Advances in the Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption from Water and Soil by Modified Biochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modified Carbon Properties and Types
3. Mechanism of Heavy Metal Adsorption by Biochar and Modified Biochar
- (1)
- Surface adsorption
- (2)
- Electrostatic adsorption
- (3)
- Ion exchange
- (4)
- Chemical precipitation
4. Biochar Modification Methods and Their Principles
5. Application of Biochar and Modified Biochar to Remove Heavy Metals from Water
6. Application of Biochar and Modified Biochar for Curing Heavy Metals in Soil
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J. Research progress of source and treatment methods of heavy metals in water. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2014, 41, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G. Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Xie, W.; Xie, Y. Composition and source identification of biomarkers in surface sediments from typical freshwater lakes in China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2017, 39, 822–828. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. The Effects of Additives on Adsorption of Heavy Metals onto Surficial Sediments. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Yen, J.H. On-site mercury-contaminated soils remediation by using thermal desorption technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Shi, T.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, R. Silane-based coatings on the pyrite for remediation of acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4391–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Bao, K.; Huang, C.; Zhao, X.; Han, W.; Yin, Z. Adsorption and pH values determine the distribution of cadmium in terrestrial and marine soils in the Nansha area, Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 33422–2016; Thermoplastic Elastomer—Determination of Heavy Metal Contents—Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometric Method. China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.; You, S.; Singh, L.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Pyrolysis of waste biomass and plastics for production of biochar and its use for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.S.; Heo, J.S.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.O.; DiClemente, C.C.; Norcross, J.C. In search of how people change: Applications to addictive behaviors. Am. Psychol. 1992, 47, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.Q.; Lü, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Wu, M.; Liu, R. Fabrication of low-cost and ecofriendly porous biocarbon using konjaku flour as the raw material for high-performance supercapacitor application. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13283–13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashikawa, F.S.; Conz, R.F.; Colzato, M.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Effects of feedstock type and slow pyrolysis temperature in the production of biochars on the removal of cadmium and nickel from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z. Application of biochar for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno—Jiménez, E.; Gomez—Eyles, J.L. Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Gao, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, M. Effective removal of heavy metal by biochar colloids under different pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Harris, W. Surface chemistry variations among a series of laboratory-produced biochars. Geoderma 2011, 163, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Yuan, L. Adsorption characteristics of modified biochar on Cr. J. Fudan 2021, 60, 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X. Removal of Cu(II) from Aqueous Solutions and Its Fixation in Red Soil by Biochars from Crop Straws. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Ma, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, Y.C.; Gu, B.H. Mechanistic investigation of mercury sorption by Brazilian pepper biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures based on X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and flow calorimetry. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12156–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.Y.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ye, C.H.; Yu, B.G.; Zhou, X.L.; Ma, A.Y. Superefficient removal of heavy metals from wastewater by Mg-loaded biochars: Adsorption characteristics and removal mechanisms. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9160–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z.A.; Yilmaz, E.; Habila, M.; Soylak, M. Solid phase extraction of metal ions in environmental samples on 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol impregnated activated carbon cloth. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Faur—Brasquet, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Removal of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II) by adsorption onto activated carbon cloths. J. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8404–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K.M.; Li, X.Y. The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on microplastics. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zhu, D.Q.; Sun, C. Effect of heavy metals on the sorption of hydrophobic organic compounds to wood charcoal. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L. Comparison of rice husk- and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Role of mineral components in biochars. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, E.F.; Zhu, Y.G.; Reid, B.J.; Sun, G.X. The role of biochar properties in influencing the sorption and desorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and As(III) in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Fang, Z.; Tsang, P.E.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D. Stabilisation of nanoscale zero-valent iron with biochar for enhanced transport and in-situ remediation of hexavalent chromium in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chen, M. Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Shen, B.; Wu, C. Review of biochar for the management of contaminated soil: Preparation, application and prospect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monser, L.; Adhoum, N. Modified activated carbon for the removal of copper, zinc, chromium and cyanide from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 26, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Du, Q.; Yang, F. Preparation of montmorillonite modified biochar with various temperatures and their mechanism for Zn ion removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 121692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyà, J.J.; Ortigosa, M.A.; Laguarta, S.; Manso, J.A. Experimental study on the effect of pyrolysis pressure, peak temperature, and particle size on the potential stability of vine shoots-derived biochar. Fuel 2014, 133, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Chang, J.S.; Ren, N. Singlet oxygen-dominated peroxydisulfate activation by sludge-derived biochar for sulfamethoxazole degradation through a nonradical oxidation pathway: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Din, A.T.M.; Ahmad, A.L. Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo-based activated carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasucka, P.; Pan, B.; Ok, Y.S.; Mohan, D.; Sarkar, B.; Oleszczuk, P. Engineered biochar—A sustainable solution for the removal of antibiotics from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Ghosh, G.K.; Avasthe, R. Conversion of crop, weed and tree biomass into biochar for heavy metal removal and wastewater treatment. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shi, S.; Liu, J. Study of the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of biochar. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Gao, F.; Mosa, A. Sorption of heavy metal ions onto crayfish shell biochar: Effect of pyrolysis temperature, pH and ionic strength. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, W. Effect on Cr(VI) adsorption performance of acid-base modified biochar. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, A.; Layne, C.A.; Perez, F.; Hassan, E.I.B.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T.E. KOH-activated high surface area Douglas Fir biochar for adsorbing aqueous Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, F.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) and naphthalene from water: Affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Akakuru, O.U.; Xu, X.; Wu, A. Research progress and mechanism of nanomaterials-mediated in-situ remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil: A critical review. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Cui, L.; Li, L.; Pan, G.; Xie, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; et al. Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: Results from a cross-site field experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Bi, X.; Peng, Y.; Bai, M. Research advances of the phosphorus-accumulating organisms of Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas and Tetrasphaera: Metabolic mechanisms, applications and influencing factors. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, W.; Kookana, R.; Katayama, A. Characteristics of biochar and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.; Zhou, Y.H.; Liu, Y.G.; Wen, J.; Tan, X.F.; Liu, S.J.; Jiang, L.H. Appraising the effect of in-situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated sediment by biochar and activated carbon on Cu immobilization and microbial community. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, W. Remediation effectiveness of Phyllostachys pubescens biochar in reducing the bioavailability and bioaccumulation of metals in sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Xue, W. Biochar facilitated the phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated sediments: Metal behavior, plant toxicity, and microbial activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; An, W.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; Fu, A.; Xiao, R.; Chen, H.; Xue, S. Red mud-modified biochar reduces soil arsenic availability and changes bacterial composition. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Liu, Y.G.; Tan, X.F.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhou, Y.H.; Liu, S.B.; Yin, Z.H.; Jiang, L.H.; Li, M.F.; Wen, J. The effect of several activated biochars on Cd immobilization and microbial community composition during in-situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, G. Remediation and its biological responses of Cd contaminated sediments using biochar and minerals with nanoscale zero-valent iron loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, K.; Fu, Y.; Ma, W.; Xie, X.; Sun, Y. Effect of modified biochar on immobilization remediation of weakly alkaline Cd-contaminated soil and environmental quality. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2020, 40, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar]
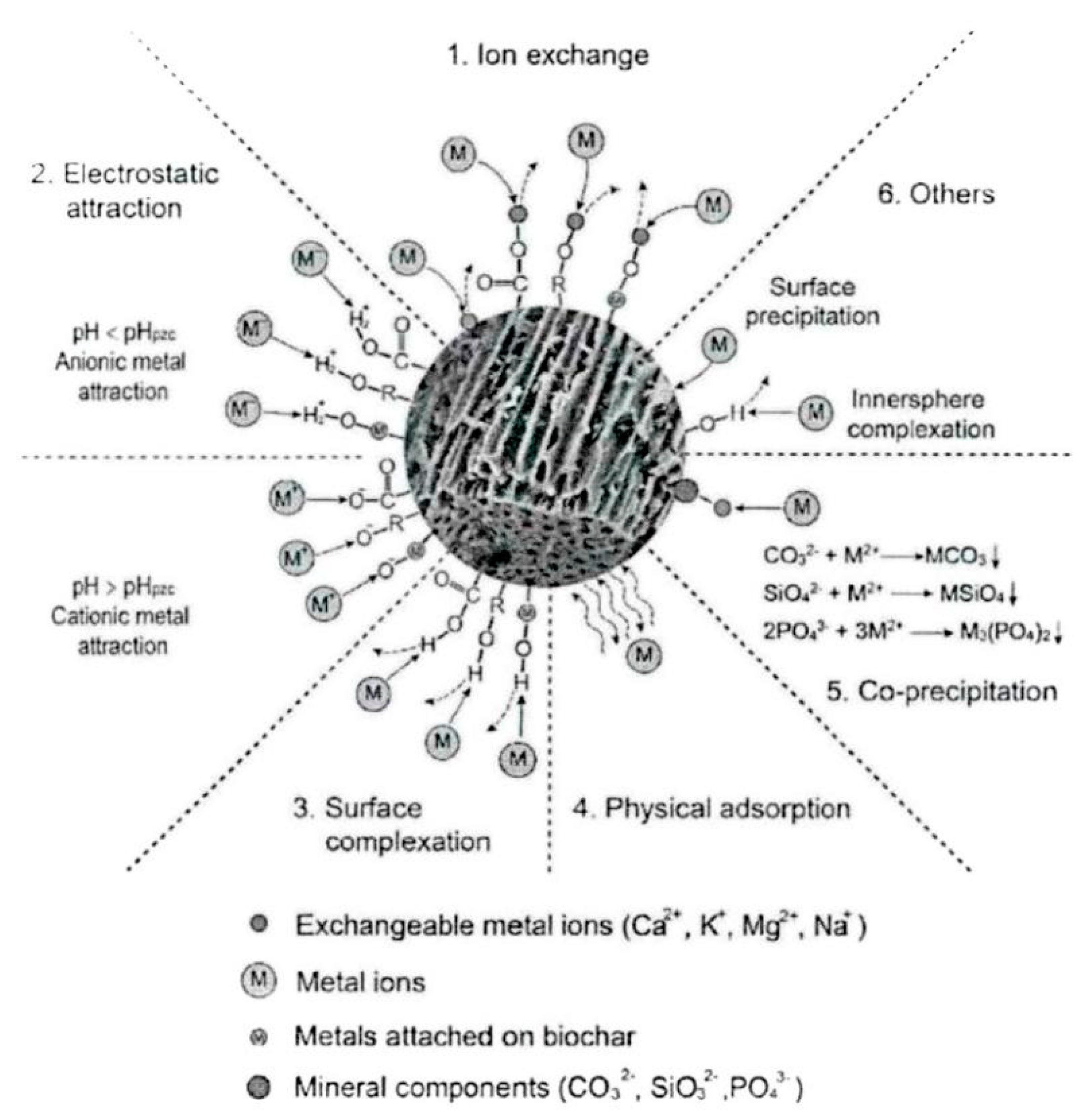

| Mechanism | Principle | Main Influencing Factors | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface absorption | The surface of biochar is rich in acidic groups such as carboxyl groups and phenolic hydroxyl groups, which can form specific metal complexes with heavy metal ions in water/soil and form active adsorption sites, etc. | 1. Surface chemical bond group 2. Diffusion effect of heavy metal ions 3. Temperature | [17,18,19,20] |
| Electrostatic Adherence | Formation of ionic bonds (formed when atoms gain or lose electrons) between anions and cations by electrostatic interaction (chemical bonding). | 1. Zeta potential 2. pH value. 3. Degree of dispersion | [21,22,23] |
| Ion Exchange | The charged cations and protons on the surface of biochar exchange with dissolved heavy metal ions in an exchange reaction. | 1.Nature of the surface functional groups 2. Size of the pollutants 3. Live nature 4. pH value | [24,25] |
| Chemical Precipitation | Anions react with heavy metal ions to form a water—insoluble precipitate. | 1. pH value. 2. Electrolyte concentration 3. Complexing effect 4. Homonymous ion effect | [29,30,31,32] |
| Modification Method | Modified Materials | Modification Principle | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical modification | CO2, H2O, Air | By reacting the gas with the biochar at high temperatures, the pores of the biochar are increased, and its specific surface area is expanded. | [34] |
| Redox modification | FeCl3, MnSO4, CO2, NH3 | Using oxidizing and reducing agents to carry out redox reactions on the functional groups on the surface of biochar to increase the surface active matching point. | [35] |
| Acid–base surface modification | CO2, NH3, KOH, NaOH | Using acid and alkali treatment of raw materials or direct treatment of biochar to change the acid and alkali functional groups on the surface of the biochar. | [36] |
| Adsorbent compound modification | Nanocomposites such as chitosan | Nanocomposites such as chitosan are rich in amino—functional groups with strong binding capacity and thus can be used as adsorption sites for heavy metals. | [37,38] |
| Activation modification | KOH, NaOH, ZnCl2, H3PO4 | The activator reacts with the functional groups on the surface of the biochar at high temperatures and introduces a large number of active sites, increasing the number of pores on the surface of the biochar and increasing the diameter of the pores. | [39,40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, S. Advances in the Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption from Water and Soil by Modified Biochar. Water 2022, 14, 3894. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233894
Wang Y, Li H, Lin S. Advances in the Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption from Water and Soil by Modified Biochar. Water. 2022; 14(23):3894. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233894
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yizhuo, He Li, and Shaohua Lin. 2022. "Advances in the Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption from Water and Soil by Modified Biochar" Water 14, no. 23: 3894. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233894
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, H., & Lin, S. (2022). Advances in the Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption from Water and Soil by Modified Biochar. Water, 14(23), 3894. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233894








