Abstract
Under the influences of global environmental change, the water cycle exhibits a characteristic “natural-social” duality. The theoretical framework of this dualistic water cycle model has become relatively mature and the frameworks for the natural and social water cycles of the process description are now relatively clear. Although many studies in this field focus on further improvement of the model, it is difficult to apply it to the multi-scenario regulation of water resources. To address this gap, based on the comprehensive integrated platform, this paper uses visual knowledge map technology and component technology to visualize the theoretical framework of the dualistic water cycle, and establishes a framework system for the visualization of the dualistic water cycle process. Three different water resource regulation scenarios were established in the system and example applications of water resources regulation using the system were realized. The simulation results of the system show that the system intends to assist the business function of water resources regulation, and it is able to set up a number of dynamic scenarios that can be controlled by users and assist the application of regional water resources regulation. The system’s regulatory process is visual, trustworthy, and operational, and it realizes the simulation application of water resources regulation under the framework of the dualistic water cycle.
1. Introduction
The water cycle represents the objective basis of water resource formation and evolution in the watershed, and is also the leading factor regulating the water environment and ecosystem evolution []. So far, most quantitative research and practice on water resources in the natural sciences belong to the unitary mode of “measure-restore-model-control”, which aims to better understand the effects of human activities on the water cycle via “reducing” []. However, with the rapid development of society and increases in population, this static model has been difficult to adapt to the impact of human activities on the natural water cycle. The water resource problem can either be attributed to the imbalance caused by the decomposition process of the water cycle in the basin or by the evolution of its derivative process. To solve this water resources problem, all water activities are essentially comprehensive control means for the “natural-social” duality in the basin []. The introduction of this dualistic water circulation mode has attracted wide global attention and has led to the development of new theories and knowledge []. Most scholars of the Chinese Academy of Water Sciences have been studying the concept-theoretical-system-application of the dualistic water cycle from concept to theory-system, especially in the continuous improvement of the framework system diagram, relationship, and mathematical expression of the dualistic water cycle, which has led to the formation of a more mature theoretical system. However, although the dualistic water cycle mode can express the process framework of the water cycle more effectively, the application of dualistic water cycle theory to practice remains difficult, and the degree of coupling between the theoretical basis and business application is less ideal. Involving the vast complex systems of nature and society, it is difficult to describe them clearly in a single form of expression. The dualistic water cycle and the practical application of water resources regulation cannot be well connected, and the changes in the natural environment in water resources regulation have a certain randomness, and there are many uncertain factors in human society. At present, most of the research on dynamic water resources regulation focuses on the use of static water resources regulation scenario sets to reflect the dynamics, and the static scenario sets cannot quickly and accurately respond to various dynamic uncertain factors in water resources regulation, and cannot adapt to changes in the actual situation, which puts forward new challenges for the application of dynamic water resources regulation [,,].
To this end, many scholars in recent years have been committed to studying the practical application of the dualistic water cycle, applying it to river runoff change analysis [], water quality and water efficiency joint control [], basin ecological protection [], urban water consumption [], river health assessment [], water consumption and water efficiency [], river ecological water demand and water quality evaluation [], with the purpose of strengthening the dualistic water cycle theory system awareness and practical application through these methods, so as to establish a resource-saving and environmentally-friendly society []. However, as most of these studies were conducted for a certain research area, the application of a dualistic water circulation framework in part of the water cycle link for model optimization is compromised. Specifically, if the input conditions or study area are changed, the adaptability of the model must be re-examined, and may need to be potentially remodeled, as generalizability in these cases is not strong [,]. When encountering water resource management problems, water conservancy workers focus on how to apply models to solve practical problems, and prefer models with high reusability and with the ability to be adjusted dynamically [,,]. Therefore, if the information used can encapsulate the model into a system, new solutions may arise. The transformation of the conceptual framework into a system application framework is a new way of describing the theory, but the dualistic water cycle theory can guide the application, with the expansion of the system, refinement, and deepening, and can gradually improve the processing capacity, adaptations to the dynamic changes of the actual situation, and reflect the dynamic and real-time nature of the application.
Presently, knowledge maps and visualization technology are widely used in various fields, the purpose of which is to enhance people’s awareness of abstract information and to express abstract information concretely through human-computer interactions []. As early as 1989, Ronald A. Howard proposed the idea of building Knowledge maps, with the aim of storing human cognitive experience in computer systems and making inferential calculations in scenarios []. In recent years, with the application of geographic information systems, knowledge graph technology combined with GIS has developed rapidly []. Similarly, the area of water conservancy is often reflected in the popularized concept of a “water conservancy map” (geography, space, remote sensing, and operation) []. Its essence is to integrate multi-source data, including basic geographic data, water conservancy basic space data, water remote sensing image data, and water conservancy business thematic data, to provide users with an all-encompassing overview of water conservancy services. In the top-level design, Cai suggested the idea of a “water conservancy map” construction with unified planning of data resources along with unified development of information services as the main line []. In application construction, Zhang describes the purpose and significance of building a “water conservancy map” of watershed institutions through the integration and sharing of spatial information resources of watershed institutions []. At the specific application level, Zhou used big data technology to integrate river and lake management business information and built a “water conservancy map” service platform in Sichuan Province []. Similarly, Zhu utilized GIS and multi-source data fusion technology to realize the management and analysis of water conservancy data to build a visual bottom platform for water conservancy business [].
Whether it is the description of the theoretical framework of the dualistic water cycle or the visual application of ideas such as the “water conservancy map”, there still remains a gap with the docking application of the actual business. On the one hand, it is difficult to visualize the logical process of unstructured model calculations and the topological relationship of water resources. On the other hand, in the application of the water conservancy business, most of the applications can only utilize information services, and few systems can connect business personnel and address business applications. From data to information, from information to knowledge, and from knowledge to wisdom, business applications should be put first, from the application theme to find relevant knowledge, information, and data through continuous accumulation, to constantly strengthen the quality and degree of support applications, and to find the best and most adaptable goals to promote the development and progress of the water conservancy industry [].
The dualistic water cycle framework is a broad theoretical model, and the mathematical expression of the dualistic water cycle framework constitutes a significant system engineering, and as such, it is often too difficult to mathematically model the entire circulatory system, resulting in the current research results that the model can be applied to water resource management. Therefore, if the dualistic water cycle model can be visually described in computer language, the calculation components can be adjusted according to the actual changes for each cycle process without affecting the entire model framework, which is an important direction for the future development of the dualistic water cycle.
Based on the theoretical framework of the binary water cycle, this paper gradually generalizes the natural water cycle and the social water cycle process, decomposing the complex and huge framework into independent subsystems. On this basis, knowledge graph technology and component technology are used to visualize each individual water cycle process. In this way, a system application of multi-scenario regulation of quasi-water resources is constructed.
The approach to research presented in this paper not only provides reference for practical applications, but also explores the management methods of efficient uses of water resources through a multi-scenario simulation, which can promote the development of the water conservancy industry.
2. Theory and Methodology
2.1. Dualistic Water Cycle Framework
The dualistic water cycle is a fixed theoretical framework, which includes precipitation, evaporation, production and convergence, surface runoff, underground runoff, seepage, groundwater recharge, and other components of the natural water cycle system, to factors such as water supply, water use, drainage, recycled water utilization and other processes in the social water cycle system. The natural and social water cycles are known to interact, in which the social water cycle removes water from the natural water cycle system, and in the process, a portion of these water resources are lost in the form of evaporation, leakage, and other forms back to the natural water circulation system. In this way, the two systems are closely related.
2.1.1. Natural Water Cycle
The natural water cycle is a process of water phase transformation and repeated horizontal and vertical movement through mechanisms such as evaporation, transpiration, water vapor transport, precipitation, condensation, vegetation interception, soil infiltration, and surface and underground runoff under the action of solar radiation and gravity. It is also called the unitary water cycle []. The natural water cycle is the objective basis for the formation and evolution of water resources, connecting the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, by exchanging water, energy, and material among them. It plays the most important role in the cycling of materials in the natural environment. The natural water system includes large cycle (horizontal) and small cycle (vertical) water exchange processes between the ocean and the atmosphere or between the land and the atmosphere. The internal processes of the water cycle subsystem can also be divided into four basic processes: atmosphere, ground, soil, and underground. The diagram of the natural water cycle system is shown in Figure 1.
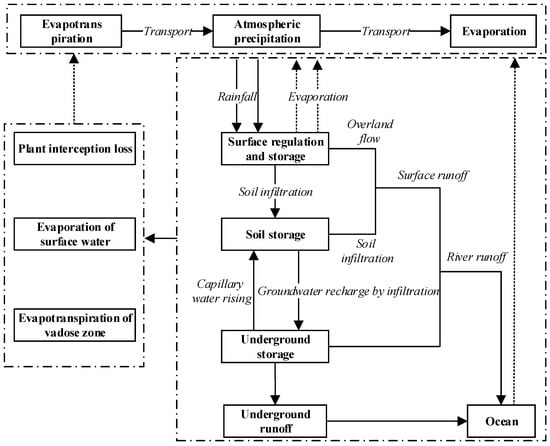
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the natural water circulation system.
2.1.2. Social Water Cycle
Modern human activities cause interactions between both social and natural systems, which are often linked by water. Human development and natural water utilization have altered the original natural water balance system, leading to the emergence of the social water circulation system. The social water cycle is a natural water cycle mixed with human activities, which has a profound impact on natural water circulation. Therefore, human activities are the main driving factors of the social water cycle. The social water cycle is defined as the “artificial collateral water cycle” within the natural water cycle, and includes four basic links: water supply, water distribution, water utilization, and water drainage []. The theoretical framework of the social water cycle provides an effective tool for rational utilization and management of water resources. The study of the social water cycle is an interdisciplinary subject, characterized by many influencing factors, complex mechanisms, and prominent regional characteristics, encompassing the process, structure, flux, and regulation of the social water cycle []. This article mainly focuses on the water cycle path under the framework of the social water cycle. It should be noted that for different industries, the micro water cycle process in the industry has its own characteristics, and when it is applied to specific industries, we should continue to make meticulous divisions and classifications under this framework, such as industrial water use and collection [,]. The diagram of the social water cycle system is shown in Figure 2.
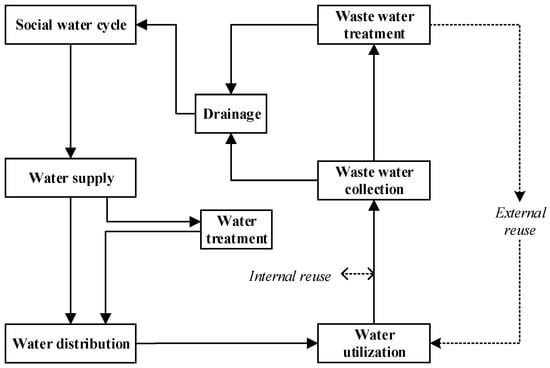
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the social water circulation system.
2.1.3. Dualistic Water Cycle
With the aggravated impact of human activities and the rapid development of the social economy, the original balance of the natural water cycle system has been irreversibly altered, and the water cycle processes such as precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, runoff generation, and confluence have been changed to a great extent. Whereas the original water cycle was dominated exclusively by natural factors, the water cycle system is now influenced by the dualistic mechanisms of nature and society. This new water cycle system dominated by joint action is called a “natural artificial” or “natural social” dualistic water cycle system []. The dualistic water cycle is a new theoretical system employed to solve complex problems by combining both the natural and social water cycles. The natural water cycle supports the social water cycle, and the social water cycle is nested within the natural water cycle. Both cycles exhibit strong interactions with one another. In this way, the dualistic water cycle provides the key technology for the cognition, quantification, and regulation of water resources []. It not only reflects the actual situation, but may also provide better services for solving the problem associated with water shortage and water resources allocation, as well as provide a theoretical basis and consideration of factors for the study of water resources uncertainty. The structure of the dualistic water circulation system is shown in Figure 3.
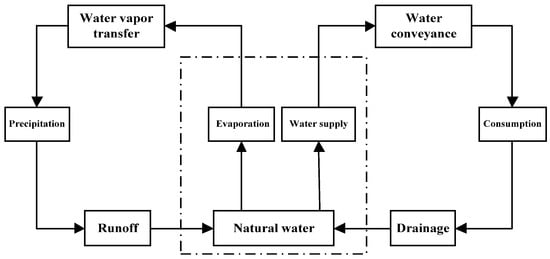
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the dualistic water circulation system.
2.2. Visual Description
The implementation of the visualization system is based on a comprehensive integration platform. This platform is designed under the service-oriented architecture, with the specific business applications based on the personality characteristics of the business in the form of knowledge graphs, components to achieve the implementation, and then through the Web service to achieve external provision of the corresponding services. At the same time, multiple business service combinations can be used to build a specific business application system. This provides a flexible and rapid basis for the visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework and the construction of water resource regulation applications, and is the foundation for the realization of dynamic water resources regulation and applications based on the visual description of the dualistic water cycle. According to the visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework and the demand for water resource regulation, the knowledge map is built using visualization tools, and the middleware (component) technology is used to build a library of different methods and components to realize specific business applications. According to the changes in the application business, the platform can modify the knowledge graph and add or delete the business components under the knowledge graph node to achieve “human-computer interaction” to meet the response to the dynamic water resources regulation application.
2.2.1. Description Tool
(1) Integrated platform. The integrated platform is designed on the basis of a service-oriented architecture. This platform can provide corresponding services through web services []. At the same time, a specific business application system can be built by combining multiple business services. It provides a flexible and fast foundation for the visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework and the construction of water resources regulation application, and is the foundation for the realization of dynamic water resources regulation application based on the visual description of the dualistic water cycle.
(2) Component technology. In the business application, the components related to the application are integrated, which gives freedom to the independent development and operation of component technology and results in high reusability. This consideration mitigates the issue of the specific application of the water resource control application. Components can be large or small, including data processing using complex mathematical models and algorithms, to solve specific water resources control applications. Each component is designed to conform to the IPO (Input Processing Output) model and be described using XML (Extensible Markup Language) standards. The input and output information flow of the business components is described using XML Schema documentation standards [].
(3) Knowledge map technology. Knowledge maps are generally divided into two types; logical flowcharts and topology diagrams. The logic flowchart is a method used to express the process of thinking or model calculation with a logic relation flowchart. In the visual description of the framework of the dualistic water cycle, the calculation model can be abstracted into the form of a logical flowchart, and the parameters, key nodes, and final results in the calculation process can be clearly defined. These can then be connected according to the logical relationship to realize the visual description. A topological relation graph refers to the graph elements connected by the combination of digital points, lines, and surfaces to describe the relationship between spatial data. In the detailed description of the dualistic water cycle, nodes, icons, and text labels can be used to describe the water sources, water conservancy facilities, and users, while lines can be used to indicate the logical relationship between them, so as to realize the visual description. The meanings of the topology diagram generalization elements are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Meaning of generalized elements in topological relation diagram.
2.2.2. Description Method
The visual description is divided into three steps: first, the subject of the visual description, as well as the information to be described under the subject, are made clear; second, the appropriate description method according to the actual situation on the basis of the subject and information are chosen; finally, the visual description knowledge diagram is drawn on the comprehensive integration platform. The visual description process is shown in Figure 4.
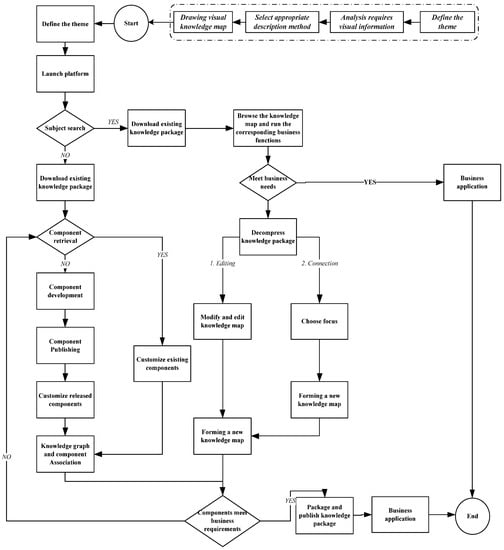
Figure 4.
Visual description process.
3. Case Study
3.1. Study Area and Data
Xiong’an New Area is located in Beijing, Tianjin, Baoding hinterland. The geographical coordinates of Xiong’an New Area are 38°43′ N–39°10′ N, 115°38′ E–116°20′ E, and its area is approximately 1770 square kilometers. The territory and its surrounding areas are located within the plains area east of Taihang Mountain, with a gradually reduced slope from the northwest to the southeast. The ground elevation is consistently between 5 to 26 m, and the ground slope is less than 2‰. The area is characterized by a warm temperate monsoon continental semi-humid and semi-arid climate. According to the meteorological data of Rongcheng county from 1968 to 2016, the mean annual temperature was reported as 12.4 °C, the extreme maximum temperature was 41.2 °C, the extreme minimum temperature was −22.2 °C, the annual sunshine was 2298.4 h, and the average annual frost-free period was 204 d. Additionally, the average annual precipitation is 495.1 mm, the extreme maximum annual precipitation is 931.8 mm, and the extreme minimum rainfall is 207.3 mm. The average evaporation over many years was 1661.1 mm. The overview of the study area is shown in Figure 5.
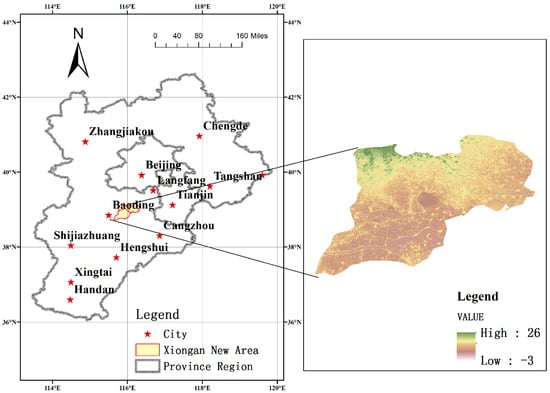
Figure 5.
Overview of the study area.
Xiong’an New Area is a state-level economic development zone approved by the Chinese government, and its hydrological, meteorological, and geographic information along with its economic and social development data are derived from the statistical yearbooks of Xiong, Anxin and Rongcheng counties. The purpose of this study is to visualize the dualistic water cycle framework, and using reference statistical yearbook data, randomly generate test data in the simulation experimental database for the calculation and presentation of simulated results. For future practical applications, these data may be replaced with measured data for analysis and calculation.
3.2. Visual Environment Construction
The description of the dualistic water cycle framework is divided into three parts, namely, the natural water cycle, the social water cycle, and the intermediate cross-cycle. The intermediate cross-cycle represents the process of returning water from the social water cycle to the natural water cycle under the influence of human activities. This cross-cycle includes mechanisms such as water collection, rainwater utilization, direct entry, evaporation, leakage, drainage, and other links. Icons and text are used to describe the logical relationships between water sources, water conservancy facilities, and users, so as to achieve the topological expression of the various processes of the water cycle. Functional components may also be added to implement business functions on the process nodes of the natural and social water cycles. The visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework and the main interface of the water resources control system are shown in Figure 6.
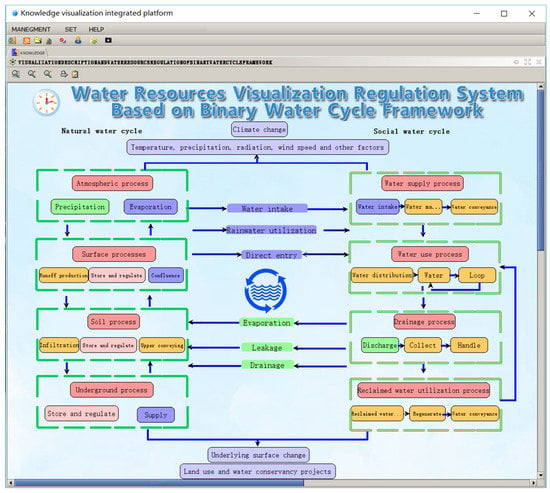
Figure 6.
Main visualization interface of the dualistic water cycle framework.
3.2.1. Visual Description of the Natural Water Cycle
The visualization description of the natural water cycle mainly includes four sub-cycle systems and six basic exchange processes. Specifically, these include the atmospheric circulation system (rainfall, evaporation), surface circulation system (production flow, confluence), soil circulation system (infiltration), and underground circulation system (replenishment). Here, water is continuously alternating, migrating, and transforming in vertical and transverse directions, and is accompanied by conversion between three-phase states (solid, liquid, and gas) and energy exchanges. The natural water cycle is a nested cycle, and the global scale water cycle includes the marine and land surface water cycles. The visualization description of the natural water cycle here is mainly for the land surface at the regional scale. The visual description of the natural water cycle is shown in Figure 7.
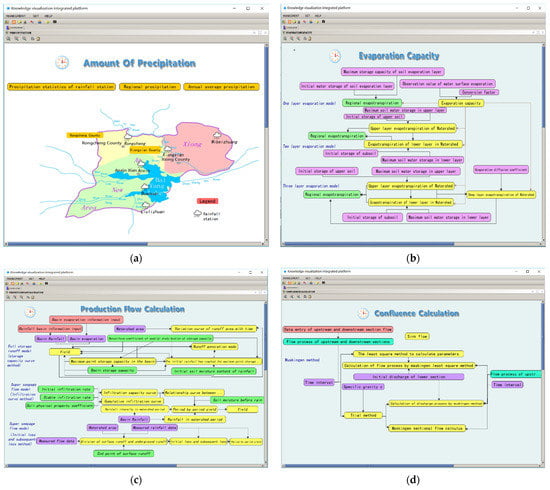
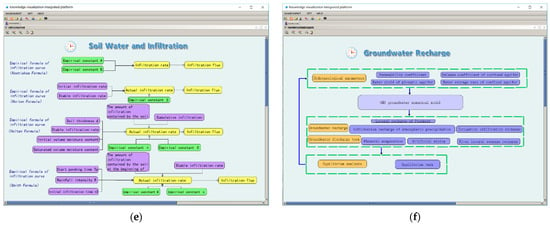
Figure 7.
Visual description of the natural water cycle. (a) Amount of precipitation interface. (b) Evaporation capacity interface. (c) Production flow calculation interface. (d) Confluence calculation interface. (e) Soil water and infiltration interface. (f) Groundwater recharge interface.
(a) Precipitation includes the precipitation statistical distribution of rainfall stations, regional precipitation, multi-year average precipitation information, and rainfall comparison information of each period. The upper part is the information node, and the lower part is the basic map. The information is added to the corresponding knowledge map and can be queried.
(b) Evaporation can be divided into three layers according to the calculation logic of the evaporation mode. The parameters and results used in the evaporation mode are represented by nodes and described by a logical relationship.
(c) The production flow mainly includes the storage capacity curve method of the full storage and production flow model, the seepage curve method of the super permeable production model, and the method of the loss after the initial loss to calculate the flow rate, which is described according to the logic flow chart.
(d) The Muskingum method is used to calculate the confluence process, and the visual knowledge diagram of confluence is described by the logic flow chart [].
(e) Four varieties of empirical formulae of infiltration (Kostiakov, Horton, Holtan, and Smith) are used to describe the infiltration visualization [,,,].
(f) By calling the GMS groundwater numerical model to obtain groundwater recharge and groundwater discharge, the results are used for balanced analysis.
3.2.2. Visual Description of the Social Water Cycle
The social water cycle is a new water cycle system generated by the continuous development of human activities and economic and social renewal, which leads to a reduction in both surface and underground runoff in the natural environment. The visual description of the social water cycle mainly includes four components: water supply processes (from atmospheric processes), water use processes (from surface processes and water supply processes), drainage processes (from water use processes and soil processes), and reclaimed water use processes (from drainage processes). The visual description of the social water cycle is shown in Figure 8.
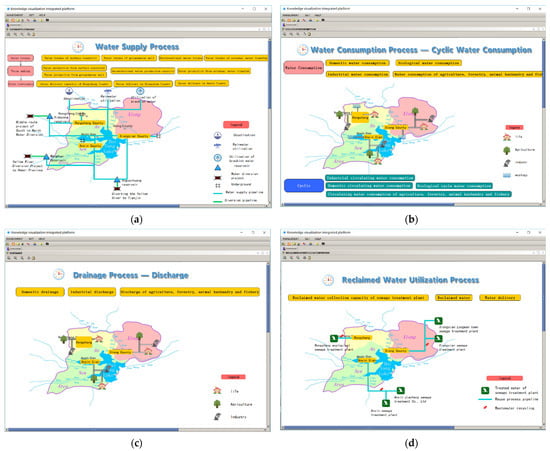
Figure 8.
Visual description of the social water cycle. (a) Water supply process interface. (b) Water consumption process interface. (c) Drainage process interface. (d) Reclaimed water utilization process interface.
(1) Water supply mainly includes the processes of water intake, water production, and water delivery. The visual description of the water supply process represents surface water, groundwater, unconventional water, and water transferred from outside through water production, and then transmits them to each user through the topological relationship diagram.
(2) Water consumption includes three links, specifically water distribution, water consumption, and circulating water. Water distribution is used to establish water supply, water demand, and the supply-demand balance through the topological relationship diagram, and describes it with the information node and digital water network. The topology diagram is used to describe the water use situation of various users in the visualization of circulating water, and its nodes represent the water use information and circulating water use information.
(3) Drainage includes factors such as discharge, collection, and treatment. The visual description of the drainage process is based on the topological diagram and digital water network used to establish the drainage information of each user, sewage treatment processes, as well as collected, discharged, and treated water information. Each node represents its corresponding water information.
(4) The reclaimed water use includes three links: water collection, regeneration, and water conveyance. The upper part is the information node and the lower part is the basic map of the study. The visualization description describes the information and relationships between the collected water, the amount of reclaimed water, and the water conveyance volume through the topological relationship and the digital water network.
3.2.3. Validation of the System
The effectiveness of system functions is underpinned by component technology and knowledge graph techniques. Every process of the natural-social cycle is complex. The advantage and effectiveness of the system lie in the fact that complex processes are split layer by layer and divided into specific processes for calculation. Taking the precipitation link in the atmospheric process as an example, precipitation refers to the phenomenon of liquid or solid water vapor condensate falling from the air to the ground. Common examples for calculating the average precipitation of regional polygons are the arithmetic mean method and the Thiessen polygon method. Each method is calculated differently. We compile the calculation process into components, and when applying, we only need to select a component from the component library to implement the functions it represents, without remodeling or programming. This is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Core components of precipitation.
In the application process, depending on the study area, we can select different components by editing the knowledge graph, such as the A region using the arithmetic mean method to calculate the average precipitation of the area surface, and the B region using the Thiessen polygon method []. This allows us to quickly calculate the results of the system. The data calculated by each icon and node can be transmitted through the linear elements on the knowledge graph, and the dynamic and rapidly adjusted properties of the system are reflected.
Compared with traditional distributed hydrological models, our effectiveness lies in the fact that we can quickly calculate new results based on changes in the scenario. The traditional distributed hydrological model selects the watershed or research area, generalizes and models the regional meteorological and hydrological elements, and then analyzes their applicability. In this paper, it is proposed that the visual simulation system can quickly adapt to the simulation of the multi-scenario sewer cycle process, and the adaptability of the system is reflected here.
3.3. Visual Simulation of Multi-Scenario Control
Based on the water resources allocation of Xiong’an New District, and following the framework of the dualistic water cycle, the processes related to water resources allocation are regulated in the process of the dualistic water cycle, which can provide the application of water resources regulation on the visual description knowledge map of water resources allocation. According to the impact of the different scenarios on the results of water resources regulation, the dynamic adjustment is carried out to realize the dynamic adaptive regulation of water resources.
3.3.1. Time Scale
For water resources regulation and control in a time scale scenario, the time scale of calculation can be selected as year or month by clicking the time selection button on the knowledge map of water resources regulation and control to open the time setting window. After setting the calculation time and clicking OK, the system will automatically analyze the supply and demand balance, and the result of the supply and demand balance calculation will change accordingly. The dynamic regulation process of water resources in the time scale scenario is shown in Figure 9.
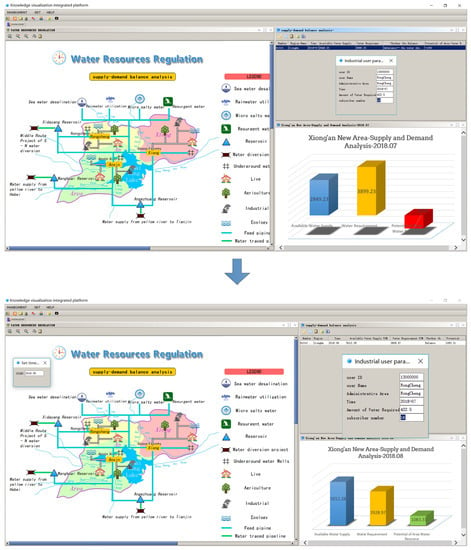
Figure 9.
Example of dynamic regulation of water resources in the time scale scenario.
3.3.2. Increased Water Demand
With increased economic development and the intensification of human activities, when a user’s water demand increases, there will be a scenario where there is a water supply available to meet the increase in water demand. In the knowledge map of water resources regulation, it is assumed that the water demand of industrial water users in Rongcheng county increases. Business personnel can click on the Rongcheng Industrial “Water User” icon to adjust this setting. In the pop-up Rongcheng industrial user adjustment interface, the business personnel manually enter the water demand of Rongcheng Industrial users, and when the “OK” button is clicked, the system will automatically perform a supply and demand balance analysis, and the results of the supply and demand balance calculation will update accordingly. If the water demand of the industrial users of Rongcheng is adjusted to make the water supply and demand balance calculation unbalanced, we can choose the water supply for the industrial users of Rongcheng, and adjust the water supply of the water source in the same way until the results of the water supply and demand balance calculation indicate that balance has been achieved. The dynamic regulation process of water resources in this scenario is shown in Figure 10.
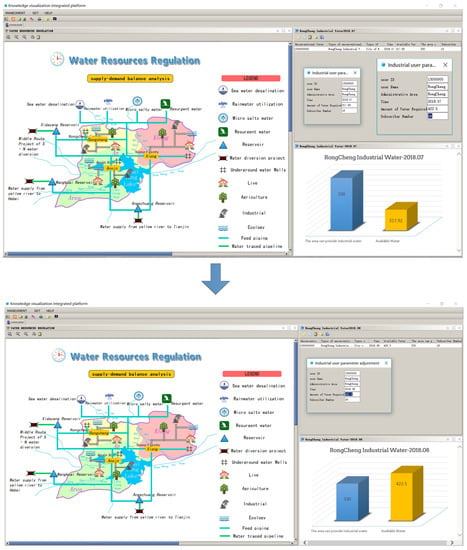
Figure 10.
Example of dynamic regulation of water resources under the situation of increasing water demand.
3.3.3. Increased Water Users
As socio-economic development progresses, a scenario becomes apparent where as a new water user appears and the number of water users increases where there is available water supply. Here, it is necessary to regulate under the editing state of water resources regulation knowledge map. Suppose an industrial water user is added in Rongcheng county, the editing state of the water resources regulation knowledge map is opened, an icon node of an industrial water user in the editing state is added, and a connection from the “Time” node and the “Water Source” node (assuming the Western Ocean reservoir is the water source of the water user) to the increased industrial water user is generated, and the “Model Computing” nodes are connected to realize the data flow between time, water source, user and model calculation. After realizing the data flow, the user may open the component library to find the water demand components of industrial water users, select the industrial water users of Rongcheng county and add the water demand “.info” file of industrial water users in Rongcheng county. After saving the knowledge map, the user can click on the “Supply and Demand Balance Analysis” node to show the impact of increasing the number of water users on the regional water supply and demand balance. If the result of the water supply and demand balance is unbalanced at this time, we can refer to the regulatory mode of the previous scenario to adjust until balance is achieved. The dynamic regulation process of water resources in this scenario is shown in Figure 11.
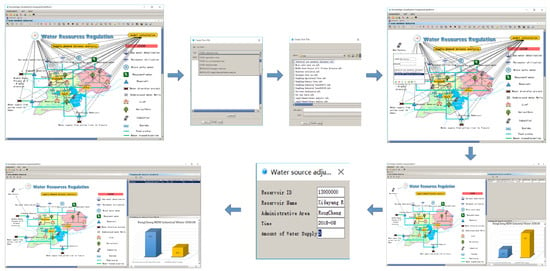
Figure 11.
Example of dynamic regulation of water resources under the situation of increasing water users.
The sustainable development and utilization of water resources aims to control and regulate the links between the natural and social water cycles, so as to realize sustainable coordination between them. The integrated platform can regulate and control the water supply and consumption, water consumption and drainage, surface water and groundwater, or water consumption and water use efficiency (or benefit) of the dualistic water cycle, which offers significant insight for water use evaluation. On the basis of visualization of the dualistic water cycle framework, from the perspective of the regional system, based on national economic water use and ecological water use, the optimal regulation of water supply and demand can be determined, which can realize the dynamic and real-time application of water resources regulation in dynamic scenarios. The results of the multi-scenario regulation of water resources are shown in Figure 12.
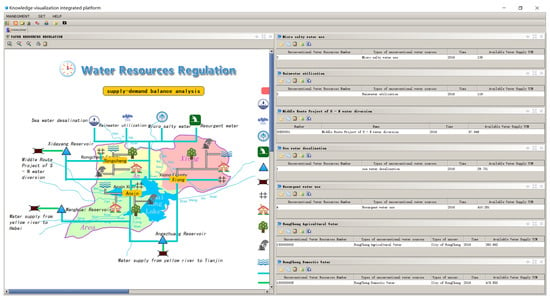
Figure 12.
Some results of the visual knowledge map of water resources regulation.
4. Discussion
Relative to the natural water cycle, the water use impact of human activities is increasing, and the water cycle is no longer characterized by a “natural” monistic model, but a “natural-social” dualistic model. Moreover, water problems, security, and crises affect the quality of social and economic development to varying degrees. For these reasons, the regulation and control of water resources have attracted great attention. For example, Zuhao Zhou et al. applied a dualistic water cycle model in the Haihe River Basin to analyze the impact of social water use on natural hydrological processes []. However, in terms of the social water cycle, this study only used statistical data as external inputs, and the coupling of the model was insufficient in the case of alternative scenarios. The visual system of the dualistic water cycle framework built in this paper can improve the dynamic adaptability by componentizing the calculation links in the natural-social water cycle process. Hao Wang et al. established a comprehensive simulation platform for the dualistic water cycle process in the Haihe River Basin (NADUWA3E) [], which evaluated water resources, ecology, and water environment by setting scenarios, but it is worth noting that the coupling mechanism of the natural-social dualistic water cycle and its related processes is complex, and the study is based on the current conditions to predict the future, while the future scenario changes cannot be dynamically changed.
Comparing the relevant research in the field of water resource regulation and application, we found that most scholars used specific algorithms and constraint models to analyze the water resources use in the study area and obtained optimization suggestions [,,]. This traditional approach requires a lot of accuracy and adaptability of the model, and once the study area is replaced, there may be cases where the model is not suitable.
Compared with the research on water regulation software development, we find that scholars mostly develop specific application software for specific problems [,,]. The disadvantage of this method is that once it needs to be modified, it needs to be reprogrammed or re-developed, the workload is huge, and the degree of reuse is too low.
The visualization system built in this paper is not sufficiently thorough in the refinement of the model, but it can quickly update the model through componentization according to the needs of specific scenarios, and can dynamically update the new calculation process and results, which can increase the applicability and generalizability of the model.
Our visualization system has been piloted in the study area. In order to verify the effectiveness of the system, we have uploaded an installation package for the visualization system on our research homepage, which can be downloaded by users to use locally. http://www.yunqishui.com/pages/g/gamePost.shtml?view=true&postId=298&u=99999 (Chinese version) (accessed on 30 January 2022)
Considering the difficulty in describing the social aspects involved in the dualistic water cycle by a single expression, the natural huge system, the dualistic water cycle, and the application of water resource regulation can not be well-docked. Here, the water resources regulation can not adapt to the changing environment and the needs of different situations, nor to economic development changes and poor operability, and while the commercialization of information technology is not sufficient. The current study designates Xiong’an New Area as the research area, on the basis of the visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework, the content of the problem treatment is componentized, and the support business application is selected. The preliminary application of water resources regulation under dynamic scenarios is realized, and the commercial application of the dualistic water cycle theory and the support of information services, computing services, and decision-making services are illustrated, which provides support for the subsequent application of the dualistic water cycle theory.
Based on the calculation of water balance and specific link information in the dualistic water cycle, this paper highlights the visual description of the dualistic water cycle framework and the content componentization of business processing, and on this basis, the practical application of dynamic water resources regulation is realized by taking water resource allocation as an example. For the refined simulation of various microscopic links in the natural water cycle and the social water cycle, we have not yet realized it. The starting point of this paper is the combination of information technology and hydrological framework model based on the macro framework, which is an active and feasible research direction. Simulation is realized under the macro framework, and in the follow-up research work, we will go deep into each micro link to visualize the simulation to achieve the coupling of macro and micro.
5. Conclusions
At present, the dualistic water cycle, water resources regulation, and control applications are not well-connected; water resources regulation is difficult to adapt to the changing environment and different situations of needs, and water conservancy business system interaction is poor. To propose solutions to these difficult problems, firstly this paper proposed the use of information visualization technology to realize the application of the dualistic water circulation framework. Secondly, the knowledge graph technology was used to visualize the dualistic water cycle framework, and finally, the dualistic water cycle visualization system was built based on the comprehensive integration platform, and the pilot application of water resource regulation was selected in the research area.
(1) Based on the integrated platform, visual knowledge map technology, and component development technology are used to describe the dualistic water cycle, business application, and modern management. This platform not only connects the theory of the dualistic water circulation application by providing a tool to solve practical problems, but also provides fast and convenient solutions for the efficient use of water resources.
(2) As the carrier and support of modern water resources evaluation, the theory of dualistic water circulation can solve the contradiction of water resources more effectively. However, with the intensification of human activities and the evolution of natural systems, the water circulation system may need to be adjusted in the future. For this reason, the integrated platform is designed to be adapted to new theories and models, including optimizations of existing components, updating databases, rewriting calculation methods, and so on. By creating a new knowledge map, the results can be optimized.
(3) This paper focuses on the visual expression of the dualistic water cycle and the dynamic adjustment of the system application model, where the advantage of this model is its dynamic adjustability. In this way, when the calculation method changes, the regulatory results will also change. Therefore, this paper does not elaborate on the process calculation of each link. This model can also be applied to water conservancy business applications such as water rights distribution and transactions, integrated water resources management, efficient utilization of water resources, water resources protection or ecological restoration, and water resources evaluation index management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and J.X.; methodology, M.Y.; software, J.L.; validation, J.L., J.X. and M.Y.; formal analysis, M.Y.; investigation, J.L.; resources, X.W.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, X.W.; supervision, J.X.; project administration, J.X.; funding acquisition, J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant No. 2016YFC0401409, Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province, grant No. 2019JLZ-16, and Science and Technology Program of Shaanxi Province, grant No. 2019slkj-13, 2020slkj-16.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The knowledge map of this paper and the software package can be downloaded from our website, http://www.yunqishui.com.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, and we are grateful for the assistance of Hao Wang and Yong Zhao from the Chinese Academy of Water Sciences. We would like to thank Shannon Elliot at Michigan State University for his assistance with English language and grammatical editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, H. Principle and Regulation of Social Water Cycle; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Guzmán, C.A.; Melgarejo, J.; Prats, D.; Torres, A.; Martínez, S. Urban water cycle simulation/management models: A review. Water 2017, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, D.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.H.; Li, H.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Chen, G.F. Theoretical framework of dualistic nature–social water cycle. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.H.; You, J.J.; Gan, Z.G.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Lu, C.Y.; Luo, X.Y. Development and application of dualistic water cycle model in haihe river basin: I. model development and validation. Adv. Water Sci. 2010, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.H.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, X.H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.Y. Development of Load Duration Curve System in Data Scarce Watersheds Based on a Distributed Hydrological Model. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Yan, D.; Qin, T.; Weng, B.; Wang, H.; Bi, W.; Li, X.A.; Dorjsuren, B. new topological and hierarchical river coding method based on the hydrology structure. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, K.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Han, A.Y. System Dynamics-Multiple Objective Optimization Model for Water Resource Management: A Case Study in Jiaxing City, China. Water 2021, 13, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.F.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, J.J.; Zhao, N.F.; Zhou, Z.H. Analysis of artificial impact of runoff change in Fuhe River Basin Based on binary water cycle simulation. Hydrology 2020, 40, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.S.; Xu, J.J.; Xiao, W.H.; Yang, Z.M.; Hou, B.D. Development and application of combined regulation model of water quantity, water quality and water efficiency based on binary water cycle. J. Water Conserv. 2020, 51, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Hu, P. Key issues of ecological protection in the Yellow River Basin from the perspective of water cycle. J. Water Conserv. 2020, 51, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.X. “Nature-Social” dual attribute and seasonal characteristics of urban water dissipation: A case study of Beijing. J. Water Conserv. 2020, 51, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Fan, W.W.; Yi, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.H. Evaluation method for regional water cycle health based on nature-society water cycle theory. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; You, J.J.; Jia, Y.W.; Gan, Y.D.; Niu, C.W.; Zhang, S.P. Dualistic water cycle based-study on control of total water use and water use efficiency—a case study on Weihe River Basin. Hydraul. Hydroelectr. Technol. 2015, 46, 2–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, Y. Water quantity-quality combined evaluation method for rivers’ water requirements of the instream environment in dualistic water cycle: A case study of Liaohe River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 11, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.M.; Wang, J.H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, Y.M. Theory of annual runoff evolution under natural-artificial dual mode and case study of Wuding River basin on the middle Yellow River. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2004, 47, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y. A dualistic water cycle system dynamic model for sustainable water resource management through progressive operational scenario analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16085–16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Bao, H. Review of social water cycle research in a changing environment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 63, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, L.; Wei, C. Study on Water Quantity and Quality-Integrated Evaluation Based on the Natural-Social Dualistic Water Cycle. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jia, Y.; Niu, C. Evaluation of regional water security in China based on dualistic water cycle theory. Water Policy 2018, 20, 510–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xifeng, W.; Zuhao, Z.; Guiyu, Y.; Yangwen, J. Development of Social-natural Dualistic Water Cycle Model and Dynamic Assessment of Water Resources in Hun River Basin in China. HKIE Trans. Hong Kong Inst. Eng. 2012, 19, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bederson, B.; Shneiderman, B. The Craft of Information Visualization: Readings and Reflections; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Burlington, SF, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, R.A. Knowledge Maps. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 903–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, P.F.; Almeida, J.S.; Pino, A.T.; Suárez Rivero, J.P. A GIS-based solution for urban water management. Water Int. 2020, 45, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xie, W.J. Construction and application of one map of national water conservancy. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2020, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Xie, W.J.; Cheng, Y.L.; Chen, D.Q.; Chen, Z.D.; Fu, J. Review on Key Technologies of one map of national water conservancy. J. Water Conserv. 2020, 51, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, W.B.; Peng, J.L. Design of “one map” shared service platform for watershed institutions based on cloud environment. People’s Pearl River 2017, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Song, C. Exploration on the construction of a picture of smart water conservancy and shared service platform. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2020, 6, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.J.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, L.F. Construction and application of Hubei province water conservancy "one map" service sharing platform. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2014, 1, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.C.; Chai, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. The platform supports the business application mode of theme service. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2015, 6, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Y.W. Theory and study methodology of dualistic water cycle in river basins under changing conditions. J. Water Conserv. 2016, 47, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.L. Water Resource; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Long, A.H.; Yu, F.L.; Wang, X.D. Study on theoretical method of social water cycle I: Definition and dynamical mechanism. J. Water Conserv. 2011, 42, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kralj, A.K. Industrial wastewater collection using a separation technique. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosiichuk, Y.B.; Khoruzy, P.D. Water Purification in Closed Water Supply Systems at Agro-Industrial Complex Enterprises. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2019, 41, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, M.J.; He, X.W.; Qin, D.Y.; Wang, D.X.; Tang, K.W.; Yin, M.; Wan, W.F.; Wang, Y.; Gan, H.; et al. Study on the rational allocation and carrying capacity of water resources in northwest China. China Water Resour. 2004, 22, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Qin, D.Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.N.; Yang, Z.Y. The dualistic water cycle pattern and its evolution regular in Haihe River basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 512–521. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.C.; Luo, J.G. Integrated service platform and application mode of water conservancy informatization. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2010, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Xie, J.C.; Zhang, Y.J. Data integration and service model for water conservancy business application. Water Conserv. Informatiz. 2011, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.R.; Nestmann, F. Physically Based and Data-Driven Models and Propagation of Input Uncertainties in River Flood Prediction. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiantzas, J.D.; Pollalis, E.D.; Soulis, K.X.; Londra, P.A. Modified Form of the Extended Kostiakov Equation Including Various Initial and Boundary Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, S.; Singh, V.P. Re-discovering Robert E. Horton’s Lake Evaporation Formulae: New Directions for Evaporation Physics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 26, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Baumgartl, T. Field Evaluation of Three Modified Infiltration Models for the Simulation of Rainfall Sequences. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfs, J.O.; Park, C.H.; Kolditz, O. A sensitivity analysis of Hortonian flow. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, Z.; Gong, J.; Jia, Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, H. A new approach to separating the impacts of climate change and multiple human activities on water cycle processes based on a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jia, Y.; Qiu, Y. Simulation of Dualistic Hydrological Processes Affected by Intensive Human Activities Based on Distributed Hydrological Model. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Niu, C.; Peng, H. Integrated simulation of the dualistic water cycle and its associated processes in the Haihe River Basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3297–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Ning, S.; Cao, X.; Jin, J.; Song, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Udmale, P. Optimal Water Resources Regulation for the Pond Irrigation System Based on Simulation—A Case Study in Jiang-Huai Hilly Regions, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, J.D.; Kim, S.; Dutta, D.; Vaze, J. Optimization of a multiple gauge, regulated river-system model. A system approach. Hydrol. Processes 2016, 30, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Ni, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, H.; Jia, W.; Zhong, J.; Ren, L. Time-varying Decision-making Method for Multi-objective Regulation of Water Resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 3411–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-S.; Srivastava, P.; Song, J.-H.; Park, J.; Her, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Song, I. Development of a Component-Based Modeling Framework for Agricultural Water-Resource Management. Water 2016, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaru, V.; Voiculescu, M.; Georgescu, L.P.; Caldararu, A. Integrated management and control system for water resources. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Cannata, M.; Neumann, J.; Rossetto, R. Open source GIS platform for water resource modelling: FREEWAT approach in the Lugano Lake. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 26, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).