SOL40: Forty Years of Simulations under Climate and Land Use Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
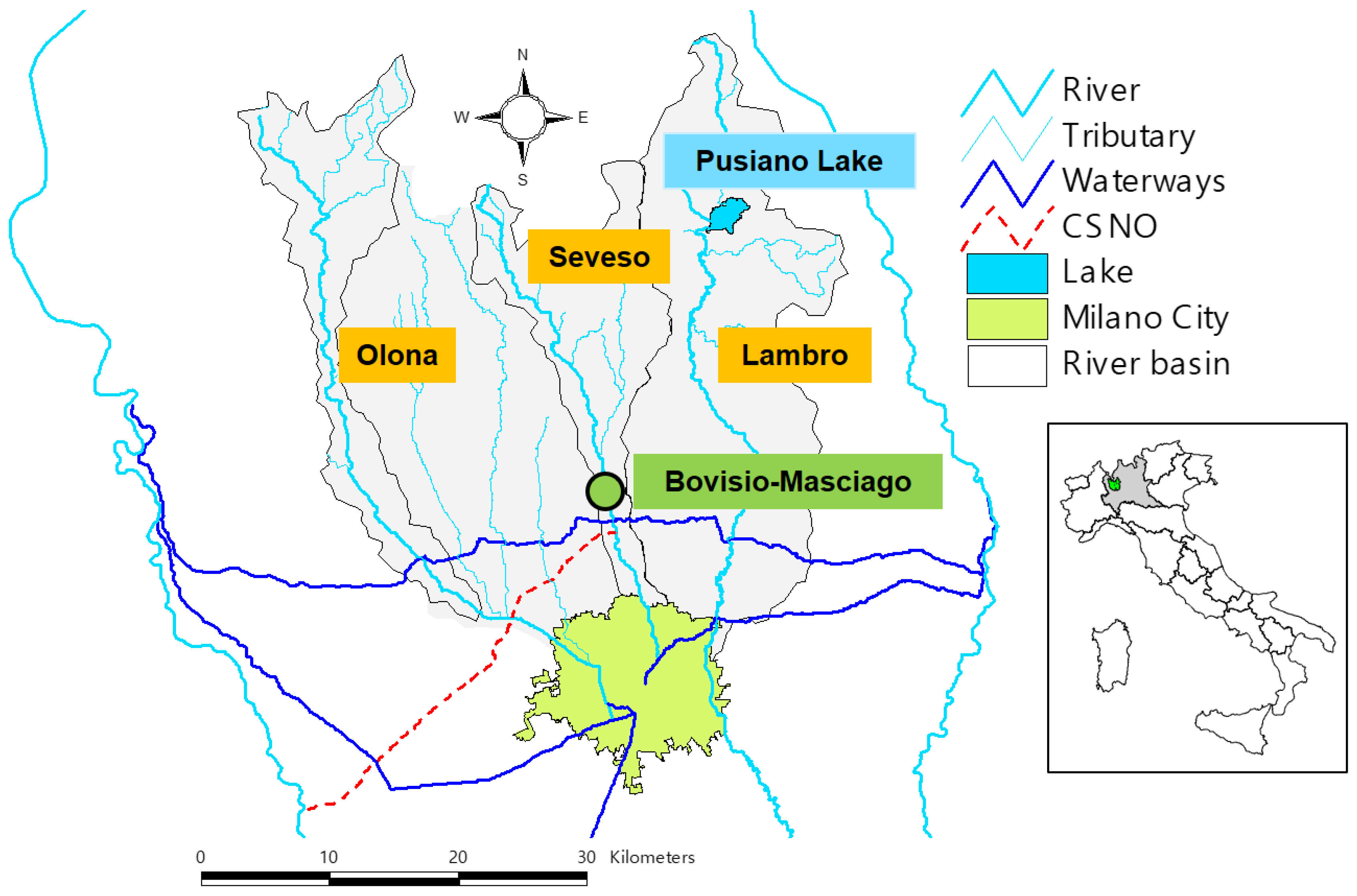
2. Area of Study
Land Use Change
3. Materials and Methods
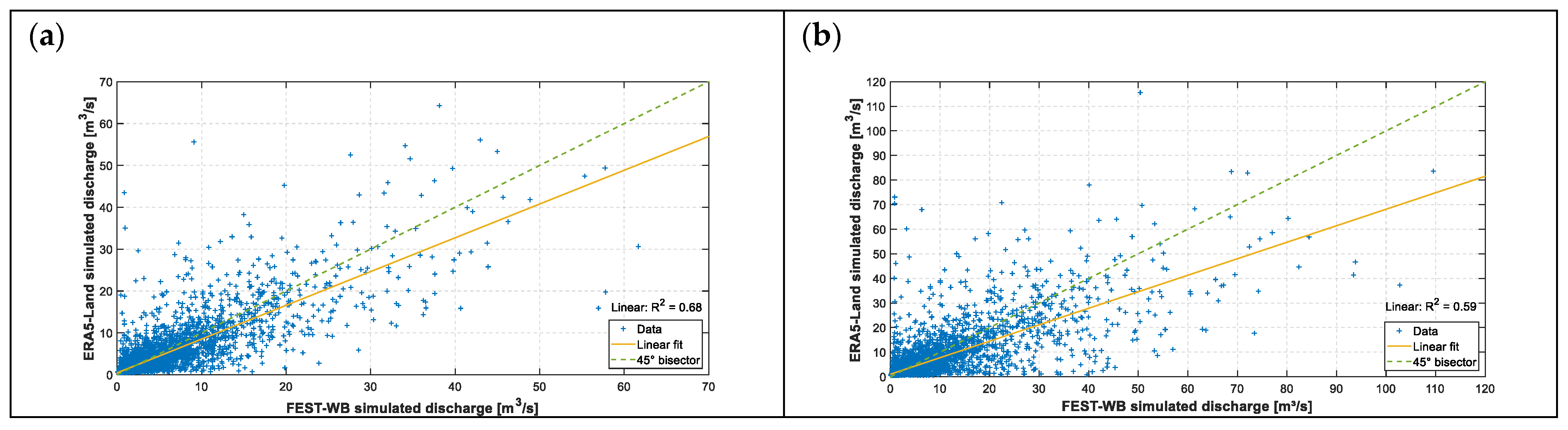
3.1. The ERA5-Land Reanalysis
3.2. The FEST-WB Model
3.3. Observed Weather Data
3.4. Statistical Analysis
3.4.1. Mean Absolute Error
3.4.2. Coefficient of Determination
3.4.3. Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE)
3.4.4. Kling–Gupta Efficiency (KGE)
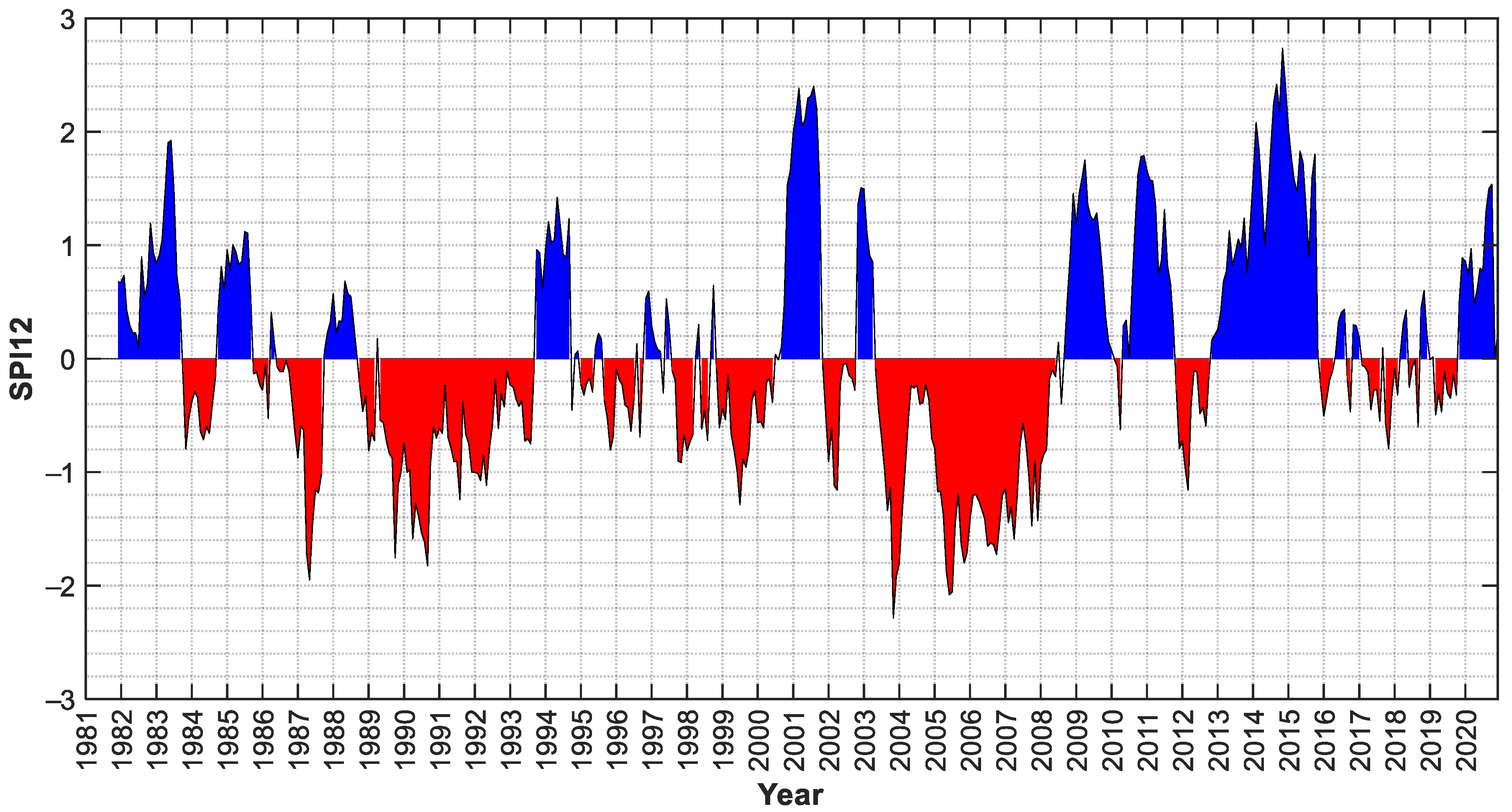
3.4.5. Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
3.4.6. Cox–Stuart Test
3.4.7. Mann–Kendall Test
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Climate Change Forcing
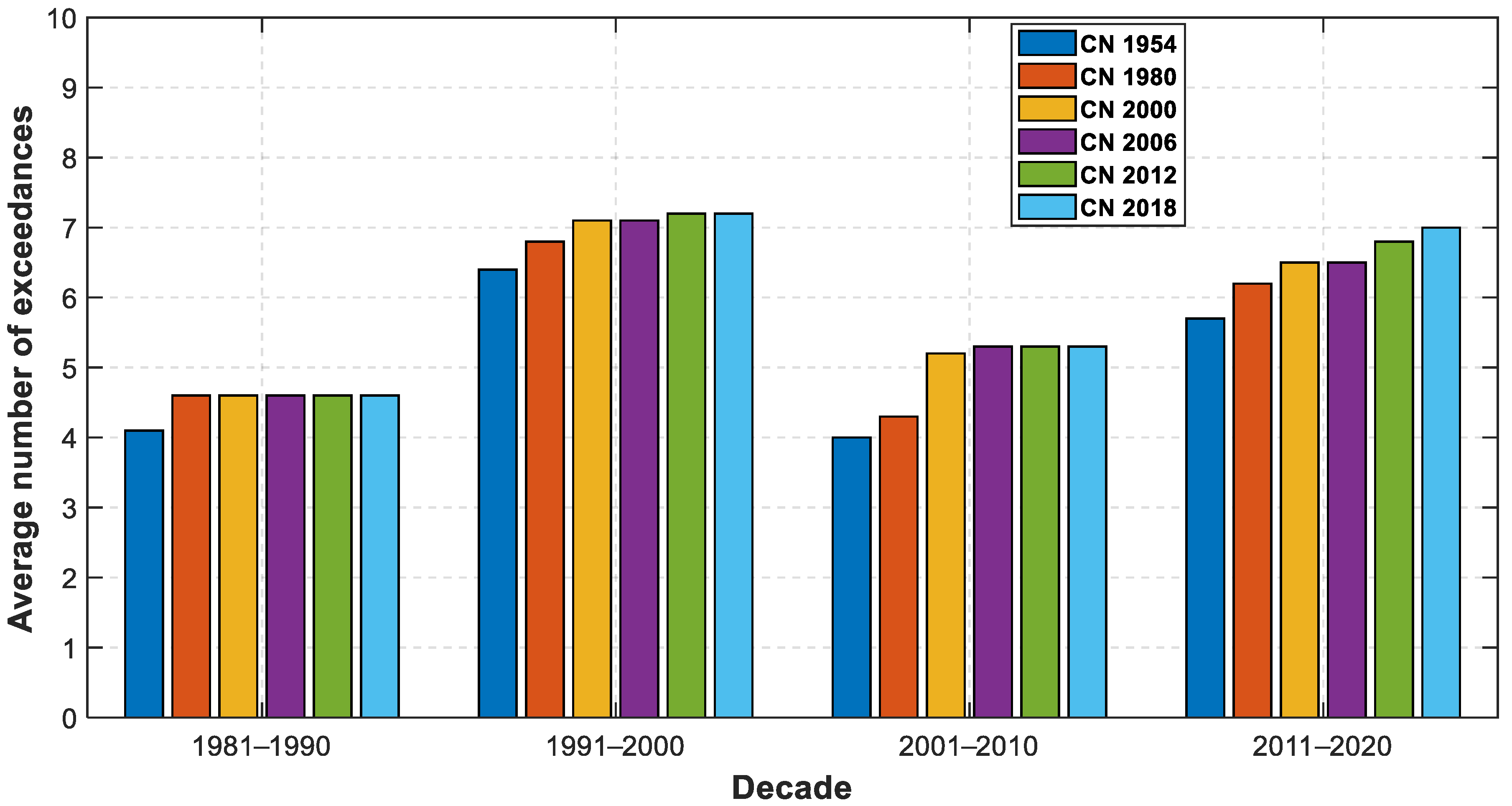
4.2. The Impact of Land Use Change
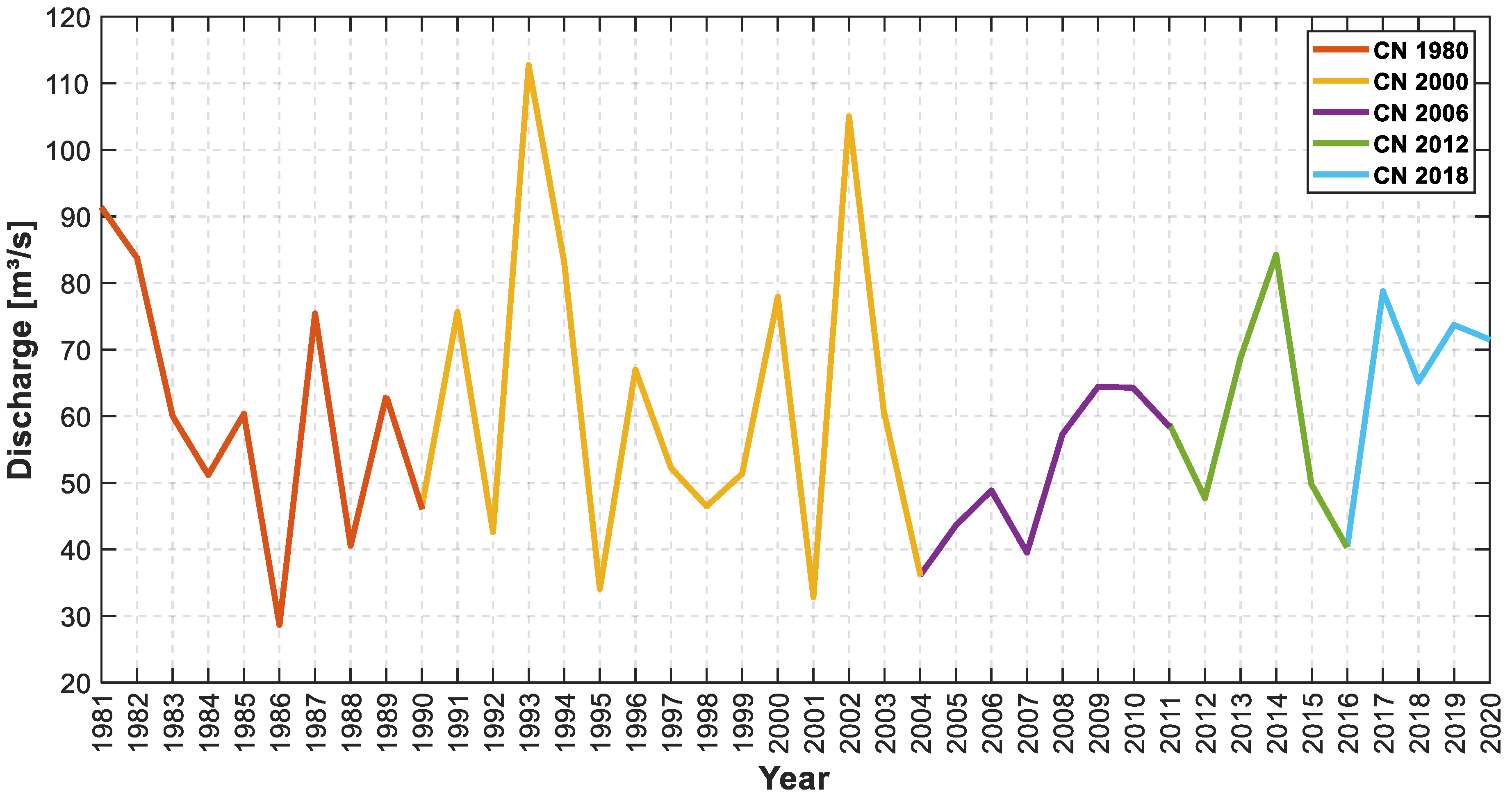
4.3. The Hydrological Response Trend Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMC | Antecedent Moisture Condition |
| ARPA | Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale (Regional Agency for Environmental Protection) |
| CLC | Corine Land Cover |
| CN | Curve Number |
| CS | Cox Stuart |
| CSNO | Canale Scolmatore di Nord-Ovest (North-West Spillway Channel) |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| FEST-WB | Flash flood Event-based Spatially-distributed rainfall-runoff Transformation-Water Balance |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| KGE | Kling-Gupta Efficiency |
| LS | Least Squares |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MK | Mann Kendall |
| MNW | Meteonetwork |
| NSE | Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| SCS | Soil Conservation Service |
| SOL | Seveso Olona Lambro |
| SPI | Standardized Precipitation Index |
References
- Munich Re. Topics Geo 2016—Natural Catastrophes 2016—Analyses, Assessments, Positions; Munich Re: München, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- The Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extremes (1970–2019). WMO-No. 1267. 2021. Available online: https://library.wmo.int/index.php?lvl=coll_see&id=13 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Rentschler, J.E.; Melda, S. 1.47 Billion People Face Flood Risk Worldwide: For over a Third, It Could Be Devastating. 2020. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/climatechange/147-billion-people-face-flood-risk-worldwide-over-third-it-could-be-devastating (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Rosso, R. Bombe d’acqua: Alluvioni d’Italia dall’unità al Terzo Millennio; Marsilio Editori spa: Venezia, Italy, 2017. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, M.; Bertolini, A.; Soldati, M.; Maugeri, M. High-resolution analysis of 1-day extreme precipitation in a wet area centered over eastern Liguria, Italy. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnara, Y.; Brunetti, M.; Maugeri, M.; Nanni, T.; Simolo, C. High-resolution analysis of daily precipitation trends in the central Alps over the last century. Int. J. Clim. 2011, 32, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Gullà, G.; Nanni, T.; Simolo, C. Precipitation variability and change in the Calabria region (Italy) from a high resolution daily dataset. Int. J. Clim. 2010, 32, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taszarek, M.; Allen, J.T.; Marchio, M.; Brooks, H.E. Global climatology and trends in convective environments from ERA5 and rawinsonde data. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. 5 November 2019. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/river-floods-3/assessment (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Impact of Land Use on Frequency of Floods in Yongding River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchioni, M.; Becciu, G. Infiltration-exfiltration system for stormwater runoff volume and peak attenuation. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 2018, 8, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ayllon, S.; Radke, J. Geostatistical Analysis of the Spatial Correlation between Territorial Anthropization and Flooding Vulnerability: Application to the DANA Phenomenon in a Mediterranean Watershed. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.S.; Gill, L.W.; Pilla, F.; Basu, B. Assessment of Variations in Runoff Due to Landcover Changes Using the SWAT Model in an Urban River in Dublin, Ireland. Sustainability 2022, 14, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areu-Rangel, O.S.; Cea, L.; Bonasia, R.; Espinosa-Echavarria, V.J. Impact of Urban Growth and Changes in Land Use on River Flood Hazard in Villahermosa, Tabasco (Mexico). Water 2019, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, K.; Surminski, S.; Hall, J.; Crick, F. Assessing surface water flood risk and management strategies under future climate change: Insights from an Agent-Based Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnes, D.J. Landslide Hazard Zonation: A Review of Principles and Practice; UNESCO Press: Paris, France, 1984; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Nemec, J. Global Runoff Data Sets and Use of Geographic Information Systems. In Proceedings of the ISLSCP Conference, Rome, Italy, 2–6 December 1985. ESA SP-248. [Google Scholar]
- Ceppi, A.; Ravazzani, G.; Salandin, A.; Rabuffetti, D.; Montani, A.; Borgonovo, E.; Mancini, M. Effects of temperature on flood forecasting: Analysis of an operative case study in Alpine basins. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravazzani, G.; Amengual, A.; Ceppi, A.; Homar, V.; Romero, R.; Lombardi, G.; Mancini, M. Potentialities of ensemble strategies for flood forecasting over the Milano urban area. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Ceppi, A.; Ravazzani, G.; Davolio, S.; Mancini, M. From Deterministic to Probabilistic Forecasts: The ‘Shift-Target’ Approach in the Milan Urban Area (Northern Italy). Geosciences 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becciu, G.; Ghia, M.; Mambretti, S. A century of works on river Seveso: From unregulated development to basin reclamation. Int. J. Environ. Impacts Manag. Mitig. Recover. 2018, 1, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M. La Modellazione Distribuita Della Risposta Idrologica: Effetti Della Variabilità Spaziale e Della Scala di Rappresentazione del Fenomeno Dell’assorbimento, Tesi di Dottorato. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy, 1990. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Rabuffetti, D.; Ravazzani, G.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system–the AMPHORE case studies in the upper Po River. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonanno, R.; Lacavalla, M.; Sperati, S. A new high-resolution Meteorological Reanalysis Italian Dataset: MERIDA. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 1756–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essou, G.R.C.; Sabarly, F.; Lucas-Picher, P.; Brissette, F.; Poulin, A. Can Precipitation and Temperature from Meteorological Reanalyses Be Used for Hydrological Modeling? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1929–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCLMS, European Union, Copernicus Land Monitoring Service©. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land Hourly Data from 1981 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2019. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/10.24381/cds.e2161bac?tab=overview (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Ravazzani, G. MOSAICO, a library for raster based hydrological applications. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA; SCS. Urban hydrology for small watersheds. Tech. Release 1986, 55, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Montaldo, N.; Toninelli, V.; Albertson, J.D.; Mancini, M.; Troch, P.A. The effect of background hydrometeorological conditions on the sensitivity of evapotranspiration to model parameters: Analysis with measurements from an Italian alpine catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 7, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; Civil Engineering Series; McGraw-Hill International Editions: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzani, G.; Ghilardi, M.; Mendlik, T.; Gobiet, A.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Investigation of Climate Change Impact on Water Resources for an Alpine Basin in Northern Italy: Implications for Evapotranspiration Modeling Complexity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravazzani, G.; Gianoli, P.; Meucci, S.; Mancini, M. Assessing Downstream Impacts of Detention Basins in Urbanized River Basins Using a Distributed Hydrological Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravazzani, G.; Barbero, S.; Salandin, A.; Senatore, A.; Mancini, M. An integrated Hydrological Model for Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources of the Upper Po River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 29, 1193–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, A.; Borga, M.; Ravazzani, G.; Crema, S. The role of storm movement in controlling flash flood response: An analysis of the 28 September 2012 extreme event in Murcia, southeastern Spain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences. Vol. 91; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006; p. 627. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Stephenson, D.B. (Eds.) Forecast Verification: A Practitioner’s Guide in Atmospheric Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WWRP/WGNE Joint Working Group on Verification Cited 2013: Forecast Verification—Issue. Methods and FAQ. Available online: http://www.cawcr.gov.au/projects/verification (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash–Sutcliffe and Kling–Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pool, S.; Vis, M.; Seibert, J. Evaluating model performance: Towards a non-parametric variant of the Kling-Gupta efficiency. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The Relation of Drought Frequency and Duration to Time Scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, D.C.; McKee, T.B. Characteristics of 20th Century Drought in the United States at Multiple Scales. Atmospheric Science Paper, 1–30 May 1997; p. No. 634. [Google Scholar]
- Keyantash, John; National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds.) Last Modified 7 August 2018. The Climate Data Guide: Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Available online: https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/standardized-precipitation-index-spi (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Beguería, S.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. SPEI: Calculation of the Standardised Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index. R package Version 1.7. 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SPEI (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Cox, D.R.; Stuart, A. Some quick sign tests for trend in location and dispersion. Biometrika 1955, 42, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutkowska, A. Properties of the Cox–Stuart Test for Trend in Application to Hydrological Series: The Simulation Study. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 2014, 44, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, D.L. A Cautionary Note Concerning the Cox and Stuart Test. Teach. Stat. 2001, 23, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E.; Sirangelo, B. Trend analysis of monthly mean values and extreme indices of daily temperature in a region of southern Italy. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Gaudio, R.; Leonardo, G.P. Precipitation trend and concentration in the Sardinia region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Yu, H.; Kan, G.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, M.; Wang, G. Re-evaluation of the Power of the Mann-Kendall Test for Detecting Monotonic Trends in Hydrometeorological Time Series. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. Trend: Non-Parametric Trend Tests and Change-Point Detection. R Package Version 1.1.4. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=trend (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hipel, K.W.; McLeod, H. Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, T.; Zwiers, F.W.; Xuebin, Z. Guidelines onanalysis of extremes in a changing climate in supportof informed decisions for adaptation. In World Meteorological Organization Collection(s) and Series; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]










| Year | Percentage of Urbanized Area |
|---|---|
| 1954 | 11.8% |
| 1980 | 32.0% |
| 2000 | 44.7% |
| 2006 | 45.6% |
| 2012 | 46.6% |
| 2018 | 46.8% |
| Variable | Is the Trend Present? (α = 5%) | p-Value (MK-Test) |
|---|---|---|
| Total annual precipitation | No | 0.537 |
| Annual number of wet days (p > 1 mm) | No | 0.172 |
| 24-h maximum annual precipitation | No | 0.552 |
| hourly maximum annual precipitation | No | 0.568 |
| Year of CN | Return Period [Years] | Probability of Yearly Exceedance [%] |
|---|---|---|
| CN 1954 | 18.56 | 5.4 |
| CN 1980 | 14.90 | 6.7 |
| CN 2000 | 11.00 | 9.1 |
| CN 2006 | 10.77 | 9.3 |
| CN 2012 | 10.54 | 9.5 |
| CN 2018 | 10.49 | 9.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceppi, A.; Gambini, E.; Lombardi, G.; Ravazzani, G.; Mancini, M. SOL40: Forty Years of Simulations under Climate and Land Use Change. Water 2022, 14, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060837
Ceppi A, Gambini E, Lombardi G, Ravazzani G, Mancini M. SOL40: Forty Years of Simulations under Climate and Land Use Change. Water. 2022; 14(6):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060837
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeppi, Alessandro, Enrico Gambini, Gabriele Lombardi, Giovanni Ravazzani, and Marco Mancini. 2022. "SOL40: Forty Years of Simulations under Climate and Land Use Change" Water 14, no. 6: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060837
APA StyleCeppi, A., Gambini, E., Lombardi, G., Ravazzani, G., & Mancini, M. (2022). SOL40: Forty Years of Simulations under Climate and Land Use Change. Water, 14(6), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060837








