Effects of Rainfall and Plant Characteristics on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Moisture in a Black Locust Plantation (Robinia pseudoacacia) on the Chinese Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
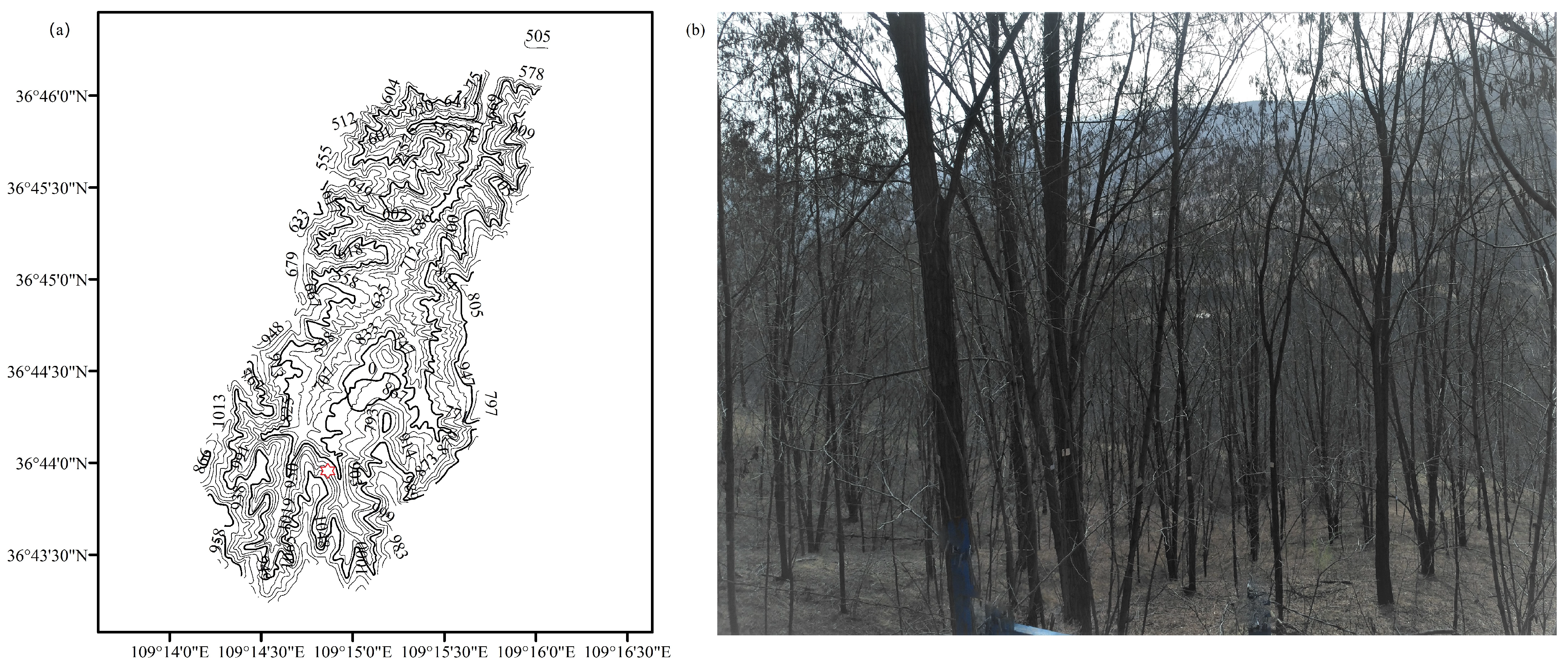
2.1. Study Site
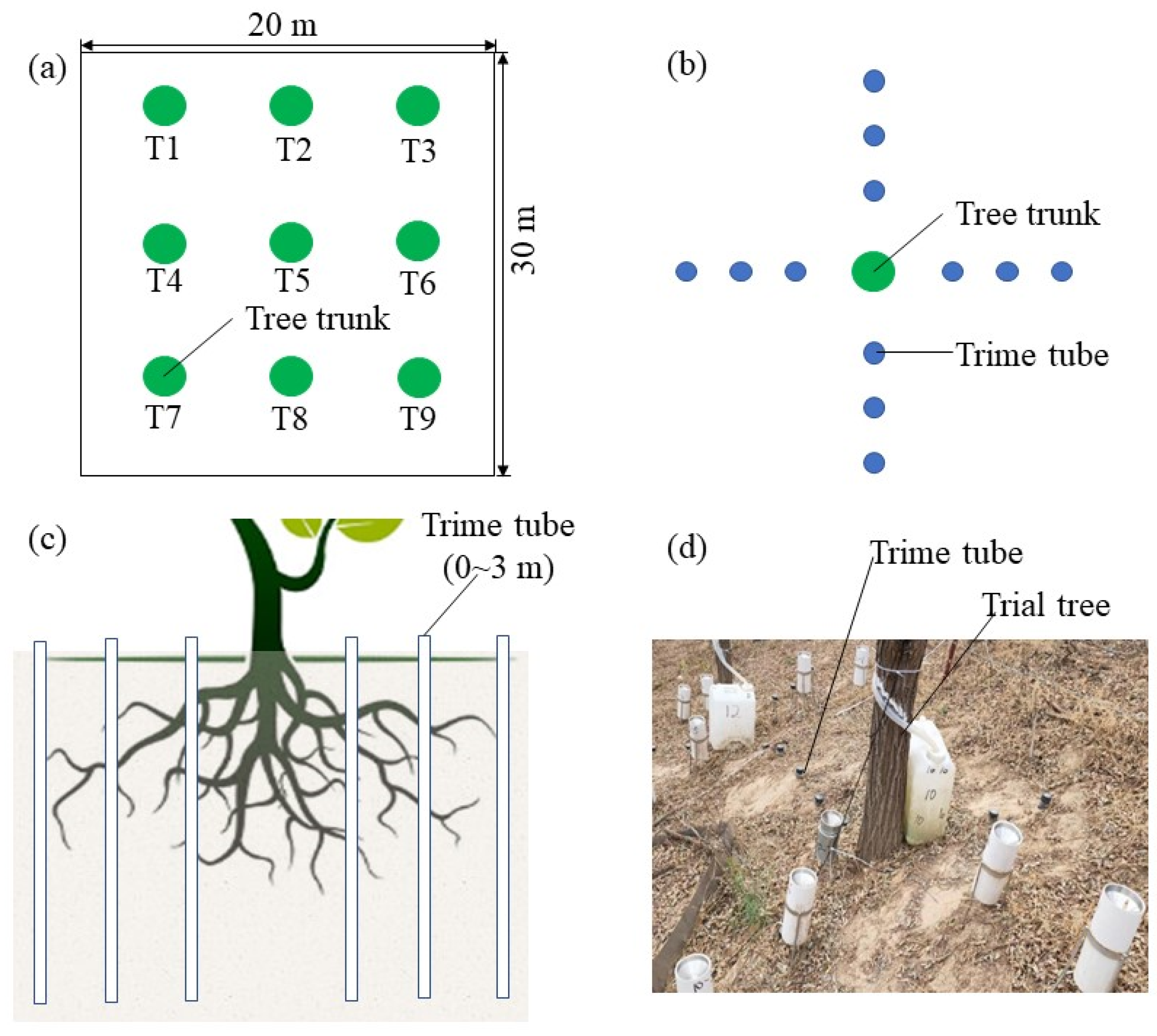
2.2. Field Experimental Design
2.3. Field Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
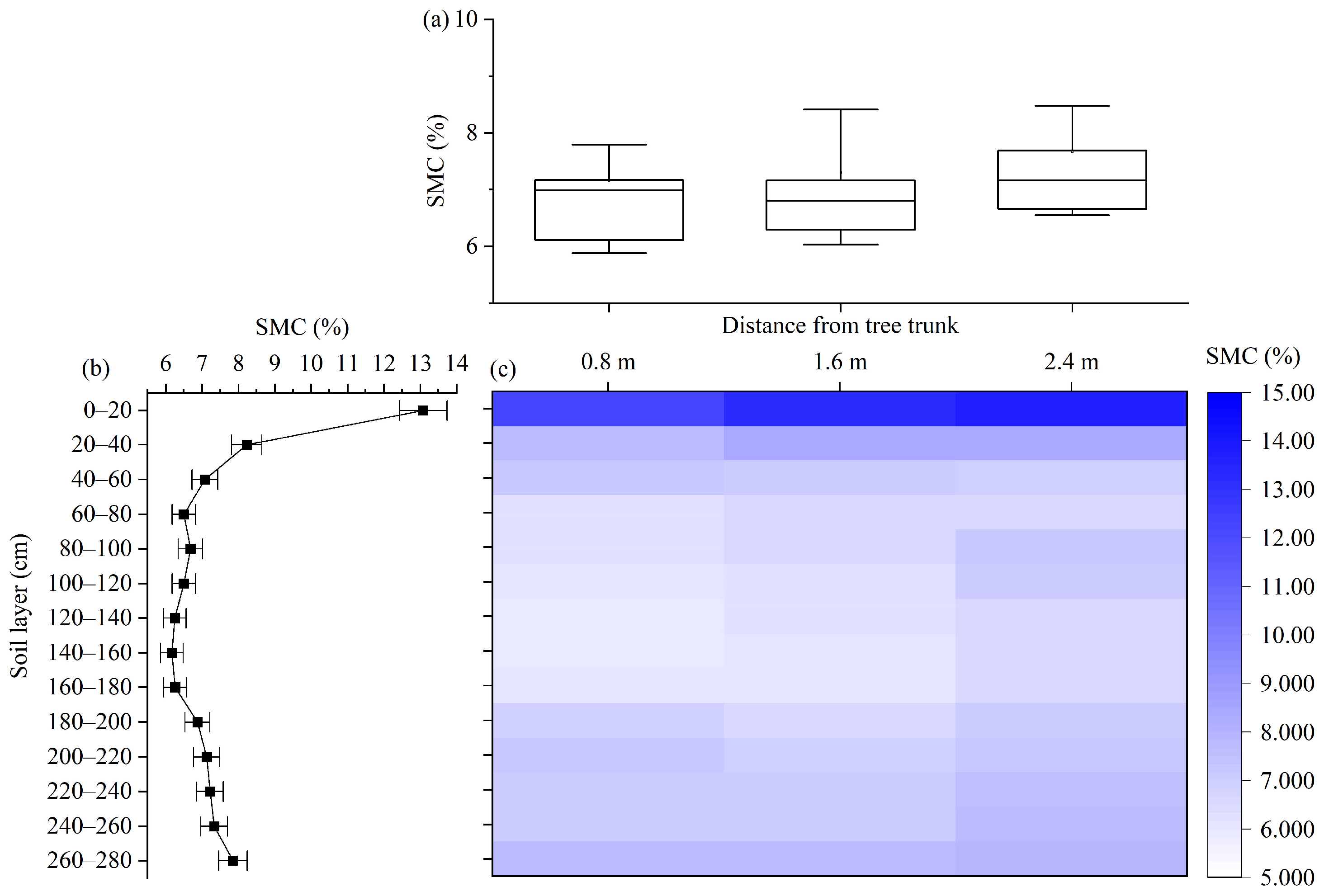
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations of the SMC
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution of the SMC
3.1.2. Temporal Dynamics of the SMC during the Growing Season
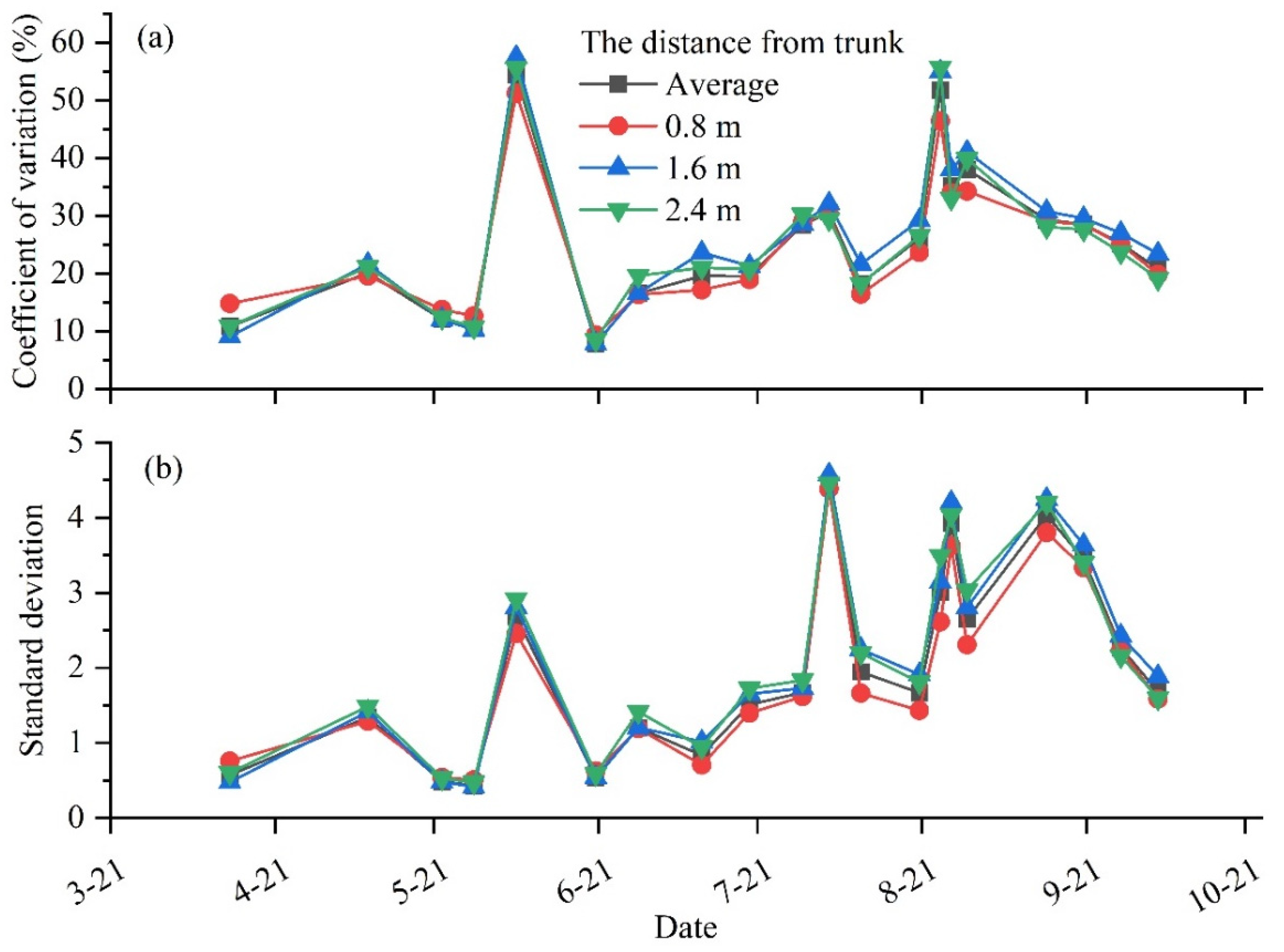
3.1.3. Spatiotemporal Variability of the SMC
3.2. Analysis of Factors Influencing Soil Moisture
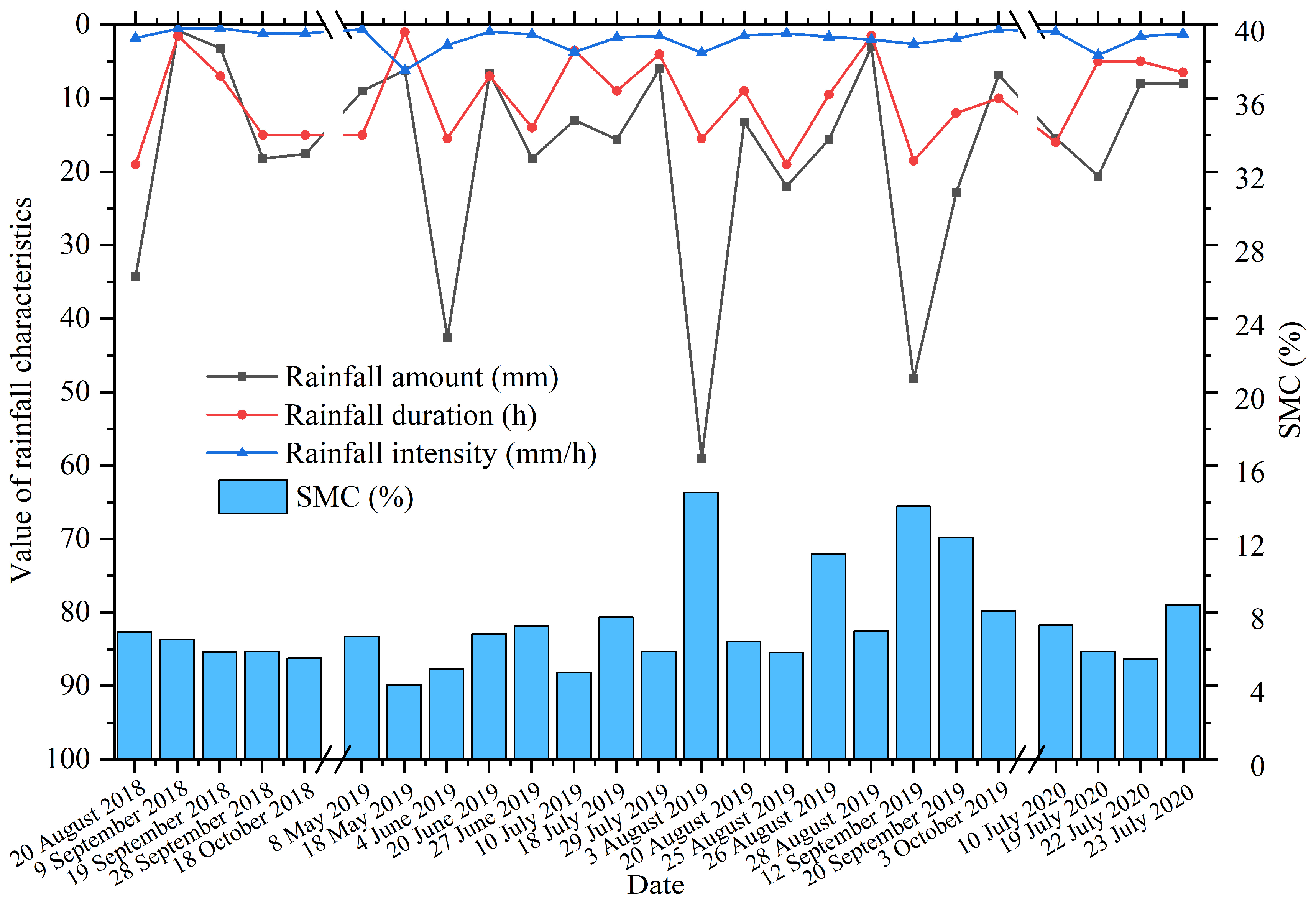
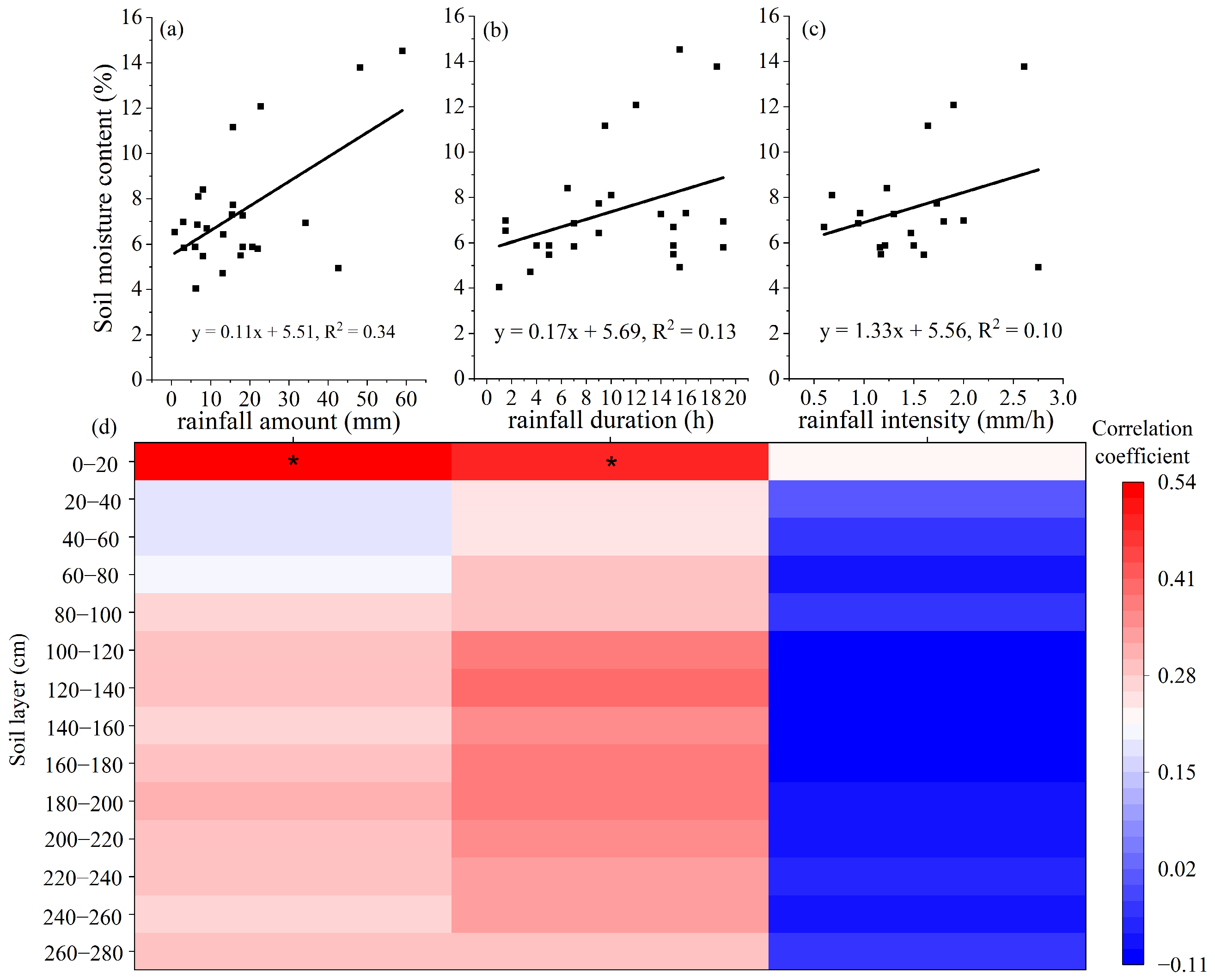
3.2.1. Effects of the Rainfall Characteristics on the SMC
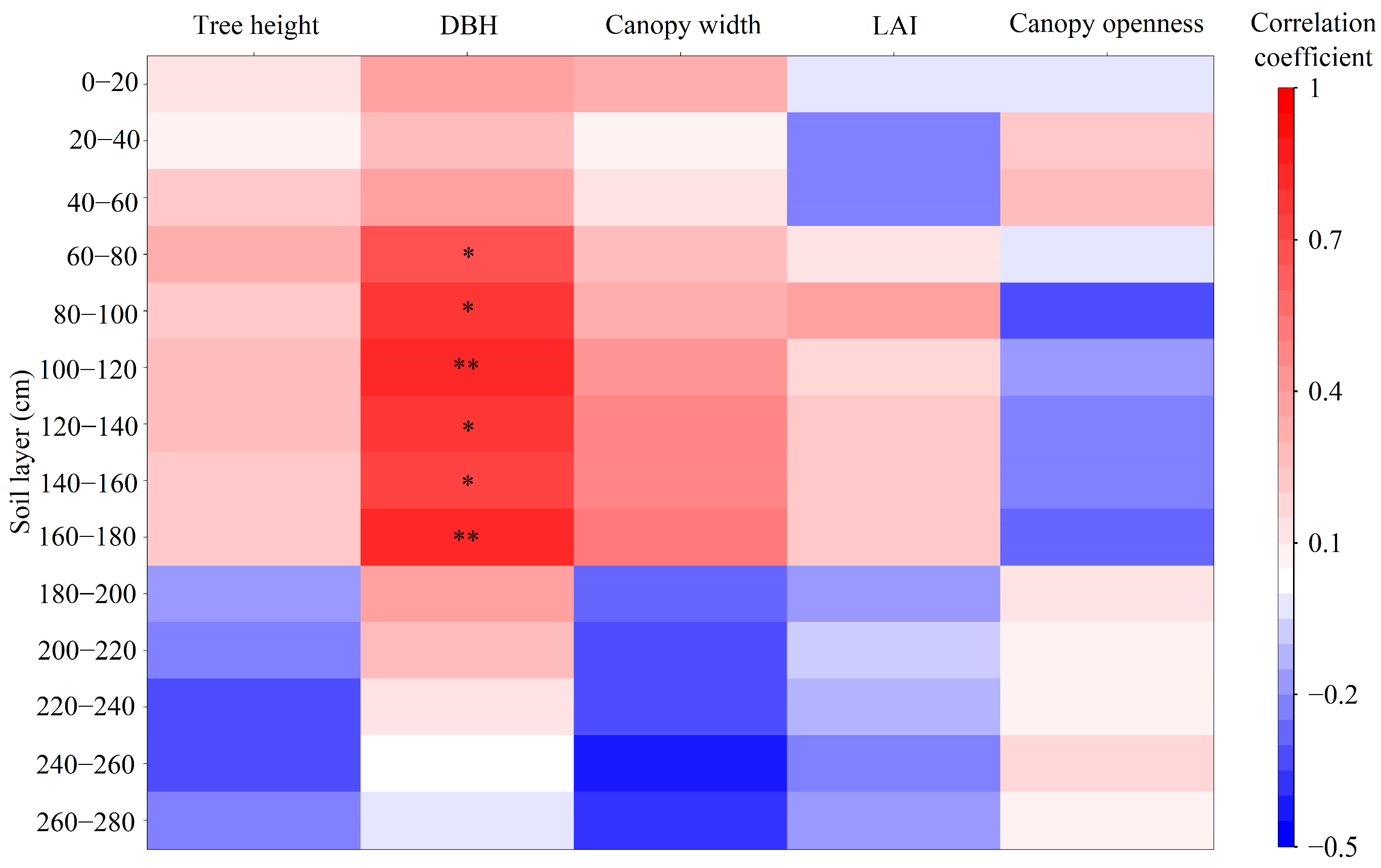
3.2.2. Effects of the Plant Characteristics on the SMC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, G.; Ma, Y.; Fu, B. Multi-temporal scale changes of streamflow and sediment load in a loess hilly watershed of China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil Erosion, Conservation, and Eco-Environment Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y. The role of climatic and anthropogenic stresses on long-term runoff reduction from the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shangguan, Z. Severe depletion of soil moisture following land-use changes for ecological restoration: Evidence from northern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 366, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Podger, G.; Davidson, A.; Dowling, T.; Zhang, L. Predicting the impact of plantation forestry on water users at local and regional scales an example for the Murrumbidgee River Basin, Australia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 251, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.; Callegari, G. Investigating the effects of afforestation on soil erosion and sediment mobilisation in two small catchments in Southern Italy. Catena 2009, 79, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Zong, Q.; Qin, P.; Liu, C. Impact of variations in vegetation on surface air temperature change over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Ma, C. Sap flow of black locust in response to short-term drought in southern Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, X.; Luo, J. Ways to Improve Low-Benefit Black Locust Forests in Loess Plateau. For. Stud. China 2005, 2, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Effect of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) on soil chemical and microbiological properties in the eroded hilly area of China’s Loess Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 65, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Kume, T.; Otsuki, K.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S. Estimating water use of a black locust plantation by the thermal dissipation probe method in the semiarid region of Loess Plateau, China. J. For. Res. 2010, 15, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H. A comparison of three methods for estimating the LAI of black locust Robinia pseudoacacia L. plantations on the Loess Plateau, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. Soil desiccation for Loess soils on natural and regrown areas. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Huang, C. Soil moisture variations at different topographic domains and land use types in the semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 165, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Q.; Chao, L.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yang, T.; Ju, Q. Ground observation-based analysis of soil moisture spatiotemporal variability across a humid to semi-humid transitional zone in China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Soil moisture–plant interactions: An ecohydrological review. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngugi, M.; Neldner, V.; Doley, D.; Kusy, B.; Moore, D.; Richter, C. Soil moisture dynamics and restoration of self-sustaining native vegetation ecosystem on an open-cut coal mine. Restor. Ecol. 2015, 5, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, N.; Hiep, N.; Bui, T. Investigating the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Soil Moisture and Agricultural Drought towards Supporting Water Resources Management in the Red River Basin of Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 9, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, M.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of land use on spatial and temporal distribution of soil moisture within profiles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, C. Future surface soil moisture trends in China under global warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 34061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Yang, L.; Li, Z. Soil Moisture Variations with Land Use along the Precipitation Gradient in the North-South Transect of the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Feng, Q.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatial variations of deep soil moisture and the influencing factors in the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2016, 2016, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, S.; Brocca, L.; Hu, W.; Wu, P. Catchment-scale variability of absolute versus temporal anomaly soil moisture: Time-invariant part not always plays the leading role. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Response of temporal variation of soil moisture to vegetation restoration in semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2014, 115, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, C.; Hirschi, M.; Seneviratne, S. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Variations of Soil Moisture Control on Surface Energy Balance and Near-Surface Air Temperature. J. Clim. 2017, 18, 7105–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, L. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Water 2013, 5, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Choi, M. Regional scale spatio-temporal variability of soil moisture and its relationship with meteorological factors over the Korean peninsula. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Luo, M.; Sa, C.; Wang, M.; Bao, Y. Quantitative assessment of the effects of climate, vegetation, soil and groundwater on soil moisture spatiotemporal variability in the Mongolian Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; González-Zamora, A.; Almendra-Martín, L. Soil moisture memory and soil properties: An analysis with the stored precipitation fraction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gao, X.; Dyck, M.; Zhang, W.; Wu, P. Soil water and root distribution of apple tree (Malus pumila Mill) stands in relation to stand age and rainwater collection and infiltration system (RWCI) in a hilly region of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 170, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Lu, N.; Ren, J.; Dong, X. Energy modeling simulation of changes in ecosystem services before and after the implementation of a Grain-for-Green program on the Loess Plateau—A case study of the Zhifanggou valley in Ansai County, Shaanxi Province, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Gao, P.; Mu, X.; Zhao, B. Vertical variations and transport mechanism of soil moisture in response to vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Huang, C.; Wang, B.; Cao, H.; Koopal, L.; Tan, W. Effect of different vegetation cover on the vertical distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon in the Zhifanggou Watershed on the loess plateau. Catena 2016, 139, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jia, X.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, M. Long-term temporal variations of soil water content under different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2017, 158, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Hu, W.; Comber, A. Half century change of interactions among ecosystem services driven by ecological restoration: Quantification and policy implications at a watershed scale in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, L.; Ji, L.; Deng, H. Spatial analysis of soil aggregate stability in a small catchment of the Loess Plateau, China: I. Spatial variability. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C. Soil moisture variability under different land uses in the Zhifanggou catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2014, 28, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, F.; Han, J.; Ge, W.; Cong, C.; Deng, L. Throughfall and its spatial heterogeneity in a black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) plantation in the semi-arid loess region, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Li, Z. Morphological, structural and physiological differences in heteromorphic leaves of Euphrates poplar during development stages and at crown scales. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.; Cao, J.; Shen, W.; Tan, Y.; He, Q.; Peng, Y. Understory Flora in Relation to Canopy Structure, Soil Nutrients, and Gap Light Regime: A Case Study in Southern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobis, M.; Hunziker, U. Automatic thresholding for hemispherical canopy-photographs based on edge detection. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 128, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preko, K.; Wilhelm, H. Detection of water content inhomogeneities in a dike model using invasive GPR guided wave sounding and TRIME-TDR (R) technique. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Li, G.; Du, S. Soil moisture variations in response to precipitation in different vegetation types: A multi-year study in the loess hilly region in China. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, A. Observing soil moisture temporal variability under fluctuating climatic conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2008, 5, 935–969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Responses of soil moisture in different land cover types to rainfall events in a re-vegetation catchment area of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2013, 101, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durocher, M.G. Monitoring spatial variability of forest interception. Hydrol. Process. 1990, 4, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levia, D.; Hudson, S.; Llorens, P.; Nanko, K. Throughfall drop size distributions: A review and prospectus for future research. WIREs Water 2017, 4, e1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, G.; Fu, B. Soil moisture decline following the plantation of Robinia pseudoacacia forests: Evidence from the Loess Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 412, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in deep soil moisture and its response to land-use shifts in the Wind–Water Erosion Crisscross Region in the Critical Zone of the Loess Plateau (2011–2015), China. Catena 2020, 193, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Shao, M.; Jia, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Soil texture determines the distribution of aggregate-associated carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous under two contrasting land use types in the Loess Plateau. Catena 2019, 172, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudle, E. Water uptake by roots: Effects of water deficit. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Ji, X.; Fang, Y. Influence of root distribution patterns on soil dynamic characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Zhu, B. Differential effects of soil texture and root traits on the spatial variability of soil infiltrability under natural revegetation in the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2023, 220, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Su, Z.; Shangguan, Z. Trade-off analyses of plant biomass and soil moisture relations on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 197, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Pumpanen, J.; Cescatti, A.; Marcolla, B.; Blanken, P.D.; Ardö, J.; Tang, Y.; Magliulo, V.; Georgiadis, T.; et al. An underestimated role of precipitation frequency in regulating summer soil moisture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 24011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Emanuel, R.; McGlynn, B.; Miniat, C. Soil Moisture Responses to Rainfall: Implications for Runoff Generation. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wan, X.; Jiang, C.; Song, X.; Wang, J. Effects of rainfall on soil moisture and water movement in a subalpine dark coniferous forest in southwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Effect of Plant Morphological Traits on Throughfall, Soil Moisture, and Runoff. Water 2020, 12, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Fu, B.; Liu, G.; Yao, X.; Wang, S. Effects of soil physicochemical properties and stand age on fine root biomass and vertical distribution of plantation forests in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Res. 2012, 27, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, Y.; Kim, S. Factors affecting soil moisture spatial variability for a humid forest hillslope. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tree Code | Tree Age/a | Tree Height/m | Diameter at the Breast/cm | Canopy Diameter/m | Canopy Openness/% | Leaf Area Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-1 | 20 | 12.1 | 19.0 | 4.4 | 47.2 | 1.3 |
| T-2 | 11.5 | 10.5 | 4.1 | 56.6 | 1.0 | |
| T-3 | 10.7 | 13.5 | 3.2 | 58.8 | 0.7 | |
| T-4 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 3.7 | 27.0 | 1.8 | |
| T-5 | 11.2 | 10.0 | 3.8 | 49.8 | 1.0 | |
| T-6 | 9.1 | 8.2 | 2.7 | 33.7 | 1.8 | |
| T-7 | 10.3 | 8.9 | 3.1 | 74.9 | 0.5 | |
| T-8 | 9.5 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 53.1 | 0.8 | |
| T-9 | 7.9 | 9.7 | 2.9 | 45.3 | 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, W.; Wang, F.; Jin, K. Effects of Rainfall and Plant Characteristics on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Moisture in a Black Locust Plantation (Robinia pseudoacacia) on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Water 2023, 15, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101870
Ding W, Wang F, Jin K. Effects of Rainfall and Plant Characteristics on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Moisture in a Black Locust Plantation (Robinia pseudoacacia) on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Water. 2023; 15(10):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101870
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Wenbin, Fei Wang, and Kai Jin. 2023. "Effects of Rainfall and Plant Characteristics on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Moisture in a Black Locust Plantation (Robinia pseudoacacia) on the Chinese Loess Plateau" Water 15, no. 10: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101870
APA StyleDing, W., Wang, F., & Jin, K. (2023). Effects of Rainfall and Plant Characteristics on the Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Moisture in a Black Locust Plantation (Robinia pseudoacacia) on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Water, 15(10), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101870







