Developing an Optimized Policy Tree-Based Reservoir Operation Model for High Aswan Dam Reservoir, Nile River
Abstract
1. Introduction
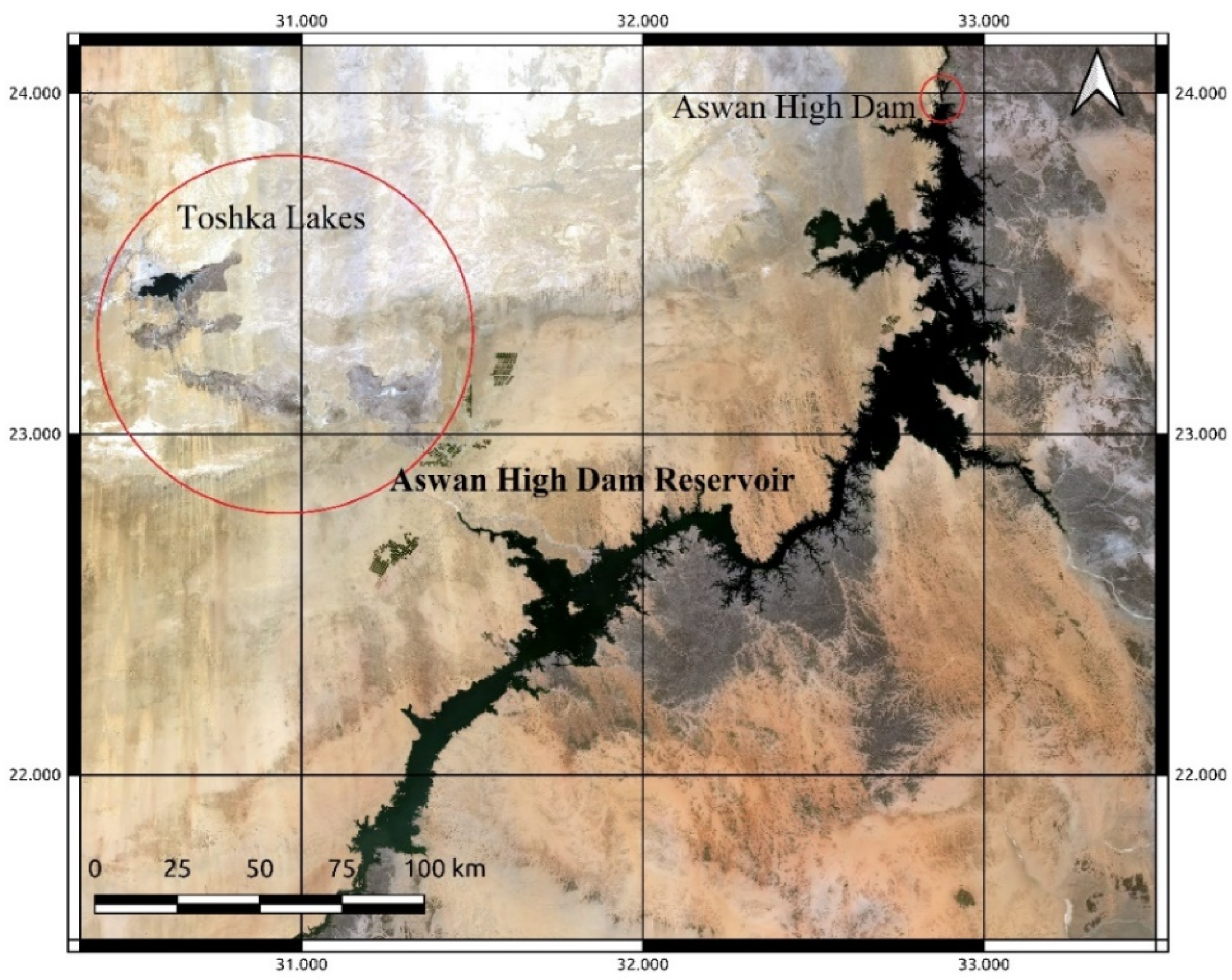
2. Aswan High Dam Reservoir Case Study
3. Data and Methodology
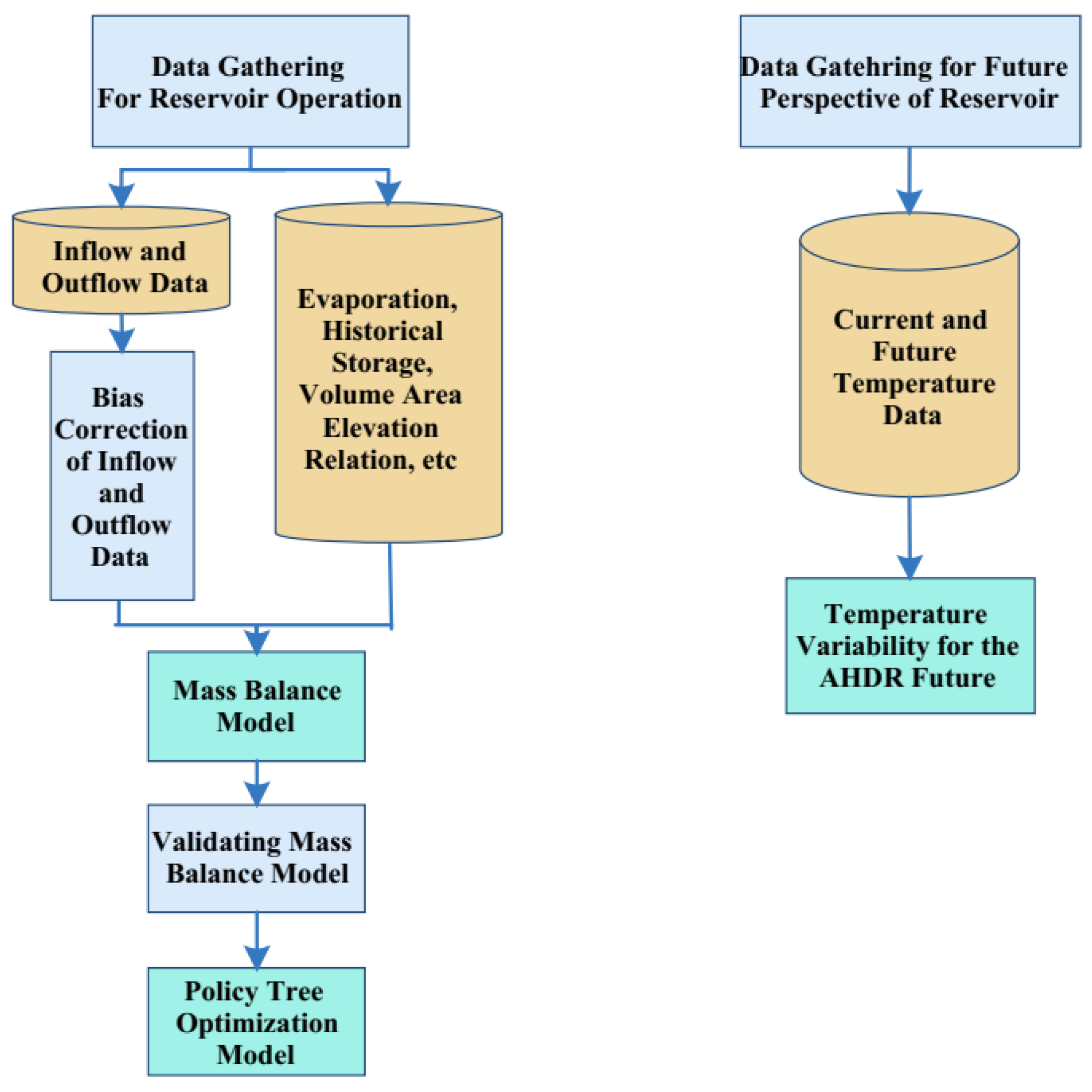
3.1. Data Gathering
3.1.1. Nile River Discharge
3.1.2. Total Precipitation (TP)
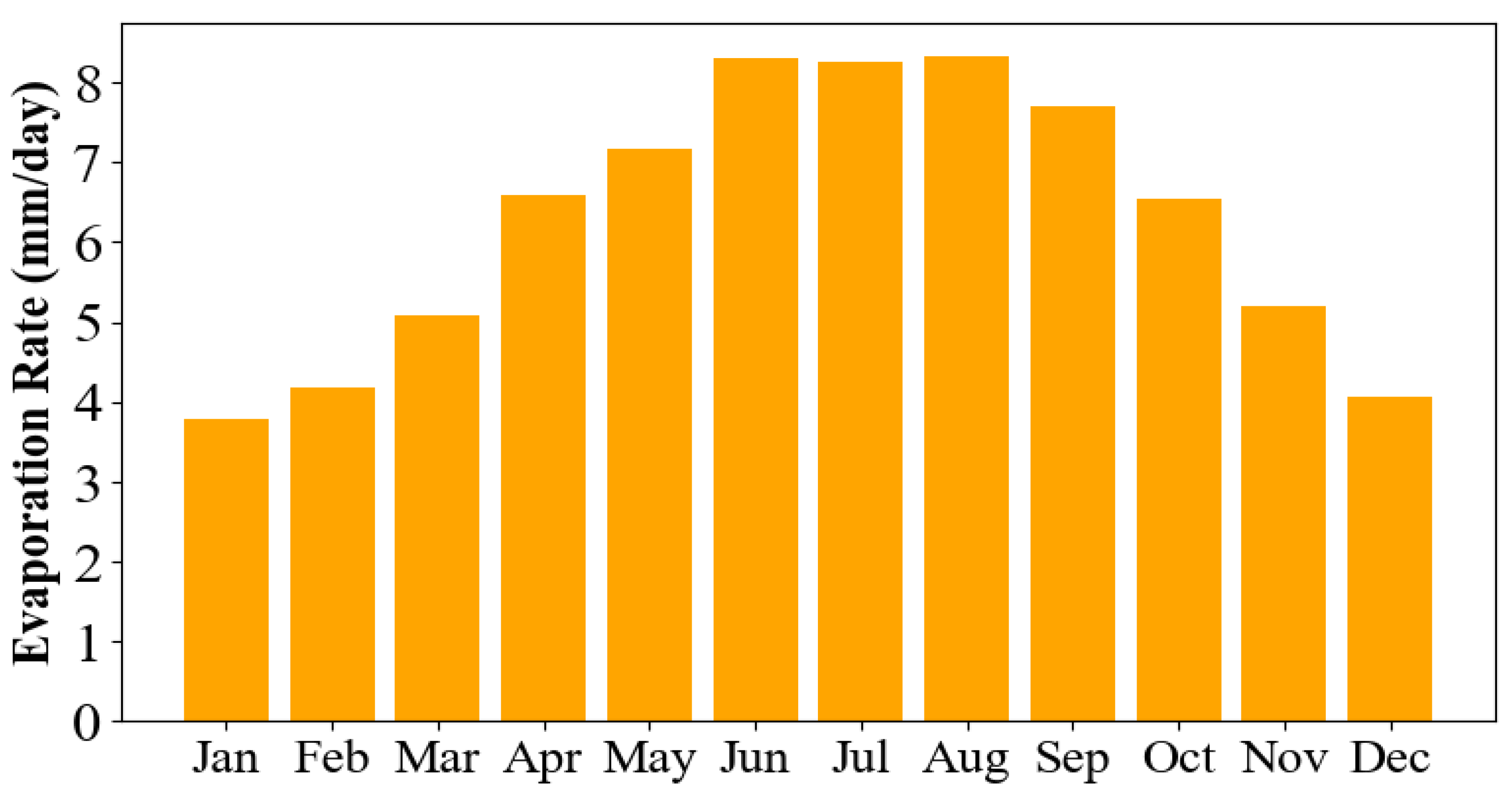
3.1.3. Total Evaporation (TE)
- Daily gridded data from GLEAM (GLEAM v3.3b), 2003–2020 were mainly based on satellite data [70].
- Ref. [51] described a model to estimate TE (= 0.06164 (1 + 0.062633 u) (1-RH) es), with known values for relative humidity (RH), wind speed at 2 m height above ground (m/s), and the saturated vapor pressure (mb).
3.1.4. Historical Lake Elevation Data
3.2. Future Perspectives for Sustainable Management of the Aswan High Dam Reservoir
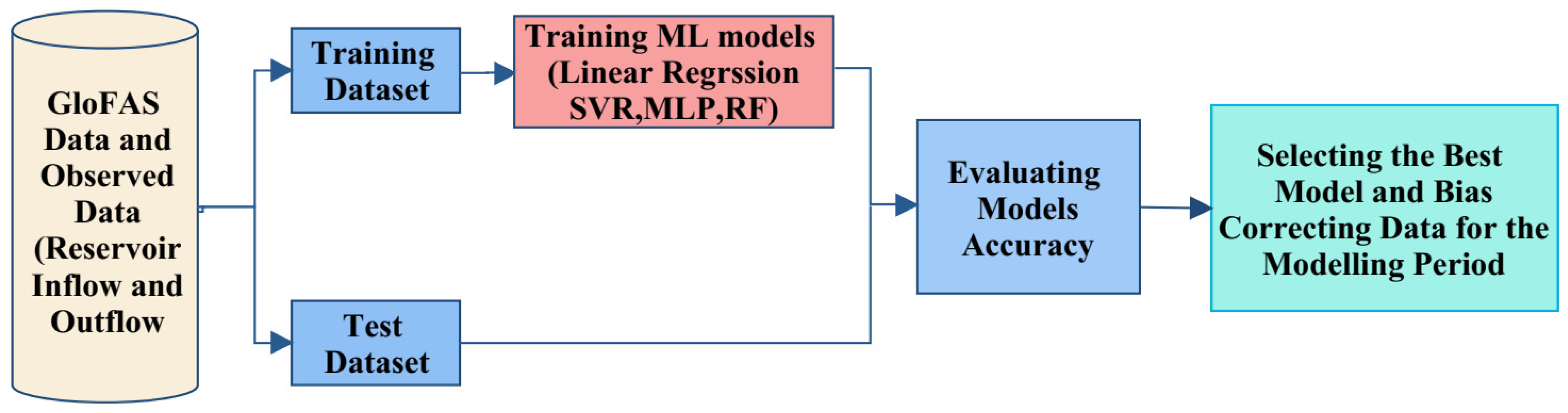
3.3. Bias Correction
3.4. Simulation Model
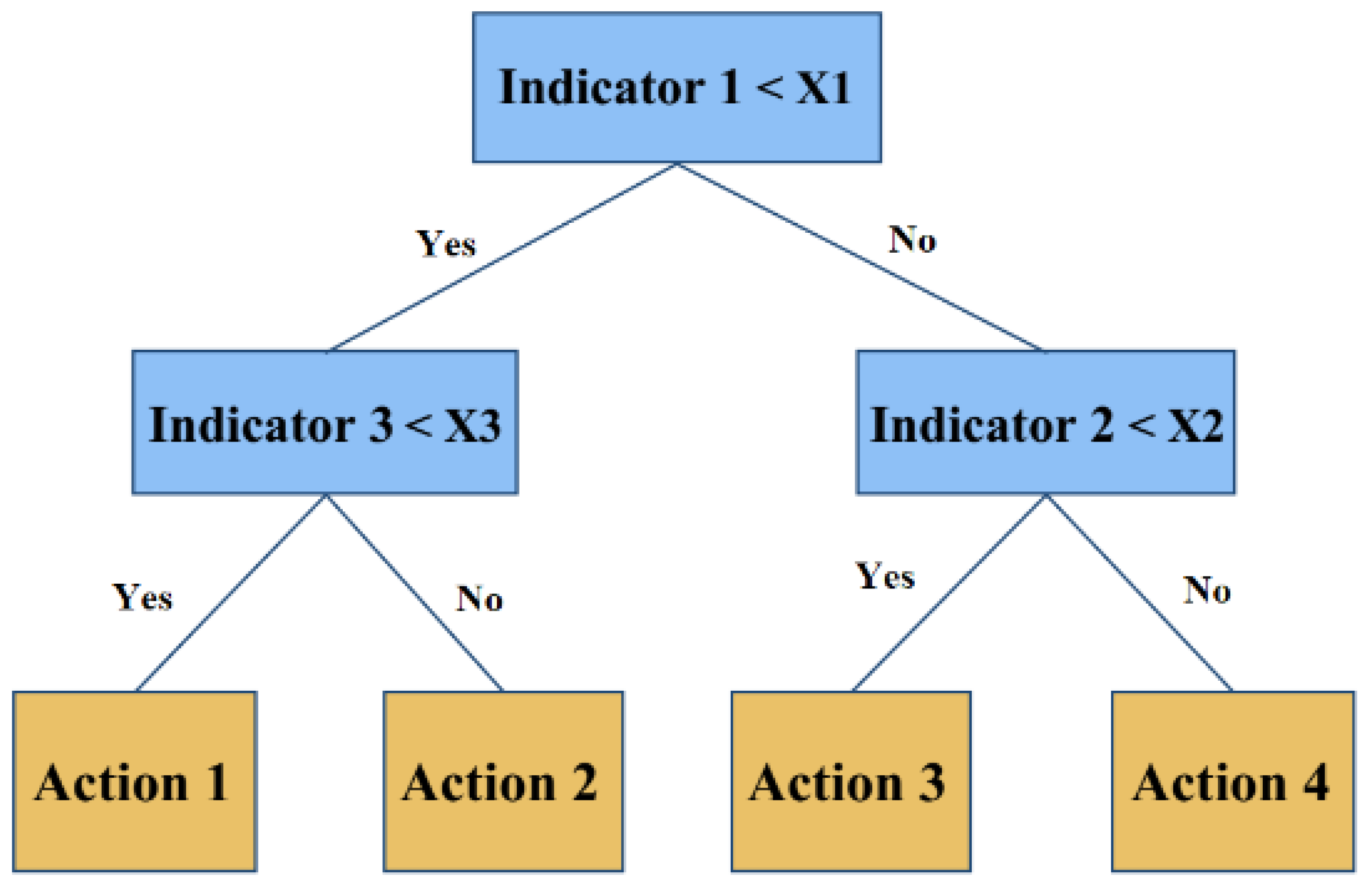
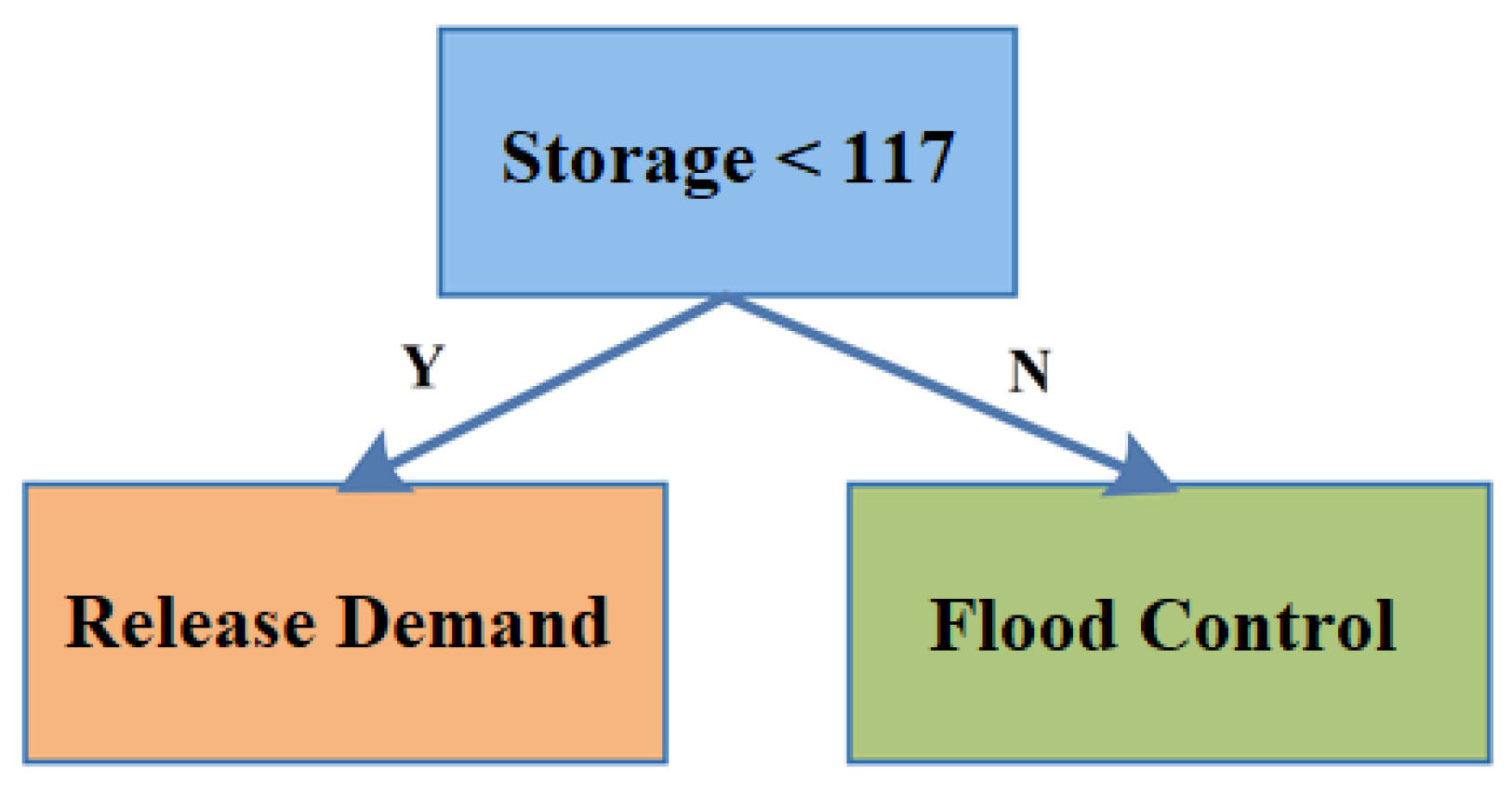
3.5. Policy Tree Optimization Model
4. Results and Discussion
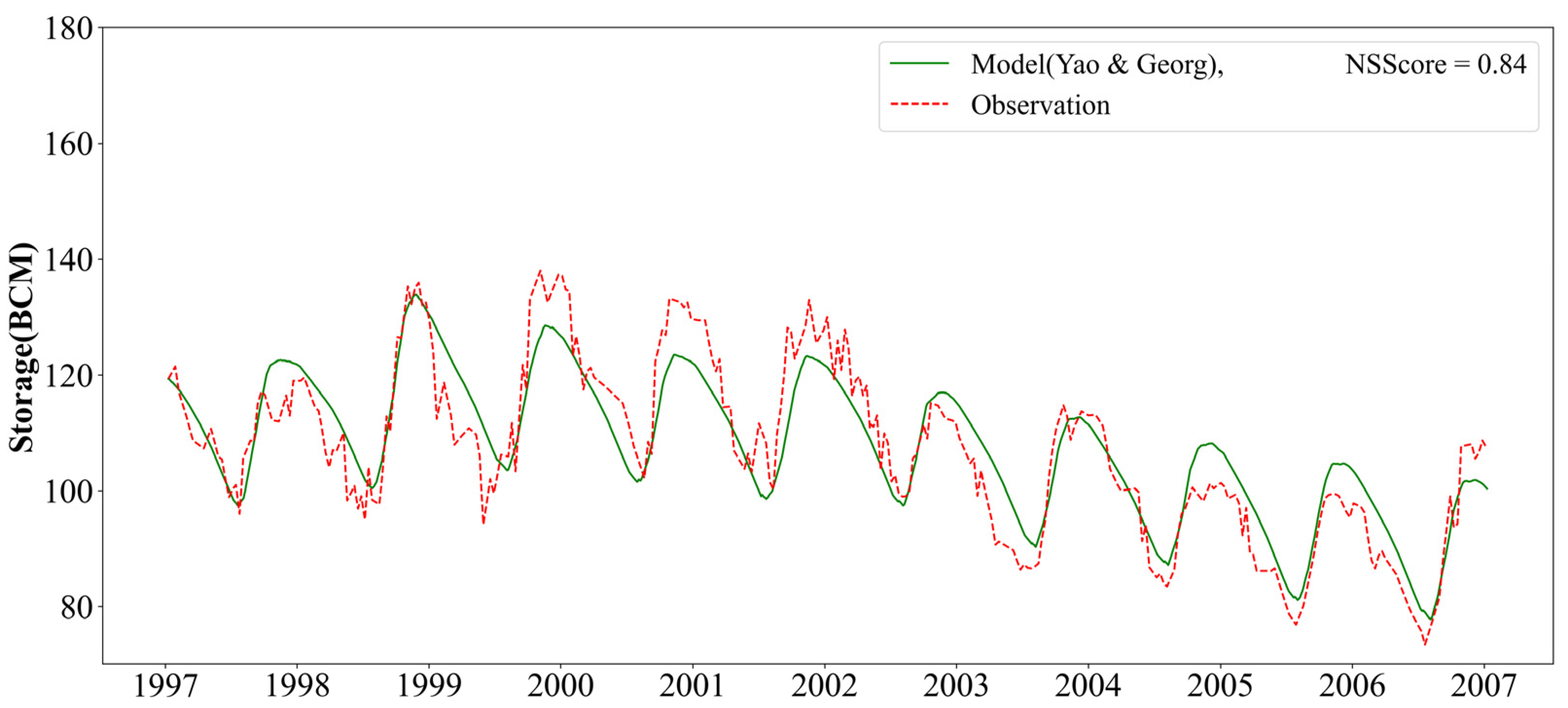
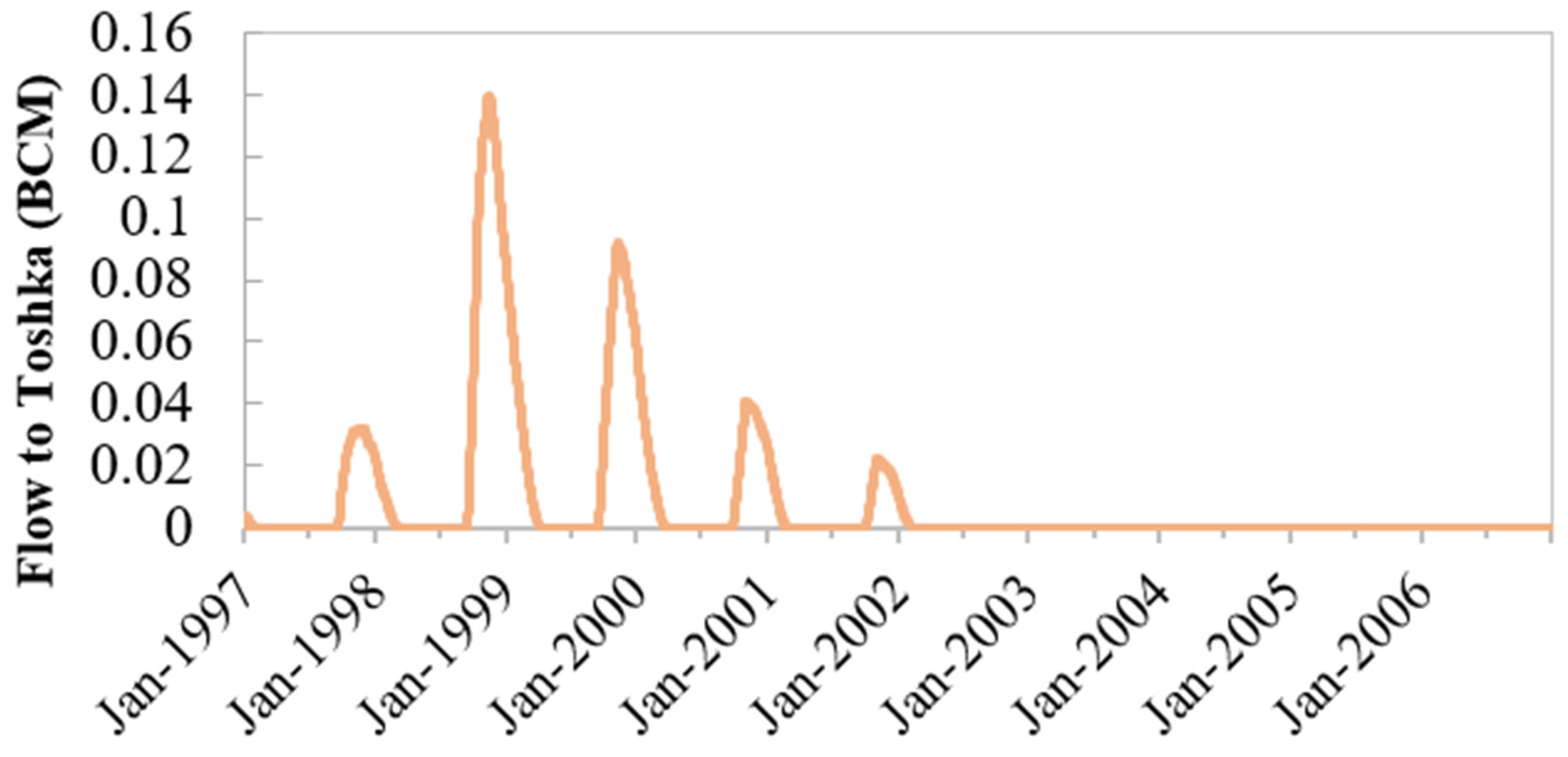
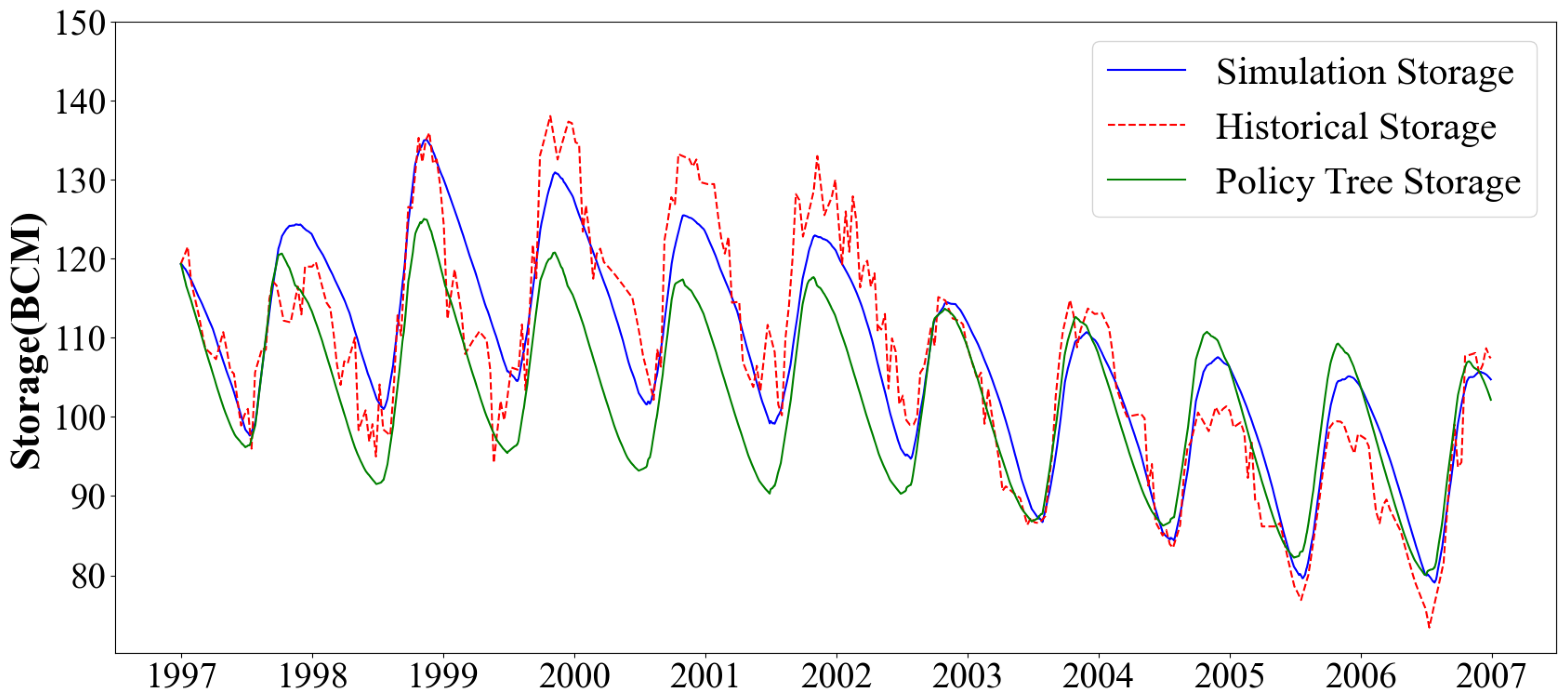
4.1. Historical Simulations
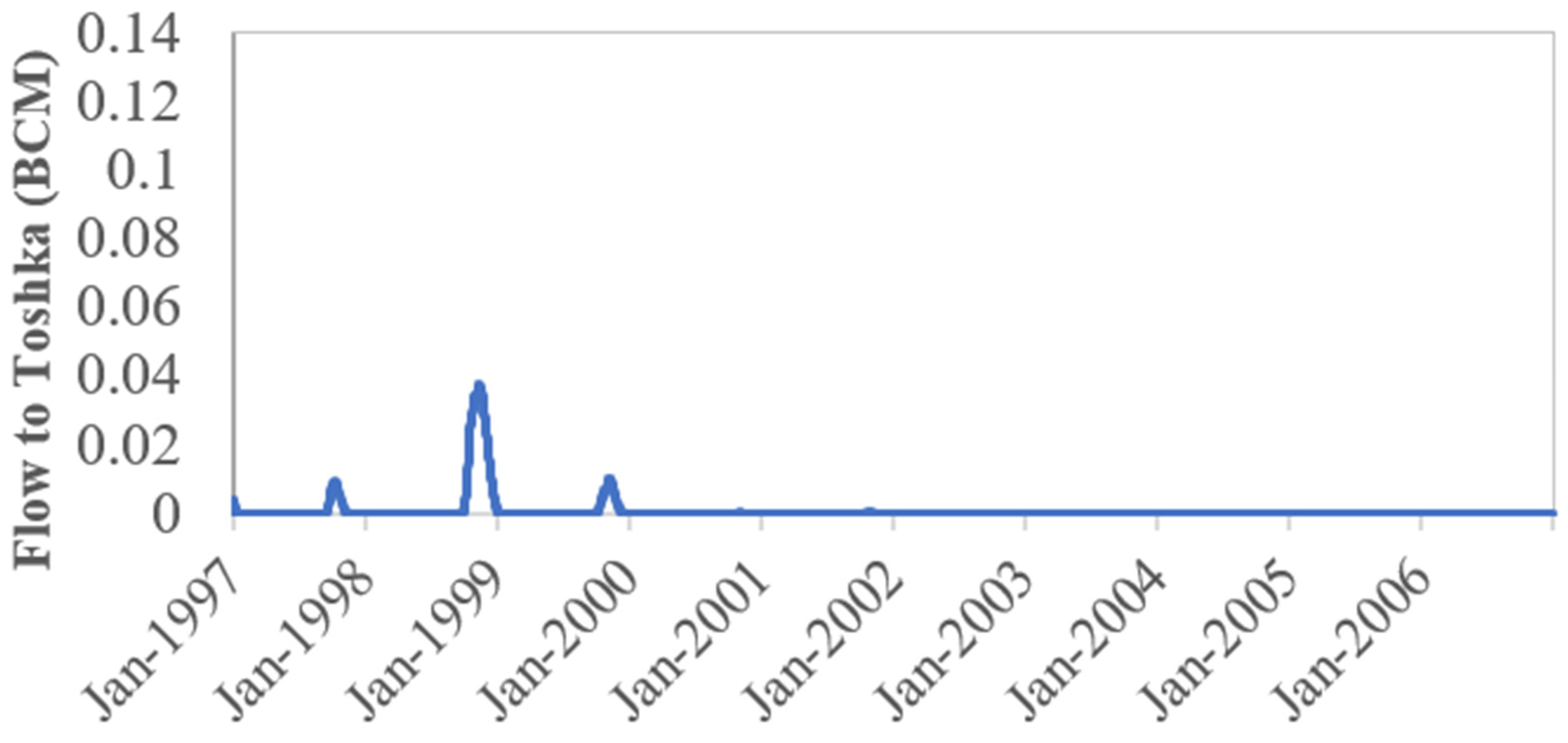
4.2. Policy Tree Optimization Model
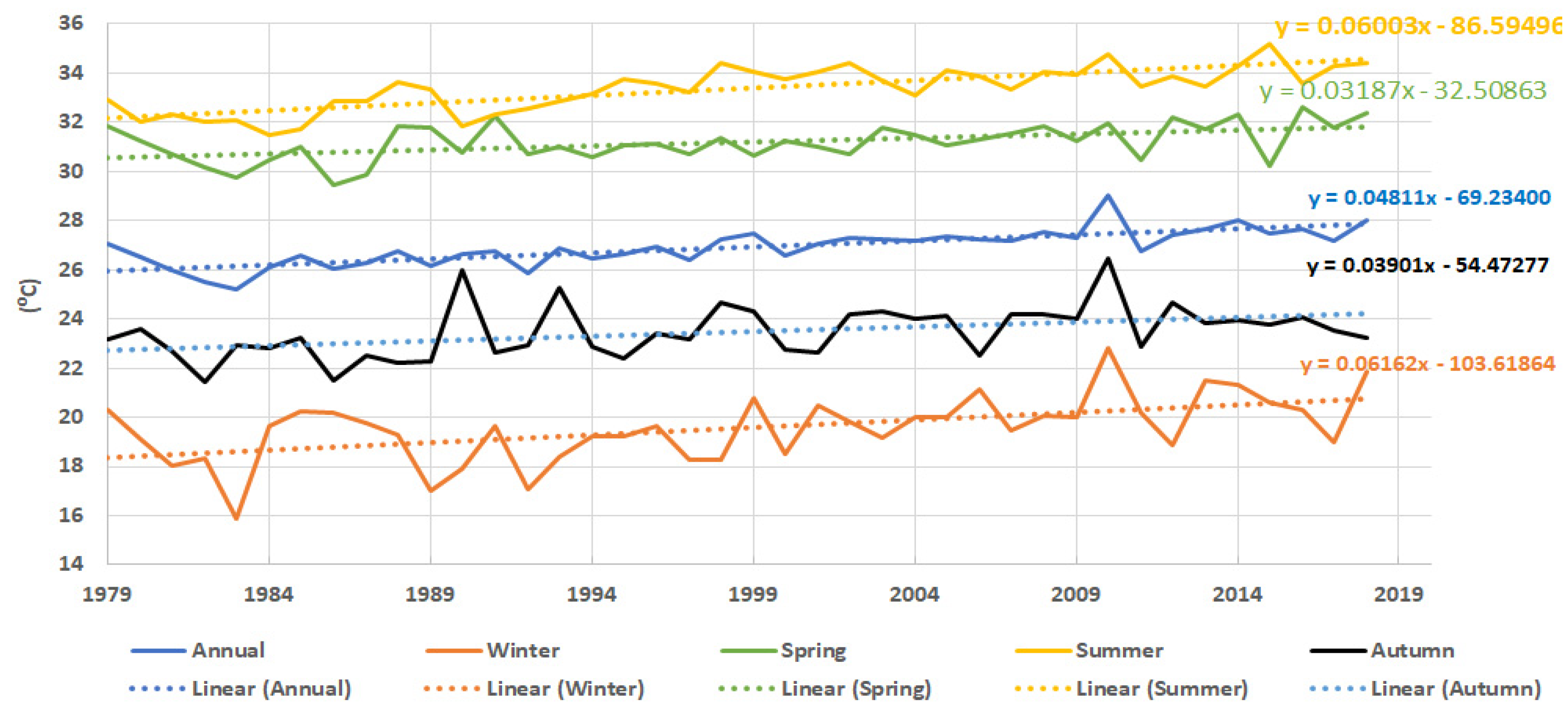
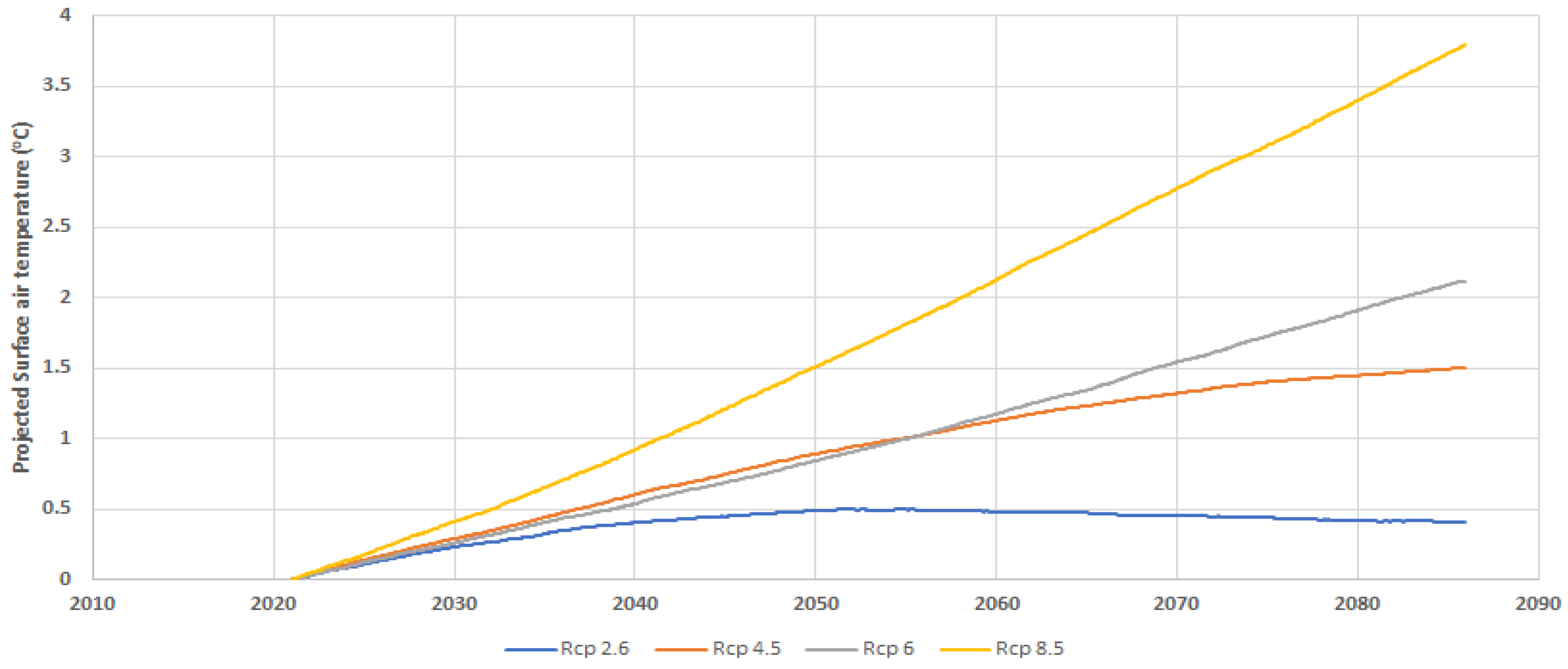
4.3. Current and Future Surface Air Temperature (T2m) over Aswan High Dam Reservoir
5. Limitations and Future Scope
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labadie, J.W. Optimal operation of multireservoir systems: State-of-the-art review. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, S.F. Water Scarcity and Conflict Between Upstream and Downstream Riparian Countries. Water Econ. Policy 2021, 7, 2150012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.D.S.; Mariño, M.A. Coupled reservoir operation-irrigation scheduling by dynamic programming. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2002, 128, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.R. Drought storage allocation rules for surface reservoir systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.W.-G. Reservoir Management and Operations Models: A State-of-the-Art Review. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 1797–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurbs, R.A. Reservoir-system simulation and optimization models. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1993, 119, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, S.; Omran, E.-S.E. Update, Conclusions, and Recommendations for Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam Versus Aswan High Dam: A View from Egypt. In Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam Versus Aswan High Dam; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 561–586. [Google Scholar]
- Entz, B. Lake Nasser and Lake Nubia. In The Nile, Biology of an Ancient River; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976; pp. 271–298. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, M.M.; Soussa, H.K. Monitoring of Lake Nasser Using Remote Sensing and Gis Techniques; ISPRS: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–23 July 2000; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rashed, M.N. Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from nasser lake. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.F.; Shahin, M.M.; Stigter, C.J. Evaporation from the reservoir of the High Aswan Dam, Egypt: A new comparison of relevant methods with limited data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1997, 56, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muala, E.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Duan, Z.; der Zaag, P. Estimation of reservoir discharges from Lake Nasser and Roseires Reservoir in the Nile Basin using satellite altimetry and imagery data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7522–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellah, R.G.A. Water resources in Egypt and their challenges, Lake Nasser case study. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 413–414. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiel, C.A.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Past and future trends of Egypt’s water consumption and its sources. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, K.G.; Jeuland, M.; Hall, J.W.; Zagona, E.; Whittington, D. Understanding and managing new risks on the Nile with the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, M.; Nechifor, V.; Calzadilla, A.; Siddig, K.; Etichia, M.; Whittington, D.; Hulme, D.; Harou, J.J. Collaborative management of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam increases economic benefits and resilience. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldardiry, H.; Hossain, F. A blueprint for adapting high Aswan dam operation in Egypt to challenges of filling and operation of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance dam. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 125708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siam, M.S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Climate change enhances interannual variability of the Nile river flow. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, J.J.; Camargo, R.R.; Laporte-Bisquit, A.; Zarfl, C.; Morgan, A.J. Using the WWF Water Risk Filter to Screen Existing and Projected Hydropower Projects for Climate and Biodiversity Risks. Water 2022, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.; Lehner, B.; Zarfl, C.; Thieme, M.; Beames, P.; van Soesbergen, A.; Higgins, J.; Januchowski-Hartley, S.R.; Brauman, K.A.; De Felice, L.; et al. Global Dam Watch: Curated data and tools for management and decision making. Environ. Res. Infrastruct. Sustain. 2021, 1, 33003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A. Trend dynamics of GRACE terrestrial water storage in the Nile River Basin. Preprint. 2019, 13, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Teklesadik, A.D.; Alemayehu, T.; Van Griensven, A.; Kumar, R.; Liersch, S.; Eisner, S.; Tecklenburg, J.; Ewunte, S.; Wang, X. Inter-model comparison of hydrological impacts of climate change on the Upper Blue Nile basin using ensemble of hydrological models and global climate models. Clim. Change 2017, 141, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.A.; Rientjes, T.; Haile, A.T.; Habib, E.; Verhoef, W. Evaluation of bias correction method for satellite-based rainfall data. Sensors 2016, 16, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, W.; Brocca, L.; Rigon, R. Comparative evaluation of different satellite rainfall estimation products and bias correction in the Upper Blue Nile (UBN) basin. Atmos. Res 2016, 178, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Ayana, E.K.; Maathuis, B.H.P.; MacAlister, C.; Philpot, W.D.; Leyton, J.M.O.; Steenhuis, T.S. Performance of bias corrected MPEG rainfall estimate for rainfall-runoff simulation in the upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldardiry, H.; Hossain, F. Understanding reservoir operating rules in the transboundary nile river basin using macroscale hydrologic modeling with satellite measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2253–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalik, K.W.; Abdelmohsen, K. GRACE and TRMM mission: The role of remote sensing techniques for monitoring spatio-temporal change in total water mass, Nile basin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 160, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A. GRACE: Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment long-term trend investigation over the Nile River Basin: Spatial variability drivers. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.K.; Hossain, F. A Multidecadal Analysis of Reservoir Storage Change in Developing Regions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2022, 23, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, E.; Burian, S.J.; Bardsley, T.; Strong, C. Incorporating potential severity into vulnerability assessment of water supply systems under climate change conditions. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04015051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, E.; Burian, S.J. Developing an integrated framework to build a decision support tool for urban water management. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 708–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, E.; Burian, S.J.; Karamouz, M. Using joint probability distribution of reliability and vulnerability to develop a water system performance index. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04017081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, E.; Azizipour, M.; Sandoval-Soils, S.; Fogg, G.E. Surface reservoir reoperation for managed aquifer recharge: Folsom reservoir system. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, A.H.; El-Manadely, M.S. An integrated neural network stochastic dynamic programming model for optimizing the operation policy of Aswan high Dam. Hydrol. Res. 2011, 42, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; El-shafie, A. Performance analysis of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm in optimizing release policy of Aswan High Dam. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldardiry, H.; Hossain, F. Re-Evaluating the Operating Rule of High Aswan Dam under the Combined Impacts of Transboundary dams and Cropping Patterns: A Satellite-based Approach. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Goharian, E.; Azizipour, M.; Sandoval-Solis, S.; Fogg, G. Using Cellular Automata Approach to Optimize the Hydropower Reservoir Operation of Folsom Dam. Water 2021, 13, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Baghban, S.; Delpasand, M.; Goharian, E.; Loáiciga, H.A. Machine-learning algorithms for forecast-informed reservoir operation (FIRO) to reduce flood damages. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Gildin, E.; Zalavadia, H. Development of proxy models for reservoir simulation by sparsity promoting methods and machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the ECMOR XVI-16th European Conference on the Mathematics of Oil Recovery, Barcelona, Spain, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Azizipour, M.; Sattari, A.; Afshar, M.H.; Goharian, E.; Solis, S.S. Optimal hydropower operation of multi-reservoir systems: Hybrid cellular automata-simulated annealing approach. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 1236–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, J.; Santos, M.; Abreu, T.; Prado, L.; Miranda, D.; Julio, R.; Viana, P.; Fonseca, M.; Bortoni, E.; Bastos, G.S. Hydropower Operation Optimization Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Review. AI 2022, 3, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, M.; Nazif, S.; Mousavi, S.F.; Karami, H.; Daccache, A. A hybrid constrained coral reefs optimization algorithm with machine learning for optimizing multi-reservoir systems operation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, M.; Lamontagne, J.R.; Reed, P.M.; Castelletti, A. A State-of-the-Art Review of Optimal Reservoir Control for Managing Conflicting Demands in a Changing World. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of water resources and Irrigation. Water for the Future, National Water Resources Plan 2017; Egyptian ministry of water resources and Irrigation: Cairo, Egypt, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-El Monsef, H.; Smith, S.E.; Darwish, K. Impacts of the Aswan High Dam After 50 Years. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, F.I. Operational estimates of lake evaporation. J. Hydrol. 1983, 66, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebaid, H.M.I.; Ismail, S.S. Lake Nasser evaporation reduction study. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawwaf, M.; Willems, P.; Pagano, A.; Berlamont, J. Evaporation estimates from Nasser Lake, Egypt, based on three floating station data and Bowen ratio energy budget. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 100, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, I.H.A.; Ali, E.M. Estimation of the evaporative losses from Lake Nasser, Egypt using optical satellite imagery. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M. Evaporation estimation for Lake Nasser based on remote sensing technology. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2013, 4, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Mahdy, M.E.-S.; Abbas, M.S.; Sobhy, H.M. Development of mass-transfer evaporation model for Lake Nasser, Egypt. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawwaf, M.; Willems, P. Analysis of the climate variability on Lake Nasser evaporation based on the Bowen ratio energy budget method. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Elsawwaf, M.; Willems, P.; Feyen, J. Assessment of the sensitivity and prediction uncertainty of evaporation models applied to Nasser Lake, Egypt. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.M.; Zaki, M. Long term estimation of water losses through evaporation from water surfaces of Nasser Lake Reservoir, Egypt. Int. J. Civ. Env. Eng. 2016, 16, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Ismail, S.S.; Elmoustafa, A.; Khalaf, S. Evaluating evaporation rate from high Aswan Dam Reservoir using RS and GIS techniques. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2018, 21, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.Q.; Allawi, M.F.; Yousif, A.A.; Armanuos, A.M.; Saggi, M.K.; Ali, M.; Shahid, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Chau, K.-W. Viability of the advanced adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system model on reservoir evaporation process simulation: Case study of Nasser Lake in Egypt. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2019, 13, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allawi, M.F.; Ahmed, M.L.; Aidan, I.A.; Deo, R.C.; El-Shafie, A. Developing reservoir evaporation predictive model for successful dam management. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashry, M.T.; Alford, D.L. Water Management Models in Practice: A Case Study of the Aswan High Dam. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1984, 65, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baradei, S.A.; Al Sadeq, M. Optimum coverage of irrigation canals to minimize evaporation and maximize dissolved oxygen concentration: Case study of Toshka, Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, G.M.; Dumont, H.J. The Toshka Lakes. In The Nile; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bastawesy, M.A.; Khalaf, F.I.; Arafat, S.M. The use of remote sensing and GIS for the estimation of water loss from Tushka lakes, southwestern desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2008, 52, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, M.A.M. Solar hydrogen from Lake Nasser for 21st century in Egypt. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, H.A. Effect of expected climate changes on evaporation losses from Aswan High Dam Reservoir (AHDR). In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, Ismailia, Egypt, 12 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K. Lake Nasser: Alleviating the impacts of climate fluctuations and change. In Increasing Resilience to Climate Variability and Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 233–250. [Google Scholar]
- Harrigan, S.; Zsoter, E.; Alfieri, L.; Prudhomme, C.; Salamon, P.; Wetterhall, F.; Barnard, C.; Cloke, H.; Pappenberger, F. GloFAS-ERA5 operational global river discharge reanalysis 1979-present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2043–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowiak, J.E.; Joyce, R.J.; Yarosh, Y. A real-time global half-hourly pixel-resolution infrared dataset and its applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. The TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA). In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, B.; Miralles, D.G.; Lievens, H.; Van Der Schalie, R.; De Jeu, R.A.; Fernández-Prieto, D.; Beck, H.E.; Dorigo, W.A.; Verhoest, N.E. GLEAM v3: Satellite-based land evaporation and root-zone soil moisture. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1903–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, E.A. Flow in a Channel Connecting Two Reservoirs; Case Study: Toshka Channel Connecting Between Aswan Reservoir and Toshka Depression. In Proceedings of the Conference on Coping with Water Scarcity, Hurghada, Egypt, 26–28 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, N.M. Updating the Surface Area and Volume Equations of Lake Nasser using Multi Beam System. In Proceedings of the 19th International Water Technology Conference, Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, 21–23 April 2016; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.P.; John, J.G.; Adcroft, A.J.; Griffies, S.M.; Hallberg, R.W.; Shevliakova, E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Cooke, W.; Dunne, K.A.; Harrison, M.J.; et al. GFDL’s ESM2 global coupled climate-carbon earth system models. Part I: Physical formulation and baseline simulation characteristics. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6646–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.P.; John, J.G.; Shevliakova, S.; Stouffer, R.J.; Krasting, J.P.; Malyshev, S.L.; Milly, P.C.D.; Sentman, L.T.; Adcroft, A.J.; Cooke, W.; et al. GFDL’s ESM2 global coupled climate-carbon earth system models. Part II: Carbon system formulation and baseline simulation characteristics. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2247–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffies, S.M.; Winton, M.; Donner, L.J.; Horowitz, L.W.; Downes, S.M.; Farneti, R.; Gnanadesikan, A.; Hurlin, W.J.; Lee, H.C.; Liang, Z.; et al. The GFDL CM3 coupled climate model: Characteristics of the ocean and sea ice simulations. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3520–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.D.; Giuliani, M. Policy tree optimization for threshold-based water resources management over multiple timescales. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 99, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Georgakakos, A.P. Nile Decision Support Tool River Simulation And Management; Georgia Water Resources Institute (GWRI): Atlanta, Georgia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, R.M.; Hekal, N.T.; Mansor, N.M. Evaporation reduction from Lake Naser using new environmentally safe techniques. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Water Technology Conference, Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, 15–18 March 2007; pp. 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, D.; Guariso, G. Water Management Models in Practice: A Case Study of the Aswan High Dam; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; ISBN 0-444-42156-4. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.H.; El-Bakry, M.M. Estimation of evaporation from Lake Nasser. Meteorol. Res. Bull. 1970, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, A.M.A. Dynamic operation rules of multi-purpose reservoir for better flood management. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshra, N.M.; Qottob, M.M. Impact of the hydroelectric peak load on water levels downstream of Aswan Old Dam and establishing new criteria for navigation. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference and Utility Exhibition on Green Energy for Sustainable Development (ICUE), Pattaya, Thailand, 19–21 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mobasher, A.M.A. Adaptive Reservoir Operation Strategies under Changing Boundary Conditions? The Case of Aswan High Dam Reservoir. Doctoral Dissertation, Technische Universität, Darmstadt, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
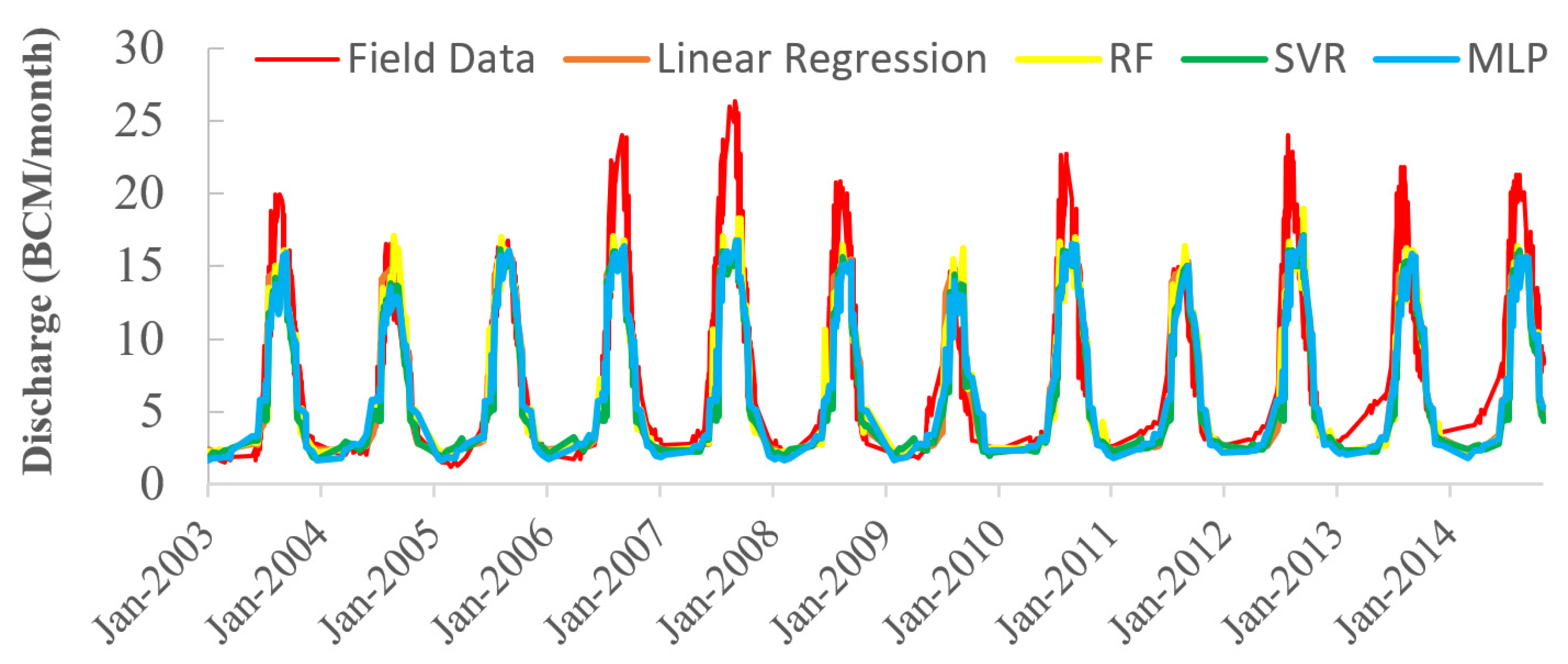
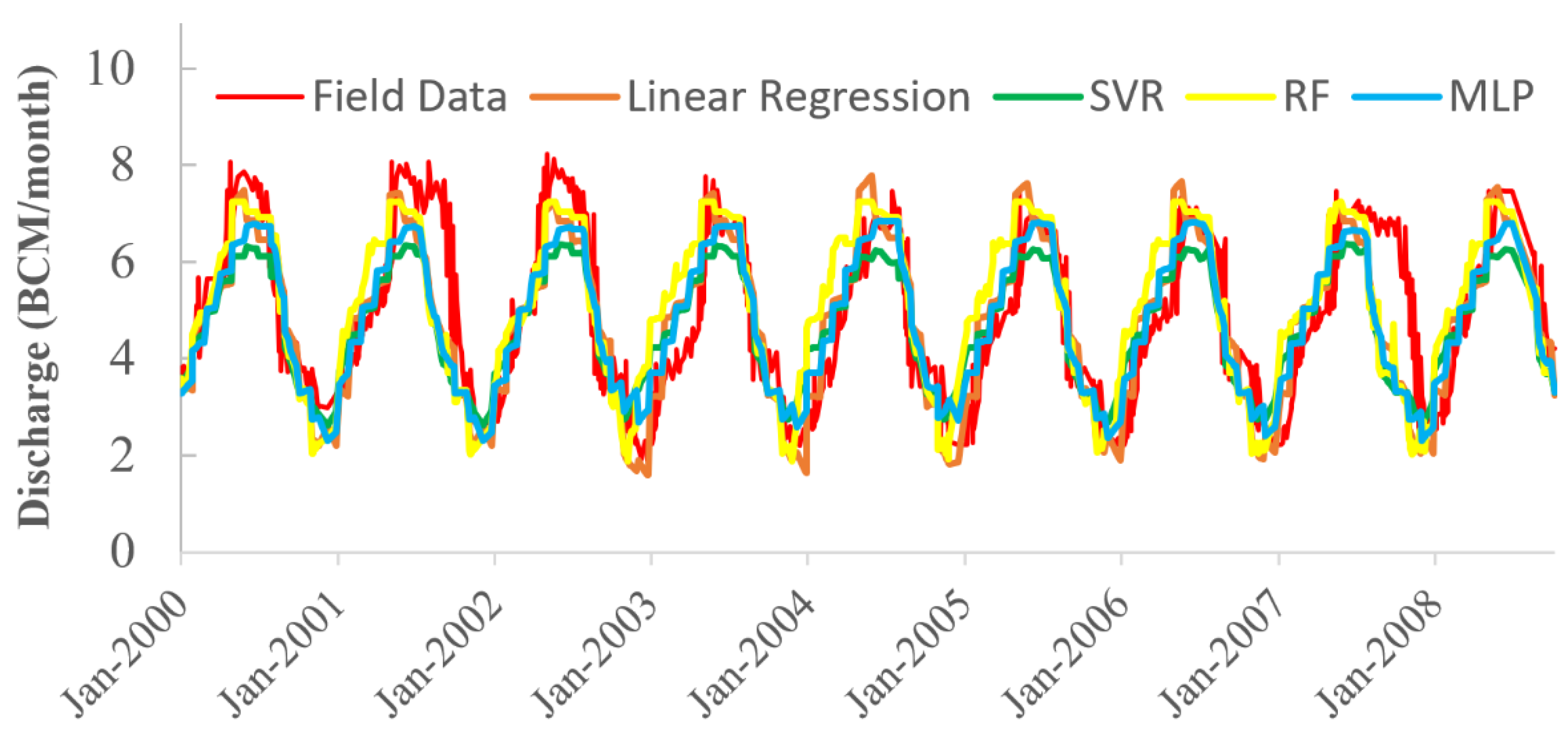






| Reservoir Inflow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Random Forest | SVR | MLP | |
| Inflow NS Validation | 0.594 | 0.649 | 0.635 | 0. 631 |
| Inflow R2 Validation | 0.628 | 0.637 | 0.652 | 0.665 |
| Inflow RMSE Validation | 4090 | 3832 | 3970 | 3848 |
| Inflow NS Calibration | 0.637 | 0.799 | 0.698 | 0.691 |
| Inflow R2 Calibration | 0.639 | 0.811 | 0.704 | 0.692 |
| Inflow RMSE Calibration | 3974 | 2953 | 3601 | 3644 |
| Downstream of Reservoir | ||||
| Outflow NS Validation | 0.598 | 0.434 | 0.558 | 0.649 |
| Outflow R2 Validation | 0.603 | 0.485 | 0.571 | 0.660 |
| Outflow RMSE Validation | 1063 | 1324 | 1096 | 992 |
| Outflow NS Calibration | 0.780 | 0.885 | 0.724 | 0.724 |
| Outflow R2 Calibration | 0.826 | 0.911 | 0.733 | 0.737 |
| Outflow RMSE Calibration | 698 | 514 | 806 | 798 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goharian, E.; Shaltout, M.; Erfani, M.; Eladawy, A. Developing an Optimized Policy Tree-Based Reservoir Operation Model for High Aswan Dam Reservoir, Nile River. Water 2022, 14, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071061
Goharian E, Shaltout M, Erfani M, Eladawy A. Developing an Optimized Policy Tree-Based Reservoir Operation Model for High Aswan Dam Reservoir, Nile River. Water. 2022; 14(7):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071061
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoharian, Erfan, Mohamed Shaltout, Mahdi Erfani, and Ahmed Eladawy. 2022. "Developing an Optimized Policy Tree-Based Reservoir Operation Model for High Aswan Dam Reservoir, Nile River" Water 14, no. 7: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071061
APA StyleGoharian, E., Shaltout, M., Erfani, M., & Eladawy, A. (2022). Developing an Optimized Policy Tree-Based Reservoir Operation Model for High Aswan Dam Reservoir, Nile River. Water, 14(7), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071061








