Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Pipeline Sediments on Entering Different Water Bodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Water and Pipe Sediments
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Techniques
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pollution Characteristics of Water Samples and Pipe Sediments
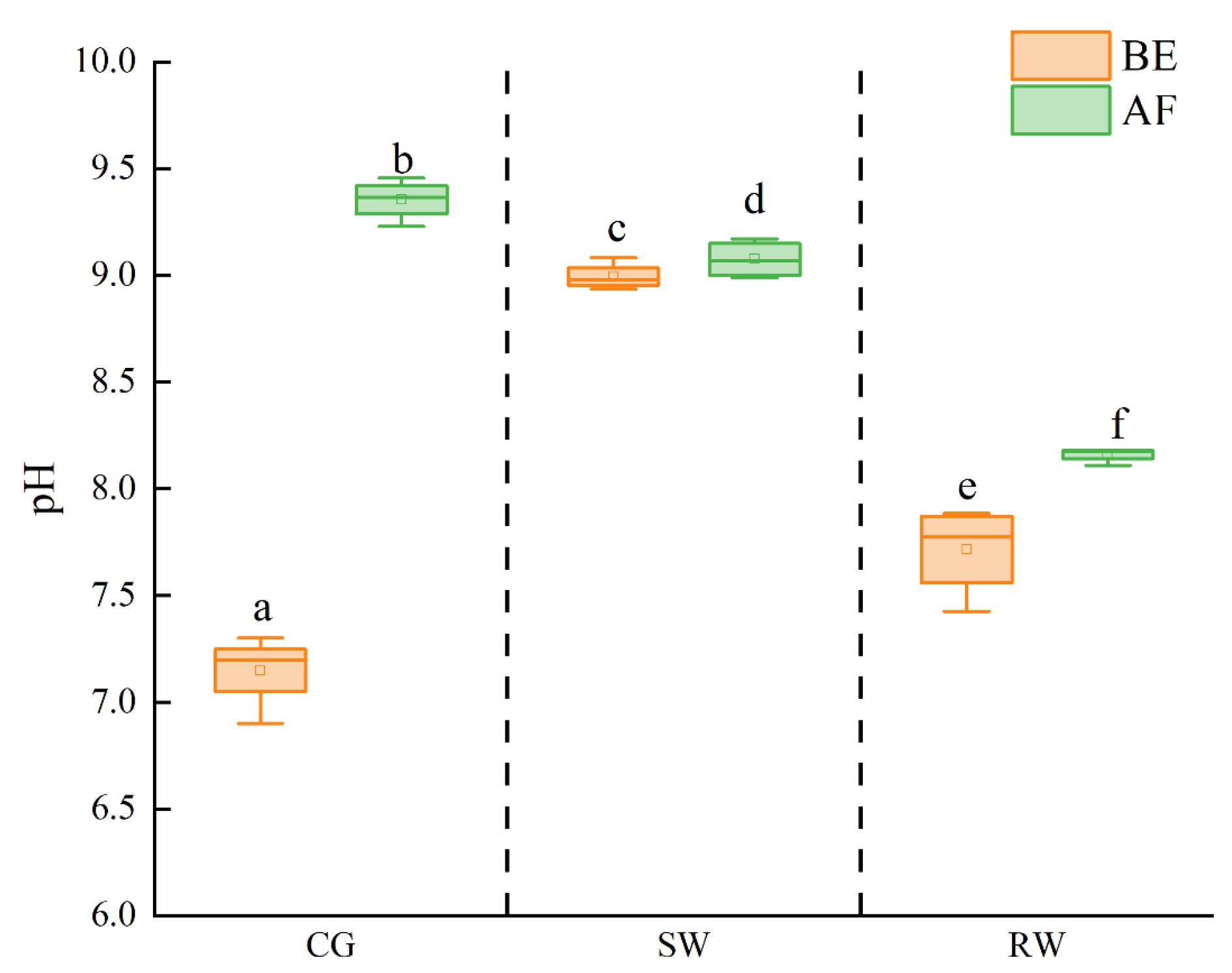
3.2. Change in pH in Water before and after Reaction
3.3. The Release Characteristics of TP
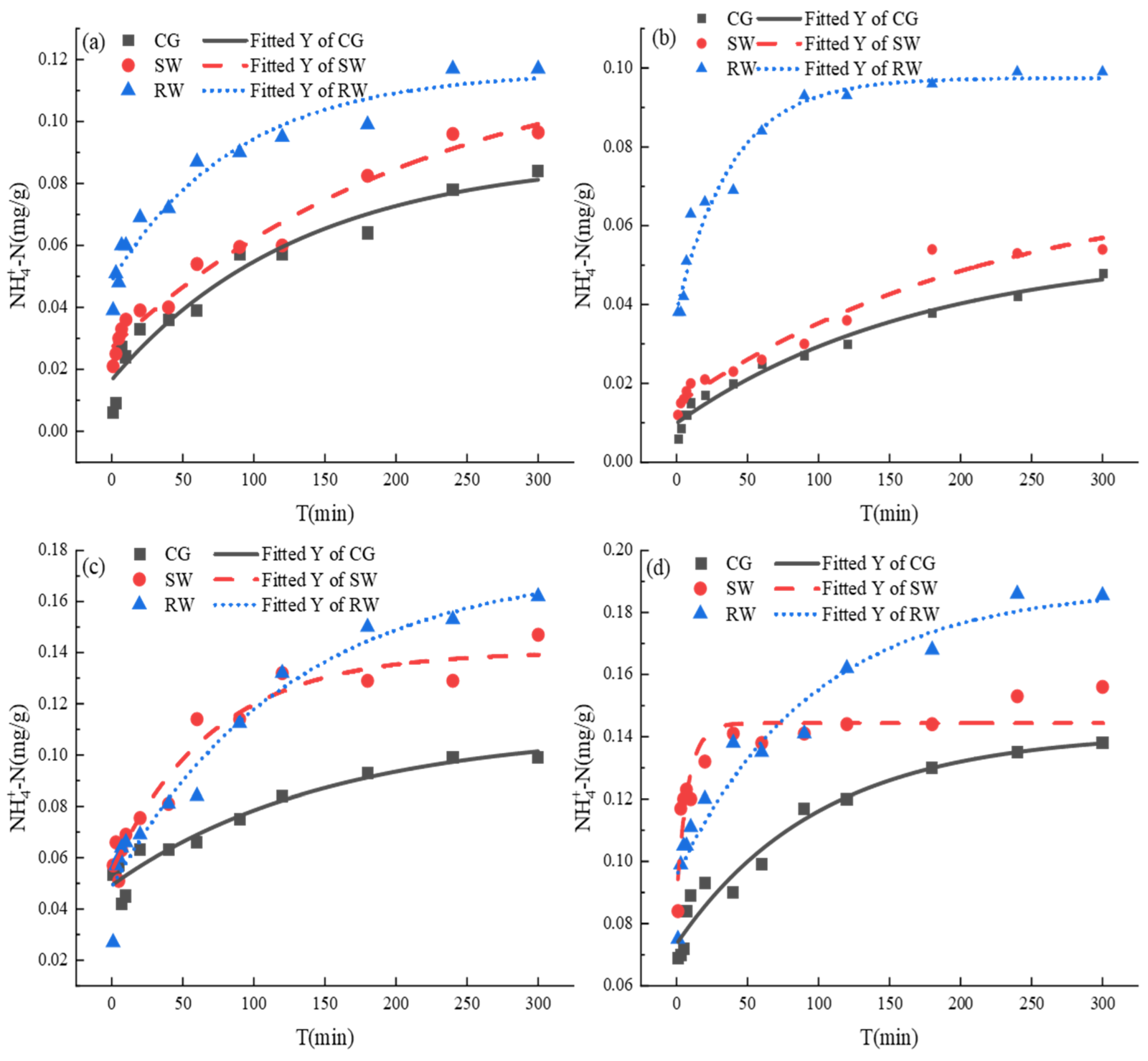
3.4. The Release Characteristics of
3.5. Percentage of TP and Released by Pipe Sediments of Different Particle Sizes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spears, B.M.; Carvalho, L.; Perkins, R.; Kirika, A.; Paterson, D.M. Sediment phosphorus cycling in a large shallow lake: Spatio-temporal variation in phosphorus pools and release. In Shallow Lakes in a Changing World: Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Shallow Lakes, Dalfsen, The Netherlands, 5–9 June 2005; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Scott, J.T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Hoffman, D.K.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. It takes two to tango: When and where dual nutrient (N&P) reductions are needed to protect lakes and downstream ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10805–10813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, W.M., Jr.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W. Rationale for control of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus to reduce eutrophication of inland waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10300–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, R.; Jinadasa, H.; Furumai, H.; Nakajima, F. A long-term suspended solids runoff simulation in a highway drainage system. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Tang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhan, Q.; Xu, W. Impacts of sewer deposits on the urban river sediment after rainy season and bioremediation of polluted sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12588–12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xiong, L.; Li, H.; Yin, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Pollution characterization and source analysis of the wet weather discharges in storm drainages. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 72, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Gromaire, M.C.; Kafi, M.; Moilleron, R.; Chebbo, G. Contributions of wastewater, runoff and sewer deposit erosion to wet weather pollutant loads in combined sewer systems. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5875–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahyerre, M.; Chebbo, G. Identification of in-sewer sources of organic solids contributing to combined sewer overflows. Environ. Technol. 2002, 23, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, P. Wastewater reuse potential analysis: Implications for China’s water resources management. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2746–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Xin, L.; Ling, B.; Yi-juan, B.; Shu-rong, Z.; Sheng-rui, W.; Lei, Z.; Ai-zhong, D. Phytoplankton Community Structures and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in Rivers Supplied with Different Water Sources. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 5616–5626. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Huang, X. Phytoplankton in an urban river replenished by reclaimed water: Features, influential factors and simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Long, Y.; Feng, M. Replenishment of urban landscape ponds with reclaimed water: Spatiotemporal variations of water quality and mechanism of algal inhibition with alum sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Risk of infection from Legionella associated with spray irrigation of reclaimed water. Water Res. 2018, 139, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G. Characteristics of change in water quality along reclaimed water intake area of the Chaobai River in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 50, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.H.; Chai, B.H.; Lu, X.X.; Zhao, J.C. Release characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments formed under different supplemental water sources in Xi’an moat, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10746–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limin, S.; Jianlong, W.; Yajun, Z. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus dissolved from urban road-deposited sediment. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 891–896. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Del Bubba, M.; Arias, C.; Brix, H. Phosphorus adsorption maximum of sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds as measured by the Langmuir isotherm. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3390–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelo, J.; Avena, M.; Fiol, S.; López, R.; Arce, F. Effects of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate at the goethite-water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Hernandez, T.; Costa, F.; Ceccanti, B.; Ciardi, C. Changes in ATP content, enzyme activity and inorganic nitrogen species during composting of organic wastes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 72, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.; Ruzhong, L.; Yuqing, W.; Ruiliang, H.; Chao, L. Phosphorus Forms and Release Risk of Sediments in Urban Sewage Treatment Plant Effluent and Receiving Stream Reach. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 801–808. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Occhipinti, M.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Majcherek, T.; Haver, D.; Oki, L. Managing urban runoff in residential neighborhoods: Nitrogen and phosphorus in lawn irrigation driven runoff. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption behavior on sediments of different origins. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, S. Nature of ammonium ion adsorption by sepiolite: Analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherms. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, J.; Svensson, G. Metal content and particle size distribution of street sediments and street sweeping waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, H. Influence of particle size on diffuse particulate pollutants in combined sewer systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H. Nutrient loads associated with different sediment sizes in urban stormwater and surface pollutants. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, F.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, X. Nitrogen and Phosphorous in Atmospheric Deposition and Roof Runoff. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Aiyi, Z.; Jian, Y. Pollutants exchange characteristics of sediment-water interface in Zhuzhou rainwater pipeline. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 15, 2322–2332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J.; Drever, J.I. Aquatic chemistry. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 1162. [Google Scholar]
- Sulin, X.; Taozhe, W.; Congyuan, G.; Daishe, W. Effects of organic matter removal on nitrogen and phosphorus ralease characteristic from surface sediments in urban shallow lakes. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 9–14+74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özacar, M. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution onto alunite. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Tian, B.; Pei, Y. Effect of low molecular weight organic acids on phosphorus adsorption by ferric-alum water treatment residuals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chendong, Z.; Xiulan, M.; Na, A.; Jing, X.; Fumin, W.; Lanpo, Z. Characteristics of Nitrogen Adsorption by Sediments in Typical Lakes and Reservoirs. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

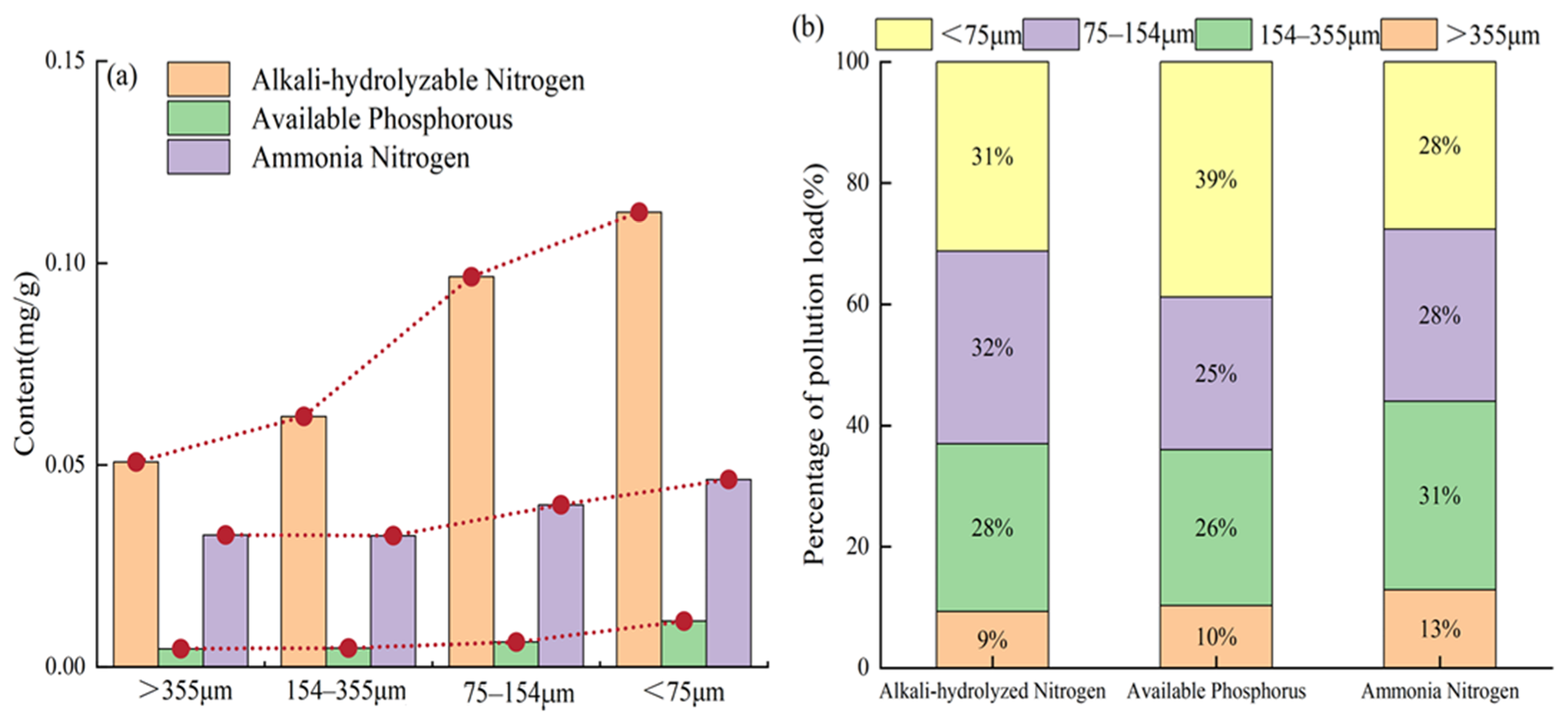


| Particle Size Range (μm) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|
| >355 | 14.86 |
| 154–355 | 36.04 |
| 75–154 | 26.66 |
| <75 | 22.44 |
| Classification | E (mg/g) | b | a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >355 μm | CG | 0.047 | 0.027 | 0.38 | 0.92 |
| SW | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.25 | 0.94 | |
| RW | 0.003 | 0.022 | 0.19 | 0.93 | |
| 154–355 μm | CG | 0.041 | 0.018 | 0.28 | 0.98 |
| SW | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.07 | 0.98 | |
| RW | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.37 | 0.85 | |
| 75–154 μm | CG | 0.064 | 0.024 | 0.42 | 0.98 |
| SW | 0.028 | 0.015 | 0.25 | 0.97 | |
| RW | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.12 | 0.98 | |
| <75 μm | CG | 0.087 | 0.018 | 0.73 | 0.93 |
| SW | 0.035 | 0.012 | 0.64 | 0.92 | |
| RW | 0.016 | 0.007 | 0.26 | 0.99 |
| Classification | E (mg/g) | b | a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >355 μm | CG | 0.0088 | 0.008 | 0.21 | 0.94 |
| SW | 0.0115 | 0.004 | 0.16 | 0.97 | |
| RW | 0.0116 | 0.011 | 0.54 | 0.95 | |
| 154–355 μm | CG | 0.0054 | 0.005 | 0.20 | 0.98 |
| SW | 0.0071 | 0.004 | 0.23 | 0.96 | |
| RW | 0.0097 | 0.025 | 0.51 | 0.96 | |
| 75–154 μm | CG | 0.0109 | 0.006 | 0.59 | 0.94 |
| SW | 0.0140 | 0.014 | 0.49 | 0.95 | |
| RW | 0.0174 | 0.007 | 0.32 | 0.96 | |
| <75 μm | CG | 0.0141 | 0.009 | 0.73 | 0.96 |
| SW | 0.0144 | 0.125 | 0.93 | 0.85 | |
| RW | 0.0188 | 0.012 | 0.70 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Xue, C.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Pipeline Sediments on Entering Different Water Bodies. Water 2023, 15, 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101903
Sun J, Xue C, Li J, Wang W. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Pipeline Sediments on Entering Different Water Bodies. Water. 2023; 15(10):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101903
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jiarong, Chonghua Xue, Junqi Li, and Wenhai Wang. 2023. "Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Pipeline Sediments on Entering Different Water Bodies" Water 15, no. 10: 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101903




