Determination of Soil Electrical Conductivity and Moisture on Different Soil Layers Using Electromagnetic Techniques in Irrigated Arid Environments in South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
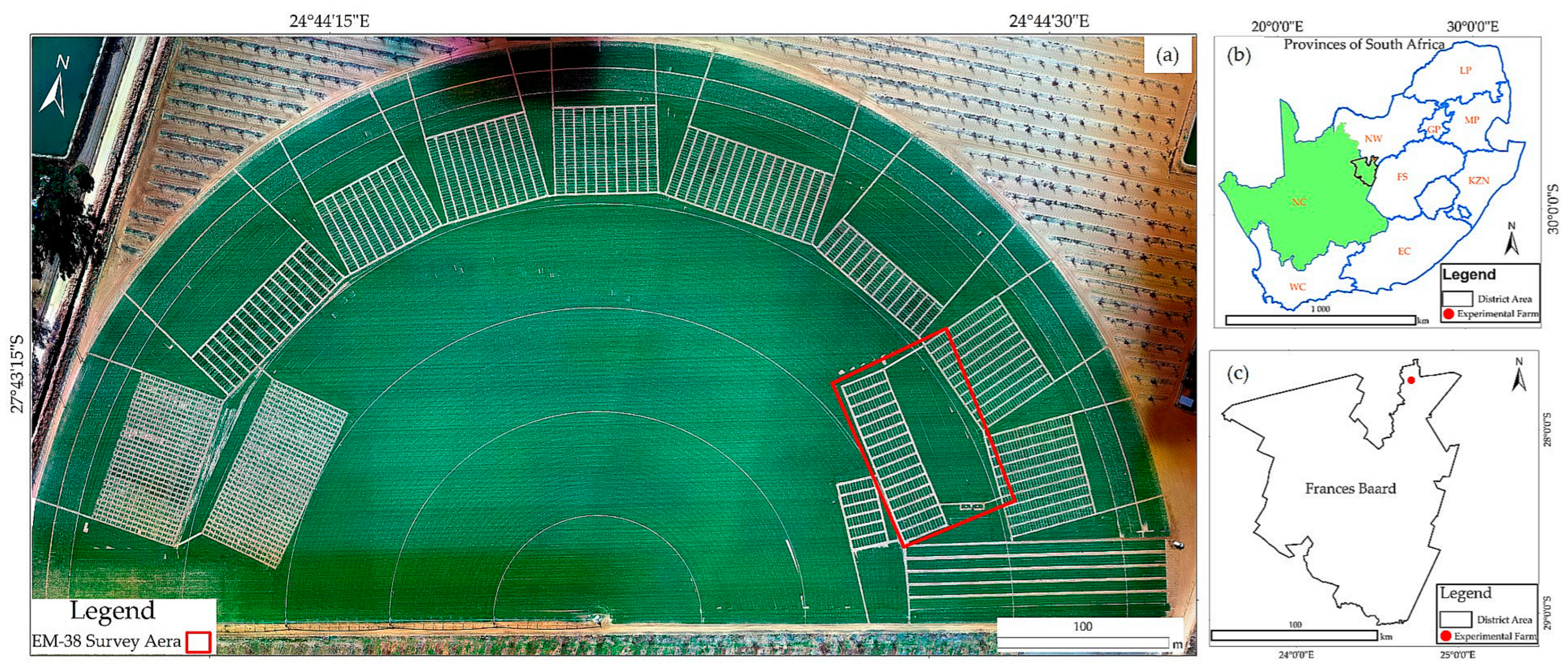
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Methods and Approaches
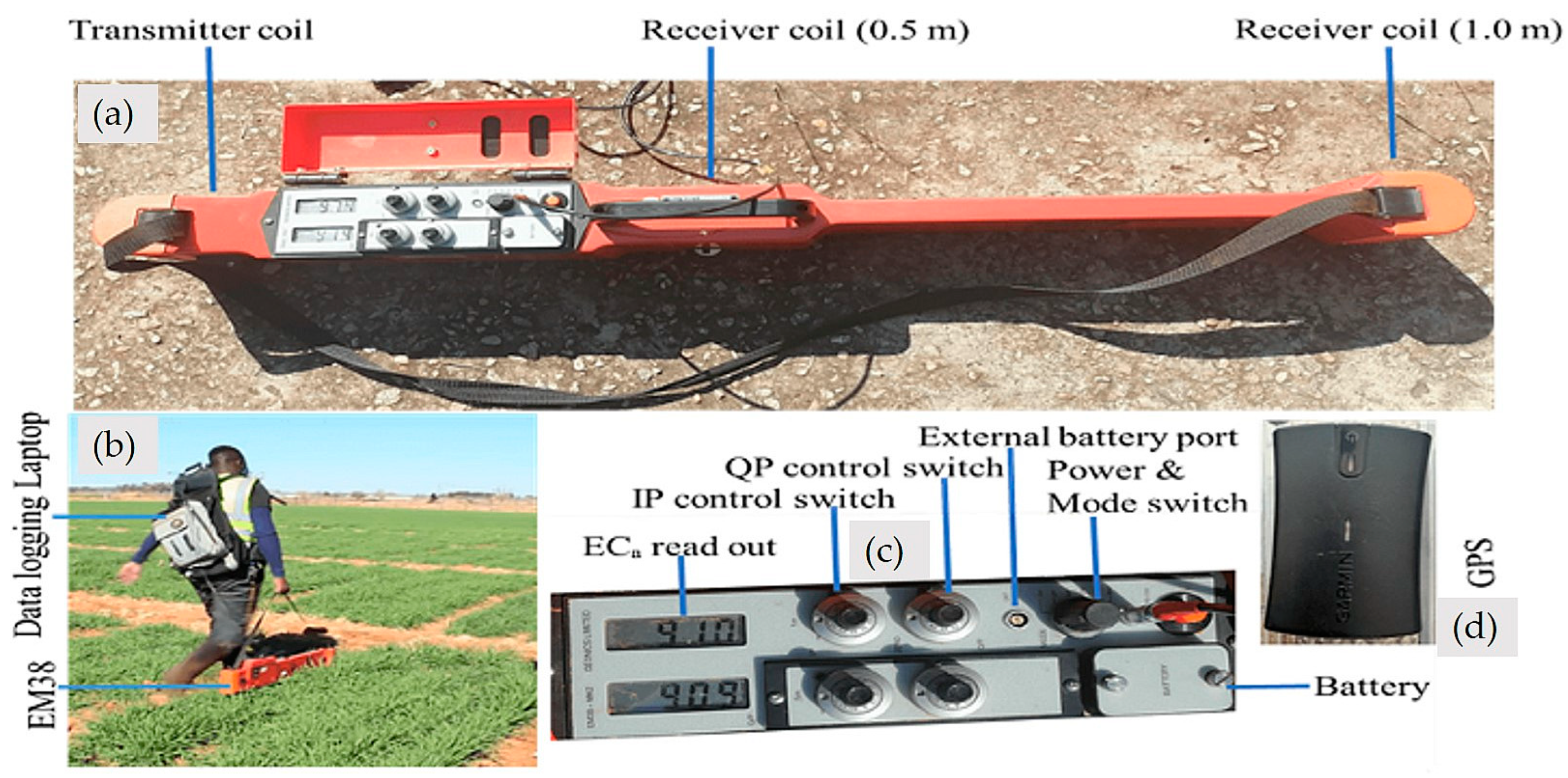
2.2.1. Soil Electrical Conductivity Surveying
2.2.2. Calibration of the Electromagnetic Induction Instrument (EM38)
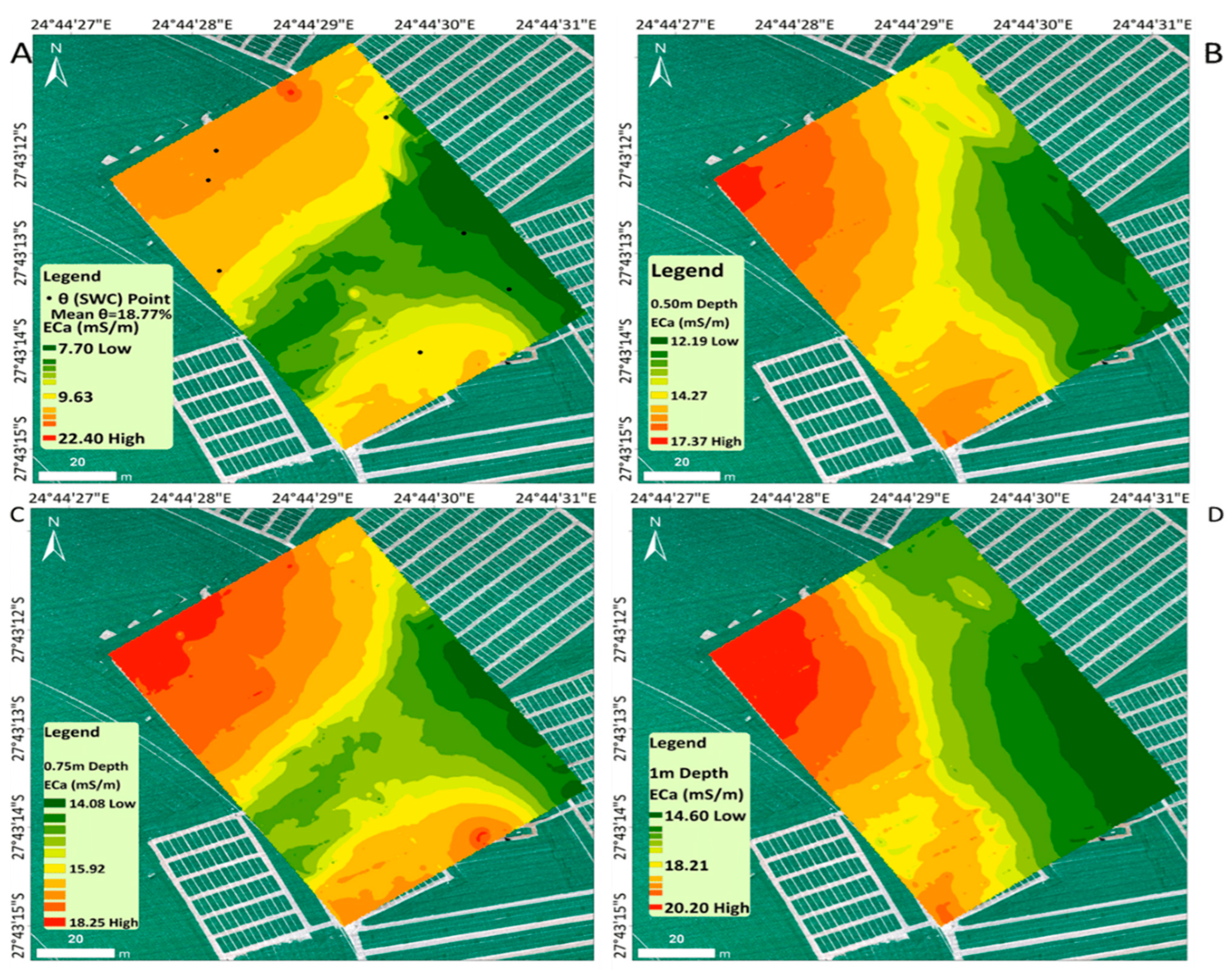
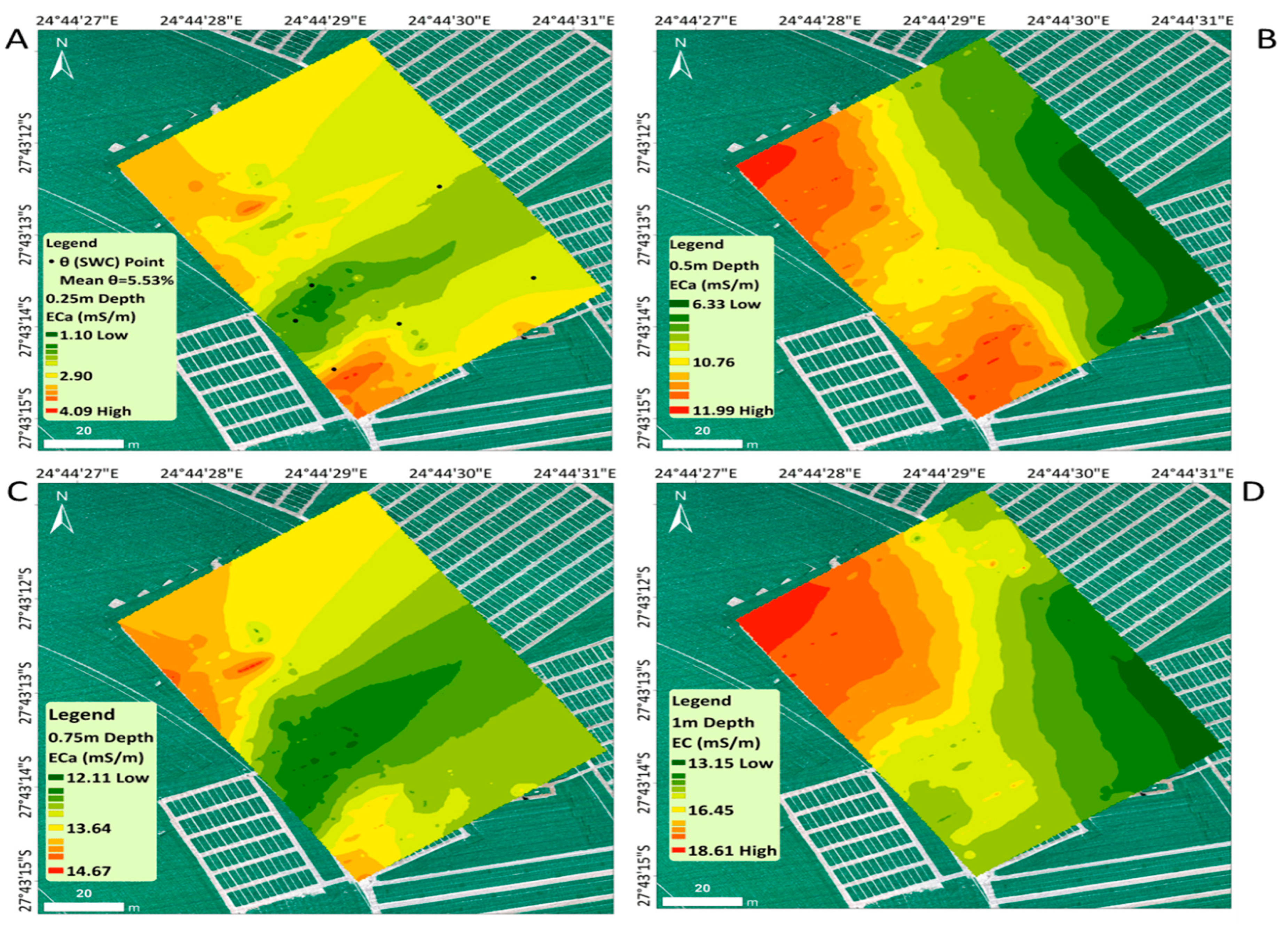
2.2.3. Spatial Distribution of Soil Electrical Conductivity
2.2.4. Assessment of Soil Salinity
2.2.5. Conversion from ECa to SWC
2.2.6. Data Processing and Evaluation Approach
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Soil Electrical Conductivity to Determine Soil Water Content
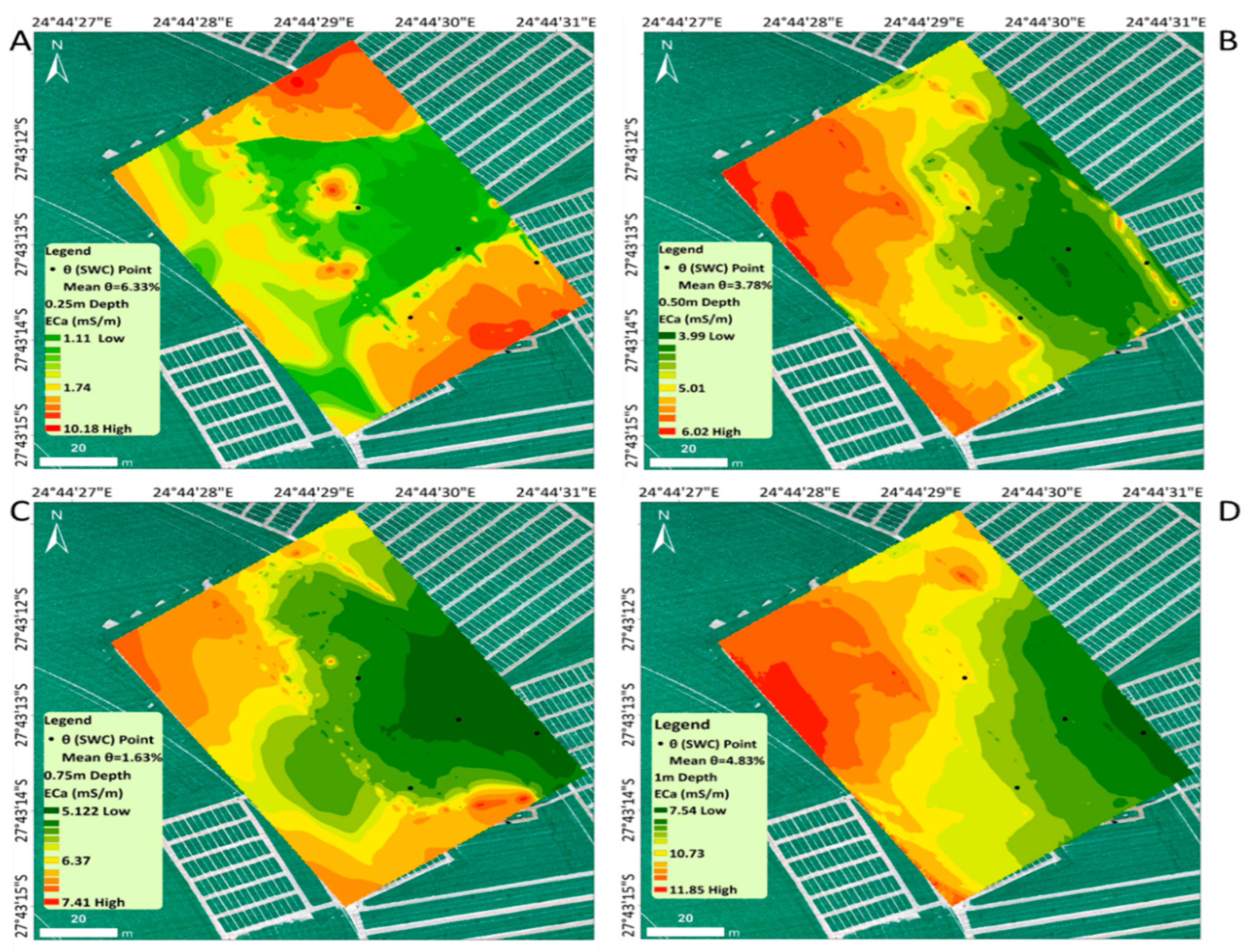
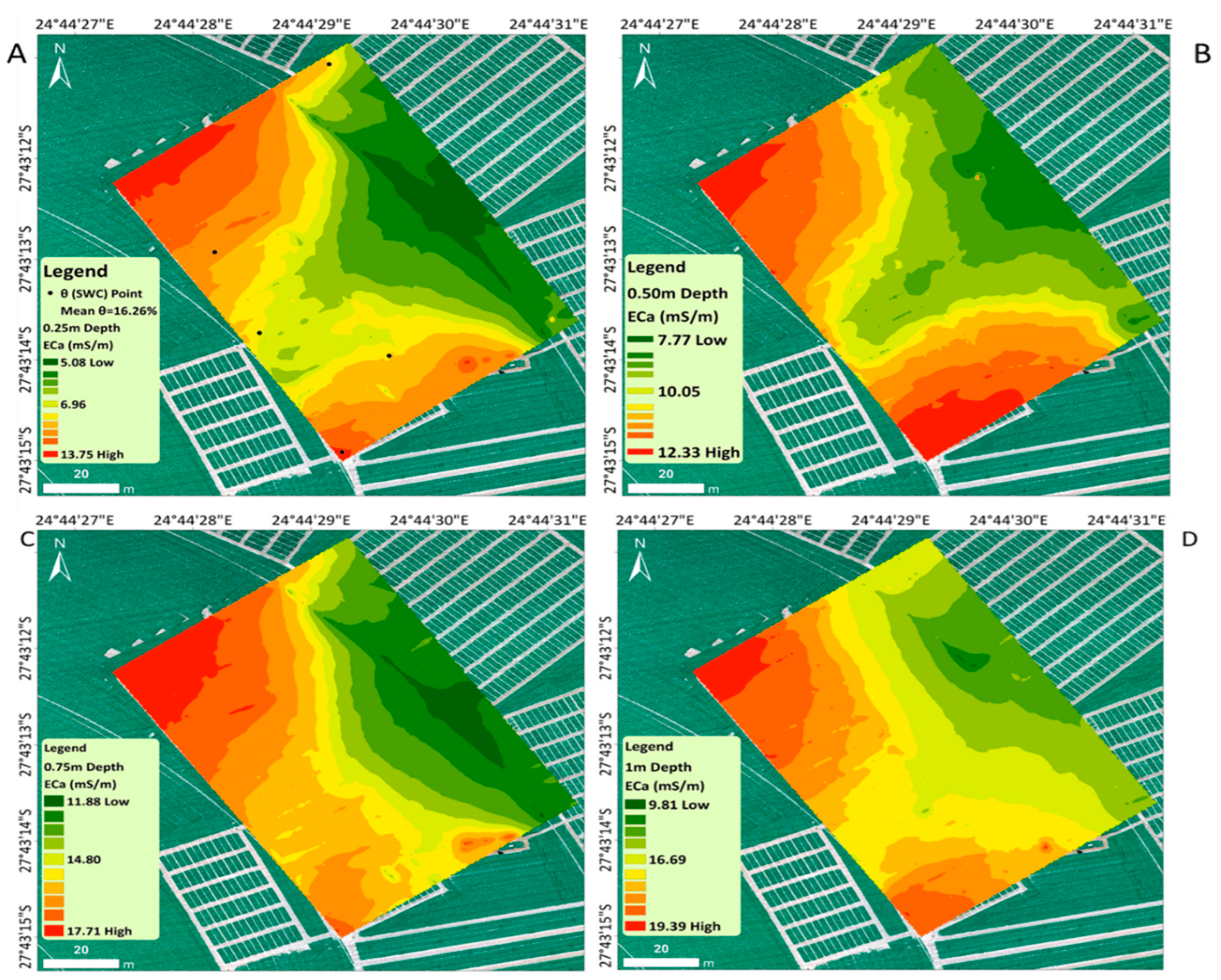
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution of Soil Electrical Conductivity
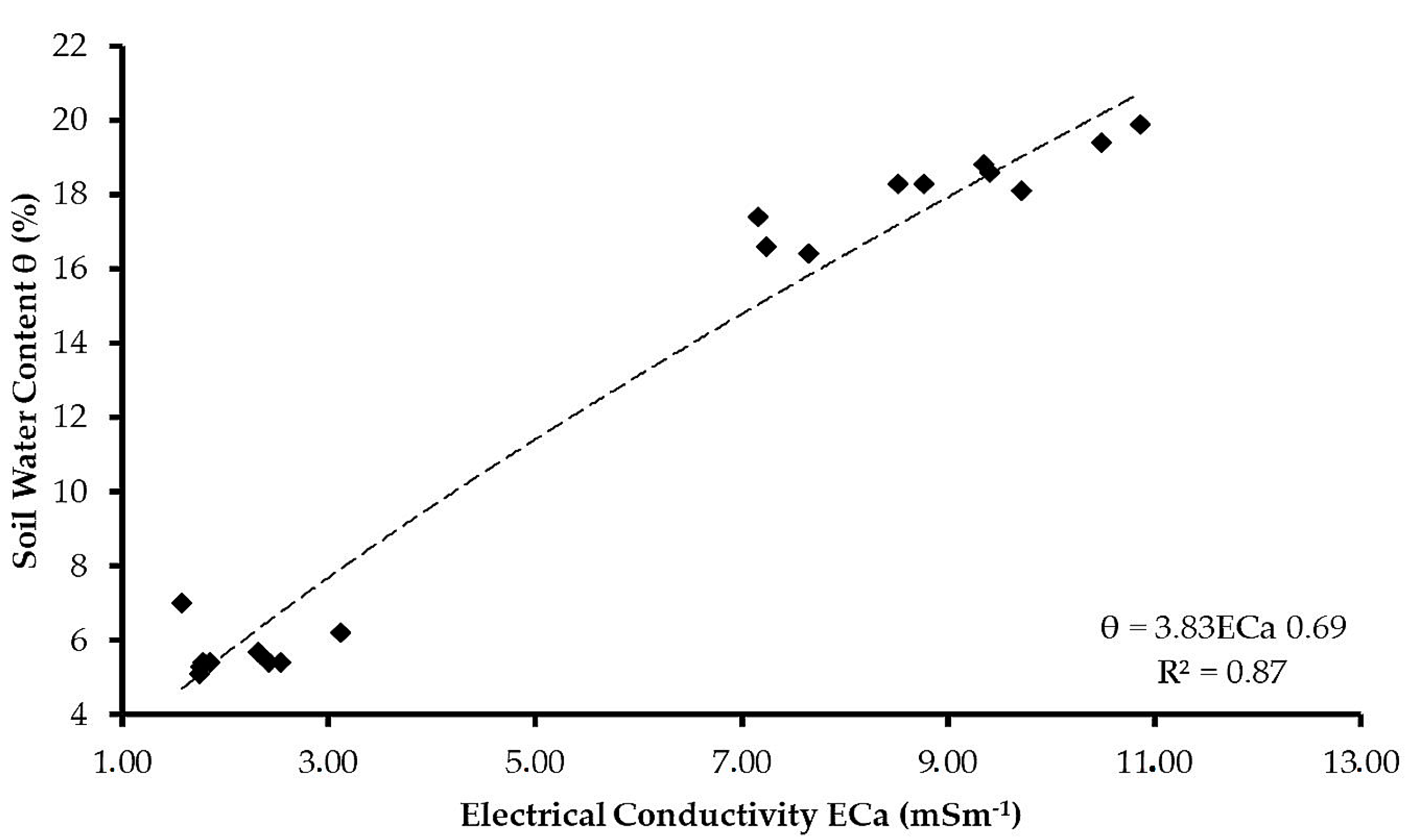
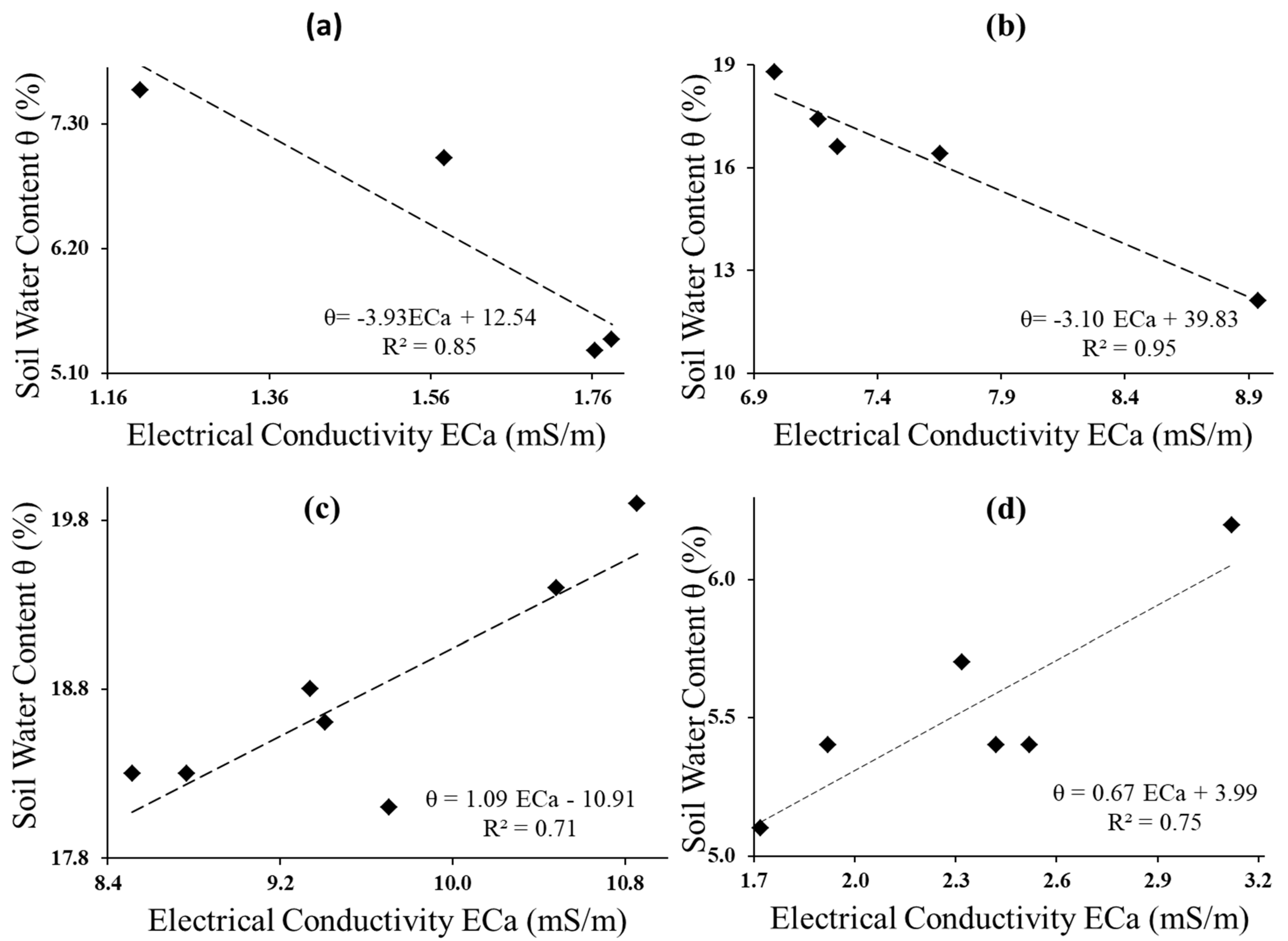
3.1.2. Relationship between In Situ Soil Electrical Conductivity and In Situ Soil Water Content
3.1.3. Soil Electrical Conductivity Conversion to Soil Water Content
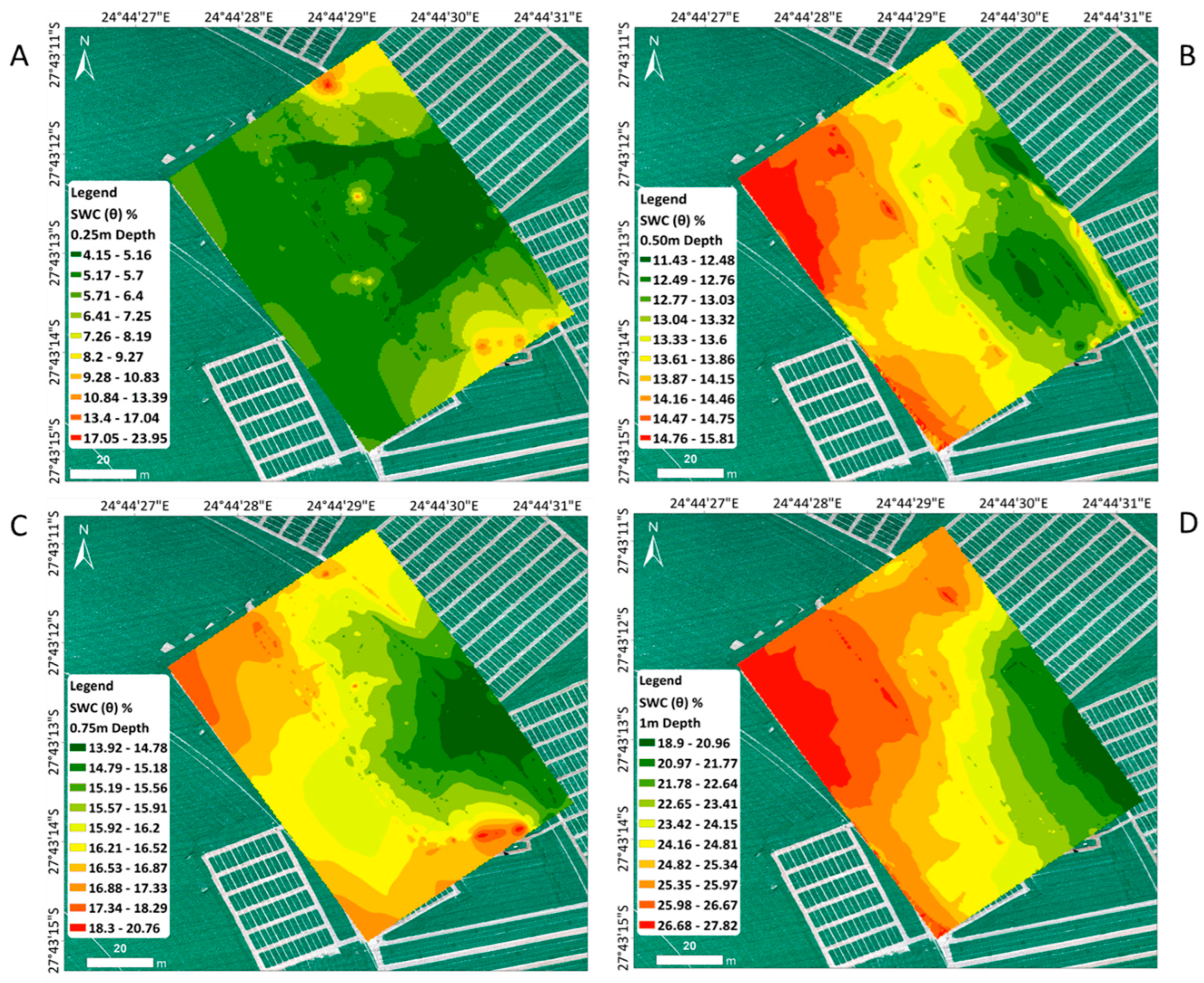
3.2. The Spatial Distribution of Soil Water Content
3.2.1. Relationship between the Soil Water Content Measured and Predicted Electrical Conductivity
3.2.2. The Relationship between Soil Electrical Conductivity and Soil Physiochemical Properties
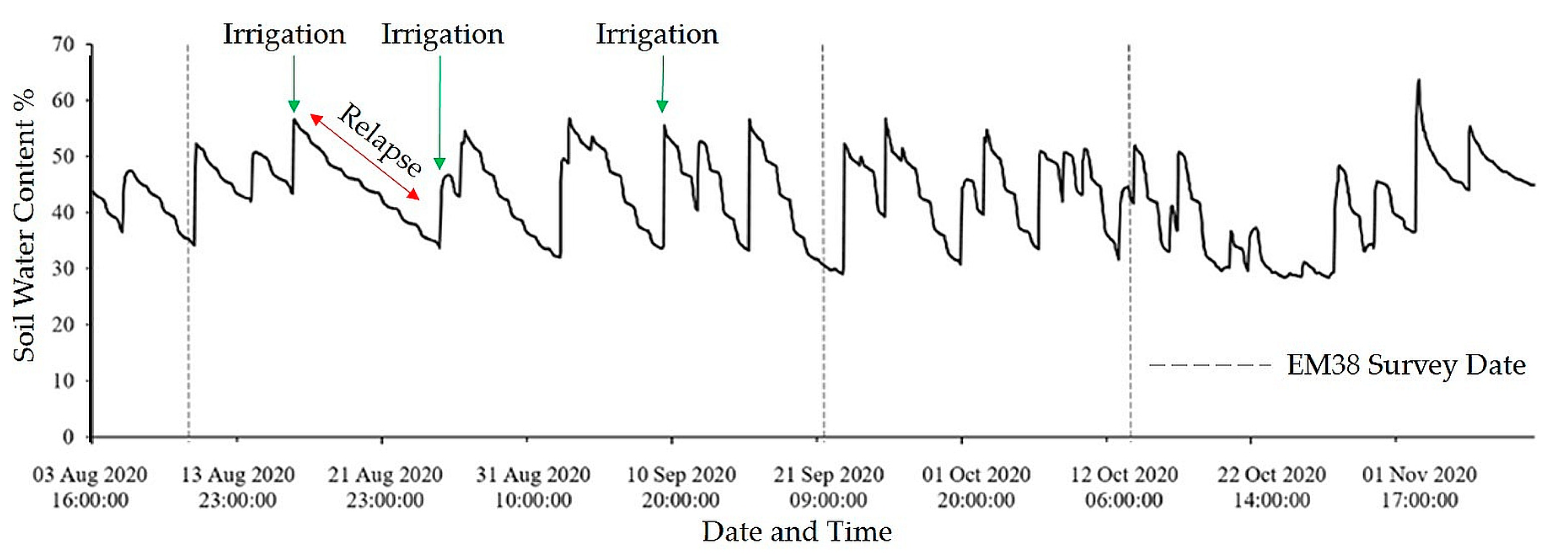
3.3. Irrigation Events
3.4. Irrigation Water and Soil Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Porporato, A.; Laio, F.; Ridolfi, L. Plants in Water-Controlled Ecosystems: Active Role in Hydrologic Processes and Response to Water Stress. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, W.; Veroustraete, F.; Feyen, J. Assessment of Evapotranspiration and Soil Moisture Content Across Different Scales of Observation. Sensors 2008, 8, 70–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; D’Odorico, P.; Evans, J.P.; Eldridge, D.J.; McCabe, M.F.; Caylor, K.K.; King, E.G. Dryland Ecohydrology and Climate Change: Critical Issues and Technical Advances. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2585–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.; Ternan, J.L.; Fitzjohn, C.; De Alba, S.; Perez-Gonzalez, A. Soil Moisture Variability and Land Use in a Seasonally Arid Environment. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrozencik, R. Trends in U.S. Irrigated Agriculture: Increasing Resilience Under Water Supply Scarcity. SSRN Electron. J. 2021, 229, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaeian, S.; Andales, A.A.; Allen, L.N.; Kisekka, I.; O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Porter, D.O.; Sui, R.; Irmak, S.; Fulton, A.; Aguilar, J. Irrigation Scheduling for Agriculture in the United States: The Progress Made and the Path Forward. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Srivastava, P.; Ortiz, B.V.; Morata, G.; Takhellambam, B.S.; Lamba, J.; Bondesan, L. Field-Scale Spatial and Temporal Soil Water Variability in Irrigated Croplands. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.; Mieno, T.; Brozović, N. Satellite-Based Monitoring of Irrigation Water Use: Assessing Measurement Errors and Their Implications for Agricultural Water Management Policy. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR028378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, B.; Courault, D.; Guérif, M. Surface Temperature and Evapotranspiration: Application of Local Scale Methods to Regional Scales Using Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M. (INVITED)Advances in Fiber Optic Sensors for Soil Moisture Monitoring: A Review. Results Opt. 2022, 7, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salouti, M.; Khadivi Derakhshan, F. Biosensors and Nanobiosensors in Environmental Applications. In Biogenic Nano-Particles and Their Use in Agro-Ecosystems; Ghorbanpour, M., Bhargava, P., Varma, A., Choudhary, D.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 515–591. ISBN 9789811529849. [Google Scholar]
- Songara, J.C.; Patel, J.N. Calibration and Comparison of Various Sensors for Soil Moisture Measurement. Measurement 2022, 197, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, T.E.; Cosh, M.H.; Cuenca, R.H.; Dorigo, W.A.; Draper, C.S.; Hagimoto, Y.; Kerr, Y.H.; Larson, K.M.; Njoku, E.G.; Small, E.E.; et al. State of the Art in Large-Scale Soil Moisture Monitoring. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 1, 1888–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, U. Retrieval of Soil Moisture from Passive and Active L/S Band Sensor (PALS) Observations during the Soil Moisture Experiment in 2002 (SMEX02). Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.W.; Tang, J.; Sarwar, A.; Shah, S.; Saddique, N.; Khan, M.U.; Imran Khan, M.; Nawaz, S.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Aziz, M.; et al. Soil Moisture Measuring Techniques and Factors Affecting the Moisture Dynamics: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregui, L.M.; Quemada, M. Drainage and Nitrate Leaching in a Crop Rotation under Different N-Fertilizer Strategies: Application of Capacitance Probes. Plant Soil 2006, 288, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, J.L.; Paltineanu, I.C. Soil Water Dynamics Using Multisensor Capacitance Probes in Nontraffic Interrows of Corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinglan, Y.; Wang, G.; Hu, P.; Lai, X.; Xue, B.; Fang, Q. Root-Zone Soil Moisture Estimation Based on Remote Sensing Data and Deep Learning. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlandson, T.L.; Berg, A.A.; Bullock, P.R.; Ojo, E.R.; McNairn, H.; Wiseman, G.; Cosh, M.H. Evaluation of Several Calibration Procedures for a Portable Soil Moisture Sensor. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, A.M.; Ibrahim, H.G.; Elmetwalli, A.H.; Khedher, K.M.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Elsayed, S. Designing Low-Cost Capacitive-Based Soil Moisture Sensor and Smart Monitoring Unit Operated by Solar Cells for Greenhouse Irrigation Management. Sensors 2021, 21, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.-W.; Shi, J.-J.; Huang, J.-F. Soil Moisture Monitoring Based on Land Surface Temperature-Vegetation Index Space Derived from MODIS Data. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Sethi, R.R.; Sahoo, N. Evaluation and Integration of Soil Salinity and Water Data for Improved Land Use of Underproductive Coastal Area in Orissa. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 59, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlitchnyi, A.A.; Plotnitskiy, S.V.; Stepovaya, O.Y. Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture Content within Catchments and Its Modelling on the Basis of Topographic Data. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Bertaki, M. Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture under Climate Change. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Advances in the Quality of Global Soil Moisture Products: A Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qu, J.; Hao, X.; Cosh, M.; Prueger, J.; Zhu, Z.; Gutenberg, L. Downscaling of Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval by Combining MODIS/Landsat and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, N. Precision Agriculture—A Worldwide Overview. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongnian Zeng, Z.F. Assessment of Soil Moisture Using Landsat ETM+ Temperature/Vegetation Index in Semiarid Environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’04, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2004; Volume 6, pp. 4306–4309. [Google Scholar]
- Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Lovergine, F.P.; Palmisano, D.; Davidson, M.W.J. Dataset of Sentinel-1 Surface Soil Moisture Time Series at 1 Km Resolution over Southern Italy. Data Brief 2021, 38, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; González-Zamora, A.; Sánchez, N.; Gumuzzio, A.; Herrero-Jiménez, C.M. Satellite Soil Moisture for Agricultural Drought Monitoring: Assessment of the SMOS Derived Soil Water Deficit Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadoss, J.; Falco, N.; Dafflon, B.; Wu, Y.; Franklin, M.; Hermes, A.; Hinckley, E.-L.S.; Wainwright, H. Remote Sensing-Informed Zonation for Understanding Snow, Plant and Soil Moisture Dynamics within a Mountain Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Gillies, R.R.; Schmugge, T.J. An Interpretation of Methodologies for Indirect Measurement of Soil Water Content. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.-J.; Leng, P.; Li, Z.-L. A Method for Estimating Surface Soil Moisture from Diurnal Land Surface Temperature Observations over Vegetated Regions: A Preliminary Result over an AmeriFlux Site and the REMEDHUS Network. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J.; Jackson, T.J.; McKim, H.L. Survey of Methods for Soil Moisture Determination. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, B. EM38 for Measuring and Mapping Soil Moisture in a Cracking Clay Soil. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New England, Armidale, UK, 2008. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1959.11/2534 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Lu, Y.; Song, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y. An Examination of Soil Moisture Estimation Using Ground Penetrating Radar in Desert Steppe. Water 2017, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J., III. Measuring Surface Soil Moisture Using Passive Microwave Remote Sensing. Hydrol. Process. 1993, 7, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R.; Parkin, G.W. Advances in Soil Water Content Sensing: The Continuing Maturation of Technology and Theory. Vadose Zone J. 2005, 4, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Rubino, P.; Montemurro, F. Precision Nitrogen Management of Wheat. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altdorff, D.; Galagedara, L.; Nadeem, M.; Cheema, M.; Unc, A. Effect of Agronomic Treatments on the Accuracy of Soil Moisture Mapping by Electromagnetic Induction. CATENA 2018, 164, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Plant, R.E. Applications of Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Precision Agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeh, J.A. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Soil Water Content Using Electromagnetic Induction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11660/6471 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Eigenberg, R.A.; Doran, J.W.; Nienaber, J.A.; Ferguson, R.B.; Woodbury, B.L. Electrical Conductivity Monitoring of Soil Condition and Available N with Animal Manure and a Cover Crop. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.; Huang, J.; Vanderlinden, K.; Giráldez, J.V.; Triantafilis, J. Potential to Predict Depth-Specific Soil-Water Content beneath an Olive Tree Using Electromagnetic Conductivity Imaging. Soil Use Manag. 2018, 34, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.N.; Lamb, D.W.; Falzon, G.; Schneider, D.A. Apparent Electrical Conductivity (ECa) as a Surrogate for Neutron Probe Counts to Measure Soil Moisture Content in Heavy Clay Soils (Vertosols). Soil Res. 2014, 52, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Wiebold, W.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Bollero, G.A.; Bullock, D.G.; Clay, D.E.; Palm, H.L.; Pierce, F.J.; Schuler, R.T.; et al. Relating Apparent Electrical Conductivity to Soil Properties across the North-Central USA. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, N.R.; Sudduth, K.A.; Drummond, S.T. Soil Electrical Conductivity as a Crop Productivity Measure for Claypan Soils. J. Prod. Agric. 1999, 12, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.I.; Ilunga, F. Geospatial Analysis for Irrigated Land Assessment, Modeling and Mapping. In Multi-Purposeful Application of Geospatial Data; Rustamov, R.B., Hasanova, S., Zeynalova, M.H., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-108-3. [Google Scholar]
- Verwey, P.M.J. The Influence of the Irrigation on Groundwater at the Vaalharts Irrigation Scheme. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, D.; van Niekerk, A. Evaluation of a WorldView-2 Image for Soil Salinity Monitoring in a Moderately Affected Irrigated Area. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, W.M. Vaalharts: Environmental Aspects of Agricultural Land and Water Use Practices. Ph.D. Thesis, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mpandeli, S.; Naidoo, D.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Nhemachena, C.; Nhamo, L.; Liphadzi, S.; Hlahla, S.; Modi, A.T. Climate Change Adaptation through the Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Southern Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razas, M.A.; Hassan, A.; Khan, M.U.; Emach, M.Z.; Saki, S.A. A Critical Comparison of Interpolation Techniques for Digital Terrain Modelling in Mining. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2023, 123, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp-van Meerveld, H.J.; McDonnell, J.J. Assessment of Multi-Frequency Electromagnetic Induction for Determining Soil Moisture Patterns at the Hillslope Scale. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nell, J.P.; Van Huyssteen, C.W. Prediction of Primary Salinity, Sodicity and Alkalinity in South African Soils. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2018, 35, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Kong, L.; Guo, A. Effects of Physical Properties on Electrical Conductivity of Compacted Lateritic Soil. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 5, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkeltaub, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Jia, X.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, M.; Binley, A. Soil Moisture and Electrical Conductivity Relationships under Typical Loess Plateau Land Covers. Vadose Zone J. 2022, 21, e20174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, K.J.; Laughlin, D.C.; Clarkson, B.D.; Schipper, L.A. Forest Canopy Restoration Has Indirect Effects on Litter Decomposition and No Effect on Denitrification. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwesh, N.; Allam, M.; Meng, Q.; Helfdhallah, A.A.; Ramzy, S.M.N.; El Kharrim, K.; AAl Maliki, A.; Belghyti, D. Using Piper Trilinear Diagrams and Principal Component Analysis to Determine Variation in Hydrochemical Faces and Understand the Evolution of Groundwater in Sidi Slimane Region, Morocco. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, G.; Hausman, J.-F.; Legay, S. Silicon and the Plant Extracellular Matrix. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedy, R.C.; Scanlon, B.R. Soil Water Content Monitoring Using Electromagnetic Induction. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2003, 129, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.T.F.; Asseng, S. Determining the Causes of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Wheat Yields at Sub-Field Scale Using a New Method of Upscaling a Crop Model. Plant Soil 2006, 283, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, M.D.; McDonnell, J.J. A New Tool for Hillslope Hydrologists: Spatially Distributed Groundwater Level and Soilwater Content Measured Using Electromagnetic Induction. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyliger, A.; Chinilin, A.; Ermolaeva, O. Spatial Interpolation of Gravimetric Soil Moisture Using EM38-Mk Induction and Ensemble Machine Learning (Case Study from Dry Steppe Zone in Volgograd Region). Sensors 2022, 22, 6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.K.; Padhi, J. Assessing Field-Scale Soil Water Distribution with Electromagnetic Induction Method. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, K.; Schmidhalter, U. The Application of EM38: Determination of Soil Parameters, Selection of Soil Sampling Points and Use in Agriculture and Archaeology. Sensors 2017, 17, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, F.; Celkova, A. Salinity and Sodicity Hazard in Water Flow Processes in the Soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Laslett, G.M.; McBratney, A.B. Calibrating an Electromagnetic Induction Instrument to Measure Salinity in Soil under Irrigated Cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.; Boulton, R. Supporting the Uptake and Application of EMI Technologies on Cotton Farms. Presented during the Measuring Soil Water Using em38 Technology Workshop. 20–21 July 2015. Available online: https://blackearth.com.au (accessed on 15 May 2023).





| Soil Class | EC Concentration (mS/m) |
|---|---|
| Non-Saline | <200 |
| Slightly Saline | 200−400 |
| Moderately Saline | 800−1600 |
| Strongly Saline | >1600 |
| Saline-Sodic (Non-Alkaline) | >400 pH < 8.5 |
| Saline-Sodic (Alkaline) | >400 with pH > 8.5 |
| Sodic | <400 with pH > 8.5 |
| Day of the Year | Model | r | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 August 2020 | θ = −3.93 ECa + 12.54 | −0.92 | 0.04 |
| 22 September 2020 | θ = −3.10 ECa + 39.83 | −0.98 | 0.02 |
| 23 September 2020 | θ = 1.09 ECa − 10.91 | 0.84 | 0.05 |
| 14 October 2020 | θ = 0.67 ECa + 3.99 | 0.87 | 0.04 |
| ECe | Na | K | Mg | Ca | PH | SWC | ECa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECe | 1.00 | |||||||
| Na | 0.88 | 1.00 | ||||||
| K | 0.49 | 0.77 | 1.00 | |||||
| Mg | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 1.00 | ||||
| Ca | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 1.00 | |||
| PH | 0.09 | −0.13 | −0.31 | −0.01 | −0.28 | 1.00 | ||
| SWC | −0.15 | −0.02 | 0.03 | −0.16 | 0.18 | 0.51 | 1.00 | |
| Eca | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.07 | −0.56 | 0.37 | −0.08 | −0.13 | 1.00 |
| Irrigation Date and Time | Survey Date and Time | Water Irrigated | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 August 2020/14:00 | 11 August 2020/15:00 | 10 mm | Dry |
| 21 September 2020/08:00 | 22 September 2020/15:00 | 10 mm | Wet |
| 23 September 2020/12:00 | 23 September 2020/16:00 | 3 mm | Wet (Fertigation) |
| 12 October 2020/21:00 | 14 October 2020/16:00 | 10 mm | Wet-Dry |
| Measured Parameter Unit | EC mS/m | Ca mg/L | Mg mg/L | Na mg/L | K mg/L | SAR mileq/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 66.6 | 44 | 22 | 51 | 10.91 | 1.108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratshiedana, P.E.; Abd Elbasit, M.A.M.; Adam, E.; Chirima, J.G.; Liu, G.; Economon, E.B. Determination of Soil Electrical Conductivity and Moisture on Different Soil Layers Using Electromagnetic Techniques in Irrigated Arid Environments in South Africa. Water 2023, 15, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101911
Ratshiedana PE, Abd Elbasit MAM, Adam E, Chirima JG, Liu G, Economon EB. Determination of Soil Electrical Conductivity and Moisture on Different Soil Layers Using Electromagnetic Techniques in Irrigated Arid Environments in South Africa. Water. 2023; 15(10):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101911
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatshiedana, Phathutshedzo Eugene, Mohamed A. M. Abd Elbasit, Elhadi Adam, Johannes George Chirima, Gang Liu, and Eric Benjamin Economon. 2023. "Determination of Soil Electrical Conductivity and Moisture on Different Soil Layers Using Electromagnetic Techniques in Irrigated Arid Environments in South Africa" Water 15, no. 10: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101911






