Abstract
To clarify the impact of coking industry activities on the soil-groundwater Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) occurrence, a typical coking site in Shanxi Province was taken as the study area, and soil and groundwater samples were collected to analyze the pollution level, composition, and distribution of PAHs in soil-groundwater. The sources of PAHs in the study area were identified based on the positive matrix decomposition model (PMF); the health risks of PAHs were calculated based on the carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk model from the Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Soil Pollution for Construction Land (HJ 25.3-2019) and toxicity equivalent quantity (TEQ). The results showed that ∑PAHs of soil ranged from 0 to 6077.7 mg/kg, with an average value of 198.02 mg/kg; ∑PAHs of groundwater ranged from 0 to 18.30 mg/L, with an average value of 9.39 mg/L. In horizontal distribution, ∑PAH content and types in the tar processing area were much higher than those in the surrounding area, and PAHs might migrate to the southwest through infiltration; in vertical distribution, ∑PAH content reached a peak at 5 m underground. According to the PMF model results, four primary sources of ∑PAHs were identified, which were the coking production source (55.0%), coal and petroleum combustion source (22.6%), atmospheric deposition source (13.1%) and residents living source (9.3%). The total average ∑PAH carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks of soil in the study area were 7.05 × 10−6 and 0.695; the average TEQBaP−∑PAHs was 1.650 mg·TEQ/g; as for groundwater, they were 3.08 × 10−6 and 32.04; the average TEQBaP−∑PAHs was 9.390 μg·TEQ/L, indicating that PAHs both in soil and groundwater had potential health risks. This study provides a basis for the same coking site type for pollution control, secondary utilization, and data support for future site restoration.
1. Introduction
Coal is the most significant energy source in China, and many coal-related industries using coal as energy are the pillars of China’s economic development [1]. The coal industry, mainly composed of the coking industry, a vital driving industry for economic growth, widely exists in all regions of our country. While supporting local economic development, it has also become an essential source of pollution [2]. Due to the complex production process, large discharge scale, and multiple pollutant types in coking industry activities, organic pollution to the local soil and groundwater is generally caused [3]. The concentration of organic pollutants may even exceed by tens of thousands times the international screening values. Many analogous coking sites exist in Shanxi, Hebei, Jiangsu, and even South China, which causes tremendous pressure on the soil and groundwater ecological environment [4]. In addition, with the expansion of cities and the adjustment of national industrial policies, many coking factories have been closed or moved away from their original sites; the pollution problems left behind are more challenging to solve. Therefore, pollution level investigation, pollution source identification, and health risk assessment are necessary before such sites’ secondary development and utilization. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are widely regarded as one of the major pollutants that reflect the soil-groundwater quality in coking sites and have been used as a regular test item for risk assessment and environmental monitoring [5,6].
PAHs consist of two or more condensed aromatic rings, which are essential persistent organic pollutants discharged in the long-term process of the coking industry [7]. PAHs are widely concerned because of their carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and mutagenicity, and 16 of them are listed as priority environmental pollutants by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) and “Environmental Priority Pollutant Blacklist of China” [5,8,9,10]. The generation of PAHs in soil-groundwater can be mainly divided into natural activities and human activities [11,12]. Natural activities include volcanic activity, microbial endogenous synthesis, forest fires, etc. The concentration of PAHs produced by natural activities is usually regarded as the environmental background value. In most cases, the generation of PAHs is mainly caused by human activities, which can be divided into three categories [13,14]. One is the pyrolysis of organic matter, especially the incomplete combustion of organic polymer matters such as coal, petroleum, and biomass; the other is the leakage and blowdown in the process of crude oil exploitation, transportation, production, and use, that is, the source of oil leakage; the third category is daily activities, including emission by various vehicles, exhaust gas generated during, cooking, smoking, and heating residents bath water, etc., which will also enter the soil and groundwater along with atmospheric deposition. In the process of coking production, incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and leakage of products and by-products are the most important sources of continuous generation of PAHs. The natural attenuation of PAHs in the environment is very slow, so after the generation, PAHs will be released into the soil–groundwater–sediment system through solid waste storage, wastewater discharge, surface water recharge, surface runoff infiltration, leakage, and atmospheric deposition and partly released into the atmosphere from shallow soil, high chimneys, and other ways, and the cycle is repeated [15,16]. Therefore, soil and groundwater become the most critical storage sites of PAHs in coking sites, leading to the widespread distribution of PAHs in water, air, soil, and sediment [10].
In the past few decades, many coal-related industrial sites have been closed or moved away from their original sites, and the secondary utilization of relevant sites has been gradually carried out. However, due to the continuous pollution of the surrounding environment discharged in the past production process, treating and controlling PAHs before secondary utilization is necessary. Therefore, it is urgent to investigate the pollution PAH level, identify pollution sources, and assess health risks in soil-groundwater of industrial sites, to which domestic and foreign scholars have begun to pay extensive attention [17]. Jiang et al. investigated and evaluated the distribution, sources, and environmental dangers of PAHs in the groundwater of a coal mine area in China. PAHs are mainly derived from coal, biomass, and petroleum combustion, and the site has moderate ecological risk [18]. Hye-Ok Kwon et al. collected soil samples from an industrial area in Ulsan, South Korea, to investigate the levels, patterns, spatial distribution, and sources of PAHs in the summer of 2010; the results showed that the sources of PAHs in Ulsan were mainly traffic pollution and industrial production, and the pollution in the industrial zone was more severe than that in rural and urban areas [19]. Qiao et al. investigated the impact factors and health risks of PAHs in the groundwater of representative coal mining regions in China (Lanzhou, Shijiazhuang, Golmud, and Du’an). They concluded that PAHs are mainly from combustion, partly from petroleum in most regions [20]. Zhang et al. investigated the spatial distribution, source identification, and health risk assessment of PAHs and their derivatives in the soil of a coking plant in China. They concluded that the site had potential health risks from the cancer risks (CRs) and toxic equivalent quantities (TEQs) [21]. However, it should be noted that current studies mainly focus on the pollution level, distribution, source identification, and health risk assessment of coal-related complex industrial sites; studies specifically aimed at coking sites are still few. Moreover, in existing studies on the comprehensive evaluation of coking sites, most choose either soil or groundwater to study. There are few studies on a soil-groundwater joint investigation and assessment, which will lead to an incomplete comprehensive evaluation of the site, inaccurate identification of the PAHs source, and even inconvenience to the subsequent migration and transformation mechanism of PAHs and the prevention and control of pollutants in the site.
To better understand the influence of coking industry activities on the level and distribution of PAHs in the soil-groundwater, a preliminary investigation on the PAH pollution level of a typical coking site in Shanxi Province, China, was conducted; based on the investigation results, the most seriously polluted key pollution area, which is also the coking site restoration demonstration area determined in the early stage of the funding support project, was selected as the research area. The principal objectives were as follows: (1) based on sampling points, to investigate the pollution level and to analyze the occurrence and distribution difference of PAHs in soil-groundwater; (2) by the positive matrix decomposition (PMF), to identify the PAHs sources from the soil-groundwater joint scale and determine each source’s proportion; (3) in two different ways, which were toxicity equivalent quantity (TEQ) based on BaP and the carcinogenic–noncarcinogenic health risk assessment model, to assess the PAH potential health risks in soil-groundwater from the level of the study area, sampling points, and samples. The present study provides valuable references for soil-groundwater control, protection, development, and utilization in the study area and similar areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in Shanxi Province, China, which is a crucial pollution area of a closed coking plant, including the tar processing area, coke oven area, etc. The stratum lithology of the study area from shallow to deep is miscellaneous fill (2.86 m), medium-coarse sand (2.39 m), silty soil (4.88 m), medium sand (2.45 m), silt (2.46 m), and silty clay (1.0–3.4 m), respectively; these mentioned above are the average exposed thickness. The average buried depth of groundwater is 17.4 m; the overall flow direction is from northwest to southeast, and the average hydraulic slope is 0.8%.
2.2. Sample Collection
Twenty sampling sites were set up in the study area, including ten soil and ten groundwater sites. All PAHs were sampled and detected at each sampling site; 101 soil and 10 groundwater samples were collected (Figure 1).
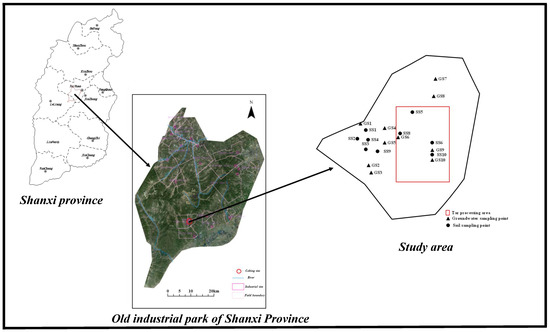
Figure 1.
The layout of sampling points in the study area.
A 40 mL brown glass bottle was selected for sampling when collecting soil samples. The bottle contained about 10 mL of methanol as a protective agent, and 5 g of soil was taken into the bottle with a non-disturbed sampler and tightened. When collecting groundwater samples, a 1 L brown glass bottle was chosen for sampling, and the entire bottle was filled with water samples, plugged and screwed tightly. The sample bottles were sealed immediately after collection, transported to the laboratory under ice bag protection as soon as possible, and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C, and shock-proof and sun-proof measures were taken. Sample pretreatment was completed within 48 h, and quality assurance and quality control procedures were strictly implemented from the fieldwork to the analysis process.
2.3. Sample Pretreatment
The determination of semi-volatile organic compounds in soil and sediment by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (HJ 824-2017) was used to detect and analyze PAHs in soil. The preserved soil was freeze-dried and then sifted through a sieve with a diameter of 0.25 mm. After that, the screened soil samples were quantitatively weighed to 20 g and extracted with a solid phase extraction instrument. The extraction liquid nitrogen was blown and concentrated to 1 ml, and the internal labeling machine was added for detection. The determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water quality by liquid–liquid extraction and solid-phase extraction high-performance liquid chromatography (HJ 478-2009) was used to determine the PAHs in groundwater. The 1 L sample was taken and extracted by an automatic solid phase extractor, and the treated extraction liquid was determined to be 0.5 mL on the machine for detection.
2.4. Instrument Analysis Conditions
PAHs were analyzed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GCMS--QP2010SE) with an inlet temperature of 280 °C, no shunt. The initial temperature was 35 °C, held for 2 min, and then increased to 150 °C with a rate of 15 min−1 for 5 min and then increased to 290 °C with a speed of 3 °C⋅min−1 and held for 2 min. The total running time was 57 min, and the carrier gas was high-purity helium. MS conditions were as follows: electron bombardment source: 70 eV; Ion source temperature: 230 °C.
2.5. Quality Control and Quality Assurance (QA/QC)
Quality control and quality assurance are divided into on-site and testing institutions.
Field quality control samples include parallel, blank, and transport blank samples. Field parallel sample refers to the repeated sampling of 2 or more identical samples under the same conditions in the site investigation and sampling process to judge the variety of sampling and laboratory precision. According to the requirements of “The determination of semi-volatile organic compounds in soil and sediment by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HJ 824-2017)”, quality control includes method blank (MB), surrogate or tracer, laboratory-controlled sample (LCS), duplicate samples (DUP), matrix samples (MS), and matrix samples duplicate (MSD).
2.6. PMF Models
PMF model is a quantitative source analysis model based on the multivariate analysis method, which is used to investigate the contribution of emission sources to the PAH level according to the observation results of sampling points [22,23]. The PMF model has the advantages that the result does not need to be transformed, the elements in the decomposition matrix are non-negative, and the data standard deviation can be used for optimization [24]. It has been successfully applied to the source analysis of PAHs in water, the atmosphere, soil, and sediment [6,25,26]. Thus, the PMF 5.0 model introduced by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA, 2014) was used to analyze groundwater sources in the study area. The PMF model can be regarded as the matrix X of i × j, and the equation is
where i is the number of samples, j is the type of PAHs, n is the number of factors, f is the composition matrix of each source, and g is the contribution matrix of each PAH in the sample [21].
The method detection limit (MDL) is used to determine the uncertainty of each sample, called Unc. If the concentration of PAH is lower than MDL, Unc = 5/6 MDL; otherwise, Unc = , where C is the concentration of PAH (μg/L).
2.7. Health Risk Assessment
In this study, health risks in the study area were assessed in two ways.
First, due to the toxicity and mutagenicity of different PAHs, relative toxicity and mutagenicity are frequently used to assess the total health risk of PAHs. Toxicity equivalent quantity based on BaP(TEQBaP−∑PAHs), toxicity equivalent quantity based on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin—TCDD (TEQTCDD−∑PAHs), mutagenic equivalent quantity based on BaP(MEQBaP−∑PAHs), and ΣPAHcarc/ΣPAH are widely used to characterize the total carcinogenic risk caused by PAHs [27,28]. The toxic equivalent factor (TEFBaP and TEFTCDD), and the mutagenic equivalent quantity (MEFBaP) were positively correlated with toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity, respectively. The equations are
where is the concentration of the ith PAHs, and TEFBaP−i, TEFTCDD−i, and MEFBaP−i are the toxic equivalent factor (TEFBaP and TEFTCDD) and mutagenic equivalent factor (MEFBaP−i) of the ith PAHs [27]. ΣPAHcarc/ΣPAH is the ratio of PAHs concentration sum with carcinogenicity and the ΣPAHs concentration. The closer the value of ΣPAHcarc/ΣPAH was to 1, the more hazardous ΣPAH was to humans.
Moreover, based on whether or not PAHs are carcinogenic pollutants included by Occupational Exposure Limits for Hazardous Factors in the Workplace Part 1: Chemical Hazardous Factors GBZ 2.1-2019 and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), the health model of risk assessment was divided into the carcinogenic risk model and non-carcinogenic risk model.
The health risk formulas of multiple exposure pathways are derived from the calculation formulas stipulated in the Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Soil Pollution for Construction Land (HJ 25.3-2019). Carcinogenic health risks (expressed as risk) and non-carcinogenic health risks (expressed as noncancer hazard quotient, HQ) of PAHs in soil and groundwater were calculated through the HERA++ software developed by Chen Mengfang and his team at Nanjing Institute of Soil Research, China [29].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Excel 2019 was used to consolidate and quantify the data. The PMF analysis of the data was achieved using the PMF 5.0 model. SPSS25.0 was used for descriptive statistical analysis of the data. Evaluation of soil-groundwater health risks used HERA++, ArcGIS 10.8, and Origin 2017 for spatial analysis and comprehensive cartographic processing of experimental data.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence of PAHs in Soil Underground
Pollution Level of PAHs in Soil Underground
The statistical results of 16 PAHs in soil and groundwater samples are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively.

Table 1.
PAH content in the soil (Unit: mg/kg).

Table 2.
PAH content in groundwater (Unit: mg/L).
The ∑PAHs in soil ranged from 0 to 6077.70 mg/kg, with a mean of 198.02 mg/kg, and were detected in 100% of sampling points and 67.33% of samples. The average concentration of naphthalene was the highest (128.06 mg/kg), far exceeding the standard value, and obtained the highest detection rate of points (100%) and samples (67.33%), and BaP held the highest exceeding standard rate of points (64.15%) and samples (16.83%). Moreover, the point detection rate of naphthalene (Nap), acenaphthylene (Acy), acenaphthene (Ace), phenanthrene (Phe), fluorene (Flu), pyrene (Pyr), anthracene (Ant), fluoranthene (Flua), chrysene (Chr), benzo(a)anthracene (BaA), benzo(b)fluoranthene (BbF), benzo(K)fluoranthene (BkF), benzo(a)pyrene (BaP), and indene(1,2,3-cd)pyrene (InP) all exceeded or equaled 50%, so risk assessment was necessary. The variation coefficient of PAHs was generally high, indicating that the pollutant content of different sampling points varied greatly, proving that the PAHs structure of different sites in the study area differed.
The soil’s low-, medium-, and high-ring PAHs were 94.06%, 5.61%, and 0.33%, respectively (Figure 2). The content of low-ring PAHs (2–3 rings) was significantly higher than that of medium-ring and high-ring PAHs (4–6), but the detection frequency of medium-ring and high-ring PAHs was equal to or slightly lower than that of low-ring PAHs. This result was related to the physical characteristics of PAHs. Compared with low-ring PAHs, medium-ring and high-ring PAHs had higher octanol-water partition coefficients and more stable structures, which means they are more resistant to degradation and can migrate to a more comprehensive range of soils without structural changes [26,30].
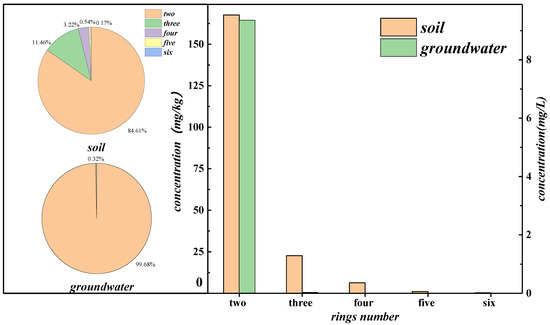
Figure 2.
Structural comparison of PAHs in soil-groundwater.
The ∑PAHs of groundwater ranged from 0 to 18.30 mg/L, with a mean of 9.39 mg/L. The point detection rate of PAHs was 65.38%. Like the soil, the average concentration of naphthalene in groundwater was the highest (8.92 mg/L). Unlike the soil, low- and medium-ring PAHs are mainly found in groundwater, while high-ring PAHs in groundwater are almost undetected. Low-, medium-, and high-ring PAHs of groundwater were 99.68%, 0.32%, and 0%, respectively (Figure 2). Apart from the difference in initial content, the phenomenon is also attributed to medium- and high-ring PAHs being more adsorbable and more challenging to enter groundwater through infiltration [31]. The phenomenon mentioned above is further analyzed in Section 3.2.2.
Naphthalene is the highest pollutant in soil and groundwater in the study area, caused by the property of naphthalene itself and the industrial structure of the study area. Regarding properties, naphthalene is the most water-soluble and migratory PAH and can continue to migrate horizontally and vertically in the form of atmospheric precipitation and surface infiltration [32]. Secondly, as the PAH with the simplest structure, naphthalene is also a potential degradation product of other PAHs [33,34]. In terms of industrial structure, the study area is dominated by the coking industry. Naphthalene pollution will be caused to varying degrees in refining, processing, and storing coal tar. Hence, naphthalene is ubiquitous in soil-groundwater in the study area, and its content is the highest compared with other PAHs. It is worth mentioning that it was frequently found that black oil-like substances were associated with sampling these samples, so it was speculated that there was a “tar phase” in the groundwater as a “slow release pollution source”, continuously releasing organic matter to the soil and groundwater. The finding above has significant implications for subsequent experiments and simulation of PAH transport.
3.2. Spatial Distribution of PAHs
3.2.1. Horizontal Distribution of PAHs
Figure 3 shows the PAH composition and structure changes of soil and groundwater sampling sites. As shown from the figure, soil-groundwater PAH species in the tar processing area increased significantly compared with the surrounding area. The main PAHs of SS5, SS6, SS7, SS8, and SS10 were Nap, Ace, Flu, Phe, Flua, and Pyr, mainly 2–4 rings. The main PAHs of GS6, GS7, GS8, GS9, and GS10 are Nap, Acy, Ace, and Flu; this is related to the function of the tar processing area. Tar is further refined in this area and stays much longer than in other areas. The infiltration of PAHs into soil and groundwater is more serious, so the types and composition of PAHs are more complex. Compared with soil, the proportion of low-ring PAHs (two rings) occupied in groundwater increased significantly because Nap, Acy, and Ace, as typical low-ring PAHs, have more substantial water solubility and migration ability to groundwater. In contrast, medium- and high-ring PAHs such as Flua and Pyr are more detected in shallow soil samples.
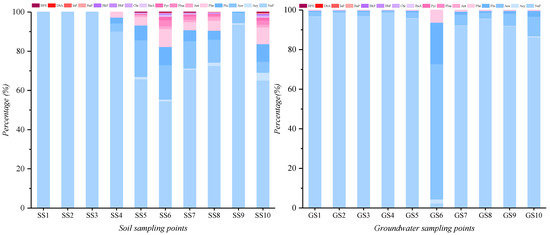
Figure 3.
PAHs composition changes in the sampling points.
By summarizing the concentrations of PAHs in the study area, the spatial distribution changes of PAH content in soil and groundwater were, respectively, formed (Figure 4).
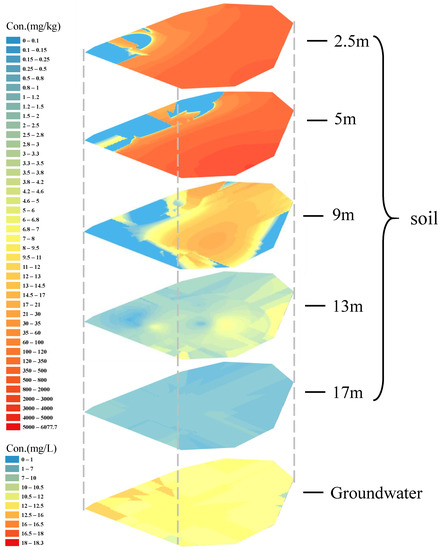
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of PAHs content in the study area.
With depth changes, the spatial distribution of ∑PAHs in soil and groundwater varied significantly. As the depth increased, ∑PAHs concentration first increased (0 to 5 m) and then kept reducing (5 to 17 m). More profound than 5 m, the concentration gap of ∑PAHs in different regions was reduced gradually. However, the spread area expanded, and the distribution uniformized, meaning the pollutants in the vertical migration process continued to diffuse horizontally [35]. Until entering groundwater, the content gap of ∑PAHs in different locations reached the minimum; this is because the retardation ability of PAHs in groundwater is much weaker than that in soil, and the migration ability of PAHs is further enhanced, thus, easier to disperse with groundwater flow. Moreover, the distribution of PAH content at 17 m depth and groundwater indicated that PAHs migrated to the southwest direction, which may be caused by lithologic differences. With the same depth condition, the adsorption capacity of soil in the southwest direction may be weaker, so the migration degree of PAHs to the southwest direction is more severe during the infiltration process.
3.2.2. Vertical Distribution of PAHs
Figure 5 shows the vertical composition and content changes of PAHs in soil and groundwater in the study area. With the depth increase and lithology changes, PAH changes also presented the relevant regularity. Within 0–3 m, ∑PAH content decreased with increasing depth; within 3–5 m, ∑PAH contents increased significantly, and ∑PAH content at 5 m became the highest. Moreover, the proportion of high-ring PAHs that increased shows that the vast majority of the medium- and high-ring PAHs are trapped in the depth range. Within 5–11 m, ∑PAH content was still high, and it is also the maximum depth of high-ring PAHs occurrence; deeper than 11 m, ∑PAHs sharply declined, except for little acenaphthylene, acenaphthene fluorene, and phenanthrene; only naphthalene can be detected in large quantities.
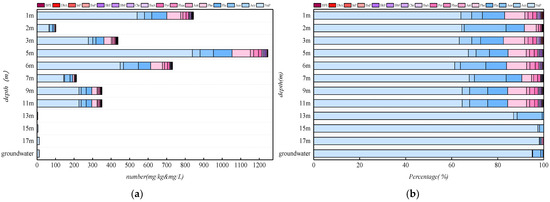
Figure 5.
Vertical distribution of PAHs in the study area (a) content distribution (b) composition.
This phenomenon mainly relates to the stratum lithology of the study area and the migration ability of PAHs [36]. Primary pollution sources in the study area were closed for 10 years. After a long downward migration, PAH content in miscellaneous fill (0 to 3 m) is relatively low, only higher near the ground; the adsorption capacity of medium-coarse sand (3–5 m) is more robust than that of miscellaneous fill, which can intercept more PAHs. Therefore, the PAH content at 3–5 m was higher than that of 0–3 m, and the medium- and high-ring PAHs near the 5 m range increased sharply, indicating that the lower silt has a significant blocking effect on them, and piled up in large quantities at the stratified boundary. The highest ∑PAH content was found in the silty soil layer (5–11 m), indicating that most ∑PAHs were trapped in the silty soil due to its retardation, and 11 m is the maximum longitudinal migration distance of medium- and high-ring PAHs. Deeper than 11 m, ∑PAH content with depth increase is declined, and the silty clay (15 to 17 m) block effect is more excellent than medium sand/silt (11 to 15 m), so the proportion of Nap within 15–17 m further increases. Over 17 m depth, PAHs migrated and diffused into groundwater aquifers, and naphthalene, the most migratory and water-soluble PAH, accounted for more than 95% of groundwater pollution.
3.3. Source Identification of PAHs (PMF Method)
Positive matrix factorization (PMF) is a method that represents a matrix as the product of two or more matrices to decompose complex data [37,38,39,40]. One-hundred and eleven samples of all PAHs detected from twenty sampling points in the study area were analyzed using the PM5.0 model (Figure 6). Using random start mode, the PMF factors number was set to 3–10 and was determined by comparing the Qtrue value with the Qrobust value. The iterative calculation was carried out 100 times, respectively. Under the premise that the Qrobust remained stable, the iterative result with the minimum Qrobust value was used for further analysis.
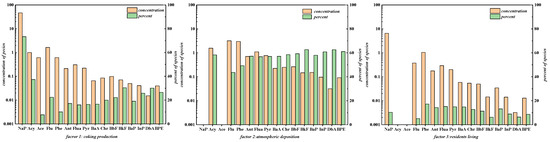
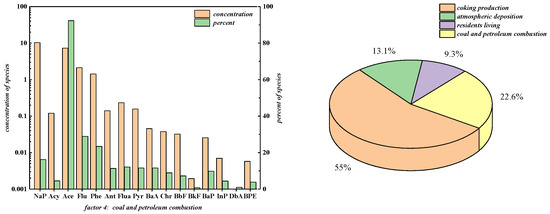
Figure 6.
PAH source identification results based on the PMF model.
Meanwhile, the residuals of almost all samples vary between −3 and 3 to increase the model’s reliability. Four factors were finally determined for quantitative source analysis in the study area combined with the possible pollution sources in the previous investigation. The Qtrue value (128.7) was quite close to the Qrobust value (130.5). It should be noted that due to the complex migration and transformation behaviors of PAHs, such as convective dispersion, evaporation, and secondary land use, the contribution of each source to PAHs cannot be fully reflected by the inspection data alone [39,40].
Factor 1 contributed 55.0% of PAHs and was highly dependent on Nap. More than 70% of naphthalene was produced by factor 1, which was inferred to be the coking production source, including tar processing and product leakage. First, Nap is regarded as one of the critical substances in determining the source of coking production, and it has been indicated as the source of oil leakage in previous studies [18,23]. This result is in line with the actual situation because the study area is the primary coking production, tar processing, and storage site; there have been a lot of tar and naphthalene products for a long time.
Factor 2 explains 13.1% of PAHs, which was inferred to be the source of atmospheric deposition because it is the primary source of Acy, Flu, Phe, Ant, Flua, Pyr, BaA, Chr, BbF, BaP, InP, DbA, and BPE, most of which are medium- and high-ring PAHs. The content and proportion of PAHs mentioned above were relatively uniform, which is the most significant feature of PAHs from atmospheric deposition [41,42]. In the study area, atmospheric particles emitted from the chimneys of coking and power plants settled on the surface, and the above-mentioned medium- and high-ring PAHs were enriched in these particles, infiltrating soil and groundwater [42,43,44].
Factor 3 accounted for 9.3% of the total pollution contribution of PAHs and was associated with a large amount of Flu, Phe, Ant, Flua, Chr, Pyr, BbF, BkF, BaP, and BPE, indicating residents living source. Flu, Phe, and Ant are all highly dependent on coal combustion. Flua and Pyr have always been considered indicators of incomplete coal combustion [44,45], which is a significant feature of using coal-fired boilers for daily life, such as heating, bathing, and cooking. Moreover, Chr, BbF, BkF, and BaP are derived from natural gas combustion, while wood combustion will produce BaA and BPE [9,38,46,47]. Coal-fired boilers and natural gas are widely used in Shanxi for heating, bathing, cooking, and other daily life activities. A few areas also use wood [48]. Therefore, the release of PAHs for factor 3 was caused by residents living in the study area.
Factor 4 explained 22.6% of PAHs, the primary source of Ace, and the source of Flu, Phe, Ant, Flua, Pyr, BaA, Chr, BbF, and BaP, inferred to be coal and petroleum combustion sources. Because Ace and Flu usually come from coal and petroleum burning, Phe and Ant are also highly dependent on coal combustion, and petroleum combustion produces a large amount of four-ring PAHs; BbF and BaP result from the incomplete combustion of gasoline, while BaA comes from diesel combustion. The result is reasonable considering the millions of tons of coal consumed yearly, totaling more than 10 million tons during production in the study area [36,43]. The literature provides a similar picture of coal burning [18]. It should be pointed out that PAHs in factor 4 were probably those attached to waste liquid and solid after coal combustion and directly infiltrated into soil-groundwater with surface infiltration rather than underground with atmospheric subsidence because nearly no high-ring PAHs (≥5) contributed to factor 4, which is a significant feature of atmospheric subsidence PAHs [31].
In summary, the PMF model indicated four sources of pollution, namely, coking production source (55.0%), atmospheric deposition source (13.1%), residents living source (9.3%) and coal and petroleum combustion sources (22.6%). The results were consistent with the previous investigation.
3.4. Health Risk Assessment
In this paper, two methods were used to assess the PAHs’ health risks in the study area, which were toxicity equivalent quantity based on BaP (TEQBaP−∑PAHs), toxicity equivalent quantity based on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin—TCDD (TEQTCDD−∑PAHs), mutagenic equivalent quantity based on BaP (MEQBaP−∑PAHs), and the carcinogenic–noncarcinogenic health risk assessment model.
Health risk assessment was carried out in the study area from the level of the study area, sampling points, and samples, respectively (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
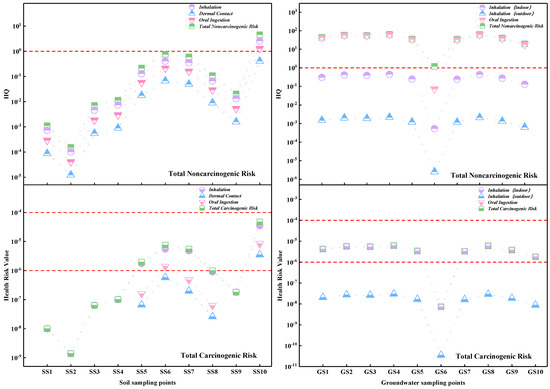
Figure 7.
Results of PAH health risk assessment (sampling points scale).
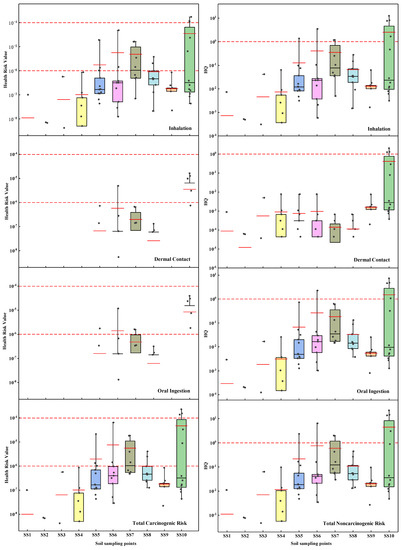
Figure 8.
Results of PAH health risk assessment (sample scale).
The total average carcinogenic health risk of PAHs in the soil of the study area was 7.05 × 10−6, which exceeded the allowable carcinogenic risk limit of USEPA (1 × 10−6), indicating that PAHs in the study area scales had the potential carcinogenic risk, which NaP, BaA, Chr, BbF, BkF, BaP, InP, and DbA caused. There were three carcinogenic pathways of PAHs: inhalation, oral ingestion, and dermal contact, with contribution rates of 76.061%, 16.925%, and 7.014%, respectively. These results indicated that inhalation (including indoor and outdoor particulate matter and steam) is the main carcinogenic pathway; the total average carcinogenic health risk of PAHs in the groundwater of the study area was 3.08 × 10−6, which also exceeded the risk of cancer of the USPEA limit (1 × 10−6), had the potential risk of cancer, and was caused by Nap. The contribution rates of inhalation (indoor steam), inhalation (outdoor steam) and oral ingestion were 99.518%, 0.482%, and 0%, respectively. The entire non-carcinogenic risk (also called hazard entropy, HQ) of PAHs in the soil of the study area was 0.695, lower than the total non-carcinogenic risk limit of USEPA (1), showing that in the study area scale, the non-carcinogenic risk of PAHs in the soil is acceptable. The entire non-carcinogenic risk of PAHs in the groundwater of the study area was 32.04, more than 32 times the non-carcinogenic risk limit, and had a significant risk of cancer, which was made up of Nap, Acy, Ace, Flu, and Phe. The contribution rates of inhalation (indoor steam), inhalation (outdoor steam) and oral ingestion were 0.700%, 0.003%, and 99.297%, respectively. Oral ingestion dominated the non-carcinogenic pathway, and the average non-carcinogenic risk of the other two pathways was within the acceptable range.
From the sampling points scale, the range of carcinogenic health risk of PAHs in the 10 soil sampling points was 1.38 × 10−9–4.68 × 10−5. SS10 had the highest risk, and SS2 had the lowest risk. The average carcinogenic risk values of SS5, SS6, SS7, and SS10 are more than 1 × 10−6, consistent with the point distribution of high content of the PAHs mentioned in Section 3.2.1, both located in the tar processing zone of the study area. The whole non-carcinogenic risk range of PAHs was 1.5 × 10−4–4.53; except for SS10, the rest of sampling points are below the USEPA limit (1). As for groundwater, the carcinogenic health risk range was 7.25 × 10−9–6.18 × 10−6; other than GS6, all sampling points of cancer health risks were higher than 1 × 10−6, with potential carcinogenic risk; the mean non-carcinogenic risk value was 1.21–63.4; all were much higher than 1, with a significant potential hazard.
From the sample scale, the carcinogenic risk range of 101 soil samples was 0–2.26 × 10−4. The risk of 16 soil samples exceeded the acceptable level recommended by the USEPA, with an excess rate of 15.84%. The average non-carcinogenic risk ranged from 0 to 22.13, and the non-carcinogenic health hazard of eight samples was higher than 1, with an exceeding-standard rate of 7.92%. Both the highest carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk samples were taken from SS10 at 5 m depth, which is also consistent with PAH content being the highest at the 5 m depth mentioned in Section 3.2.2. In addition, sampling points where samples with potential carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic hazards were taken were located in the tar processing area, namely the key contaminated area of the study area.
The soil and groundwater toxicity equivalent quantity based on BaP (TEQBaP−∑PAHs), toxicity equivalent quantity based on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin—TCDD (TEQTCDD−∑PAHs), and mutagenic equivalent quantity based on BaP (MEQBaP−∑PAHs) are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.

Table 3.
TEQBaP−∑PAHs, TEQTCDD−∑PAHs, and MEQBaP−∑PAHs in soil.

Table 4.
TEQBaP−∑PAHs, TEQTCDD−∑PAHs, and MEQBaP−∑PAHs in groundwater.
TEQBaP−∑PAHs in soil ranged from 0 to 51.257 mg·TEQ/g, with an average concentration of 1.650 mg·TEQ/g. The BaP, DbA, and NaP contributed most of the toxicity equivalent concentrations of ∑PAHs, which were 0.590 mg·TEQ/g, 0.550 mg·TEQ/g, and 0.128 mg·TEQ/g. BaP and DbA have high contributions due to their high toxicity equivalent factor, while NaP is due to its widespread detection and high average concentration in soil. TEQTCDD−∑PAHs in soil ranged from 0 to 289.136 μg·TEQ/g, with an average concentration of 6.276 μg·TEQ/g, which was caused by BaA, Chr, BbF, BkF, BaP, InP, and DbA; all of them are middle- and high-ring PAHs. MEQBaP−∑PAHs in soil ranged from 0 to 40.218 mg·MEQ/g, with an average concentration of 1.204 mg·MEQ/g, similar to TEQBaP−∑PAHs. Bap contributed most of the mutagenic equivalent quantity because of its high mutagenicity. TEQBaP−∑PAHs in groundwater ranged from 0 to 18.300 μg·TEQ/L, with an average concentration of 9.390 μg·TEQ/L. The contribution percent of NaP reached 95%, which was consistent with carcinogenic-noncarcinogenic health risk assessment model. MEQBaP−∑PAHs in groundwater ranged from 0 to 0.022 μg·MEQ/g, with an average concentration of 0.011 μg·MEQ/g. Apparently, the mutagenicity of the study area in groundwater was completely caused by Acy, because the other PAHs which can cause the mutagenicity were not detected. Based on the similar reason, the TEQTCDD−∑PAHs in groundwater was 0. The mean ΣPAHcarc/ΣPAH values in soil and groundwater were 0.022 and 0, respectively; both of them are far below 1, meaning that the carcinogenic hazard was quite low, which was not consistent with the health risk assessment model. This is because NaP, the most widespread pollutant, was seen as noncarcinogenic in this method but, actually, was ruled as a carcinogenic PAH by the IARC.
Compared with other studies, the study area’s average TEQBaP−∑PAHs is far higher than other coking sites. TEQBaP−∑PAHs of a coking plant in the Taihu Basin, Jiangsu province, China, ranged from 15.71 to 867.35 ng·TEQ/g in soil, with an average concentration of 189.29 ng·TEQ/g [49]. Another typical coking plant held an average TEQBaP−∑PAHse of 14.8 u g·TEQ/g [21]. Consistent with the TEQBaP−∑PAHs, the measured concentration of PAHs (Table 1 and Table 2) in the study area is also much higher than that in the other coking site. However, compared with soot from coal (25–80 mm) combustion, with average TEQBaP−∑PAHs, TEQTCDD−∑PAHs, and MEQBaP−∑PAHs are 158.76 mg·TEQ/g, 0.61 mg·TEQ/g, and 94.28 mg·MEQ/g, respectively. Soil toxicity is all much lower [50]. It is also consistent with previous studies that soot from coal combustion is an important source of PAHs in soil [14].
To sum up, PAHs in the soil and groundwater of the coking site, particularly Nap, hold a significant health risk to the study area and the surrounding environment. It is paramount to note that the study assessed health risks based on average values, which may underestimate the health risks of shallow soils. Indeed, residents who worked or lived nearby for a long time may be at higher risk of exposure. Therefore, the protection level of workers and residents should be improved in the process of pollutant control and secondary utilization of similar coking sites.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a core contaminated area of a typical coking site was investigated and assessed. The main conclusions are as follows.
Naphthalene exists widely in soil and groundwater and with the highest average content of all PAHs. Naphthalene accounted for more than 99% of groundwater pollution. The horizontal and vertical distribution is mainly related to the study area’s stratigraphic structure and the PAHs’ migration ability. The PMF model inferred that there were four primary pollution sources in the study area; the fossil fuels combustion and production leakage are the primary PAHs source, which is consistent with the production function of the study area. The health risks in soil and groundwater both exceed the limits and had potential health risks, mainly caused by NaP. The TEQBaP−∑PAHs, TEQTCDD−∑PAHs, and MEQBaP−∑PAHs of the study area are also far high than the soil of other coking sites, which means the PAH hazard is serious. However, these indicators are much lower than soot of coal combustion. This is a reason that coal combustion is widely considered a primary source of PAHs in soil. Comparing the two methods, the primary carcinogenic PAH was different because NaP was not included in the TEQTCDD−∑PAHs and MEQBaP−∑PAHs; therefore, the carcinogenicity counted in this way may be underestimated.
In conclusion, PAHs of soil-groundwater in the study area are of non-negligible health risk. Especially for groundwater, both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks are serious. Corresponding control and treatment measures should be taken, and long-term monitoring should be conducted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and Q.F.; Methodology, Z.L., Q.F., J.D., X.Z. (Xueqiang Zhu) and Y.R., Software, Z.L. and X.Z. (Xin Zhang); Data curation, Z.L. and Y.R.; writing—original draft, Z.L.; visualization, Z.L., X.Z. (Xin Zhang) and L.M.; writing—review and editing, Q.F., J.D., X.Z. (Xueqiang Zhu) and L.M.; funding acquisition, Q.F., J.D. and L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number (No. 2020YFC1806501).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding and lead authors, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liang, L.K.; Ru, X.; Wei, J.Y.; Lin, Z.D.; Wei, C.H.; Qian, Y.; Li, F.S. Spatiotemporal simulation and comprehensive evaluation of atmospheric coal-related PAHs emission reduction in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Zhu, Y.W.; Hu, B.F.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Shi, K.J.; Xu, L.C. Pollution Characteristics, Spatial Patterns, and Sources of Toxic Elements in Soils from a Typical Industrial City of Eastern China. Land 2021, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yin, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J. Contamination, Sources, and Health Risks Associated with Soil PAHs in Rebuilt Land from a Coking Plant, Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.; Lai, D.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H. Effectiveness of predicting the spatial distributions of target contaminants of a coking plant based on their related pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 33945–33956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simic, S.B.; Miljkovic, P.; Baumgertel, A.; Lukic, S.; Ljubicic, J.; Cakmak, D. Environmental and Health Risk Assessment Due to Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil near Former Antimony Mine in Western Serbia. Land 2023, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.X.; Xing, J.-B.; Wang, H.-W.; Liu, J.-T.; Chen, X. Analysis on Contamination Characteristics, Pollution Source Identification and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons of Groundwater in a Large Coking Plant Site of Province. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2021, 44, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyszczak, A.; Czech, B. Occurrence and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons derivatives in environmental matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulange, M.; Lorgeoux, C.; Biache, C.; Michel, J.; Michels, R.; Faure, P. Aging as the main factor controlling PAH and polar-PAC (polycyclic aromatic compound) release mechanisms in historically coal-tar-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Zeng, H.Q.; Gong, X.F.; Li, J.; Wang, L.Q. PAHs Source Identification in Sediments and Surrounding Soils of Poyang Lake in China Using Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Analysis. Land 2022, 11, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodygin, E.; Abakumov, E.; Nizamutdinov, T. The Content of Polyarenes in Soils of Antarctica: Variability across Landscapes. Land 2021, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Li, C.H. Investigation of Indoor Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Rural Northeast China: Pollution Characteristics, Source Analysis, and Health Assessment. Buildings 2022, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yu, K.P.; Lin, C.C. Risk assessment of inhalation exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Taiwanese workers at night markets. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2011, 84, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, G.P.; Lineman, D.; Johnston, C.G.; Leff, L. Characterization, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in long-term contaminated riverbank sediments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3519–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pies, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Petrowsky, J.; Yang, Y.; Ternes, T.A.; Hofmann, T. Characterization and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in river bank soils. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, M.S.; Ma, L.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Gong, Y.Y.; Li, D.M. New insight into human health risk from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on surfaces of buildings and facilities for industrial legacy regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Sun, M.M.; Xie, S.N.; Liu, K.A.; Feng, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, J.H.; Hu, F.; Li, H.X.; Zong, L.G.; et al. Feasibility of Tea Saponin-Enhanced Soil Washing in a Soybean Oil-Water Solvent System to Extract PAHs/Cd/Ni Efficiently from a Coking Plant Site. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, F.Z.; Liu, J.J.; Fang, B.; Yang, W.Q.; Meng, C.Y.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Y.L. Inhalation bioaccessibility, health risk assessment, and source appointment of ambient PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Caofeidian, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47574–47587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.L.; Zhao, D.S.; Chen, X.; Zheng, L.G.; Li, C.; Ren, M.X. Distribution, source and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater in a coal mining area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.O.; Choi, S.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils from a multi-industrial city, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zheng, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, Y. Influencing factors and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; He, R.; Deng, W.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; An, T. Spatial distribution, source identification, and human health risk assessment of PAHs and their derivatives in soils nearby the coke plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Lin, T.; Guan, J.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Qin, X.Y.; Liao, J.F.; Liu, Q.M.; Huang, Y.F. Identification and Regulation of Critical Source Areas of Non-Point Source Pollution in Medium and Small Watersheds Based on Source-Sink Theory. Land 2021, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Qi, H.; Sun, D.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, D.G. Seasonal variations of sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to a northeastern urban city, China. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Fu, K.; Xu, Y. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhen, Q.; Han, F.; Zhang, X. Distribution, Origins and Hazardous Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Topsoil Surrounding Oil Fields: A Case Study on the Loess Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Y. Effects of total organic carbon content and leaching water volume on migration behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils by column leaching tests. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Lang, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Peng, P.; Wang, X.M. Source contributions of PAHs and toxicity in reed wetland soils of Liaohe estuary using a CMB-TEQ method. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, N.N.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Liu, T.T.; Gai, C. Emission, distribution and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) during municipal solid waste (MSW) and coal co-combustion. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Qian, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, R.; Du, Y.; Chen, M. A comparison of risk modeling tools and a case study for human health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in contaminated groundwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Yao, T. Distribution and vertical migration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in forest soil pits of southeastern Tibet. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Feng, Q.; Liang, H.; Gao, B.; Alam, E. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons PAHs in underground coal mining environment of Xuzhou. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1564–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchamen Mougnol, J.B.; Waanders, F.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Al Alili, A.R. Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, X.R.; Bai, X.J.; Wu, L.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Zhang, Z.Y. Removal, migration, and distribution of naphthalene in bioretention facilities: The influences of particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 46940–46949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.N.; Yuan, H.; Wang, H.L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.Z. A Review on Modification Methods of Adsorbents for Naphthalene in Environment. Catalysts 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-T.; Xiang, X.-X.; Zhang, S.-C.; Liu, M.-L.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Yao, H.; Sun, S.-B. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of PAHs in Soils with Different Land Use Types During Rapid Urbanization. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 3369–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.B. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a sediment core from Lake Taihu and their associations with sedimentary organic matter. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 129, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Z.; Zhang, D.; Tan, L.H.; Zhao, S.P.; Wang, J.W.; Yao, L.; Cao, W.G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in traditional Chinese medicines an analytical method based on different medicinal parts, levels, distribution, and sources.pdf. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4671–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.O.; Ogogo, K.N.; Mummullage, S.; Harden, F.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Source apportionment and risk assessment of PAHs in Brisbane River sediment, Australia. Ecol. Indic 2017, 73, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Cai, J.J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.M. Source apportionment of PM2.5 during haze episodes in Shanghai by the PMF model with PAHs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, H.; Wilson, C.P.; Townsend, T.G.; Xiang, P.; Liu, Y.G.; Ma, L.N.Q. Source identification of PAHs in soils based on stable carbon isotopic signatures. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 923–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B.; Sethi, S.S.; Chintalacheruvu, M.R. Distribution, risk assessment, and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using positive matrix factorization (PMF) in urban soils of East India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Cai, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Distribution, Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Surface Sediments at the Basin Scale: A Case Study in Taihu Basin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 110, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.Y.; Suratman, S.; Latif, M.T.; Khan, M.F.; Simoneit, B.R.T.; Mohd Tahir, N. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of Southern Terengganu, South China Sea, Malaysia: Source assessment using diagnostic ratios and multivariate statistic. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 15849–15862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, L.L.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Shao, M.; Wang, Y.H. Source apportionment and toxicity of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Pu, Q.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Li, Y. Potential Toxicity Risk Assessment and Priority Control Strategy for PAHs Metabolism and Transformation Behaviors in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.H.; Li, G.L.; Wang, X.M.; Peng, P. Combination of Unmix and PMF receptor model to apportion the potential sources and contributions of PAHs in wetland soils from Jiaozhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Niu, J.; Guo, W.; An, X.; Zhao, L. Ecological and health risk-based characterization of agricultural soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the vicinity of a chemical plant in China. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, X.B.; Liu, S.G.; Yuan, T.; Qu, W.G.; Zhang, Y.J. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risks of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Pollution at a Typical Industrial Legacy Site in Tianjin, North China. Land 2022, 11, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Tian, J.M.; Kong, X.G. Characteristics of PAHs in soils under different land-use types and their associated health risks in the northern Taihu Basin, China. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatylowicz, E.; Skoczko, I. Evaluation of the PAH Content in Soot from Solid Fuels Combustion in Low Power Boilers. Energies 2019, 12, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).