
| Var15 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 0.00100 | 0.819 | 0.812 | 0.765 | 1.647 |
| Var16 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 0.00125 | 0.819 | 0.812 | 0.765 | 1.647 |
| Var17 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 0.00110 | 0.819 | 0.812 | 0.765 | 1.647 |
| Var18 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 0.00090 | 0.819 | 0.812 | 0.765 | 1.647 |
| Var19 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 0.00075 | 0.819 | 0.812 | 0.765 | 1.647 |
| Var20 | 1.00 | 0.375 | 0.00100 | 0.808 | 0.804 | 0.785 | 1.684 |
| Var21 | 1.00 | 0.375 | 0.00125 | 0.803 | 0.799 | 0.783 | 1.705 |
| Var22 | 1.00 | 0.375 | 0.00110 | 0.805 | 0.801 | 0.777 | 1.698 |
| Var23 | 1.00 | 0.375 | 0.00090 | 0.804 | 0.800 | 0.779 | 1.700 |
| Var24 | 1.00 | 0.375 | 0.00075 | 0.804 | 0.800 | 0.782 | 1.701 |
| Var25 | 1.25 | 0.500 | 0.00100 | 0.815 | 0.811 | 0.791 | 1.653 |
| Var26 | 1.25 | 0.500 | 0.00125 | 0.814 | 0.810 | 0.779 | 1.658 |
| Var27 | 1.25 | 0.500 | 0.00110 | 0.814 | 0.810 | 0.779 | 1.658 |
| Var28 | 1.25 | 0.500 | 0.00090 | 0.818 | 0.813 | 0.786 | 1.643 |
| Var29 | 1.25 | 0.500 | 0.00075 | 0.816 | 0.812 | 0.790 | 1.648 |
| Var30 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 0.00100 | 0.822 | 0.816 | 0.781 | 1.629 |
| Var31 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 0.00125 | 0.823 | 0.818 | 0.787 | 1.620 |
| Var32 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 0.00110 | 0.824 | 0.819 | 0.782 | 1.617 |
| Var33 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 0.00090 | 0.819 | 0.814 | 0.784 | 1.638 |
| Var34 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 0.00075 | 0.820 | 0.815 | 0.781 | 1.637 |
| Var35 | 1.25 | 0.550 | 0.00100 | 0.827 | 0.821 | 0.784 | 1.608 |
| Var36 | 1.25 | 0.550 | 0.00125 | 0.824 | 0.820 | 0.791 | 1.614 |
| Var37 | 1.25 | 0.550 | 0.00110 | 0.829 | 0.823 | 0.778 | 1.601 |
| Var38 | 1.25 | 0.550 | 0.00090 | 0.827 | 0.821 | 0.780 | 1.606 |
| Var39 | 1.25 | 0.550 | 0.00075 | 0.827 | 0.821 | 0.785 | 1.608 |
| Var40 | 1.25 | 0.450 | 0.00100 | 0.811 | 0.808 | 0.800 | 1.664 |
| Var41 | 1.25 | 0.450 | 0.00125 | 0.811 | 0.808 | 0.801 | 1.667 |
| Var42 | 1.25 | 0.450 | 0.00110 | 0.810 | 0.807 | 0.800 | 1.668 |
| Var43 | 1.25 | 0.450 | 0.00090 | 0.811 | 0.808 | 0.800 | 1.664 |
| Var44 | 1.25 | 0.450 | 0.00075 | 0.811 | 0.809 | 0.809 | 1.662 |
| Var45 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 0.00100 | 0.798 | 0.796 | 0.815 | 1.715 |
| Var46 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 0.00125 | 0.798 | 0.796 | 0.814 | 1.718 |
| Var47 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 0.00110 | 0.798 | 0.796 | 0.812 | 1.718 |
| Var48 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 0.00090 | 0.792 | 0.791 | 0.809 | 1.740 |
| Var49 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 0.00075 | 0.798 | 0.796 | 0.810 | 1.715 |
| Var50 | 1.10 | 0.500 | 0.00100 | 0.827 | 0.820 | 0.777 | 1.611 |
| Var51 | 1.10 | 0.500 | 0.00125 | 0.826 | 0.820 | 0.775 | 1.614 |
| Var52 | 1.10 | 0.500 | 0.00110 | 0.827 | 0.820 | 0.771 | 1.613 |
| Var53 | 1.10 | 0.500 | 0.00090 | 0.822 | 0.815 | 0.766 | 1.636 |
| Var54 | 1.10 | 0.500 | 0.00075 | 0.829 | 0.823 | 0.781 | 1.601 |
| Var55 | 1.10 | 0.625 | 0.00100 | 0.830 | 0.821 | 0.761 | 1.608 |
| Var56 | 1.10 | 0.625 | 0.00125 | 0.826 | 0.819 | 0.768 | 1.618 |
| Var57 | 1.10 | 0.625 | 0.00110 | 0.829 | 0.821 | 0.762 | 1.610 |
| Var58 | 1.10 | 0.625 | 0.00090 | 0.824 | 0.816 | 0.758 | 1.630 |
| Var59 | 1.10 | 0.625 | 0.00075 | 0.832 | 0.822 | 0.755 | 1.603 |
| Var60 | 1.10 | 0.550 | 0.00100 | 0.826 | 0.820 | 0.777 | 1.612 |
| Var61 | 1.10 | 0.550 | 0.00125 | 0.834 | 0.827 | 0.776 | 1.580 |
| Var62 | 1.10 | 0.550 | 0.00110 | 0.828 | 0.821 | 0.773 | 1.608 |
| Var63 | 1.10 | 0.550 | 0.00090 | 0.826 | 0.820 | 0.772 | 1.615 |
| Var64 | 1.10 | 0.550 | 0.00075 | 0.827 | 0.821 | 0.778 | 1.608 |
| Var65 | 1.10 | 0.450 | 0.00100 | 0.820 | 0.815 | 0.789 | 1.635 |
| Var66 | 1.10 | 0.450 | 0.00125 | 0.817 | 0.812 | 0.777 | 1.648 |
| Var67 | 1.10 | 0.450 | 0.00110 | 0.821 | 0.816 | 0.787 | 1.632 |
| Var68 | 1.10 | 0.450 | 0.00090 | 0.825 | 0.820 | 0.788 | 1.613 |
| Var69 | 1.10 | 0.450 | 0.00075 | 0.818 | 0.812 | 0.777 | 1.647 |
| Var70 | 1.10 | 0.375 | 0.00100 | 0.803 | 0.800 | 0.799 | 1.700 |
| Var71 | 1.10 | 0.375 | 0.00125 | 0.799 | 0.797 | 0.797 | 1.714 |
| Var72 | 1.10 | 0.375 | 0.00110 | 0.801 | 0.798 | 0.794 | 1.710 |
| Var73 | 1.10 | 0.375 | 0.00090 | 0.801 | 0.799 | 0.799 | 1.705 |
| Var74 | 1.10 | 0.375 | 0.00075 | 0.798 | 0.795 | 0.795 | 1.721 |
| Var75 | 0.90 | 0.500 | 0.00100 | 0.834 | 0.824 | 0.751 | 1.596 |
| Var76 | 0.90 | 0.500 | 0.00125 | 0.832 | 0.822 | 0.751 | 1.605 |
| Var77 | 0.90 | 0.500 | 0.00110 | 0.833 | 0.823 | 0.754 | 1.601 |
| Var78 | 0.90 | 0.500 | 0.00090 | 0.835 | 0.825 | 0.754 | 1.592 |
| Var79 | 0.90 | 0.500 | 0.00075 | 0.835 | 0.824 | 0.754 | 1.593 |
| Var80 | 0.90 | 0.625 | 0.00100 | 0.828 | 0.818 | 0.748 | 1.620 |
| Var81 | 0.90 | 0.625 | 0.00125 | 0.828 | 0.817 | 0.745 | 1.625 |
| Var82 | 0.90 | 0.625 | 0.00110 | 0.828 | 0.817 | 0.745 | 1.625 |
| Var83 | 0.90 | 0.625 | 0.00090 | 0.828 | 0.817 | 0.745 | 1.625 |
| Var84 | 0.90 | 0.625 | 0.00075 | 0.828 | 0.816 | 0.735 | 1.631 |
| Var85 | 0.90 | 0.550 | 0.00100 | 0.832 | 0.820 | 0.739 | 1.612 |
| Var86 | 0.90 | 0.550 | 0.00125 | 0.834 | 0.823 | 0.747 | 1.599 |
| Var87 | 0.90 | 0.550 | 0.00110 | 0.833 | 0.821 | 0.742 | 1.608 |
| Var88 | 0.90 | 0.550 | 0.00090 | 0.832 | 0.820 | 0.742 | 1.611 |
| Var89 | 0.90 | 0.550 | 0.00075 | 0.833 | 0.822 | 0.748 | 1.603 |
| Var90 | 0.90 | 0.450 | 0.00100 | 0.825 | 0.816 | 0.751 | 1.631 |
| Var91 | 0.90 | 0.450 | 0.00125 | 0.827 | 0.818 | 0.754 | 1.622 |
| Var92 | 0.90 | 0.450 | 0.00110 | 0.823 | 0.814 | 0.755 | 1.639 |
| Var93 | 0.90 | 0.450 | 0.00090 | 0.826 | 0.816 | 0.748 | 1.632 |
| Var94 | 0.90 | 0.450 | 0.00075 | 0.823 | 0.814 | 0.754 | 1.638 |
| Var95 | 0.90 | 0.375 | 0.00100 | 0.812 | 0.806 | 0.769 | 1.675 |
| Var96 | 0.90 | 0.375 | 0.00125 | 0.812 | 0.806 | 0.769 | 1.675 |
| Var97 | 0.90 | 0.375 | 0.00110 | 0.816 | 0.810 | 0.770 | 1.659 |
| Var98 | 0.90 | 0.375 | 0.00090 | 0.813 | 0.807 | 0.769 | 1.672 |
| Var99 | 0.90 | 0.375 | 0.00075 | 0.808 | 0.802 | 0.764 | 1.691 |
| Var100 | 0.75 | 0.500 | 0.00100 | 0.827 | 0.816 | 0.741 | 1.630 |
| Var101 | 0.75 | 0.500 | 0.00125 | 0.827 | 0.815 | 0.737 | 1.633 |
| Var102 | 0.75 | 0.500 | 0.00110 | 0.825 | 0.814 | 0.735 | 1.642 |
| Var103 | 0.75 | 0.500 | 0.00090 | 0.827 | 0.816 | 0.742 | 1.629 |
| Var104 | 0.75 | 0.500 | 0.00075 | 0.828 | 0.817 | 0.740 | 1.626 |
| Var105 | 0.75 | 0.625 | 0.00100 | 0.835 | 0.818 | 0.711 | 1.620 |
| Var106 | 0.75 | 0.625 | 0.00125 | 0.837 | 0.821 | 0.720 | 1.609 |
| Var107 | 0.75 | 0.625 | 0.00110 | 0.835 | 0.818 | 0.711 | 1.620 |
| Var108 | 0.75 | 0.625 | 0.00090 | 0.837 | 0.821 | 0.718 | 1.610 |
| Var109 | 0.75 | 0.625 | 0.00075 | 0.835 | 0.819 | 0.717 | 1.618 |
| Var110 | 0.75 | 0.550 | 0.00100 | 0.834 | 0.821 | 0.735 | 1.609 |
| Var111 | 0.75 | 0.550 | 0.00125 | 0.833 | 0.821 | 0.735 | 1.610 |
| Var112 | 0.75 | 0.550 | 0.00110 | 0.833 | 0.821 | 0.736 | 1.610 |
| Var113 | 0.75 | 0.550 | 0.00090 | 0.833 | 0.820 | 0.730 | 1.615 |
| Var114 | 0.75 | 0.550 | 0.00075 | 0.834 | 0.821 | 0.735 | 1.609 |
| Var115 | 0.75 | 0.450 | 0.00100 | 0.831 | 0.818 | 0.735 | 1.620 |
| Var116 | 0.75 | 0.450 | 0.00125 | 0.828 | 0.817 | 0.739 | 1.628 |
| Var117 | 0.75 | 0.450 | 0.00110 | 0.830 | 0.819 | 0.746 | 1.616 |
| Var118 | 0.75 | 0.450 | 0.00090 | 0.830 | 0.818 | 0.739 | 1.622 |
| Var119 | 0.75 | 0.450 | 0.00075 | 0.831 | 0.819 | 0.736 | 1.618 |
| Var120 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 0.00100 | 0.819 | 0.809 | 0.741 | 1.661 |
| Var121 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 0.00125 | 0.820 | 0.810 | 0.742 | 1.659 |
| Var122 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 0.00110 | 0.820 | 0.809 | 0.741 | 1.660 |
| Var123 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 0.00090 | 0.820 | 0.809 | 0.737 | 1.661 |
| Var124 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 0.00075 | 0.820 | 0.809 | 0.738 | 1.660 |
References
- Beven, K. Searching for the Holy Grail of Scientific Hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Arheimer, B.; Borga, M.; Brázdil, R.; Claps, P.; Kiss, A.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lang, M.; et al. Understanding Flood Regime Changes in Europe: A State-of-the-Art Assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2735–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Aerts, J.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Baldi, M.; Becker, A.; Bichet, A.; Blöschl, G.; Bouwer, L.M.; Brauer, A.; Cioffi, F.; et al. Floods and Climate: Emerging Perspectives for Flood Risk Assessment and Management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2014, 2, 1559–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, T.; Boyle, D.P.; Lees, M.J.; Wheater, H.S.; Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S. A Framework for Development and Application of Hydrological Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2001, 5, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W. Getting the Right Answers for the Right Reasons: Linking Measurements, Analyses, and Models to Advance the Science of Hydrology. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W03S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, W.; Lapin, A.; Schilling, O.S.; Tang, Q.; Schiller, E.; Braun, T.; Hunkeler, D.; Vereecken, H.; Sudicky, E.; Kropf, P.; et al. Integrating Hydrological Modelling, Data Assimilation and Cloud Computing for Real-Time Management of Water Resources. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, S.; Morin, E.; Gerzi Rosenthal, A.; Metzger, A.; Barshai, C.; Weitzner, D.; Voloshin, D.; Kratzert, F.; Elidan, G.; Dror, G.; et al. Flood Forecasting with Machine Learning Models in an Operational Framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4013–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Sippel, S. Machine Learning Applications in Hydrology. In Forest-Water Interactions; Levia, D.F., Carlyle-Moses, D.E., Iida, S., Michalzik, B., Nanko, K., Tischer, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 233–257. ISBN 9783030260866. [Google Scholar]
- Anaraki, M.V.; Farzin, S.; Mousavi, S.-F.; Karami, H. Uncertainty Analysis of Climate Change Impacts on Flood Frequency by Using Hybrid Machine Learning Methods. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liang, F. Machine Learning for Hydrologic Sciences: An Introductory Overview. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.; Dandy, G. Neural Networks for the Prediction and Forecasting of Water Resources Variables: A Review of Modelling Issues and Applications. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2000, 15, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, F.; Kang, D. Multi-Step Ahead Probabilistic Forecasting of Daily Streamflow Using Bayesian Deep Learning: A Multiple Case Study. Water 2022, 14, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghanparast, F.; Mohammadi, G. Using Deep Learning Algorithms for Intermittent Streamflow Prediction in the Headwaters of the Colorado River, Texas. Water 2022, 14, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, N.S.; Deka, P.C. Support Vector Machine Applications in the Field of Hydrology: A Review. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 19, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Hurtado, J.C.; Alfonso, L.; Solomatine, D.P. Rainfall and Streamflow Sensor Network Design: A Review of Applications, Classification, and a Proposed Framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3071–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Clark, J.; Buytaert, W.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M. Water Sensor Network Applications: Time to Move beyond the Technical? Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2612–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Cheng, C.-T.; Chau, K.-W. Using Support Vector Machines for Long-Term Discharge Prediction. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.-S.; Yang, T.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Kuo, C.-M.; Tseng, H.-W. Comparison of Random Forests and Support Vector Machine for Real-Time Radar-Derived Rainfall Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chan, L.; Zhu, N. Flood Forecasting Using Support Vector Machines. J. Hydroinform. 2007, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, J.; Česák, J. Applicability of a Nu-Support Vector Regression Model for the Completion of Missing Data in Hydrological Time Series. Water 2016, 8, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, G.S.; Kratzert, F.; Sampson, A.K. What Role Does Hydrological Science Play in the Age of Machine Learning? Water Resour. 2021, 57, e2020WR028091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, A.P.; Napiorkowski, J.J. A Comparison of Methods to Avoid Overfitting in Neural Networks Training in the Case of Catchment Runoff Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, K.M.S.D.; Ella, V.B.; Suministrado, D.C.; Pereira, G.S.; Agulto, E.S. A Low-Cost Wireless Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring of Water Level in Lowland Rice Field under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation. Water 2022, 14, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogena, H.R.; Huisman, J.A.; Oberdörster, C.; Vereecken, H. Evaluation of a Low-Cost Soil Water Content Sensor for Wireless Network Applications. J. Hydrol. 2007, 344, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirnoori, A.; Saadatpour, M.; Rasekh, A. Using Mobile and Fixed Sensors for Optimal Monitoring of Water Distribution Network under Dynamic Water Quality Simulations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, J.; Bernsteinová, J.; Miřijovský, J. Building a High-Precision 2D Hydrodynamic Flood Model Using UAV Photogrammetry and Sensor Network Monitoring. Water 2017, 9, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, B.; Rehmani, M.H. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks for Urban Areas: A Survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 60, 192–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, J.; Su, Y.; Bernsteinová, J. Runoff Response to Climate Warming and Forest Disturbance in a Mid-Mountain Basin. Water 2015, 7, 3320–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Langhammer, J.; Jarsjö, J. Geochemical Responses of Forested Catchments to Bark Beetle Infestation: Evidence from High Frequency in-Stream Electrical Conductivity Monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čurda, J.; Janský, B.; Kocum, J. The Effects of Physical-Geographic Factors on Flood Episodes Extremity in the Vydra River Basin. Geogr.-Sb. CGS 2011, 116, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenicek, M.; Ledvinka, O. Importance of Snowmelt Contribution to Seasonal Runoff and Summer Low Flows in Czechia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3475–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlček, L.; Kocum, J.; Šefrna, L.; Janský, B.; Kučerová, A. Retention Potential and Hydrological Balance of a Peat Bog: Case Study of Rokytka Moors, Otava River Headwaters, Sw. Czechia. Geografie 2012, 117, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, J.; Bernsteinová, J. Which Aspects of Hydrological Regime in Mid-Latitude Montane Basins Are Affected by Climate Change? Water 2020, 12, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Hydrometeorological Institute. Surface Water Monitoring Network; Czech Hydrometeorological Institute: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019; Available online: http://portal.chmi.cz/ (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Fiedler US1200, US3200, US4200 Ultrasonic Level Meters. Available online: https://www.fiedler-magr.cz/en/products/water-level-meters/ultrasonic-level-meters/us1200-us3200-us4200-ultrasonic-level-meters (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Fiedler M4016-G3 Gauge Stations. Available online: https://www.fiedler-magr.cz/en/solutions/monitoring-surface-water/gagin-stations (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Fiedler SR03 Rain Gauge. Available online: https://www.fiedler-magr.cz/en/products/meteorological-stations-and-measuring-sensors/rain-gauges/sr03-rain-gauge-500cm2 (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Eckhardt, K. How to Construct Recursive Digital Filters for Baseflow Separation. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.A.; Linsley, R.K. Predicting the Runoff from Storm Rainfall; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Oudin, L.; Hervieu, F.; Michel, C.; Perrin, C.; Andréassian, V.; Anctil, F.; Loumagne, C. Which Potential Evapotranspiration Input for a Lumped Rainfall–Runoff Model?: Part 2—Towards a Simple and Efficient Potential Evapotranspiration Model for Rainfall–Runoff Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, N.; Rodríguez, R.; Yépez, S.; Osores, V.; Rau, P.; Rivera, D.; Balocchi, F. Comparison of Three Daily Rainfall-Runoff Hydrological Models Using Four Evapotranspiration Models in Four Small Forested Watersheds with Different Land Cover in South-Central Chile. Water 2021, 13, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbia, S.S.; Smullen, T.; Gill, L.; Johnston, P.; Pilla, F. Spatially Distributed Potential Evapotranspiration Modeling and Climate Projections. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, D. PE-Oudin. 2020. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/PE-Oudin/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Pruitt, C. Hydrogeog/Hydro Package. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/hydrogeog/hydro (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Czech Meteorological Society Meteorological dictionary—Antecedent Precipitation Index. Available online: http://slovnik.cmes.cz/heslo/1196 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Huang, C.-L.; Wang, C.-J. A GA-Based Feature Selection and Parameters Optimizationfor Support Vector Machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 2006, 31, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 38, p. 314. [Google Scholar]
- Bisgin, H.; Bera, T.; Ding, H.; Semey, H.G.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z.; Barnes, A.E.; Langley, D.A.; Pava-Ripoll, M.; Vyas, H.J.; et al. Comparing SVM and ANN Based Machine Learning Methods for Species Identification of Food Contaminating Beetles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Ma, C.; Ma, J.; Huangfu, X.; He, Q. Machine Learning in Natural and Engineered Water Systems. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.R.; Smola, A.J.; Rätsch, G.; Schölkopf, B.; Kohlmorgen, J.; Vapnik, V. Predicting Time Series with Support Vector Machines. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 999–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Dibike, Y.B.; Velickov, S.; Solomatine, D.; Abbott, M.B. Model Induction with Support Vector Machines: Introduction and Applications. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2001, 15, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780262536578. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Performance Evaluation of Hydrological Models: Statistical Significance for Reducing Subjectivity in Goodness-of-Fit Assessments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.P.; Vogel, R.M.; Lamontagne, J.R.; Mizukami, N.; Knoben, W.J.M.; Tang, G.; Gharari, S.; Freer, J.E.; Whitfield, P.H.; Shook, K.R.; et al. The Abuse of Popular Performance Metrics in Hydrologic Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallouin, T. Hydroeval: An Evaluator for Streamflow Time Series in Python. 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4709652 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Terink, W. Hydrograph-Py. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/WilcoTerink/Hydrograph-py (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabalas, A.; Gowen, E.; Poliakoff, E.; Casson, A.J. Machine Learning Algorithm Validation with a Limited Sample Size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHMI. Floods in the Czech Republic in June 2013; Daňhelka, J., Kubát, J., Šercl, P., Čekal, R., Eds.; CHMI: Prague, Czech Republic, 2014; ISBN 9788087577424. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasák, T. Report on the Flood in Upper Vltava River Basin—December 2015; CHMI: Prague, Czech Republic, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, S. Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression; University of Southampton: Southampton, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support Vector Regression Machines. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1997, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J.; Williamson, R.C.; Bartlett, P.L. New Support Vector Algorithms. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 1207–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Environmental Modelling: An Uncertain Future? CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780203932483. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Herrnegger, M. Toward Improved Predictions in Ungauged Basins: Exploiting the Power of Machine Learning. Water Resour. 2019, 55, 11344–11354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble Flood Forecasting: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, A.; Davies, E.G.R. A Workflow to Address Pitfalls and Challenges in Applying Machine Learning Models to Hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 152, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.-H.; Ho, H.V.; Lee, G.; Jung, S. Application of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network for Flood Forecasting. Water 2019, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, S.; Vacondio, R.; Mignosa, P. Flood Stage Forecasting Using Machine-Learning Methods: A Case Study on the Parma River (Italy). Water 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, T.; Montanari, A. Convergence of Approaches toward Reducing Uncertainty in Predictions in Ungauged Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W06301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Chambel, A.; Cudennec, C.; Destouni, G.; Fiori, A.; Kirchner, J.W.; McDonnell, J.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Sivapalan, M.; et al. Twenty-Three Unsolved Problems in Hydrology (UPH)—A Community Perspective. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotamäki, N.; Thessler, S.; Koskiaho, J.; Hannukkala, A.O.; Huitu, H.; Huttula, T.; Havento, J.; Järvenpää, M. Wireless In-Situ Sensor Network for Agriculture and Water Monitoring on a River Basin Scale in Southern Finland: Evaluation from a Data User’s Perspective. Sensors 2009, 9, 2862–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.-W. Flood Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediero, L.; Soriano, E.; Oria, P.; Bagli, S.; Castellarin, A.; Garrote, L.; Mazzoli, P.; Mysiak, J.; Pasetti, S.; Persiano, S.; et al. Pluvial Flooding: High-Resolution Stochastic Hazard Mapping in Urban Areas by Using Fast-Processing DEM-Based Algorithms. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, I.; Andrieu, H.; Leblois, E.; Janey, N.; Payrastre, O. Influence of Rainfall Spatial Variability on Rainfall–Runoff Modelling: Benefit of a Simulation Approach? J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitterson, J.; Knightes, C.; Parmar, R.; Wolfe, K.; Avant, B.; Muche, M. An Overview of Rainfall-Runoff Model Types. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 24–28 June 2018; Available online: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3977&context=iemssconference (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Berger, K.P.; Entekhabi, D. Basin Hydrologic Response Relations to Distributed Physiographic Descriptors and Climate. J. Hydrol. 2001, 247, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.P.; Martz, L.W.; Kite, G.W.; Garbrecht, J. Using Digital Terrain Analysis Modeling Techniques for the Parameterization of a Hydrologic Model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2002, 17, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, T.; Coulibaly, P. Streamflow Prediction in Ungauged Basins: Review of Regionalization Methods. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 958–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sabo, J.L.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Liu, M. Landscape Heterogeneity and Hydrological Processes: A Review of Landscape-Based Hydrological Models. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1461–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Ficklin, D.L. Climatic and Physiographic Controls of Spatial Variability in Surface Water Balance over the Contiguous U Nited S Tates Using the B Udyko Relationship. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7630–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Van Lanen, H.A.J. A Process-Based Typology of Hydrological Drought. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1915–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Stations | Start of Monitoring | Monitoring Interval | Data Provider |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water levels | ROK, BRE, PTA | 2006 | 10 min | CU |
| MOD | 1933 | 1 h | CHMI | |
| Precipitation | ROK, BRE, PTA, MOD | 2008 | 10 min | CU |
| Snow cover | ROK, BRE, PTA | 2011 | 10 min | CU |
| Air Temperature | ROK, BRE, PTA | 2008 | 10 min | CU |
| Indicator | Stations | Source Data | Timestep | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseflow index | ROK, BRE, PTA, MOD | Hourly discharges at stations | 1 h | Digital recursive filter [38] |
| API 30 API 7 | MOD, BRE, ROK | Hourly precipitation at stations | 1 h | Antecedent precipitation index [39] |
| PET | MOD, BRE, ROK | Hourly air temperatures at stations | 1 h | Potential evapotranspiration, Oudin method [40]. |
| Daily Step | Hourly Step | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | R2 | NSE | KGE | RMSE | R2 | NSE | KGE | RMSE |
| Training 2014–2016 | 0.920 | 0.900 | 0.775 | 1.009 | 0.857 | 0.834 | 0.698 | 1.440 |
| Validation 2012 | 0.840 | 0.831 | 0.773 | 1.352 | 0.765 | 0.758 | 0.712 | 1.758 |
| Validation 2015 | 0.948 | 0.904 | 0.690 | 1.022 | 0.903 | 0.827 | 0.516 | 1.511 |
| Simulation Period | Daily Step | Hourly Step | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario | From | To | R2 | NSE | KGE | RMSE | R2 | NSE | KGE | RMSE |
| Convective storms 2014 | 18.07.2014 | 10.08.2014 | 0.848 | 0.825 | 0.784 | 0.695 | 0.838 | 0.819 | 0.766 | 0.953 |
| Convective storm 2016 | 08.06.2016 | 08.07.2016 | 0.922 | 0.876 | 0.677 | 0.974 | 0.893 | 0.827 | 0.546 | 1.749 |
| Convective storm 2018 | 05.06.2018 | 03.07.2018 | 0.986 | 0.860 | 0.521 | 1.485 | 0.888 | 0.880 | 0.863 | 1.688 |
| Frontal precipitation 2013 | 21.05.2013 | 19.06.2013 | 0.982 | 0.944 | 0.743 | 1.715 | 0.970 | 0.865 | 0.511 | 2.902 |
| Frontal precipitation 2017 | 25.10.2017 | 05.11.2017 | 0.990 | 0.921 | 0.694 | 1.268 | 0.881 | 0.844 | 0.705 | 2.289 |
| Frontal precipitation 2020 | 26.10.2020 | 12.11.2020 | 0.983 | 0.965 | 0.850 | 0.642 | 0.899 | 0.592 | 0.586 | 2.123 |
| Rain on snow 2015 | 13.11.2015 | 15.12.2015 | 0.958 | 0.913 | 0.693 | 2.475 | 0.902 | 0.870 | 0.701 | 3.229 |
| Rain on snow 2016 | 15.02.2016 | 01.03.2016 | 0.996 | 0.880 | 0.540 | 2.676 | 0.979 | 0.878 | 0.541 | 3.176 |
| Rain on snow 2020 | 25.01.2020 | 15.02.2020 | 0.979 | 0.878 | 0.583 | 2.763 | 0.933 | 0.920 | 0.823 | 2.398 |
| Snowmelt 2012 | 09.04.2012 | 15.05.2012 | 0.972 | 0.694 | 0.228 | 3.031 | 0.946 | 0.594 | 0.041 | 3.768 |
| Snowmelt 2016 | 15.03.2016 | 20.05.2016 | 0.953 | 0.941 | 0.841 | 0.583 | 0.867 | 0.855 | 0.774 | 0.951 |
| Snowmelt 2020 | 05.03.2020 | 30.03.2020 | 0.981 | 0.868 | 0.514 | 2.027 | 0.960 | 0.899 | 0.648 | 1.995 |
| Minimum | 0.848 | 0.694 | 0.228 | 0.583 | 0.838 | 0.592 | 0.041 | 0.951 | ||
| Maximum | 0.996 | 0.965 | 0.850 | 3.031 | 0.979 | 0.920 | 0.863 | 3.768 | ||
| Mean | 0.963 | 0.880 | 0.639 | 1.694 | 0.913 | 0.820 | 0.625 | 2.268 | ||
| Median | 0.980 | 0.879 | 0.685 | 1.600 | 0.900 | 0.860 | 0.674 | 2.206 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Langhammer, J. Flood Simulations Using a Sensor Network and Support Vector Machine Model. Water 2023, 15, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112004
Langhammer J. Flood Simulations Using a Sensor Network and Support Vector Machine Model. Water. 2023; 15(11):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanghammer, Jakub. 2023. "Flood Simulations Using a Sensor Network and Support Vector Machine Model" Water 15, no. 11: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112004
APA StyleLanghammer, J. (2023). Flood Simulations Using a Sensor Network and Support Vector Machine Model. Water, 15(11), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112004







